Experimental Research Design Overview and Key Concepts
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
236 Terms
What distinguishes strong experimental designs from weak experimental designs?
Strong experimental designs have rigorous controls, random assignment, and clear operational definitions, while weak designs lack these elements, leading to potential biases and confounding variables.
What are the characteristics of weak experimental designs?
Weak experimental designs often lack random assignment, have small sample sizes, or do not control for extraneous variables, making it difficult to draw valid conclusions.
What are the requirements of strong experimental research designs?
Strong experimental research designs require random assignment, control groups, manipulation of independent variables, and clear operational definitions.
What are between-participants designs, and what are their strengths and weaknesses?
Between-participants designs involve different participants in each condition. Strengths include reduced carryover effects, while weaknesses include the need for larger sample sizes and potential group differences.
What are within-participants designs, and what are their strengths and weaknesses?
Within-participants designs involve the same participants in all conditions. Strengths include reduced variability and smaller sample sizes, while weaknesses include potential carryover effects and fatigue.
What are mixed designs in experimental research?
Mixed designs combine both between-participants and within-participants elements, allowing researchers to leverage the strengths of both designs while mitigating their weaknesses.
What are the advantages of using a pretest in experimental research?
Pretests can help establish baseline measurements, assess participant characteristics, and enhance the sensitivity of the experiment to detect changes.
What are factorial designs, and what are their strengths and weaknesses?
Factorial designs involve studying multiple independent variables simultaneously. Strengths include the ability to examine interactions and main effects, while weaknesses include increased complexity and potential for confounding.
What is the difference between main effect and interaction effect in experimental research?
A main effect refers to the impact of a single independent variable on the dependent variable, while an interaction effect occurs when the effect of one independent variable differs depending on the level of another independent variable.
What considerations should be made when deciding on an appropriate experimental design?
Considerations include the research question, available resources, participant characteristics, the potential for confounding variables, and the desired level of control.
What is research design?
The outline, plan, or strategy used to investigate the research problem.
What is the purpose of research design?
To control for unwanted variation and suggest how data will be statistically analyzed.
What is the goal of research design?
To choose the strongest design that is possible, ethical, and feasible.
What are weak experimental designs?
Designs that do not control for many extraneous variables and provide weak evidence of cause and effect.
When should weak experimental designs be used?
Only when a stronger design cannot be used to answer the research question.
What is a one-group posttest-only design?
A design where a posttest is administered to a single group after an experimental treatment, but lacks a pretest or control group.
What are the limitations of a one-group posttest-only design?
It is rarely useful due to threats to internal validity and is only useful when specific background information on the dependent variable exists.
What is a one-group pretest-posttest design?
A design where a treatment condition is interjected between a pretest and posttest of the dependent variable.
What threats to internal validity exist in a one-group pretest-posttest design?
History, testing, regression, instrumentation, and maturation.
What is a posttest-only design with nonequivalent groups?
A design comparing the performance of an experimental group with that of a nonequivalent control group at the posttest.
What are the internal threats addressed in a posttest-only design with nonequivalent groups?
History, maturation, regression, and attrition.
What is the purpose of a control group in experimental designs?
To serve as a source of comparison to the experimental group and control for rival hypotheses.
What is a posttest-only control-group design?
A design where participants are randomly assigned to groups, creating equivalence and using a control group to eliminate most threats to internal validity.
What are the weaknesses of a posttest-only control-group design?
It does not guarantee equivalence of groups, especially with small sample sizes, and lacks a pretest to assess equivalence.
What is a within-participants design?
A design where participants are included in all conditions, also known as repeated measures designs.
What is counterbalancing in within-participants designs?
A technique used to eliminate linear sequencing effects.
What are the strengths of within-participants designs?
Increased sensitivity due to control of individual differences and fewer research participants needed.
What are the weaknesses of within-participants designs?
They can be difficult for participants and may have differential carryover effects.
What is a mixed design in research?
A design that contains both between-participants and within-participants variables.
What is a factorial design?
A design that studies two or more independent variables to determine their separate and joint effects on the dependent variable.
What is a main effect in a factorial design?
The influence of one independent variable on the dependent variable, ignoring the second independent variable.
What is an interaction effect in a factorial design?
The combined effect of two or more independent variables on the dependent variable, indicating that the effect of one variable depends on another.
What does a 2 x 2 design indicate?
It indicates two independent variables, each with two levels.
What are the strengths of factorial designs?
They allow for more precise hypotheses, control of extraneous variables, and determination of interactive effects.
What are the weaknesses of factorial designs?
Using more than two independent variables may be logistically cumbersome and higher-order interactions can be difficult to interpret.
What factors should be considered when choosing an experimental design?
Use of control group, number of comparison groups, pretests, within-participants or between-participants, and number of independent and dependent variables.
What is NOT a purpose of creating a research design for a research problem?
To analyze the data collected.
In the one-group pretest-posttest design, which threat to internal validity is NOT controlled?
Testing.
What factors should be considered when deciding on a research design?
Number of groups, use of a control group, and use of a pretest.
What experimental design is represented by training 6 people on a speed reading program and then measuring their reading speed?
One-group posttest-only design.
What experimental design is illustrated by two teachers testing a new trigonometry program by comparing their students' scores?
Non-equivalent posttest-only design.
What experimental design is exemplified by physicians testing a new analgesic on patients and measuring pain ratings before and after?
One-group pretest-posttest design.
What fault does the one-group posttest-only design include?
The treatment condition is given to all research participants.
What is the major fault in the one-group pretest-posttest design?
There is no way to examine the effects of history and maturation on the results.
What methodological advantage does the one-group pretest-posttest design have over the one-group posttest-only design?
Pretest scores can be compared to posttest scores.
How does the nonequivalent posttest-only design differ from the one-group posttest-only design?
It has a comparison group.
What is the major fault in the non-equivalent posttest only design?
The two groups may not be equivalent at the beginning.
What is the scenario described where two classes are closely matched on IQ scores but taught with different methods?
They are compared on scores from a standardized test at the end of the year.
What is a major confounding variable in a study without a pretest?
Maturation is a major confounding variable.
What distinguishes strong research designs from weak ones?
Strong designs have greater internal validity.
What is the group called that experiences the experimental treatment in Dr. Sheffield's study?
The experimental group.
Why is a control group included in a good experiment?
It gives information about how participants would perform without the experimental treatment.
Which characteristic is least important for a good control group?
Having the same number of participants as the experimental group.
What are the two most important techniques for eliminating potential rival hypotheses?
Random assignment of participants and use of control groups.
What is NOT a benefit of incorporating a pretest into experimental design?
It can sensitize the participants to the experimental treatment.
What could be a reason for Hannah's technique not significantly increasing performance in her ping-pong study?
A ceiling effect.
What could explain why Hannah's technique does not decrease the time to finish a ping-pong game?
A floor effect.
What is the purpose of random assignment in experiments?
To eliminate biases and ensure that groups are equivalent.
What is the role of a comparison group in an experiment?
To provide a baseline for comparison against the experimental group.
What is an example of a rival hypothesis in an experimental study?
Participants' prior experience affecting their performance.
What does external validity refer to in research design?
The extent to which results can be generalized to other settings or populations.
What is the significance of a pretest in experimental design?
It allows for assessment of each group's initial position on the dependent measure.
What is the main goal of using control groups in experiments?
To isolate the effect of the independent variable.
What does internal validity refer to in research?
The degree to which a study accurately establishes a causal relationship.
Why might a pretest be detrimental to an experiment?
It can sensitize participants to the treatment.
What is the difference between an experimental group and a control group?
The experimental group receives the treatment, while the control group does not.
What is the importance of matching participants in research studies?
To ensure that groups are equivalent on critical variables.
What can be a consequence of not having a control group in an experiment?
It can lead to ambiguous results regarding the treatment's effectiveness.
What is a ceiling effect in experimental research?
When participants' performance is already at the maximum level, making it hard to detect improvement.
What is a floor effect in experimental research?
When participants' performance is at a very low level, limiting the ability to measure improvement.
What is a common reason for pretesting participants before introducing the independent variable?
Pretesting gives the experimenter direct evidence of change in performance.
What does the posttest-only control group design require?
It requires a control condition.
In a between-participants posttest-only design, how is each participant tested?
Each participant is tested in only one treatment condition.
What is the important difference between the between-participants posttest-only design and the flawed non-equivalent posttest-only design?
The former uses random assignment of participants to groups.
What factor makes the between-participants posttest-only design a strong experimental design?
Random assignment helps ensure that the two experimental groups are essentially equivalent at the outset.
What is true about all repeated-measures designs?
Every participant will be tested in each of the conditions of the study.
What distinguishes a within-participants design from a between-participants design?
The former involves all participants experiencing all levels of the independent variable.
What is the major advantage of a within-participants design?
The experimenter doesn't have to worry about whether the groups of participants are equivalent to each other.
What is a major disadvantage of a within-participants design?
It is very susceptible to order and carryover effects.
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of a within-participants design?
It is relatively immune to carryover effects.
What is an experimental design that incorporates more than one independent variable called?
A factorial design.
What is the defining characteristic of a factorial experimental design?
The manipulation of more than one independent variable.
What does pretesting eliminate in the context of experimental design?
The need for random assignment of participants to groups.
What is required for the posttest-only control group design besides random selection?
A control condition.
In a between-participants design, how do participants experience treatment conditions?
Each participant experiences only one treatment condition.
What does the nonequivalent posttest-only design lack compared to the between-participants posttest-only design?
It does not manipulate an independent variable.
What is a key characteristic of repeated-measures designs?
Participants will be tested more than once per condition.
What is a disadvantage of conducting tests multiple times in a within-participants design?
It can lead to order and carryover effects.
How does a within-participants design affect the interpretation of data?
Data are generally easier to interpret than from between-participants designs.
What is a common misconception about within-participants designs?
That they are immune to carryover effects.
What is the relationship between the number of participants needed in within-participants versus between-participants designs?
Within-participants designs tend to require fewer participants.
What is the effect of random assignment in experimental designs?
It helps ensure that groups are equivalent at the outset.
What does the term 'factorial design' imply about the study?
It involves multiple independent variables.
What is the average score of participants in one group called in a factorial design?
Cell mean
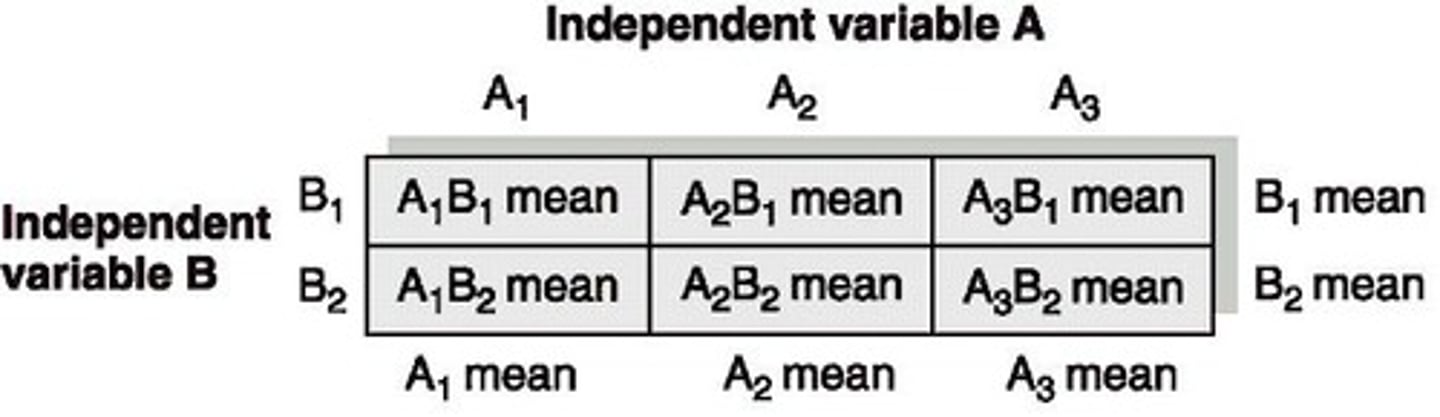
What do the A1 mean, A2 mean, and A3 mean represent in a factorial design?
Marginal means
What do the B1 mean and B2 mean represent in a factorial design?
Marginal means

In a table representing groups in a factorial design, what does each group correspond to?
Cell
What is the combination of levels of two or more independent variables called?
Cell
What type of design is used when there are two levels of one independent variable and three levels of another?
2X3 factorial design
What type of design is used when participants are assigned to different groups based on independent variables?
Between-participants design