TEAS A&P/Bio Must Know Questions
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
DNA Sense strand
This is the coding strand.
When mRNA takes a copy of a section of DNA, the mRNA strand has the same nucleotides as the sense strand of the original DNA strand (except it uses U instead of T).
That’s why the sense strand is called the coding strand — its code is what ends up in the mRNA, even though mRNA is built from the opposite strand.This mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm, where its sequence is used to make proteins — not the antisense strand's sequence.
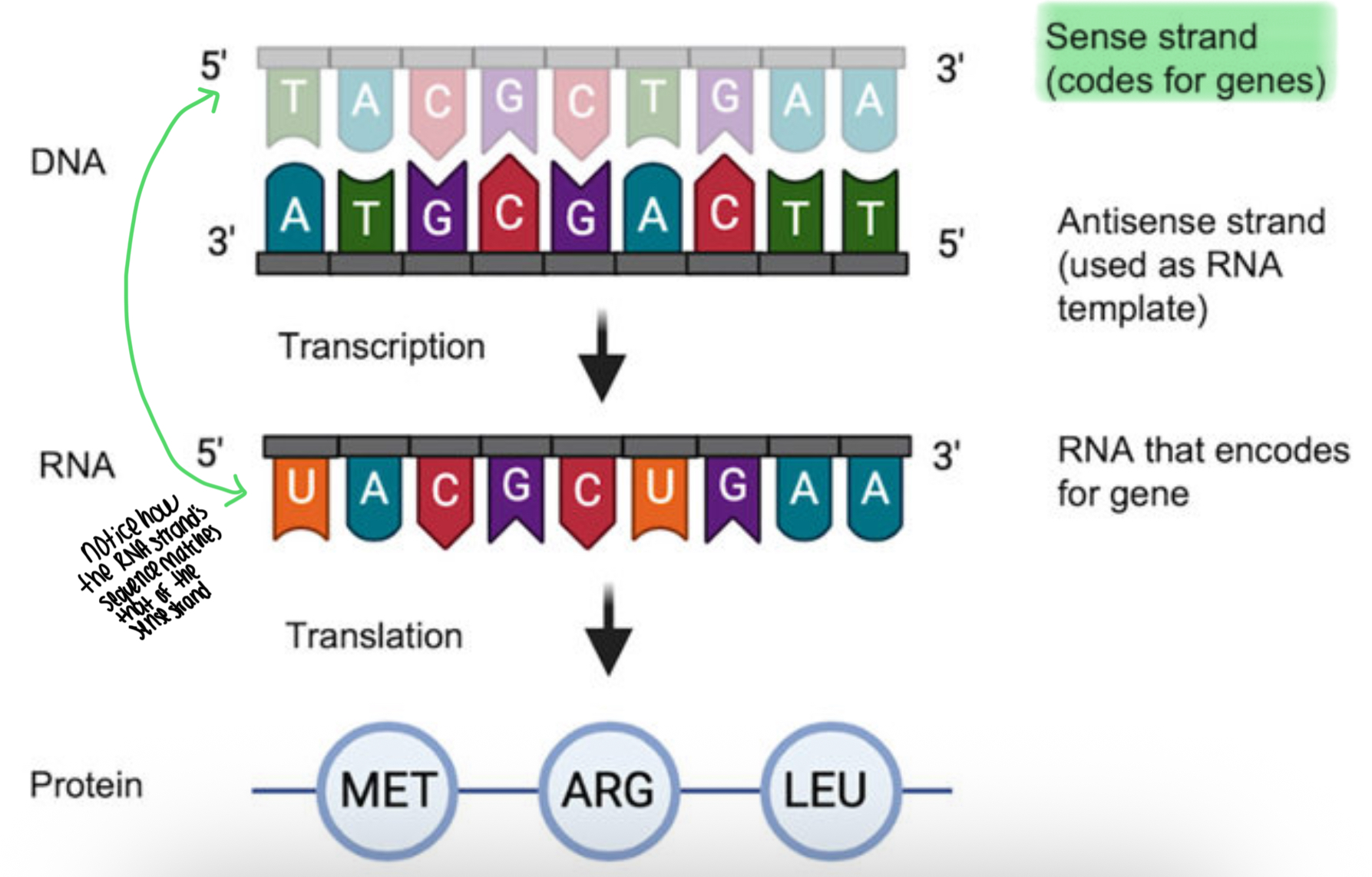
MRNA is built from ___’ to ___’
5’ to 3’
This is because the antisense strand is read from 3’ to 5’ so mRNA must build from 5’ to 3’
DNA Anti Sense Strand
This is the non-coding strand of DNA, complementary to the sense strand. It serves as a template for mRNA synthesis during transcription, ensuring that the correct sequence of nucleotides is copied to produce functional proteins.
This strand is read from 3’ to 5’
Codon
In the ribosomes, mRNA is read as 3 nucleotides at a time. Every 3 bases = 1 codon
Each codon codes for an amino acid
A sequence of three nucleotides that corresponds to a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein synthesis. Codons are found in mRNA and are essential for translating genetic information into proteins.
Start codon
AUG
The ribosome will only begin coding for amino acids when it reaches the AUG start codon.
stop codon
A sequence of three nucleotides that signal the termination of translation, indicating that the protein synthesis is complete. Common stop codons include UAA, UAG, and UGA.
Genes
segments of DNA that code for particular proteins
Some genes code for RNA
chromatin
Loose DNA wrapped around histone proteins
Condenses during mitosis/meiosis —> chromosomes
Chromosomes (prokaryotic vs eukaryotic)
prokaryotic: 1 circular chromosome
Eukaryotic : multiple linear chromosomes (46-- 23 pairs)
T/F Chromosome is made up of DNA + Histone proteins
True
locus
specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located.
Variable
A variable is something you change on purpose in an experiment to see what effect it has (indep variable)
A good experiment has only one variable because you want to test just one thing at a time.
If you change more than one thing at the same time You won’t know which variable caused the results.
Example: In an experiment where a student only changes the pH of the water when watering tomato plants, that is the independent variable—the thing being tested. Everything else, like the pots, soil, sunlight, water amount, and location, stays the same. These are called constants. The student is only testing one thing — the acidity of the water.
Repetition
A good experiment includes repetition.
To get reliable results, scientists usually test each condition more than once. Helps make sure the results are accurate.
Example: If you water only one plant with acidic water and it doesn’t grow well, that might be just luck. But if you water 5 plants the same way and all don’t grow well, you can be more sure that acidic water really affects the plants.
Which system is responsible for filtering waste and toxins from the blood that the circulatory system sends to it.
urinary/renal system
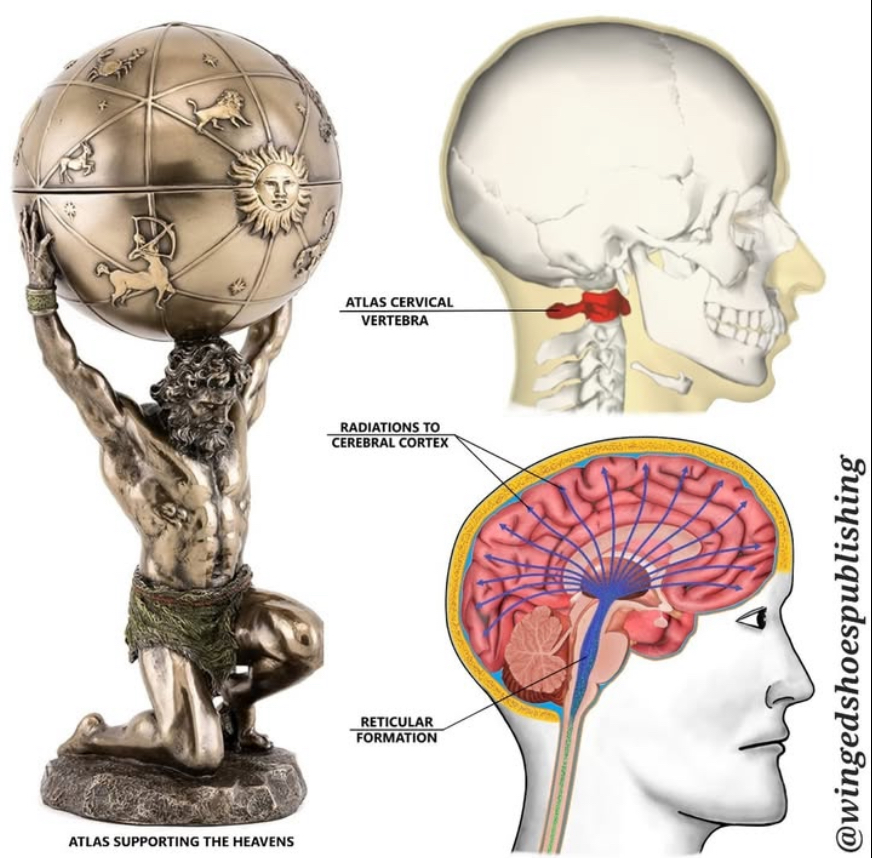
Atlas (C1 Vertebra)
The first cervical vertebra, known as the atlas, supports the skull and allows for nodding movements of the head.
Anabolism undergoes _____ reactions, while catabolism undergoes _____.
condensation, hydrolysis
Anabolic processes are those that use energy to build larger molecules. In cells, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is used as a source of energy.
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together to make a larger molecule and, in the process, also produces a water molecule. Condensation reactions are important in protein synthesis. Anabolic processes are often reduction reactions.
Catabolism breaks down molecules and usually generates energy. Catabolic reactions are often oxidation reactions. Hydrolysis is a catabolic process where water is added to a molecule and then split, resulting in the molecule breaking apart into two different molecules. Hydrolysis is the opposite of condensation.
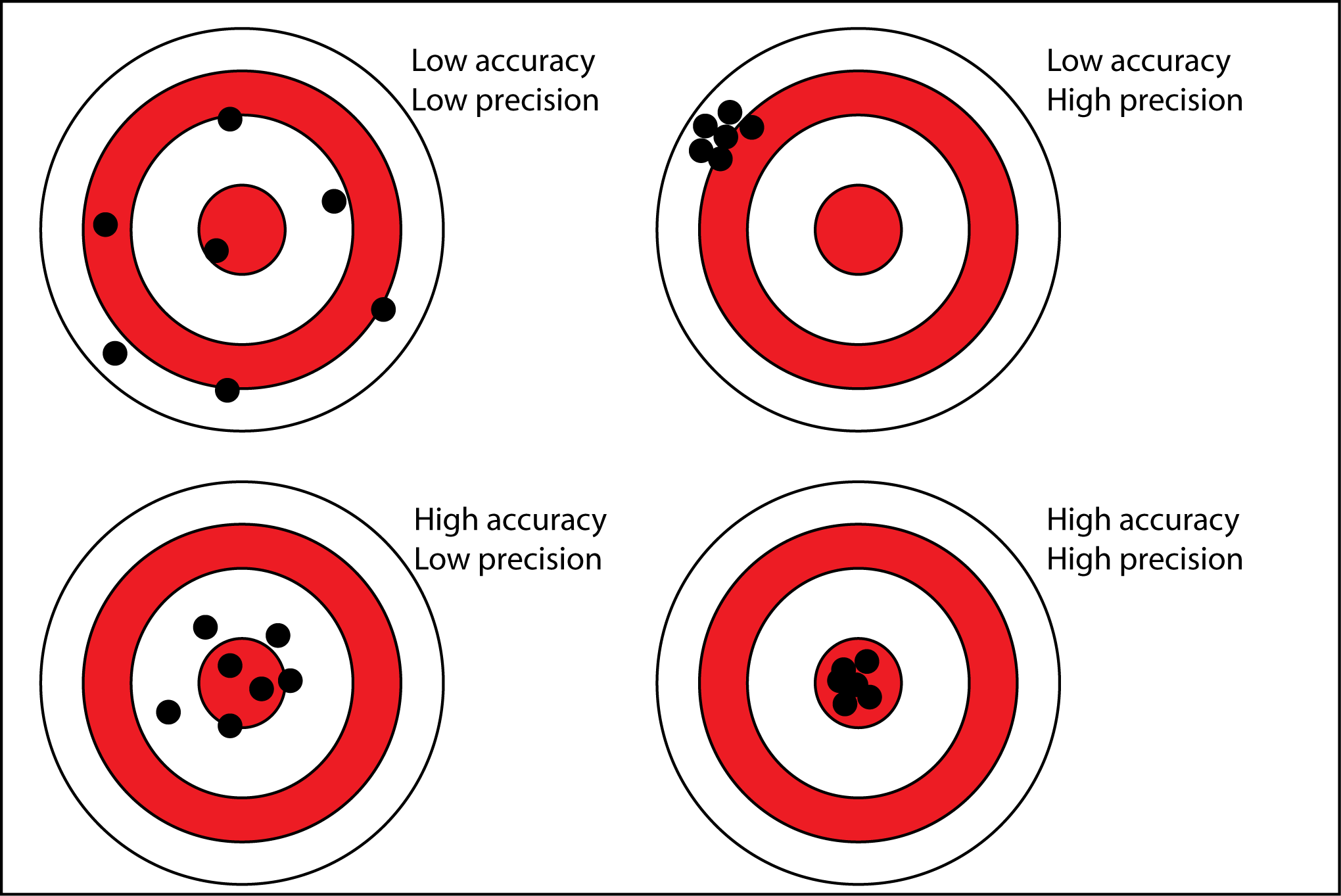
Accuracy vs Precision
Precision = consistency. How consistent your measurements are with each other, even if they’re not correct.
Accuracy = correctness. How close the measurement is to the REAL value
To increase accuracy, measure something more than once.
Mutations
A change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA (a change in one or more DNA bases)
Can cause diff proteins to be produced, which can affect an organism’s traits.
Mutations can happen by substitution, insertion, or deletion of nucleotides.
Mutations can occur during _____
DNA replication
Why? DNA polymerase makes a mistake
Mutations originate in ____ and are passed on to what other nucleic acid?
DNA, RNA (During transcription)
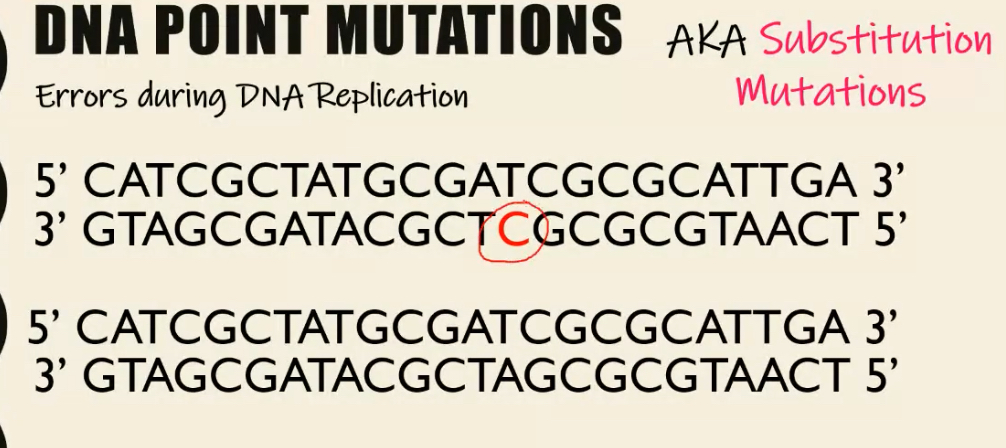
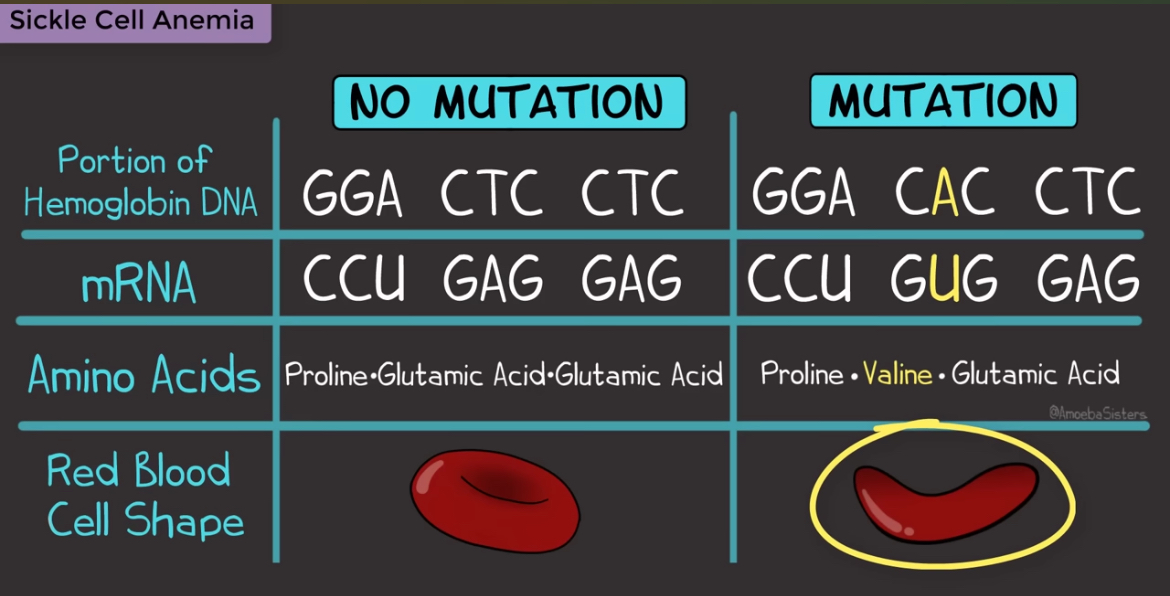
Substitution (Point) Mutations
When one nucleotide is replaced by a different nucleotide
Causes an incorrect base pair
Point refers to the fact that these mutations happen at a single point
insertion
when an extra nucleotide is inserted into the sequence
deletion
One of the nucleotides in the sequence gets deleted.
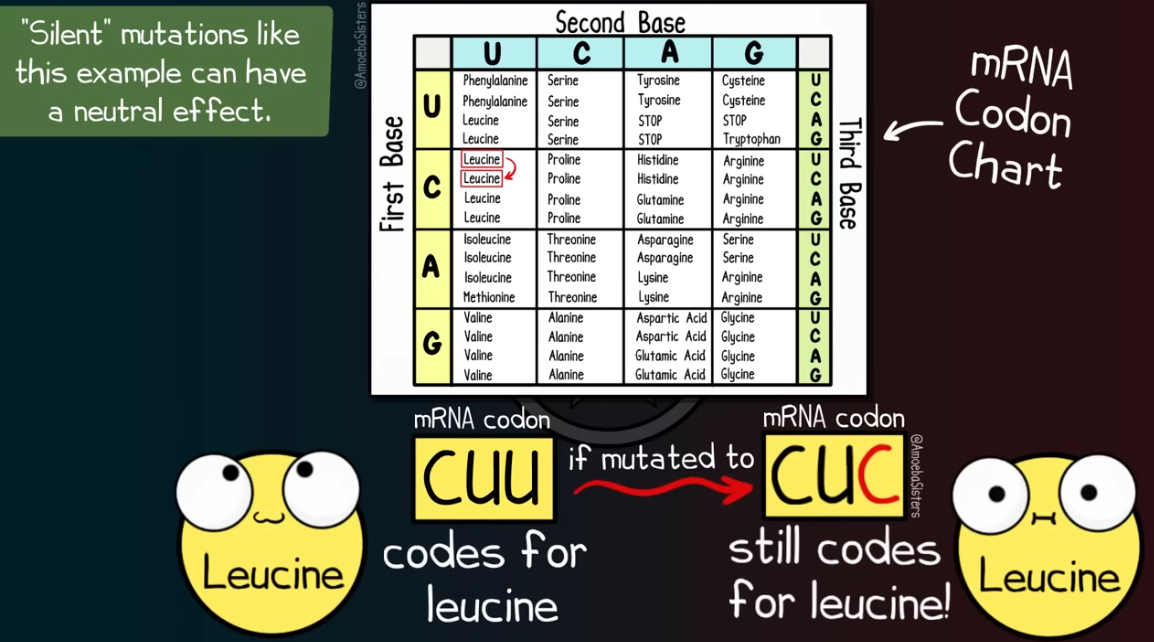
What are 2 reasons for why DNA mutations are usually harmless and do not impact protein production?
Different codons can code for the same amino acid, so even if a mutation changes one nucleotide, usually the protein doesn’t change.
Most DNA doesn’t code for proteins (like introns), so mutations there don’t matter.
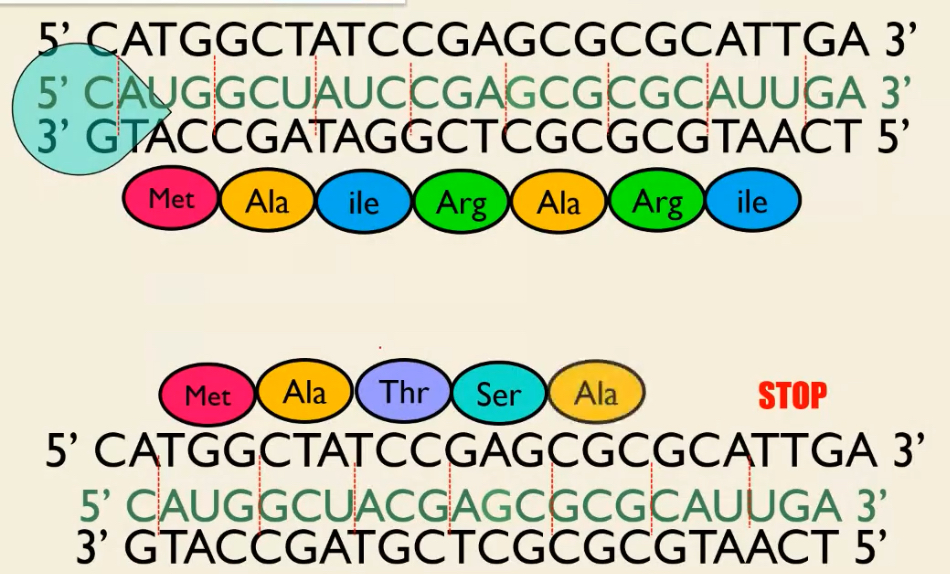
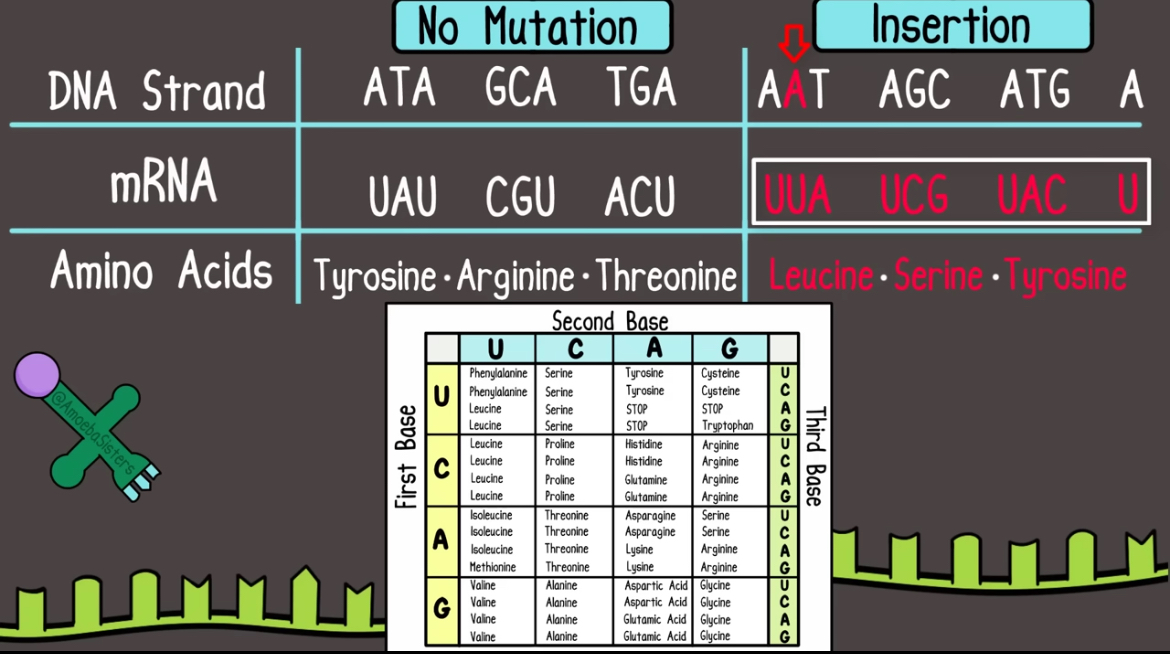
Frameshift Mutation
Caused by insertion or deletion mutations
“Shifting” the whole reading frame. How you divide mRNA into codons is shifted.
This causes mRNA to code for diff amino acids
In order for a mutation to be passed on from parent to offspring, the mutation must occur in what cells?
a sperm or egg cell
A mutation in your skin cell (somatic cell) that causes skin cancer wont cause your baby to have cancer.
Only when a mutation happens during meiosis will the mutation be passed onto the offspring
introns vs exons
A gene has 2 parts: introns and extrons
introns = the parts that do not code for protein (non-coding parts). A mutation in the intron will not cause any change in protein products because this gene doesn’t code for anything .
Exons = the parts that do code for protein
RNA Splicing
before the RNA is used to make a protein, the cell does a cleanup step called RNA splicing.
The cell removes the introns (non-coding portions of DNA) from the RNA.
It then connects the exons together to make the final message (called mRNA).
The ribosome only sees the final mRNA, which has only exons.
So it never reads the introns, because they’ve been cut out before translation starts.
rank the following from large to small: genes, chromosomes, nucleotides, dna, codons
chromosomes, dna, genes, codons, nucleotides
Mendelian vs Non Mendelian Genetics Ratios
Mendelian:
Monohybrid heterozygous x heterozygous cross
3:1 phenotypic ratio
1 AA: 2 Aa : 1 aa genotype ratio
Dihybrid heterozygous x heterozygous cross (AaBb x AaBb)
9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio
Non Mendelian:
shows up when inheritance doesn’t follow Mendel’s simple rules
Incomplete dominance
Neither allele is completely dominant
Phenotype is a blend
Codominance
Both alleles fully expressed
Ex: blood type AB
Each gene has how many alleles?
2
one allele from mom (eg: A), one from dad (eg: a)
Example: Your gene for eye color (or any gene) has 2 alleles:
B and B = both alleles for brown (homozygous dominant)
B and b = one brown, one blue (heterozygous)
b and b = both alleles for blue (homozygous recessive)
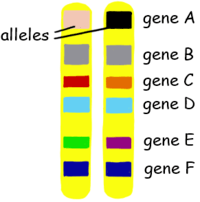
Why is DNA replication a semi-conservative process?
DNA Helicase separates the 2 strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds btwn base pairs. Now you’re left with 2 single strands
Each old strand acts as a template. DNA polymerase reads each old strand and builds a new matching strand next to it by adding complementary bases.
End result:
Each new molecule has one original (old) strand — the template. The whole strand — including the sugar-phosphate backbone and the base pairs — is kept as-is and used as a template
One newly made strand — built using the template

During DNA replication, DNA polymerase reads the old strand in ___ direction and synthesizes the new strand in ____ direction
3’ to 5’ (rmbr 3 comes before 5)
5’ to 3’
The old strand is referring to the template strand
Where is tRNA found?
Cytoplasm
During transcription, the DNA template strand is read by the enzyme from ___ to ___ and mRNA is made from ___ to __
3’ to 5’
5’ to 3’
After transcription, mRNA has the same sequence as which DNA Strand?
Sense strand (runs from 5’ to 3’)
Proteins will be made using which DNA sequence?
The sequence found in the sense strand . This is because mRNA has the same sequence as the sense strand, and mRNA directs protein production
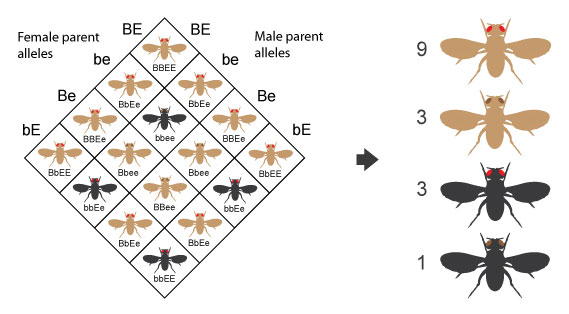
For the DiHybrid Mendelian Phenotype Ratio 9:3:3:1, what does 9 represent?
9 represents having the dominant trait for both genes
these individuals have at least one dominant allele for each gene, which causes them to show the dominant version of both traits.
3 represents organisms that have only one trait that is dominant, the other trait is recessive (eg: Yyrr, YYrr or yyRr, yyRR)
1 represents both traits are recessive (Eg: yyrr)
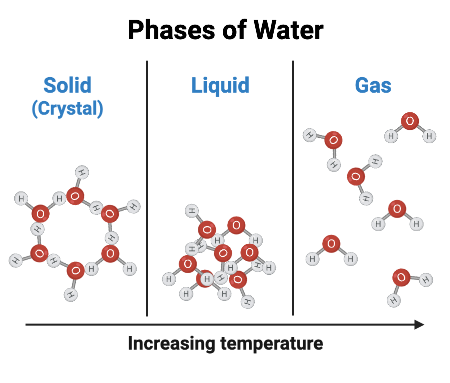
When heat is removed from water during condensation, which of the following are formed?
a.Atoms
b.Covalent bonds
c.Intermolecular bonds
d.Ionic bonds
Condensation = when water vapor (gas) turns back into liquid water.
In gas form, water molecules are moving fast and far apart.
When heat is removed, they slow down and stick together.
The "sticking" happens through intermolecular bonds, specifically hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
These intermolecular bonds pull the water molecules close enough to become liquid again.
/Why it’s NOT covalent bonds:
Covalent bonds are strong bonds inside each water molecule — holding the hydrogen and oxygen atoms together (H—O—H).
These bonds already exist in water vapor and liquid — they don’t break or form during condensation.
During condensation, we’re just forming new attractions between separate water molecules, not changing the molecules themselves.
Why is water called the universal solvent ?
WATER IS CALLED THE UNIVERSAL SOLVENT BECAUSE IT IS CAPABLE OF DISSOLVING MORE SUBSTANCES THAN ANY OTHER LIQUID; particularly, polar substances.
For example: in a solution, water is often the solvent. The solute will usually be things like alcohol, salt, sugar, dissolved in water
Hypertonic vs hypotonic solutions
Hypertonic solutions = higher concentration of solutes than solvent
Ex: if you place a cell in a hypertonic solutions, water moves OUT of the cell (low solute conc in cell —> high solute conc outside of cell)
Hypotonic solutions = lower concentration of solutes than solvent
Ex: if you place a cell in a hypotonic solution, water moves INTO the cell (low solute conc outside cell —> high solute conc inside cell)
What role do bile salts play in fat digestion, and how is it different from enzymatic digestion?
Only the bile salts in bile play a role in digestion, and they do so mechanically (not enzymatically) by emulsifying fats into smaller globules called micelles that can be acted on by Lipases in the small intestine. Emulsifying fats into micelles increases surface area for lipases to act on
Which organ is responsible for converting ammonia (a toxic waste product of the metabolism of amino acids) to urea
Liver
Then the urea is sent to the urinary system for excretion
Which hormone is responsible for the release of pancreatic juices and bile
CCK ( produced by the enteroendocrine I cells of the small intestine )
Which section of the GI tract is responsible for absorbing vitamin B12, bile salts, and any nutrients that were not absorbed by the jejunum.
Ileum
Which part of the nephron reabsorbs 100% of the useful nutrients filtered by the glomerulus, and what structural feature helps with this function?
The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT); it has microvilli that increase surface area for reabsorption.
It is the only tubule that possesses microvilli.
Why is the renal medulla salty?
Because the loop of Henle (especially the thick ascending limb) pumps out sodium and other ions from the filtrate into the medulla, creating a high salt concentration that helps the kidney concentrate urine.
Which part of the nephron is involved in passive, obligatory water reabsorption?
the descending limb of the loop of Henle — it is permeable to water, so water is reabsorbed passively by osmosis into the salty medulla
This part of the nephron loop contains simple squamous epithelial cells that make it easier for water to flow thru, unlike the ascending loop of Henley which has a layer of cuboidal cells
Which tubules in the kidneys are responsible for H+ excretion and hormonally regulated water reabsorption (via aldosterone or ADH)
H⁺ excretion: Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting duct
Water reabsorption:
Aldosterone acts on the DCT and collecting duct to increase Na⁺ reabsorption (water follows).
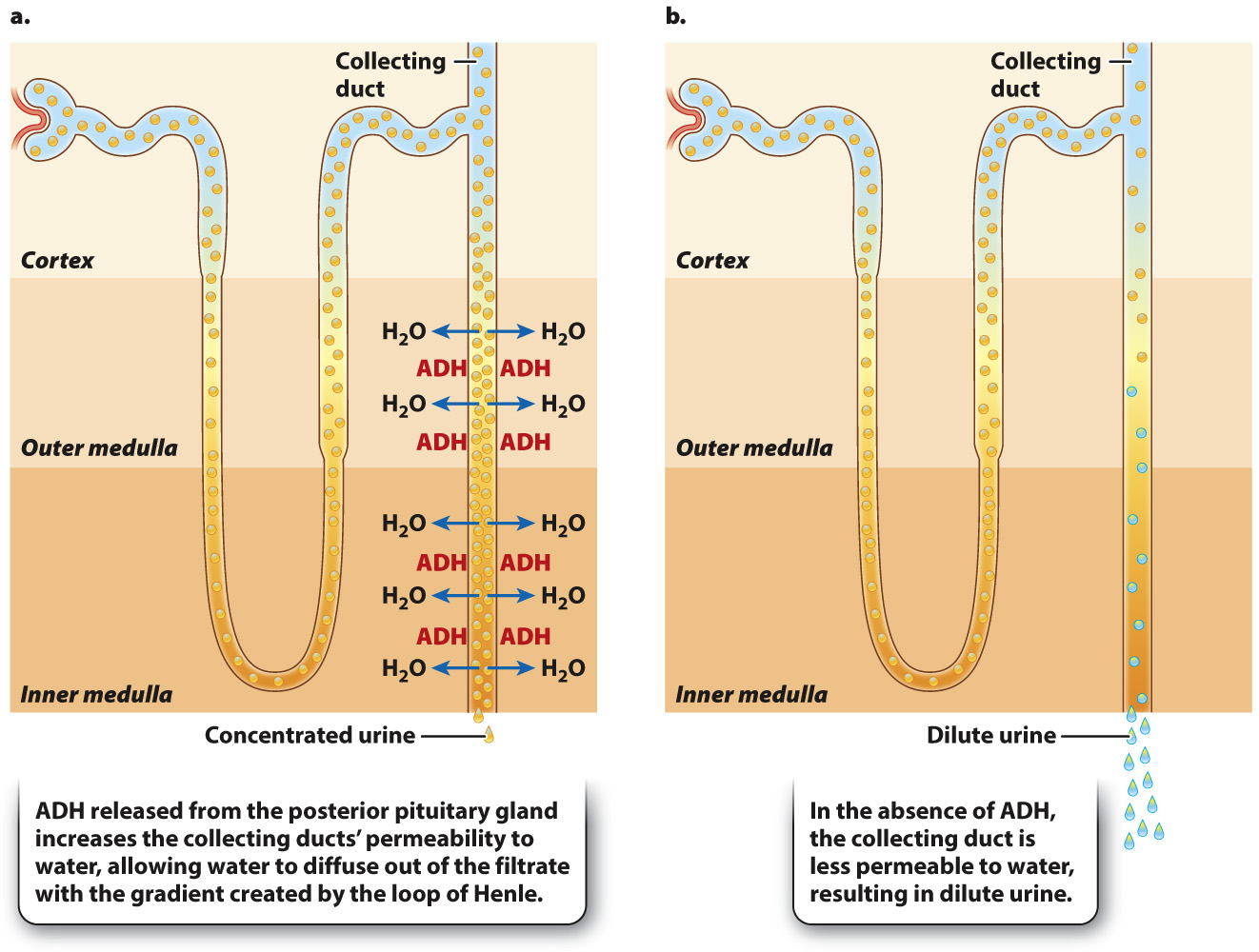
ADH acts on the collecting duct to make it more permeable to water, increasing reabsorption.
Which 2 hormones are responsible for the concentration of urine?
The concentration of urine is also regulated by hormones. The permeability of the distal convoluted tubule to sodium is dependent on aldosterone. Aldosterone promotes the reabsorption of Na+, and since water follows the sodium, the urine becomes more concentrated.
The permeability of the collecting duct is dependent on both aldosterone and ADH. ADH increases the duct's permeability by water by inserting aquaporins that allow the passage of water.
Contraction of the detrusor muscle in the bladder is controlled by which branch of the ANS?
PNS
Contraction forces urine into the urethra, helping initiate urination (micturition).
What hormone is released when osmoreceptors detect an increase in blood osmolality, or when baroreceptors detect a decrease in blood pressure?
ADH or RAAS system activation
ADH stimulates the reabsorption of water in the kidney so that less water is excreted in the urine. This increases the volume and pressure of the blood.
Which cells in the kidney detect low sodium (Na⁺) levels and stimulate renin release from juxtaglomerular cells?
Macula densa cells — they sense low Na⁺ in the distal tubule and signal juxtaglomerular cells to release renin.
How does renin regulate blood pressure through aldosterone?
Renin starts the RAAS pathway, leading to the production of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption in the DCT + collecting duct in the kidneys, and water follows sodium, which raises blood volume and blood pressure.
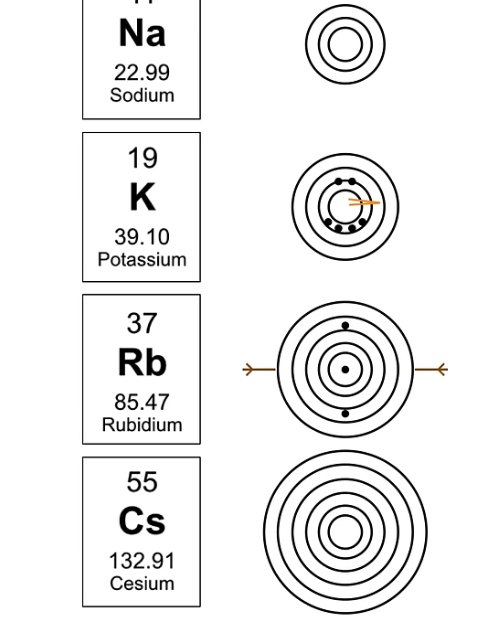
What is atomic radius and what is the trend on the periodic table?
The size of the atom itself; the distance from the nucleus to the furthest out electron in the electron cloud.
Trend: atomic radius increases as you move down the periodic table, decreases as you move to the right.
Why does it decrease? As you add more protons you add more electrons and the attraction of the electrons to the nucleus becomes greater, causing the electron cloud to move inwards.
Ionization energy and its periodic table trend
The amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. Think of it as the cost of taking an electron from an atom
High Ionization = difficult to remove electrons (high cost)
Low Ionization = easily gives up electrons (low cost)
Trend: Ionization energy increases as you move left to right. Decreases as you move down (meaning its easier to remove the electrons as you move down, bc the atomic radius is larger)
The smaller an atom is, the harder it is to remove an electron from it.
Electronegativity and its periodic trends
The measure of an atom’s attraction to electrons. How much an atom wants electrons
Trend: Electronegativity increases as you move left to right. Decreases as you move down.
Which cells found around the seminiferous tubules produce testosterone, which stimulates the production of sperm.
leydig cells
What are the 3 phases of the ovarian cycle
Follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase
In which phase does FSH stimulates the maturation of the follicle, which then secretes estrogen.
Follicular phase
Which phase is indicated by the release of a secondary oocyte from the ovary, which is induced by a surge in LH
Ovulation, secondary oocyte ruptures from tertiary follicle
The luteal phase begins with the formation of:
Corpus luteum
Tertiary follicle after ovulation will develop into corpus luteum
This is due to the surge in LH
Corpus luteum secretes which hormones that cause the inhibition of FSH and LH
Progesterone and estrogen
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) and LH (Luteinizing Hormone) are the hormones that tell the ovaries to grow and release eggs.
So after ovulation, when the body thinks it might be pregnant, it slows down egg production by stopping FSH and LH.
👉 It's like the body saying:
"Wait! We might have a baby starting to grow—let’s not release any more eggs right now!"
Uterine cycle consists of which 3 phases
Menstrual, proliferative, secretory
Proliferative phase
Initial restoration of uterine lining due to the rise in estrogen
regeneration and growth of the uterine Lining.
Secretory phase
endometrium becomes increasingly vascular, and nutrients are secreted to prepare for implantation
Due to progesterone
Endometrial arteries and glands elongate
Without implantation, the endometrium is shed during
Menstruation
Parturition
Birth
Primary vs secondary organs of lymphatic system
Primary: thymus and bone marrow; both sites of lymphocyte maturation. bone marrow = lymphocyte production
Secondary: spleen, tonsils, lymph nodes, MALT- site where lymphocytes encounter antigens and mount an immune response
Rh negative vs rh positive
Rh positive: contain rh antigen on rbc surface (gives you + blood sign)
Rh negative: does NOT contain rh antigen on rbc surface ( - blood sign)
A person who is rh positive cannot give a person who is rh negative blood. This is because the rh positive antigen will trigger an immune reaction in an rh negative person.
Validity vs reliability
Reliability = consistency
If you do the experiment again and again, do you get the same results each time?
to improve reliability :
Repeat the experiment
Have others repeat the experiment
Validity = accuracy
Are you really testing what you think you’re testing?
Are the results correct and not affected by outside factors?
To improve validity:
Random sample
Keep everything the same except one variable
External respiration is the exchange of gas between the ___ and the ____
External respiration is the exchange of gas between the Lungs and the blood.
Internal respiration is the exchange of gas between the ___ and ____
Internal respiration is the exchange of gas between the blood and tissues
Business letter format
Date
Address
Greeting
Body
Closing