OCHEM 237 Chapter 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Curved-Arrow Notation, Resonance, Acids and Bases, and Chemical Equilibrium
Last updated 2:55 AM on 1/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
1
New cards
electron-deficient
________ compounds have atoms that are short of an octet of electrons
2
New cards
acids
electron-deficient compounds are ____ because they have more protons than electrons
3
New cards
acids
more protons are what gives ____ their sour taste
4
New cards
water
a proton in water ends up on the ___ molecule because it acts as a base
5
New cards
Lewis acid
the electron-deficient compound in a Lewis Acid-Base Association Reaction is the ___ ___
6
New cards
Lewis base
the compound that donates the electron pair in a Lewis Acid-Base Association Reaction is the __ __
7
New cards
Lewis base, Lewis acid
curve-arrow notation indicates a “flow” of electrons from the electron donor (______)__ to the electron acceptor __(_______) to form the new bond
8
New cards
rich, poor
“the ___ give to the ___”
9
New cards
conserved
in Lewis Acid-Base Reactions, total charge is ____
10
New cards
net charge
reactants and products must have the same ___ ____
11
New cards
spectator ion
if the net charge is not zero, a ____ __ is assumed but may not be shown
12
New cards
do
the “rich” DO or DO NOT have electrons
13
New cards
do not
the “poor” DO or DO NOT have electrons
14
New cards
association
Lewis Acid-Base ______ reactions combine two compounds
15
New cards
dissociation
Lewis Acid-Base _____ reactions separate one compound into two
16
New cards
deficient
In Electron-Pair Displacement Reactions, not all acceptors are electron-_______
17
New cards
depart, receiving
In Electron-Pair Displacement Reactions, an electron pair must ___ from the atom ____ the electron pair
18
New cards
octet rule
In Electron-Pair Displacement Reactions, the ___ ___ is preserved
19
New cards
two
Electron-Pair Displacement Reactions require ___ curved arrow(s)
20
New cards
nucleophile
a species that donates an electron pair to form a new bond
21
New cards
electrophile
a species that accepts an electron pair from the donator
22
New cards
leaving group
the group that accepts electrons from the breaking bond
23
New cards
nucleophiles
(Nucleophiles OR Electrophiles) are electron-rich and Lewis Bases
24
New cards
electrophiles
(Nucleophiles OR Electrophiles) are electron-poor and Lewis Acids
25
New cards
nucleophilic
the specific atom in a compound that donates the electron pair is the _____ center
26
New cards
electrophilic
the specific atom in a compound that receives the electron pair is the _____ center
27
New cards
condensation
any reaction that releases water
28
New cards
reverse, irreversible
each reaction has a finite, nonzero ___ reaction (but some are so small, like 0.00001, that we say the reaction is essentially ____)
29
New cards
nucleophilic
the _____ electron pair can originate from a bond in addition to an unshared electron pair
30
New cards
electrons, nuclei
resonance structures always differ only by movement of ___; ___ do not move
31
New cards
derive
curved-arrow notation is used to help ____ resonance structures
32
New cards
octet configuration
in determining the importance of resonance contributors, an ___ ____ is always favored over electronegativity status
33
New cards
acids
protons can ONLY be ____ because they don’t have any electrons to give
34
New cards
higher, more
resonance contributors have (higher/lower) energy than the hybrid structure, thus the hybrid structure is (more/less) stable
35
New cards
less
higher energy = ____ stable
36
New cards
more
lower energy = ____ stable
37
New cards
octet rule, electronegativity status, neutrality favored over separate charges
When evaluation relative energies of molecules in order to determine resonance importance, list the three rules in order of most to least important
38
New cards
Bronsted acid
a species that donates a proton (H+)
39
New cards
Bronsted base
a species that accepts a proton
40
New cards
proton
a Bronsted acid-base reaction is an electron-pair displacement reaction where a ______ is the electrophilic center
41
New cards
conjugate base
when a Bronsted acid loses a proton, its ____ ____ is formed
42
New cards
conjugate acid
when a Bronsted base gains a proton, its ____ ____ is formed
43
New cards
amphoteric
compounds that can act as either an acid or a base
44
New cards
water
an example of an amphoteric compound
45
New cards
equilibrium
a state where the entire reaction system is happy
46
New cards
products
when Keq >1, the ____ are favored at equilibrium
47
New cards
reactants
when Keq
48
New cards
big
a sample containing A converts into a (big or small) amount of B at equilibrium when Keq>1
49
New cards
small
a sample containing A converts into a (big or small) amount of B at equilibrium when Keq
50
New cards
neither
when Keq=1, _____ are favored at equilibrium
51
New cards
difference
Keq is related to the standard free energy ____ between products and reactants
52
New cards
more, lower
the compound that is (more or less) stable (higher or lower standard free energy) is favored at equilibrium
53
New cards
less
the more free energy a molecule has, the (more or less) stable it is and vice versa
54
New cards
negative
if B (product) is favored at equilibrium, then ∆G is _____
55
New cards
positive
if A (reactant) is favored at equilibrium, then ∆G is _____
56
New cards
spontaneous, does
when the ∆G is negative, the reaction is ______ (it does/does not happen)
57
New cards
not spontaneous, does not
when the ∆G is positive, the reaction is _______ (it does/does not happen)
58
New cards
if Keq >1, then ∆G__
59
New cards
>0
if Keq
60
New cards
=0
if Keq=1, then ∆G__
61
New cards
proton
the strength of a Bronsted acid is determined by how well it transfers a _____ to a Bronsted base
62
New cards
water
the standard base traditionally used in Bronsted reactions is _____
63
New cards
any Bronsted acid
what is this the equilibrium constant for?
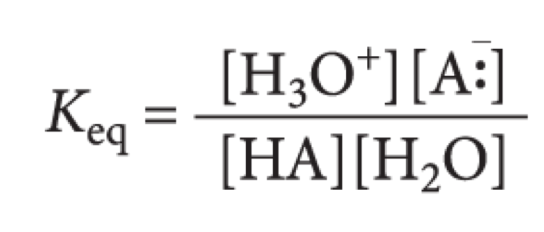
64
New cards
dissociation
each acid has its own unique _____ constant, typically expressed as pKa
65
New cards
dissociation constant
which constant is this?
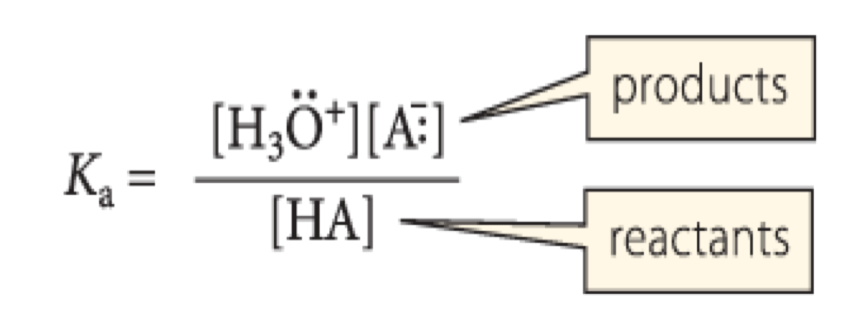
66
New cards
bigger, smaller
weak acids have a (smaller or bigger) pKa and a (smaller or bigger) Ka
67
New cards
smaller, bigger
strong acids have a (smaller or bigger) pKa and a (smaller or bigger) Ka
68
New cards
10⁻¹⁴, 14
The Ka of water = ___ and its pKa =
69
New cards
high
bases have a (high or low) pH
70
New cards
low
acids have a (high or low) pH
71
New cards
less, more
reactions spontaneously go from (more or less) stable reactants to (more or less) stable products
72
New cards
stronger
more reactive = (weaker/stronger) acid or base = less stable
73
New cards
strongest, strongest
one side of the reaction will have the ___ acid and the ___ base
74
New cards
stable
are high pKas more reactive or stable?
75
New cards
reactive
are low pKas more reactive or stable?
76
New cards
50% dissociated
when pH=pKa, molecule is __ ______
77
New cards
Henderson-Hasselbach, dissociation states of conjugate acid-base pairs
which equation is this? and what does it find?
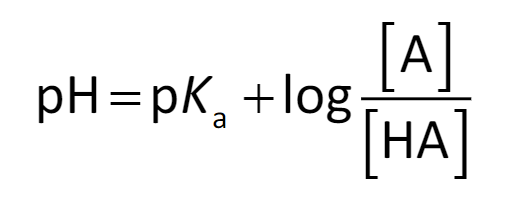
78
New cards
acidic
when pH < pKa, the compound is in ____ form
79
New cards
basic
when pH > pKa, the compound is in the ____ form
80
New cards
ions
___ tend to be water soluble
81
New cards
neutral organics
___ ___ tend to not be water soluble
82
New cards
less
in order for a compound to be in its acidic form, the pH needs to be (more or less) than the pKa by at least 1 unit
83
New cards
more
in order for a compound to be in its basic form, the pH needs to be (more or less) than the pKa by at least 1 unit
84
New cards
charge effect, element effect, hybridization effect, resonance effect, polar/induction effect
list the 5 major factors in acidic strength from most to least important
85
New cards
more, more
for the charge effect, a positively charged ion is (more/less) acidic than a neutrally charged ion which is (more/>less) acidic than a negatively charged ion
86
New cards
increases
for the element effect, acidity (increases/decreases) the farther right you go on the periodic table
87
New cards
electronegativity
the element effect deals with an element’s ________
88
New cards
increase
for the element effect, acidity tends to (increase/decrease) the farther down you go on the periodic table (not always 100% right)
89
New cards
increases
for the hybridization effect, acidity (increases/decreases) with increasing s character
90
New cards
alkanes, alkenes, alkynes
for the hybridization effect, order alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes in order of least to most acidic
91
New cards
triple
which compound would be most acidic: one made up of single bonds or triple bonds?
92
New cards
always
for the resonance effect, resonance is ____ stabilizing
93
New cards
electronegativity
for the polar/induction effect, acidity increases when you have a neighboring atom with high _______
94
New cards
it happens at a distance
the polar/induction effect is weaker than the element effect because ______
95
New cards
adds,
for the polar/induction effect, the closer an electron-withdrawing group is to the charged atom, the more it ____ stability, increasing the acid’s strength
96
New cards
removes
for the polar/induction effect, the closer an electropositive group is to the charged atom, the more it ____ stability, decreasing the acid’s strength
97
New cards
positively
the term electron-deficient does not mean “_____ charged”
98
New cards
charge delocalization
resonance: when the same charge is delocalized onto multiple atoms
99
New cards
charge separation
resonance: opposite charges are created where there was none to start with
100
New cards
small, large
___ changes in ∆G lead to ___ changes in Keq