Section E - Carbohydrate Structure and Metabolism
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Olson
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are the four major pathways of Glucose utilization?
Synthesis of Structural Polymers (yields extracellular matrix and cell wall polysaccharides)
Oxidation via PPP (yields Ribose 5-Phosphate)
Storage (yields Glycogen, Starch, and Sucrose)
Oxidation via Glycolysis (yields Pyruvate)
What is Glycolysis?
What are the major inputs? Outputs?
Glycolysis is the central pathway of glucose intermediary metabolism
Inputs — 6 carbon carbohydrates, i.e. Glucose
Outputs — 2 Pyruvates or Lactates (3 carbons)
What does the term ‘Intermediary Metabolism’ mean?
Term used to describe pathways that are used for (1) synthesis of molecules needed by our cells or (2) degradation of molecules for ATP synthesis or elimination from the cell (anabolic and catabolic pathways, respectively)
These pathways go through a series of Intermediates (hence the name)
What is the committed step in a metabolic pathway?
First reaction in which the product has no other fate except to proceed through the pathway towards a certain product outcome
What are the two phases of Glycolysis?
Preparatory Phase
Payoff Phase
What happens during the Preparatory Phase of Glycolysis?
ATP is consumed
delta G of the intermediates increases (more +)
Hexose (5) carbon chains are turned into Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
What happens during the Payoff Phase of Glycolysis?
Energy is conserved as 2 ATP and 2 NADH
Production of 2 Pyruvates (or Lactates)
What are the three main noteworthy chemical transformations that occur during Glycolysis?
Degradation of Glucose carbon skeleton (glucose oxid.) —> Pyruvate
Phosphorylation of ADP by compounds with high phosphoryl group transfer potential —> ATP
Transfer of a Hydride ion (H-) to NAD+ (red. via e- from Glucose oxid.) —> NADH
What is the overall reaction equation for Glycolysis?
Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + Pi —> 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O
Which two thermodynamic processes can Glycolysis be divided into?
Conversion of Glucose —> Pyruvate (EXERGONIC)
Glucose + 2 NAD+ —> 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2H+
delta G’˚1 = -146 kJ/mol
Formation of ATP from ADP and Pi (ENDERGONIC)
2 ADP + 2 Pi —> 2 ATP + 2 H2O
delta G’˚2 = +62.0 kJ/mol
What gives us the Overall Standard Free-Energy Change (∆G′°Sum) of Glycolysis?
The sum of the two thermodynamic processes that Glycolysis is divided into (Conversion of Glucose to Pyruvate and Formation of ATP from ADP and Pi)
∆G′°Sum = -85kJ/mol
Is Glycolysis reversible or irreversible under standard, cellular conditions?
Irreversible, because of an overall negative free energy change (∆G′°Sum < 0)
What two ways are used to extract energy from Pyruvate?
Aerobic Processes that lead to formation of CO2
Oxid. rxns in the Citric Acid Cycle
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Anaerobic Processes
Reduction to Lactate
What other way can energy be used from Pyruvate, excluding extracting the energy through Aerobic or Anaerobic processes?
Pyruvate can provide the carbon skeleton for Alanine Synthesis or Fatty Acid Synthesis
What is the first step in Glucose metabolism?
Hexokinase phosphorylates at Glucose C6, yielding Glucose 6-Phosphate
What is the phosphate donor in the first step of Glucose Metabolism in the cell?
What is required for Hexokinase activity during this step?
Is this first step reversible or irreversible under intracellular conditions?
Phosphate donor for the first step of Glucose Metabolism is ATP
Hexokinase requires Mg2+ for activity
This first step is irreversible under intracellular conditions
What is Glucose 6-phosphate?
When is it produced?
High energy compound that cannot be transported out of the cell
Produced during the first step of Glucose Metabolism
What is the second step of Glucose Metabolism?
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) catalyzes the transfer of a Phosphoryl group from ATP to Fructose 6-Phosphate, yielding Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate
Why is the second step of Glucose Metabolism so important?
Is this second step reversible or irreversible under cellular conditions?
It is the first “committed” step in Glycolysis, as well as the Rate-Limiting Step (slowest step of the pathway)
Irreversible
What causes Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) activity to increase?
Activity increases when either (1) ATP supply is depleted or (2) ADP and AMP accumulate
What is Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate?
How is it made? Activated?
Potent allosteric activator compound
It is made by the bifunctional enzyme PFK-2
It is activated by hormone signals indicating a need for energy
What is Citrate?
Key intermediate in the Aerobic Oxid. of Pyruvate, FAs, and AAs
What effect does Citrate have on PFK-1?
Citrate allosterically regulates PFK-1
High [Citrate] increases the inhibitory effect of ATP
It serves as an intracellular signal that the cell has its needs met for energy-yielding metabolism (through oxid. of fats and proteins)
What happens during the Payoff Phase of Glycolysis?
Each of the two molecules of Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate undergo oxidation at C1
Energy from this oxidation rxn is conserved as 1 NADH and 2 ATP per triose phosphate oxidized
What is Substrate-Level Phosphorylation?
Formation of ATP by phosphoryl group transfer from a substrate; it is DIFFERENT than Respiration-Linked Phosphorylation
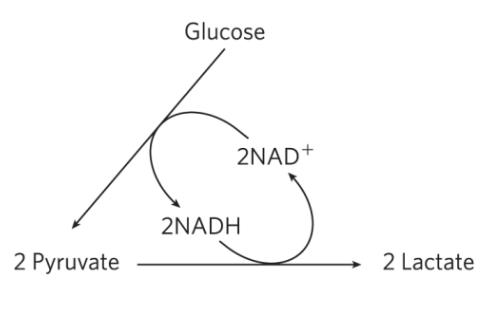
How is NAD+ regenerated?
Why is it important this molecule is regenerated?
Pyruvate is reduced into Lactate, regenerating 2 NAD+
We need NAD+ in order for Glycolysis to occur as Glycolysis converts 2 NAD+ to 2 NADH
What is Pyruvate Kinase?
What does it require to function?
Enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the phosphoryl group from Phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, yielding Pyruvate
Requires K+ and either Mg2+ or Mn2+
Where do we get other monosaccharides from in our diet?
Lactose in dairy —> Galactose and Glucose
Sucrose —> Fructose and Glucose
Fruits and Vegetables —> D-Mannose
What is Galactose?
What enzyme phosphorylates Galactose?
Galactose is a product of Lactose hydrolysis and is an important component in the infant diet
Galactose is phosphorylated at C1 by Galactokinase
What is Galactokinase?
What is the reaction equation for Galactokinase function?
Galactokinase is the enzyme responsible for phosphorylating Galactose at the C1 by using ATP
Galactose + ATP —(Mg2+)—> Galactose 1-Phosphate + ADP
How does Galactose convert into Glucose 1-Phosphate?
Via conversion through UDP-galactose and UDP-glucose intermediates
What causes Galactosemia Diseases?
How are they treated?
Galactosemia diseases are caused by a genetic defect in the enzymes of the pathway where Galactose is converted to Glucose 1-Phosphate
They are typically treated by carefully controlling dietary Galactose
How can Fructose and Mannose be used for Glycolysis?
They can be phosphorylated and funneled into Glycolysis
How is Fructose phosphorylated in the Small Intestine and Liver?
Small Intestine: via Hexokinase
Fructose + ATP —(Mg2+)—> Fructose 6-Phosphate + ADP
Liver: via Fructose 1-Phosphate Aldose
Fructose + ATP —(Mg2+)—> Fructose 1-Phosphate + ADP
How does Fructose 1-Phosphate Aldolase work?
Cleaves Fructose 1-Phosphate into Dihydroxyacetone and Glyceraldehyde
What happens to the products of Fructose 1-Phosphate hydrolysis?
They are entered into Glycolysis as Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
What is the main function of Triose Phosphate Isomerase?
Triose Kinase?
Triose Phosphate Isomerase — converts Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate into Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
Triose Kinase — phosphorylates Glyceraldehyde into Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate using ATP
How is Mannose used for Glycolysis?
Mannose is converted into Fructose for Glycolysis
What does Hexokinase do to Mannose?
Phosphohexose Isomerase?
Hexokinase — phosphorylates Mannose at C6
Mannose + ATP —(Mg2+)—> Mannose 6-Phosphate + ADP
Phosphohexose Isomerase — converts Mannose 6-Phosphate into Fructose 6-Phosphate
What are the three catabolic fates of Pyruvate?
NADH must be recycled to regenerate NAD+
Under aerobic conditions, Pyruvate is oxid. to Acetyl-CoA
Under anaerobic conditions (hypoxia), Pyruvate is red. to Lactate or Ethanol
Which pathway does Glucose 6-Phosphate feed into?
What determines this?
Glucose 6-Phosphate feeds into both Glycolysis and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP)
It is partitioned between both pathways, based on relative conc. of NADP+ and NADPH
What is the main function of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway?
Oxidizes Glucose 6-Phosphate, producing pentose phosphates and NADPH
What is responsible for beginning the oxidative portion of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway again?
The conversion of Pentose Phosphates into Glucose 6-Phosphate
What are some examples of cells and tissues that use the Pentose Phosphate Pathway?
Rapidly Dividing Cells — use Ribose 5-Phosphate to make RNA, DNA, and coenzymes
Liver, Adipose, and Lactating Mammary Glands — required NADPH from the PPP to carry out extensive FA synthesis
Liver, Adrenal Glands, and Gonads — require NADPH from the PPP for active synthesis of Cholesterol and Steroid hormones
What is Glycogen?
Polymeric storage form of Glucose in animals, found primarily in the muscle and liver
What does Glycogen breakdown in the muscle provide?
In the liver?
In the muscle — delivers glucose needed for muscle contraction within seconds
In the liver — reservoir for maintaining homeostasis of blood glucose
What is the primer for Glycogen Synthesis?
Glycogenin Dimer
How many glucose residues are located in a Glycogen Beta-Granule?
What linkages exist in the glucose residues?
Why is this important?
12-14 residues in each chain
(alpha1 —> 4) linkage chains and (alpha1 —> 6) linked branches
These linkages are important as they provide many free nonreducing ends
What is the starting molecule for Glycogenesis?
Where is this molecule sourced from?
What is the name for the first reaction this molecule is involved in for Glycogenesis?
Starting molecule is Glucose 6-phosphate
Sourced from Glucose (converted via Hexokinase) or from Lactate (converted by the Liver through Gluconeogenesis)
First step reaction is Phosphoglucomutase Reaction
What happens during the Phosphoglucomutase reaction?
Glucose 6-Phosphate is converted into Glucose 1-Phosphate
What are the steps of Glycogenesis?
COME BACK TO THIS ONE
What is the second step of Glycogenesis?
Formation of UDP-glucose
Glucose 1-Phosphate is converted into UDP-glucose via UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase
Glucose 1-Phosphate + UTP —> UDP-glucose + PPi
What is the main function of UDP-glucose Pyrophosphorylase?
Enzyme that converts Glucose 1-Phosphate into UDP-glucose
What is the main function of UDP-glucose?
Sugar nucleotide that donates the Glucose necessary for Glycogenesis
What are Sugar Nucleotides?
Compounds in which the anomeric carbon of a sugar is activated via attachment to a nucleotide through a phosphate ester linkage
What is the Anomeric Carbon?
Carbon that opens and closes to form the monosaccharide ring structure
What is the main function of Glycogenin?
Protein that serves as a primer to start Glycogenesis