ECHO Week 1:Reading & Knowledge Check: Normal Cardiac Anatomy Chapter 1 Quiz
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Please read Chapter 1, pages 1-17, in Echocardiography The Notebook 8 and answer following questions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Which valve is between the right ventricle and right atrium?
Mitral valve
Aortic valve
Pulmonary valve
Tricuspid valve
Tricuspid valve
Which veins return blood from the myocardium directly into the cardiac chambers without entering the cardiac venous system?
Inferior vena cava
Superior vena cava
Left cardiac veins
Thebesian veins
Middle cardiac vein
Thebesian veins
What is normal diastolic IVC diameter?
1.2-2.1 m
1.2-2.1 sm
1.2-2.1 cm
1.2-2.1 mm
1.2-2.1 cm
Which are the first order of flow through heart?
Right atrium
SVC and IVC
Left atrium
Right ventricle
Pulmonary veins
Tricuspid valve
Right atrium
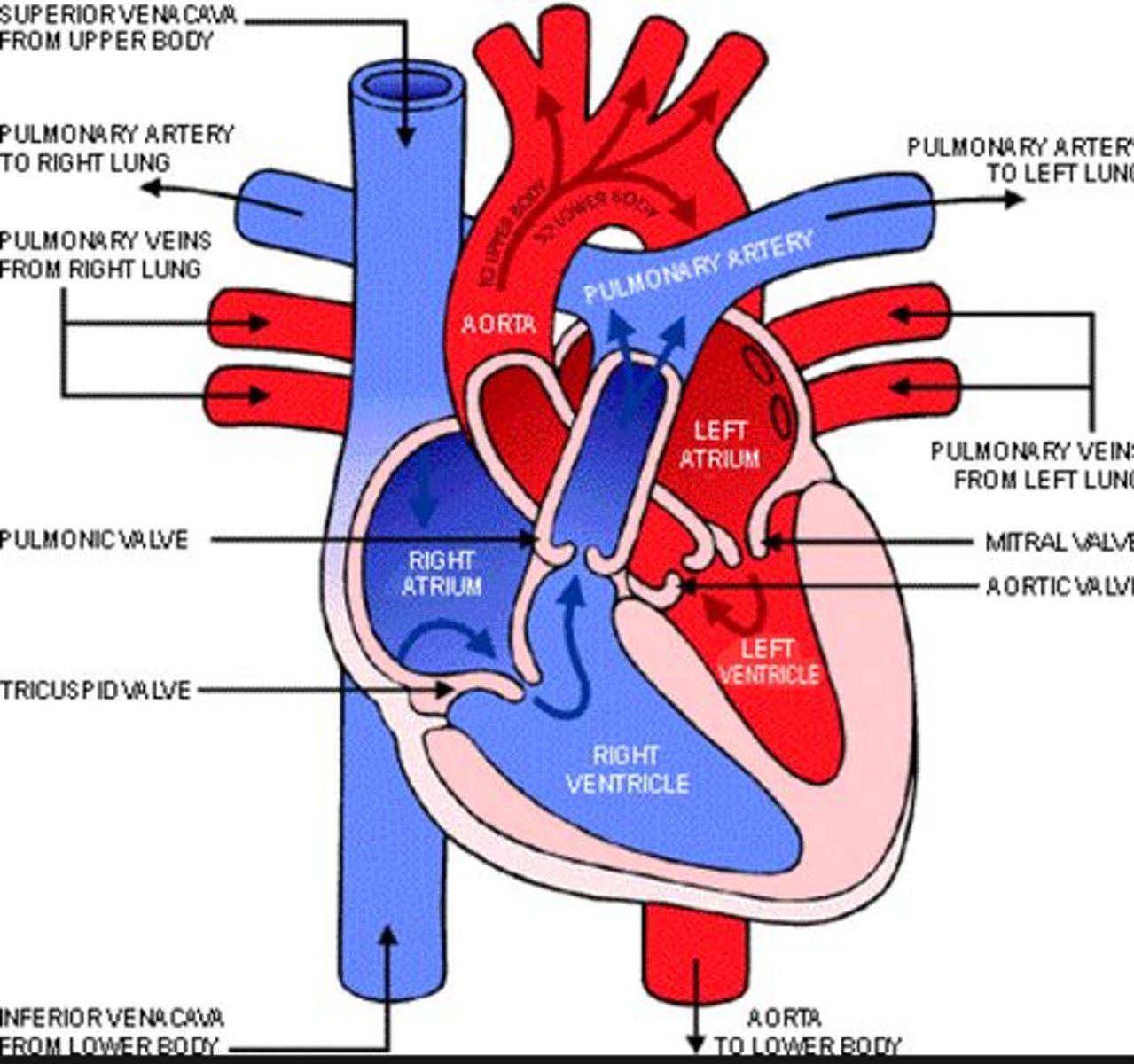
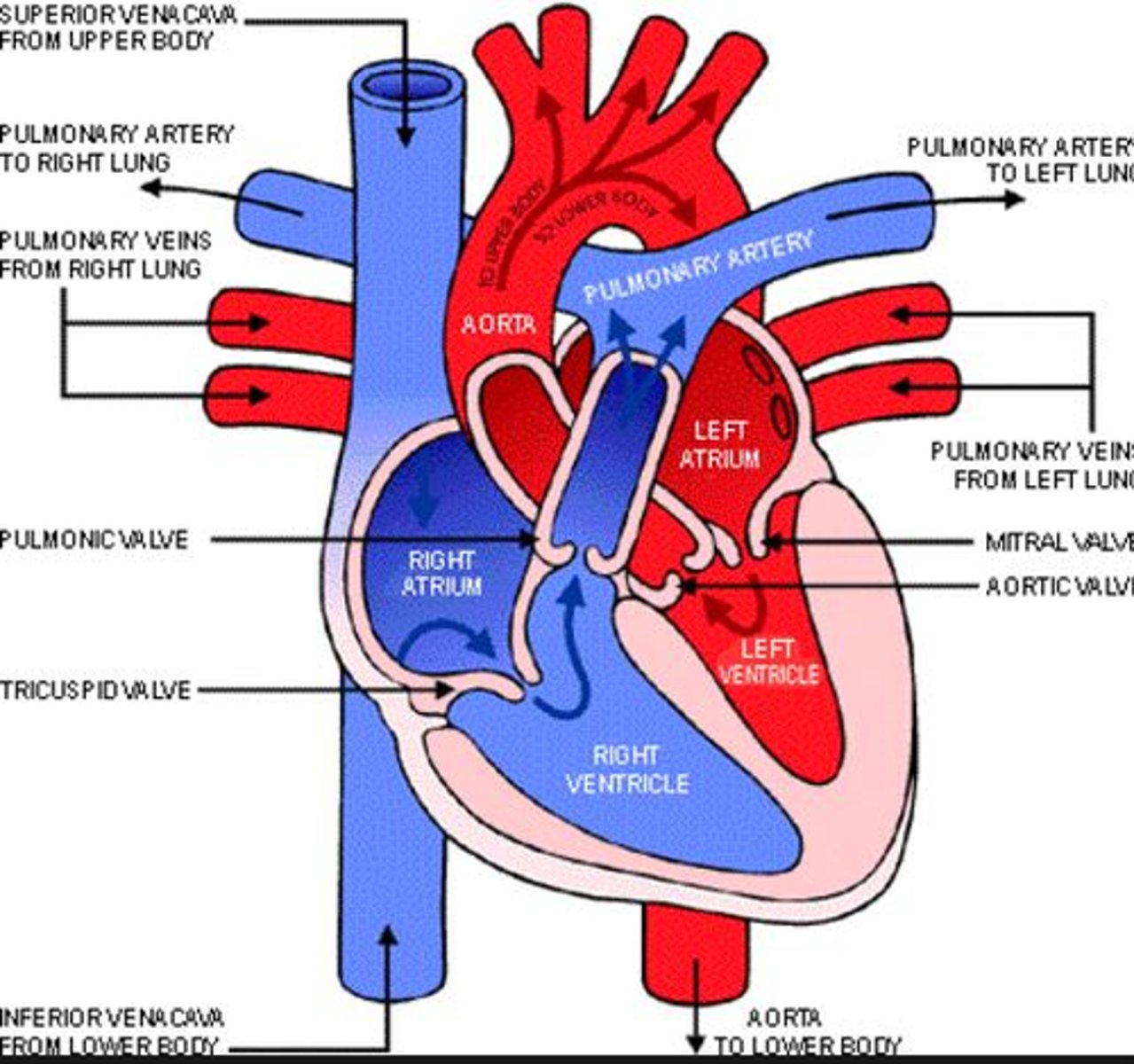
All of the following are true about the right heart EXCEPT:
pumps oxygenated blood to lungs
associated with pulmonary system
low pressure, low resistance
low oxygen saturation
pumps oxygenated blood to lungs
What is the function of cardiac valves?
Ensure one-way blood flow
Prevent backflow through heart
All answers
All answers
Which is the last order of flow?
Aorta
Left ventricle
Right ventricle
Aortic valve
Pulmonary valve
Left ventricle
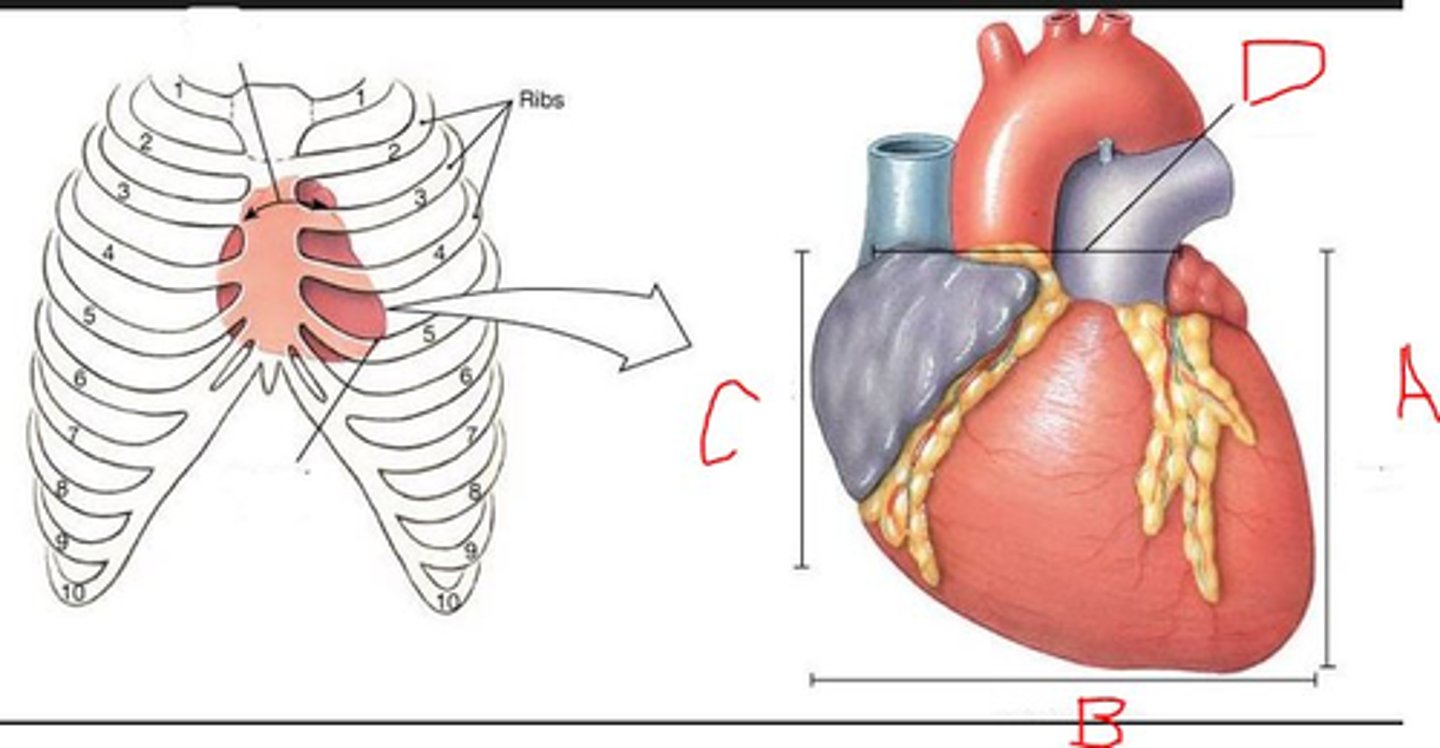
The base of the heart is near rib
2
5
2
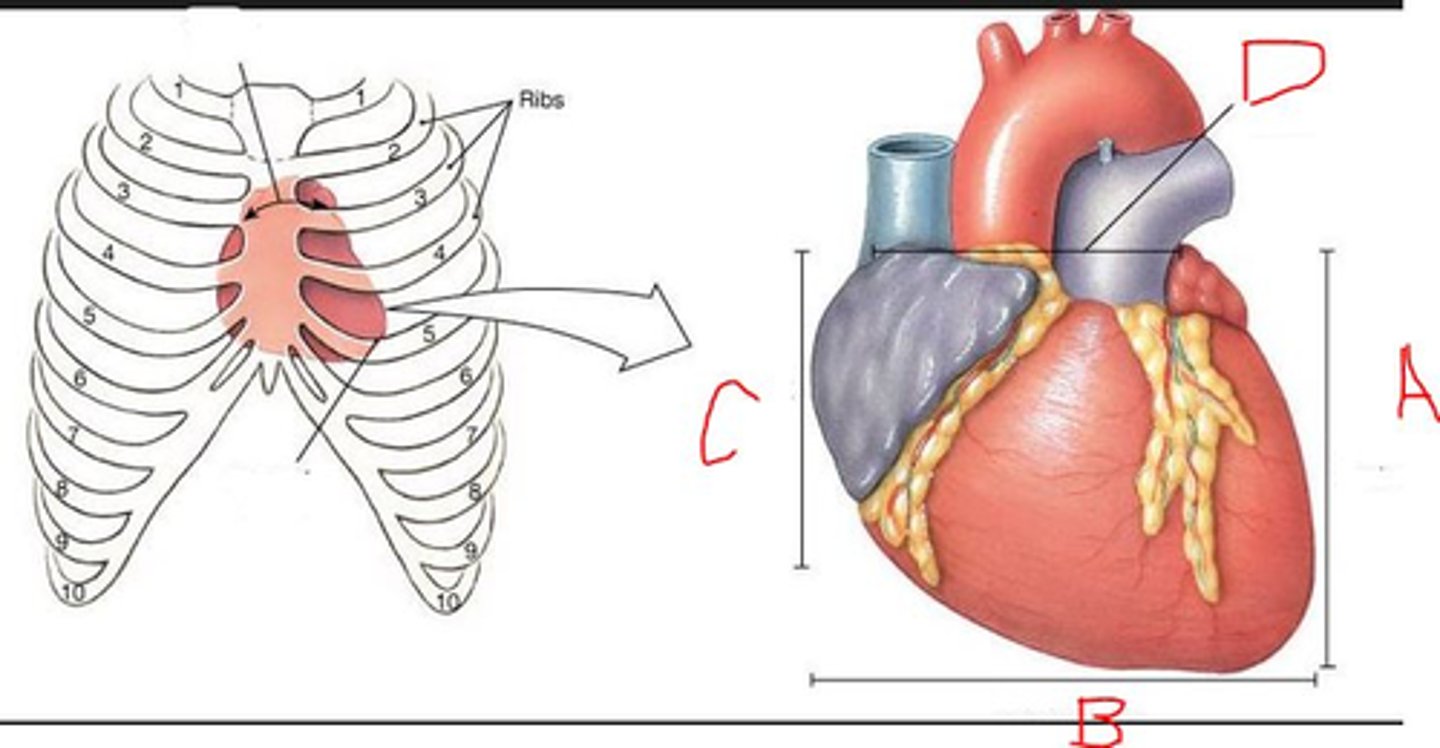
Which letter indicates superior heart?
D
C
A
B
D
Which valves are the atrioventricular valves?
None
Tricuspid and mitral valve
Pulmonic and aortic valve
Tricuspid and mitral valve
What is the order of flow from left heart to right heart?
Right atrium: Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the body through the vena cava, coronary sinus, and superior and inferior venae cavae.
Right ventricle: Blood passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle, which contracts to push the blood towards the lungs.
Lungs: Blood travels to the lungs through the pulmonary artery to be oxygenated.
Left atrium: Oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins and enters the left atrium.
Left ventricle: Blood passes through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
Aorta: Blood passes through the aortic valve into the aorta, which distributes oxygenated blood to the body's tissues through its branches
Which structure bridges the arteries and veins together?
Great vessels
Capillaries
Arterioles
Venules
Capillaries
What is the order of flow from the right heart to the main pulmonary artery?
1. Right atrium
Blood enters the heart through the vena cava and flows into the right atrium.
2. Right ventricle
The atrium contracts, forcing blood through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve closes.
3. Pulmonary valve
The right ventricle then pumps blood through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonary artery.
4. Lungs
The pulmonary artery carries oxygen-depleted blood from the heart to the lungs, where it's oxygenated. The oxygenated blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins, entering the left atrium.
The cardiovascular system is responsible for all of the following EXCEPT:
delivers wastes
maintain body's metabolic requirements
delivery of oxygen and nutrients
circulates blood
delivers wastes
Which circulatory system has greater resistance to the heart?
Neurologica
lPulmonary
Digestive
Systemic
Systemic
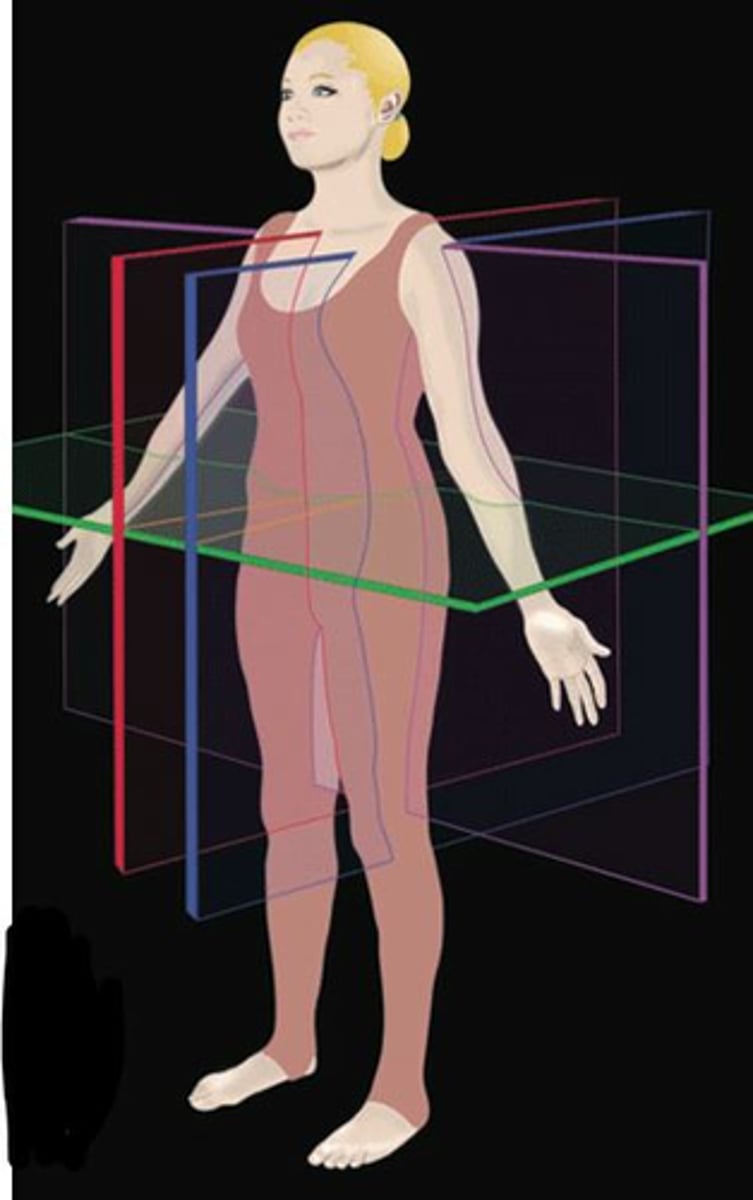
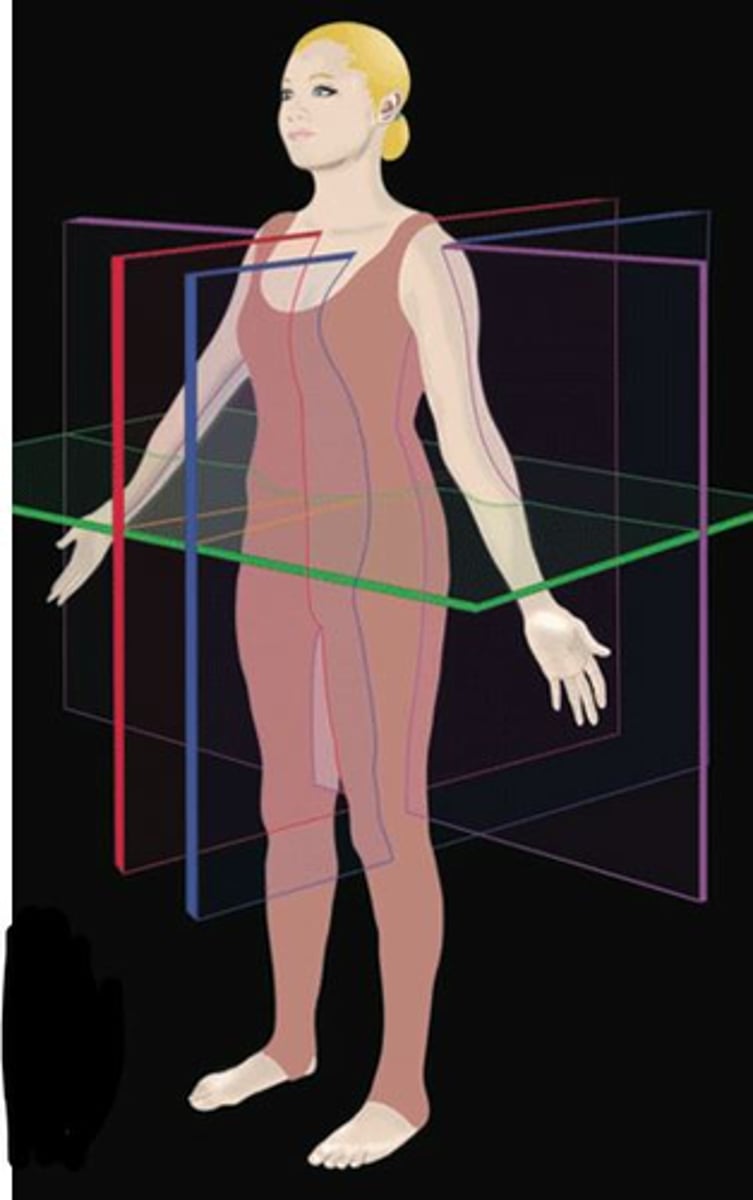
Which plane separates right from left?
Blue
Green
Red
Purple
Red
Which are filling chambers?
Atria
Ventricles
Atria
Which system is responsible for returning blood from heart's arterial system?
Coronary sinus
Pulmonary system
Peripheral venous system
SVC
Coronary sinus
Which plane separates frontal and dorsal aspects of body?
Green
Blue
Red
Purple
Purple
Which organ is the driving force behind cardiovascular system?
Arteries
Heart
Aorta
Veins
Heart
Which systolic pulmonary pressure indicates pulmonary hypertension?
> 25 cmHg
> 25 mHG at rest
< 25 mmHG at rest
> 25 mmHG at rest
> 25 mmHG at rest
Which are pumping chambers?
Ventricles
Atria
Ventricles
Which valves are semilunar valves?
Pulmonic and aortic valve
Tricuspid and mitral valve
None
Pulmonic and aortic valve
Which is an indirect measurement of the left atrial pressure?
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)
Pulmonary artery pressure
Pulmonary wedge pressure
Systolic pulmonary artery pressure
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)
The heart wall consists of
Myocardium
Epicardium
Endocardium
All answers
All answers
How can the heart perform all of its duties?
Arterioles
Arteries
Capillaries
All answers
All answers
T or F: The pericardium encases the heart to protect it against infection and trauma.
True
All is true about the RA EXCEPT:
Reservoir for systemic venous return
Pumps blood out to root of aorta
Thebesian valve is located between coronary sinus between right atrium
Fills more during inspiration because pressure gradient between RA and pressure in veins
Pumps blood out to root of aorta
The apex of the heart is near rib:
1
2
5
4
5
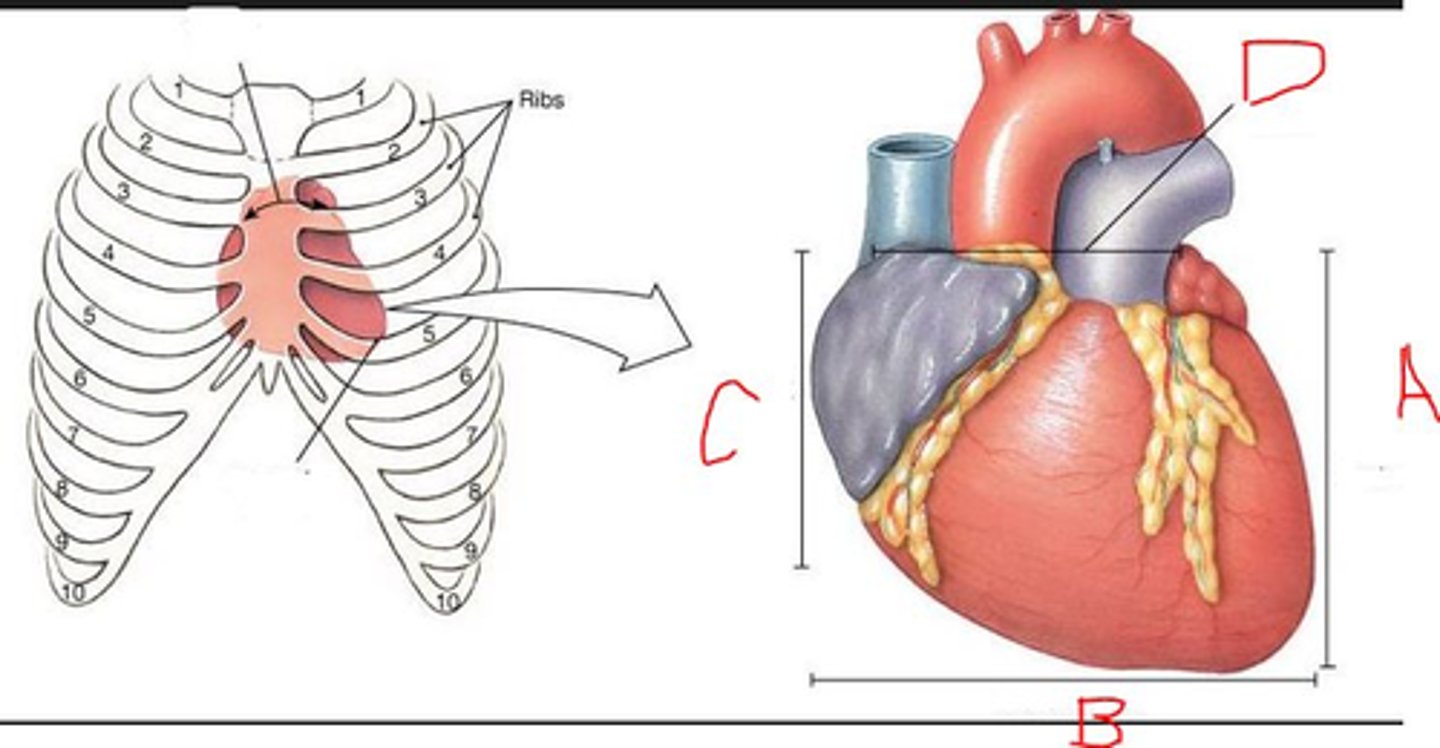
Which is the left side of heart?
C
D
A
B
A
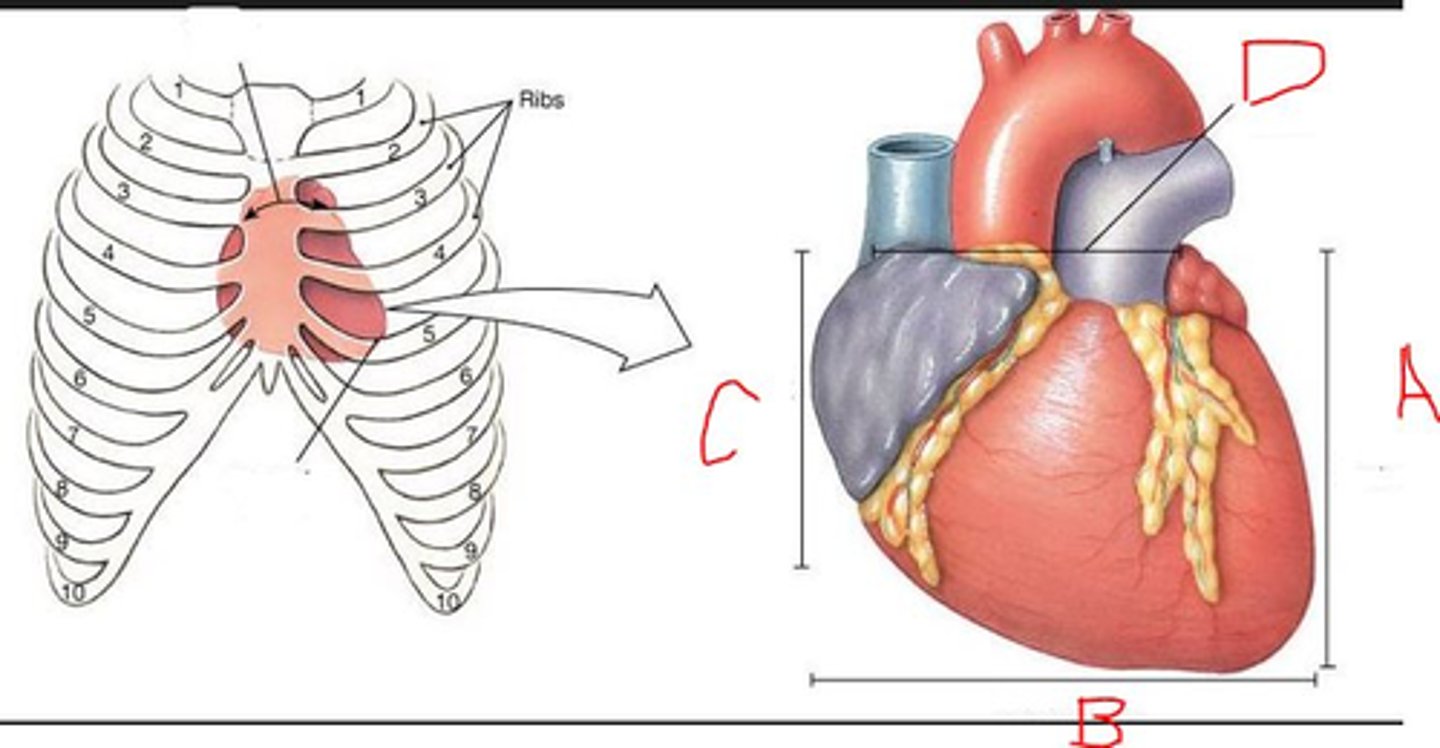
Which are the great artery(ies)?
IVC/SVC
Both Aorta and Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary artery
Aorta
Both Aorta and Pulmonary artery
All of the following are true about left heart EXCEPT:
oxygenated blood is rich in oxygen to perfuse tissues in body
high pressure, high resistance
associated with circulatory system
receives deoxygenated from pulmonary ciculation
Receives deoxygenated blood from pulmonary circulation
Which two bones cradle the heart?
Vertebral column and lungs
Sternum and vertebral column
Sternum and diaphragm
Sternum and cartlidge
Sternum and vertebral column
The definition of blood pressure is
the arterial blood pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the systemic circulatory system
the arterial blood pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the pulmonary circulatory system
the arterial blood pressure exerted by the blood on the outside walls of the systemic circulatory system.
the arterial blood pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the systemic circulatory system
Which valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Mitral valve
Aortic valve
Tricuspid Valve
Pulmonary valve
Mitral valve
Which is the right ventricular diastolic pressure:
2-8 mmHg
3-12 mmHg
4-12 mmHg
2-12 mmHg
2-8 mmHg
How does the heart increase the demand for oxygenated blood when you exercise?
Increase cardiac output
Decrease cardiac output
Cardiac function stays the same
Increase cardiac output
Which statement below is systolic function:
Venticles ability to relax and fill
Ventricles ability to efficiently eject blood out of the heart into the systemic and pulmonary circulatory systems.
Ventricles ability to efficiently eject blood out of the heart into the systemic and pulmonary circulatory systems.
During diastole the semilunar valves:
open
close
close
AV valves open during:
systole
diastole
diastole
What is required in order for heart to provide proper circulation through body?
Normal volume
Normal pressure
Both normal volume and normal pressure
Both normal volume and normal pressure
Discuss the action associated with diastole. What is happening?
Diastole is a phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart's chambers relax and refill with blood. It's the opposite of systole, when the heart's chambers contract.
Which work together to keep the TV and MV closed during systole to prevent backflow into atria?
Papillary muscles
Chordae tendineae
All answers
Pressure gradient
All Answers
A decrease in systolic function indicates following heart diseases EXCEPT:
Pulmonary embolism
Ischemia
Hypertension
Congestive heart failure
Hypertension
During diastole the semilunar valves:
close
open
close
Why is blood easily flowing from atria to the ventricle?
high pressure gradient
no pressure gradient
low pressure gradient
no pressure gradient
Discuss the action associated with systole. What is happening?
Systole is the contraction of the heart's ventricles during a heartbeat, which forces blood into the body's circulatory system. This contraction occurs between the first and second heart sounds of the cardiac cycle, and usually lasts 0.3 to 0.4 seconds
T or F: Overall, cardiac function is determined by both systolic and diastolic function.
True
AV valves closed during:
diastole
systole
systole
T or F: The mechanical events of the heart is seen on EKG.
False
At what percentage does a normal ventricular wall concentrically thicken and contract towards center of chamber?
80%
20%
15%
30%
15%
Which nervous system increases heart rate as part of the Fight or Flight Response?
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Which immediately precedes diastole:
Isovolumic Contraction Time (IVCT)Isovolumic Relaxation Time (IVRT)
Isovolumic Contraction Time
Which of the below statements best describes systole:
period when AV valves and tricuspid valve open
period when all four valves are clsoed
period of contraction when the blood is ejected from the heart
period of relaxation when the venticles fill with blood
period of contraction when the blood is ejected from the heart
T or F: Chambers normally concentrically decrease in size during systole.
False
What is Preload?
The volume (load) in the heart at end-diastole
What is Afterload?
The resistance that the heart must pump against
What is Inotropic Force?
contractility of the heart muscle or the force of the contraction
What is Chronotropic Force?
rate of contraction or heart rate
What is Hyperkinetic?
Excessive wall motion
What is Hypokinetic?
Decreased wall motion
What is Akinetic?
No movement or thickening of myocardium; may indicate MI or hibernation
What is Hibernation?
Ischemic segment that is akinetic but not infarcted that can be reversed with restored coronary blood flow
What is Dyskinetic?
Movement away from center of the cavity; may indicate myocardial infarction
What is Heart Rate?
Number of heart beats per minute
What is Stroke Volume?
Volume of blood ejected with each heart beat
What is Cardiac output?
Volume of blood the left ventricle pumps out each minute
What is Cardiac Index?
Cardiac output corrected for body surface area
What is Body Surface Area?
Total surface area of the body
In the PLAX view, what are we visualizing?
Right and left sides of the heart
Tricuspid, mitral and aortic valves, descending aorta
Right ventricle, tricuspid, mitral and aortic valves
Mitral and aortic valves, left ventricle, septum and LV posterior wall, aortic root, right ventricular anterior wall and a portion of the right ventricle, descending aorta, pericardium
Mitral and aortic valves, left ventricle, septum and LV posterior wall, aortic root, right ventricular anterior wall and a portion of the right ventricle, descending aorta, pericardium
What are the different levels and views we obtain from the Short axis view?
Parasternal long axis, short axis, apical
Short axis LV apex and papillary level, mitral vale and aortic valve
Short axis, long axis, apical
Short axis apical 4, 2, 3
Short axis LV apex and papillary level, mitral vale and aortic valve
What cardiac chambers are visualized in the Apical views:
Right and left ventricles
Left and right atrias
Right atrium and right ventricle
Left and right ventricles, left and right atrias
Left and right ventricles, left and right atrias
How do we evaluate the hemodynamics of the heart from the Apical views in this video?
2-D echocardiography
Continuous wave doppler
Color doppler
Pulsed wave doppler
Continuous wave Doppler
What color presentation represents flow away or towards the transducer in the Apical views?
red/away, blue/towards
blue/away, red/towards
In the apical views, color doppler is not parallel with blood flow
blue/away, red/towards
In the PLAX view, we are evaluating all the following, except:
Tricuspid valve
Left ventricular systolic function
Pericardial effusion and /or pleural effusion
Mitral valve
Aortic valve
Pericardial effusion and /or pleural effusion
The subcostal view is mainly used to evaluate _________?
systolic function
mitral valve function
aortic valve function
pericardial effusion
pericardial effusion
Which side of the ultrasound screen is the screen dot for echocardiography?
right
left
Right
What organ serves as an acoustic window for the subcostal/subxiphoid view?
diaphram
lungs
stomach
pancrease
liver
liver