Applied Cellular Pathology (Sarah Hughes)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Histology
the study of tissues at the microscopic level, focusing on the structure, composition, and function of cells and their organization in various organisms.
Fixation
is the process of preserving tissue samples by using chemicals or physical methods to maintain their structure and allow for accurate microscopic examination.
Types of fixative
include formaldehyde, buffered formalin concrete, neutral buffered formalin
properties of formalin
40% formaldehyde
buffered formalin concentrate
10% Neutral buffered formalin
Routes of a specimen
fixation, dissection, processing, embedding, microtome,staining
processing
the method of preparing a specimen for microscopy after fixation, including dehydration, clearing, and infiltration with embedding medium.
microtomy
the process of cutting thin sections of a specimen for microscopic examination.
staining
the technique used to enhance contrast in specimens, making specific structures more visible under a microscope.
Fresh tissue
that has not undergone any processing or preservation methods, often requiring immediate fixation for analysis. clinically urgent usually intraoperative
How are fresh tissue frozen
Standard freezing- Cryobar
Most common
Quick
Cheap and easy
Usually -20C to -40C
Used in cryostat (cryobar set at -50C)
Liquid N2
-196 C rapid freezing on contact
Used to store some fresh specimens
Boil on contact
Risk- asphyxiation and freeze burns
Cryospray- Mohs
Different technique for Mohs
Tissue is frozen onto a glass
slideAllows for orientation
purposeThis is inverted onto a chuck to embed onto
freezing medium
Explain the effects frozen tissue can have on the tissue
Slow freezing give large hexagonal ice crystals
Intracellular ice crystals damage cell membrane
Rapid freezing gives small cubic ice crystals
Less distortion of cell membrane
Ice crystal artefact
Rate of cooling depends upon the rate of conduction. This depends upon the temperature difference between the tissue and the coolant
What are inter-operative frozen sections
Inter-operative frozen sections are quickly prepared tissue samples that are frozen and sliced during surgery to provide immediate pathological information, helping surgeons make real-time decisions.
What different techniques can be performed on fresh tissue
What steps are involved in the production of a frozen section
Specimen received in lab and booked in
Pathologist examines specimen
Sample area of suspicion
Rapid frozen onto a freezing medium
Sections cut
Section stained
Reported by pathologist
Specimen fixed and processed to paraffin
Freezing
is a preservation method where fresh tissue is rapidly cooled to maintain cellular structure and prevent degradation, often used for intraoperative
What are the advantages of frozen sections
Quick
Cost-effective
Compatible with other techniques
Only method for demonstration of some methods e.g. oil red o
Diagnostic sections
What are the disadvantages of frozen sections
Morphology is not as good
Difficult to cut
Artefact
Storage
Time pressure
High-risk specimens
what are the risks and hazards associated of working in the lab with frozen sections
Burns - exposure to cryogenic temperatures can cause burns; potential
Sharps - handling sharp instruments poses injury risks;
Biological - exposure to biological hazards from pathogens;
Chemical - and risk of chemical exposure from reagents used in processing.
What is Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
A laboratory technique used to identify specific antigens in cells or tissue sections by utilising antibodies tagged with a detectable marker.
Aiding in the diagnosis of diseases such as cancer.
What are the uses of IHC
Define cell types in tumours
Cell types in inflammatory cells
Identify infectious pathogens
Prognostic indicators
Predicative indicators in targeted therapy
What two ways to expose the antigen
Common methods include using heat or enzymatic digestion to enhance antigen retrieval for better staining.
Direct IHC
A method where the primary antibody is directly conjugated to a detectable marker, allowing for immediate visualization of antigen-antibody binding.
Indirect IHC
A technique where an unlabeled primary antibody binds to the target antigen, followed by a labelled secondary antibody that binds to the primary antibody, amplifying the signal for improved visualization.
What is the process of IHC
Fixation
Take to water
Antigen retrieval/Wash
Block/wash
Primary antibody/wash
Detection system/wash
Chromagen/wash
Counterstain wash
Quality control
What is the purpose of the positive controls
confirming the reliability of the assay results to validate the IHC process
contains relevant tissue antigen
confirms antibody is working
low expression
What is the purpose of negative controls
Not routinely used ely
Detects non-specific interactions
Known to not contain target antigen
Name the positive controls used in IHC labs
Positive
Beta catenin
Melan-A
Negative
What is the importance of fixation in IHC
IHC secondary investigation
Fixation is optimised for routine H&E
Fixation alteration can affect IHC and cause
Can lead to antigens being in other cellular compartments that is not expected e.g. oestrogen receptor can be seen on the outside of the nucleus in poorly fixed breast tissue.
If inadequately fixed can lead alterations in architecture and in highly cellular tissue can lead to specimen being unusable to IHC.
Ideal fixative: preserve morphology, preserve antigen immunoreactivity, prevent antigen extraction during IHC and not interfere with antigen antibody interactions
What is antigen retrival
The process of unmasking antigens in paraffin-embedded tissue sections to enhance antibody binding during immunohistochemistry.
What are the two types of antigen retrival
Enzyme digestion
Heat-mediated antigen retrieval (HMAR)
What are three enzymes seen in enzyme digestion
Trypsin: most common. It removes the cross-links as well as aiding antigenic precursors by digesting protein aggregates which can block access to antigens.
Chymotrypsin: slower agent, many commercial agents use a combined chymotrypsis and trypsin component.
Protease: ready-made for commercial used on automated stainers
How and why are enzyme degestion is used
Selectively breaking the protein links to reveal antigen epitopes without disrupting the protein structure.
Water bath at 37 degrees in a controlled manner
What are the advantages and disadvantages of enzyme digestion
Advantages
Only way to demonstrate some epitopes e.g. renal
Disadvantages
Has to be expertly controlled
Can destroy some epitopes
What is monoclonal antibodies
Derived from a single clone of B
cellsBind to single epitope—highly
specificHigher production times and cost
due to complex manufacturing
processesCommonly used in precision-
focused research applications like
diagnostic assays (ELISA, western
blot, etc.), therapeutics (e.g.,
targeted cancer therapies
What is monoclonal advantages and disadvantages
ADVANTAGES
Precise, improves effectiveness and reduces side effects
No batch to batch or lot to lot variation
Inexpensive to produce
DISADVANTAGES
Targeted epitope must survive fixation
Target epitope must be unique to one antigen cross reactivity cannot be removed
What is polyclonal antibodies
Derived from multiple clones of B
cellsRecognize multiple epitopes—
broader specificityVersatile and widely employed in
various research applicationsQuicker and more cost-effective to
produceCommonly used in research
applications where broad
specificity is needed like
immunohistochemistry (IHC),
immunofluorescence (IF), Western
blot, and early diagnostic tests
What is polyclonal advantages and disadvantages
ADVANTAGES
Less batch to batch variation than with larger animals
Recognizes more than one epitope on an antigen
DISADVANTAGES
Recognises more than one epitope on an antigen
Cross reaction
What are the advantages and disadvantages of DAKO (automated IHC)
ADVANTAGES
Complete kit
Ready-to-use reagents
Increased sensitivity
Faster than other techniques
No wastage
Reduction in operator error
Elimination of endogenous biotin
Can be used with automation
DISADVANTAGES
COST!! Approx £800 per kit
What are chromagens
Chemical compounds Interacts with the final antibody-antigen complex to produce a visualised colour
commonly used in immunohistochemistry.
Horseradish peroxidase converts DAB (3,3-diaminobenzidine)- To brown
Alkaline phosphatase converts AEC (3-amino-9-ethyl carbazole)- To red
Liver panel
PAS/DPAS, reticulin, orcein, perls
renal panel
Mehtenanime silver, EVG, PAS
Special stains
regressive staining vs progressive staining
Progressive staining refers to techniques where staining increases over time
while regressive staining involves removing excess stains to achieve the desired visualization of specific cellular components.
What are the types of speical stains
Histochemical
Utilises a true chemical reaction as if it would happen in a test tube e.g. Periodic Acid Schiffs (PAS) for demonstration of carbohydrates
Lysochrome
Staining of neutral lipids/fats
Elective solubility- hydrophobic nature of the lipid allows the dye to penetrate the lipid
Impregnation
Deposition of silver in a tissue section
Argyrophil/Argentaffin/Ion exchange
Injection
Introduction of coloured compounds into tissue to highlight structures
Fluorochrome
Adding a fluorochrome with the tissue and then visualised under fluorescent microscope e.g. amyloid
Trapping agents
Prevents the dye from escaping once entered e.g. Gram stain
what are the disadvantages of using automated staining
Cannot adapt stain
Staff being de-skilled
Cost of capital purchase
Preservatives in staining reagents limits sensitivity
Kits can go to waste
Limited number of stains
what are the advantages of using automated staining
Closed system
Reproducibility
Amount of slides
Multiple stains run at the same time
Free up lab staff time
Standard protocols
What is the advantage of using hand staining
Adaptability to changes
Cheaper
Easy to train staff on singular methods
Controlled by eye
What is the disadvantage of using hand staining
Level of interpretation
Variability
In-house solution cost
Labour intensive
Exposure to hazardous chemicals
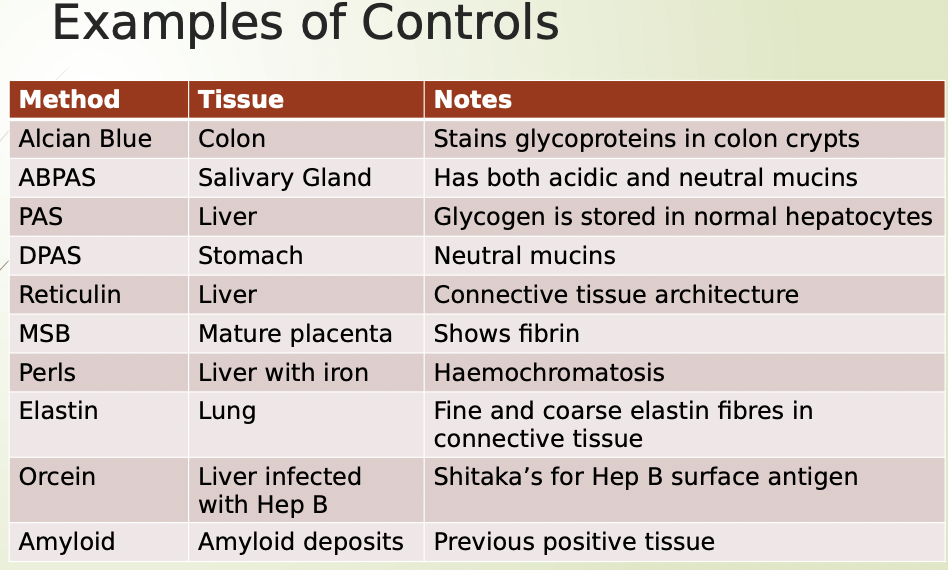
What are some of the controls for special stains
PAS- positive for fungi
Acid fast bacilli in ABPAS
Mycobacterium positive in Ziell Nielson
Name some more examples of special stain controls