H&N- History taking, clinical examination and investigations
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
common presenting symptoms in head and neck cases
sore throat
dysphonia - hoarseness
dysphagia
odynophagia
visible mouth obstruction/throat ulcer
neck lump
common methods of investigation for head and neck pathology
fine needle aspiration
CT/MRI/PET scan
US scan
Plain Xray
Contrast swallow
Endoscopy
when would you NOT do a fine needle aspiration?
Lump is PULSATILE
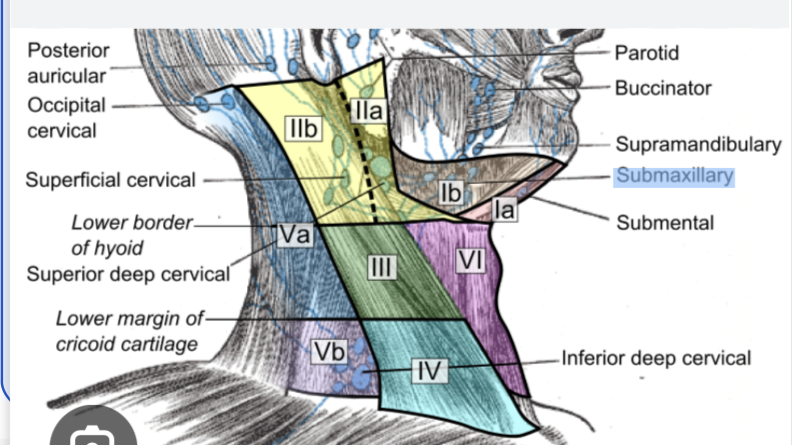
neck node levels
I: submental and submandibular
II: upper jugular nodes, upper third of sternocleidomastoid muscle
III: middle jugular nosed, middle third of sternocleidomastoid muscle
IV: lower jugular node, lower third of sternocleidomastoid muscle
V: posterior triangle lymph nodes, bounded by the clavicle, sternocleidomastoid muscle and trapezius muscle
VI: anterior compartment nodes, located in central part of neck
what examines oral cavity, pharynx, larynx?
indirect laryngoscopy, rigid laryngoscopy, fibreoptic nasolaryngescopy
what does auscultation pick up in neck?
thyroid bruit
carotid bruit
treatment modalities for H&N cancer
radiation therapy
surgery - secure airway - intubate
front of neck abscess - tracheostomy, cricothyroidotomy
chemotherapy
after laryngeal carcinoma what are you left with?
laryngeal stoma where you breathe and cough through
reccurent laryngeal nerve cancer
lung cancer spreads to mediastinum into lymph node → nodal metastases swell up and eat away at recurrent laryngeal nerve (presents with hoarseness with those with lung cancer)
H&N cancers are mainly which histological description?
squamous carcinoma
describe common salivary gland conditions
salivary gland swelling
tumour e.g. benign pleomorphic adenoma
inflammation e.g. parotitis
salivary gland stones
submandibular glands
duct calculus
how to diagnose and manage viral tonsilitis
majorly viral
reactive lymph node
sore throat
swollen tonsils
dysphagia
fever
headache
coughing
swollen neck
earache
white or yellow coating on tonsils
manage - rest and drink plenty fluids
how to diagnose and manage bacterial tonsilitis
pus covering
neck nodes
fever
no cough
manage - antibiotics e.g. phenoxymethyl penicillin
6-7 attacks in 1 year (5 per year over two years, 3 per year over three years)
•Disrupting daily activities
•More than 1 quinsy (painful abscess in tissue around tonsils) → Offer Tonsillectomy
how to assess hoarse patient
how long
any recent URTI
persistent (more worrying) or intermittent
pain
cough/choking/swallowing
asthma/rhinosinusitis/reflex - conditions that irritate the throat
voice use
smoker
medication
what are benign causes of hoarseness?
nodules
cysts
vocal abuse
laryngitis
infection
smoking
reflux
how to assess a patient with dysphagia
what is difficult to swallow? - solids or liquids
persistent or intermittent
pain
where
localised in neck
localised lower down
lumen - foreign body gets stuck liquids pass fine
wall - tumour, stricture, neuromuscular - liquids unable to get down as need control, pouch food goes down by gravity
extra luminal - thyroid, heart, mediastinal mass
how to assess patient with neck lump
examination:
site
size
shape
sore
skin
stuck
soft
history:
how long
site
fluctuates?
sore?
H&N symptoms
B symptoms (lymphoma symptoms: weight loss, drenching night sweats, poor appetite, lethargy)
travel
description of reactive lymph node in neck
oval
soft
smooth
mobile
tender
benign reactive lymph nodes examples
tonsilitis
nasal inflammation
swollen adenoids
branchial cyst
lipoma
thyroglossal cyst
stridor and management
caused by infection, tumour, foreign body
can be on inspiration (main) - higher obstruction
expiration
biphasic - stridor on both inspiration and expiration
management: Treat ABC - humidified O2 ,steroids, adrenaline nebuliser
secure airway e.g. intubate, front of neck abscess (FONA) - cricothyroidotomy, tracheostomy
common sites of head and neck pathologies
oral cavity, larynx, nasopharynx
what is a thyroid bruit a sign of?
Grave’s thryoiditis
what is a carotid bruit a sign of?
carotid stenosis
what colour should the vocal cords be normally
pearly white