Anatomy & Physiology - Ch. 3, Cells
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
an adult human body has about _____ cells
70 trillion
why does cell count fluctuate?
cells are continuously being born, and always dying as well
** HOMEOSTASIS!!!
differentiation
cell develops to gain specialized function
how many cell types?
at least 260
what are cells measured in?
micrometers (10^-6)
the egg, red blood, and smooth muscle cells all are _____ in size and have __________ that allow their functions to work
small
distinctive shapes (NOT all bubble shaped)
changing cell shape alters its ability to…
function
a typical cell (does or doesn’t) exist? Explain.
DOESN’T
size, shape, structure all vary
all cells share ___ main parts
4
MUST be present
which cell’s 4 main parts that MUST be present?
cell membrane
cytoplasm
nucleus
inclusions
Inclusions
cell HAS to have chemicals
different chemicals for different cells
the name tells where the chemicals are at
chemicals in cell for this one
Chemical Composition of the Body: Water
64%
Chemical Composition of the Body: Proteins
16%
Chemical Composition of the Body: Fats
16%
Chemical Composition of the Body: Minerals
4%
Chemical Composition of the Body: Carbohydrates
1%
Chemical Composition of the Body: Vitamins
less than 1%
Nutrients
collective term for chemicals/molecules your body needs to break things up, rebuild, & break apart again
cycle continues until death
make up doesn’t = perfect 100% bc estimates
** HOMEOSTASIS in chemical level
** Assimilation
Water
how we move chemicals everywhere
gets stuff where it needs to go
Carbohydrates
long units of simple sugars (glucose)
major source of ATP
quick energy (sugar rush)
Carbohydrate Shape?
hexagons and pentagons
Fats
long carbon chains called “fatty acids”
usually 3 long chains
used as a storage of energy, making structures and steroids
slow, long term energy
anything ESSENTIAL means that it must be ______ to be in your body
ingested
carbohydrate picture/shape?
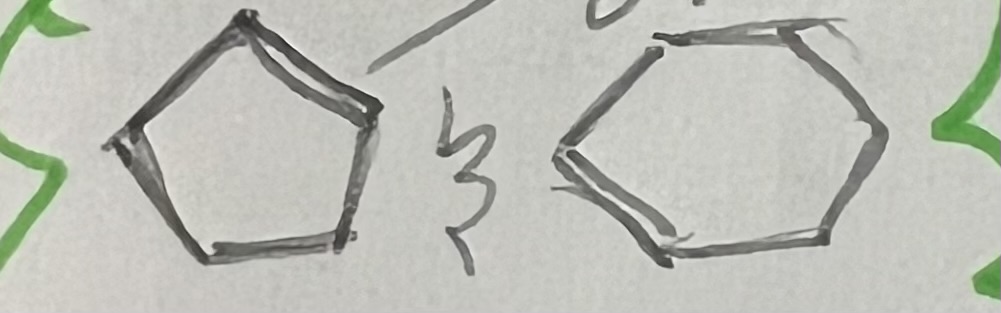
fat picture/shape?
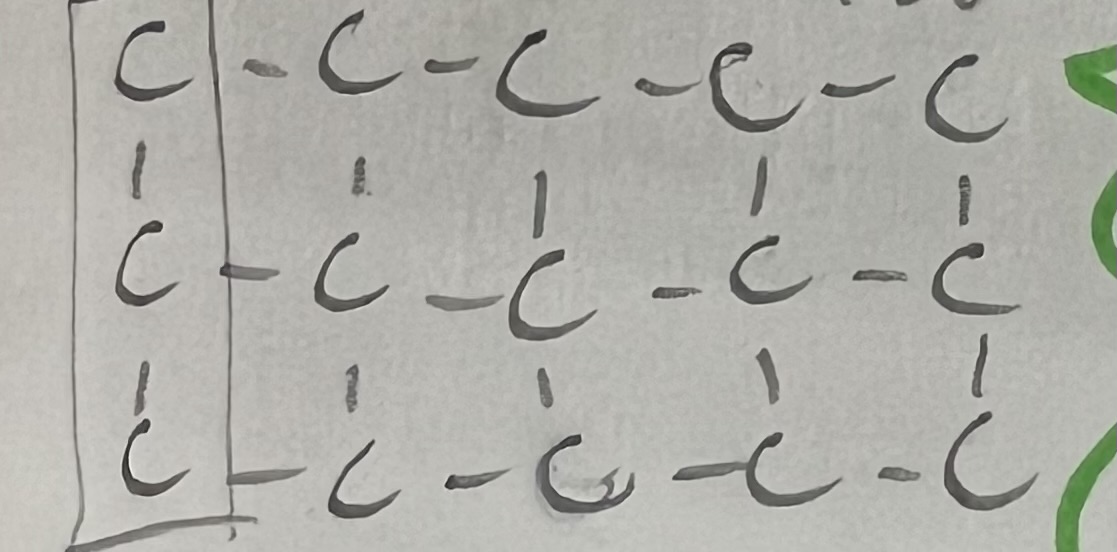
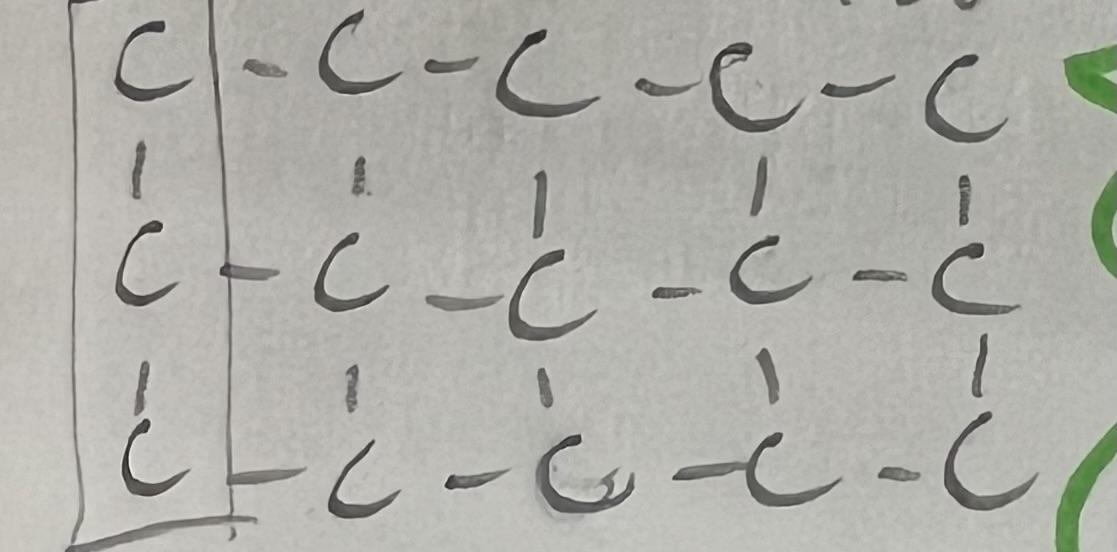
what is the first ‘box’ called in this picture?
glycerol
glycerol?
back bone of fat
proteins
makes up many structures and chemicals of the body (do ‘everything’)
most complex chemical structures
brings N into the body (not much needed)
made of Amino acids (contain N) that are linked by peptide bonds
20 total, 9 essential (must be ingested)
Minerals
inorganic (metals → + charged)
vitamins: A, B, C, D, E, K
promote actions of minerals
Ions: Ca²+, Na+, K+, Fe²+
organic
carbon-based (O, H)
Cell Membrane (a lot to it)
what does it do?
properties?
protects, absorb, secrete, excretes
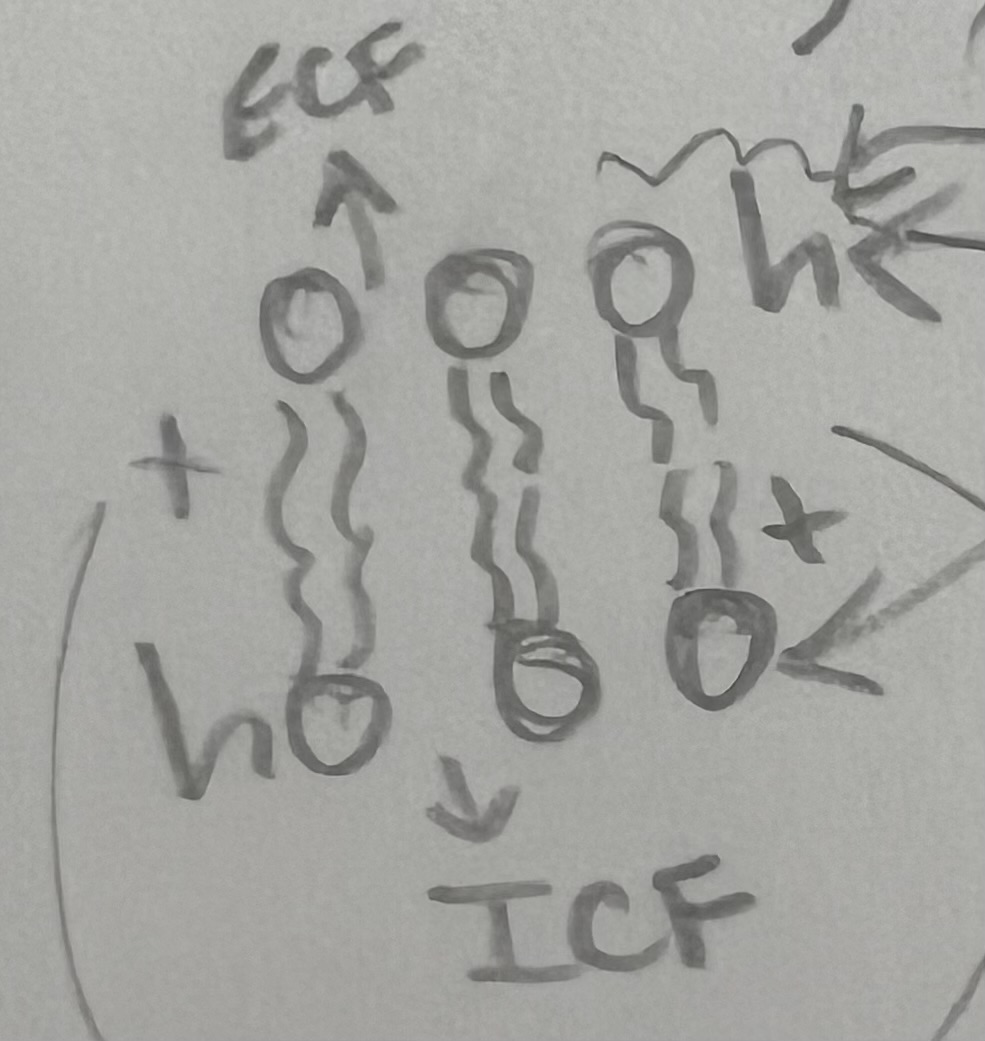
surface membrane that separates the external environment from the internal environment (ECF vs. ICF)
actively functioning part of the living material
extremely thin, but flexible
** controls entrance & exit of substances → most IMPORTANT function
selectively (semi) permeable = certain things go in or out
just follows orders, doesn’t think
cell membrane: Signal Transduction
allows cells to to receive and respond to incoming messages
link to cells and the BODY’s internal environment (ECF)
Cell Membrane Composition
fluid mosaic model (little pieces make big picture)
some carbohydrates, cholesterols, glycolipids (signal transductions)
lipids > proteins
50 lipids per 1 protein
**most importantly made up of phospholipids and proteins
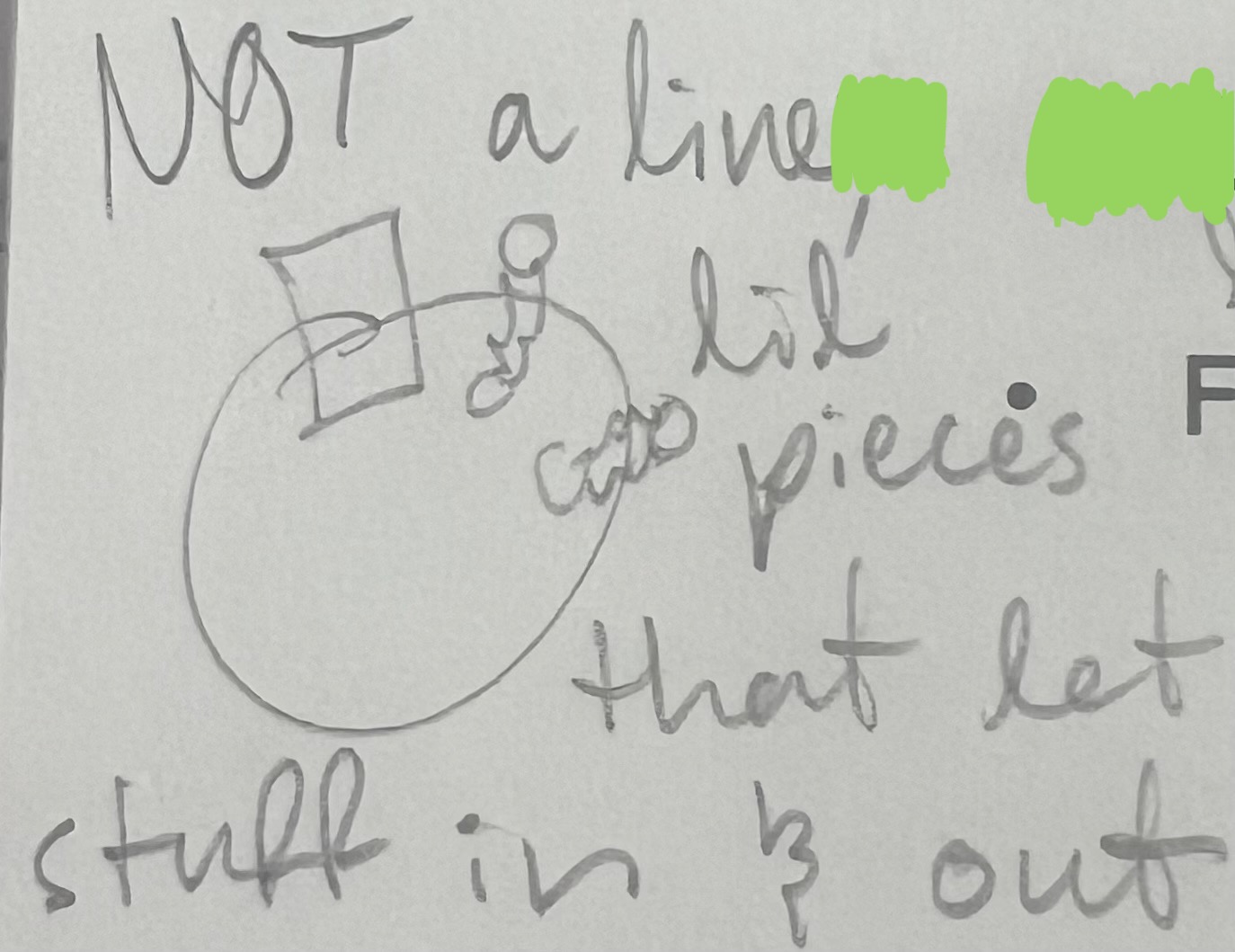
Cell membrane composition: Phospholipids
lipids that contain phosphorus (PO4³^-)

Phospholipids: ‘Heads’
water-soluble phosphate group from the outer surface (hydrophilic)
always on the outside bc they like water
polar: have charge → want to react
Phospholipids: ‘Tails’
water-INsoluble fatty acid chains that make up the interior of the membrane (hydrophobic)
nonpolar: no charge → don’t want to react
** oil (FAT) doesn’t mix with water
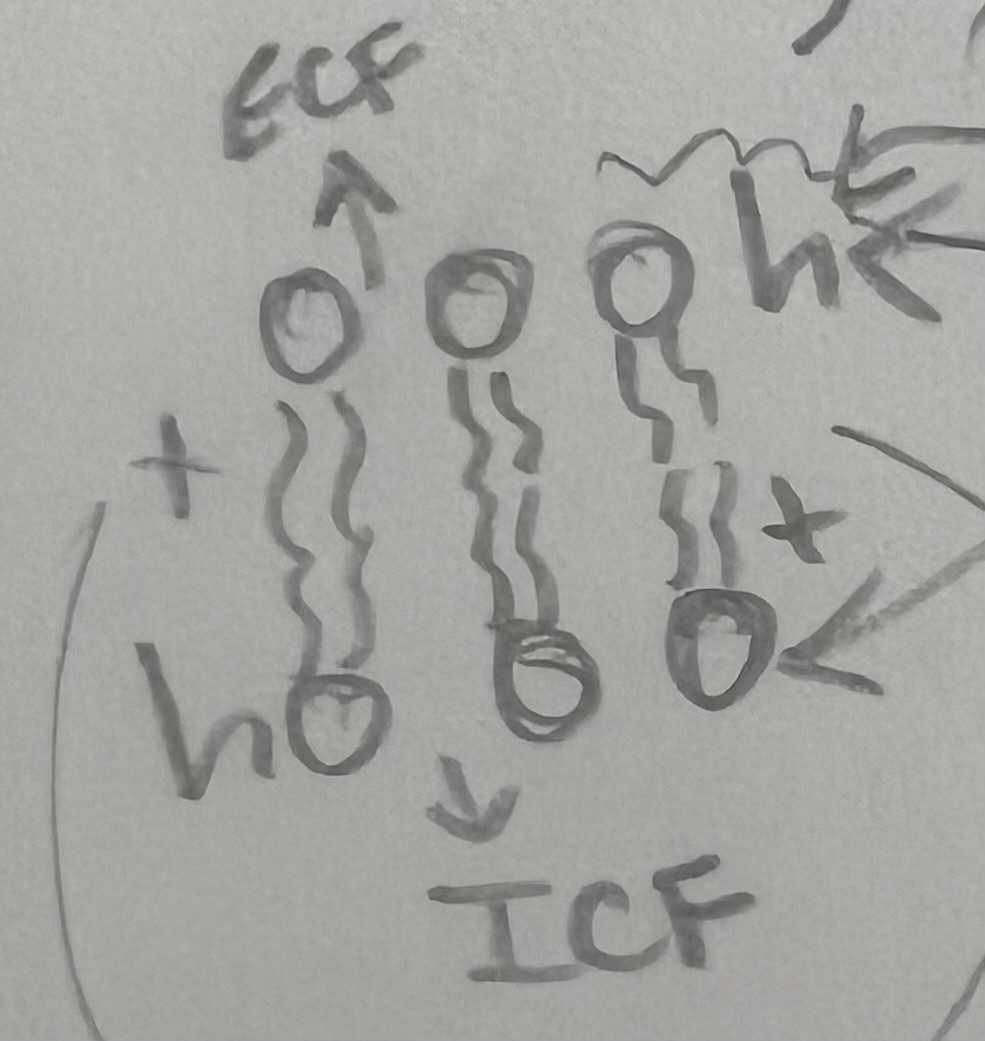
Tails: the oil with lipid soluble
inside is oily
water soluble = lipid soluble bc of oily nature in the inner membrane (substances pass easily)
** membranes only let things in that have compatible chemical structure, not ‘need’ and ‘don’t want’ (water and heroine for example)
oxygen, CO2, steroids
Tails: the oil with water soluble
water soluble molecules do NOT pass easily (tails resist)
amino acids, sugars, proteins, ions: CHARGED → all have trouble passing through
non-polar also means that it doesn’t react or it is…
stable
the presence of __________ also affects cell membrane permeability
cholesterols
Protein types?
membrane
integral
peripheral
membrane protein
many different types, provide specialized functions
cell membrane sketch
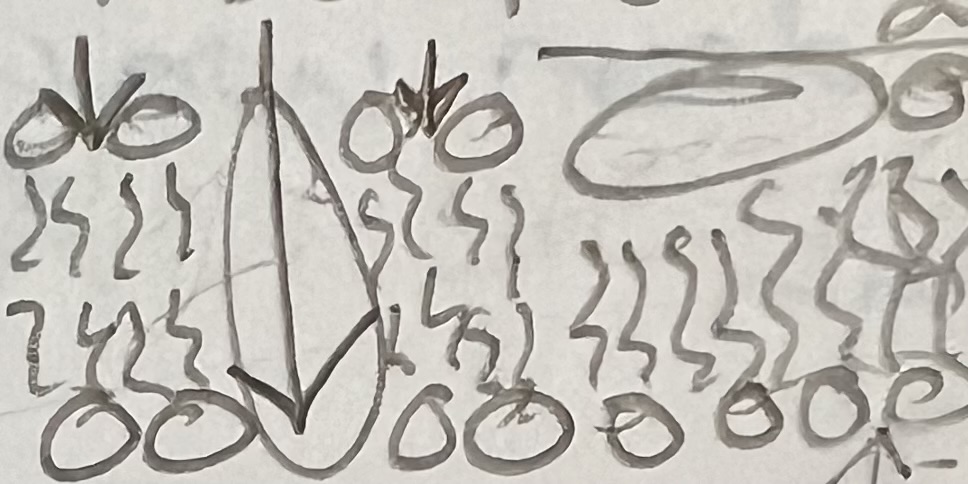
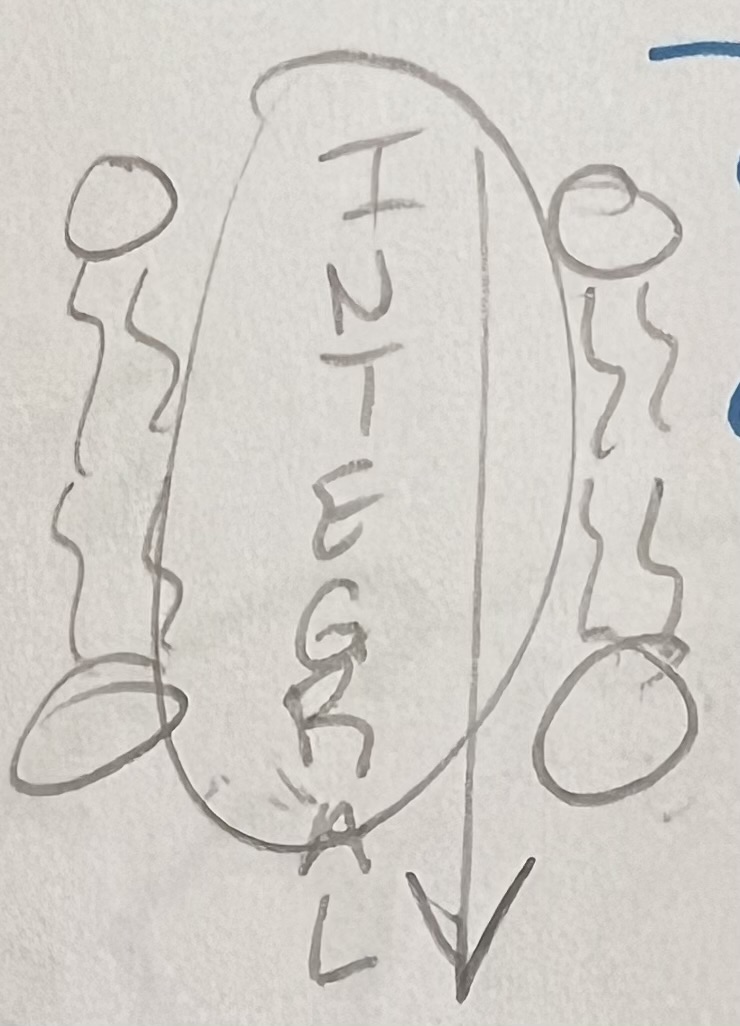
Integral Protein
extends from ECF (outside) to the ICF (inside)
provide routes into and out of the cell for smaller molecules & ions
bind to specific molecules (like hormones)
provide pores for water molecules to enter
water: can’t go across phospholipids, but has many more doorways/paths, like this one
** BEST door ways bc door goes all the way through
Integral Protein sketch?
Peripheral Protein
does not extend all the way through, remains at surface
many are enzymes and take part in signal pathways
act as “cellular adhesion molecules”: allow certain cells to touch or bind
makes bigger, better structures
→ cluster to form tissue
→ identify cells as ‘it’s cells’
** NOT a good door way, only is one when it need to be one
Peripheral protein sketch?
which protein acts as the best ‘door’? the worst?
Integral, Peripheral
what is the most important molecule that Integral proteins provide a pathway for?
WATER (bc it can’t cross phospholipids)
Aquaporins
door for water
many peripheral proteins are ________ and take part in _____ ____________ pathways
enzymes, transduction pathways
What are the two main functions of the Peripheral protein?
make bigger structures by cells clustering tgr
identify cells as ‘it’s own cells’
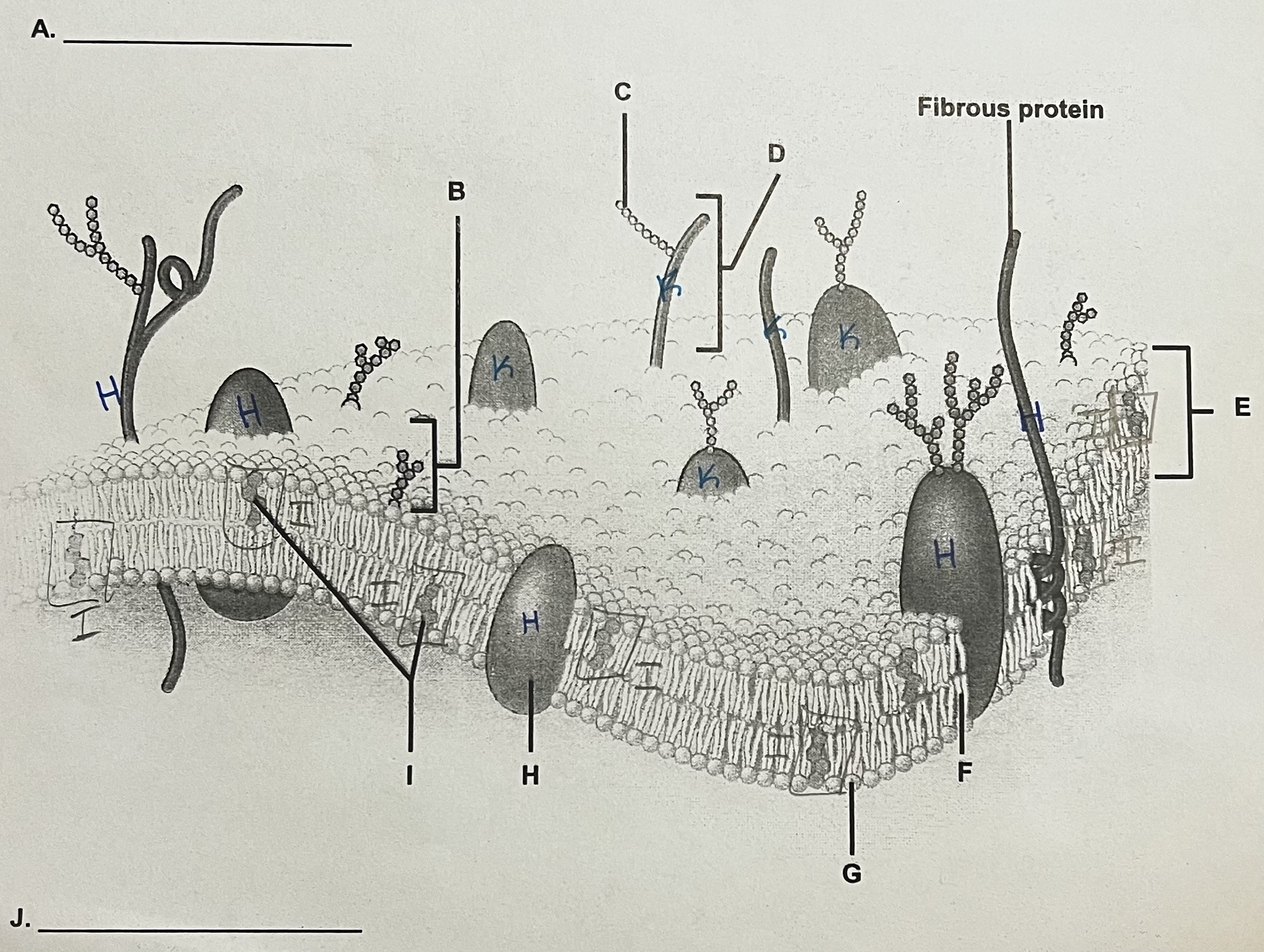
A?
ECF (outside)
** side where the most stuff is sticking out
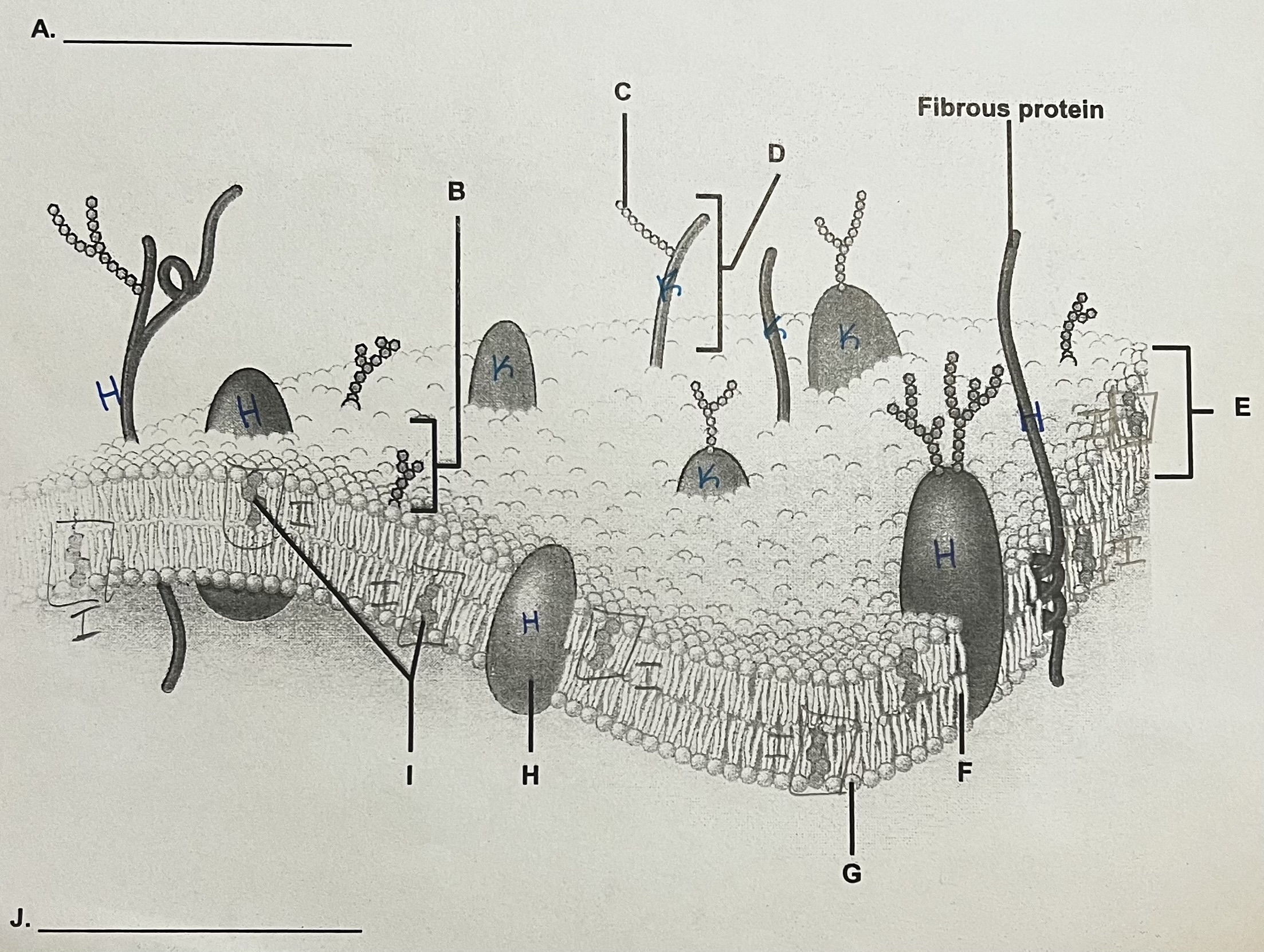
B?
Glycolipid
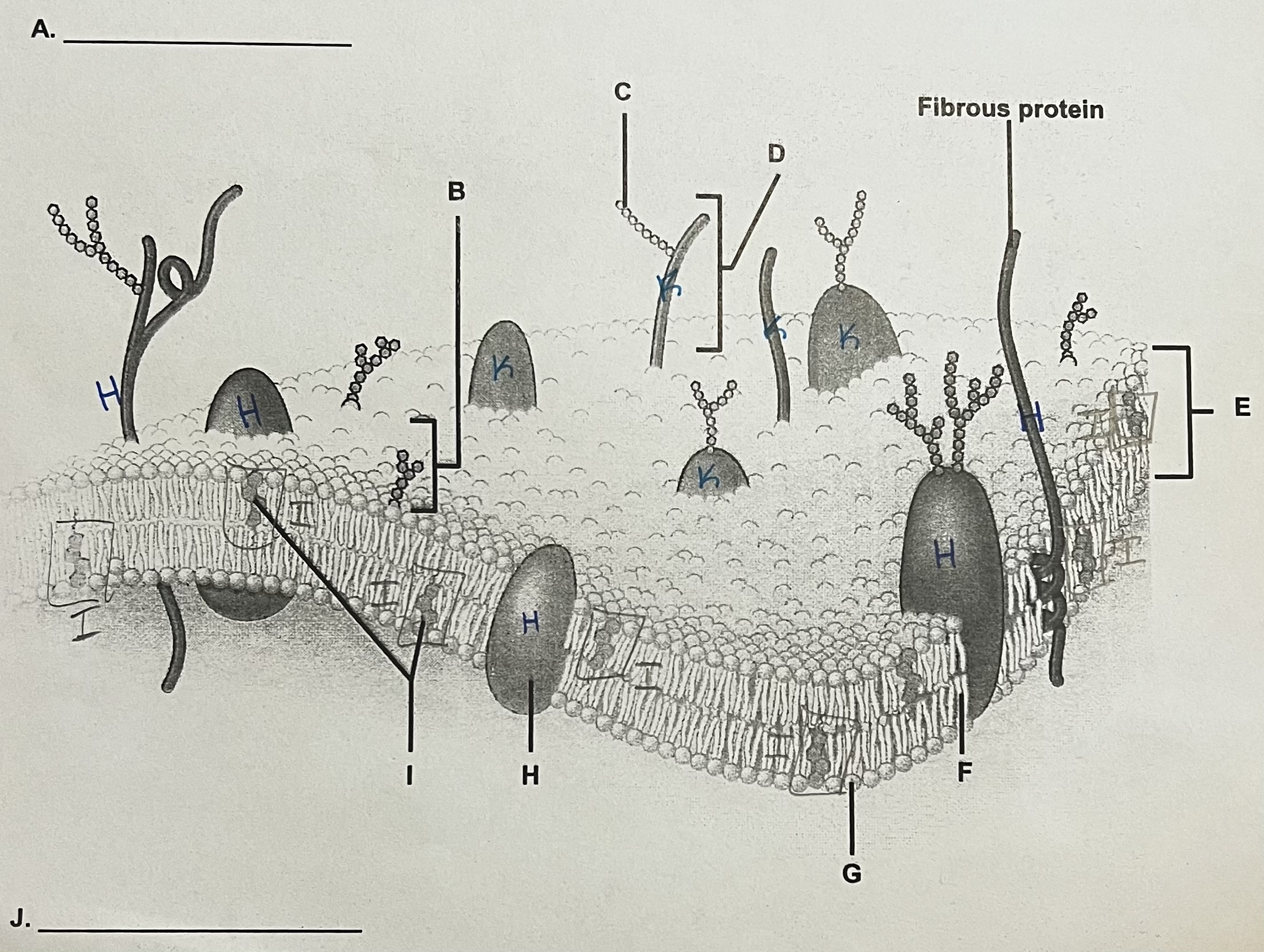
C?
Carbohydrate (sugar)
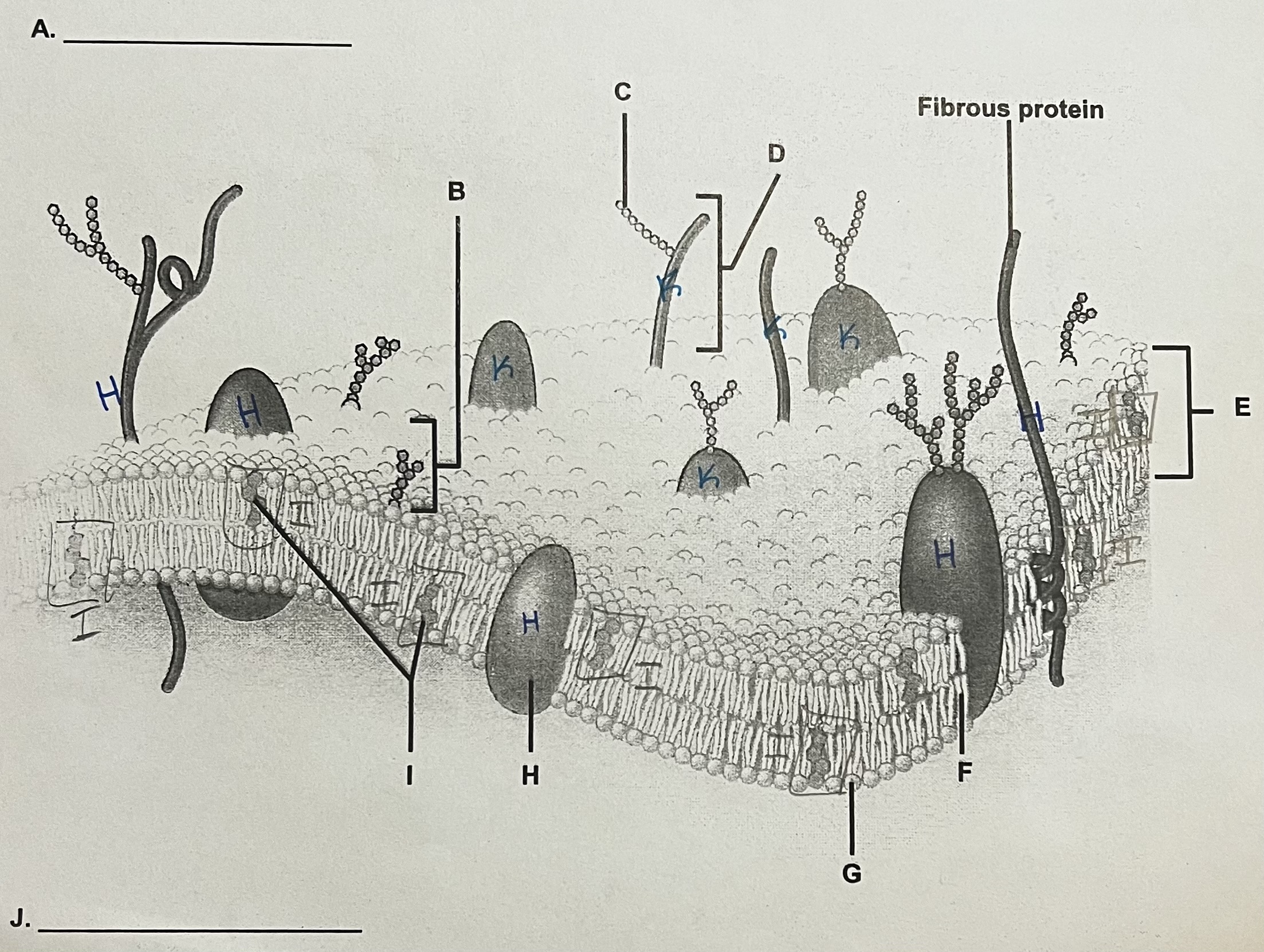
D?
Glycoprotein
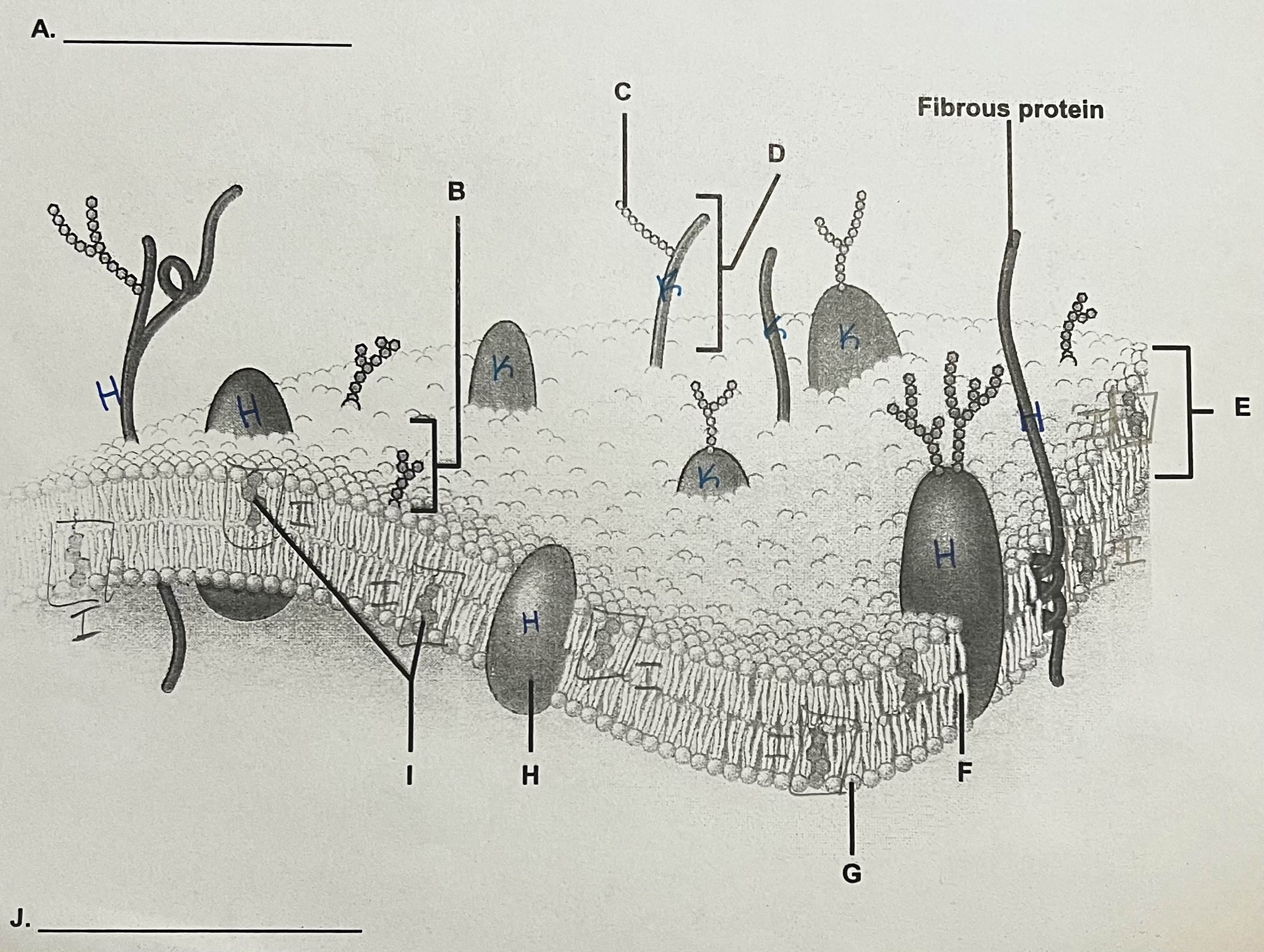
E?
Phospholipid Bilayer
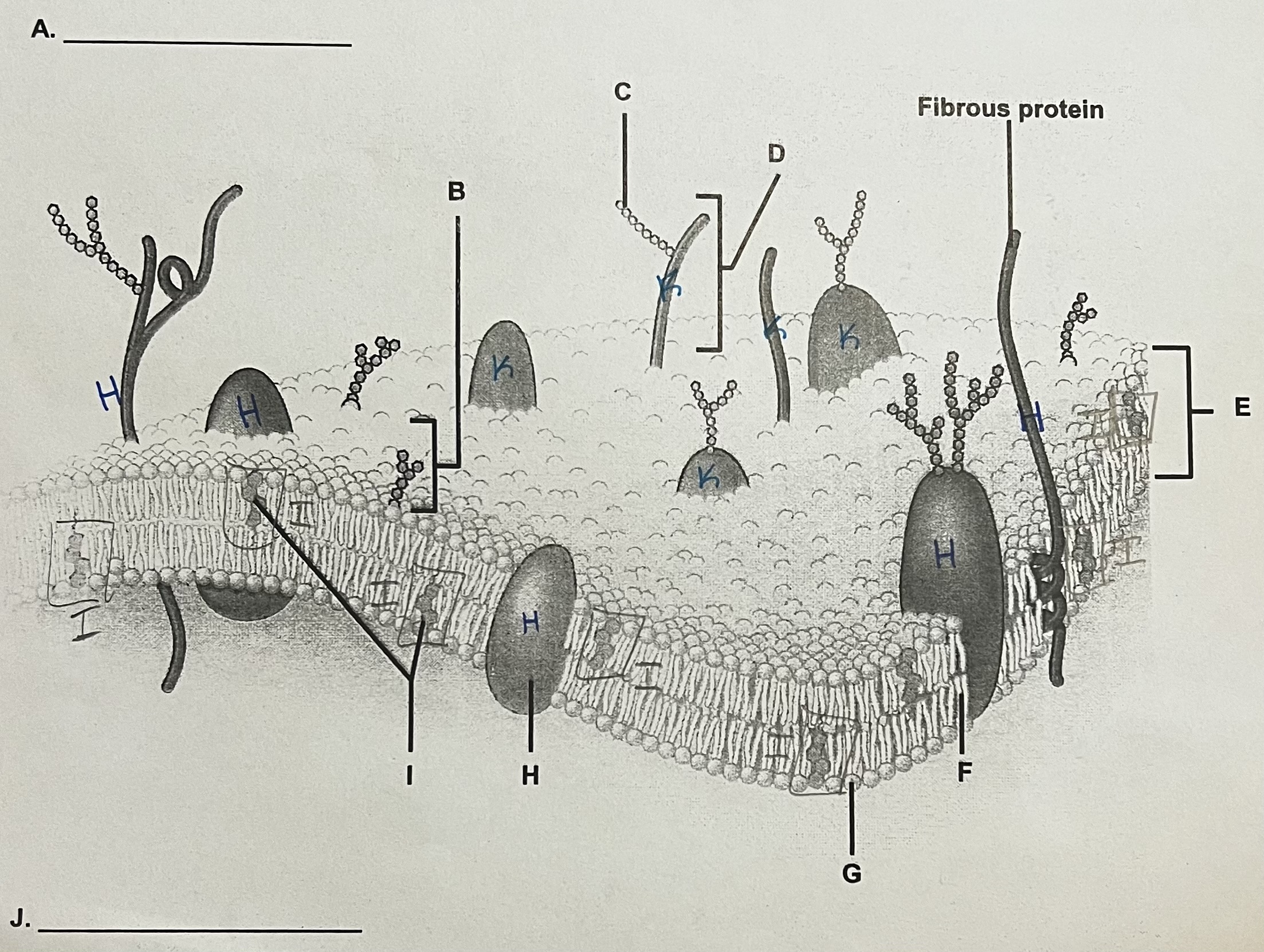
F?
Lipid Tails
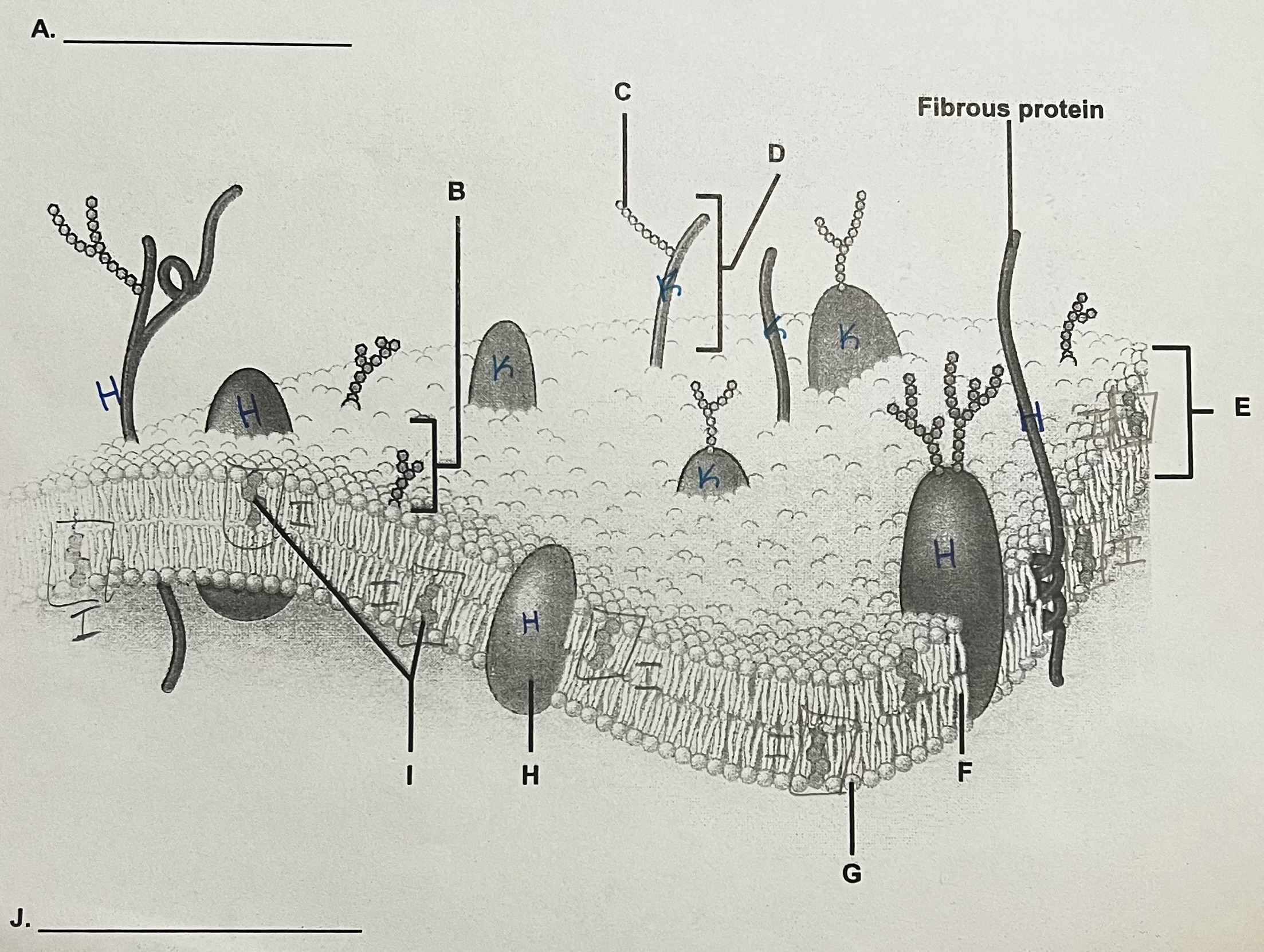
G?
Phosphate Heads
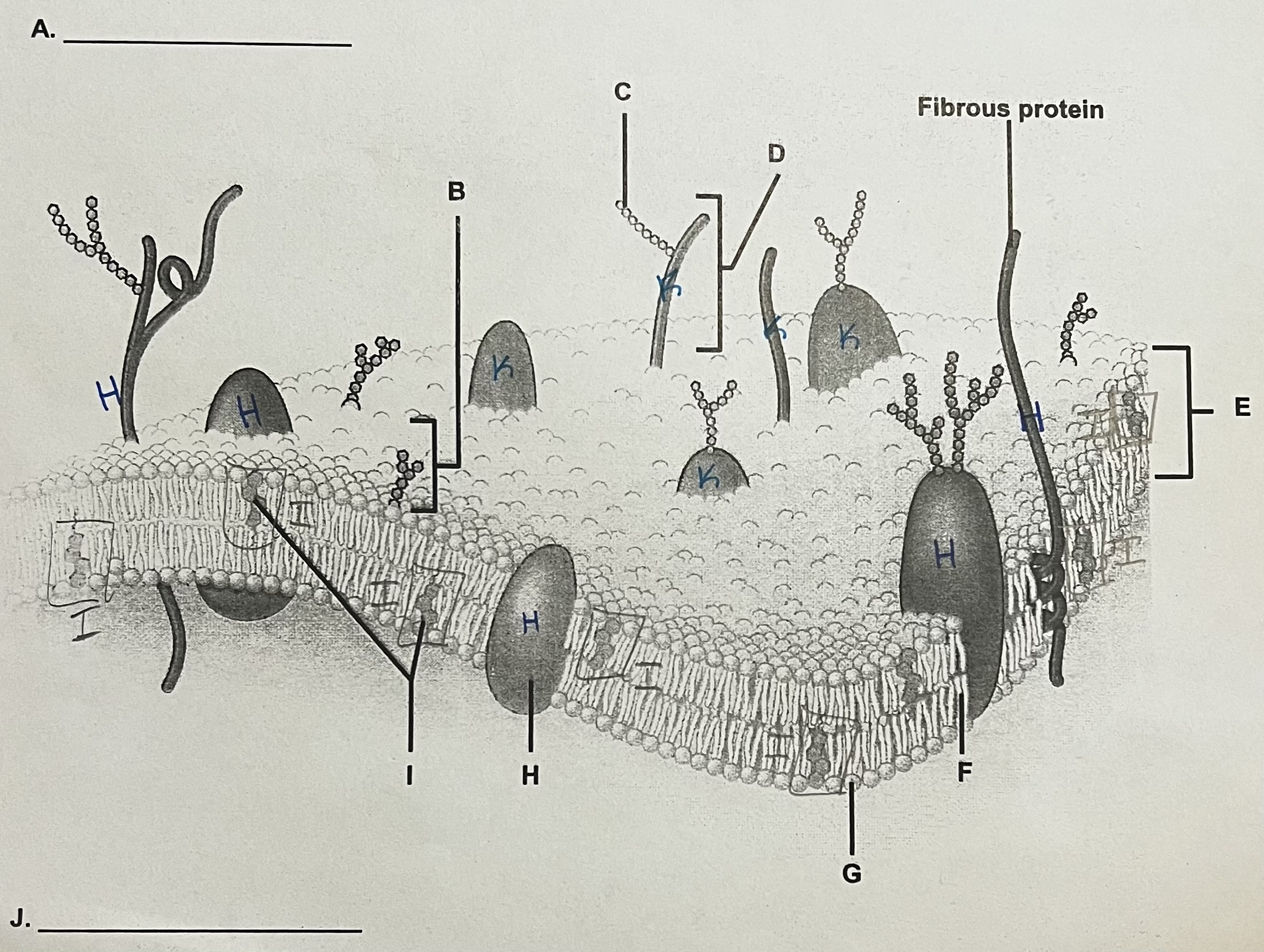
H?
Integral Protein (have to see both ends)
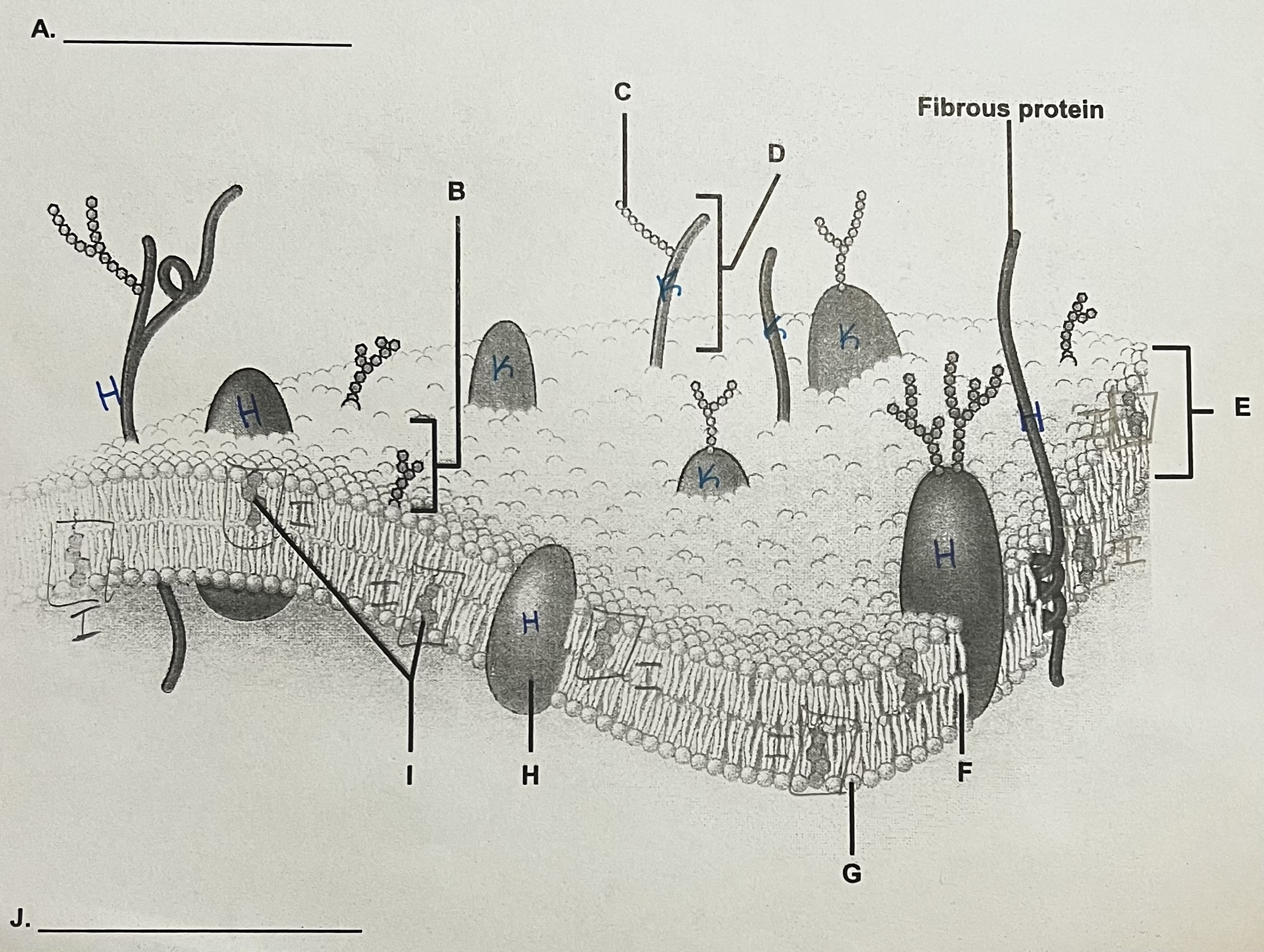
I?
Cholesterol
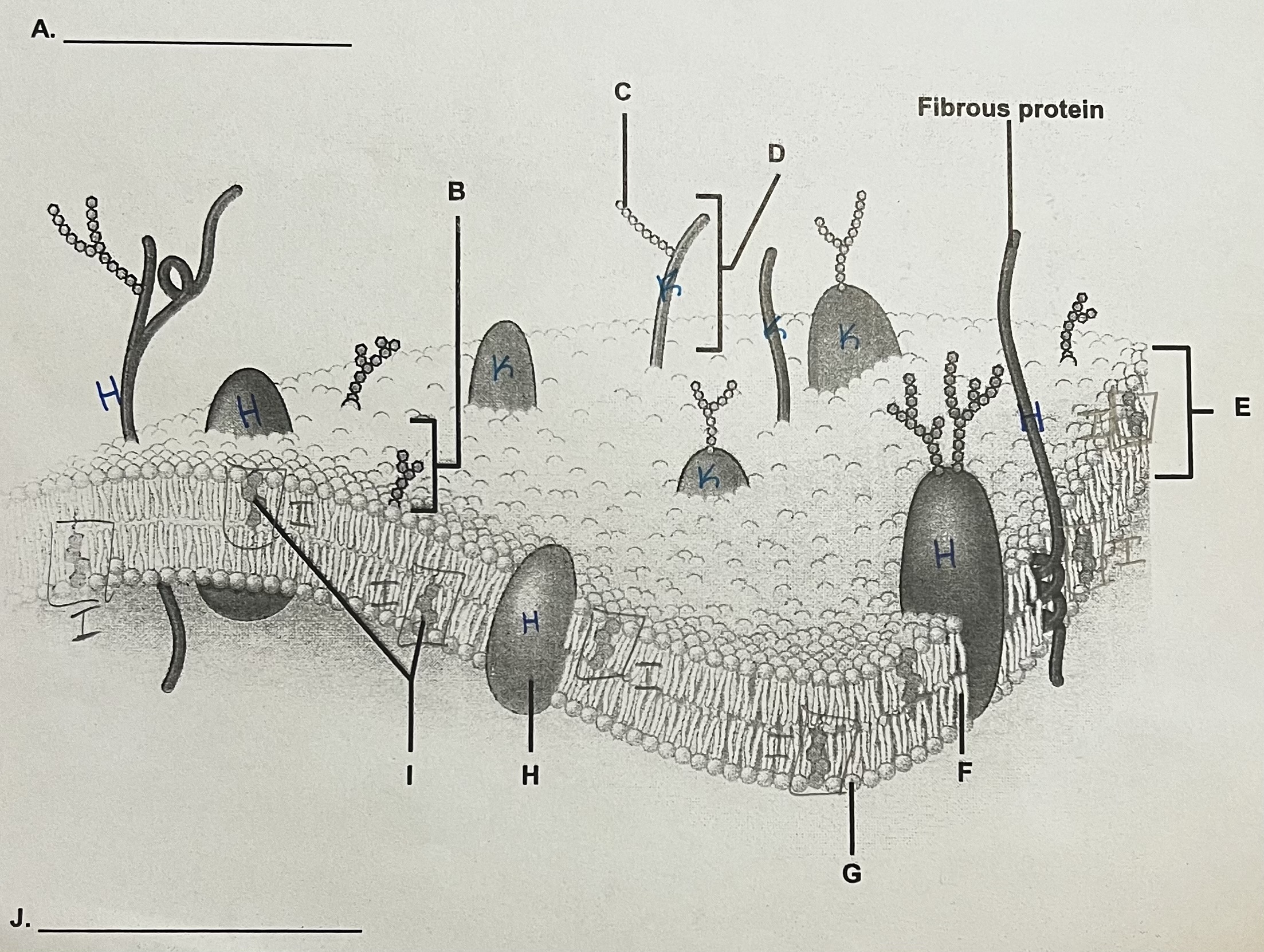
J?
ICF
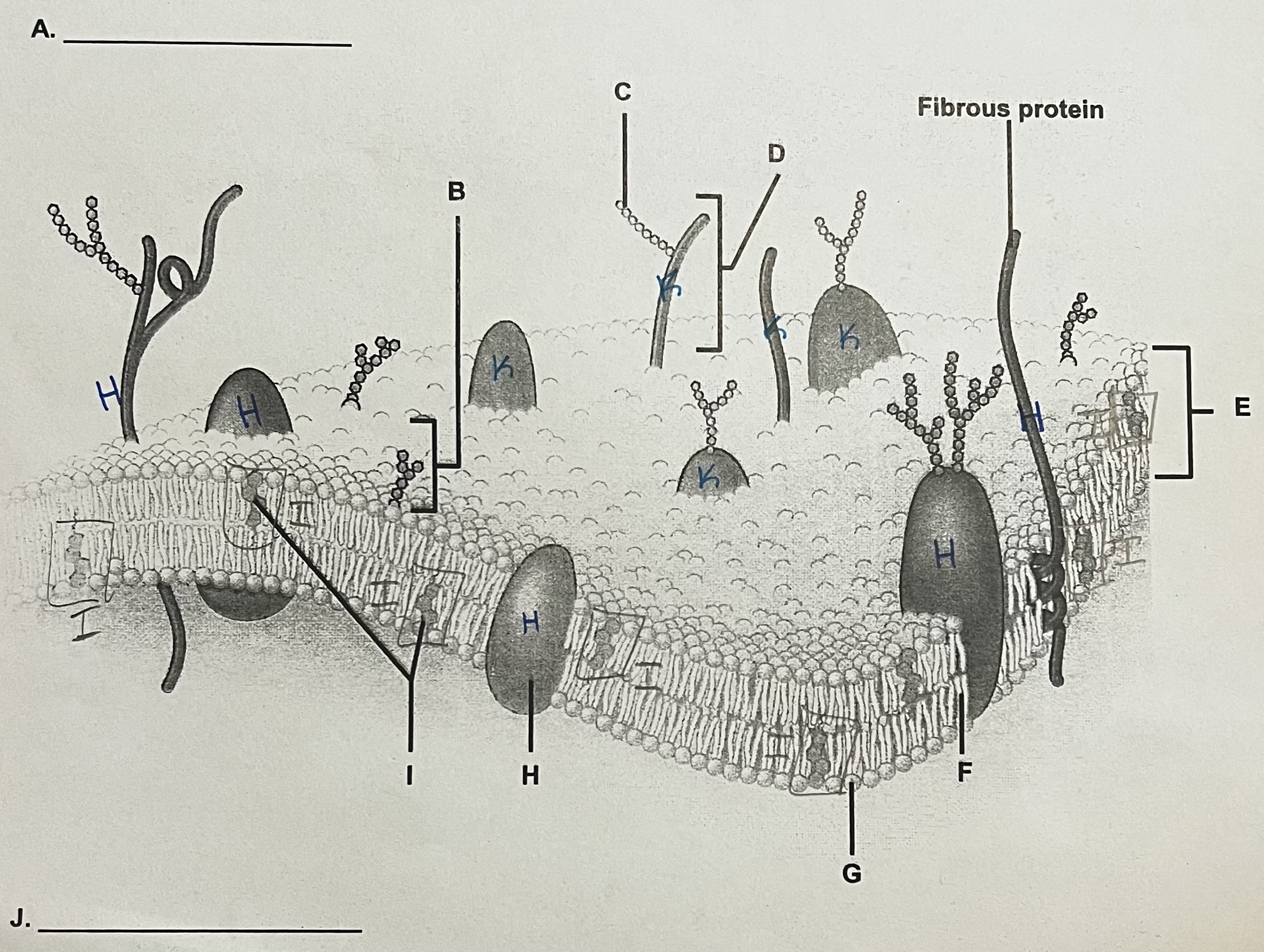
K?
Peripheral Protein
can only see part of it → assume it doesn’t go all the way through
Cytoplasm
intracellular fluid environment
what does the cytoplasm contain?
Cytosol
Organelles
Inclusions
**COI
Cytosol
fluid that surrounds organelles & disolves solutes
cell soln. (break up word)
Organelles
parts of a cell that have specific functions
Cytosol make up
75-90% water
proteins
carbs
lipids
inorganic substances
why does can’t cytosol have less than 50% water?
it needs water to move stuff
Cytosol traits?
not very viscous (how syrupy something is, lvl of fluidity)
- means it has a consistency like water
transparent
cytoskeleton picture/look?

cytoskeleton
series of protein rods & tubules that form a supportive framework
support framework for cell
some organelles?
Ribosomes
ER
Gogi Complex
Mitochondria
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Ribosomes
tiny, ‘dots’ composed of proteins & RNA
assemble amino acids to form protein chains (amino acids make proteins)
found in the cytoplasm & on the ER
make proteins
Ribosome pic/look like?
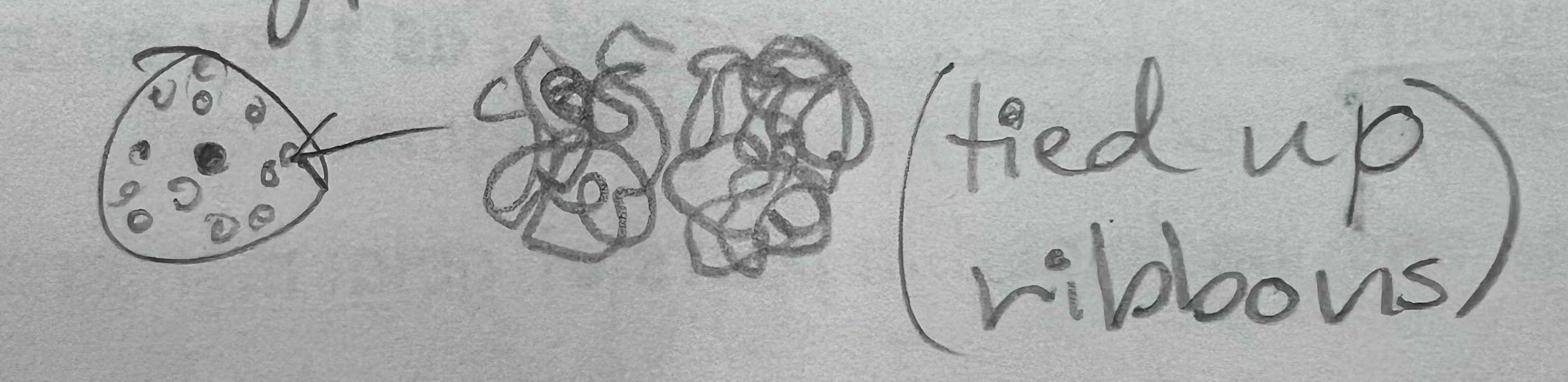
Endoplasmic Reticulum
ER
membrane-bound, flattened sacs, elongated canals, & fluid-filled vesicles (vacuole)
interconnected w/ the cell membrane & other organelles
ER pic/look like?
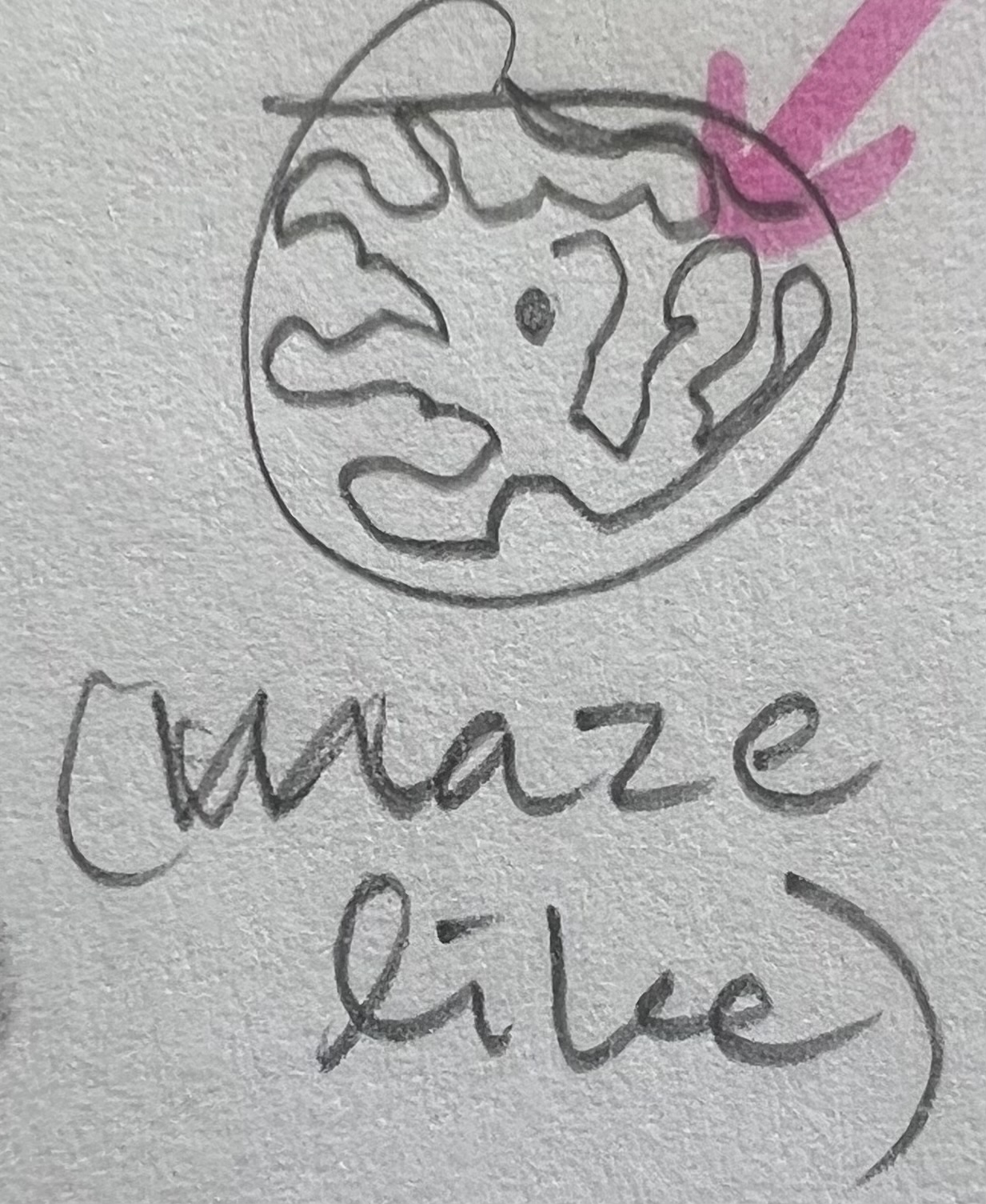
ER Function?
bc it is interconnected → communicates (w/ cell membrane & other organelles)
provides a tubular transport system for molecules throughout the cell
→ good at this bc it’s everywhere
Vacuole
bubble → puts stuff in it to prevent from reacting
vacuole pic/looks like?
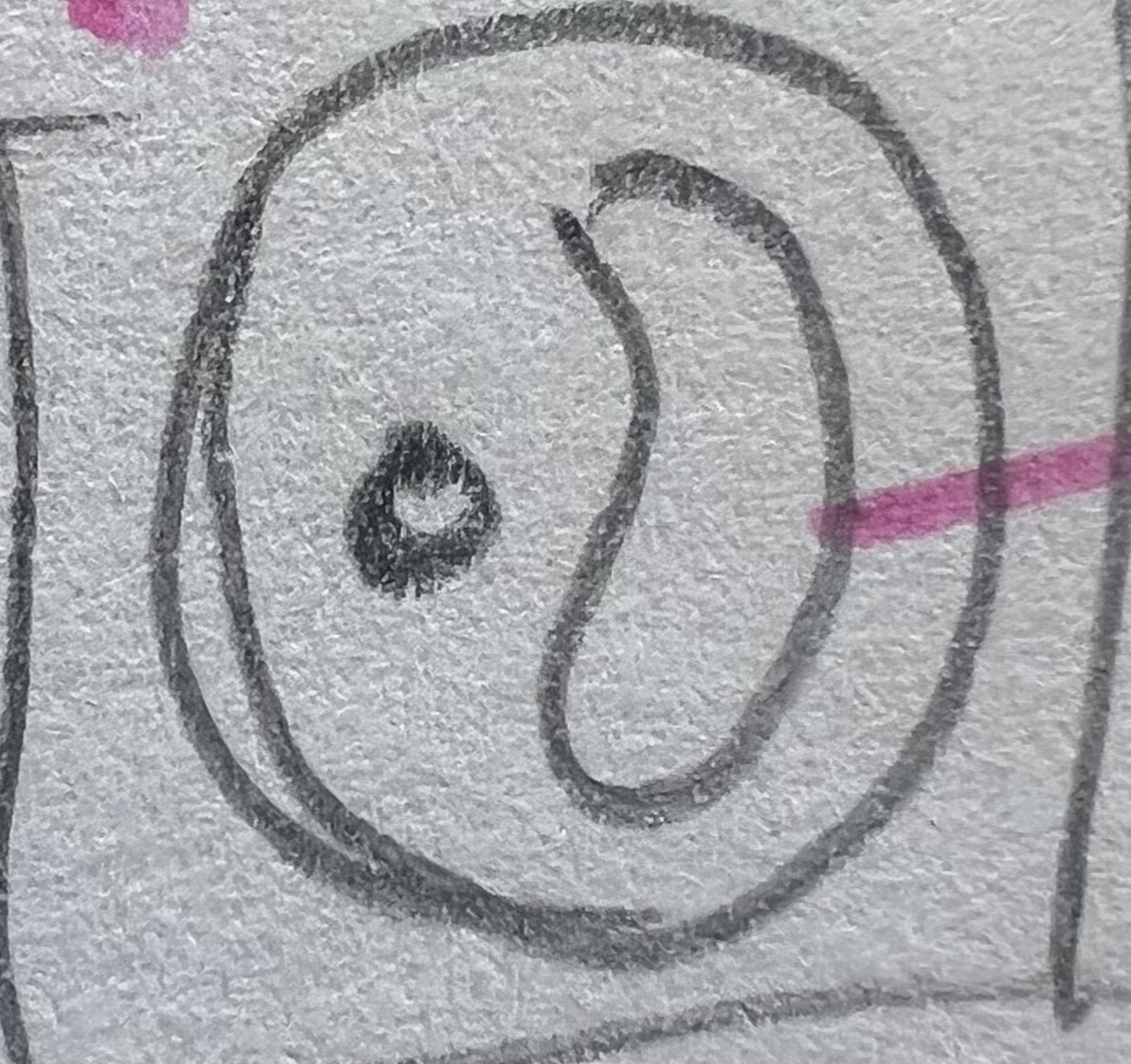
2 Types of ER?
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Rough ER
contains ribosomes on the surface
help w/ protein synthesis (makes proteins)
Smooth ER
have no ribosomes
helps…
lipids synthesis
fat absorption (in GI tract) → take things & move em through out body
breaking down drugs
Gogi Complex (body or apparatus are other names)
stack of 6+ membranes called cisternae (picture)
What does the Gogi Complex do?
refines, packages, & delivers proteins synthesized by the rough ER
refines: chemically changed so it can be delivered
chemically modified glocoprotein as they pass from sac to sac
Golgi Complex look like/pic?
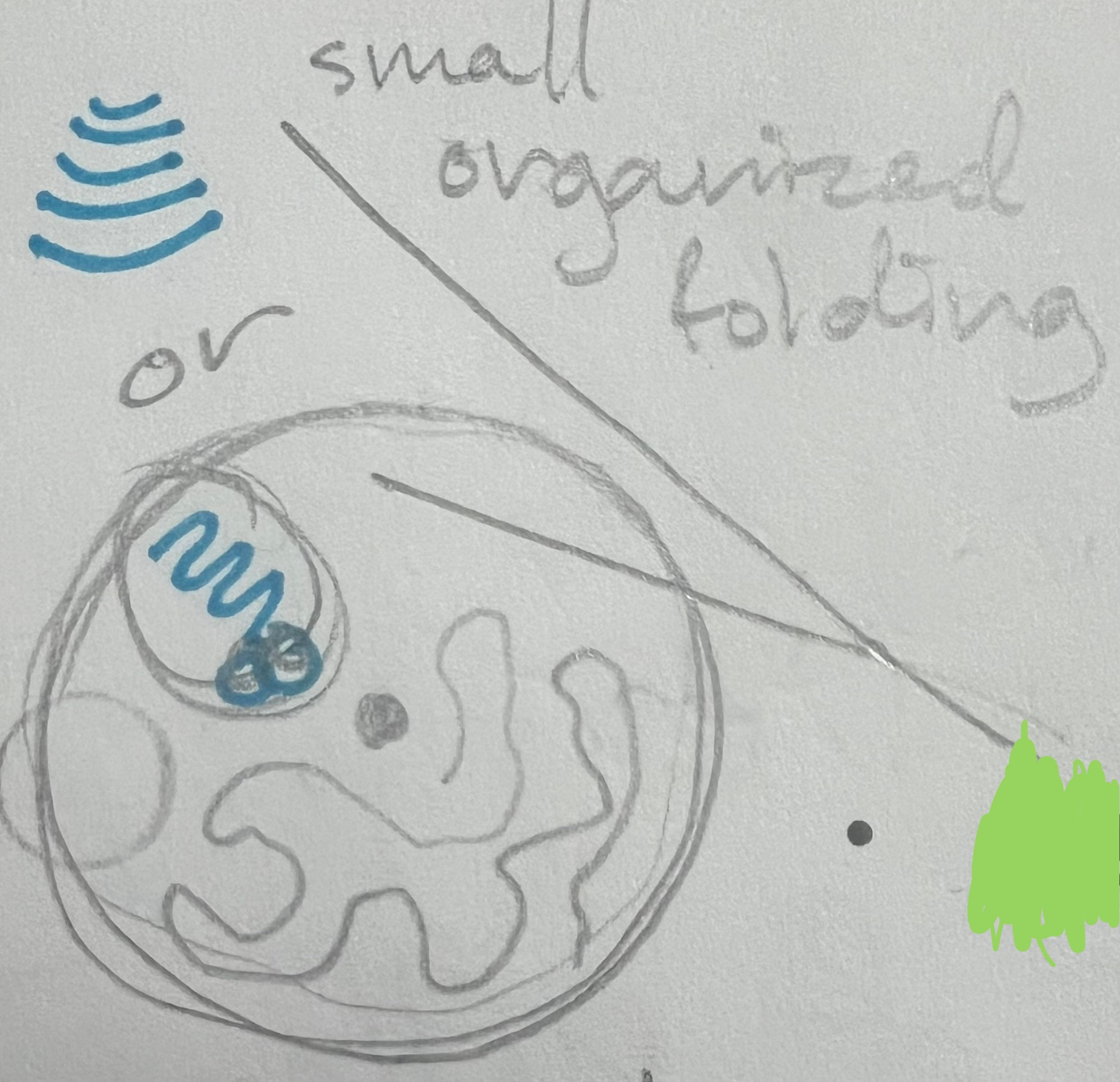
Golgi Complex: Transport Vesicles
chemically modified proteins and lipids are packaged in the golgi membrane to form these
Mitochondria
cristae
contains OWN DNA for making a small # of protein & specialized RNA (chemicals)
filled w/ matrix
typical cell contains 1,700 mito.
Cristae
double-layer membrane, inner layer forms folds
(+) surface area where chemical rxns can occur
Matrix
mitochondria filled w/ enzyme-solution fluid
Mitochondria function?
can divide
makes some proteins & RNA (chemicals)
release energy from glucose & organic nutrients forming…ATP → eat to get energy
Mitochondria pic/look like?
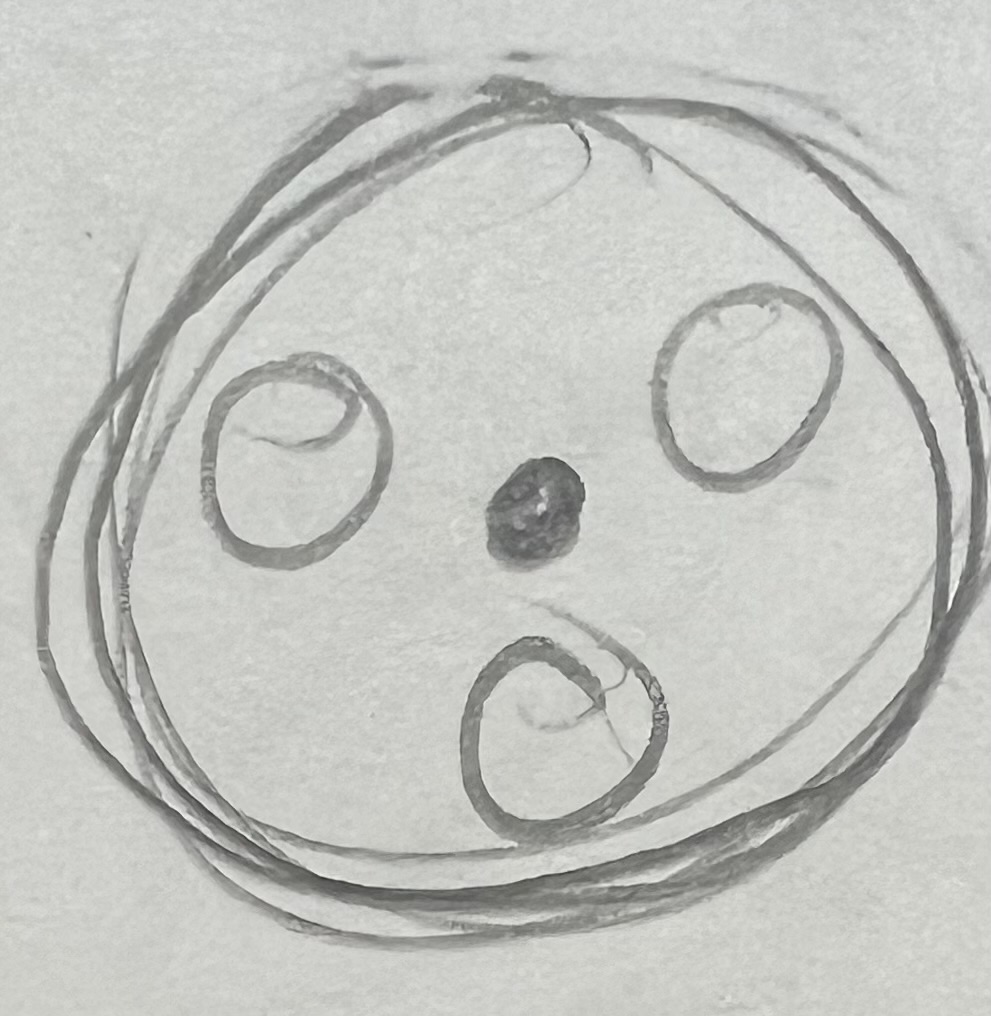
Lysosomes
destroy
contain enzymes to dismantle debris (proteins, carbs, nucleic acids, bacteria, old worn cell parts)
contains more than 40 diff enzymes
only function under acidic conditions so they do not destroy the cells around them (bc kills all organic matter)
ph helps control
no one knows how they don’t kill themselves
Lysosomes pic/look like?

Peroxisomes
present in all cells, but much more abundant in liver and kidney cells
contains enzymes (peroxidases) → biochem rxns
Peroxisomes pic/look like?
also bubble bc more specific lysosome
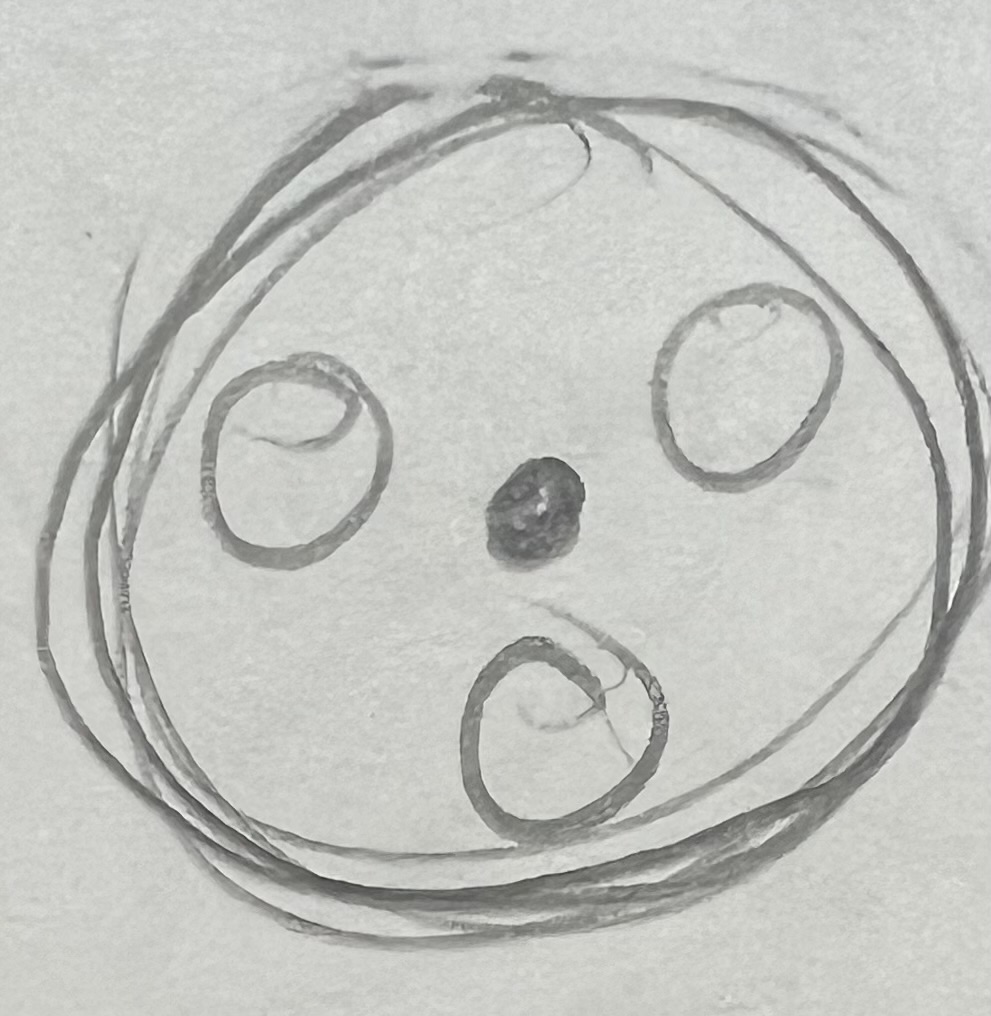

Peroxisomes function?
catalyze (accelerate) metabolic rxns to release H2O2 (which is toxic)
→ then uses enzymes (catalase) to destroy H2O2 (breaks down H2O2 → H2 and O2) to make it NOT toxic
helps form bile salts → digest fats
breakdown large lipid chains and rare biochemicals (acid-based)
detoxification of alcohols
Centrosome
located near the nucleus of animal cells
each consists of 2 tubelike proteins organized in 9 groups of 3
ALWAYS work in a pair
activate in cell division (mitosis)
1 centrosome = 2 centrioles
centrioles
2 hollow cylinders that make up a centrosome
Centrosome/centrioles function?
don’t do much bc activate when cells are dividing (cells don’t divide much)
help form fibers that will control chromosomal movement (like flagella & cilia)