Chapter 5 Integumentary System
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
epidermis
Superficial layer of the skin; composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
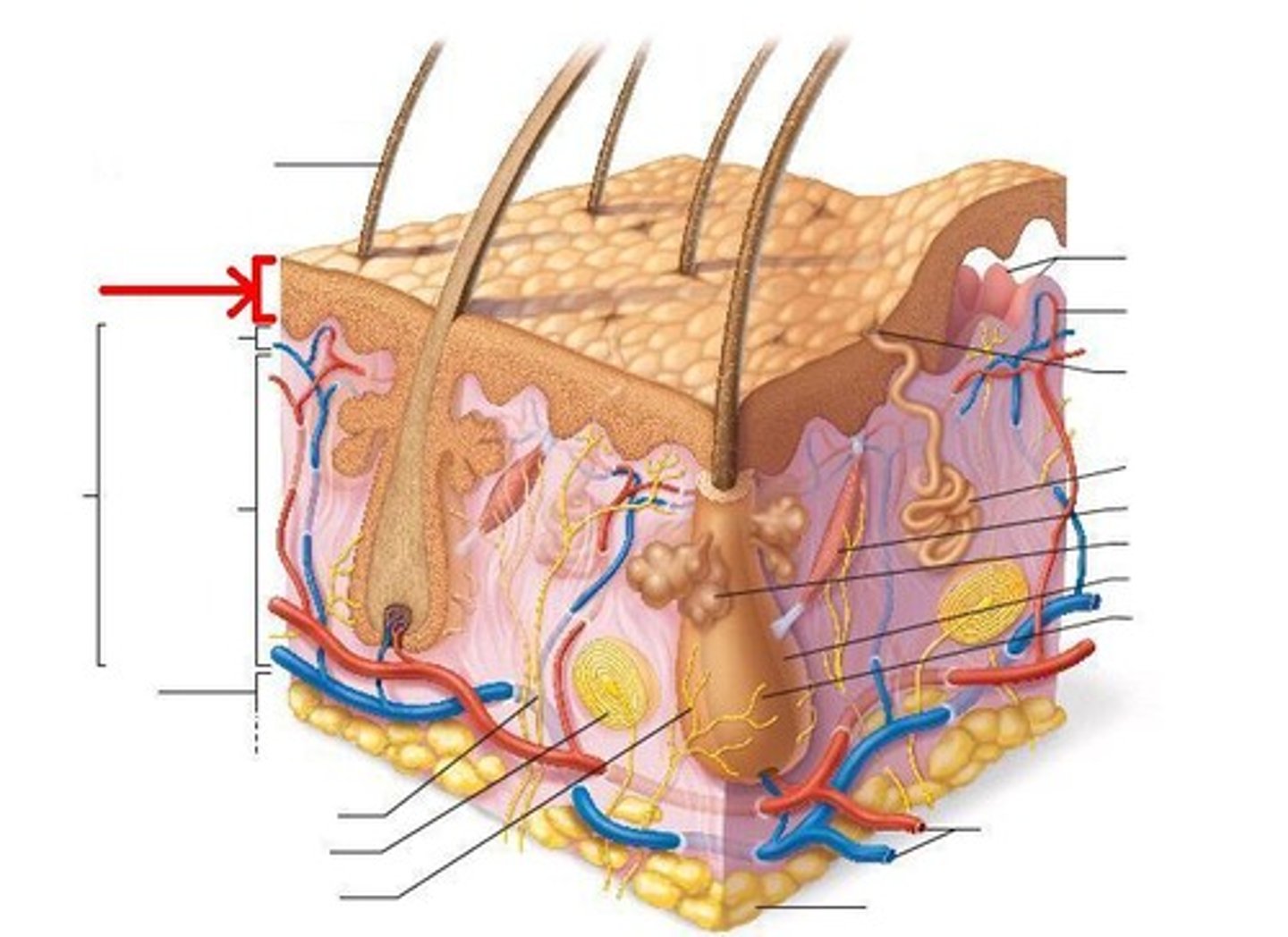
dermis
the deep layer of the skin; composed of dense, irregular connective tissue
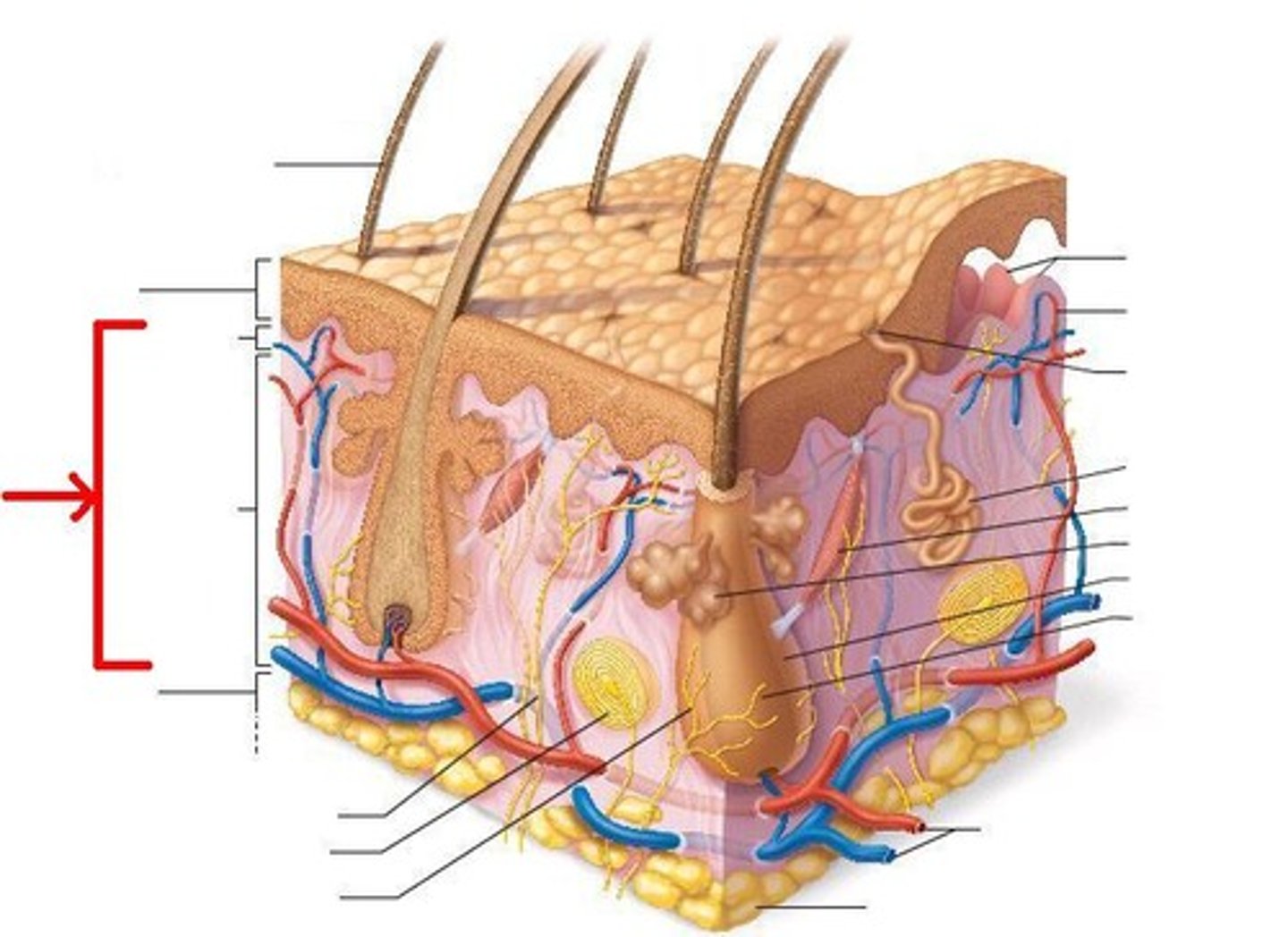
Hypodermis (subcutaneous layer)
Deep to the dermis; not technically part of the skin; made of adipose tissue; helps insulate
Pancinian corpuscles
Composed of connective tissue and cells that detect deep pressure and vibrations
keratinocytes
an epidermal cell that produces keratin.
melanocytes
cells that produce melanin
Merkel cells
cells of the epidermis that play a role in transmission of sensory messages
Langerhans cells
epidermal macrophages that help activate the immune system
thin skin
Type of skin that lacks a stratum lucidum, has hair, and is found covering most of the body
thick skin
The skin type on the palms and soles is characterized by the absence of hair follicles and presence of stratum lucidum
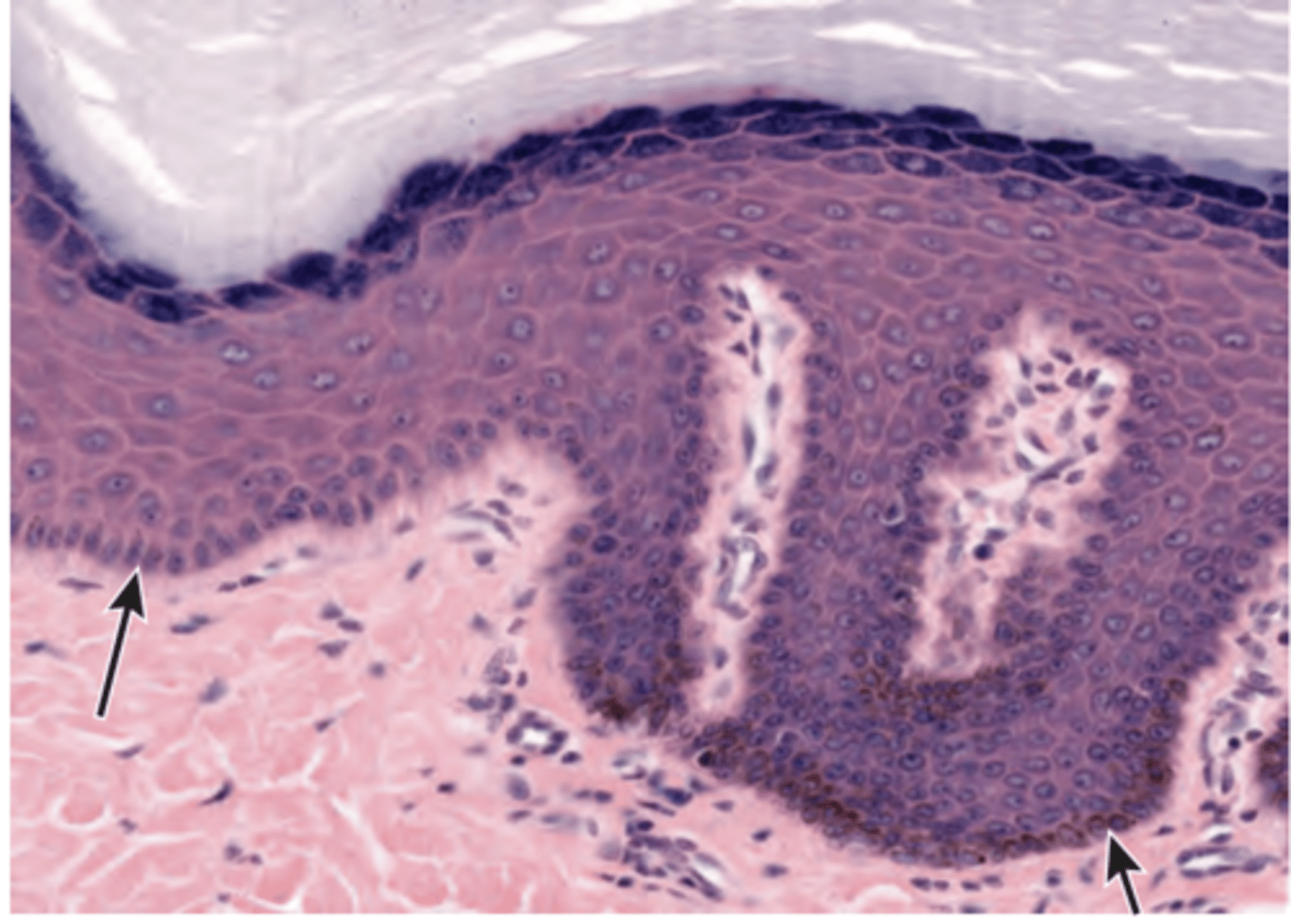
stratum basale (germinativum)
base layer of skin, one cell layer, always under division
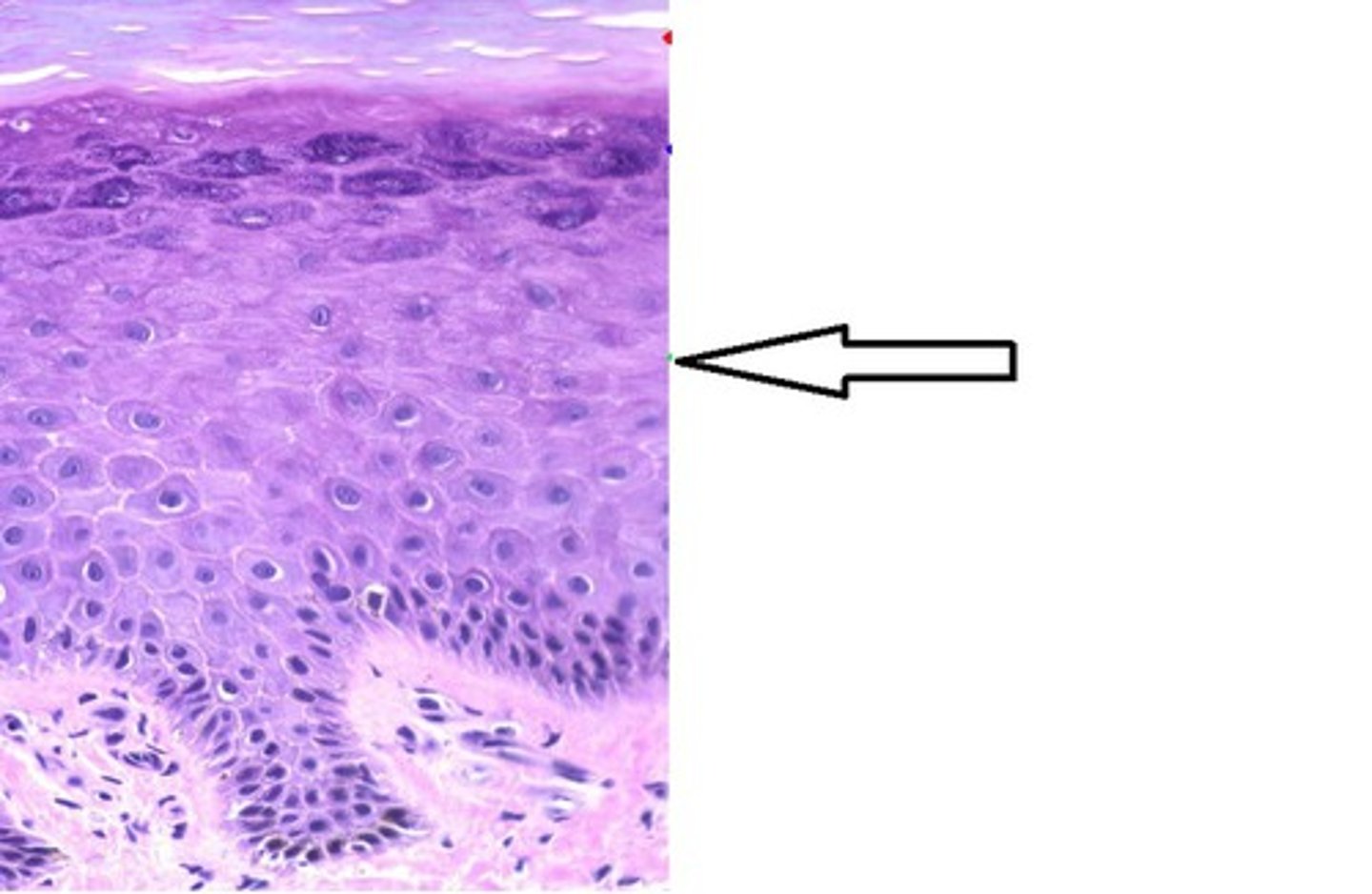
stratum spinosum
layer of the epidermis superficial to the stratum basale, characterized by the presence of desmosomes
stratum granulosum
a layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between the deeper, metabolically active strata and the dead cells of the more superficial strata
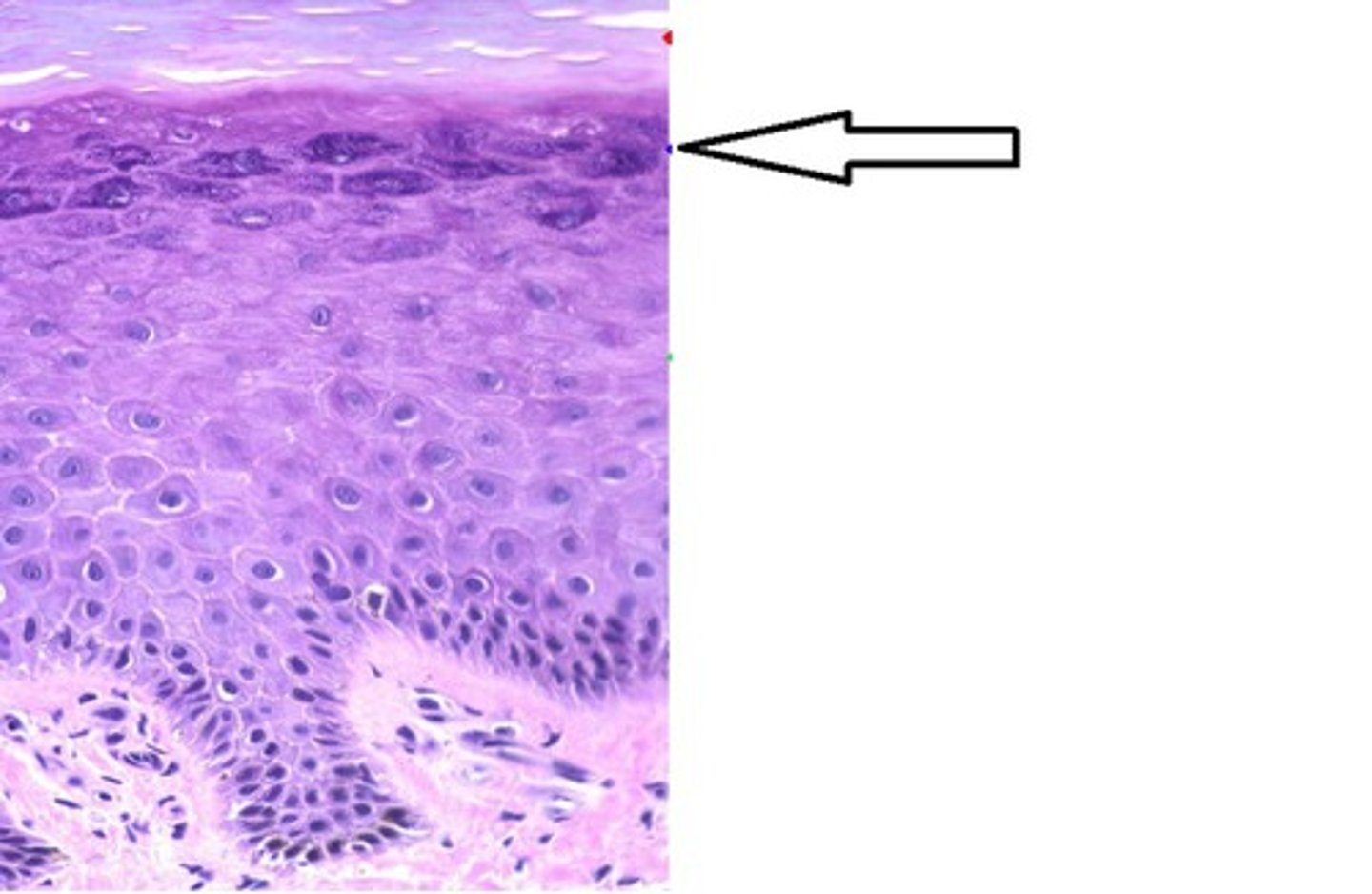
stratum lucidum
Clear, transparent layer of the epidermis under the stratum corneum.
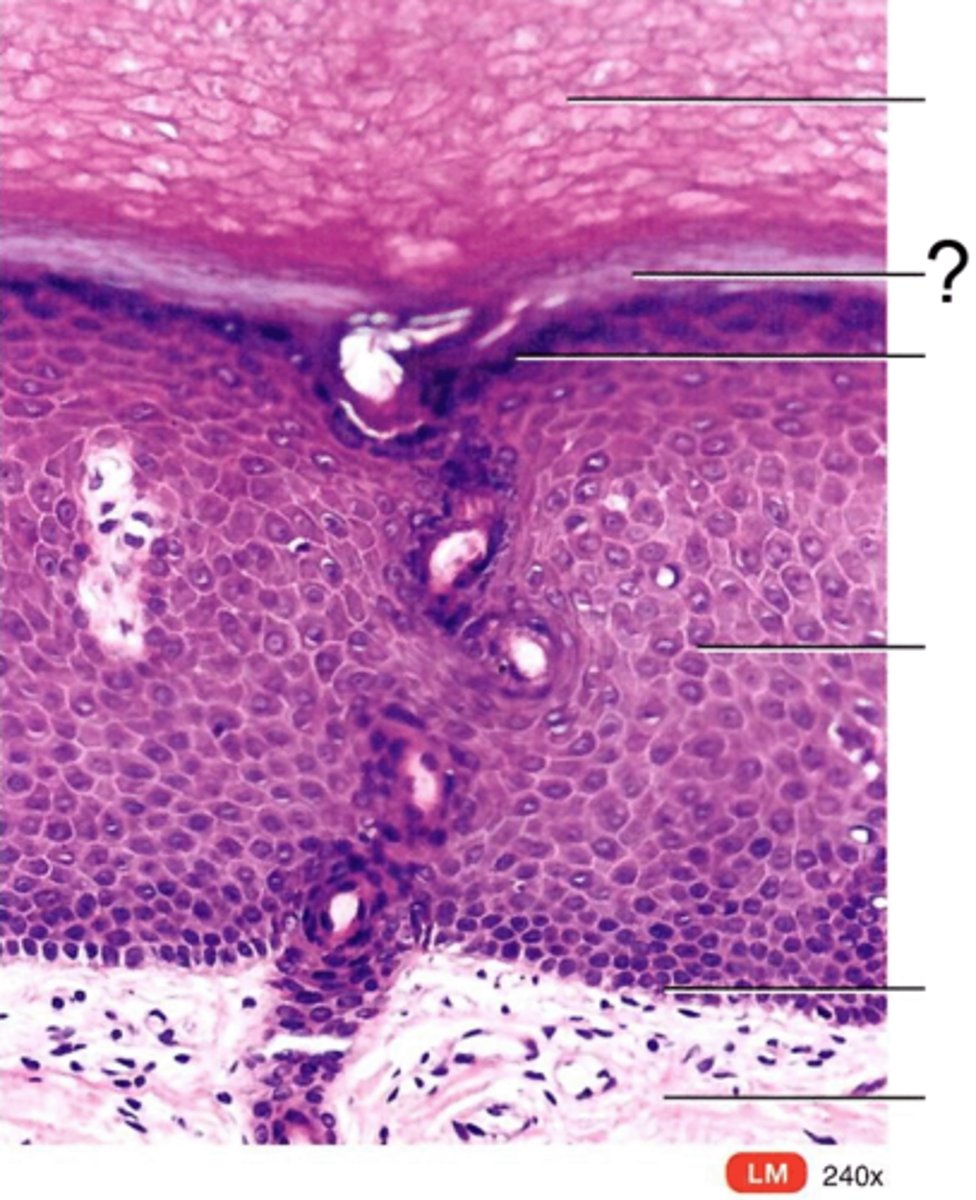
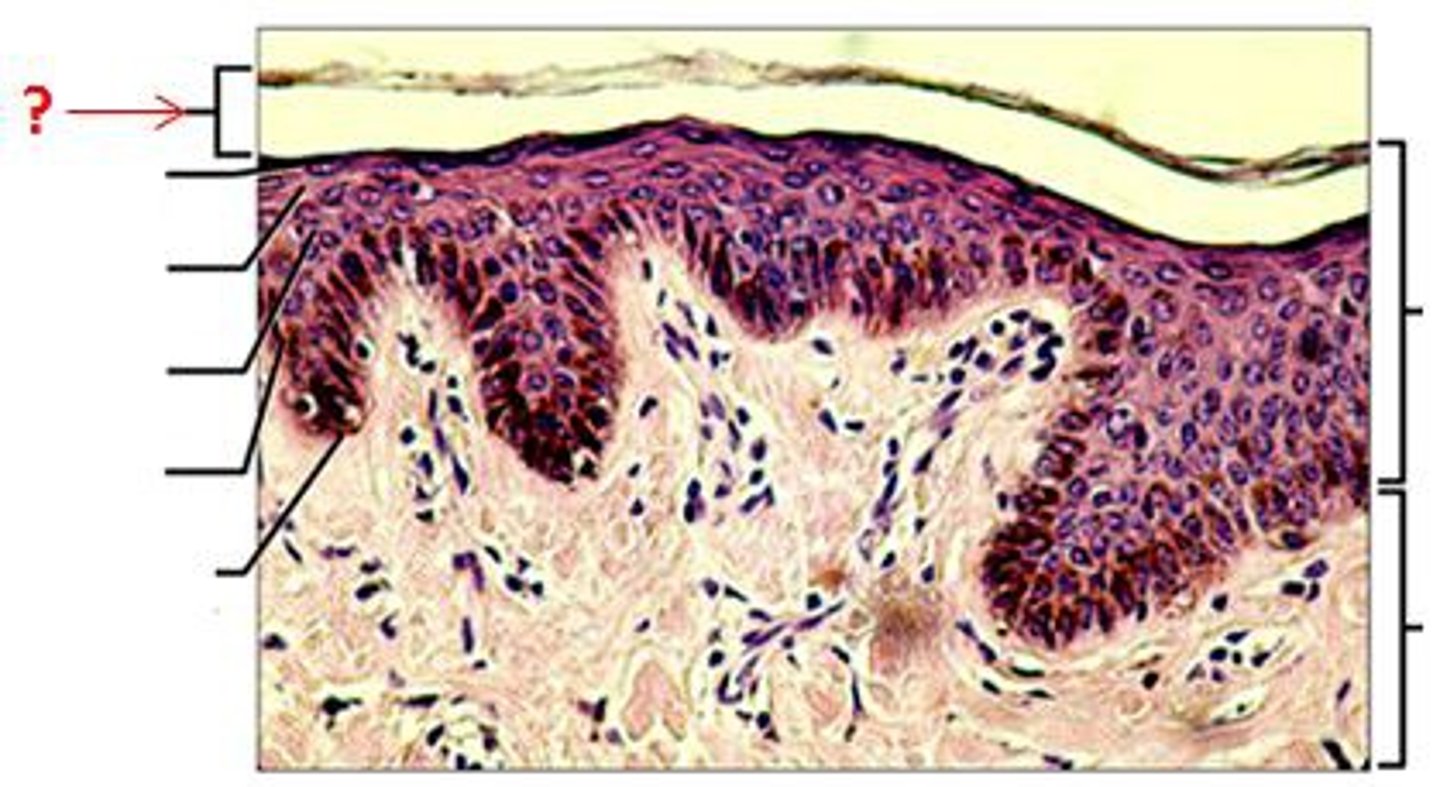
stratum corneum
outermost layer of the epidermis, which consists of flattened, keratinized (dead) cells
isograft
transplant between identical twins
xenograft (heterograft)
transplantation (dermis only) from a foreign donor (usually a pig) and transferred to a human
autograft
transplantation of healthy tissue from one site to another site in the same individual
callus
increased growth of cells in the stratum corneum layer of the epidermis caused by pressure or friction
keratinization
process of cells accumulating keratin as they move superficially; eventually die & slough off- then replaced by new cells; takes 4 weeks
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
Stimulates cells to reproduce and heal.
dandruff
excess of keratinized cells shed from the scalp
Psoriasis
chronic skin condition producing red lesions covered with silvery scales from abnormal keratinization
papillary layer
Top 1/5 of dermis, most is areolar connective tissue, dermal papillae "fingerprints"
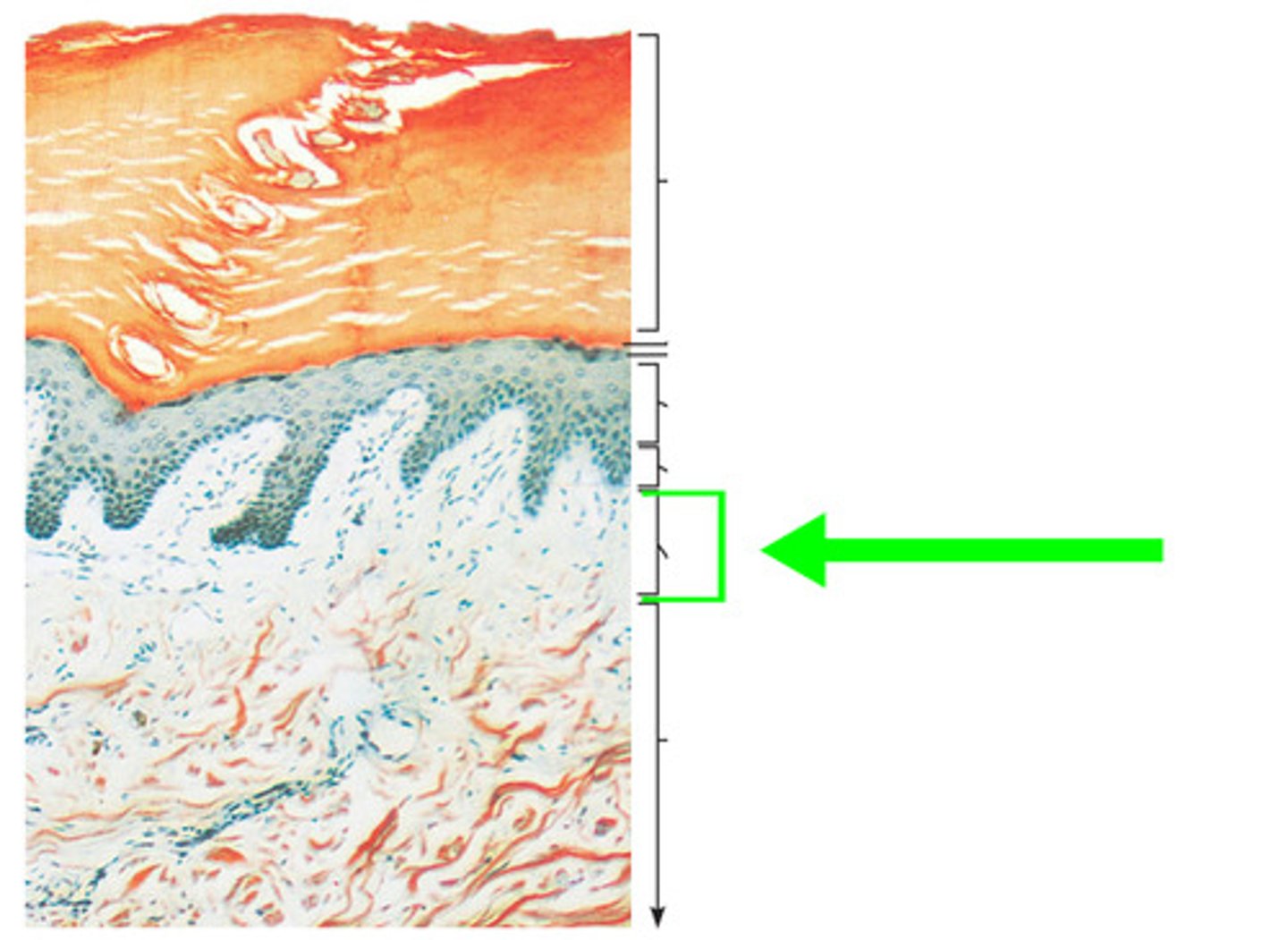
reticular layer
Bottom 4/5 of the dermis, most is dense irregular connective tissue.
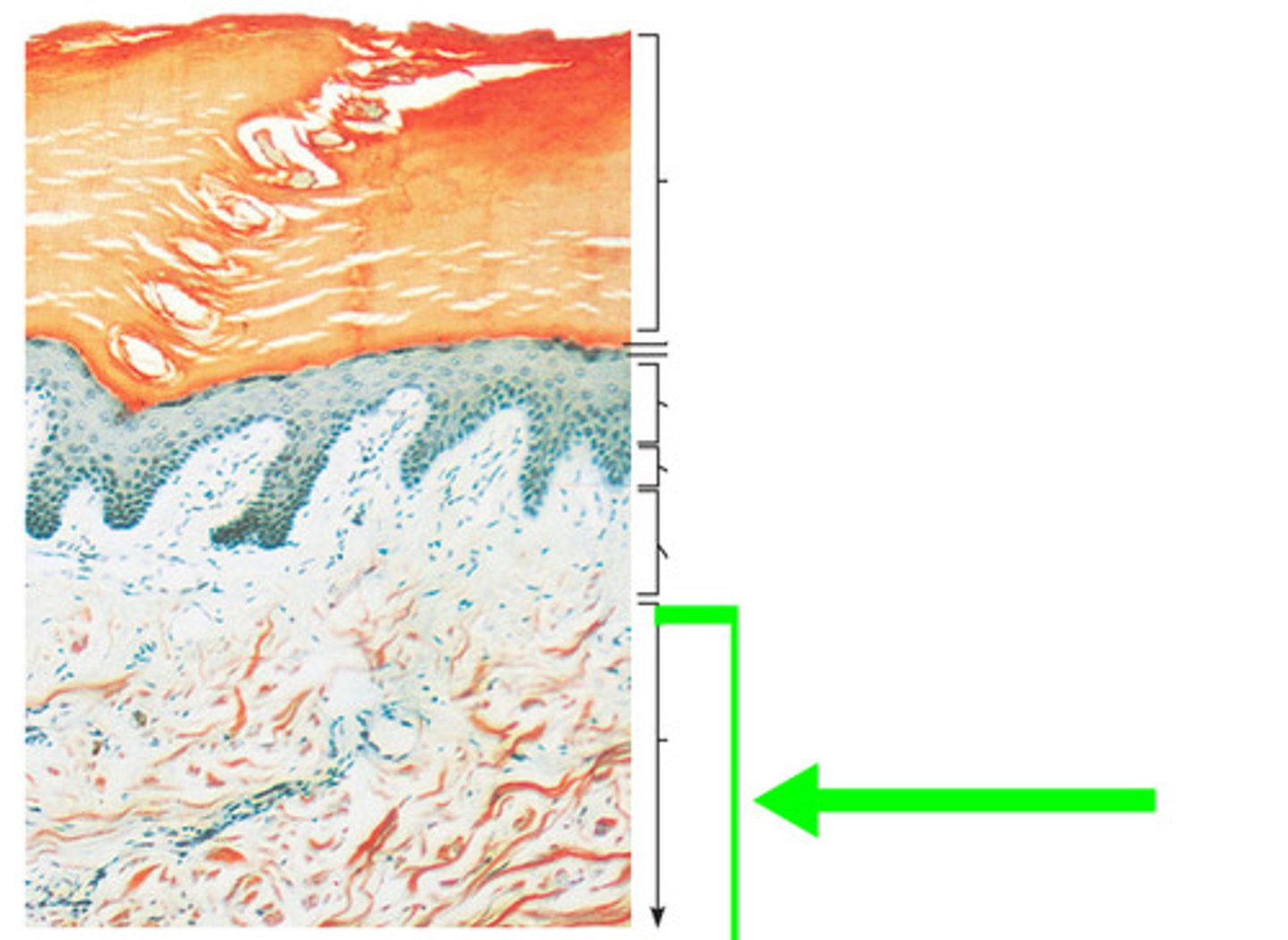
lines of cleavage (tension lines)
The bundles of collagen and elastin fiber in the dermis align themselves parallel to the direction of routine movement; this orientation of fiber bundles creates -- of ---.
Should be considered in surgical procedures to allow for healing and prevention of scarring.
epidermal ridges
downward projections of the epidermis into the dermis, create fingerprints
melanin
a dark brown to black pigment occurring in the hair, skin, and iris of the eye in people and animals. It is responsible for tanning of skin exposed to sunlight.
nevus
mole
hemoglobin
An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that reversibly binds oxygen. Gives skin a pink color.
Carotene
Yellow to orange pigment that accumulates in the stratum corneum epidermal layer and in fatty tissue of the hypodermis
Albinism
an inherited deficiency or absence of pigment in the skin, hair and irises due to a missing enzyme (tyrosinase) necessary for the production of melanin
cyanosis
a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from poor circulation or inadequate oxygenation of the blood.
vitiligo
white patches on the skin caused by the destruction of melanocytes associated with autoimmune disorders
pallor
extreme paleness, lack of blood in the skin so can see the collagen in the skin
jaundice
yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by an accumulation of bile pigment (bilirubin) in the blood from a disfunctional liver
Tattooing
a permanent coloration of the skin in which a foreign pigment is deposited with a needle into the dermis
shaft
visible part of the hair
root
part of the hair enclosed in the follicle under the skin
bulb
the base of a hair follicle and its surrounding dermal root sheath, containing the papilla of the hair and matrix
hair matrix
actively dividing area of the hair bulb that produces the hair
arrector pili
a smooth muscle attached to hair follicles that causes "goose bumps" to appear on the skin when contracted
hair root plexus
a collection of dendrites of neurons surrounding each hair follicle that are sensitive to touch
alopecia
hair loss
lanugo
fine, soft hair, especially that which covers the body and limbs of a human fetus or newborn.
vellus hair
pale, fine body hair of children and adult females
terminal hair
Long, coarse, pigmented hair found on the scalp, legs, arms, and bodies of males and females.
hirsutism
excessive hair growth
sebaceous glands
oil glands in the skin
sudoriferous glands
glands that secrete sweat to the outside of the body; also assist in body temperature regulation
ceruminous glands
modified sweat glands, located in external ear canal, secretes cerumen (earwax)
mammary glands
modified sweat apocrine sweat glands that produce milk
eccrine (merocrine) glands
glands that produce sweat; found over most of the body
apocrine glands
Sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that produce odor when come in contact with bacteria on the skin
nail bed
Portion of the living skin that supports the nail plate as it grows toward the free edge.
free edge of nail
the portion of the nail that grows out away from the body
nail matrix
the part of the nail beneath the body and root from which the nail is produced
eponychium (cuticle)
narrow zone of dead skin overhanging proximal end of nail
hypochium
thickened region beneath the free edge of the nail where dirt and debris tend to accumulate
contact inhibition
the cessation of cell division in response to contact with other cells
inflammatory phase
the initial phase of wound healing in which bleeding is reduced as blood vessels in the affected area constrict
migratory phase
epithelial cells migrate to bridge the wound
proliferative phase
characterized by extensive growth of epithelial cells beneath the scab, deposition by fibroblasts of collagen fibers in random patterns, and continued growth of blood vessels
maturation phase
the stage in wound healing where a scab sloughs off once the epidermis has been restored to its normal thickness
basal cell carcinoma
Most common and least severe type of skin cancer; often characterized by light or pearly nodules. Originates in the stratum basale
squamous cell carcinoma
Type of skin cancer more serious than basal cell carcinoma; often characterized by scaly red papules or nodules. Originates in the stratum spinosum
malignant melanoma
Most serious form of skin cancer; often characterized by black or dark brown patches on the skin that may appear uneven in texture, jagged, or raised.
rule of nines
A system that assigns percentages to sections of the body, allowing calculation of the amount of skin surface involved in the burn area.
1st degree burn
Only the epidermis is damaged (red, painful, and edema)
2nd degree burn
The epidermis and part of dermis (blistered) have been damaged
3rd degree burn
Full thickness damage through all layers of the skin into nerves and muscles
pressure ulcer
erosion of the skin caused by prolonged pressure, often occurring in bedridden patients