Cervical Viscera and Root of the Neck
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the three layers of the cervical viscera?
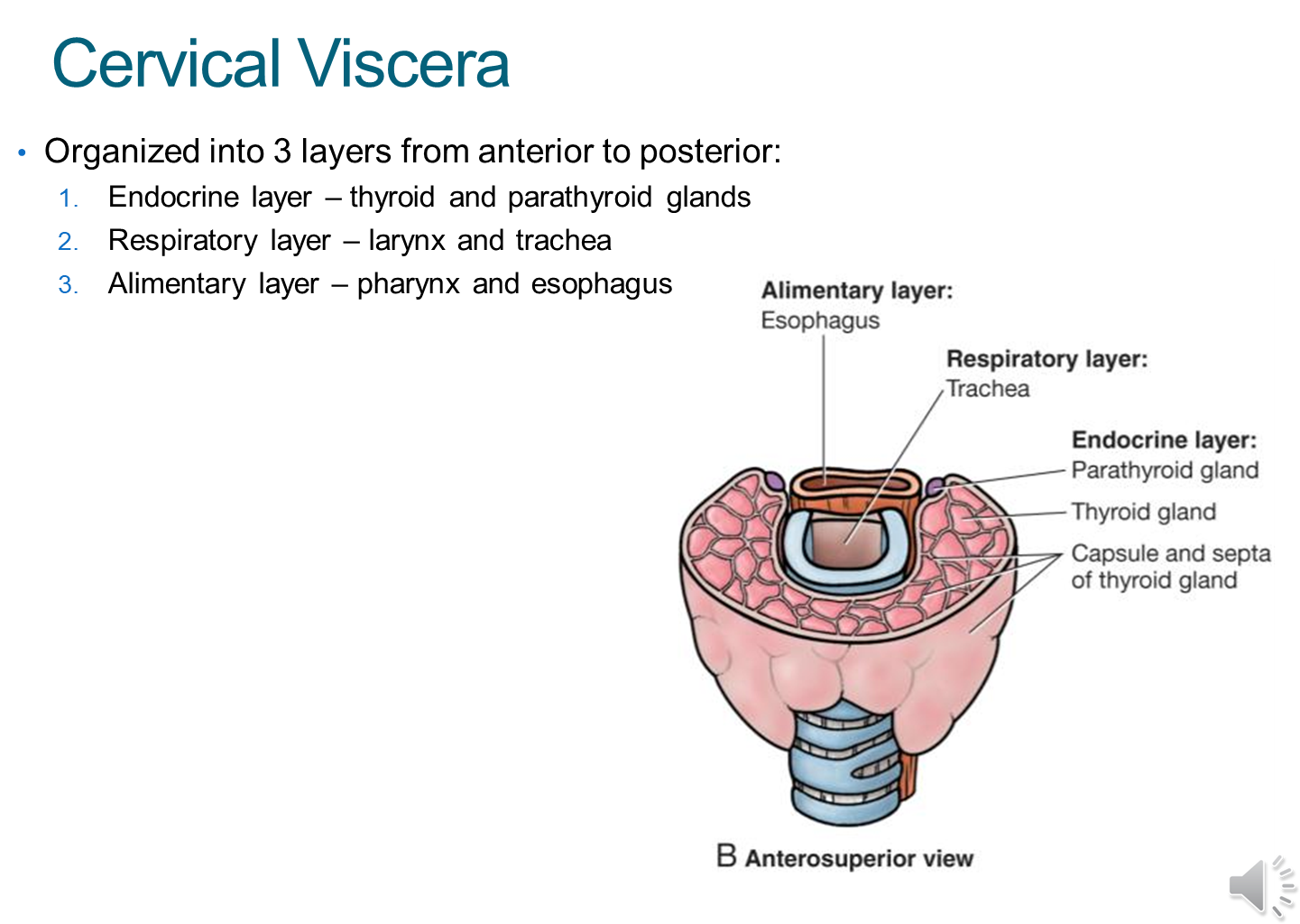
The cervical viscera is organized into three layers, from most anterior to posterior
1) Endocrine
→ thyroid and parathyroid glands
2) Respiratory
→ larynx and trachea
3) Alimentary
→ pharynx and esophagus
What is the relationship of the thyroid gland to the surrounding structures? (9)
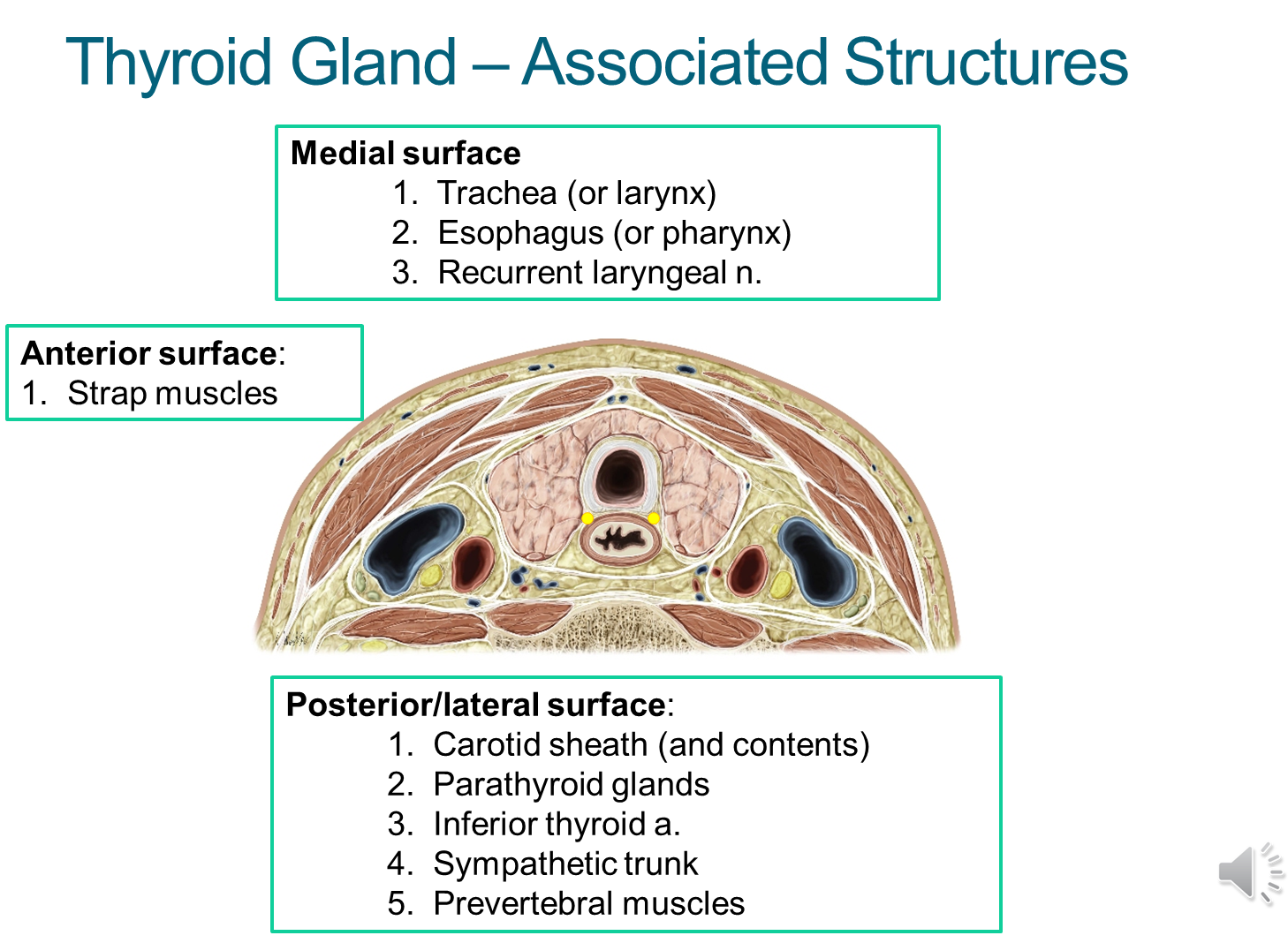
What is the function, structure, and location of the thyroid gland?
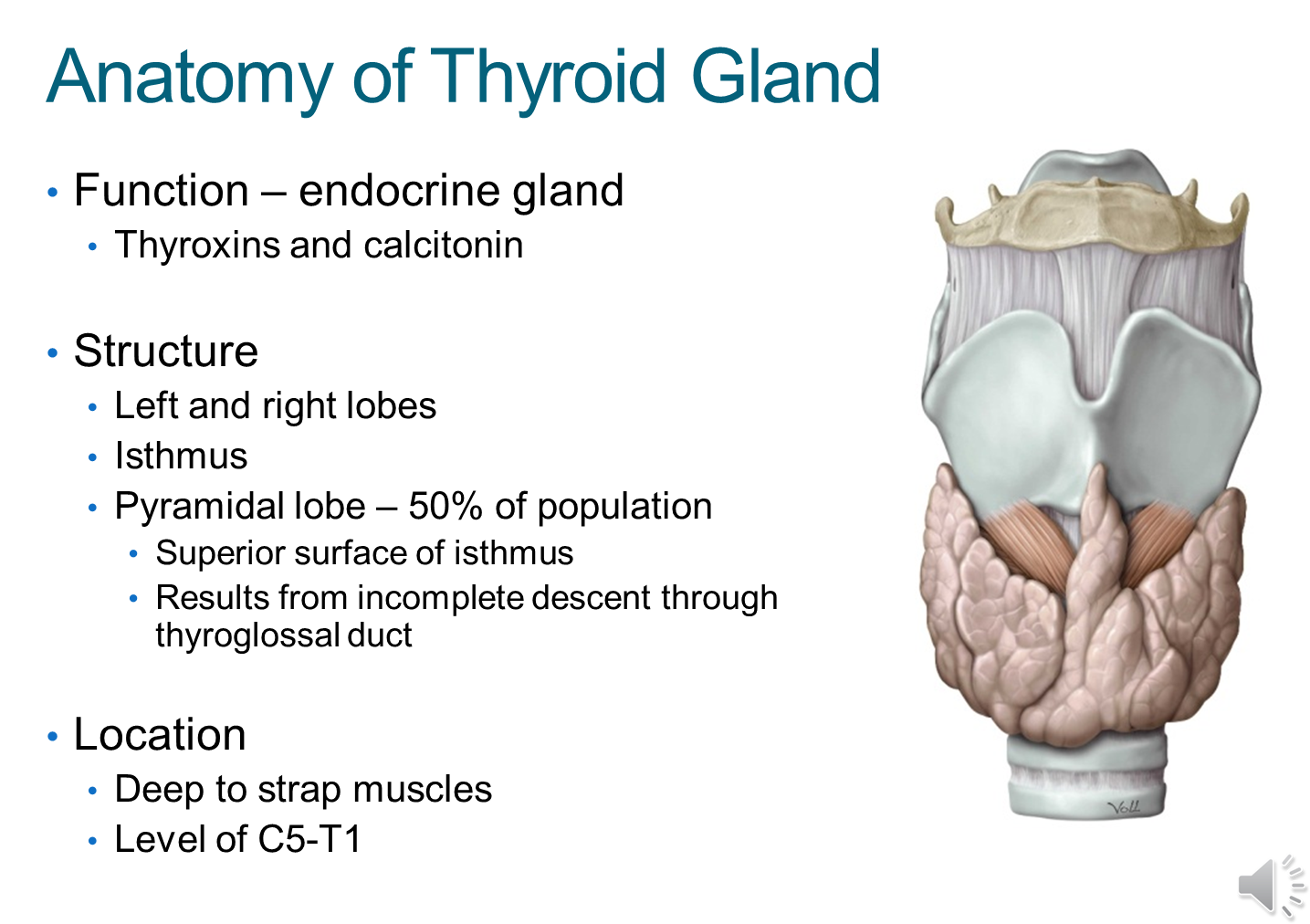
1) The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland that secretes thyroxins and calcitonin
→ thyroxins control general cell metabolism
→ calcitonin controls calcium levels
2) Composed of a left and right lobe connected in the middle by the isthmus
→ fifty percent of the patient population has an additional pyramidal lobe on the surface of the isthmus due to an incomplete descent through the thyroglossal duct
3) Located deep to the strap muscles at the level of C5-T1
What is the blood supply to the thyroid gland?
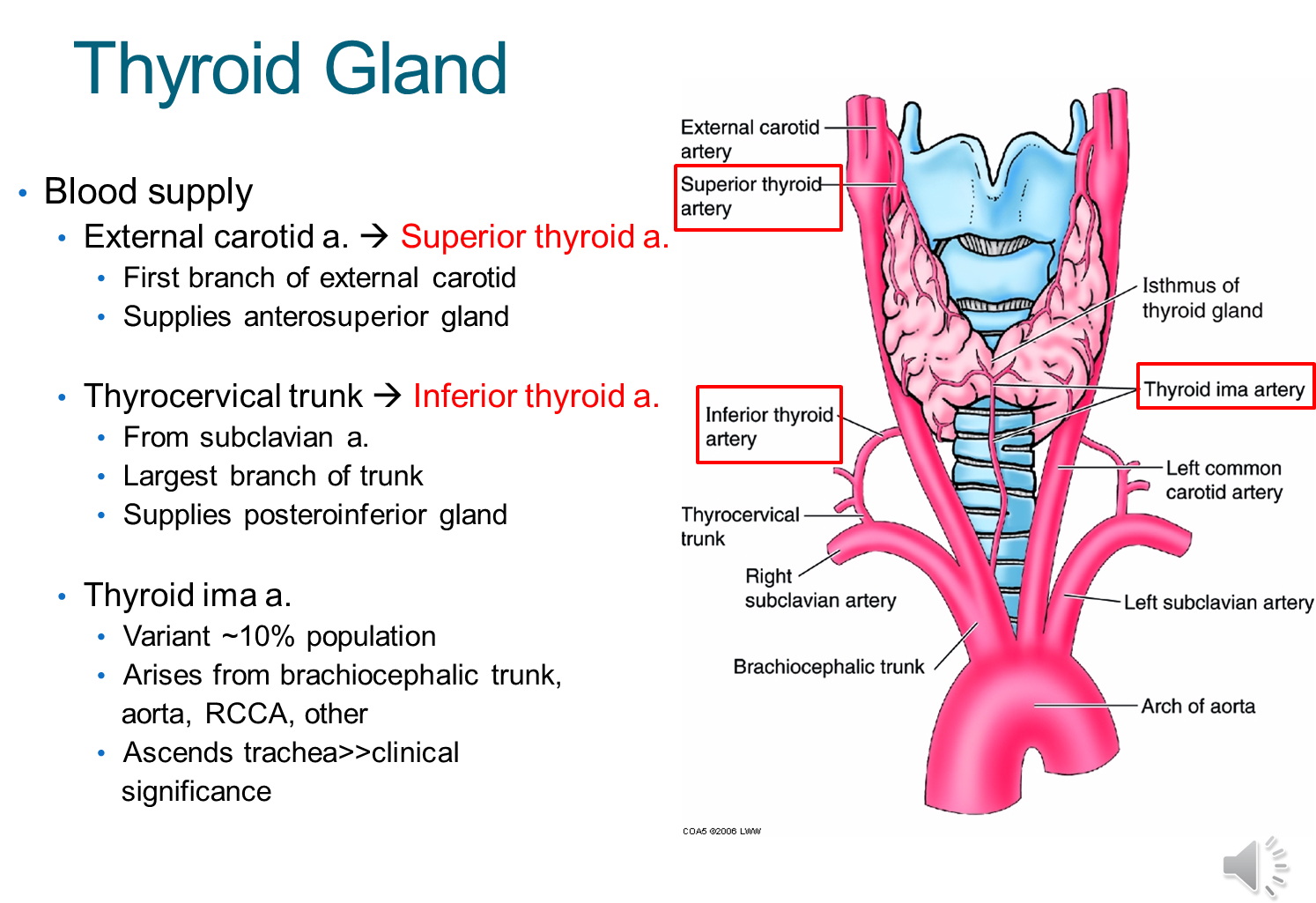
The thyroid gland is supplied by several arteries
1) External carotid artery branches into the superior thyroid artery
→ the superior thyroid artery is the first branch of the ECA and supplies the anterosuperior portion of the gland
2) Thyrocervical trunk branches into the inferior thyroid artery
→ originates from the subclavian artery and supplies the posteroinferior gland
3) Thyroid ima artery is present in a small portion of the population
→ if present it can be injured when doing an anterior approach to the trachea resulting in bleeding
What is Goiter?
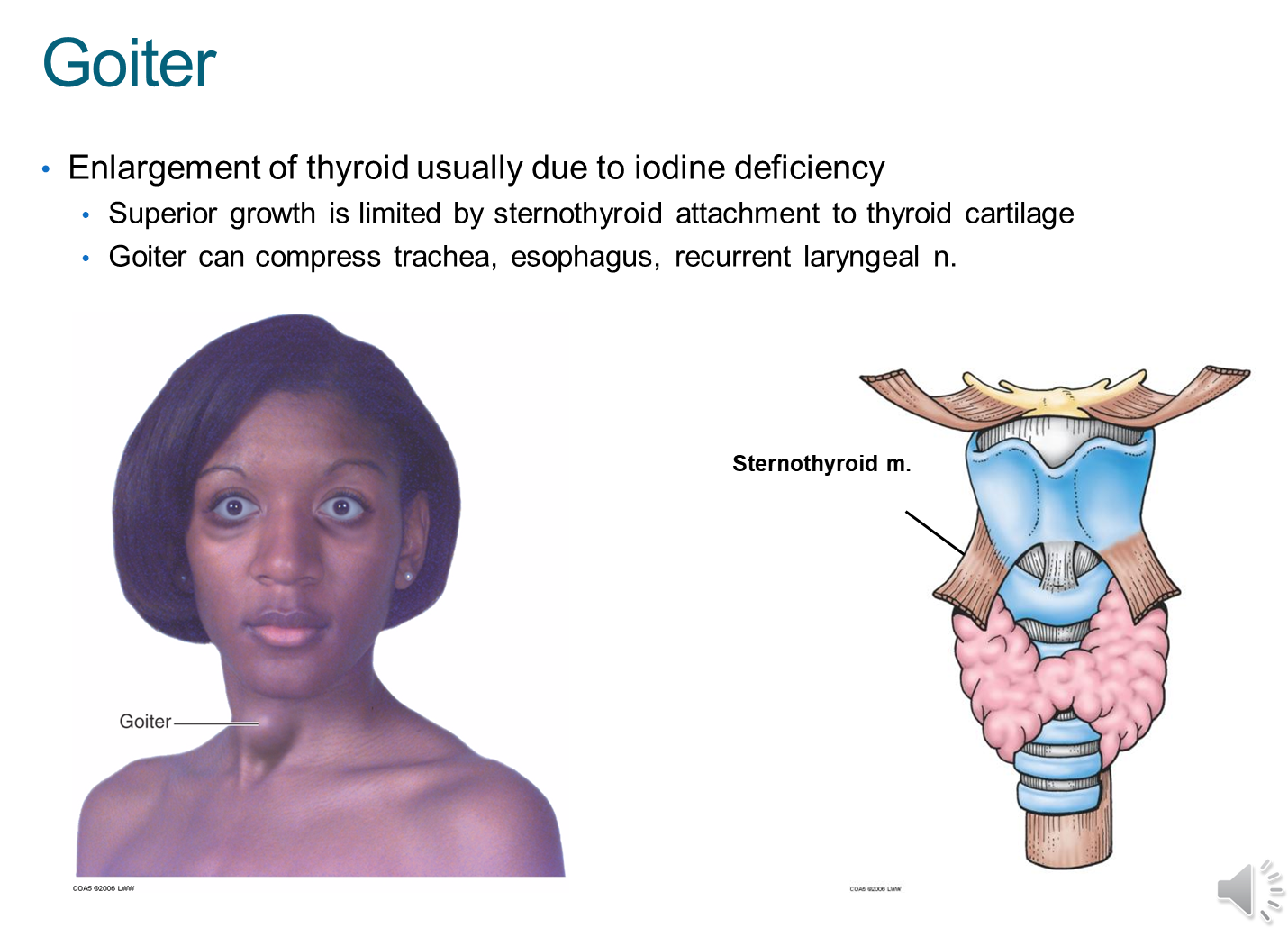
Goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland due to iodine deficiency
→ because of the strap muscles, the thyroid gland can only grow anteriorly or towards the thorax inferiorally
→ this goiter can compress the trachea, esophagus and recurrent laryngeal nerve
What are the function, structure and blood supply of the parathyroid gland?
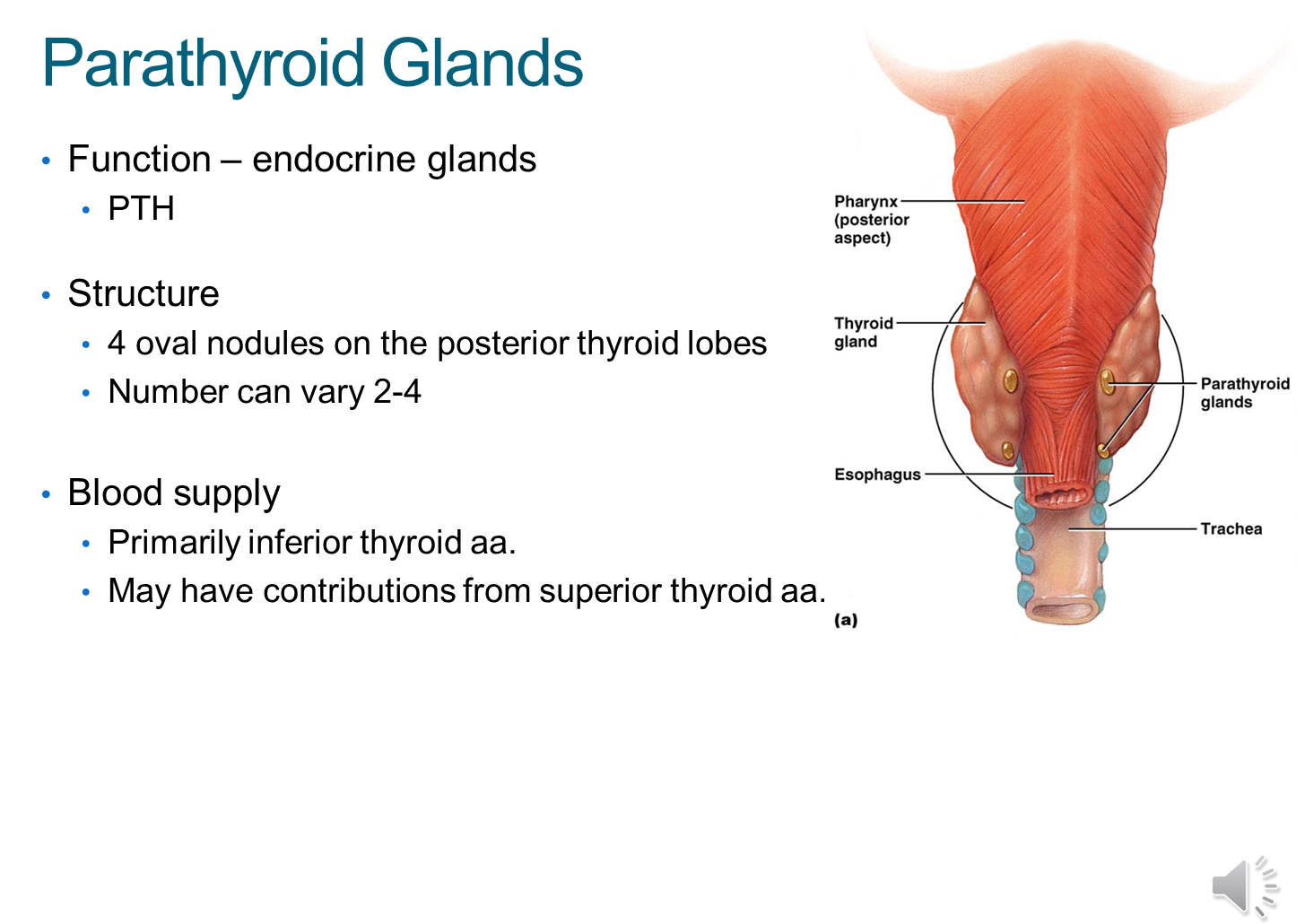
Parathyroid gland are endocrine glands that sit posteriorly to the thyroid and produce PTH which control calcium levels
1) Typically four in number and are supplied by the inferior thyroid artery
What is a Thyroidectomy? What are complications
Removal of the thyroid gland for tumor, goiter or hyperthyroidism
1) While thyroid hormones can be supplemented, parathyroid glands cannot which may result in hypoparathyroidism
→ because of this the parathyroid glands are usually transplanted as you cannot live without them
2) Injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve resulting in hoarseness
3) Hemorrhage of the vessels leading to the gland
What are the Scalene Muscles?
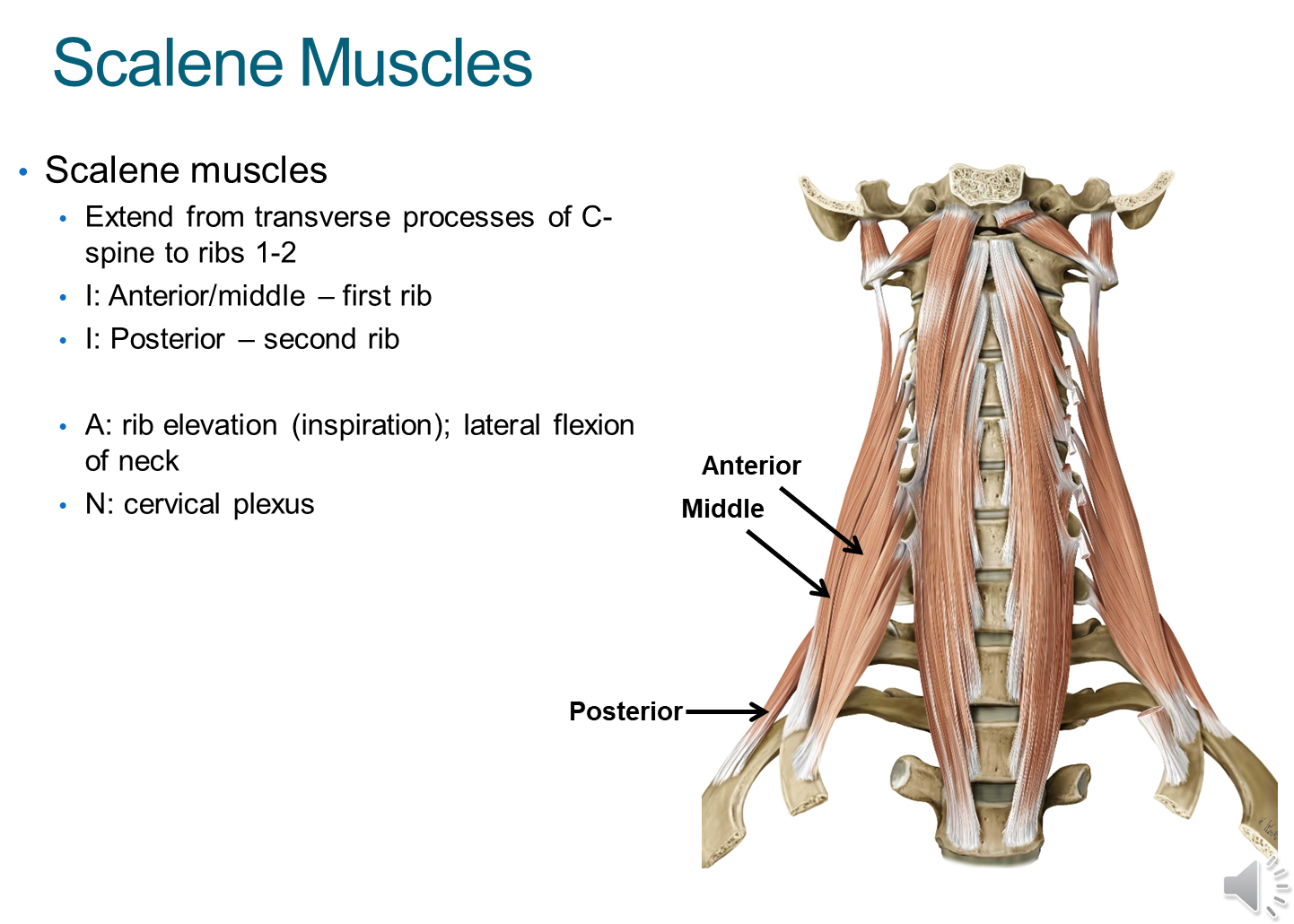
Scalene muscles are three muscles that sit around the spine. They are subdivided into anterior, middle and posterior
1) The muscles originate in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae and insert into the first two ribs
→ the anterior/middle insert into the first
→ posterior inserts into the second
2) These muscles work to elevate the ribs when you breathe and flex the neck side to side
→ innervated by the cervical plexus
What is the Interscalene Triangle?
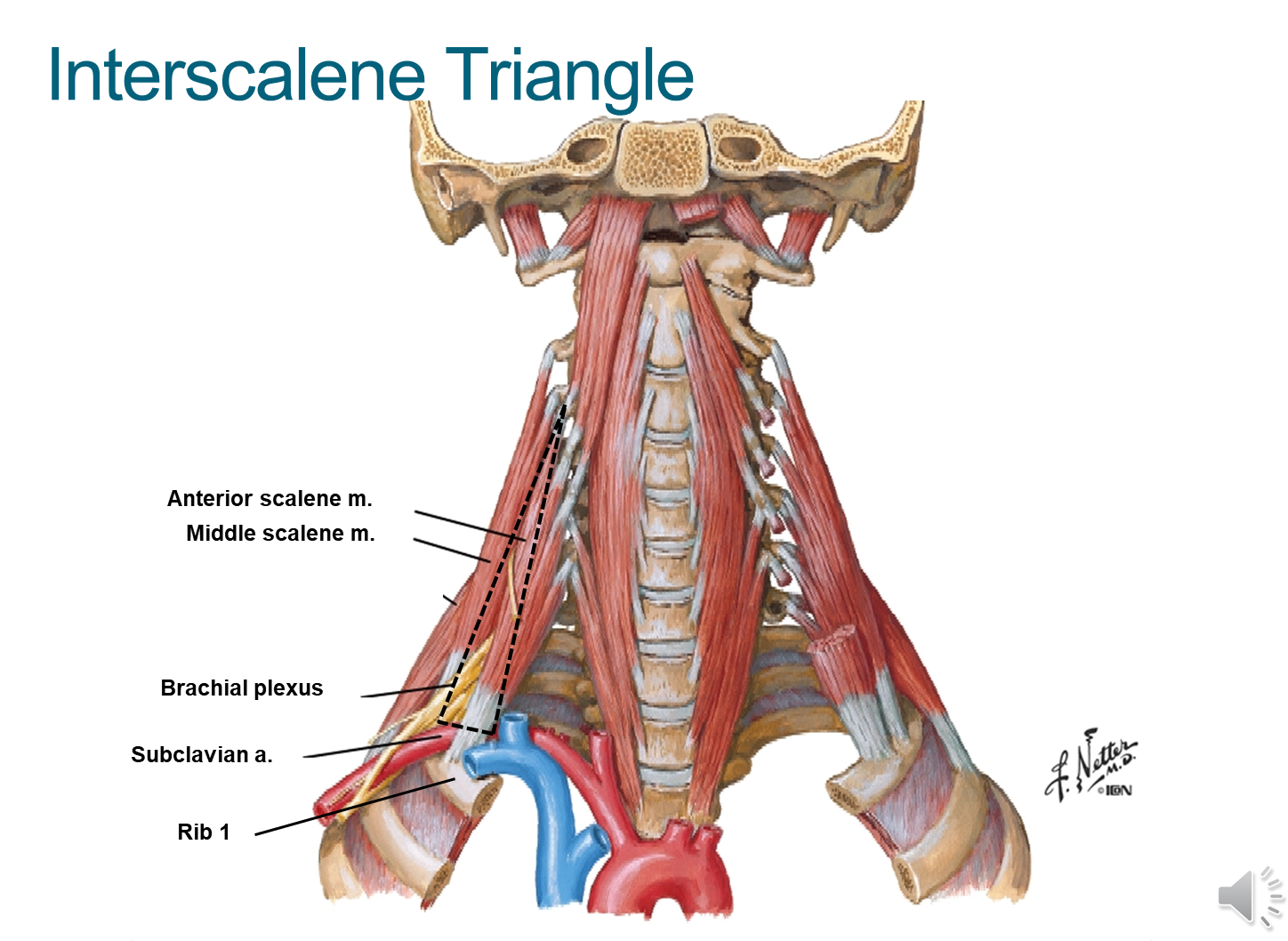
The Interscalene Triangle is a triangle formed by the borders of the anterior and middle scalene as well as the first rib
1) This triangle allows for passage of neck structures into the arms
→ subclavian artery passes through this triangle becoming the brachial artery to supply the arm
→ the brachial plexus passes through the triangle
2) When this triangle is compressed, the subclavian artery and brachial plexus can be squashed leading to scalene syndrome
→ leads to parasthesia and reduced blood flow to arms
3) Importantly, the subclavian vein does not pass through the triangle but rather anterior through the anterior scalene
What is the Root of the Neck?
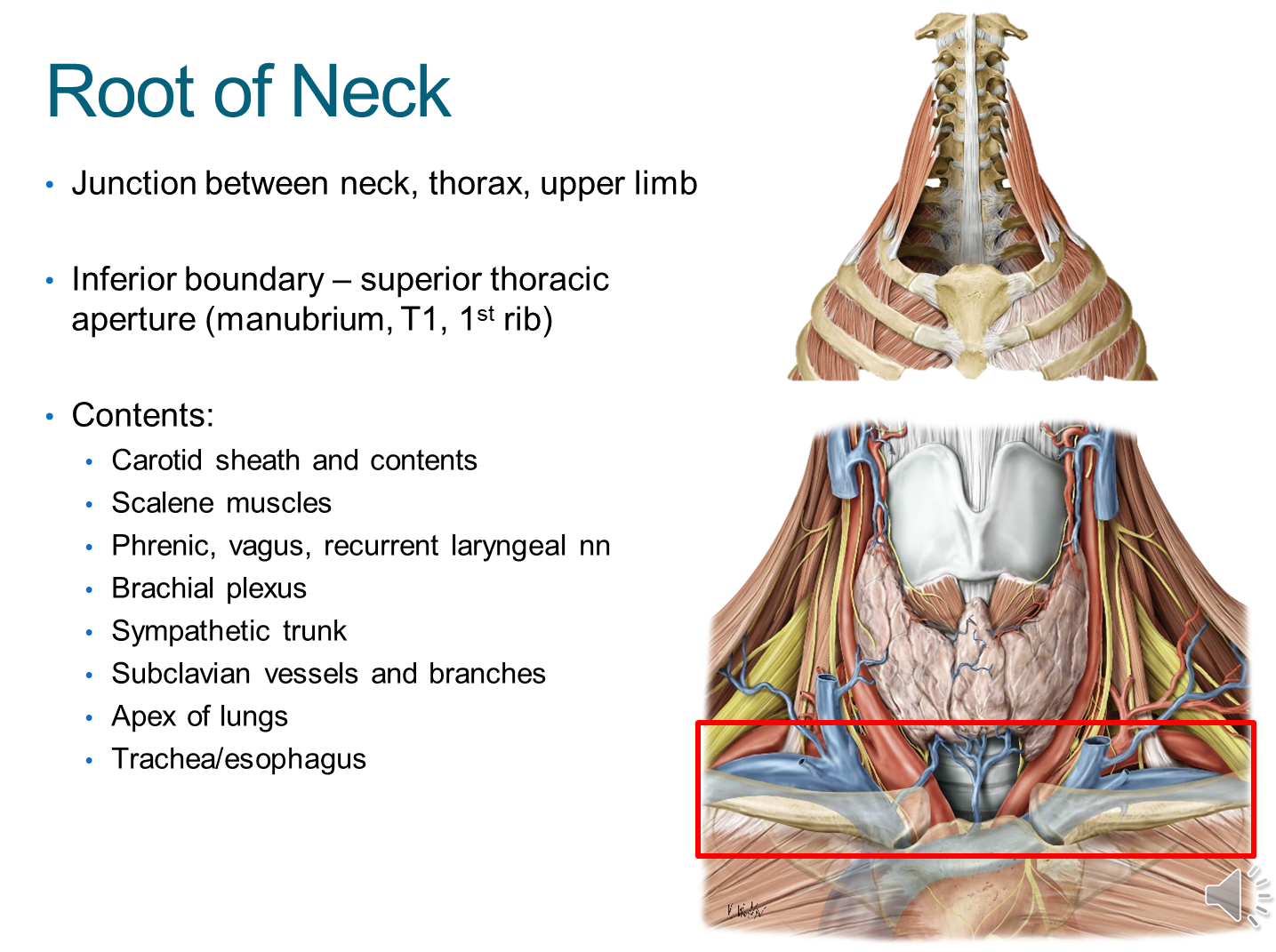
1) Root of the neck is an area between the neck, thorax and upper limbs
→ on the bottom of the root of the neck is the superior thoracic aperture formed from the manubrium, the first thoracic vertebrae and rib
2) Many structures will pass through the root of the neck on its way to the head and upper limbs
→ importantly, structures passing through the root of the neck and heading to the arms will pass through the apex of the axilla
What are the viscera of the root of the neck?
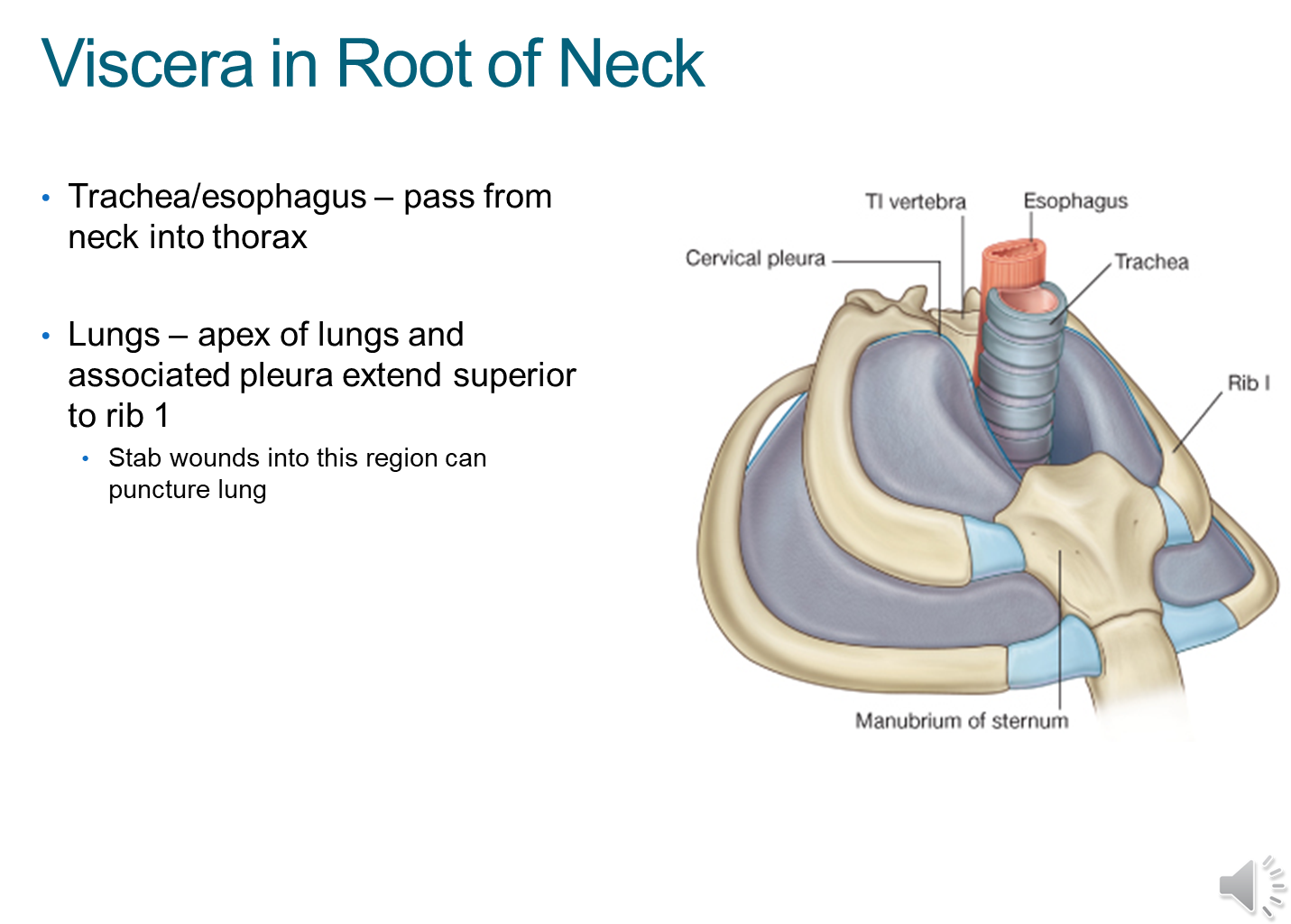
The viscera or organs in the root of the neck include
1) trachea/esophagus
2) apex of the lungs when we fully inspire
→ tumors at the apex of the lung (pancoast tumor) can impinge the neck
→ stab wounds here can cause lung puncture
What is the Subclavian Artery?
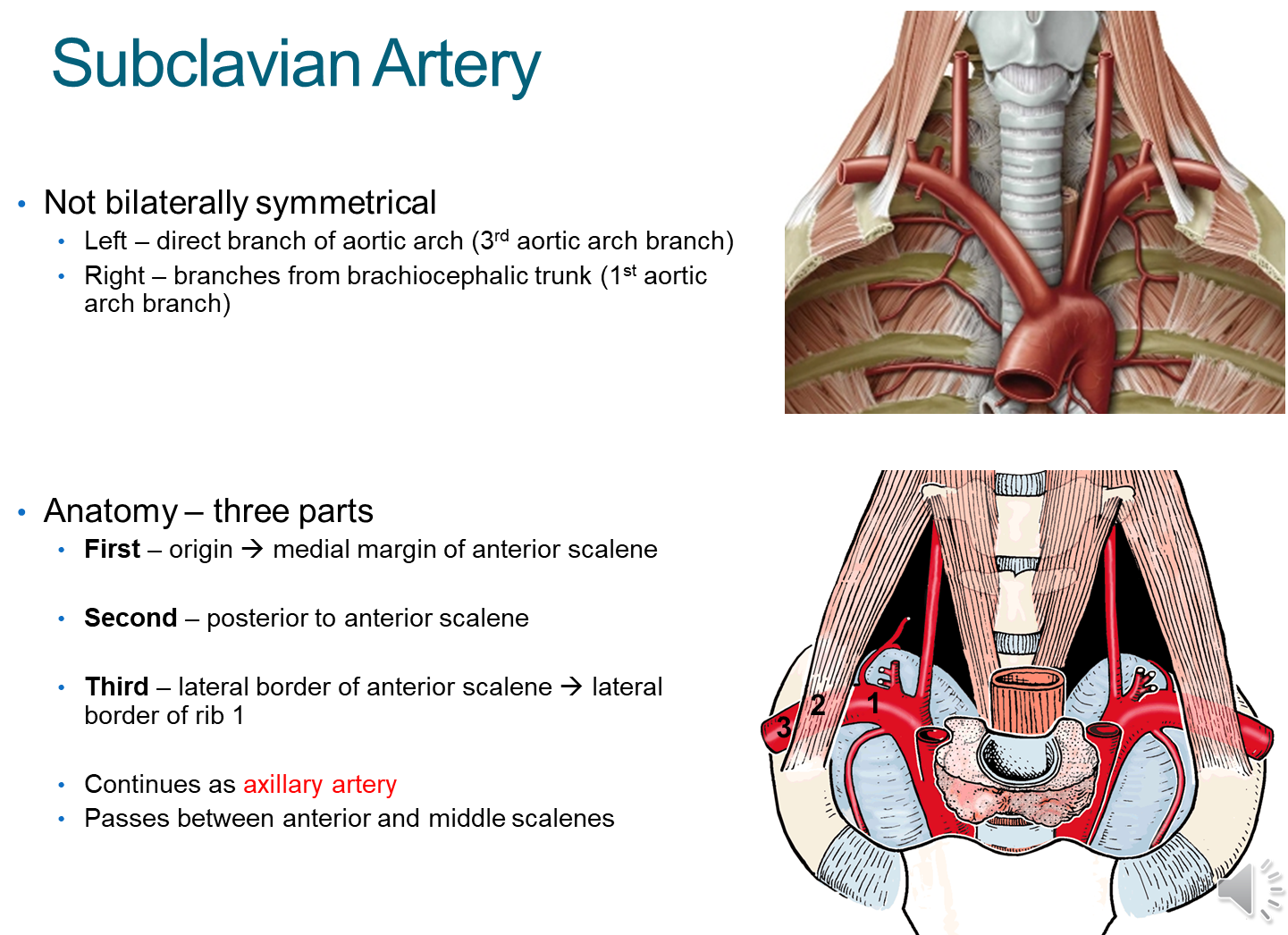
The subclavian artery is the main artery located in the root of the neck
1) Importantly this artery is non-symmetrical with different left and right branches
→ Left is a direct branch of the aortic arch
→ Right is a branch of the brachiocephalic trunk
2) The subclavian will subdivide into three parts based on its position relative to the anterior scalene muscle
→ First - medial to the scalene
→ Second - behind the scalene
→ Third - lateral to the scalene, and as it passes the first rib it becomes the axillary artery
What are the branches that break off at the first part of the subclavian?
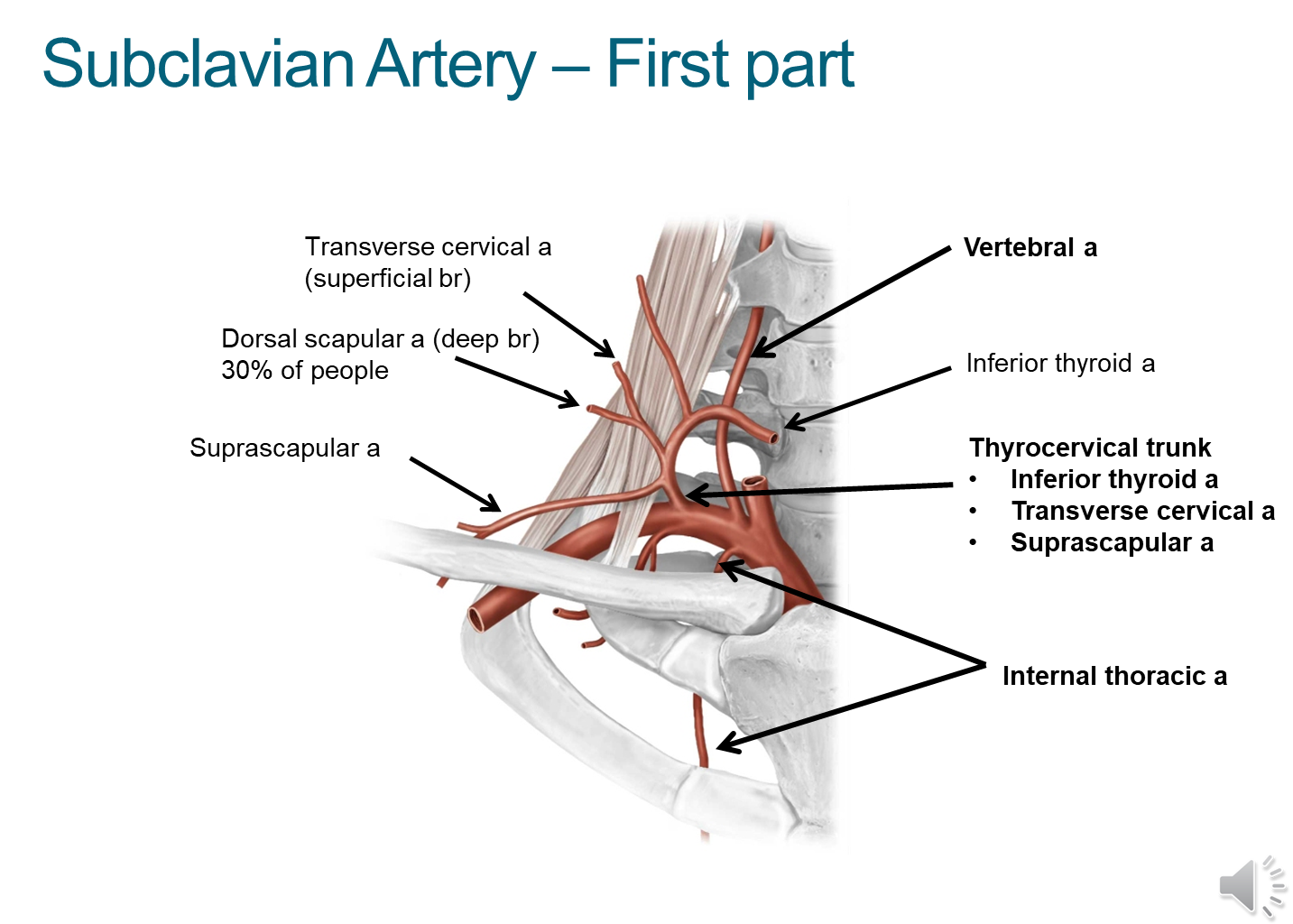
1) Vertebral Artery
→ ascends and enter into the transverse foramen and supply our brain
2) Internal Thoracic/Mammary
→ go down to the thorax and are common sites of CABG procedures
3) Thyrocervical trunk (subdivided into thre branches)
→ Inferior thyroid artery
→ Transverse cervical artery
→ Suprascapular artery
4) Some patients may also have a dorsal scapular artery located here as opposed to at the third part
What branches come off the subclavian at the second and third parts?
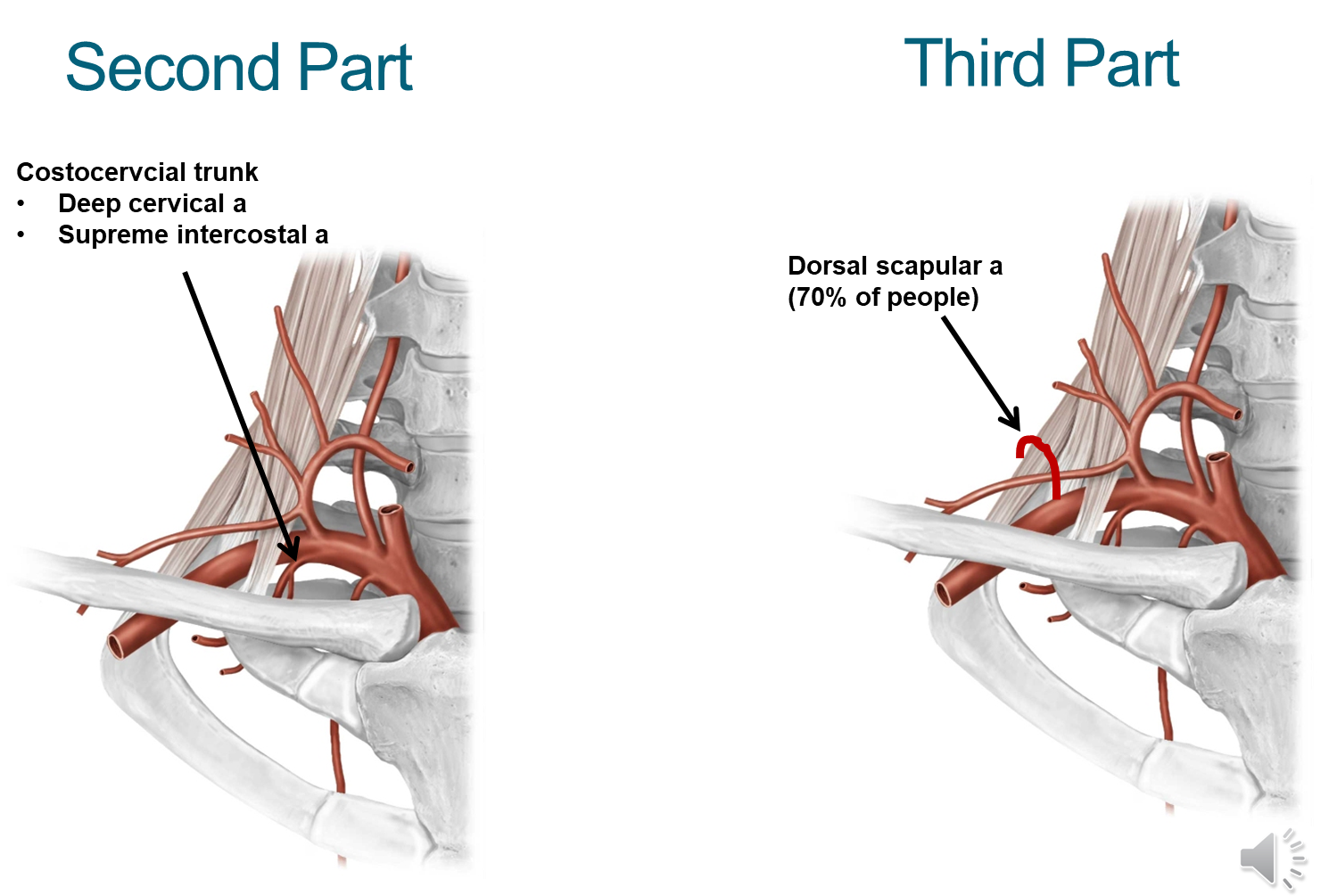
Second Part
→ Costocervical trunk that splits into the deep cervical artery and supreme intercostal artery
Third Part
→ Dorsal scapular artery (70% of the population has this) and provides blood to the shoulder
What are the four nerves found in the root of the neck?
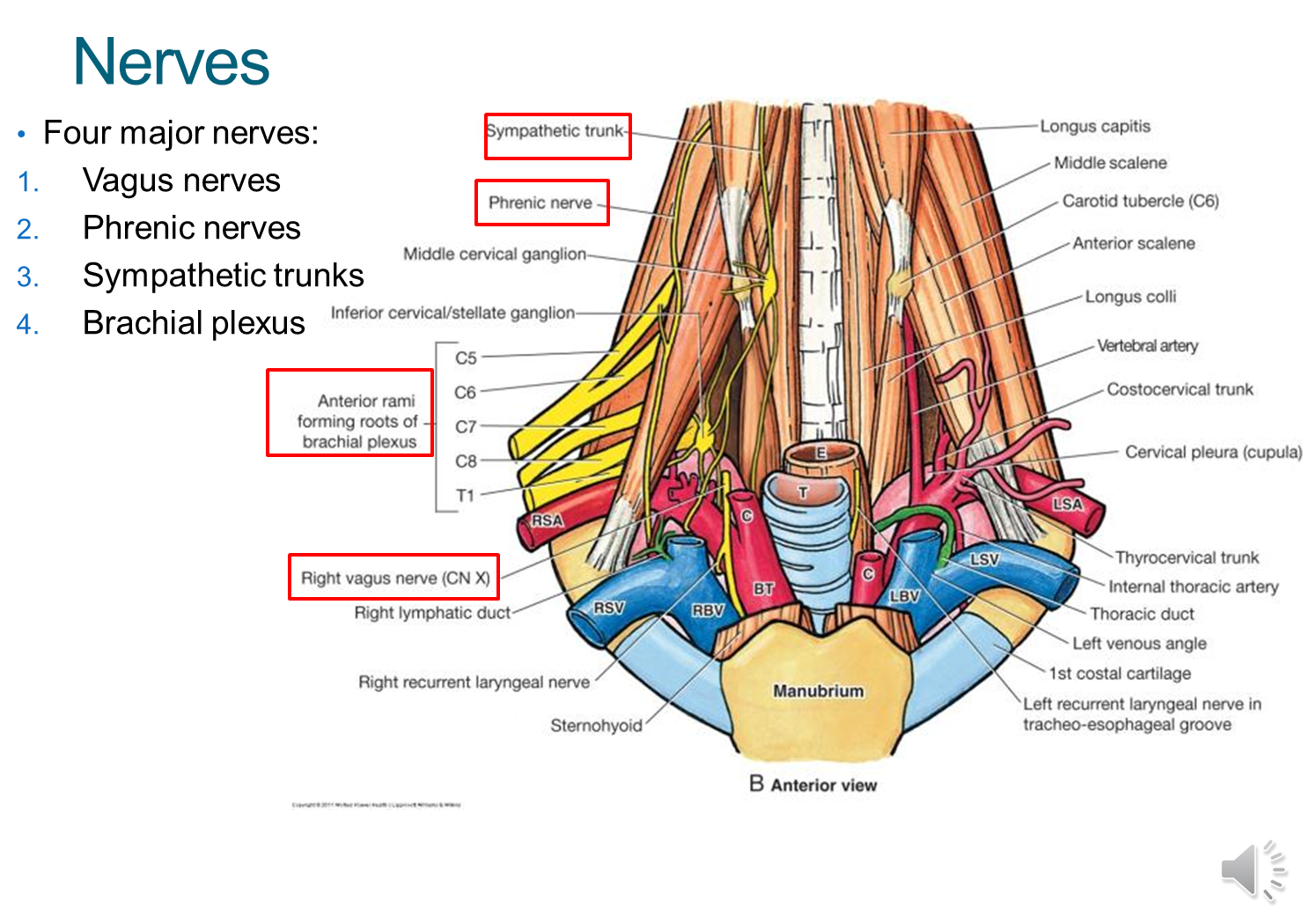
Vagus
→ CN X is posterior and between the carotid artery and internal jugular vein in the carotid sheath
Phrenic
→ C3-C5 and innervates our diaphragm and sits on top of the anterior scalene muscle
Sympathetic Trunk
→ medial to the carotid sheath, sitting on the lateral side of the vertebral bodies
Brachial Plexus
→ comes out of the interscalene triangle, and provides innervation to the muscles of the arms
What are the three sympathetic ganglia in the neck?
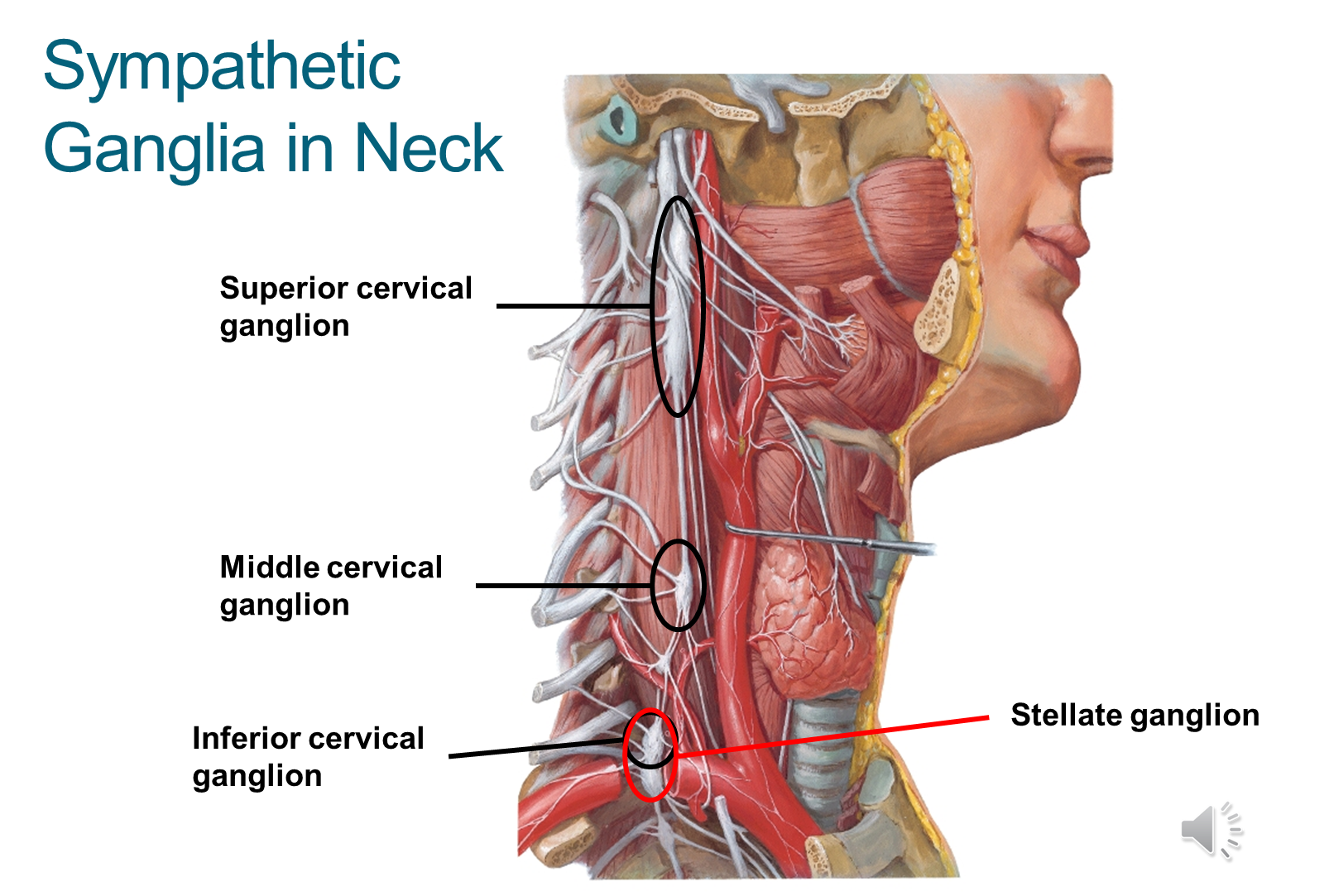
The superior ganglion is the relay site for sympathetic coming to the head
→ inferior ganglion fuses with the T1 ganglion becoming the stellate ganglion