BY 124- Ch 35 Gibbons
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Underground (typically)
Fibrous roots
Tap roots
Secondary roots/lateral roots
Root hairs
rely on sugars from shoot
Root System Characteristics
Above ground (typically)
Leaves
Stems
Lateral and apical buds
Flowers
rely on water and minerals from roots
Shoot system characteristics
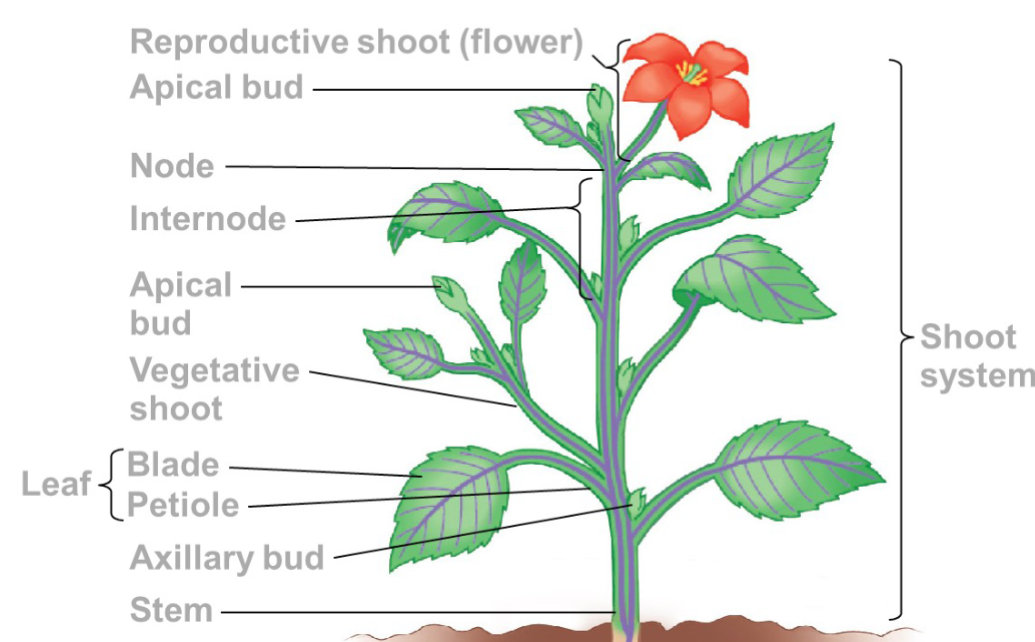
Shoot system parts
Root system parts
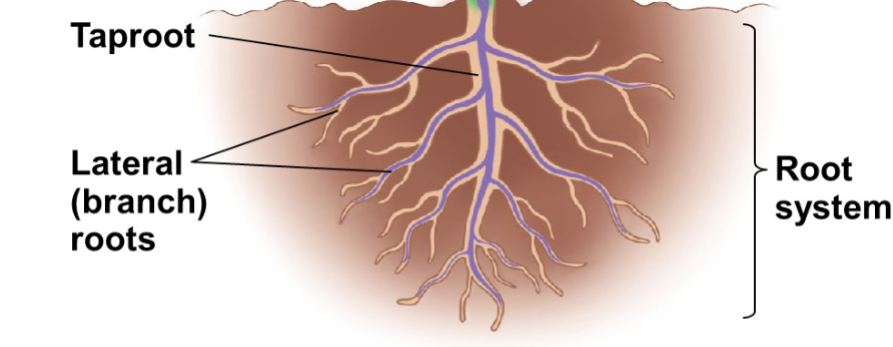
Anchor
Taproot
Fibrous root
Absorb
Occurs at lateral roots
Root hairs
Store
Some can store more in taproot
Functions of the root system
an alternating system of nodes, the points at which leaves are attached
internodes, the stem segments between nodes
Function to grow tall, maximize light exposure
A stem is a plant organ that consists of…

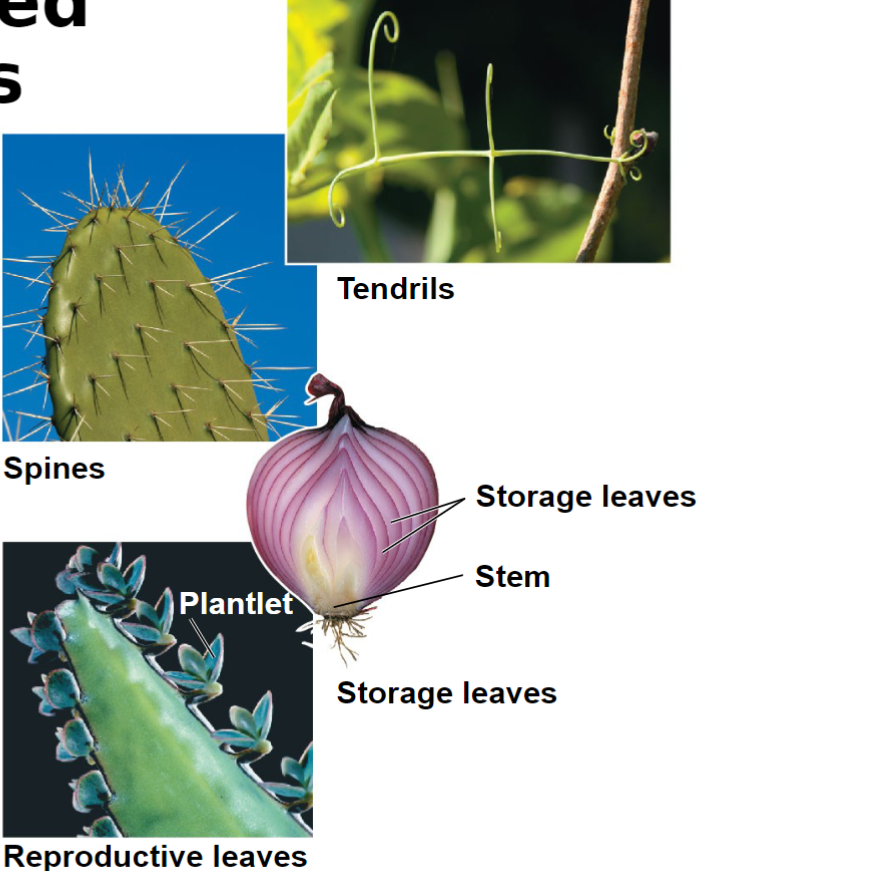
Rhizome: horizontal shoot below the surface
Stolon: horizontal shoot above the surface, asexual reproduction
Tuber: storage in the end of rhizomes or stolons
Examples of modified stems
The leaf is the main photosynthetic organ of most
vascular plants
Leaves intercept light, exchange gases, dissipate
heat, and defend the plant from herbivores and
pathogens
Leaves generally consist of a flattened blade and a
stalk called the petiole, which joins the leaf to a
node of the stem
Role of leaves

Simple Leaves: A single, undivided blade (though it may be lobed).
Compound Leaves: A leaf that is divided into multiple segments, called leaflet
Simple vs compound leaf
Modified leafs examples
What are the three plant organs?
A. Roots, shoots, and stems
B. Roots, stems, and leaves
C. Flowers, shoots, and roots
D. Stolons, tubers, and pneumatophores
B. Roots, stems, and leaves
What are the 3 types of plant tissue?
Dermal
Vascular
Ground
1. Epidermis or epidermal/dermal cells (do not
have chloroplasts)
2. Specialized dermal cells
Guard cells: gas exchange, have chloroplasts
Trichomes: reduce water loss, reflect light, defense
Root hair: helps with water absorption
3. Non cellular structures:
Cuticle: waxy coating prevents water loss, covering dermal cells
Stomata: openings for gas exchange, surrounded by guard cells
Dermal Tissue is comprised of …
Replaces epidermis on old growth of woody plants
Periderm
facilitates the transport of materials and provides mechanical support
Xylem conducts water and dissolved minerals upward from roots into the shoots
Phloem transports sugars from where they are made (primarily
leaves) to storage structures or sites of growth
Vascular tissue
Tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular
Ground tissue internal to the vascular tissue is pith
Ground tissue external to the vascular tissue is cortex
Ground tissue includes cells specialized for storage, photosynthesis, support, and transport
Ground Tissue
Plant Cell diagram
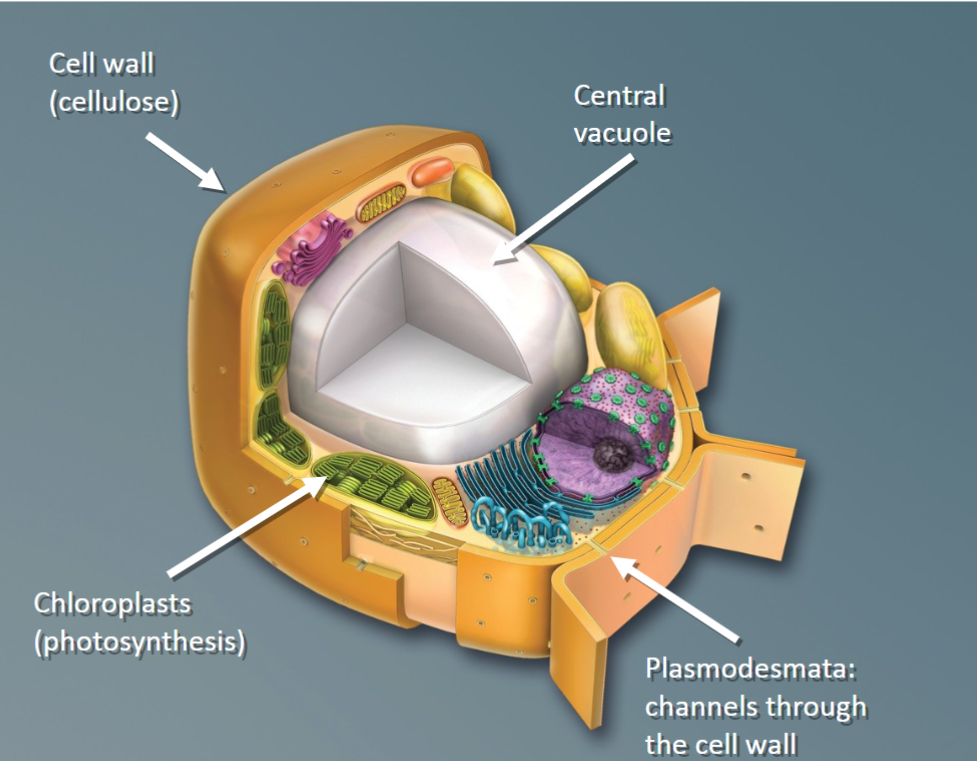
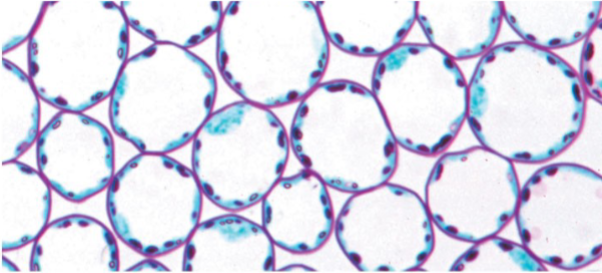
Mature parenchyma cells
Have thin and flexible primary walls
Have a large central vacuole
Perform the most metabolic functions
(Photosynthesis, cellular respiration, storage, etc)
Retain the ability to divide and differentiate
Parenchyma Cells
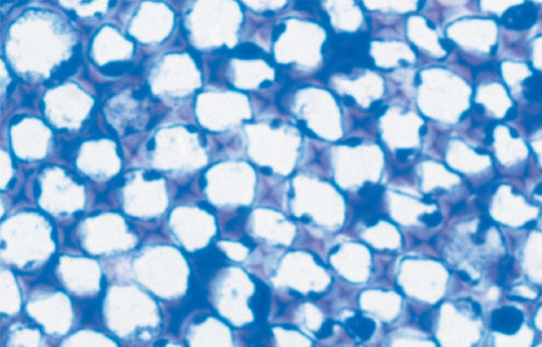
Collenchyma cells are grouped in strands and help support young parts of the plant shoot
They are living at maturity
These cells provide flexible support without restraining growth
Celery strings
Collenchyma Cells
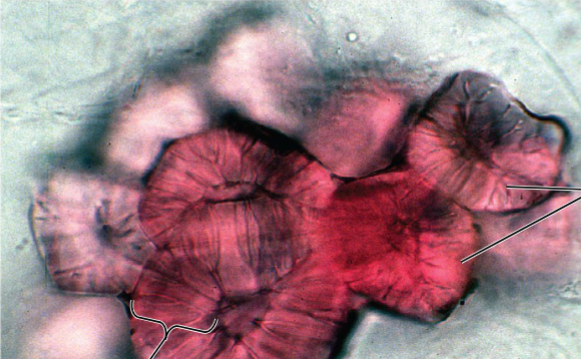
Sclerenchyma cells function in rigid support are due to thick secondary walls containing lignin, a strengthening polymer
They are dead at functional maturity
There are two types:
Sclereids are short and irregular in shape and have thick, lignified secondary walls (give pears their
texture)
Fibers are long and slender and arranged in threads (used for textiles)
Schlerenchyma Cells
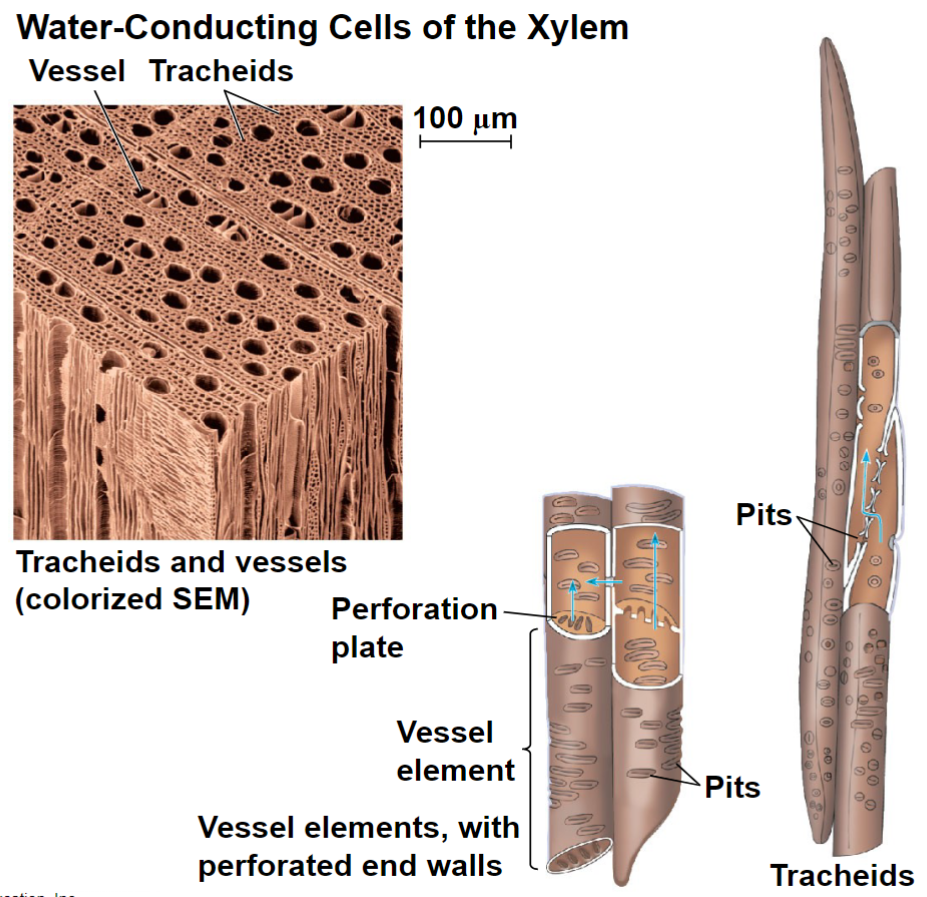
Dead and lignified at maturity
Tracheids - long, thin cells; tapered ends
Water moves between tracheids through pits, thin regions lacking secondary cell wall
Vessel elements – align end to end, form long pipes called vessels; end walls contain perforated plates
Water-conducting cells of the xylem
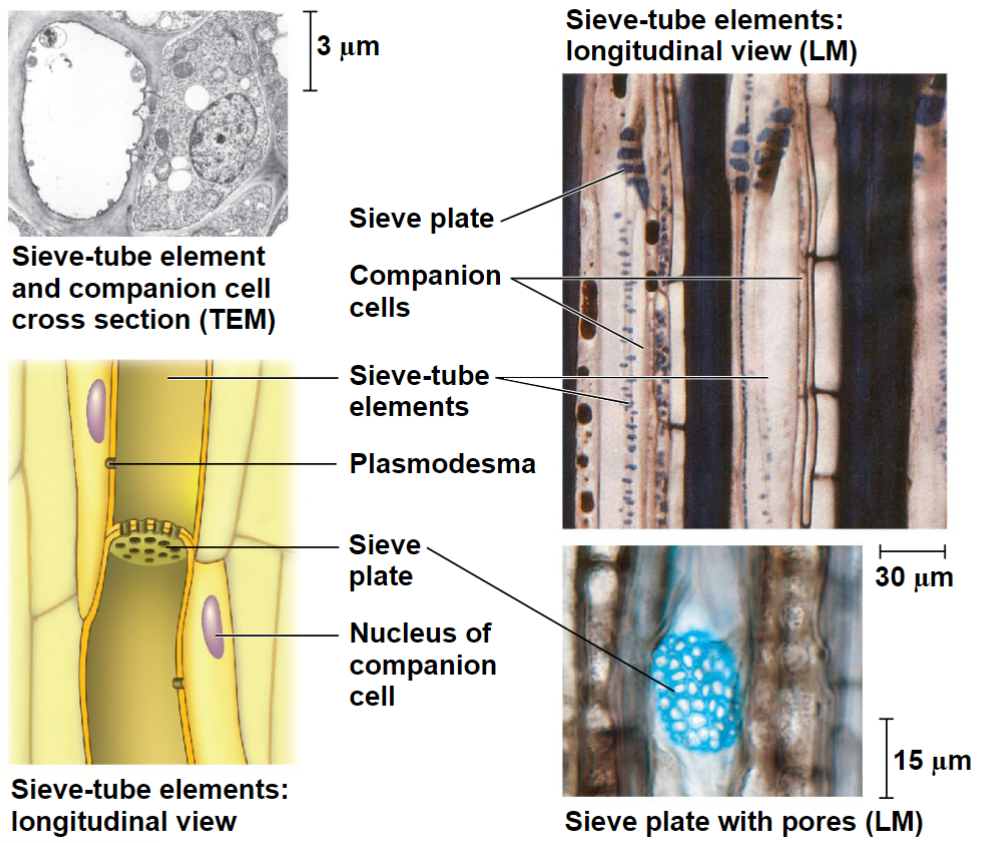
Alive at maturity, but lack organelles
Sieve-tube elements – form chains of cells (sieve-tubes) for sugar transport
Sieve plates: porous end walls between sieve-tube elements allow fluid flow between cells
Each connected to a companion cell (parenchyma) by plasmodesmata
Companion cell’s nucleus and ribosomes serve sieve-tube element
Sugar-conducting cells of the Xylem
Which of the following cells functions in flexible support of plants?
A. Collenchyma
B. Companion cells
C. Sclerenchyma
D. Parenchyma
E. Sieve tubes
A. Collenchyma
Indeterminate growth: grow throughout life with no set limit
Plant growth at meristems
Indeterminate growth is NOT immortality
Most animals have determinate growth: growth stops at a point
Plant growth types
Annuals: one season to complete life cycle
Biennials: two seasons
Perennials: multiple seasons
Plants lifespan
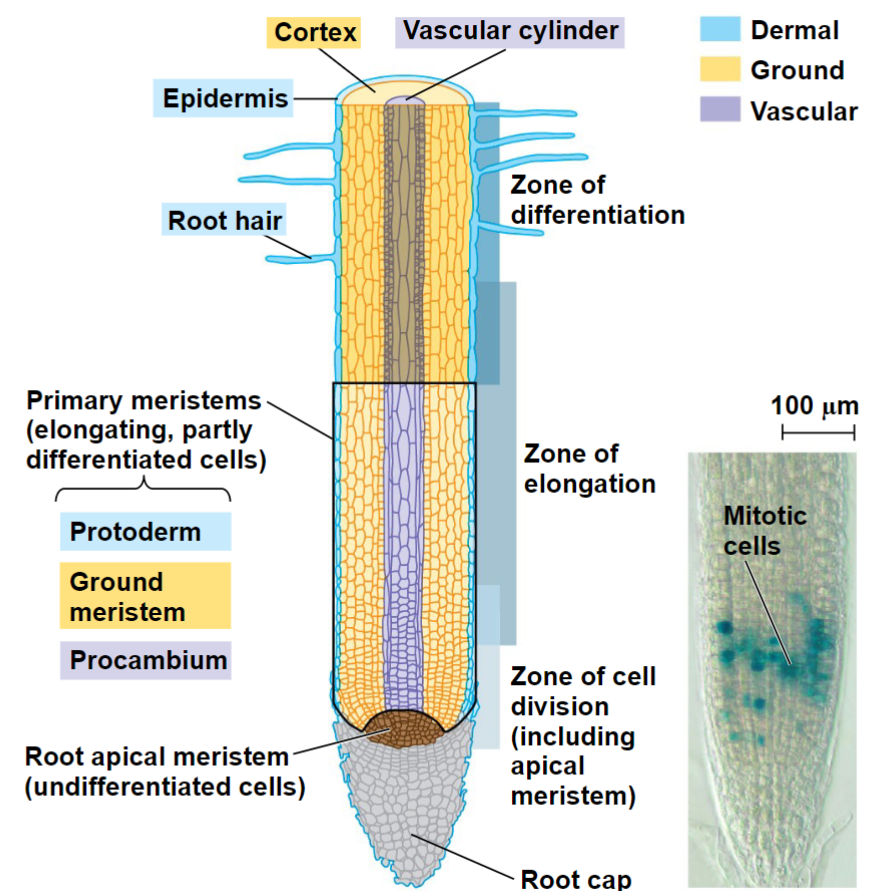
Unspecialized tissues composed of dividing cells (i.e., stem cells)
Meristems
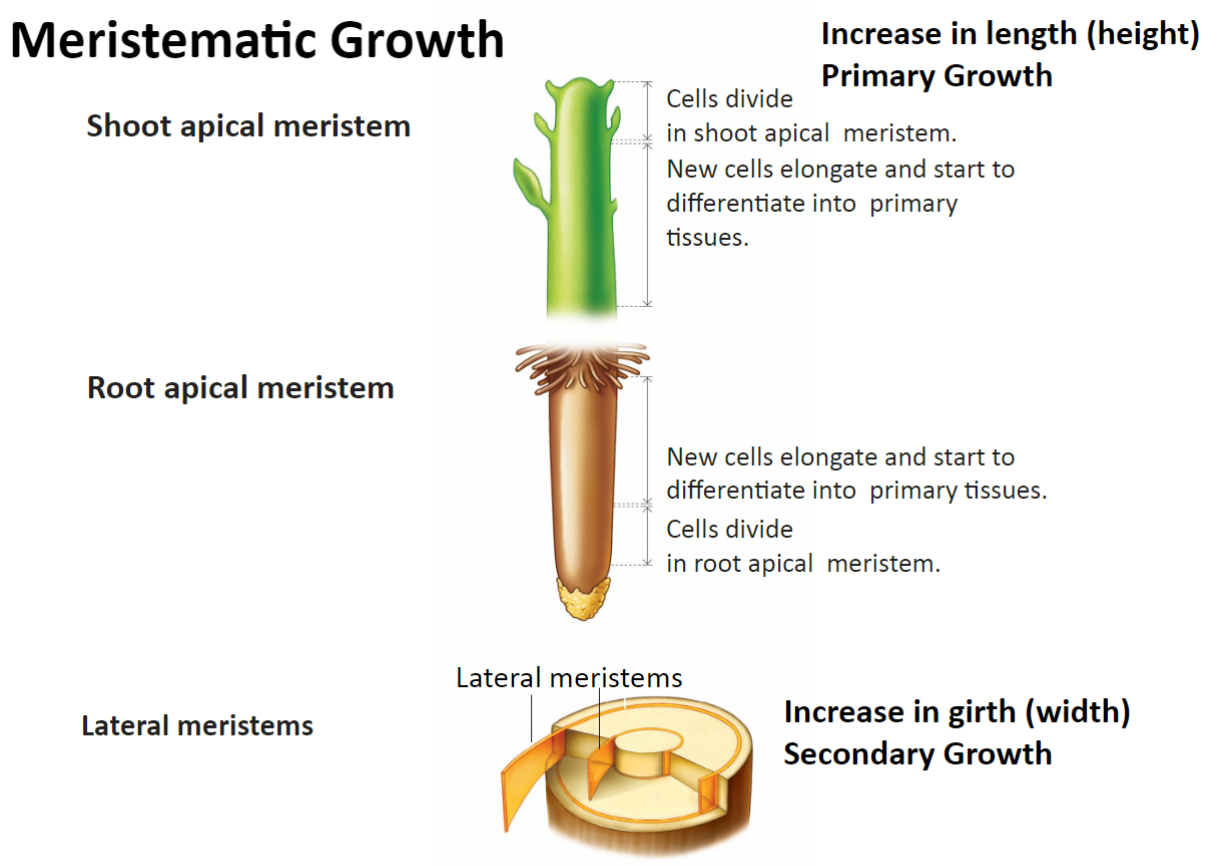
tips of roots and stems; growth in height/length of shoots and roots
Primary growth
Apical meristem
lateral surface; growth in girth of stem
Secondary growth
Lateral meristem
Meristematic Growth Chart
Embryonic tissue
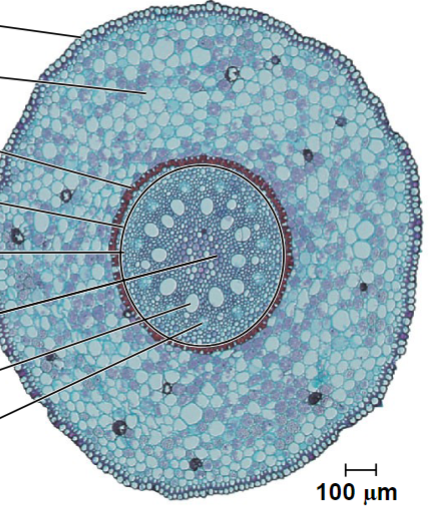
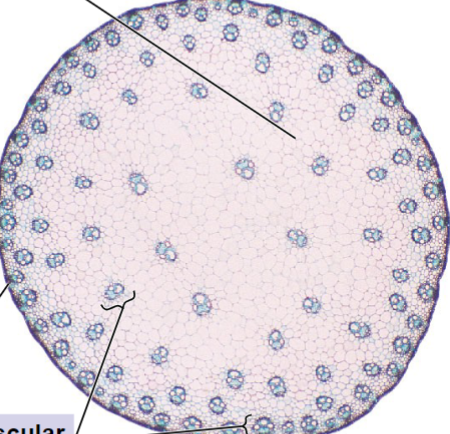
Eudicot cross-section
Monocot cross-section
The growth of a lateral root is an example of
A. Primary growth
B. Secondary growth
C. Lateral meristem
D. All of these are correct
B. Secondary growth
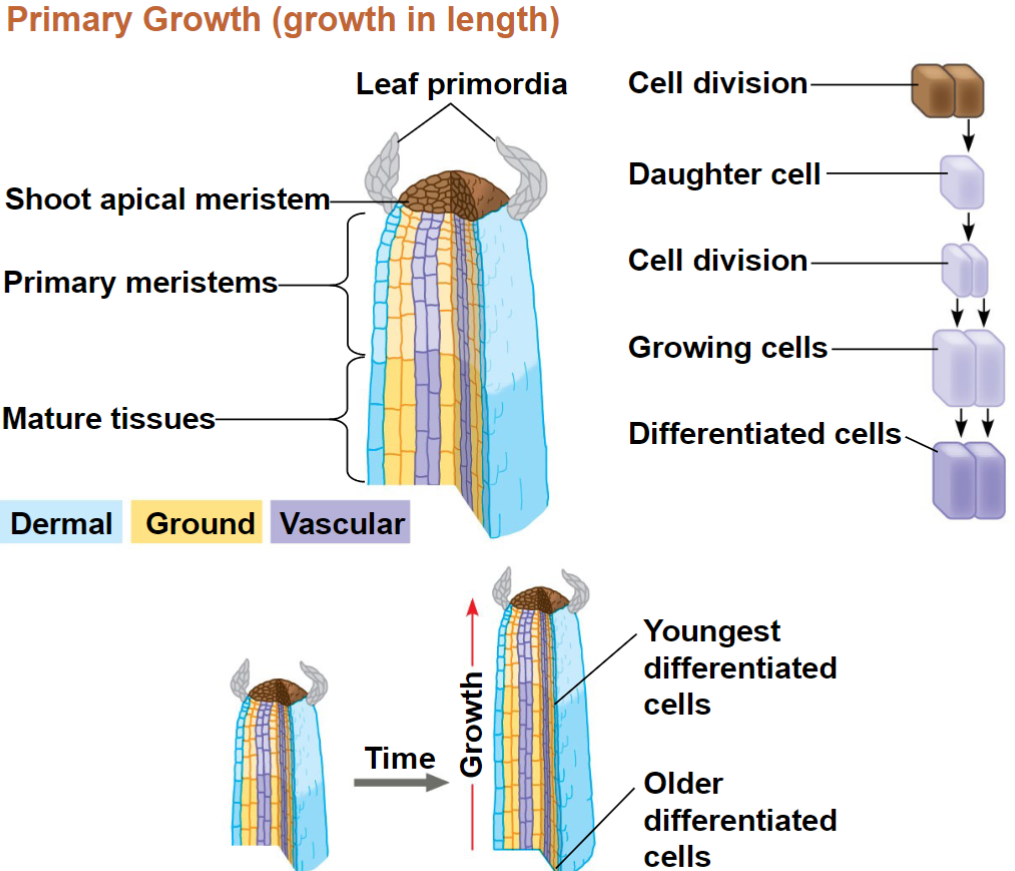
Primary Growth Chart
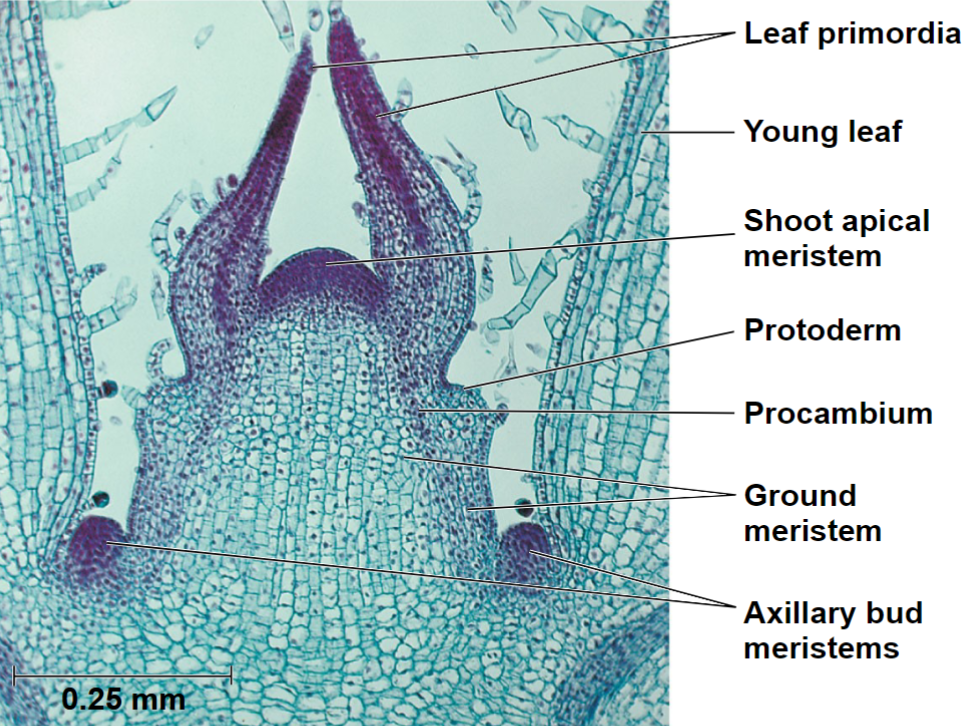
Apical meristem picture
Eudicot stem cross section
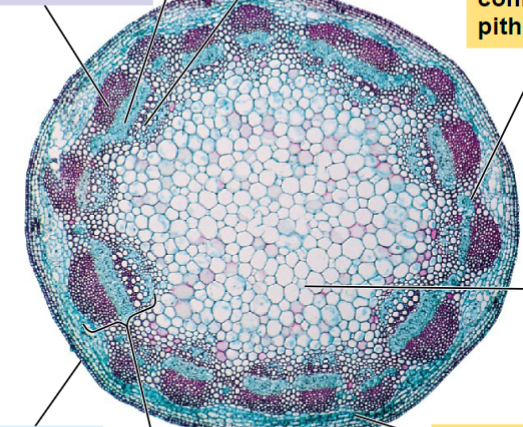
Monocot stem cross section
Based on what I’ve learned about primary growth in shoots, If I put up a basketball hoop on a tree trunk and the tree is allowed to grow, 10 years later, the hoop will be higher up.
A. True
B. False
B. False
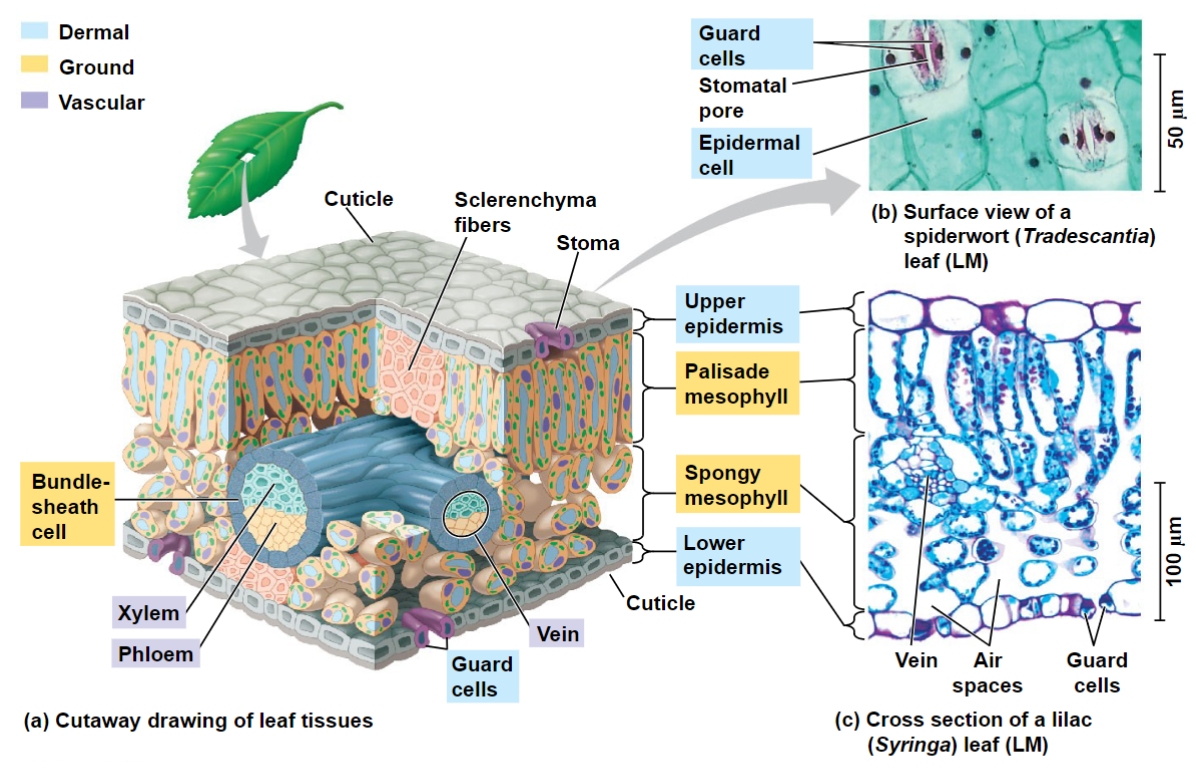
Leaves develop from leaf primordia
Stomata, pores that allow CO2 and O2 exchange
Also site of evaporative water loss
Guard cells flank stomatal opening and regulate opening and closing
Ground tissue called mesophyll
Palisade mesophyll – upper part of leaf
Spongy mesophyll – lower part of leaf; loose arrangement
Leaf Growth and Anatomy
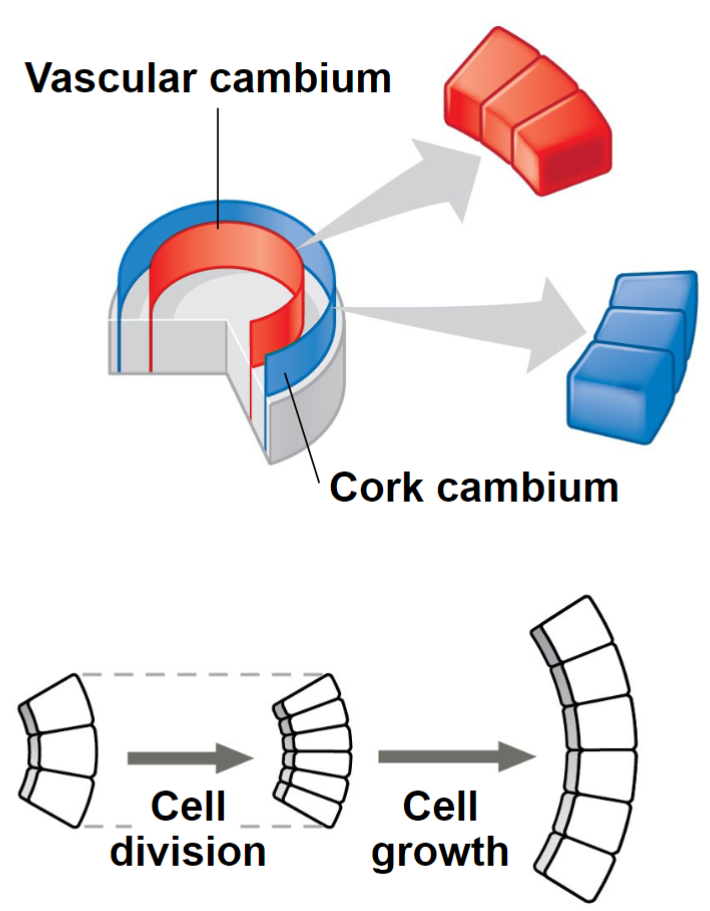
Pattern of Cell Division
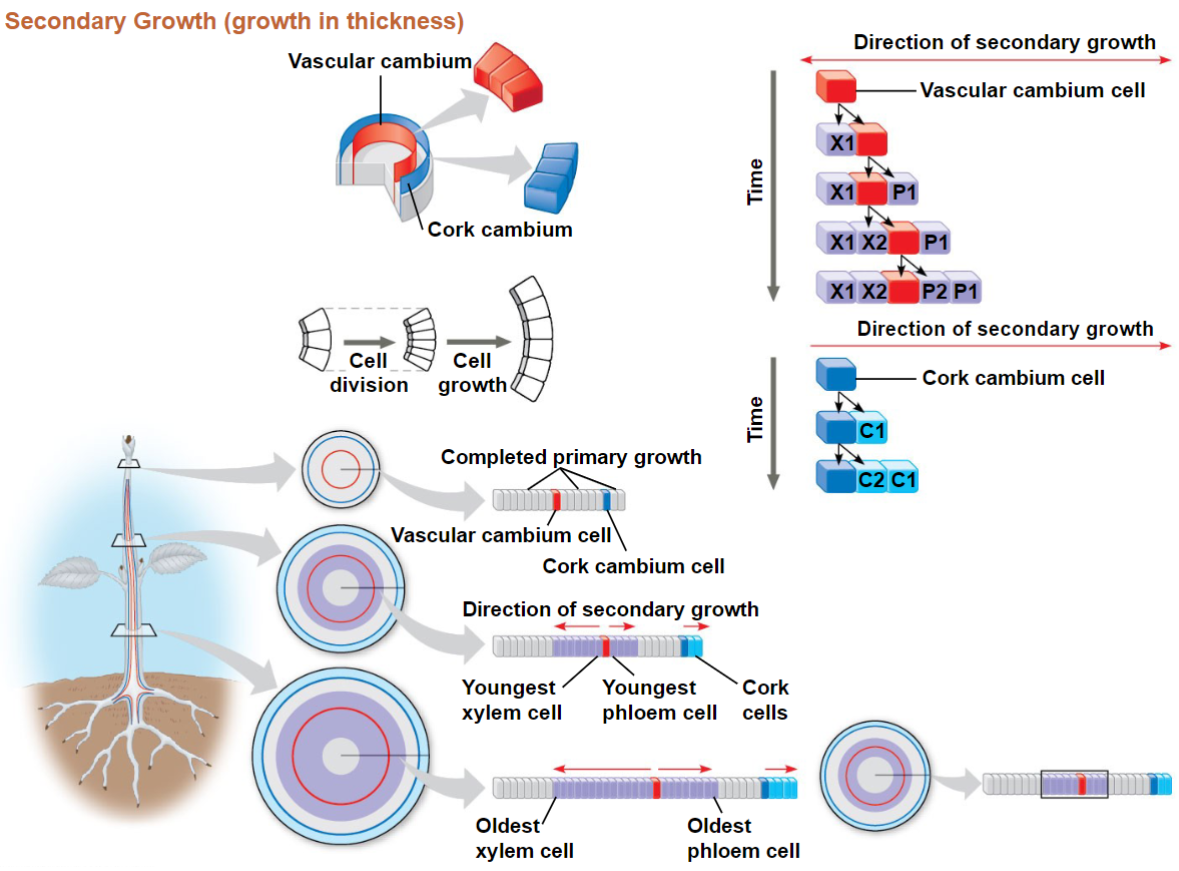
Two lateral meristems:
Vascular Cambium – vascular tissue; secondary xylem
(wood) and secondary phloem
Cork Cambium – epidermis to periderm
Secondary Growth
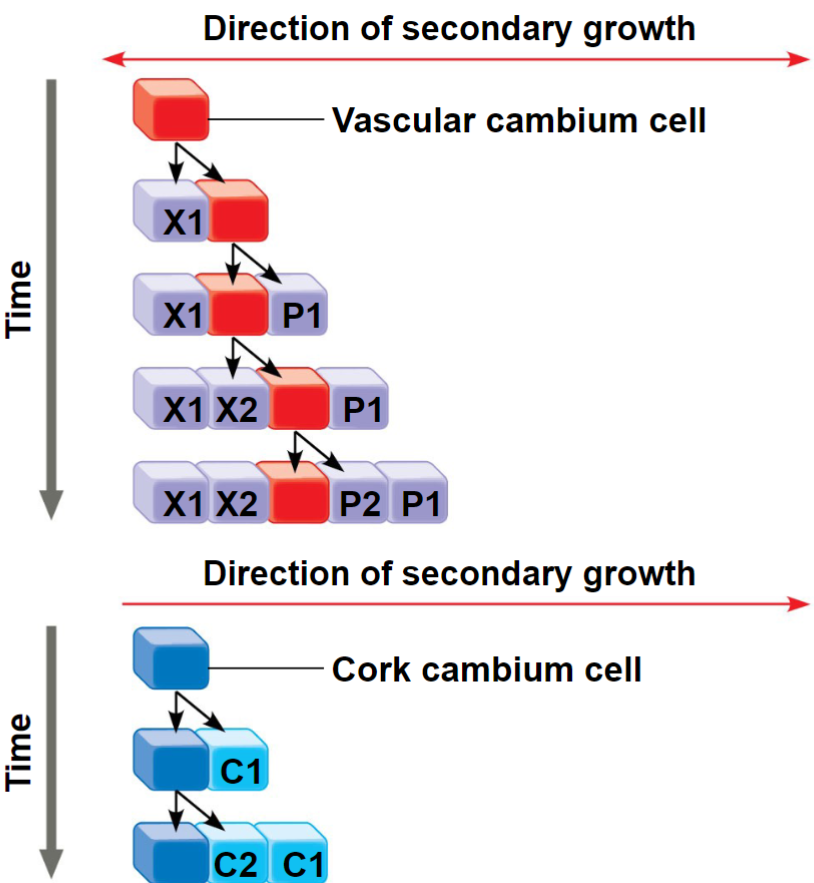
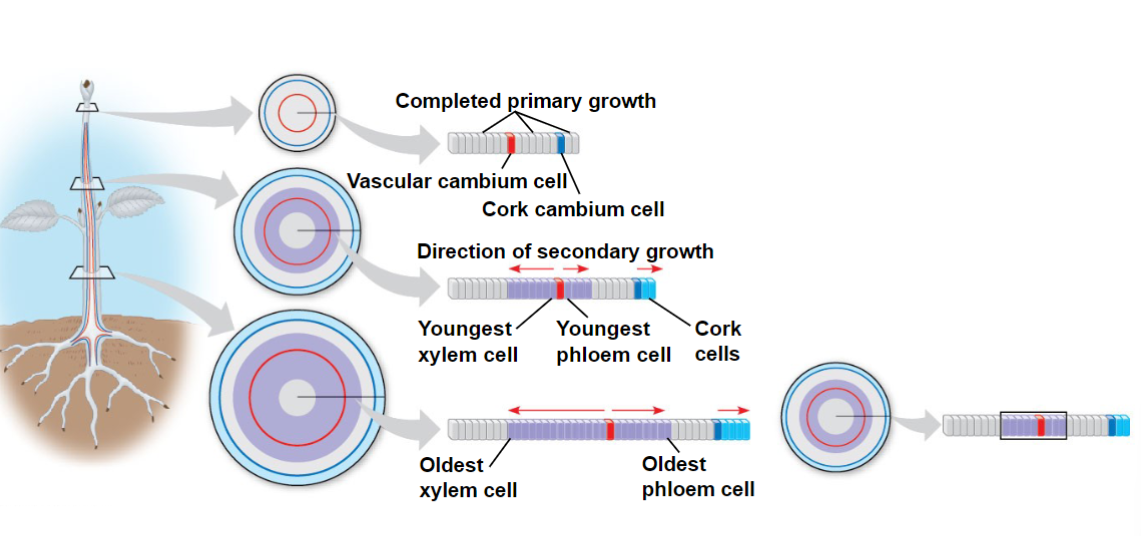
Cambium Growth
Includes both vascular and cork cambium
Choose the incorrect statement
A. Cork cambium makes new cork
B. There are two types of lateral meristem, vascular
cambium and cork cambium
C. Vascular cambium creates both new xylem and
new phloem cells
D. Vascular cambium remains close to the center of
the stem, no matter how old the tree becomes
Vascular cambium remains close to the center of the stem, no matter how old the tree becomes
A region of dividing cells in a plant is called a __________.
ground tissue
cortex
cotyledon
meristem
mycorrhizal zone
meristem
Why does pinching off the top of a plant make it bushier?
Removal of a node stimulates the internodes to grow and make the plant bushier.
Removing the apical meristem stimulates growth in the lateral meristem, thus making the plant bushier.
Removing the apical meristem causes the plant to change from its vegetative phase to its reproductive phase. The reproductive phase is bushier.
Removing the apical meristem stimulates growth in the axillary buds, thus making the plant bushier.
Removing plant stems always leads to the plant producing more leaves.
Removing the apical meristem stimulates growth in the axillary buds, thus making the plant bushier.
Annual rings in wood are evidence that in climates with a single annual growing season, the __________ divides actively when water is plentiful and temperatures are suitable for growth, and ceases to divide when water is scarce and the weather is cold.
lateral meristem
cork cambium
vascular cambium
apical meristem
marginal meristem
Vascular cambium
Water-conducting cells of plants are called ___________.
parenchyma cells
collenchyma cells
sclerenchyma cells
sieve-tube elements
tracheids and vessel elements
Tracheids and vessel elements
In woody plants, the vascular cambium initial is ________.
meiotically active and divides to form an inner layer of secondary xylem and an outer layer of secondary phloem
mitotically active and divides to form an inner layer of primary xylem and an outer layer of primary phloem
mitotically active and divides to form an inner layer of secondary xylem and an outer layer of primary phloem
meiotically active and divides to form an inner layer of primary xylem and an outer layer of primary phloem
mitotically active and divides to form an inner layer of secondary xylem and an outer layer of secondary phloem
mitotically active and divides to form an inner layer of secondary xylem and an outer layer of secondary phloem
Root hair formation is regulated by __________.
the ABC model
MADS-box
KNOTTED-1
Ubx
GLABRA-2
GLABRA-2
Sugar-conducting structures of plants are called ___________.
tracheids and vessel elements
collenchyma cells
parenchyma cells
sieve-tube elements
sclerenchyma cells
sieve-tube elements
A Hox gene homolog in plants is called __________ and is important in __________.
GLABRA-2; leaf morphology
ABC model; flowers
MADS-box; root hairs
KNOTTED-1; leaf morphology
Ubx; flowers
KNOTTED-1; leaf morphology
Phase changes are __________.
morphological changes that arise from transitions in shoot lateral meristem activity
morphological changes that arise from seasonal transitions
changes that occur only in adult plants
morphological changes that arise from transitions in shoot apical meristem activity
None of the listed responses is correct.
Morphological changes that arise from transitions in shoot apical meristem activity
The main difference between a primary root and a lateral root is that ________.
None of the listed responses is correct.
primary roots are the most important roots because they are the only roots that form in most plants
lateral roots enhance the ability of the root system to anchor the plant and acquire resources from the soil
there is no functional difference between primary and lateral roots
lateral roots are the most important roots because they form in the absence of primary roots
Lateral roots enhance the ability of the root system to anchor the plant and acquire resources from the soil
Preprophase bands __________.
run parallel to the direction of elongation as a cell matures
are present throughout the cell cycle
determine the location where the cell plate will form during cell division
constrict the cell and "pinch" it in two during cell division
run perpendicular to the cellulose microfibrils in a dividing cell
determine the location where the cell plate will form during cell division
Which example below is the site of primary growth that results in the plant increasing in height?
Nodes
Bud scales
Axillary buds
Apical meristems
Lateral meristems
Apical meristems
If you pound a nail into a tree one meter off the ground and come back to find it in 20 years, it will be __________.
None of the listed responses is correct.
more than one meter off the ground and the same depth in the tree
more than one meter off the ground and more deeply embedded in the tree
one meter off the ground and more deeply embedded in the tree
one meter off the ground and the same depth in the tree
one meter off the ground and more deeply embedded in the tree
In most leaves, chloroplast-containing cells are most closely compacted in the __________.
upper epidermis
guard cells
palisade mesophyll
vein (vascular bundle)
lower epidermis
palisade mesophyll
The ________ of a root or a stem is called the ________.
vascular tissue; stele
ground tissue; stele
dermal tissue; cuticle
dermal tissue; pith
ground tissue; pith
vascular tissue; stele
The layer that covers the apical meristem of a root is called the __________.
root cap
root hair
taproot
primordium
pericycle
root cap
Evolutionary adaptations of roots include all of the following root structures except __________.
buttress roots
prop roots
pneumatophores
stolons
aerial roots
stolons
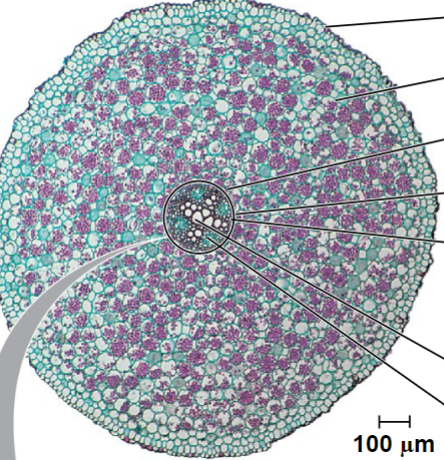
Which of the following correctly describes a feature unique to monocot stems?
Vascular bundles are scattered throughout.
Ground tissue consists mainly of parenchyma.
Vascular tissue is located all in the center.
Lateral shoots cannot originate near the surface.
Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring.
Vascular bundles are scattered throughout.
What accounts for about 90% of a plant cell's expansion?
Water stored in the nucleus
Water uptake stored in a large central vacuole
Additional organic material in a plant's cytoplasm
Mineral uptake by the roots
Additional organic material stored in vacuoles
Water uptake stored in a large central vacuole
Root tips are pushed farther into the soil mainly by __________.
differentiation (specialization) of root cells
elongation of cells
cell division in the meristem
cell division in the vascular cambium
pulling by root hairs
elongation of cells
Leaves occur at intervals along the plant stem. The region where a leaf is attached to the stem is the __________.
internode
petiole
shoot apex
None of the listed responses is correct.
node
node
The three types of tissue systems that are found in all plant organs are __________.
root hairs, trichomes, and spines
epidermal, dermal, and ground tissue systems
dermal, vascular, and ground tissue systems
epidermal, dermal, and vascular systems
epidermal, vascular, and ground tissue systems
dermal, vascular, and ground tissue systems
Leaves consist of __________.
a node and an internode
a bud and a node
an axillary bud and a terminal bud
a leaflet and a blade
a blade and a petiole
a blade and a petiole
The difference between primary growth and secondary growth is that ________.
primary growth occurs only during seed germination and secondary growth occurs throughout the life of the plant
None of the listed responses is correct.
primary growth increases the length and the diameter of roots and shoots and secondary growth increases only the diameter of stems and roots in woody plants
primary growth lengthens roots and shoots and secondary growth increases the diameter of stems and roots in woody plants
primary growth lengthens roots and shoots and secondary growth increases the diameter of stems and roots in herbaceous and woody plants
primary growth lengthens roots and shoots and secondary growth increases the diameter of stems and roots in woody plants
Most of the photosynthesis in plants takes place in specialized __________ cells called the __________.
parenchyma; pith
sclerenchyma; palisades
dermal; mesophyll
vascular; collenchyma
parenchyma; mesophyll
parenchyma; mesophyll
Repetitive patterns in plant growth are __________.
kaleidoscopes
eternal patterns
fractals
circadian patterns
None of the listed responses is correct.
fractals
_________ are the three basic plant organs.
Flowers, stems, and leaves
Roots, stems, and leaves
Roots, stems, and flowers
Stems, tissues, and cells
Roots, root hairs, and stems
Roots, stems, and leaves
Artichoke hearts are tender and have a strong taste. The leaves have a strong taste too, but most of an artichoke leaf is fibrous and too difficult to chew. The leaves must contain lots of __________.
sclerenchyma cells
phloem
epidermal cells
meristematic tissue
collenchyma cells
sclerenchyma cells
Evolutionary adaptations of leaves include all of the following except _________.
adventitious plantlets
spines
bulbs
tendrils
rhizomes
rhizomes
Evolutionary adaptations of stems include __________.
aerial stems
buttress and prop roots
pneumatophores
stolons and tubers
flowers
stolons and tubers