SVSU PHYS 106C Keen Chp 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
Rotation
the spin of an object around an internal axis
2
New cards
Horizon
the horizontal circle defining the lower edge of the sky
3
New cards
altitude
the angular distance from a point on the sky to the point on the horizon directly below it
4
New cards
latitude
a measure of location specifying north-south position on earth running from 0 degrees to the equator @ 90 degrees north & 90 degrees south
5
New cards
Longtitude
a measure of location specifying east-west position on earth
6
New cards
angular size
angular distance measured on a sphere in degrees, minutes, arcminutes, and arcseconds
7
New cards
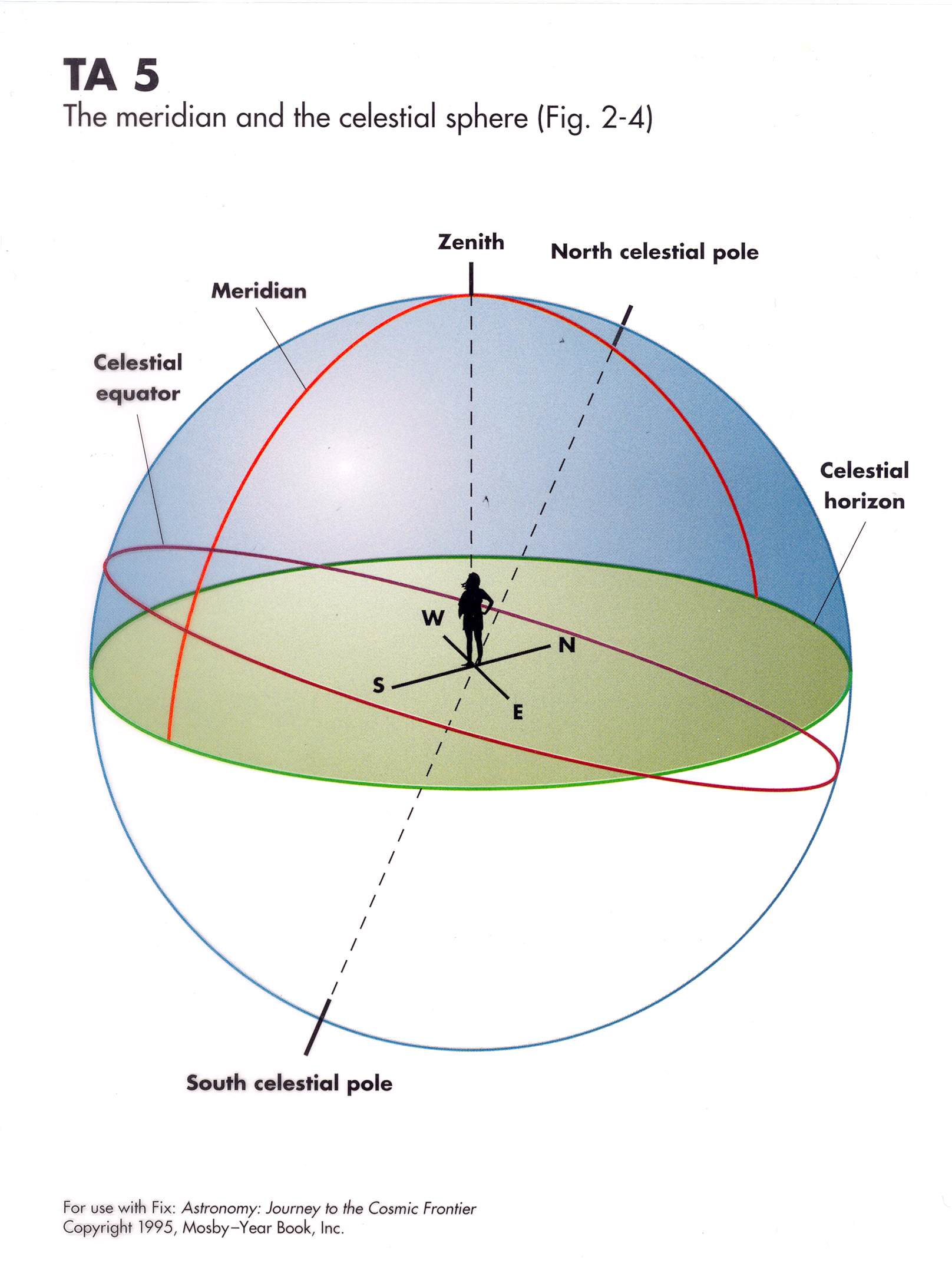
celestial sphere
an imaginary transparent sphere surrounding earth, on which positions of the stars, planets, and other celestial bodies are projected from extensions of earth's coordinate system
8
New cards
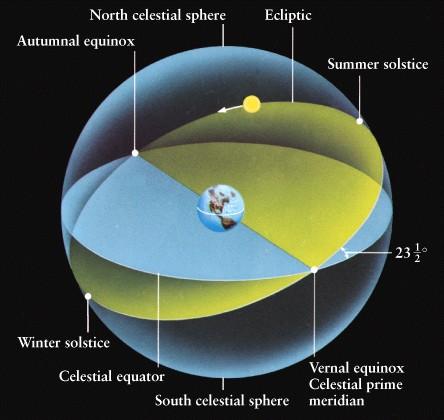
celestial equator
the extension of earth's equator onto the celestial sphere
9
New cards
Polaris
the star that is found very near earth's celestial pole
10
New cards
north celestial pole
the extension of earth's north pole on the celestial sphere
11
New cards
south celestial pole
the extension of earth's south pole on the celestial sphere
12
New cards
zenith
the point on the sky directly overhead from the observer
13
New cards
meridian
a circular arc crossing the celestial sphere and passing through the local zenith and celestial pole
14
New cards
declination
the position of an object on the celestial sphere, measured similarly to the latitude on earth
15
New cards
sidereal day
the time taken by the earth to rotate on its axis relative to the stars
16
New cards
solar day
the time between successive crossings of the same meridian on the sky by the sun
17
New cards
small angle formula
a mathematical relationship between the angular size of an object, as measured on the sky, and the object's distance and physical size
18
New cards
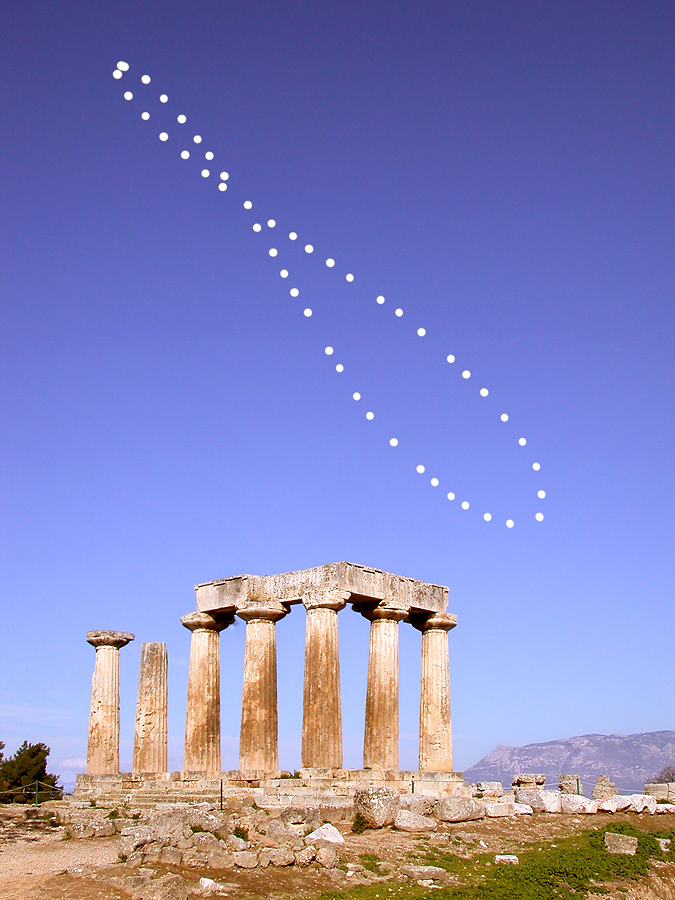
analemma
the figure-8 pattern formed by charting the daily position of the sun @ the same time of the day over the course of 1 year

19
New cards
summer solstice
the day (june 21st) with the most hours of sunlight, when the sun appears highest in the sky
20
New cards
winter solstice
the day (december 21st) with the fewest hours of daylight, when the sun appears lowest in the sky
21
New cards
equinox
A day when the hours of daylight and darkness are equal
22
New cards
orbit
the cyclical path in space that one object makes around another object
23
New cards
axial tilt or obliquity
the angle between a planet's rotation axis and a line perpendicular to the planet's orbital plane
24
New cards
precession
the rotation of a planet's spin axis, similar to that of a wobbling toy
25
New cards
constellations
a group of stars that form a pattern, and the designated region of the sky surrounding them
26
New cards
circumpolar constellation
a constellation that, from the viewer's perspective, never rises or sets.
27
New cards
ecliptic
the path that the sun appears to follow against the background as defined by earth's orbit around the sun
28
New cards
zodiac
13 constellations that lie close to the plane of the ecliptic
29
New cards
phase (of the moon)
as seen by observation of the earth, the appearance of the illuminated portion of the moon, which change cyclically so the moon orbits the earth
30
New cards
scientific model
an idea or set of ideas used to create testable explanations
31
New cards
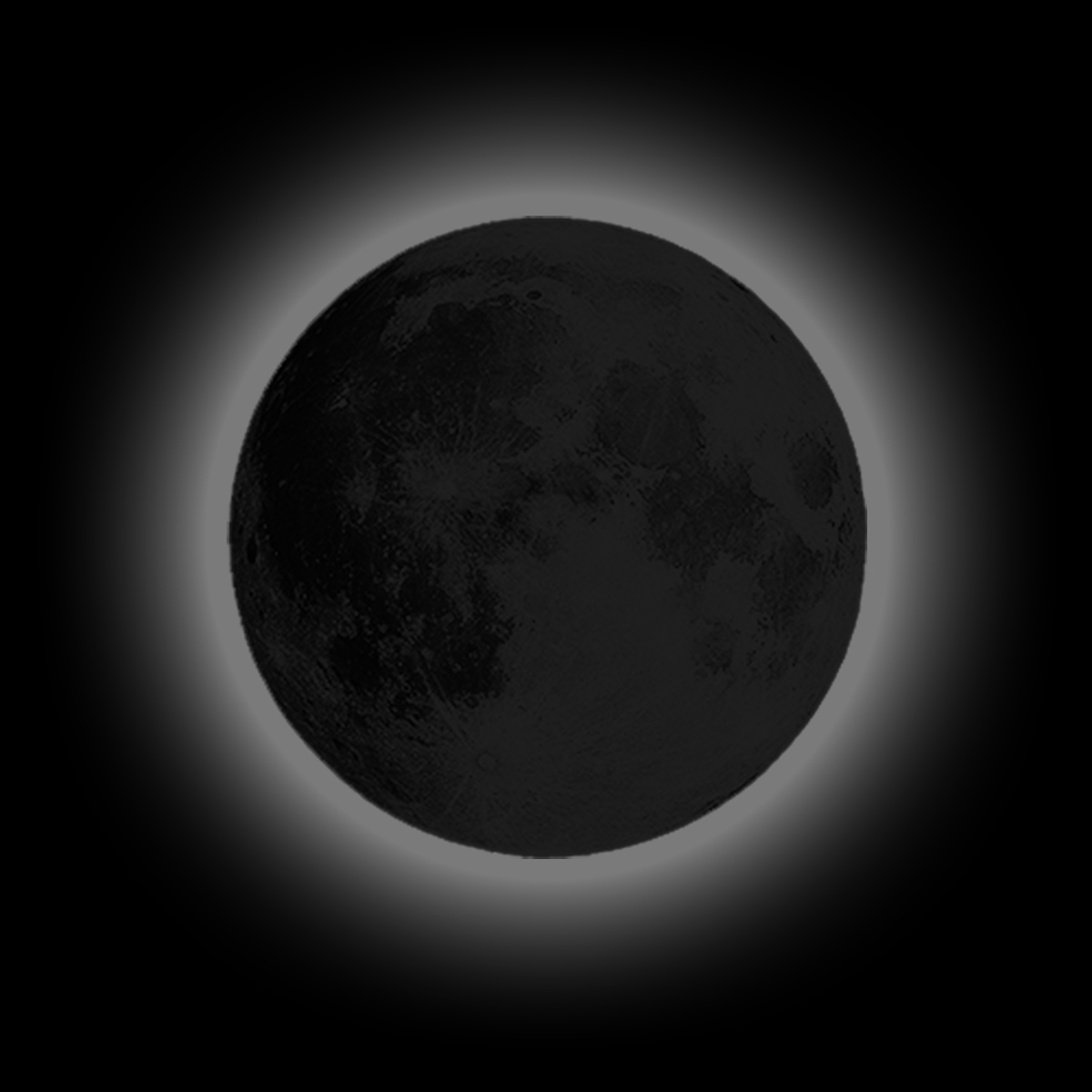
New moon
moon is between earth and the sun
lunar face illuminated points away from the earth
lunar face illuminated points away from the earth

32
New cards
waxing crescent
appears in the late afternoon sky as sun sinks in the west
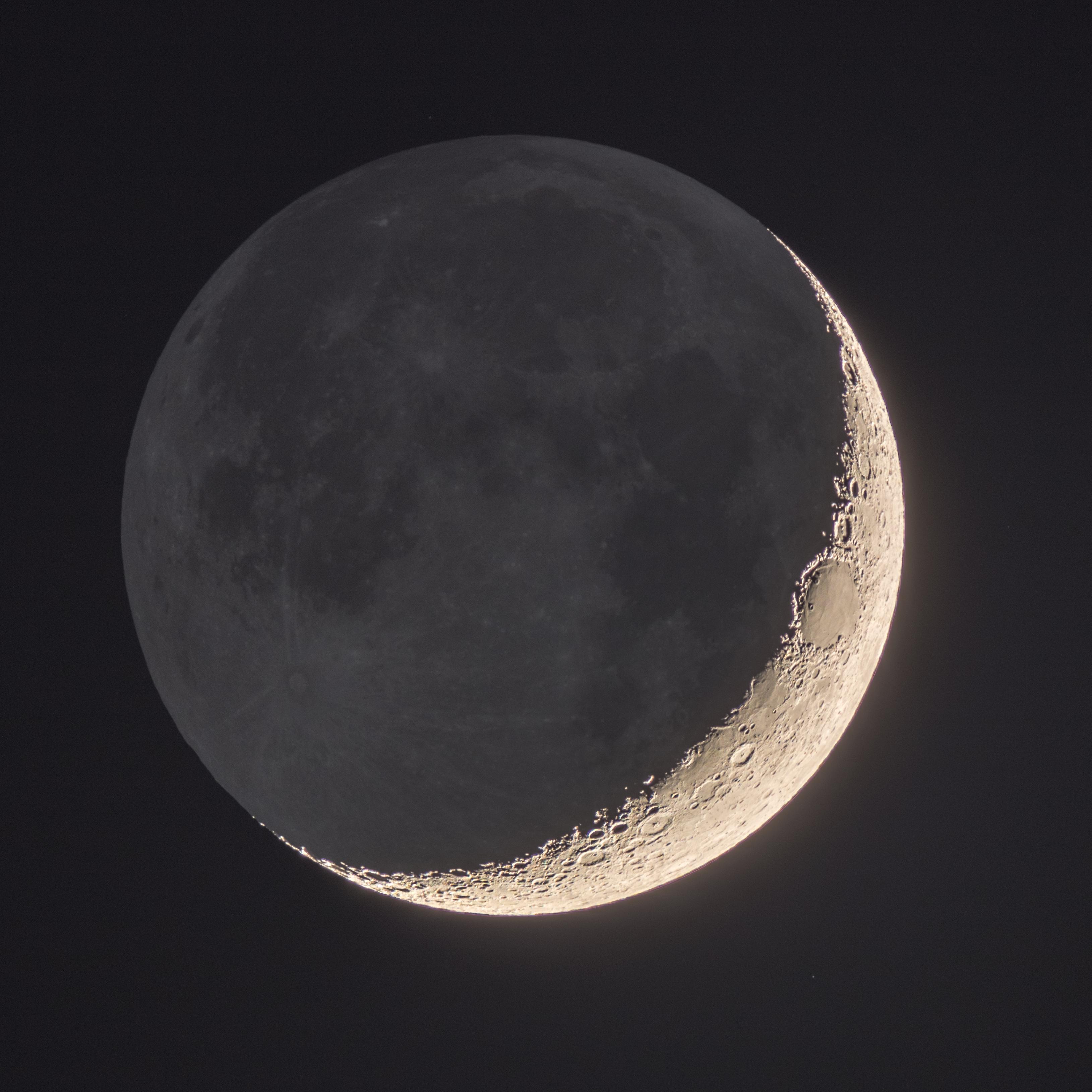

33
New cards
first quarter moon
moon at its highest altitude @ sunset
occurs seven days after new moon
occurs seven days after new moon
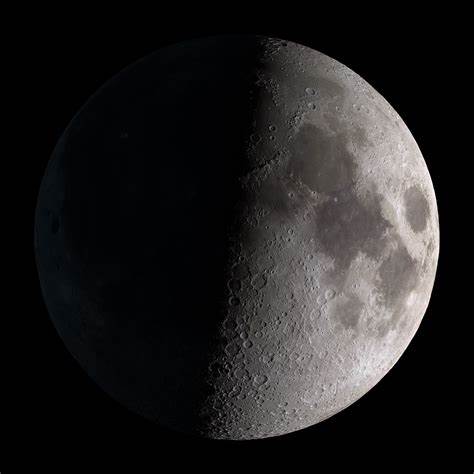

34
New cards
waxing gibbous
after first quarter
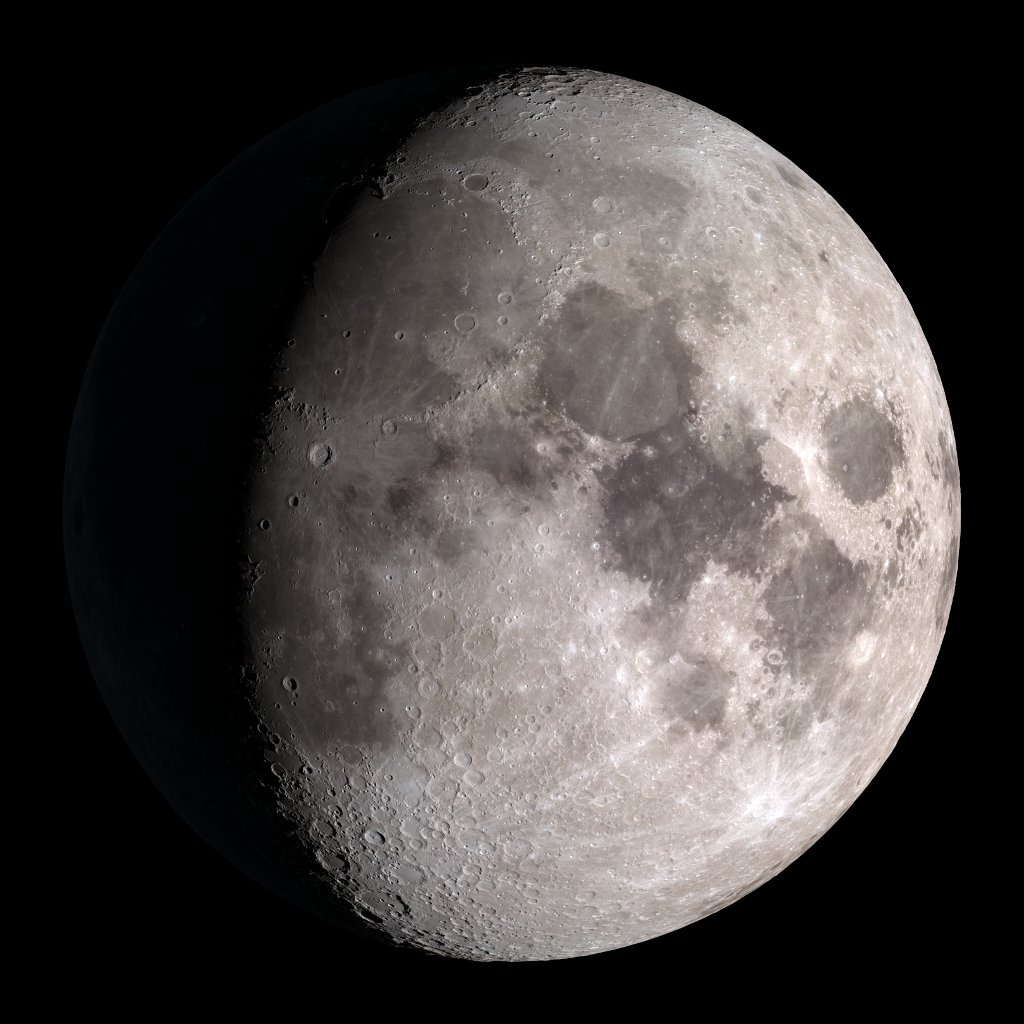

35
New cards
full moon
the time when the Moon is fully illuminated
7 days after first quarter
highest point in the night sky @ 12
7 days after first quarter
highest point in the night sky @ 12
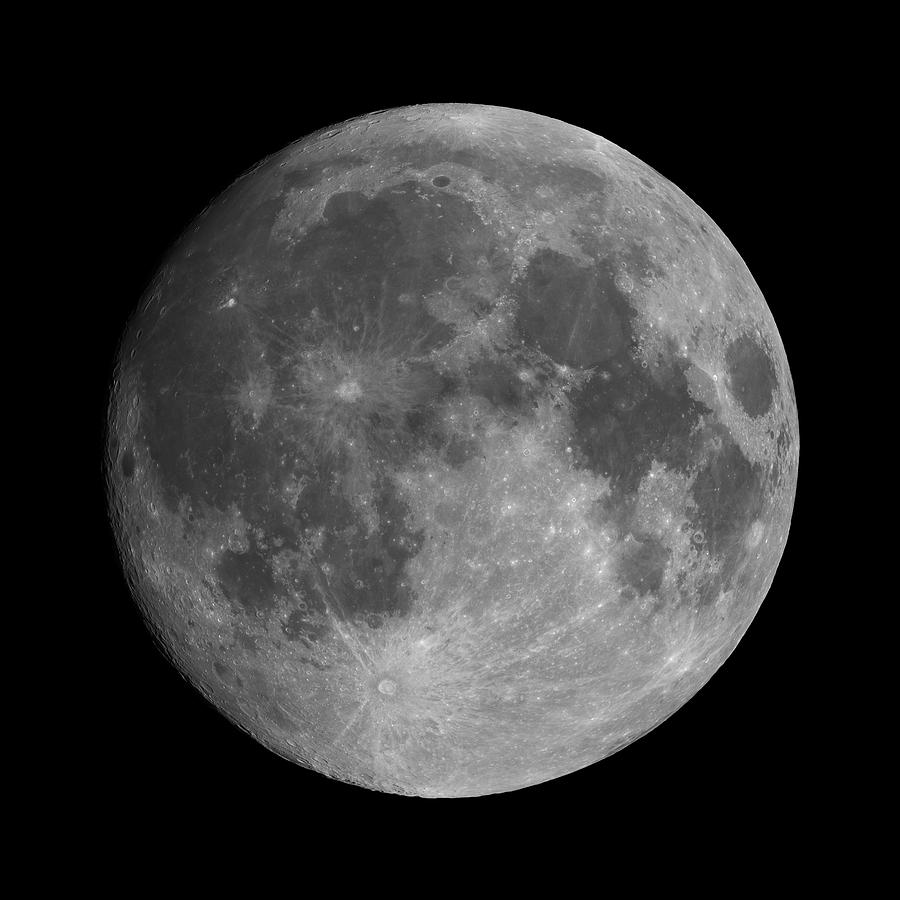

36
New cards
waning gibbous
appears on eastern horizon closer to midnight
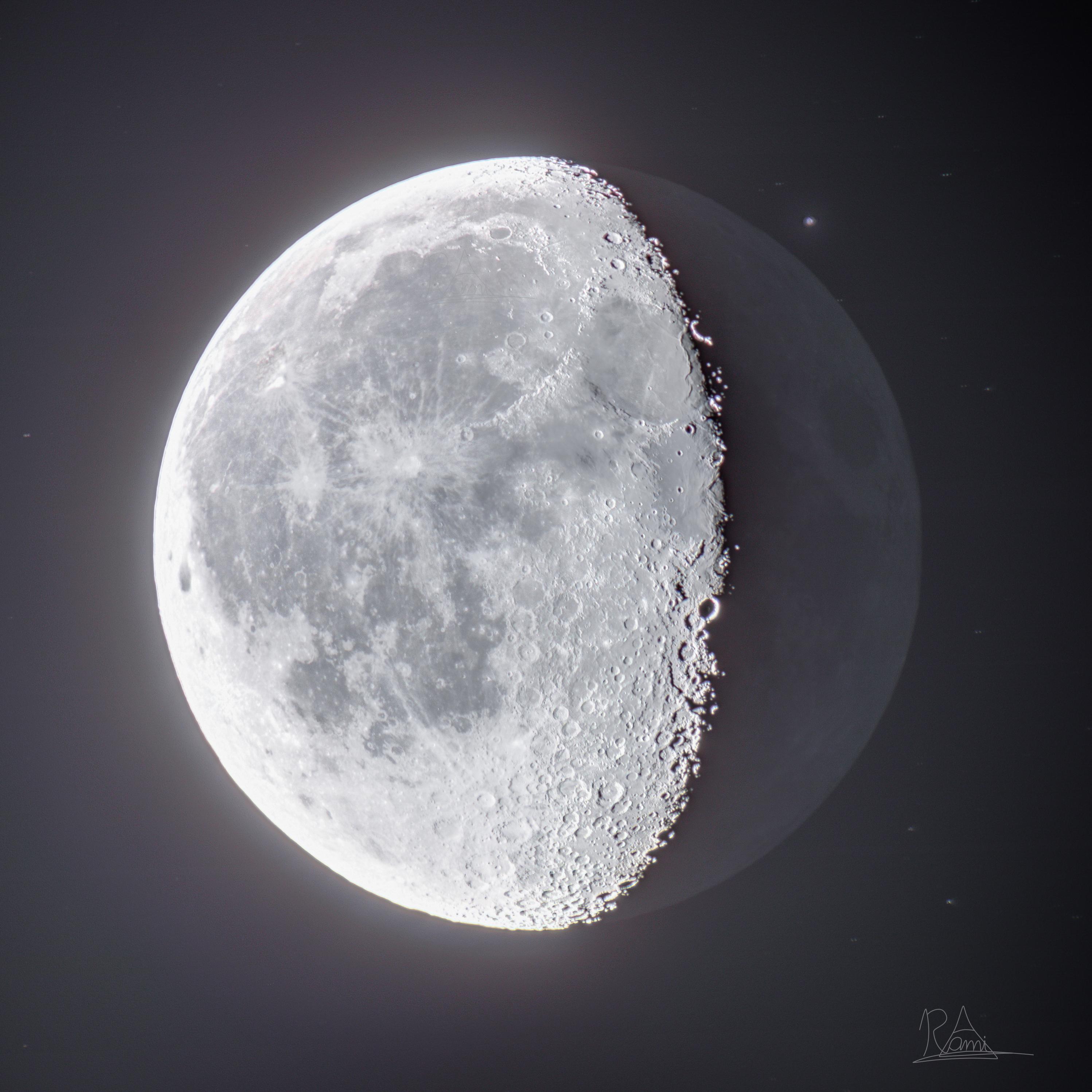

37
New cards
third quarter
7 days after full moon
rises @ midnight
rises @ midnight
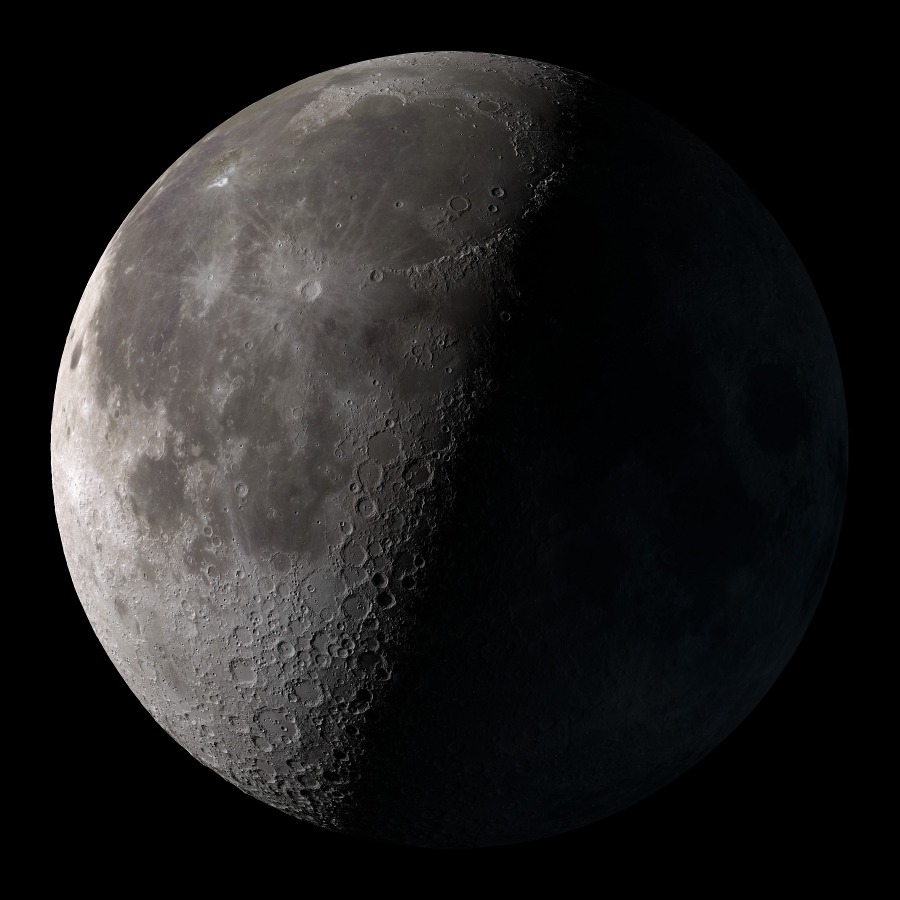

38
New cards
waning crescent
last phase before it starts back over
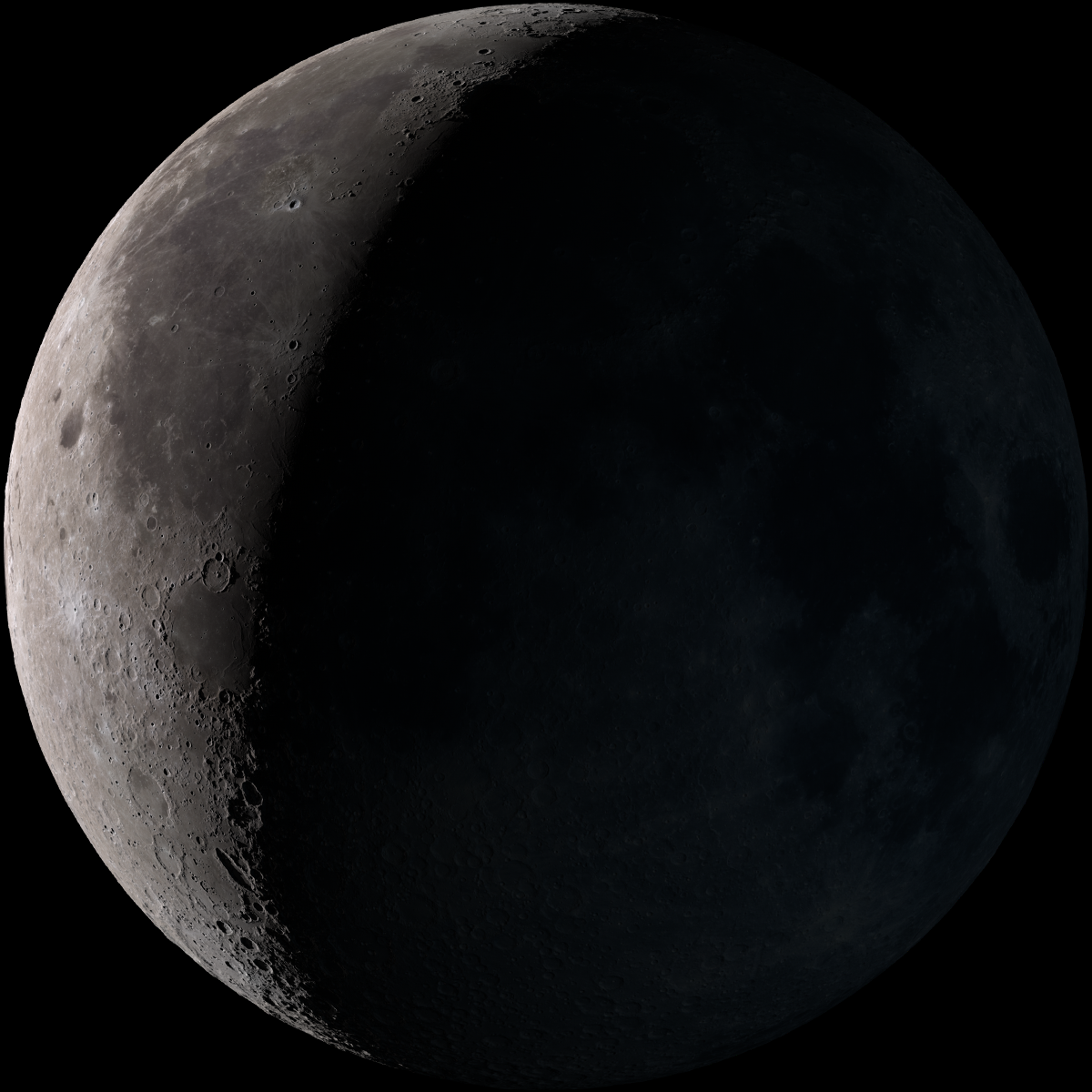

39
New cards
synodic month
the amount of time it takes the moon to cycle through its phases (29.5 days)
40
New cards
sidereal month
the amount of time it takes the moon to make a complete orbit
41
New cards
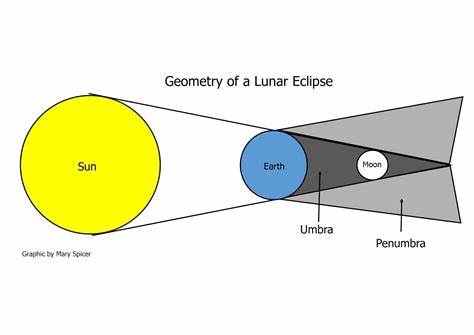
Eclipse
the passing of one celestial body through the shadow of another
42
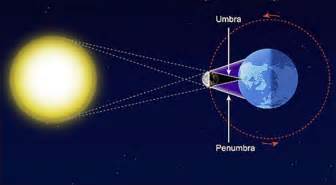
New cards
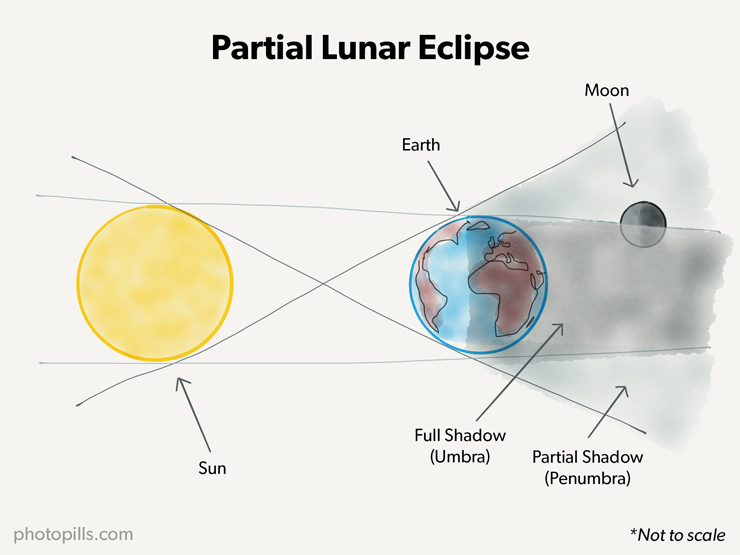
penumbra
the outer region of a shadow cast by an extended object
43
New cards
umbra
the inner region of a shadow cast by an extended object
44
New cards
Total lunar eclipse
an eclipse that occurs when the moon passes through Earth's umbral shadow
45
New cards
partial lunar eclipse
an eclipse that occurs when the moon passes partially through the earth's umbral shadow
46
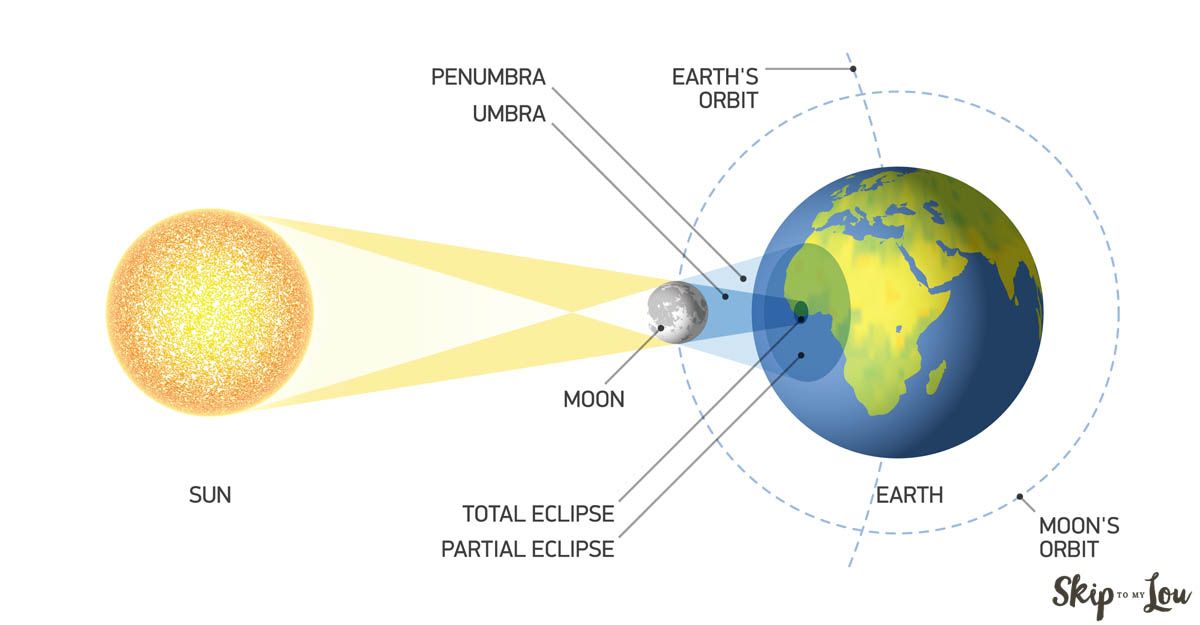
New cards
total solar eclipse
an eclipse that occurs when a region of earth's surface passes under the moon's umbral shadow and the sun disk is fully blocked
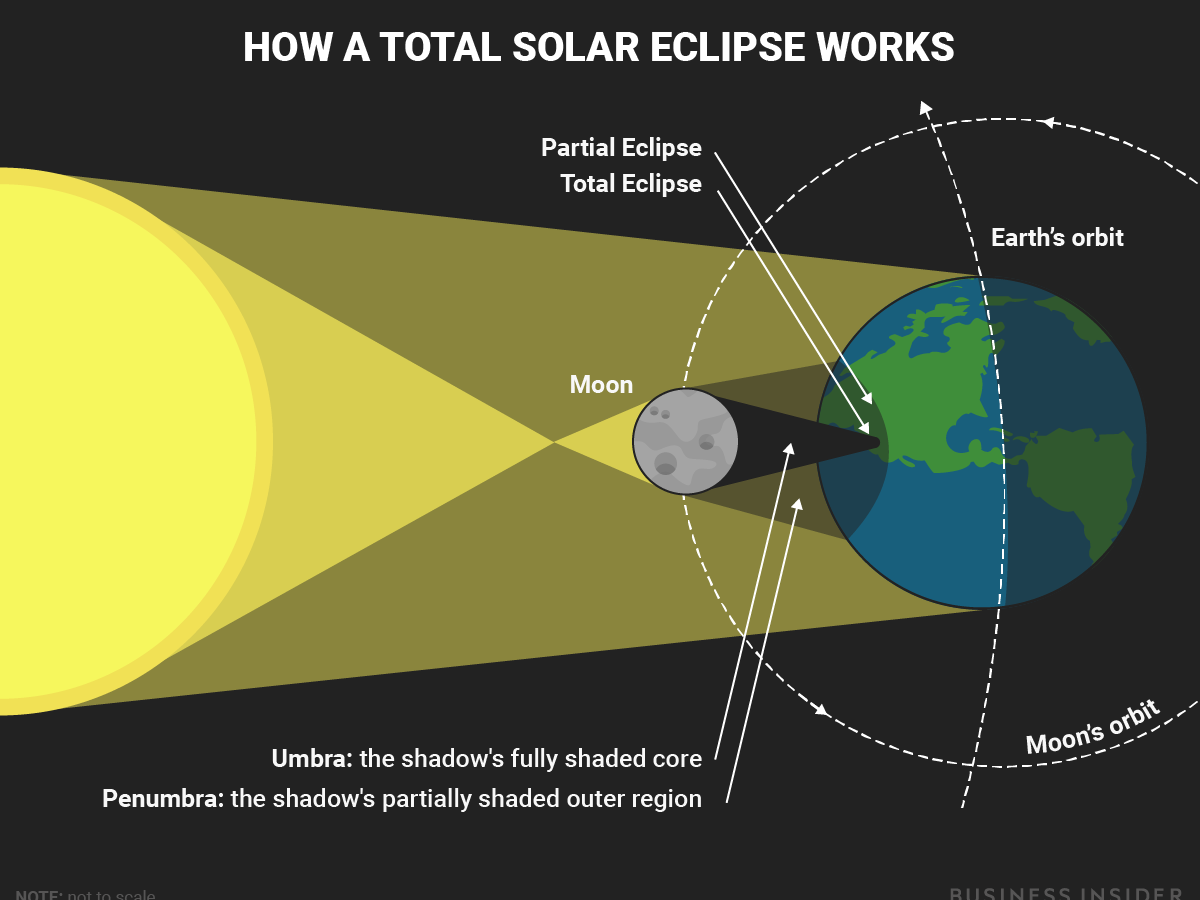
47
New cards
totality
the moment or duration of total concealment of the sun or moon during an eclipse
48
New cards
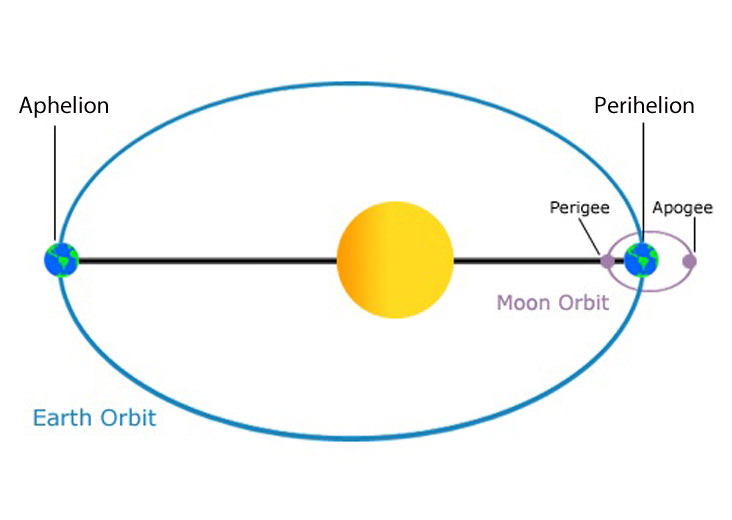
apogee
the distance of farthest approach of an object orbiting earth
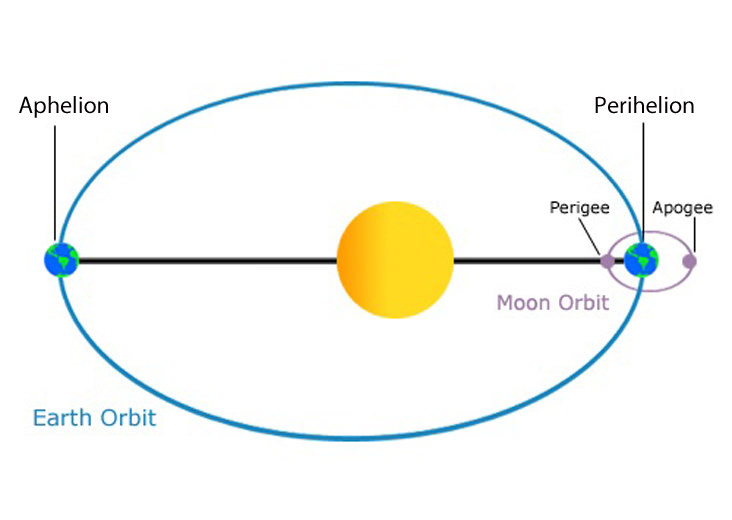
49
New cards
perigee
the distance of closest approach of an object orbiting earth
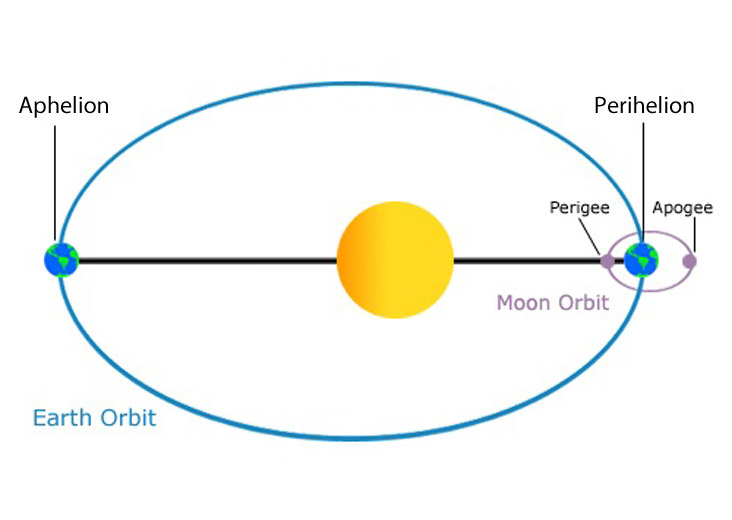
50
New cards
aphelion
the distance of farthest approach of an object orbiting the sun
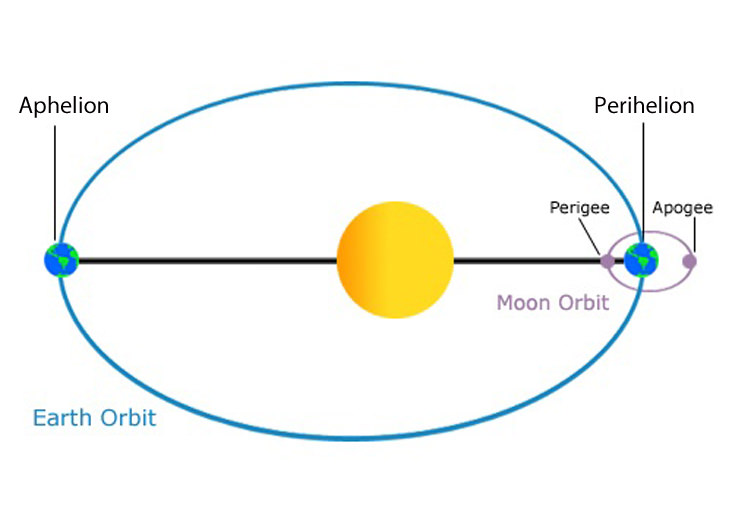
51
New cards
perihelion
the distance of closest approach of an object orbiting the sun
52
New cards
annular eclipse
a solar eclipse that occurs when the positions of the moon and sun are such that the lunar disk does not fully block out the solar disk
53
New cards
partial solar eclipse
an eclipse that occurs when a region of earth's surface passes under the moon's penumbral shadow
54
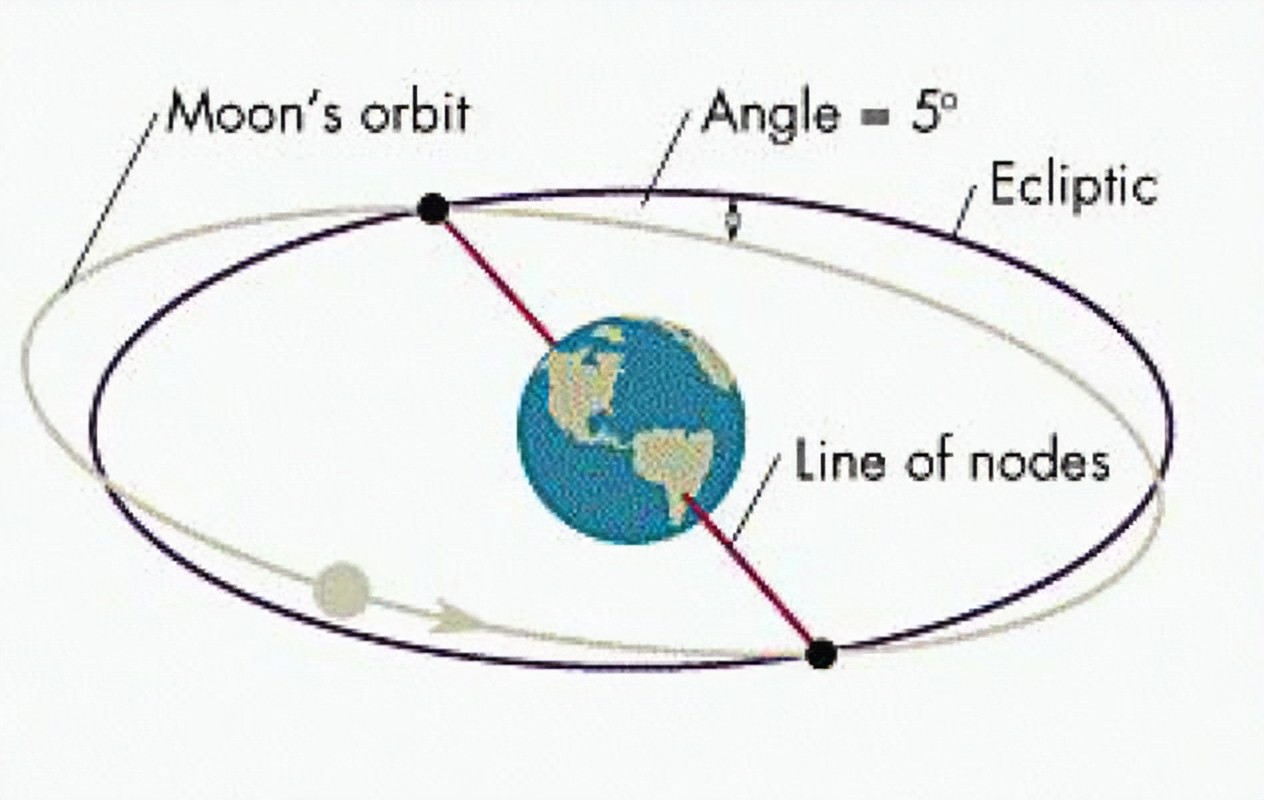
New cards
line of nods
the line defined by the intersection of the moon's orbital plane and earth's orbital plane around the sun.
55
New cards
mythology
a collection of stories used to explain phenomena whose physical basis is not understood
56
New cards
megalith
a large stone used as a monument or part of a monument
57
New cards
paleolithic period
the period extending from 2.6 million years to 10,000 years ago (earliest known use of stone tools)
58
New cards
neolithic period
the period extending from 10,000 BCE to between 4500 and 2000 BCE, when farming was introduced
59
New cards
geocentric model
a model stating that earth is the body around which all other solar system objects orbit
60
New cards
heliocentric model
a model stating that the Sun is the body around which all other solar system objects orbit
61
New cards
parallax
a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight