Carbohydrates
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Carbohydrate chemical formula
(CH2O)n
Letter indication of carbohydrates
often indicated w/ “-ose”
Carbohydrate functions
cellular fuel, stored fuel, structural signaling
Carbohydrate Subunit
monosaccharides/sugar
Aldoses
sugar with carbonyl on Carbon 1 (exterior)
Ketoses
sugar with carbonyl on Carbon 2 (interior)
Isomer
internal carbons w/ hydroxyl groups are “chiral”
Biological sugar form
typically D-form
D vs. L Isomers
determined by last chiral carbon
Cyclic Ring Form
predominates in biological forms
Hydroxyl placement on cyclic form
on last carbon or 2nd to last carbon in chain
α - form of glucose
hydroxyl (-OH) on carbon 1 is on same side of C2
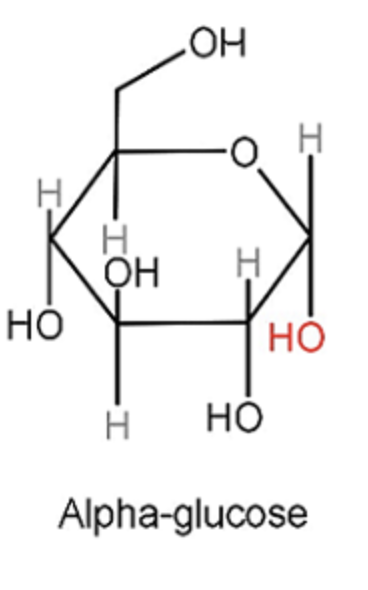
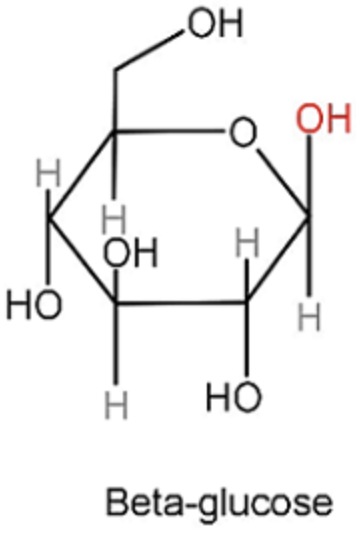
β - form of glucose
hydroxyl (-OH) on carbon 1 is on opposite side of C2
Polysaccharides
many glucose held together w/ glycosidic linkage
glycosidic linkage
hydroxyl (-OH) on C1 of glucose forms a glycosidic bond w/ carbon of another glucose; H20 Created
Carbons that the glycosidic linkage is created on
1, 4
Starch
glucose storage polymer in plants
glycogen
glucose storage for fuel (polymer) in animals
Cellulose
part of plant cell wall