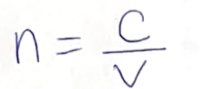Chapter 12-The Refraction of Light
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is refraction?
The bending of light as it changes speed moving between materials.
What is the angle of refraction?
The angle between the refracted ray and the normal.
What is apparent depth?
When submerged objects look shallower than they are due to refraction.
What is the critical angle?
The smallest angle of incidence for which total internal reflection occurs.
What is total internal reflection?
When all light reflects back into a denser medium instead of refracting.
What is the index of refraction?
The ratio of light speed in a vacuum to its speed in a material.
What is partial reflection/refraction?
When some light reflects and some refracts at a boundary.
What is Snell’s Law?
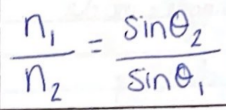
How does light’s speed change in different media?
It slows down in denser materials (higher refractive index).
How do you calculate light velocity in a medium?
v=c/nv = c/nv=c/n, where c is speed in vacuum, n is refractive index.
Why is the index of refraction dimensionless?
It’s a ratio of two speeds, so units cancel.
What conditions are required for total internal reflection?
Light travels from denser to less dense medium, angle > critical angle.
What are uses of total internal reflection?
Fibre optics, binoculars, kaleidoscopes.
What optical phenomena result from refraction?
Mirage, shimmering, flattened sun, rainbows, apparent depth.
What is the speed of light in air compared to a vacuum?
Slightly slower, but nearly the same (~3 × 10⁸ m/s).
What happens to light when it enters a denser medium?
It bends toward the normal and slows down.
What happens to light when it enters a less dense medium?
It bends away from the normal and speeds up.
What causes a mirage?
Refraction due to temperature differences in air layers.
What causes shimmering on roads?
Shimmering is caused by light bending (refraction) as it passes through layers of air with different temperatures and densities. This distorts the image and makes it appear to move.
What causes a rainbow?
Refraction, dispersion, and internal reflection of sunlight inside water droplets.
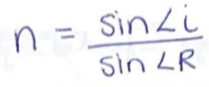
What is this formula?
A version of snells law, where n is the index of refraction
What is the index of refraction with light speed formula?