Pre Calc Final calculator part
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms

A
The ball begins at its maximum height of 15.240 meters. The height of the ball decreases until it reaches the ground 1.820 seconds after it leaves the window.
B
The ball begins at its maximum height of 15.240 meters. The height of the ball decreases until it reaches the ground 2.269 seconds after it leaves the window.
C
After leaving the window, the height of the ball increases to its maximum height of 16.228 meters. Then the height of the ball decreases until it reaches the ground 1.820 seconds after reaching its maximum height.
D
After leaving the window, the height of the ball increases to its maximum height of 16.228 meters. Then the height of the ball decreases until it reaches the ground 2.269 seconds after reaching its maximum height.
C
After leaving the window, the height of the ball increases to its maximum height of 16.228 meters. Then the height of the ball decreases until it reaches the ground 1.820 seconds after reaching its maximum height.
A
For any interval of x, the function always has a positive rate of change.
B
For any interval of x, the function always has a negative rate of change.
C
For any interval of x<-1.5, the function has a positive rate of change, and for any interval of x>-1.5, the function has a negative rate of change.
D
For any interval of x<-1.5, the function has a negative rate of change, and for any interval of x>-1.5, the function has a positive rate of change.
D
For any interval of x<-1.5, the function has a negative rate of change, and for any interval of x>-1.5, the function has a positive rate of change.
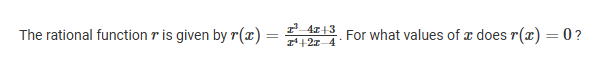
A
x=-2.303 and x=1.000 only
B
x=-1.643 and x=1.144 only
C
x=-2.303, x=1.000, and x=1.303 only
D
x=-2.303, x=-1.643, x=1.000, x=1.303, and
C
x=-2.303, x=1.000, and x=1.303 only
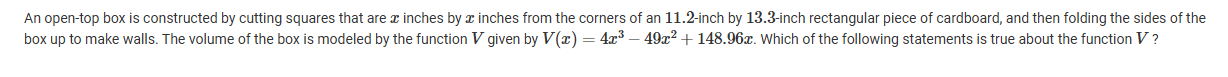
A
The contextual situation restricts the domain of V to 0<x<13.3, and the relative maximum value of V on this domain is 2724.106. This is because the longer side of the cardboard determines the domain restriction.
B
The contextual situation restricts the domain of V to 0<x<11.2, and the relative maximum value of V on this domain is 1141.504. This is because the shorter side of the cardboard determines the domain restriction.
C
The contextual situation restricts the domain of V to 0<x<6.65, and the relative maximum value of V on this domain is 133.929. This is because half of the longer side of the cardboard determines the domain restriction.
D
The contextual situation restricts the domain of V to 0<x<5.6, and the relative maximum value of V on this domain is 133.929. This is because half of the shorter side of the cardboard determines the domain restriction.
D
The contextual situation restricts the domain of V to 0<x<5.6, and the relative maximum value of V on this domain is 133.929. This is because half of the shorter side of the cardboard determines the domain restriction.
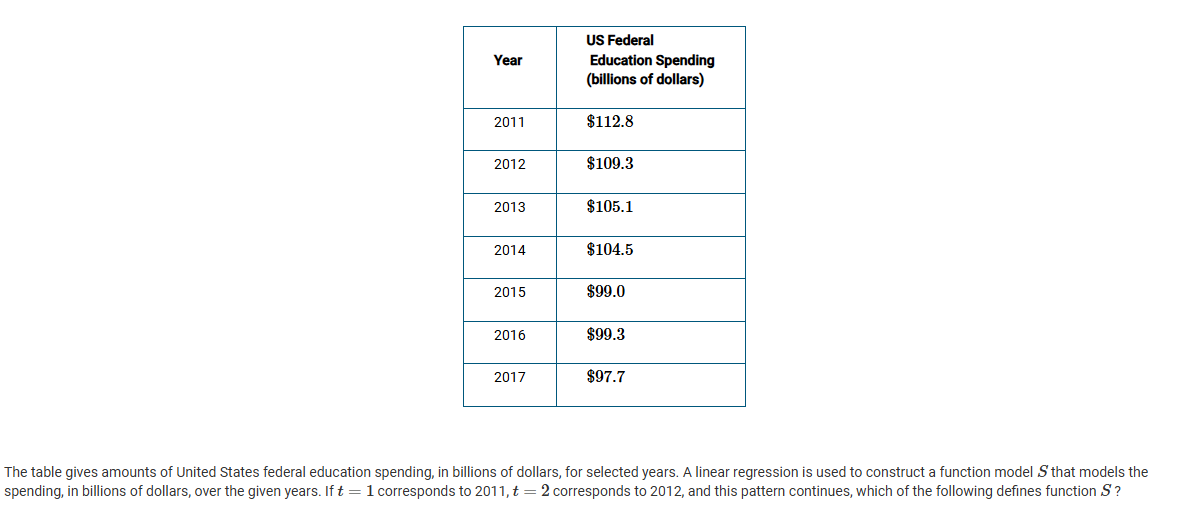
A
St=-2.55t+114.157
B
St=-2.55t+5239.657
C
St=-8.099t+113.820
D
St= -0.369t+42.308
A
St= -2.55t+114.157

A
VP=11.458P
B
VP=1650P
C
VP=11.458 / P
D
VP= 1650 / P
D
VP= 1650 / P

A
-0.382
B
-0.306
C
0.375
D
5.625
A
-0.382
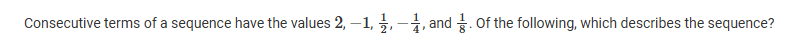
A
The terms could be part of a geometric sequence with a common ratio of -2.
B
The terms could be part of a geometric sequence with a common ratio of -1/2.
C
The terms could be part of a geometric sequence with a common ratio of 1/2.
D
The terms are part of a sequence other than a geometric sequence because the common ratio of a geometric sequence must be positive.
B
The terms could be part of a geometric sequence with a common ratio of -1/2.

A
The second term of the arithmetic sequence must be less than the second term of the geometric sequence.
B
The second term of the arithmetic sequence must be greater than the second term of the geometric sequence.
C
The second term of the arithmetic sequence must be the same value as the second term of the geometric sequence.
D
The relationship between the values of the second terms cannot be determined from the given information.
B
The second term of the arithmetic sequence must be greater than the second term of the geometric sequence.
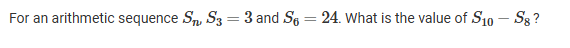
A
2
B
7
C
14
D
288
C
14
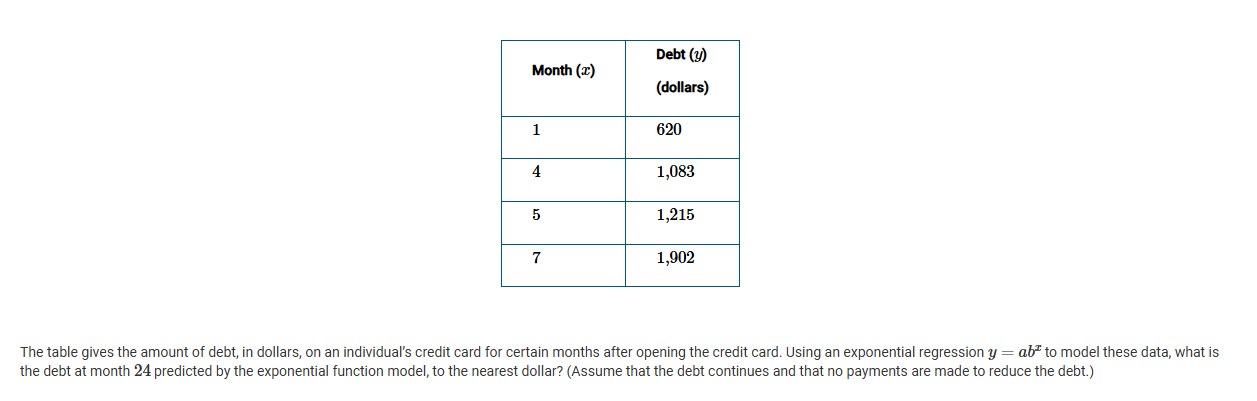
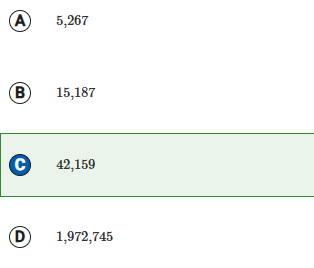
A
5,267
B
15,187
C
42,159
D
1,972,745
C
42,159
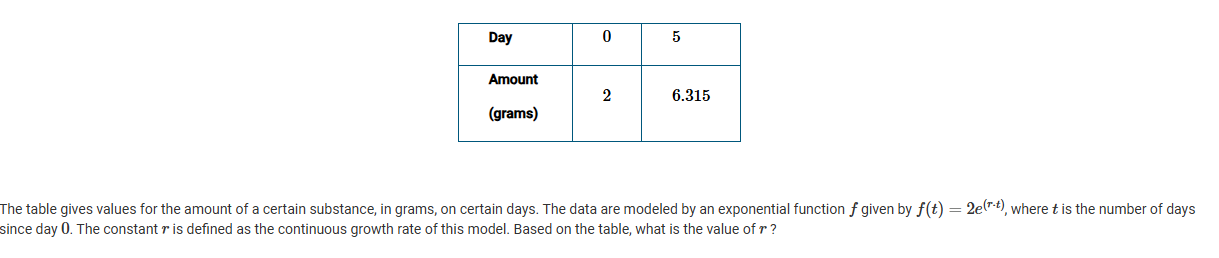
A
0.230
B
0.259
C
0.863
D
1.259
A
0.230


A
3.996
B
4.983
C
9.966
D
19.932
D
19.932
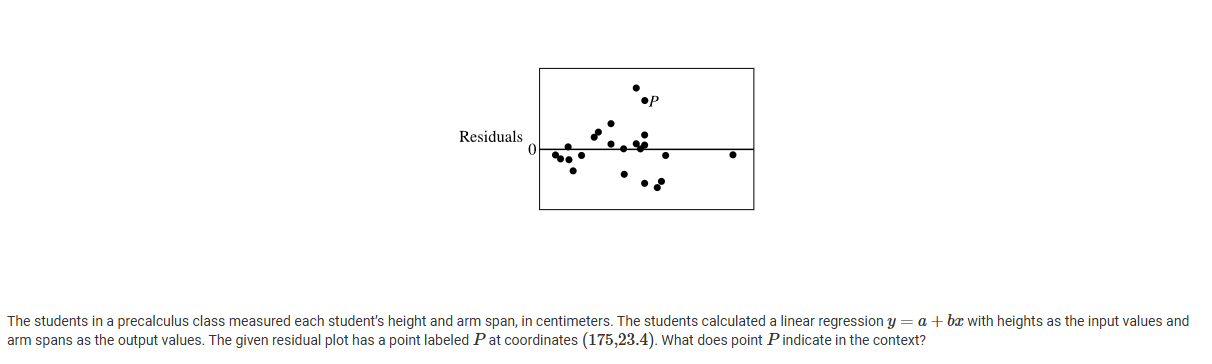
A
Because point P is above the x-axis, for the student with a height of 175 cm, the model overestimates the actual arm span value by 23.4 cm.
B
Because point P is above the x-axis, for the student with a height of 175 cm, the model underestimates the actual arm span value by 23.4 cm.
C
Because point P is above the x-axis, for the student with an arm span of 175 cm, the model overestimates the actual height value by 23.4 cm.
D
Because point P is above the x-axis, for the student with an arm span of 175 cm, the model underestimates the actual height value by 23.4 cm.
B
Because point P is above the x-axis, for the student with a height of 175 cm, the model underestimates the actual arm span value by 23.4 cm.
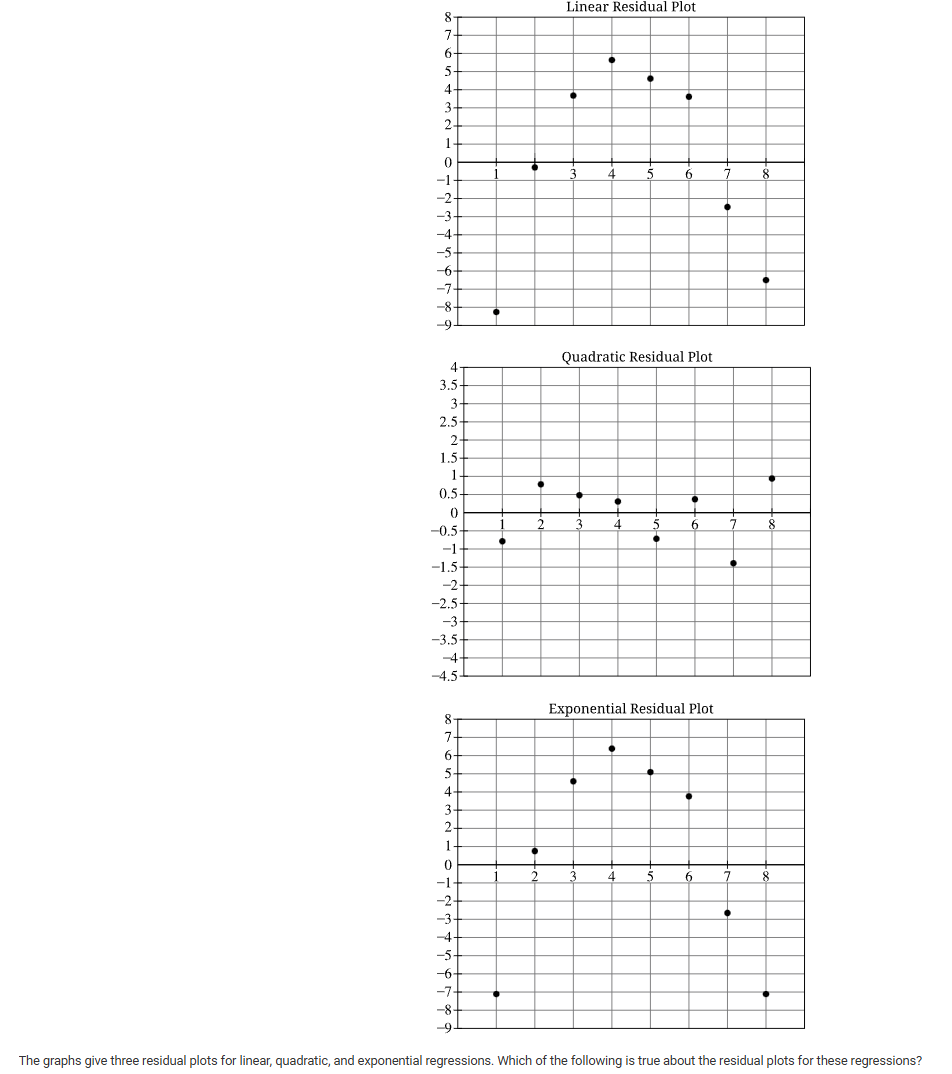
A
The residual plots for the linear and exponential regressions are without pattern, and the residual plot for the quadratic regression shows a pattern. Therefore, the quadratic model is appropriate.
B
The residual plot for the quadratic regression is without pattern, and the residual plots for the linear and exponential regressions show patterns. Therefore, the linear and exponential models are appropriate.
C
The residual plots for the linear and exponential regressions are without pattern, and the residual plot for the quadratic regression shows a pattern. Therefore, the linear and exponential models are appropriate.
D
The residual plot for the quadratic regression is without pattern, and the residual plots for the linear and exponential regressions show patterns. Therefore, the quadratic model is appropriate.
D
The residual plot for the quadratic regression is without pattern, and the residual plots for the linear and exponential regressions show patterns. Therefore, the quadratic model is appropriate.

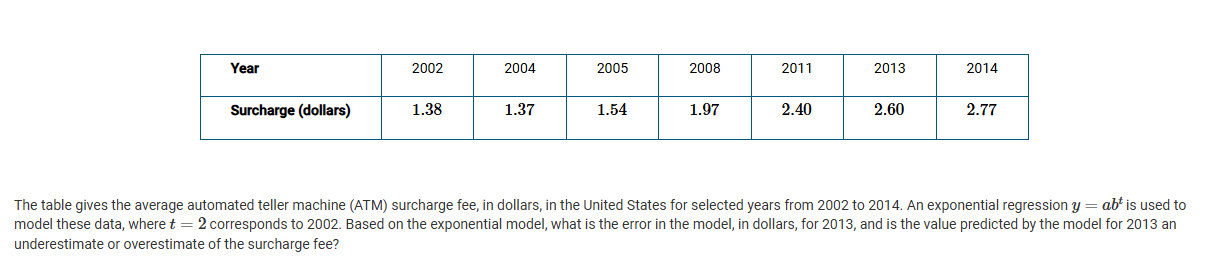
A
The error is 0.01, and the value predicted by the model is an underestimate.
B
The error is 0.01, and the value predicted by the model is an overestimate.
C
The error is 0.03, and the value predicted by the model is an underestimate.
D
The error is 0.03, and the value predicted by the model is an overestimate.
D
The error is 0.03, and the value predicted by the model is an overestimate.

A
0.3
B
0.5
C
2.0
D
3.0
C
2.0


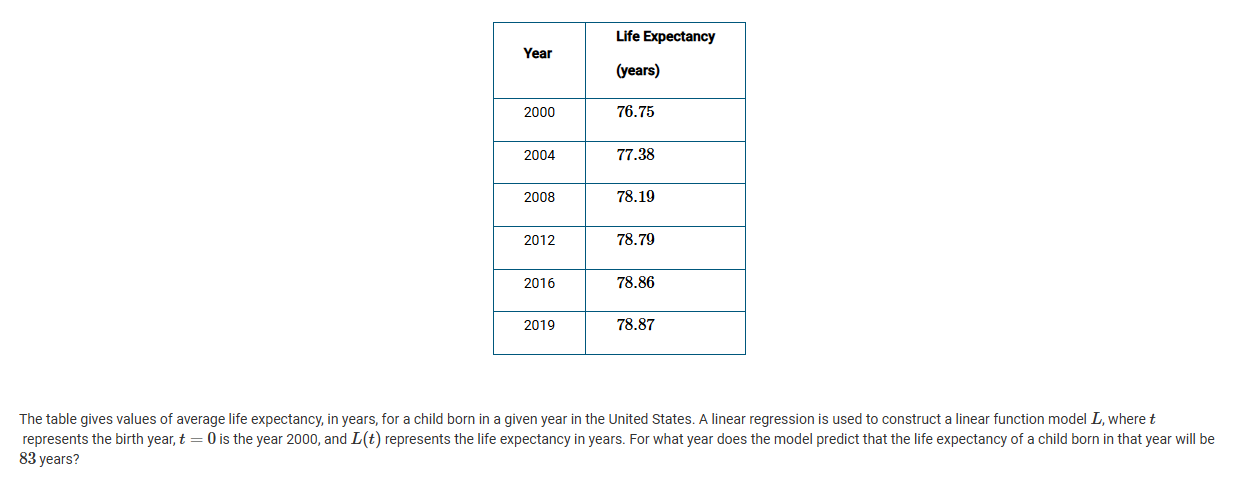
A
2032
B
2051
C
2056
D
2086
B
2051

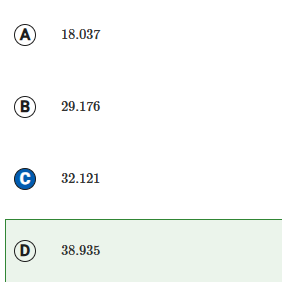
A
18.037
B
29.176
C
32.121
D
38.935
D
38.935