Science KS3 revision
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Photosynthesis
A process that plants use to make their own food.
Photosynthesis Word Equation
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
2 other components needed for photosynthesis
sunlight and chlorophyll
What do the plant roots absorb?
minerals and water
Why do plants need minerals?
to stay healthy
Why do leaves have a big surface area?
to absorb light
Where is most the chloroplasts found in a leaf?
near the top for more light
why do plants need to do photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is important because it provides oxygen for organisms, supports the food chain, balances carbon dioxide levels, and is essential for the formation of fossil fuels and plant products
Purpose of plant veins
deliver water to cells and take glucose away
Stomata
small holes in the leaf or gas exchange (carbon dioxide goes in and oxygen goes out)
root hair tissue
small hairs on the outsides of roots which help to take in as much water as possible
Xylem tissue
the tissue which carries water up through plants from the roots
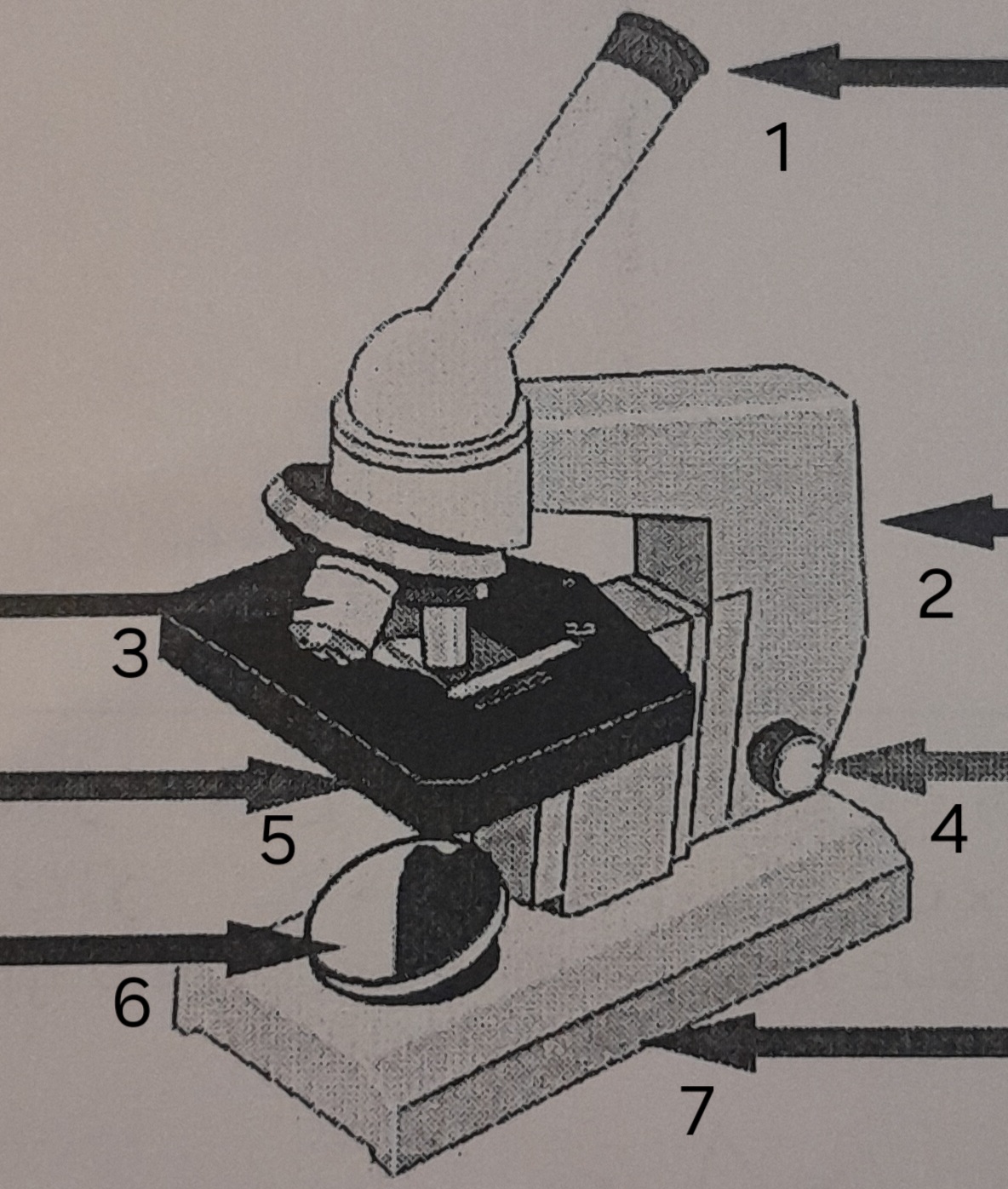
label ‘1’
eye piece
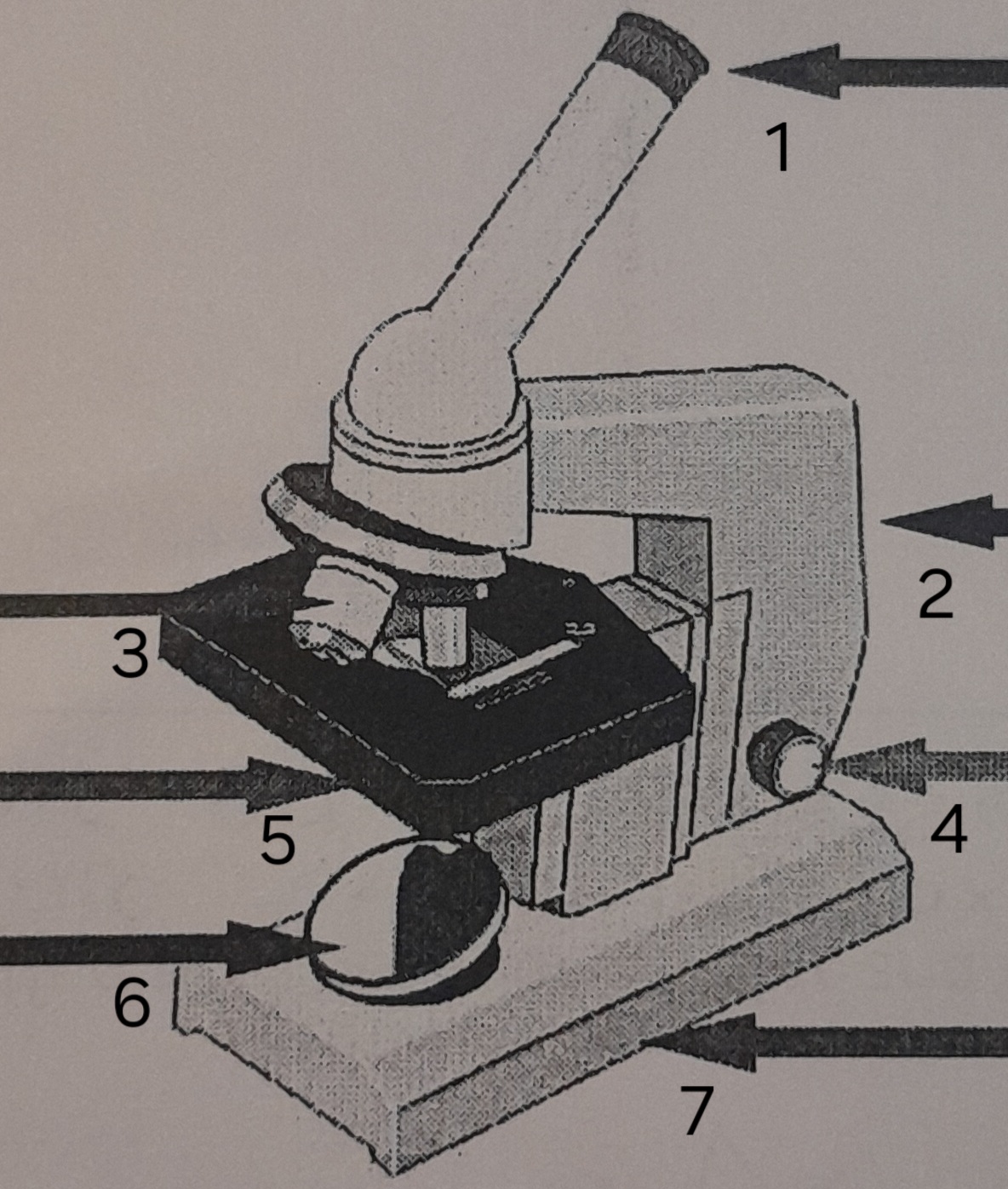
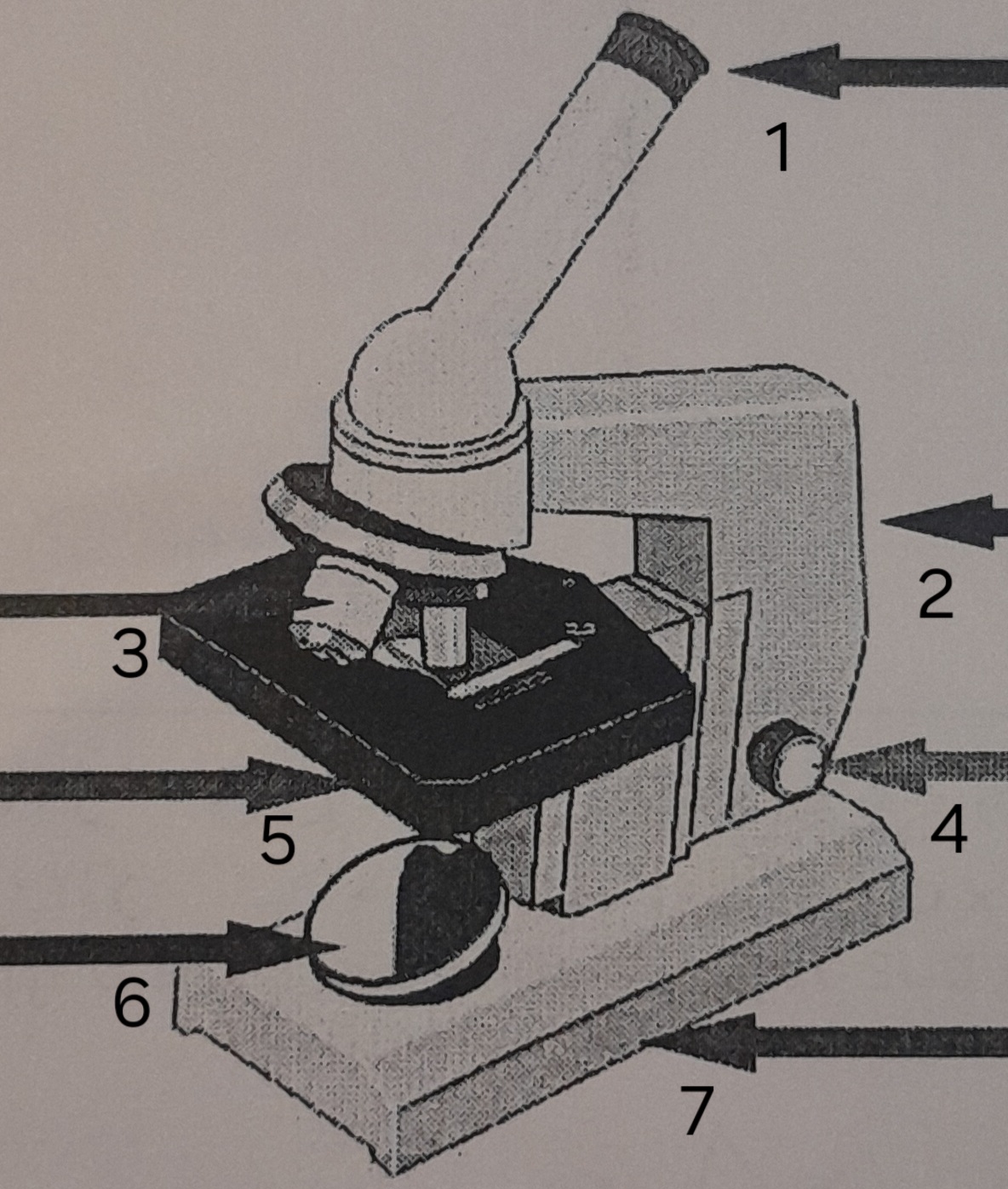
label ‘2’
Arm
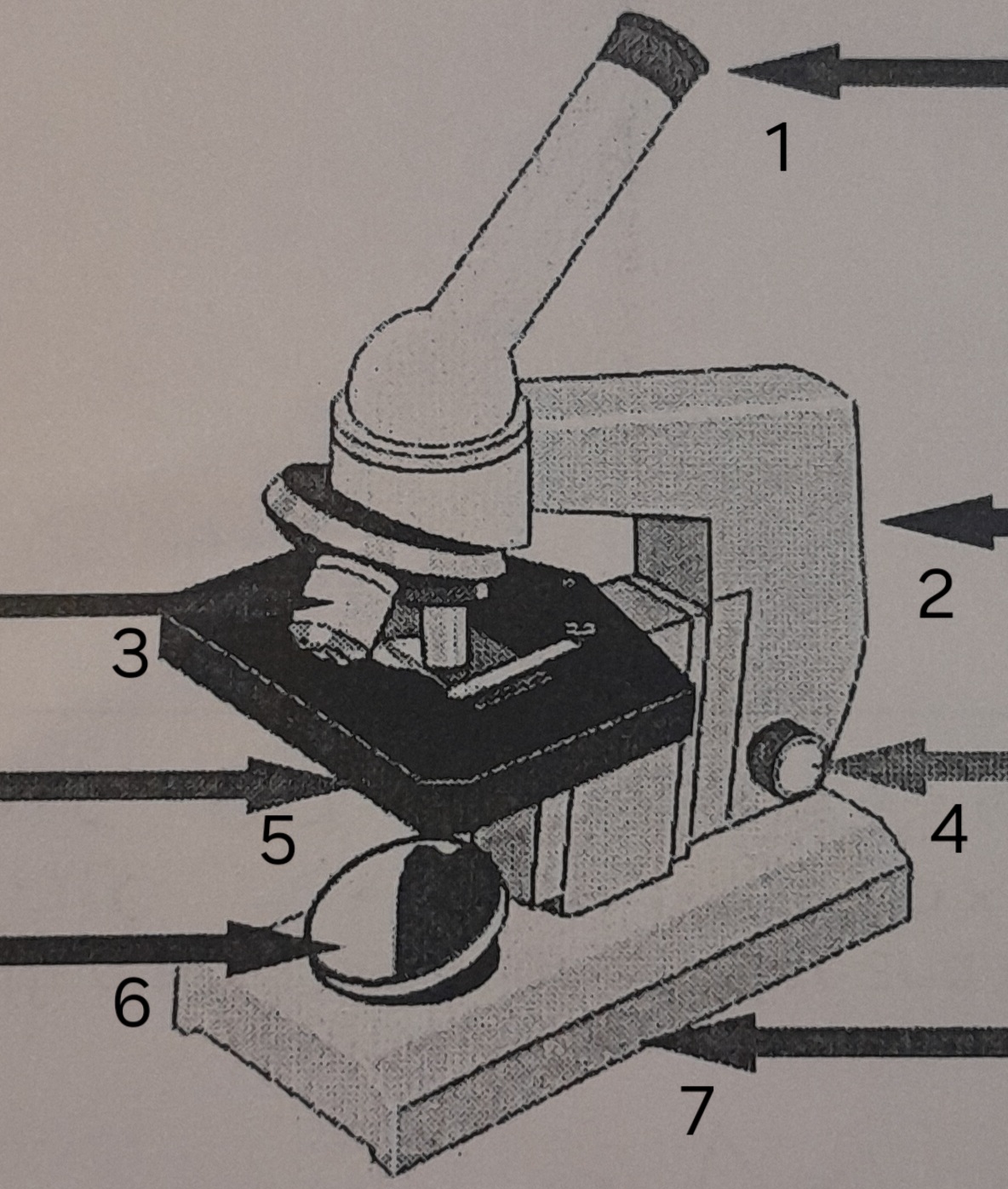
label ‘3’
Lenses
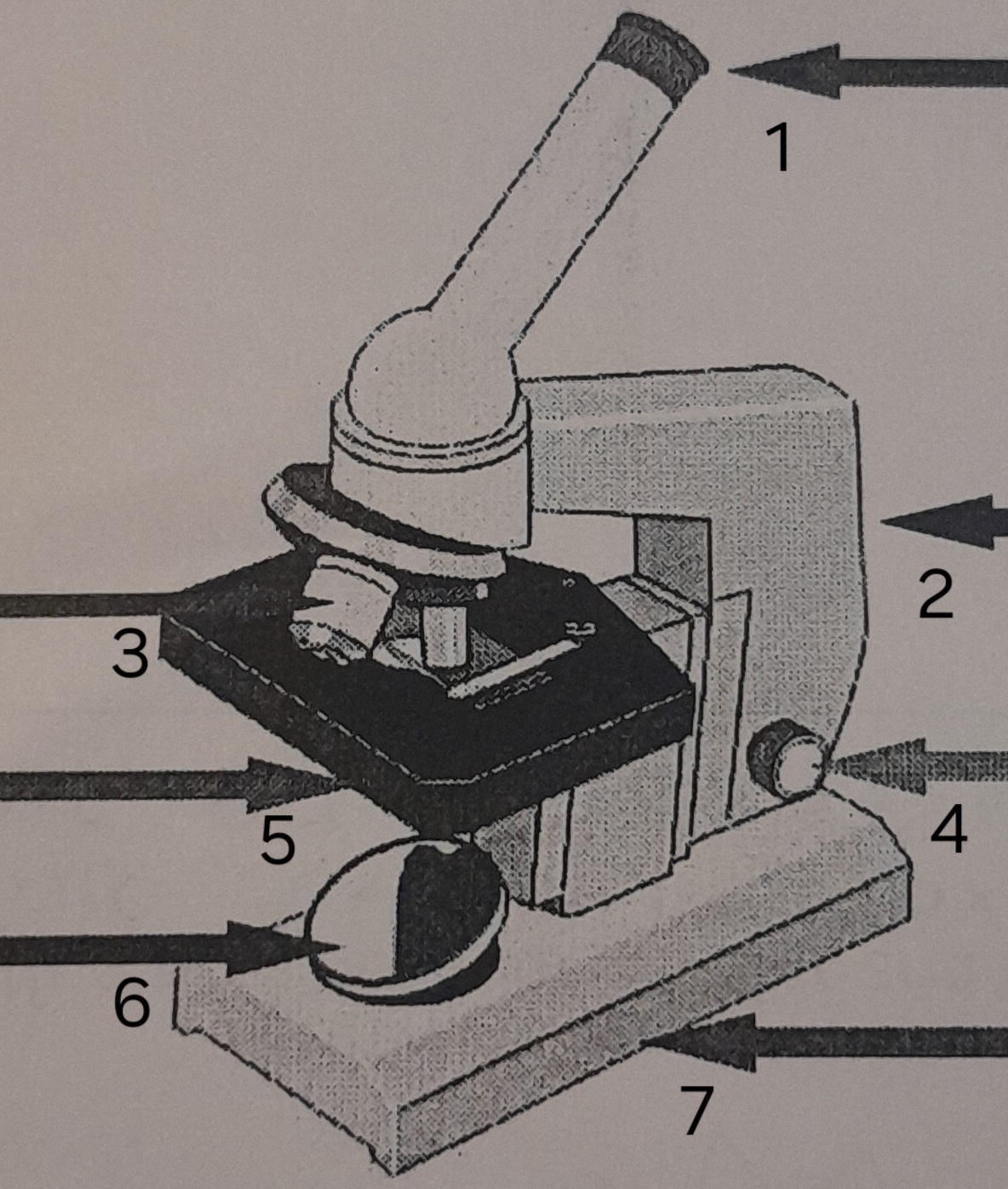
label ‘4’
Focus adjustor
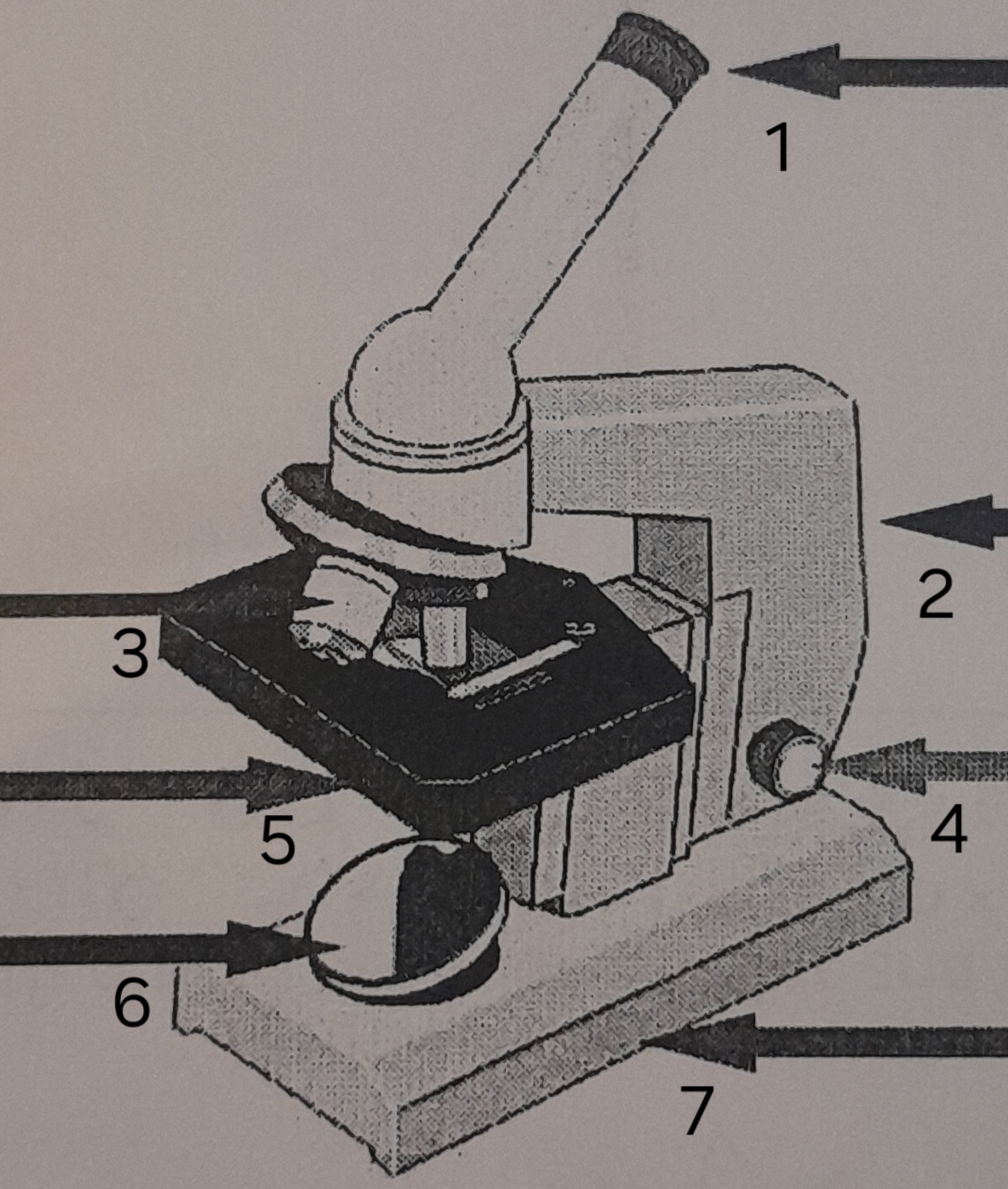
label ‘5’
Stage
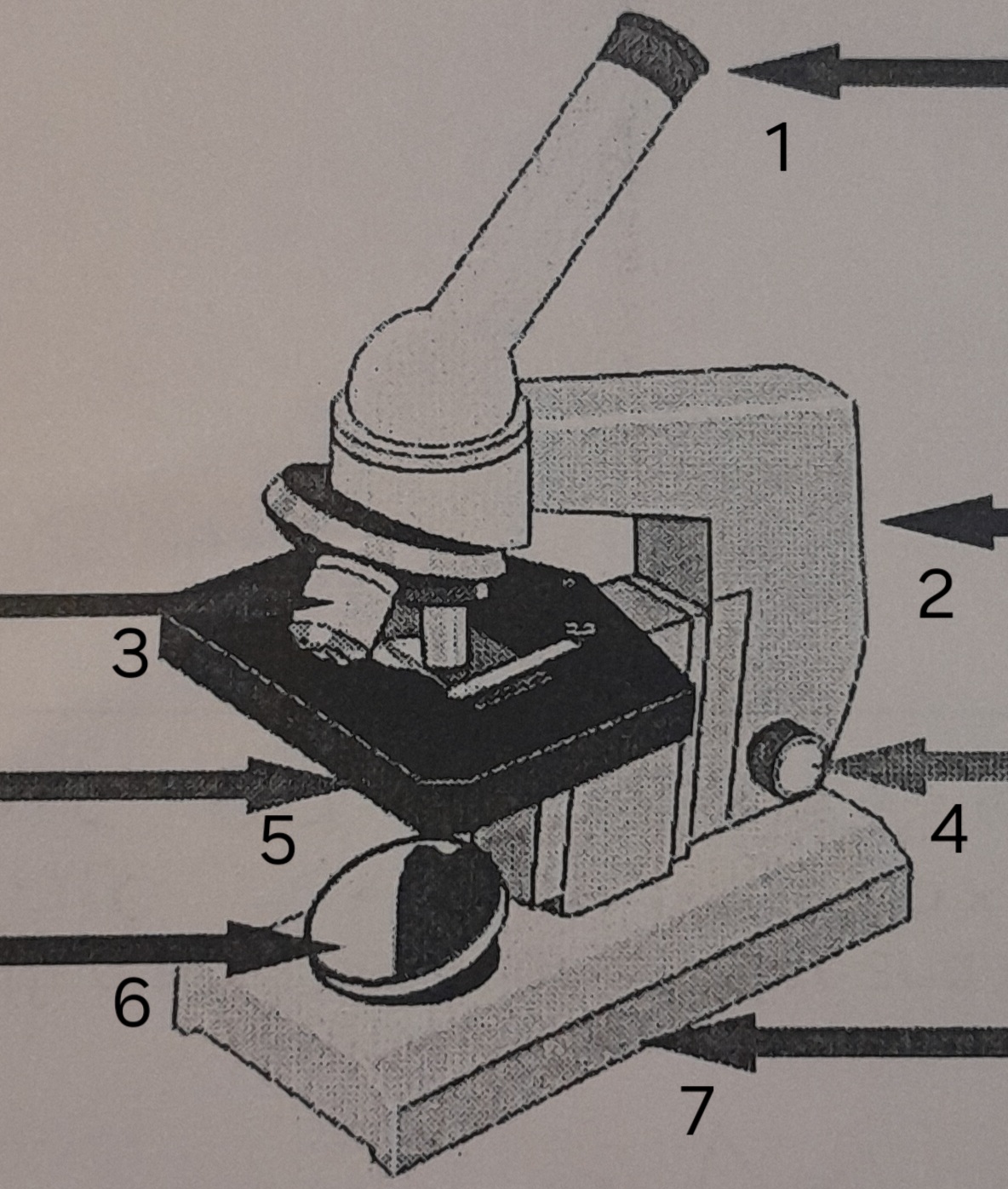
label ‘6’
mirror
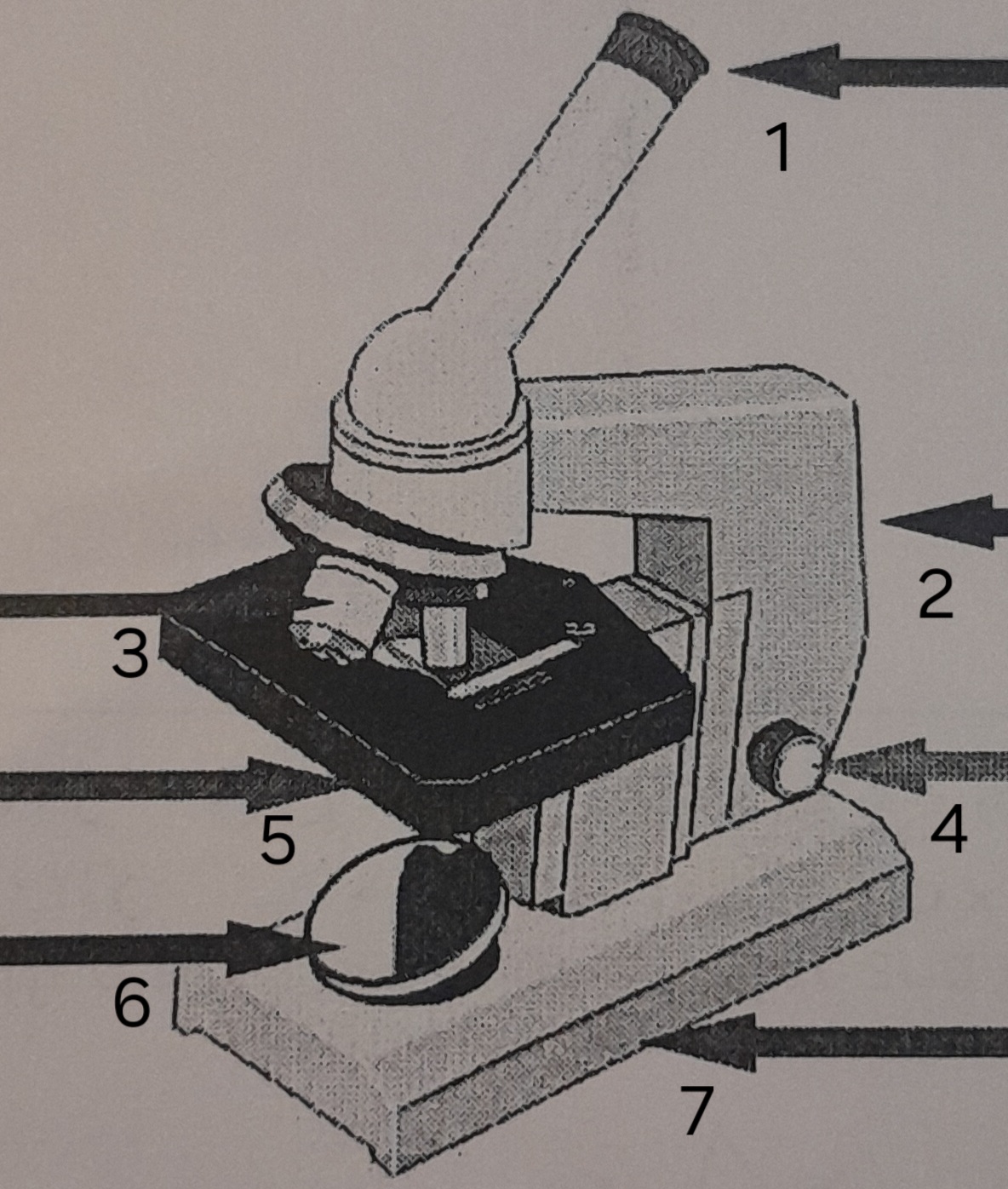
label ‘7’
Base
Why do we use a light microscope?
Cells are too small to see with the naked eye. Using a light microscope helps us to see and draw cells.
equation for aerobic respiration
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + energy
equation for anaerobic respiration
Glucose → Lactic acid + energy
differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
anaerobic doesn’t need oxygen
anaerobic produces less energy
aerobic has 2 products
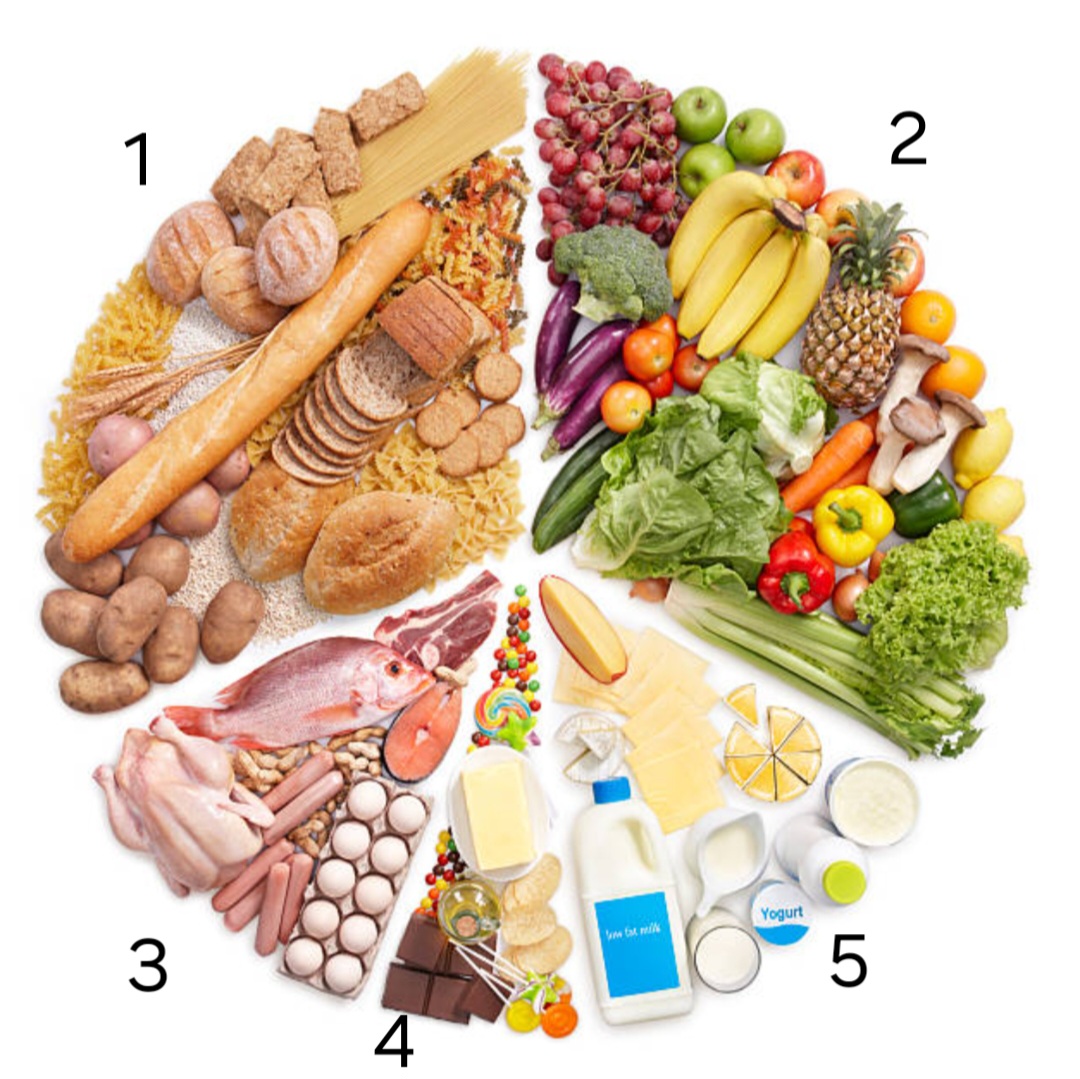

label ‘1’
carbohydrates
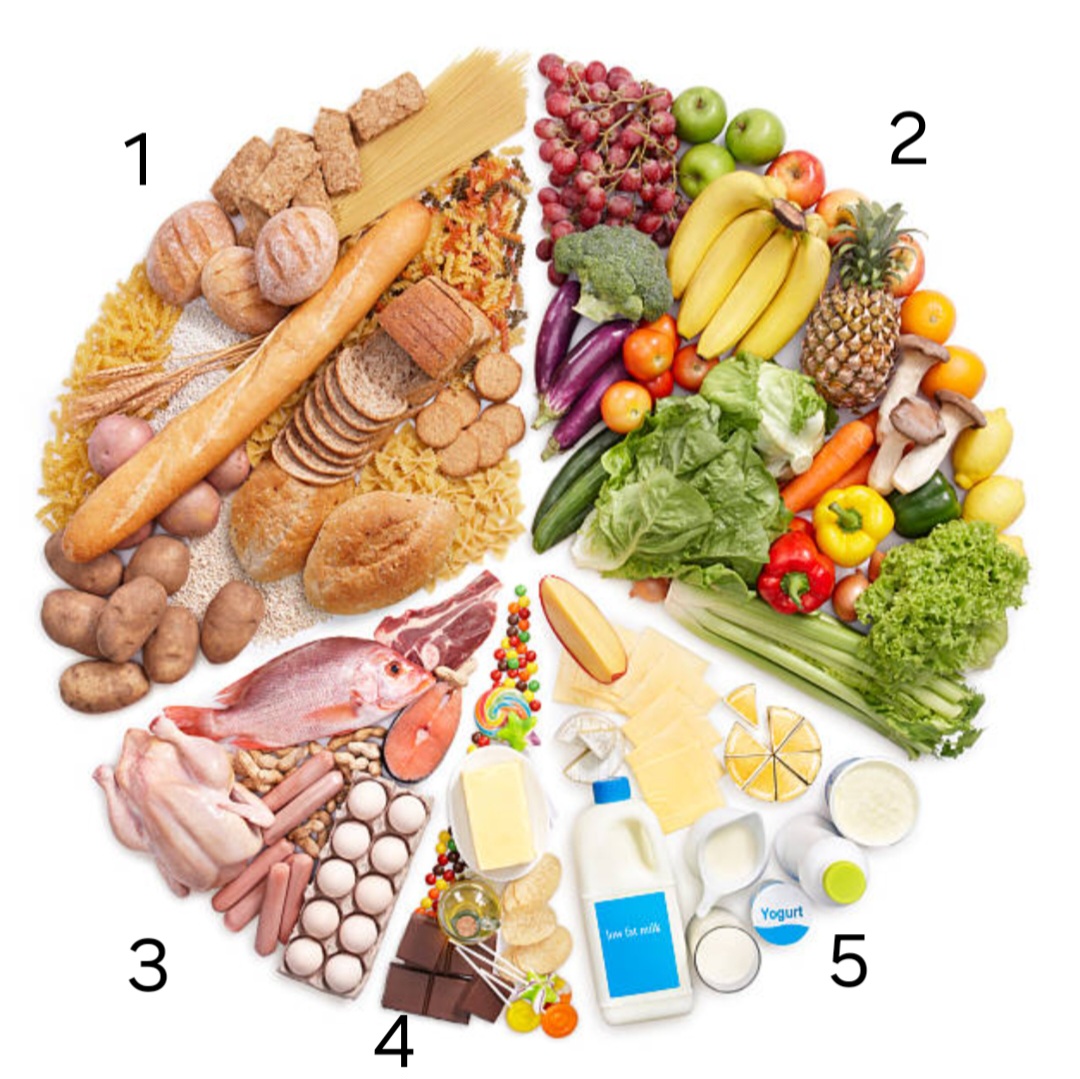

label ‘2’
fruit and vegetables
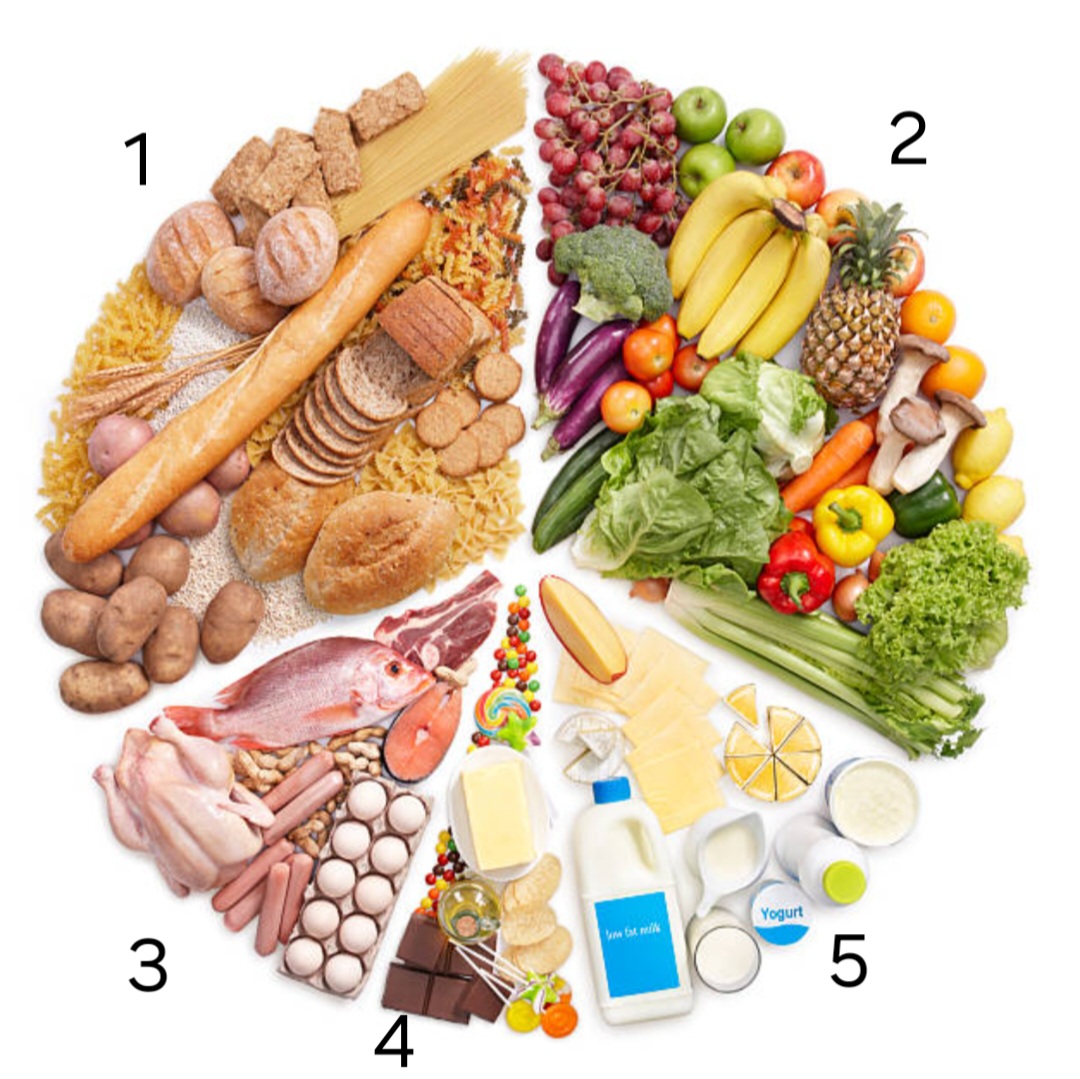

label ‘3’
protein

label ‘4’
oils and fats

label ‘5’
dairy
examples of fruit and vegetables
carrots, apples, spinach
examples of carbohydrates
bread, pasta, potatoes
examples of oils and fats
olive oil, butter, crisps
examples of dairy
milk, cheese, yogourt
examples of protein
chicken, eggs, beans
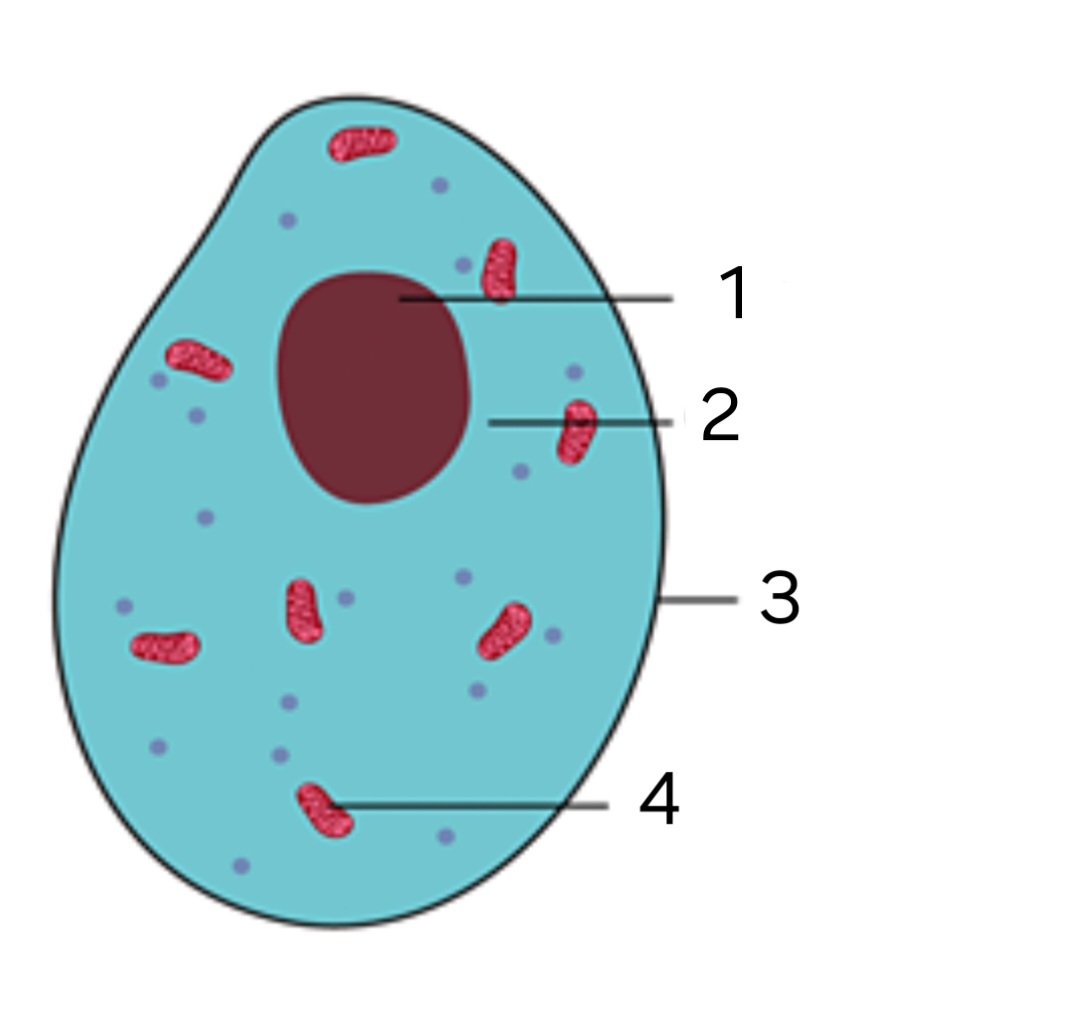
Is this an animal or a plant cell?
animal cell
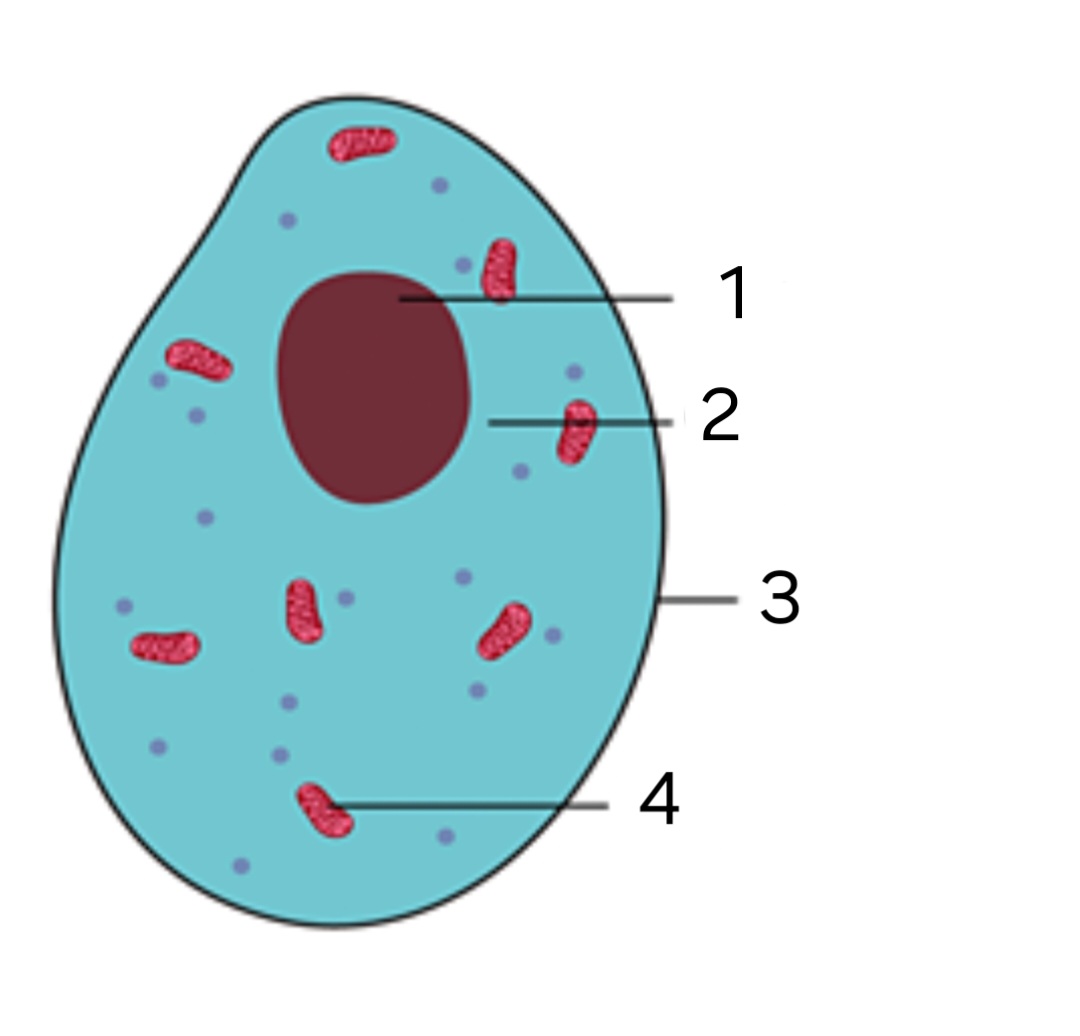
label ‘1’
Nucleus
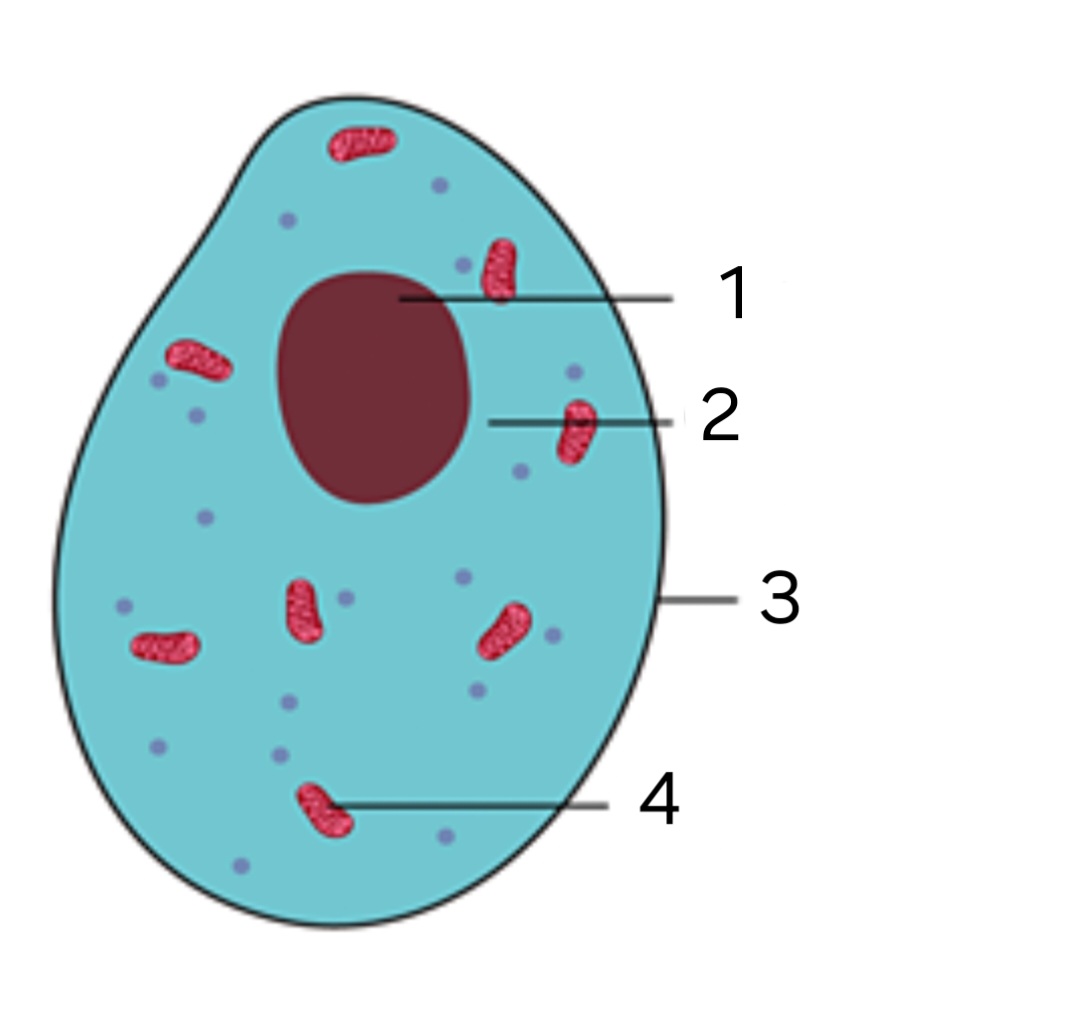
label '2’
cytoplasm
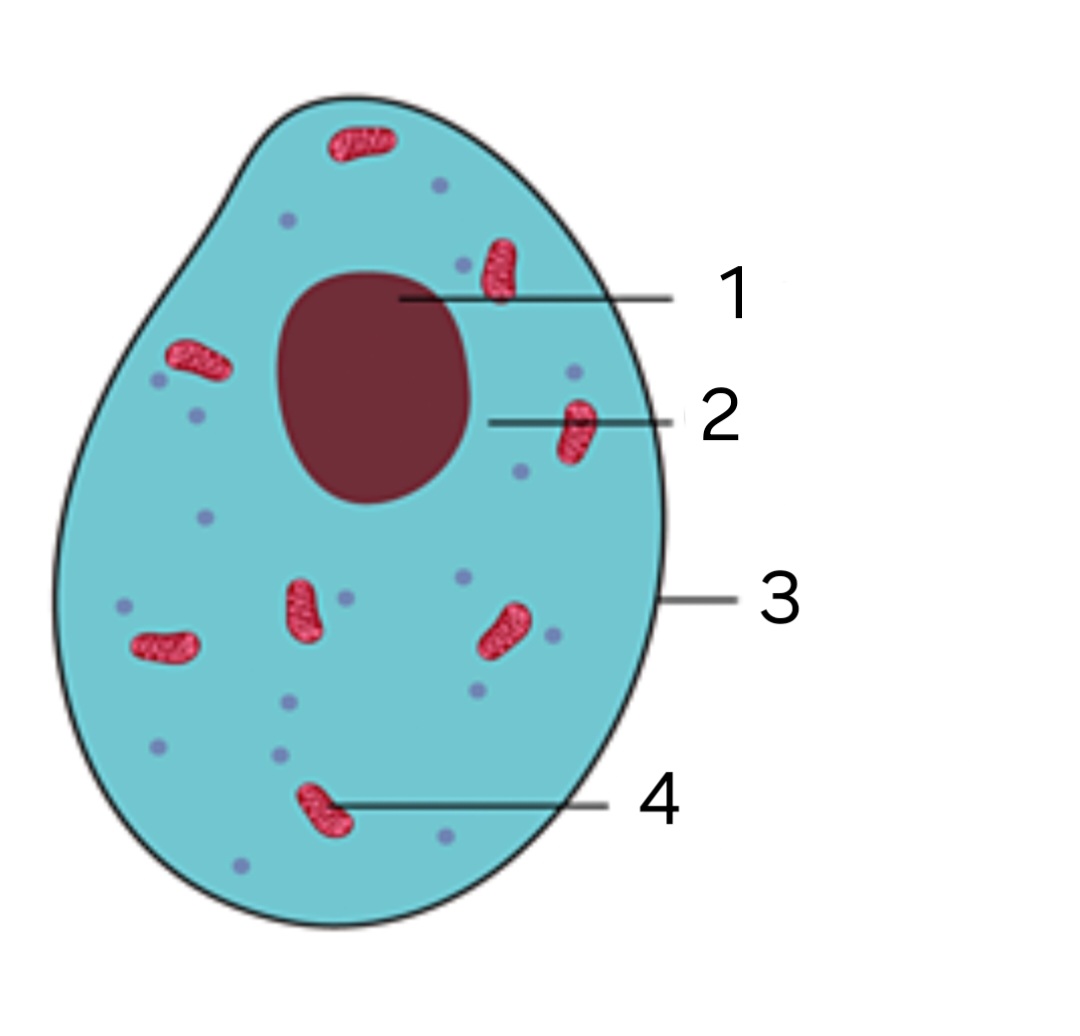
label ‘3’
Cell membrane
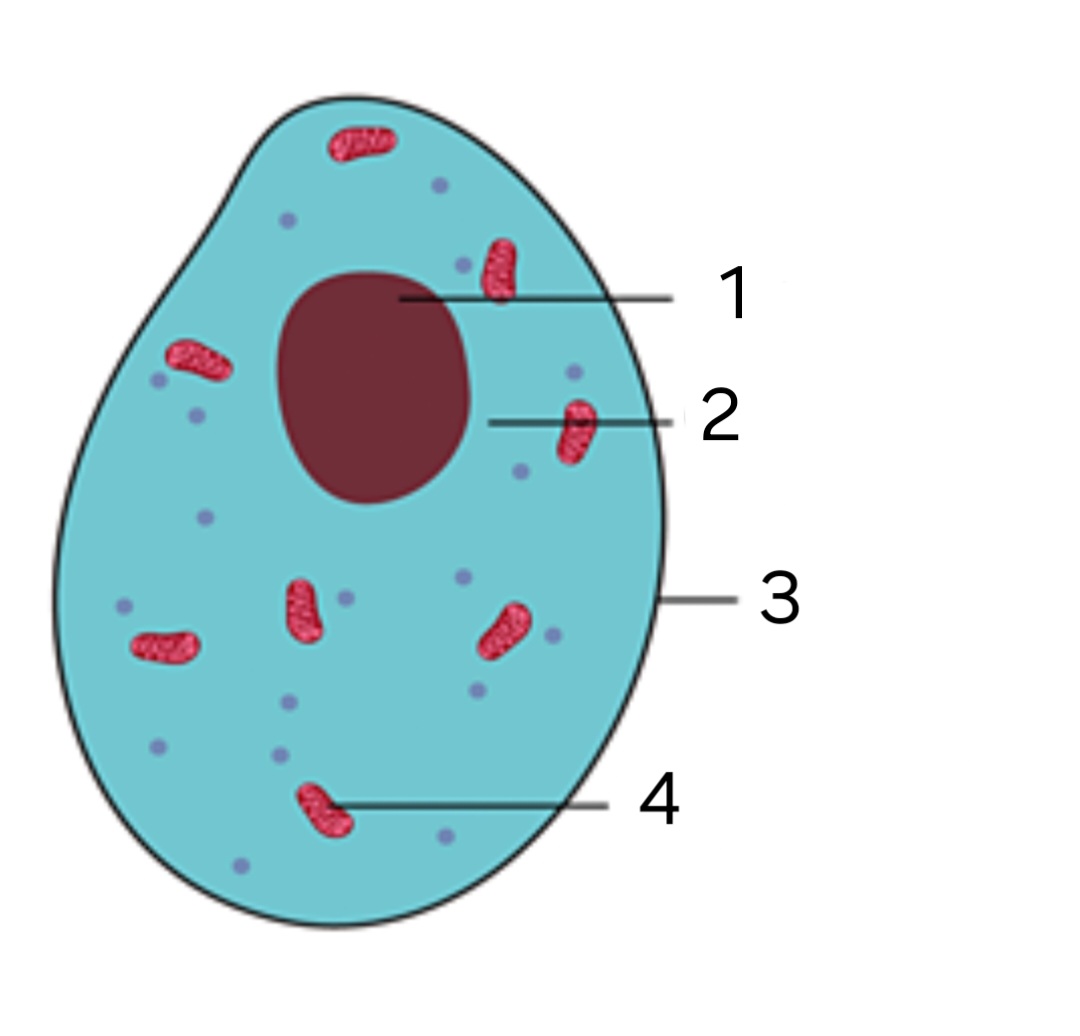
label ‘4’
mitochondria
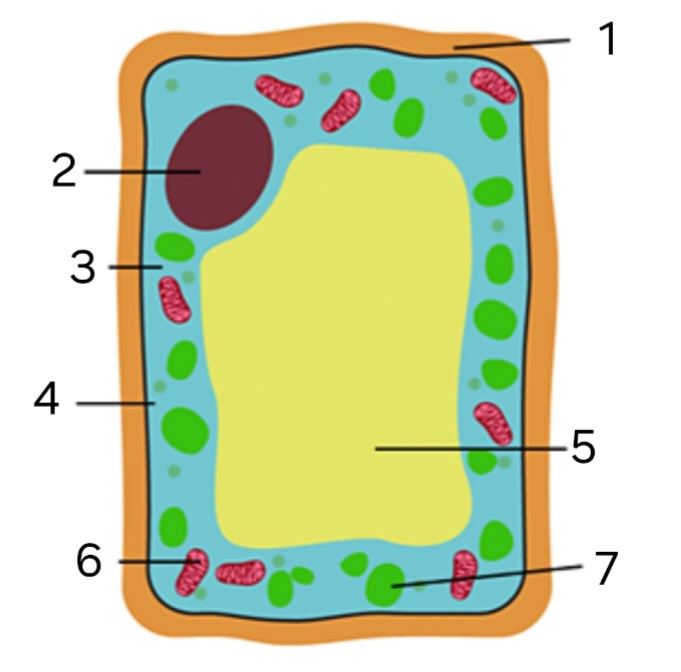
Is this an animal or plant cell?
plant cell
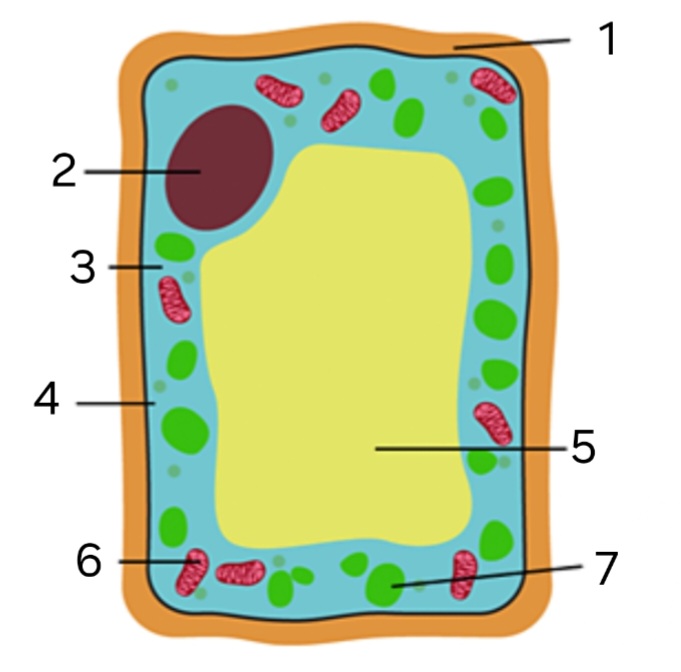
label ‘1’
cellulose cell wall
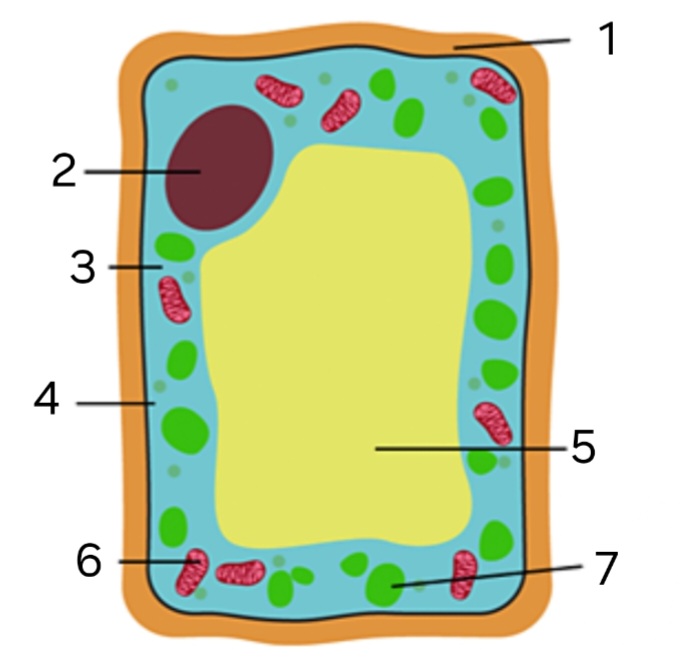
label ‘2’
nucleus
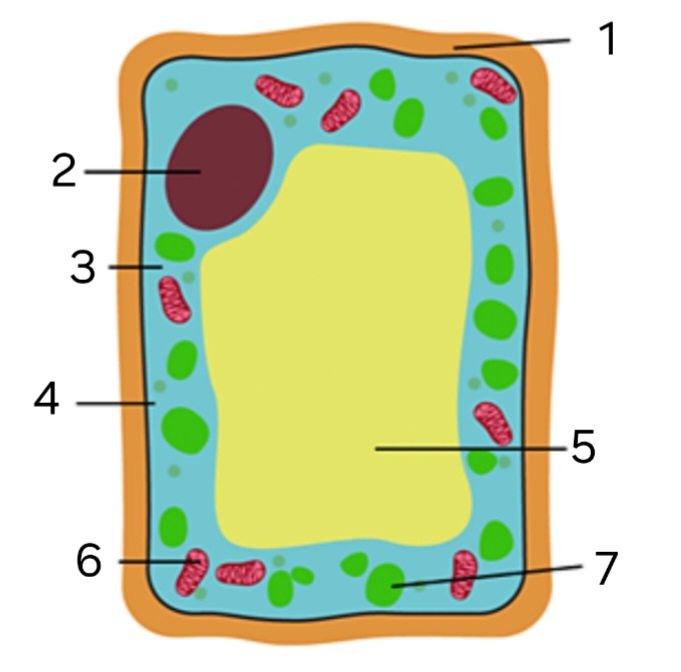
label ‘3’
cytoplasm
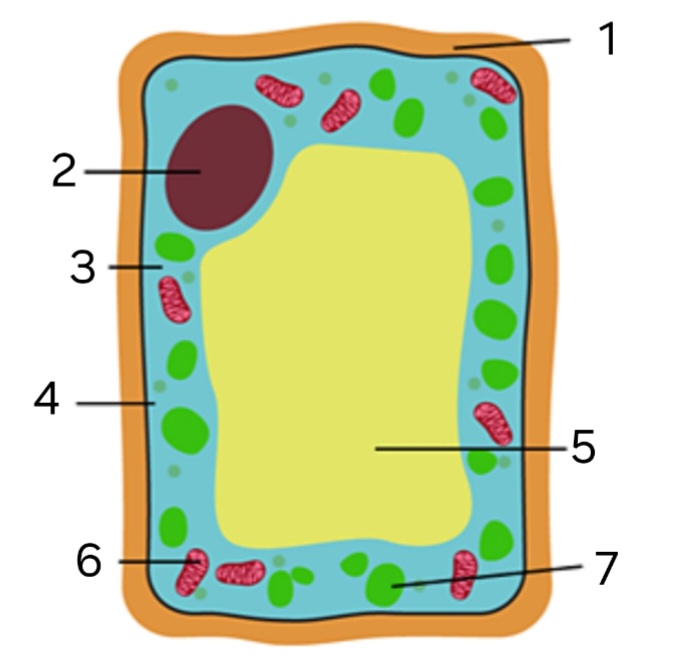
label ‘4’
cell membrane
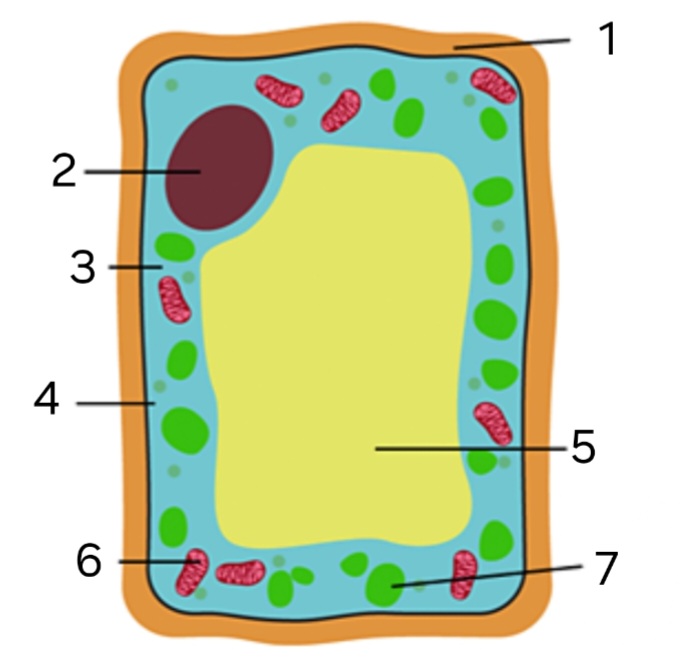
label ‘5’
large vacuole
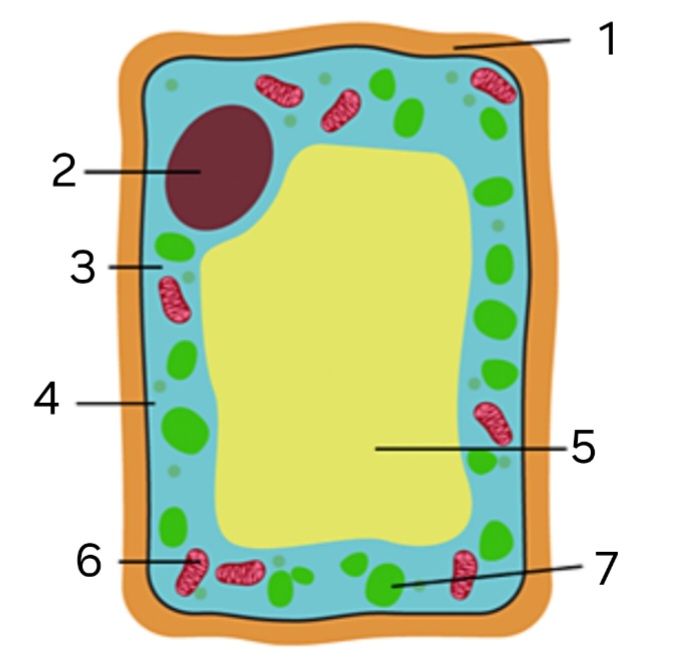
label ‘6’
mitochondria
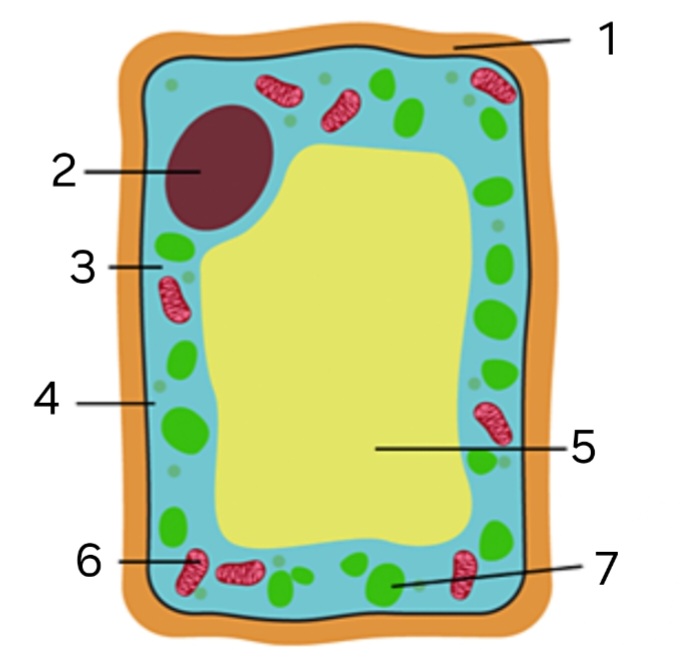
label ‘7’
chloroplast
cytoplasm function
where chemical reactions happen
nucleus function
controlls the cell
cell membrane function
controlls what enters and leaves the cell
mitochondria function
where respiration happens
cellulose cell wall function
strengthens and supports the cell
large vacuole function
storage space filled with cell sap
chloroplast function
make food for the the plant using photosynthesis
why do we need protein?
helps to repair cells
why do we need calcium?
strong bones and teeth
why do we need fibre?
help to keep our digestive system working
why do we need vitamins?
helps our body to keep working
why do we need fats?
a source of energy
calculating magnification
Total magnification = eye piece lens magnification × objective lens magnification
cells
the basic units from which all tissues and living things are made from
MRS GREN
movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, excretion, nutrition
unicellular organisms
organisms that have just one cell (bacteria, protocol, unicellular fungi, algae, archaera)
specialised
when something has features that allow it to do a particular job
respiration
being able to release energy through respiration
combustion equation
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
reactants
the starting substances - written on left of word equation
products
the new substances made - written on right of word equation
anaerobic advantages
allows for a quick, sudden burst of energy
after strenuous excersise
lactic acid enters the blood is carried to the liver and converted back to glucose
water
about 70% of the human body is water. it is essential for chemical reactions in cells and helps transport substances in the blood. Drinking water regularly replaces the water lost through urine, sweat, and breathing.
diet
the food you eat provides the raw nutrients your body needs for energy
nutrients
food substances that provide the raw materials: fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals
carbohydrates
starch and sugars
fat
liquid fats and oils. fats and oil are called lipids
fibre
made if plant cell which is not used by the body
Helps food move through the intestines and stops them getting blocked.
uses of water
a lubricant, dissolves substances to be carried around the body, fills up cells holding shape, sweat to cool you down
food labels
show the amount of different nutrients in food
starch food test
add two drops of iodine. if it turns blue-black starch is present
protein food test
add 5 drops of biuret solution if it turns purple protein is present
fat food test
rub on some white paper and hold up to the light fats will leave a greasy mark
uses of carbohydrates
the body’s main source of evergy
maintaining mass
the amount of fuel you ate using needs to be balanced by the amount you eat
kilojoules
the unit for measuring the energy in food
respiration
the process that releases energy from food
energy needs
depends on agex sexy and how active you are
vitamin a
needed for healthy skin and eyes
vitamin c
helps cells I tissues stick together properly
calcium
needed to make bones
iron
needed to make red blood cells
balanced diets
eating a range of foods in the right amount
malnutritio
having too much or too little of a nutrient in your diet
deficiency disease
caused by lacking certain nutrients for a long time
kwashiorkor
lack of protein causing a pot betty
night blindness
lack of vitamin a
scurvy
lack of vitamin c causing painful joints and bleedin
ricketts
lack of vitamin d and calcium causing bones not to form properly
anaemia
lack of iron causing tiredness and shortness or breath
starvation
lacking nearly all nutrients needed
obesity
causing by eating food containing more energy that you need
heart attack
fa clogs arteries so little blood reaches the heart