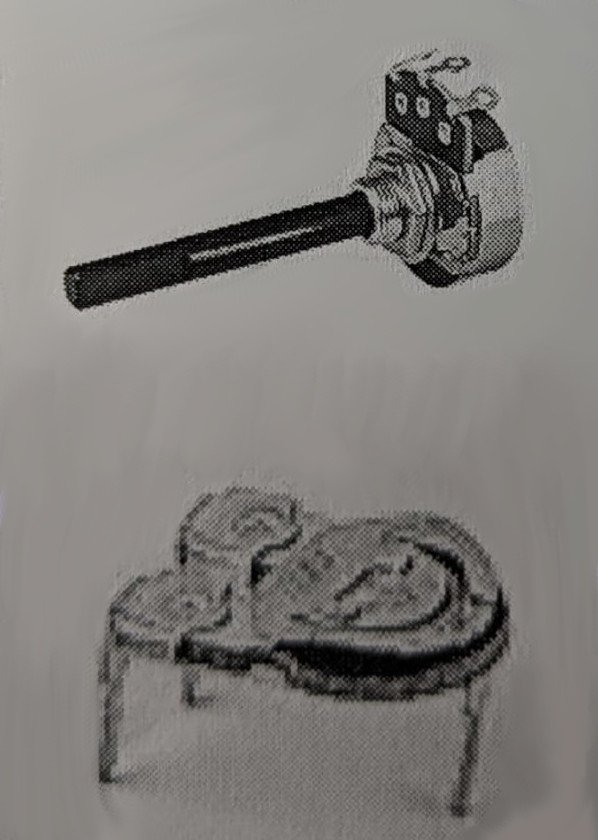GCSE CCEA Technology - Electronics
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
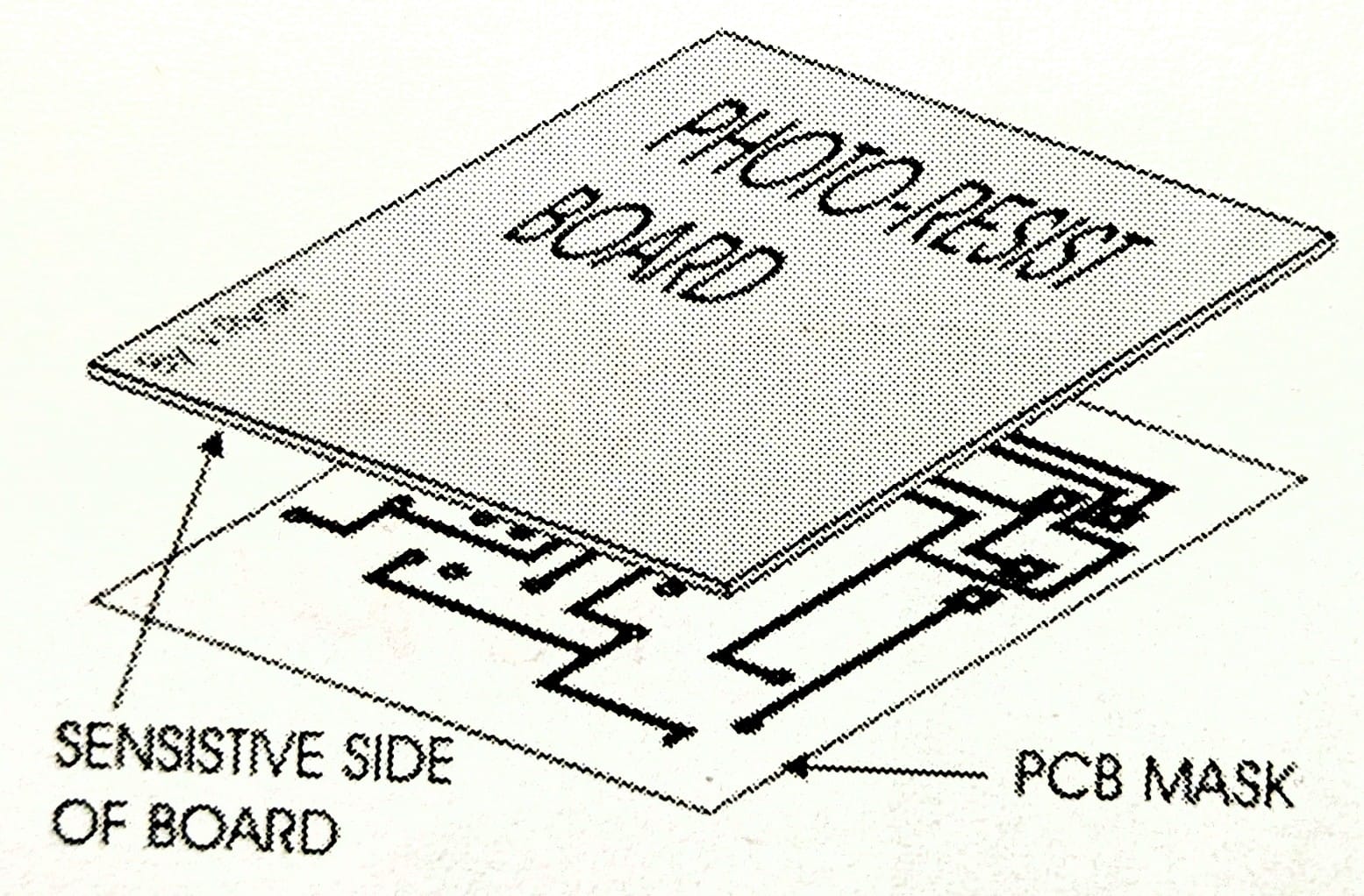
What is a photo-resist board?
Glass-reinforced plastic with copper clad and photosensitive coating; plastic film is peeled before UV exposure.
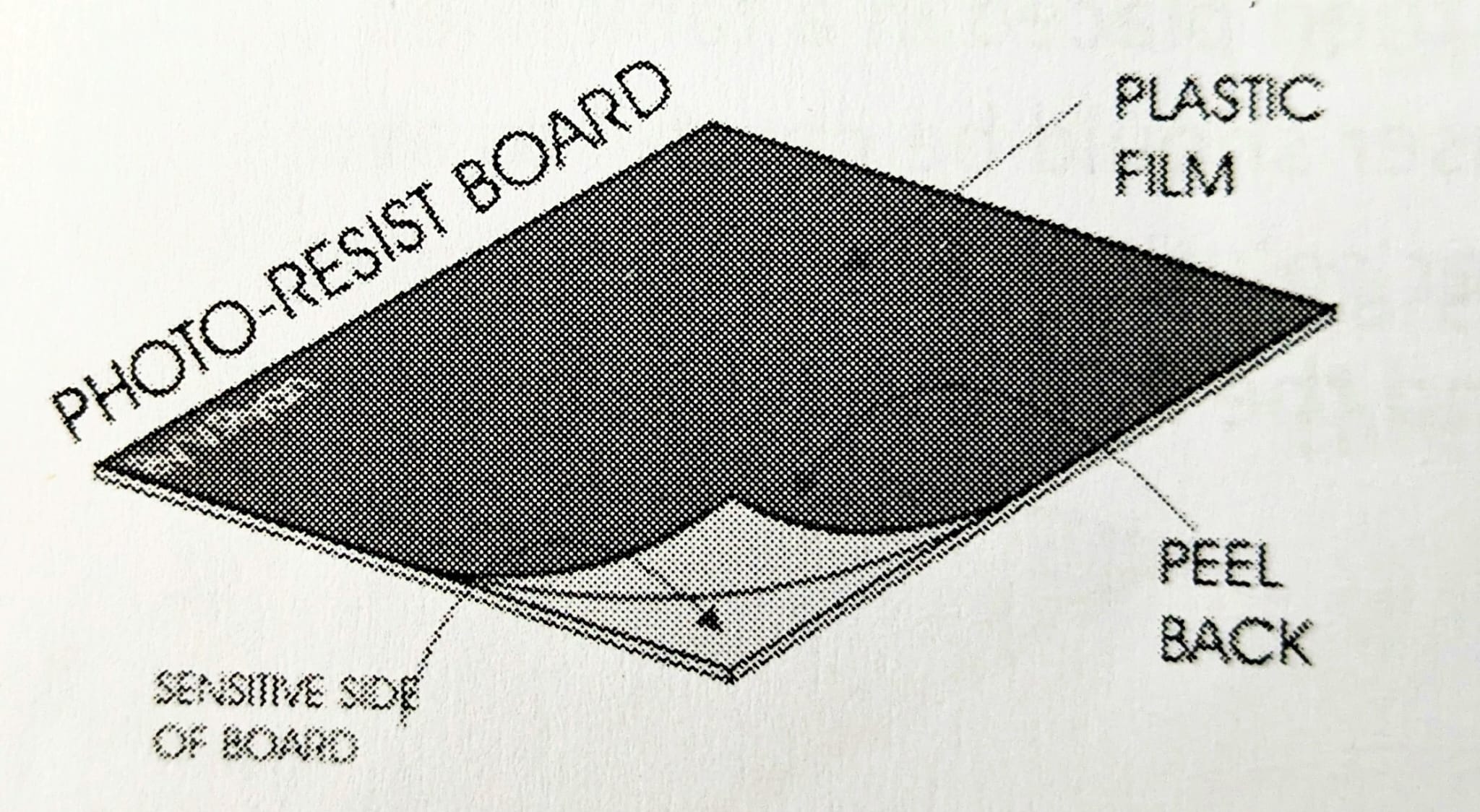
Describe the PCB mask and its placement.
Transparent sheet with PCB layout printed onto it; placed under the photo-resist board in a UV light box. Must be right-side up.
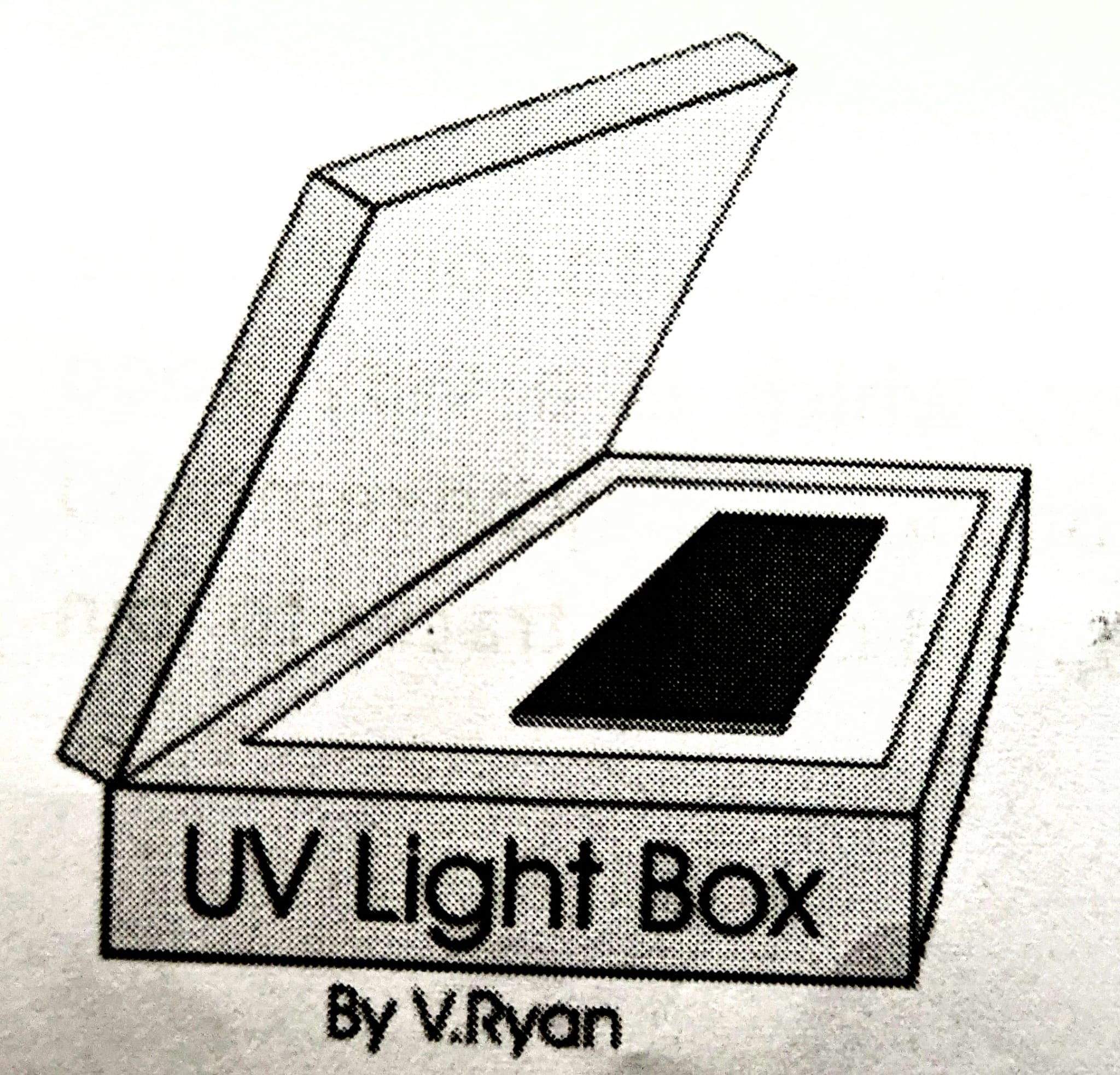
How long is UV exposure in PCB manufacturing?
2.5 minutes.
Purpose of developer solution?
Reveals PCB layout by removing exposed/non-exposed areas. Requires gloves/safety glasses and water rinse.
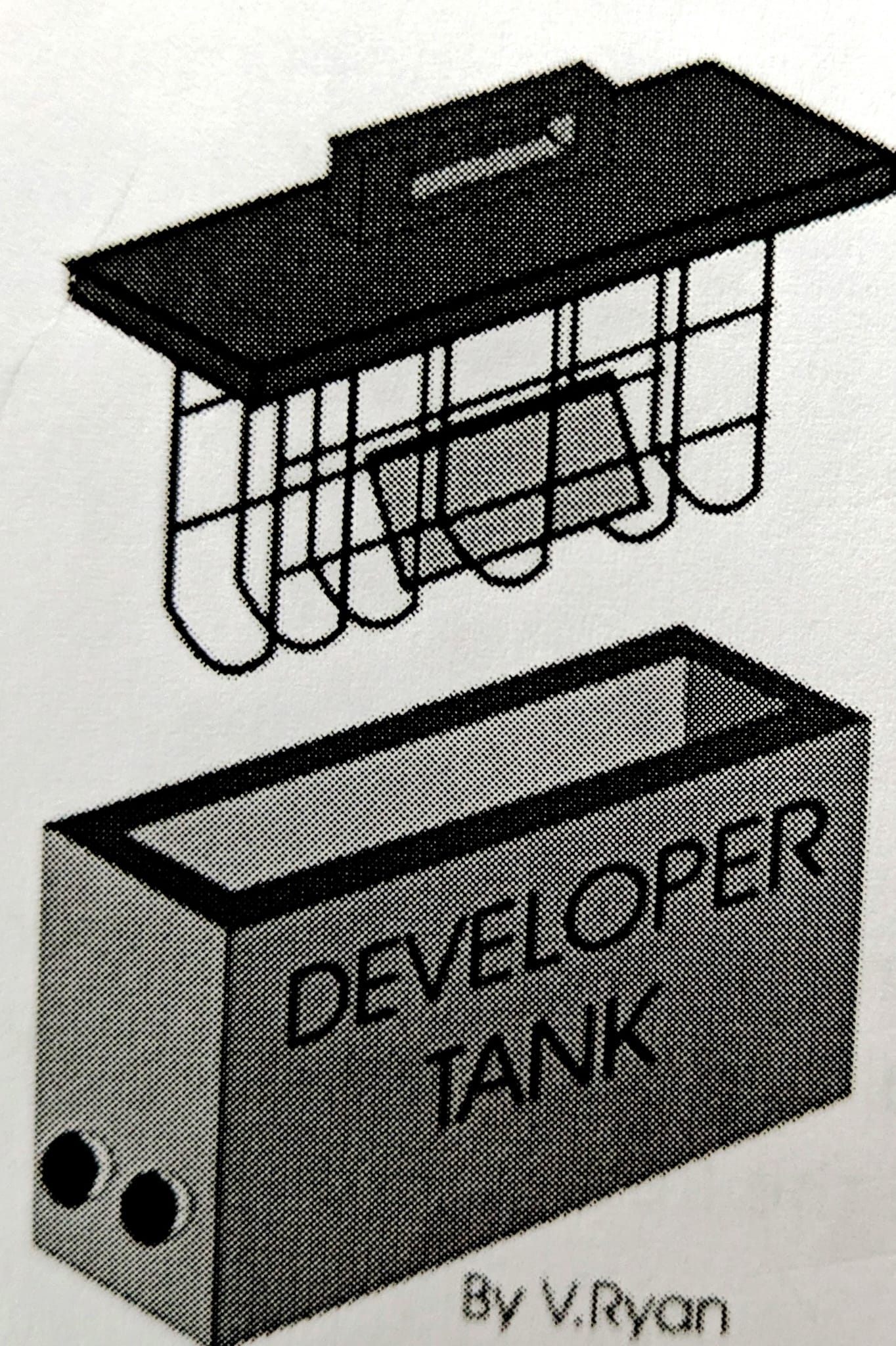
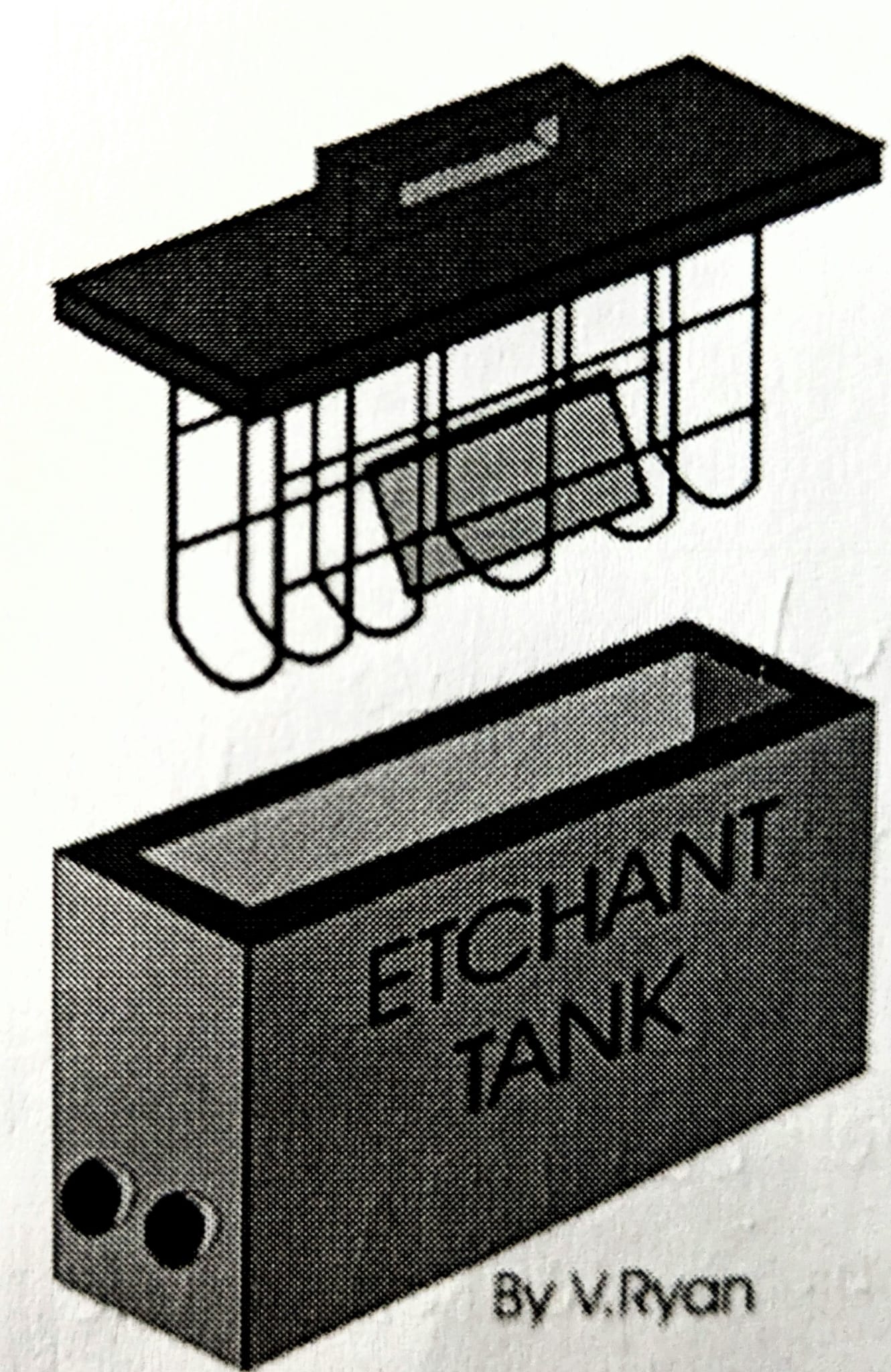
What does etching remove, and what are key precautions?
Removes unwanted copper (15-45 mins). Avoid over-etching to protect tracks.
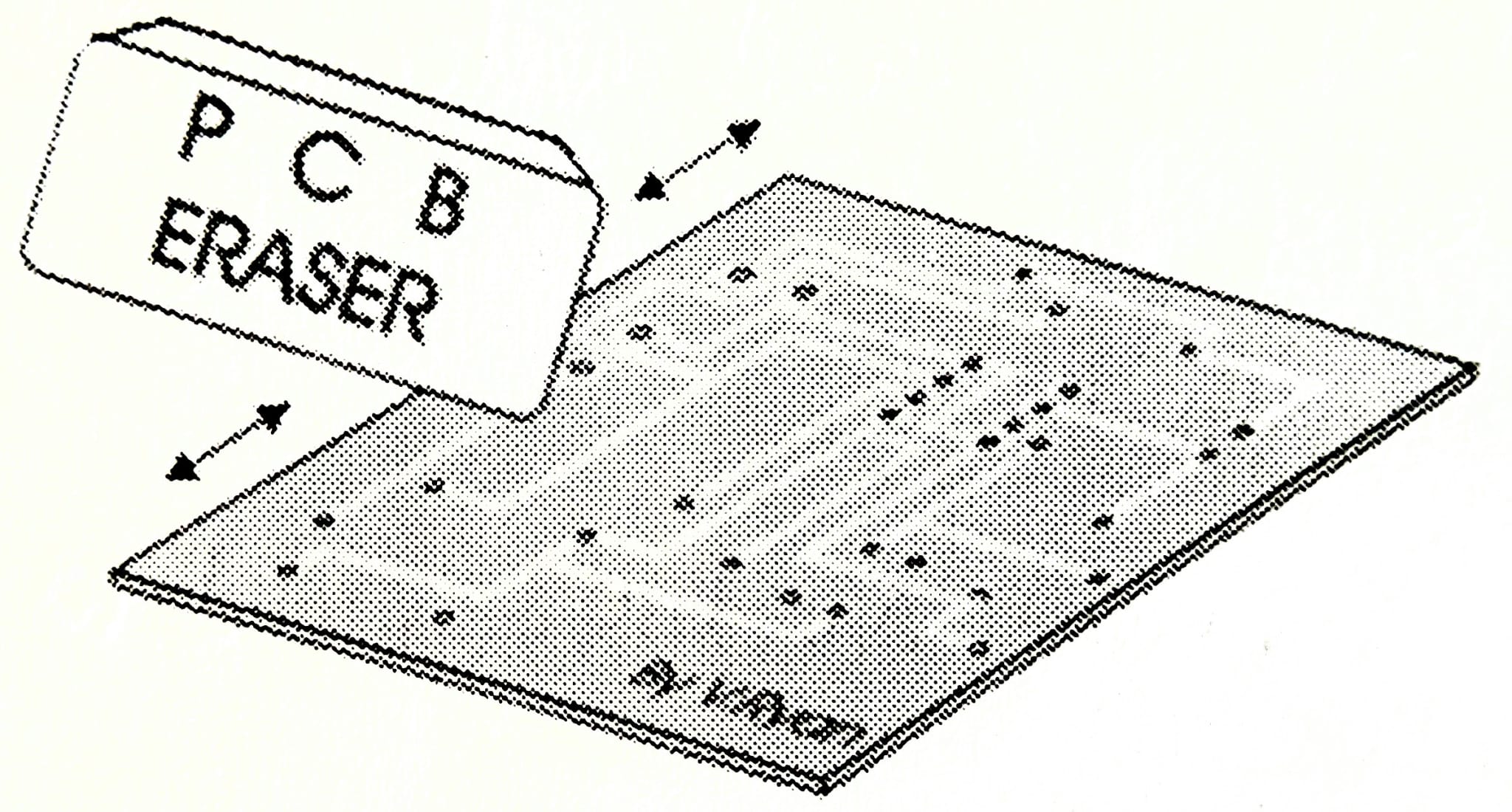
Steps after etching?
Washing, cleaning with PCB eraser, and checking for gaps with a magnifying glass.
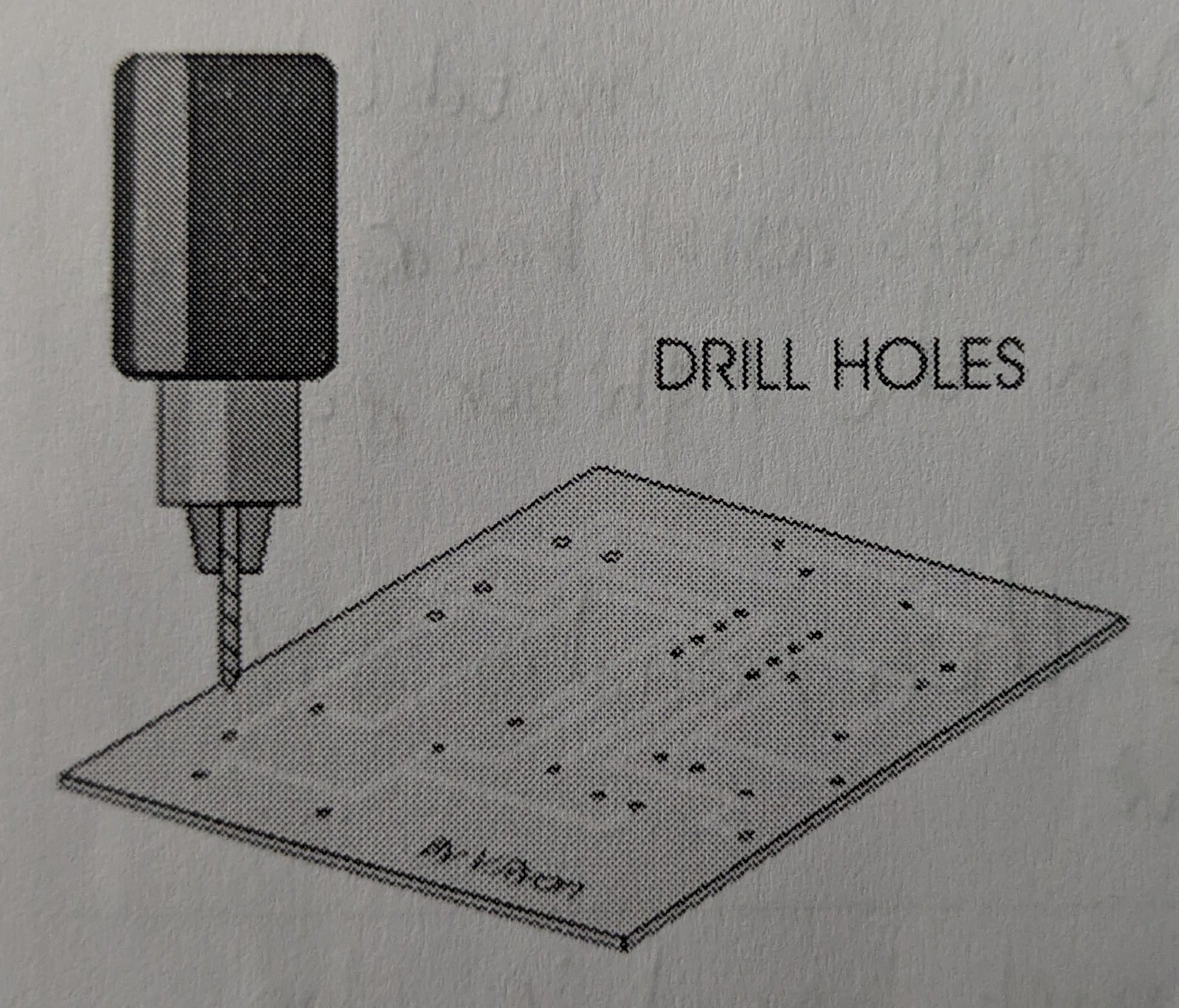
Final step in PCB manufacturing?
Drilling holes for components. Careless drilling ruins PCBs.
Define conventional current flow.
Flow of positive charges from battery (+) to (-).
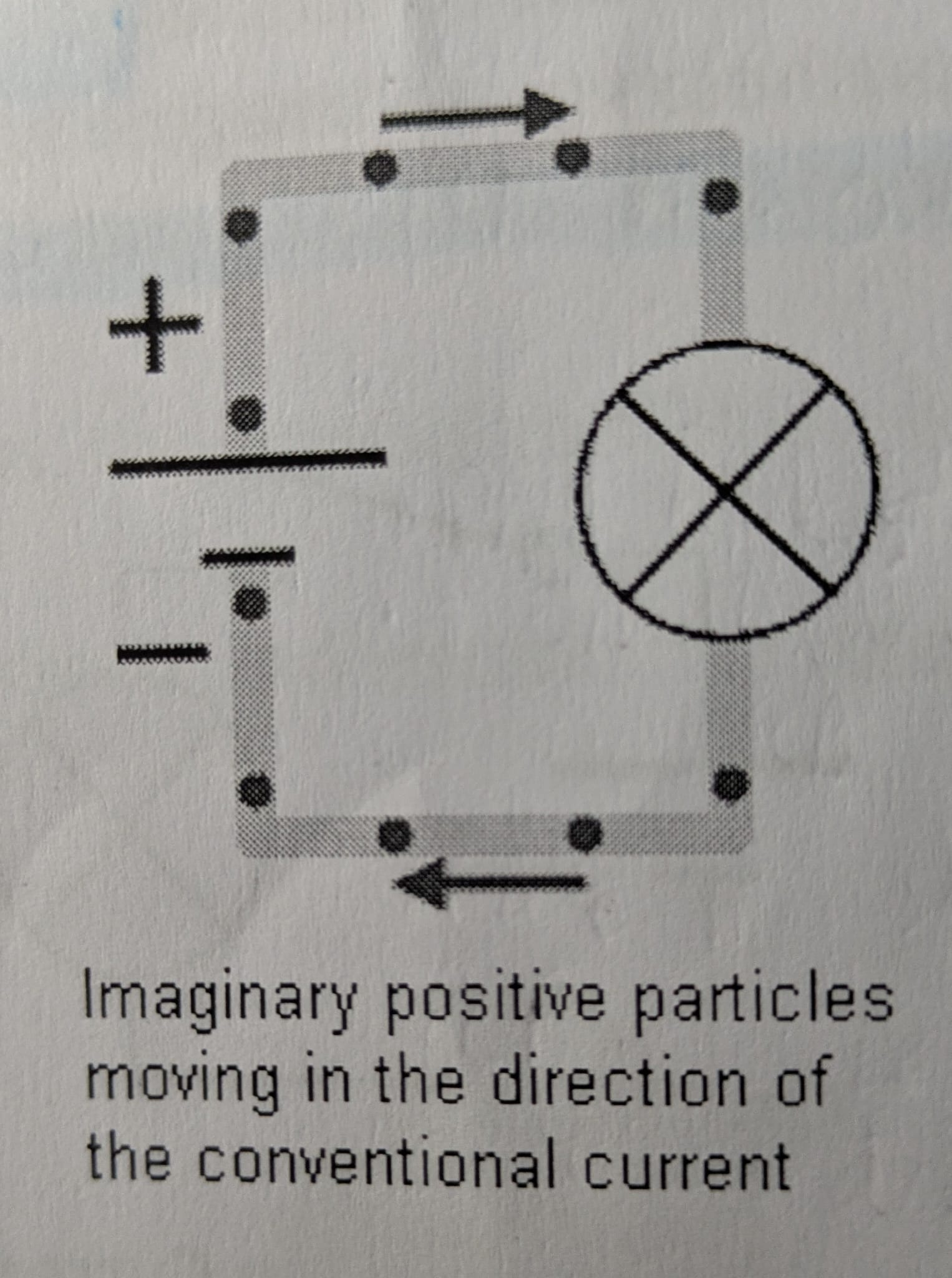
Relationship between voltage (V) and current (I).
Voltage is the 'push' that causes current flow.
Resistance unit and symbol.
Ohms (Ω).
Ohm's Law formula.
I = V/R or Current = Voltage / Resistance.
What happens to current if resistance increases?
Current decreases (inverse relationship).
Semiconductor example
Material (e.g., silicon) with conductivity between conductor and insulator.
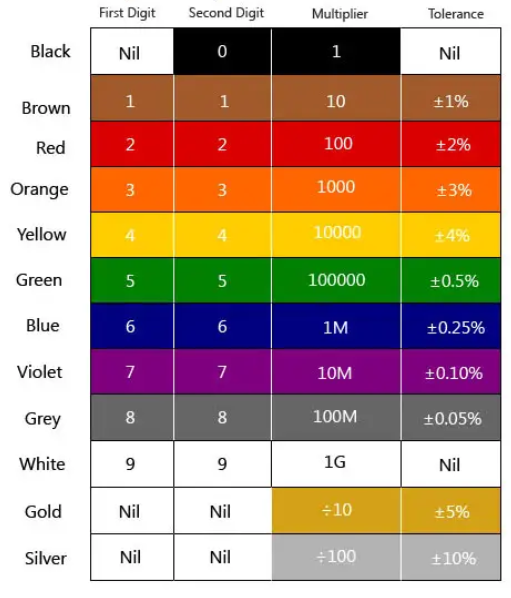
Decode: Brown-Black-Orange-Gold resistor.
10,000 Ω ±5% (10kΩ).
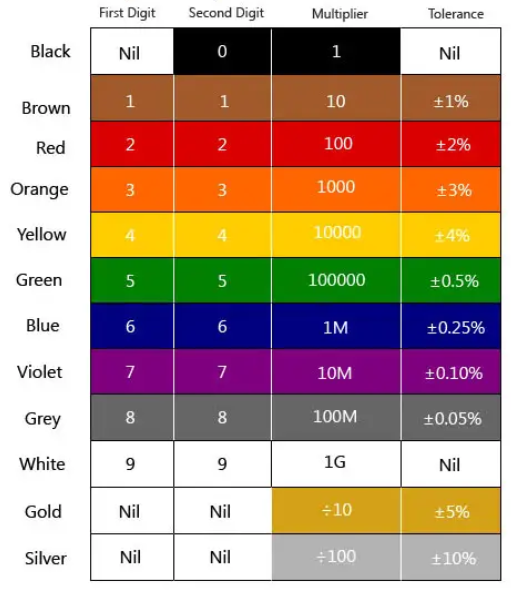
Tolerance of a silver-band resistor
±10%.
Formula for series resistors.
R total = R1 + R2
Resistor color code rules (4 bands).
Band 1: First digit
Band 2: Second digit
Band 3: Multiplier (number of zeros)
Band 4: Tolerance (Gold: ±5%, Silver: ±10%)
Voltage and use of a button cell.
1.5V or 3V; used in watches/backups. Low power, long shelf life.
Key environmental issue with batteries.
Heavy metal toxicity (Ni, Cd, Hg) contaminating soil/air if landfilled.
Main advantage of rechargeable batteries.
Reusable (1,000+ cycles), eco-friendly.
Parts of an electronic system block diagram.
Input → Control → Output.
LDR resistance change with light
Decreases in bright light (~100Ω), increases in dark (~1MΩ).
NTC (Negative temperature Coefficient) thermistor behavior with temperature
Resistance decreases as temperature increases (0°C: ~10kΩ, 100°C: ~100Ω).
Potentiometer
3-terminal variable resistor; wiper adjusts output voltage (e.g., volume control).
SPST switch
Basic on/off switch.
PTM switch
Push-to-Make (closes when pressed).
Reed switch
Closes when magnet is near.
SPDT switch
Connects to one of two outputs.
LED anode/cathode
Anode (+): longer lead; Cathode (-): shorter lead/flat side.
Diode function
Allows current flow in one direction.
Voltage divider formula
V out = V in × R2 / (R1 + R2)
Example of voltage divider
V in = 9V, R1 = 3kΩ, R2=6kΩ → V out = 6V.
Transistor terminals
Base (B), Collector (C), Emitter (E).
Toggle Switch
Maintained switch that flips between two positions.
Slide Switch
A switch that slides to open or close a circuit.
Micro Switch
Switch that requires a small force to actuate
Rocker Switch
Switch that pivots like a see-saw to open or close a circuit.
Membrane Switch
A flat switch with a pressure-sensitive surface.
PCB Production Methods
CNC milling or chemical etching.
Input-Process-Output Definition
Input takes data, process manipulates, output gives result.
Examples of control systems
Thermostat, automatic lighting.
Electrical Units
Amps (A), milliamps (mA); Volts (V), millivolts (mV); Ohms (Ω), kilohms (kΩ), mega-ohms (MΩ).
Function of Resistors, Capacitors and Inductors
Resistors limit current, capacitors store charge, inductors resist changes in current, etc.
Types of Batteries
Single cell, multi-cell.
Types of Resistors
Fixed, variable, LDR, thermistor.
Types of Transistors
NPN.
Function of LEDs
Emits light when current passes through.
Voltmeter Function
Measures voltage.
Ammeter Function
Measures current.
Conductors Definition
Offer low resistance to current flow.
Semiconductors Definition
Have conductivity between conductors and insulators.
Insulators Definition
Offer high resistance to current flow.
Potential Divider Function
Controls voltage in a circuit.
Purpose of resistors in relation to LED
Limits current to protect the LED.
Thyristor Terminals
Gate, anode, cathode.
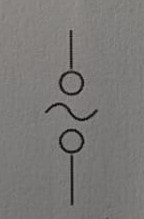
Symbol for AC supply
.
Symbol for a bulb
.
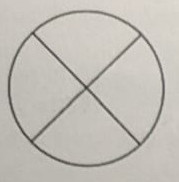
Symbol for a buzzer
.
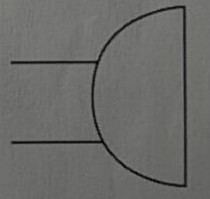
symbol for a crossing of conductors with no electrical connection
.

Symbol for a diode
.
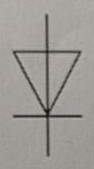
Symbol for earth
.

Symbol for a junction of conductors
.
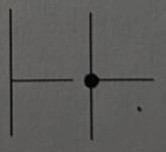
Symbol for an LDR
.
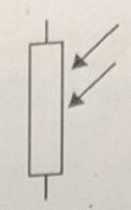
Symbol for an LED
.
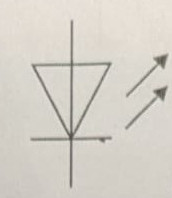
Symbol for a motor
.

Symbol for a Multi cell battery
.
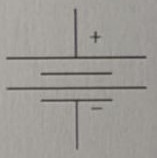
Symbol for an NPN transistor
.
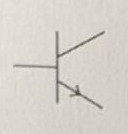
Symbol for a potentiometer
.
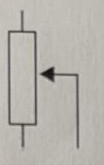
Symbol for a push to make switch
.

Symbol for a reed switch
.
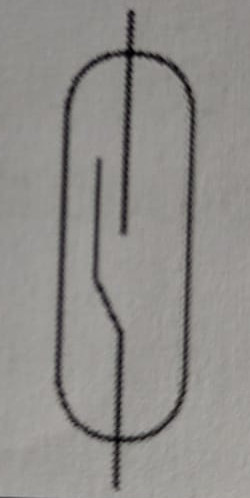
Symbol for a resistor
.

Symbol for a single cell batter
.
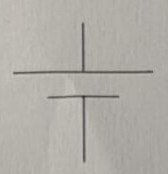
Symbol for a SPDT switch
.

Symbol for a SPST switch
.

Symbol for a terminal
.

Symbol for a thermistor
.
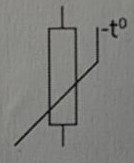
Symbol for a Thyristor
.
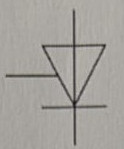
Symbol for a variable resistor
.
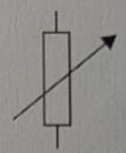
Symbol for a voltmeter
.

Two types of potentiometer
Preset potentiometer & turn type potentiometer