CELLS - cell-cell interactions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what are the three types of cell junctions?
tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions
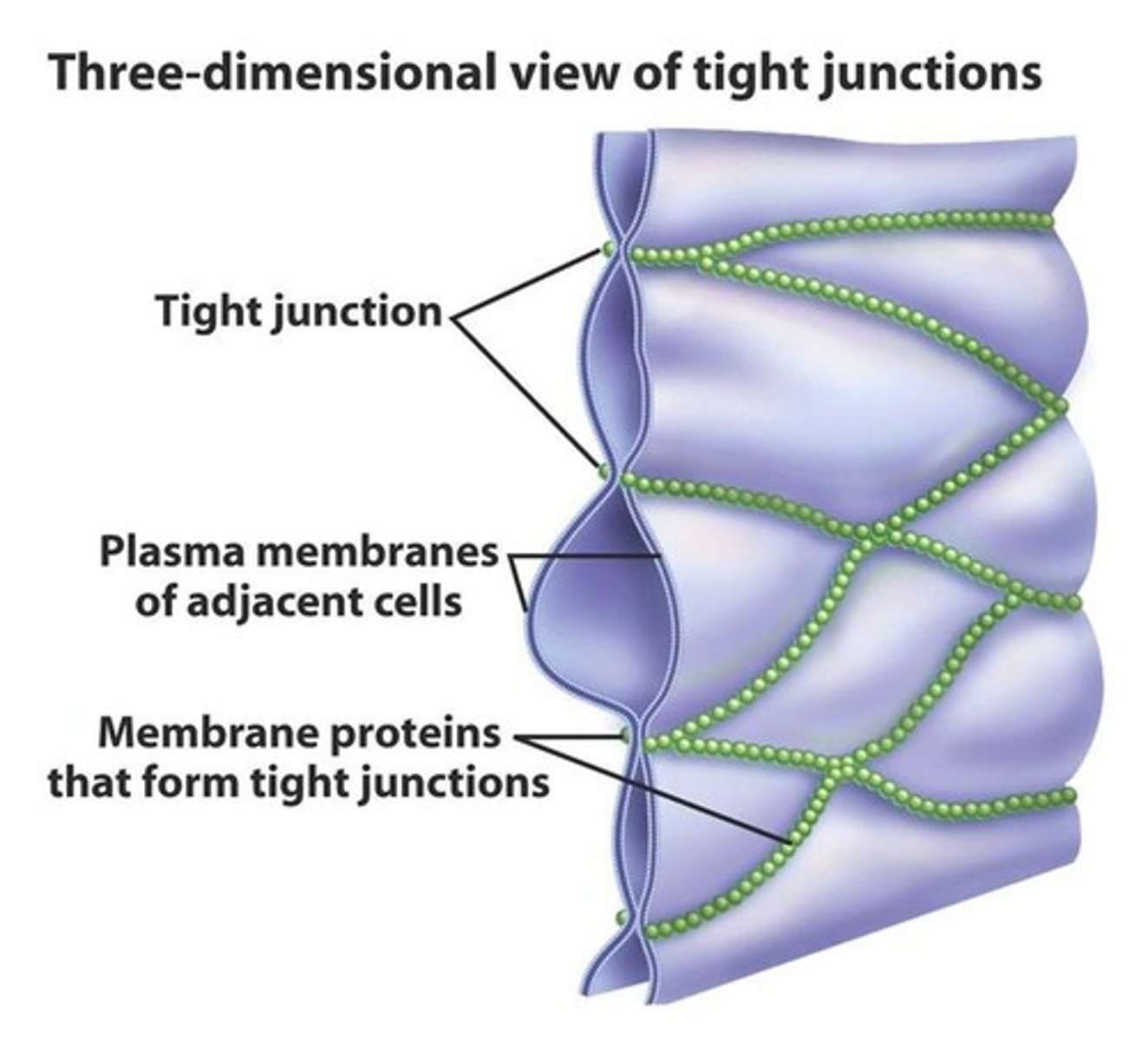
tight junctions
Membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together, preventing leakage of extracellular fluid
desmosomes
Anchoring junctions that prevent cells from being pulled apart
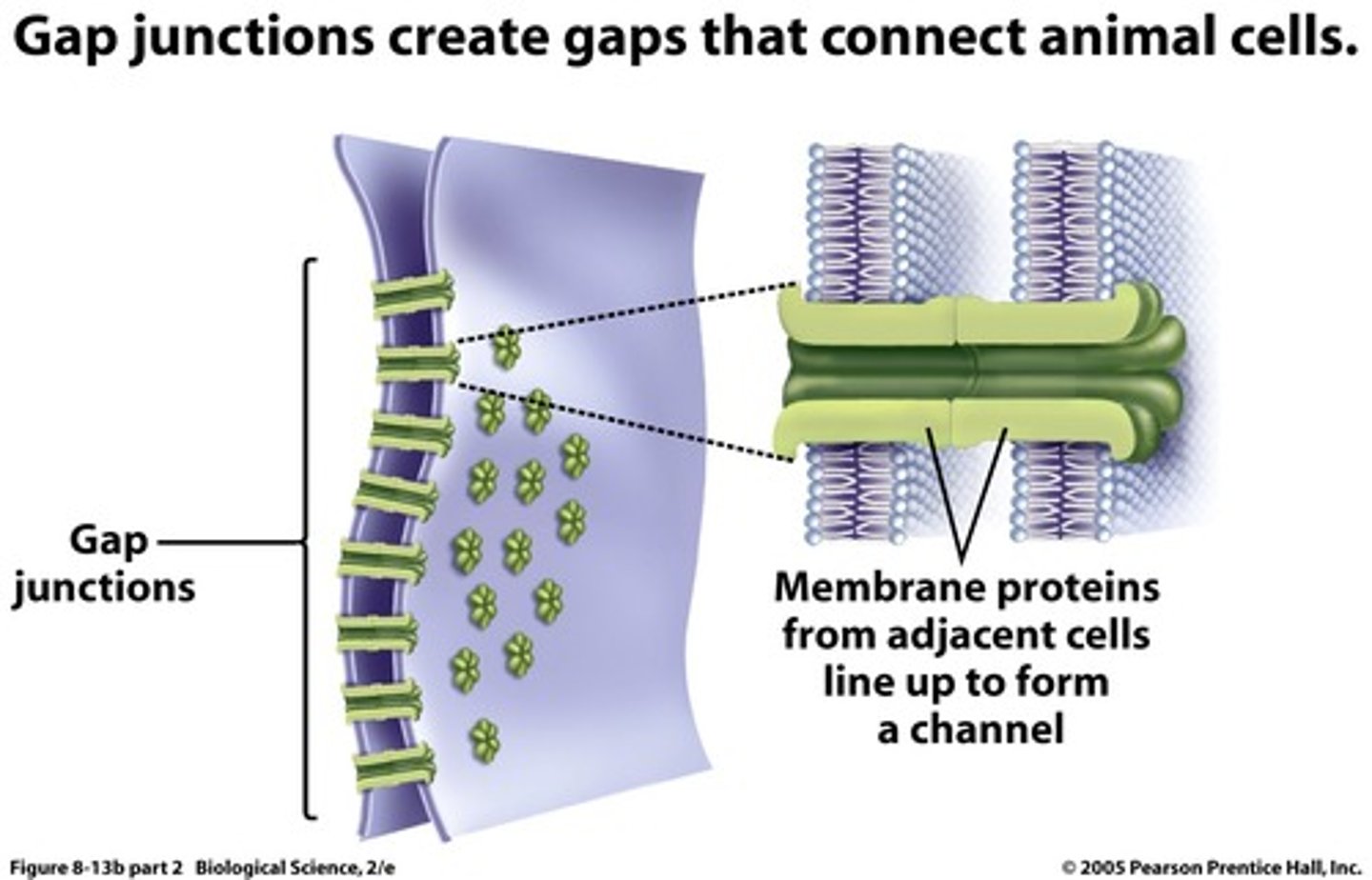
gap junctions
(communicating junctions) provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells
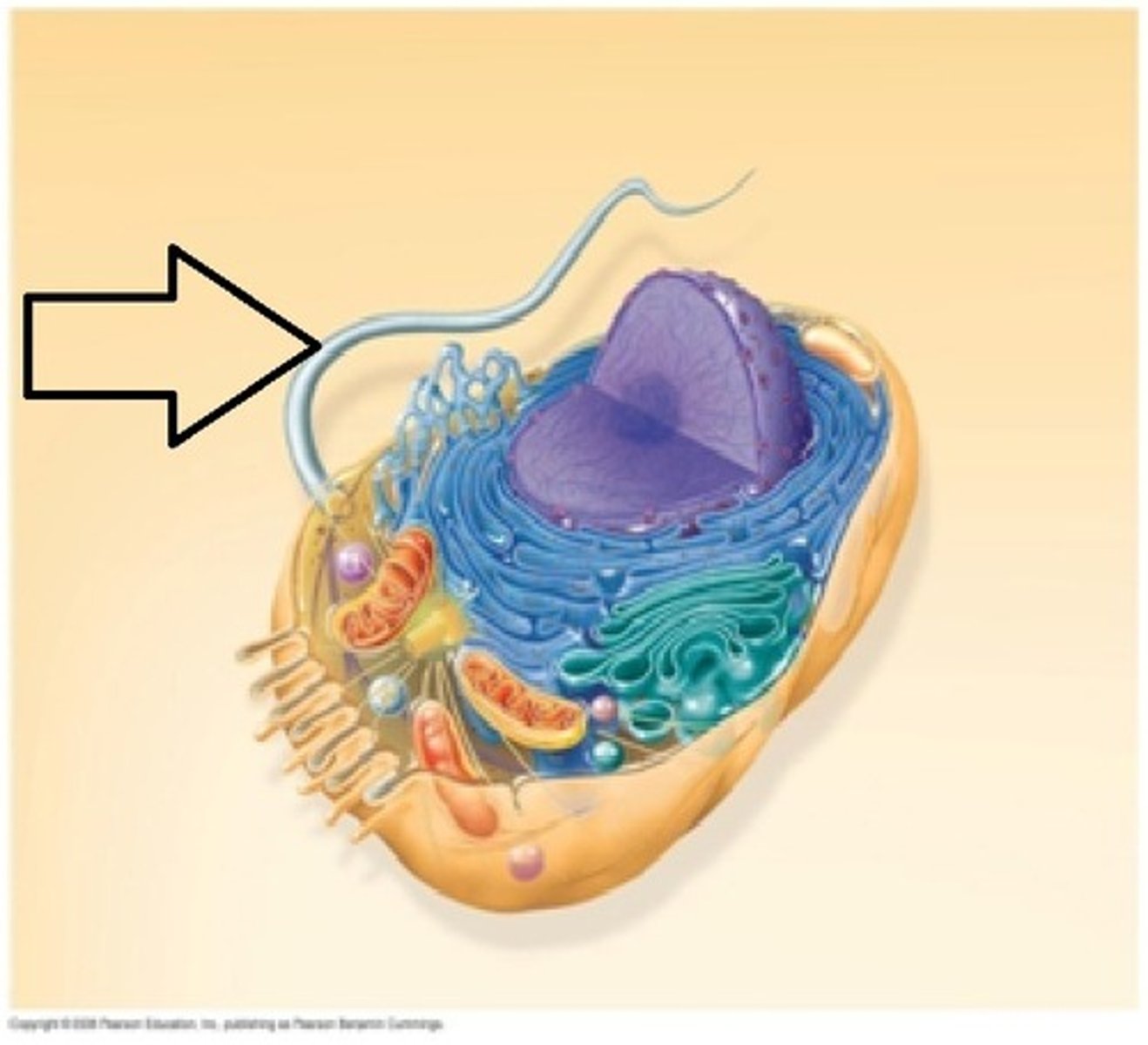
flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility. Many bacteria are flagellated, and sperm are flagellated.
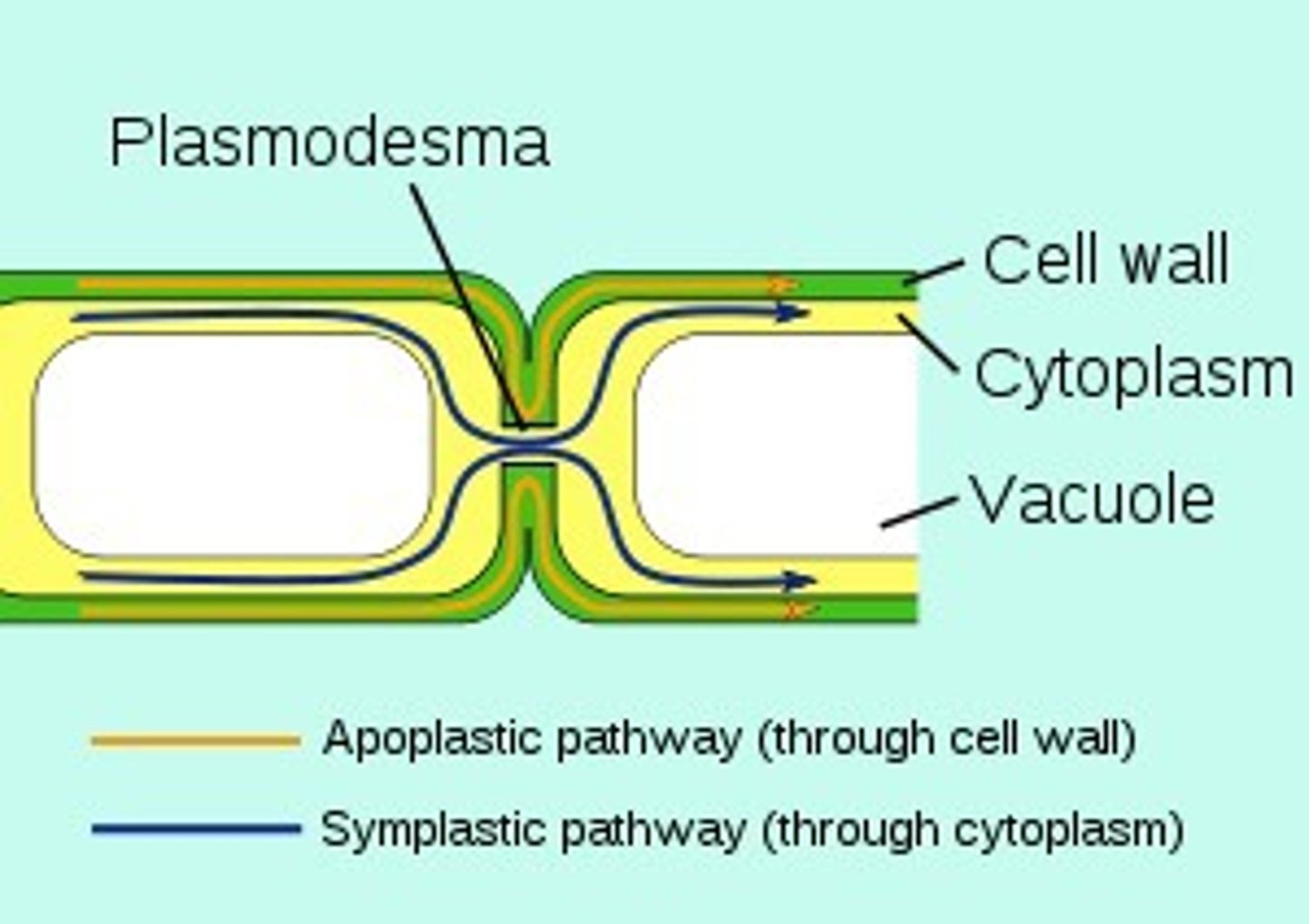
plasmodesma
An open channel in the cell wall of a plant through which strands of cytosol connect from an adjacent cell.
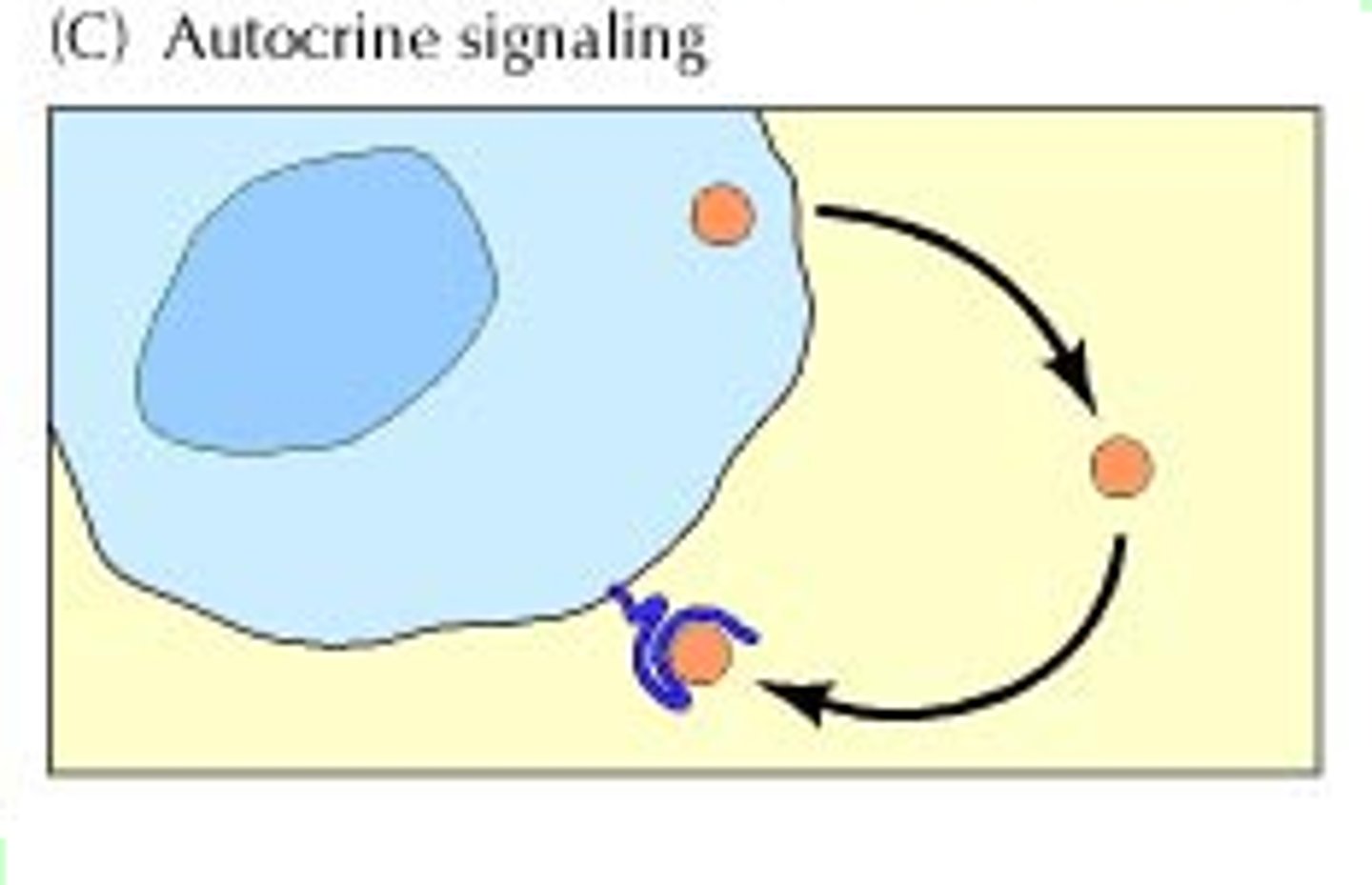
autocrine
term for hormones that act on same cells that secrete them
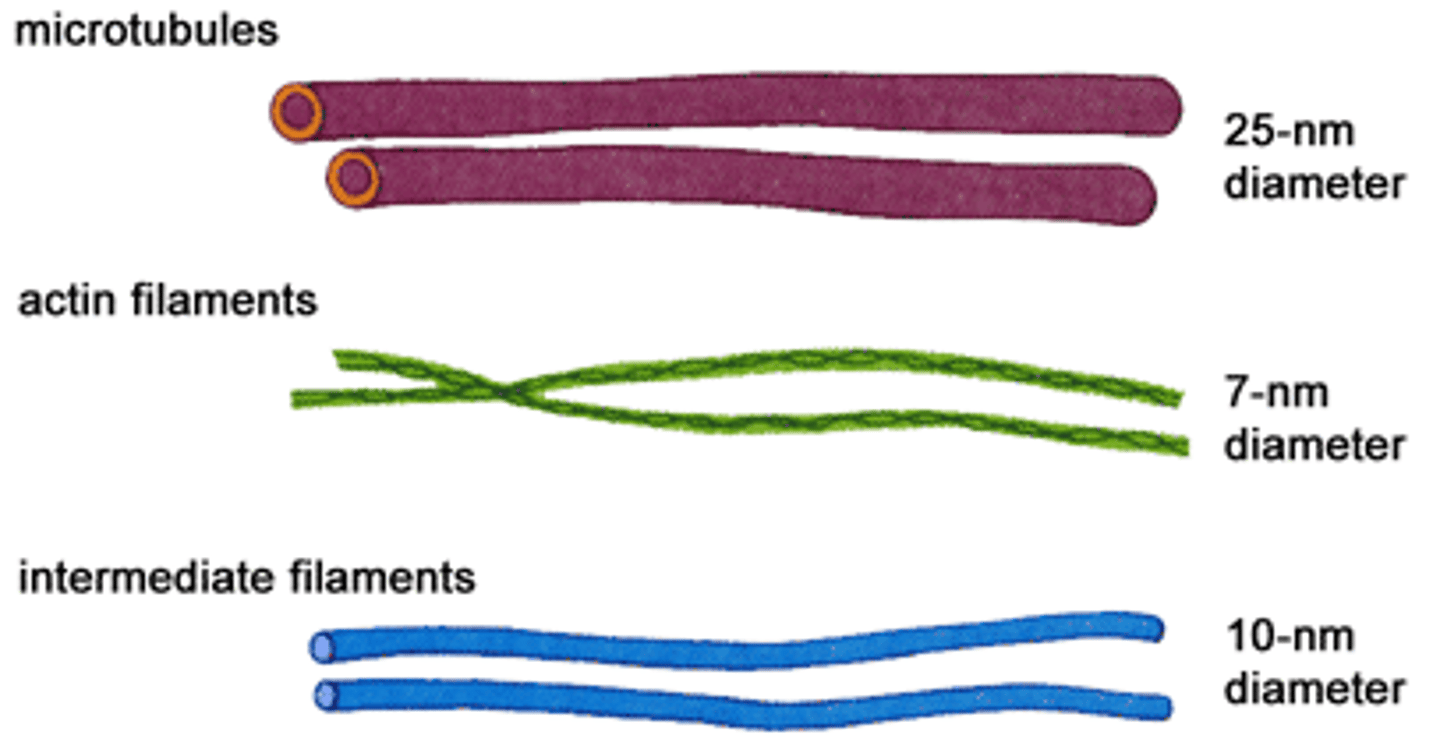
microtubule
A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that makes up part of the cytoskeleton in all eukaryotic cells and is found in cilia and flagella.
microfilament
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
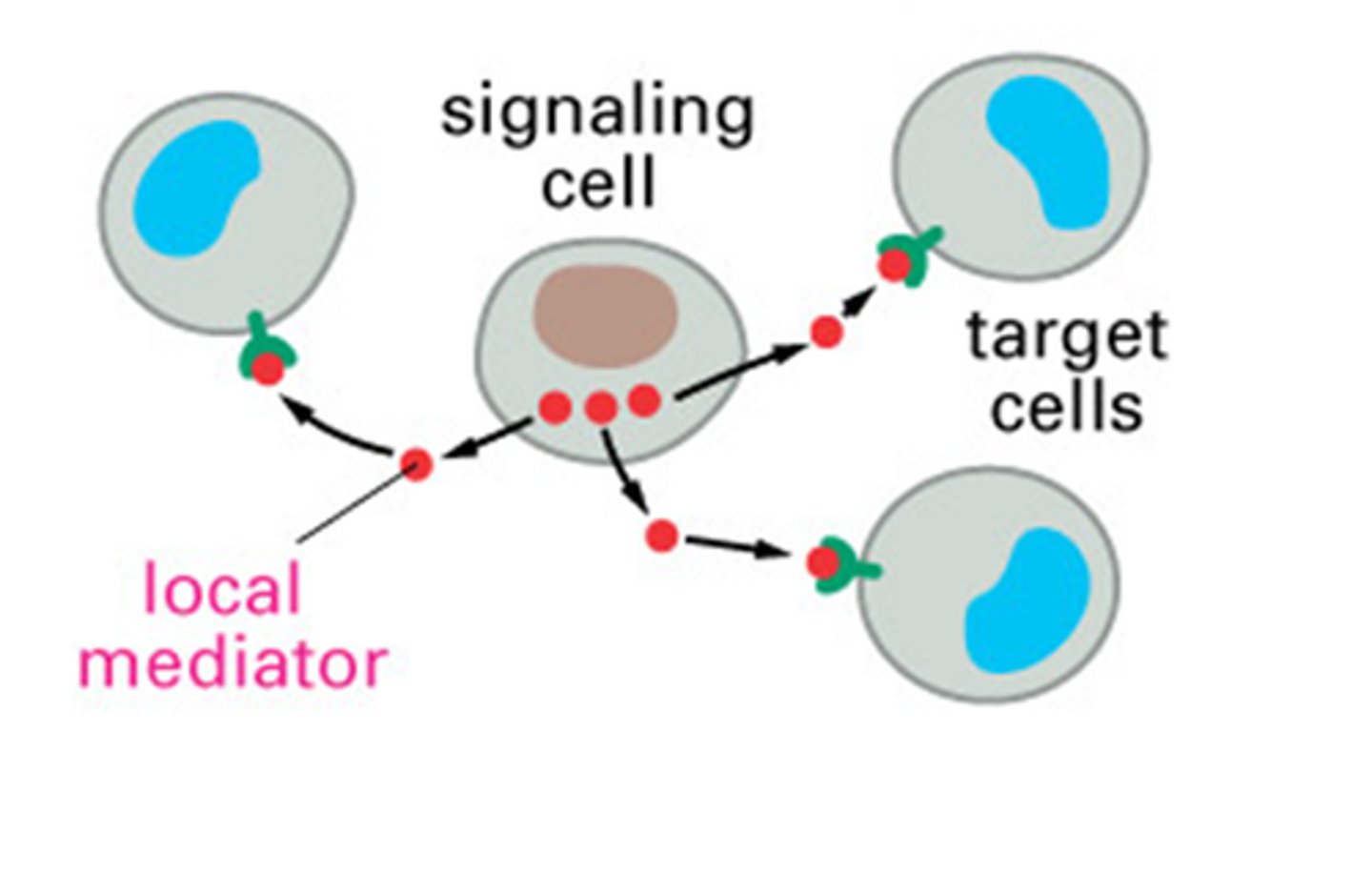
paracrine
Referring to a secreted molecule that acts on a neighboring cell.
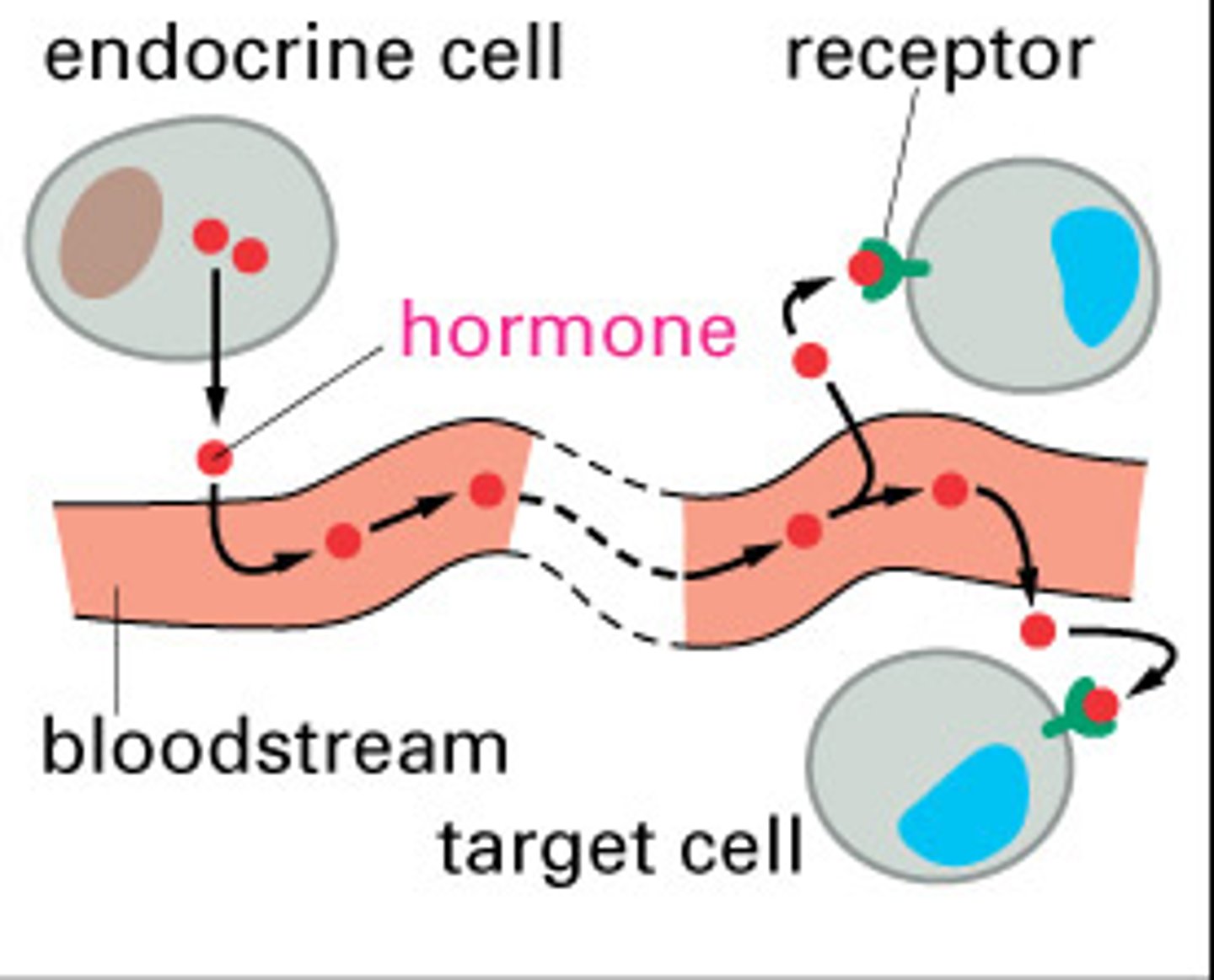
endocrine
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
intermediate filament
A component of the cytoskeleton that includes filaments intermediate in size between microtubules and microfilaments.
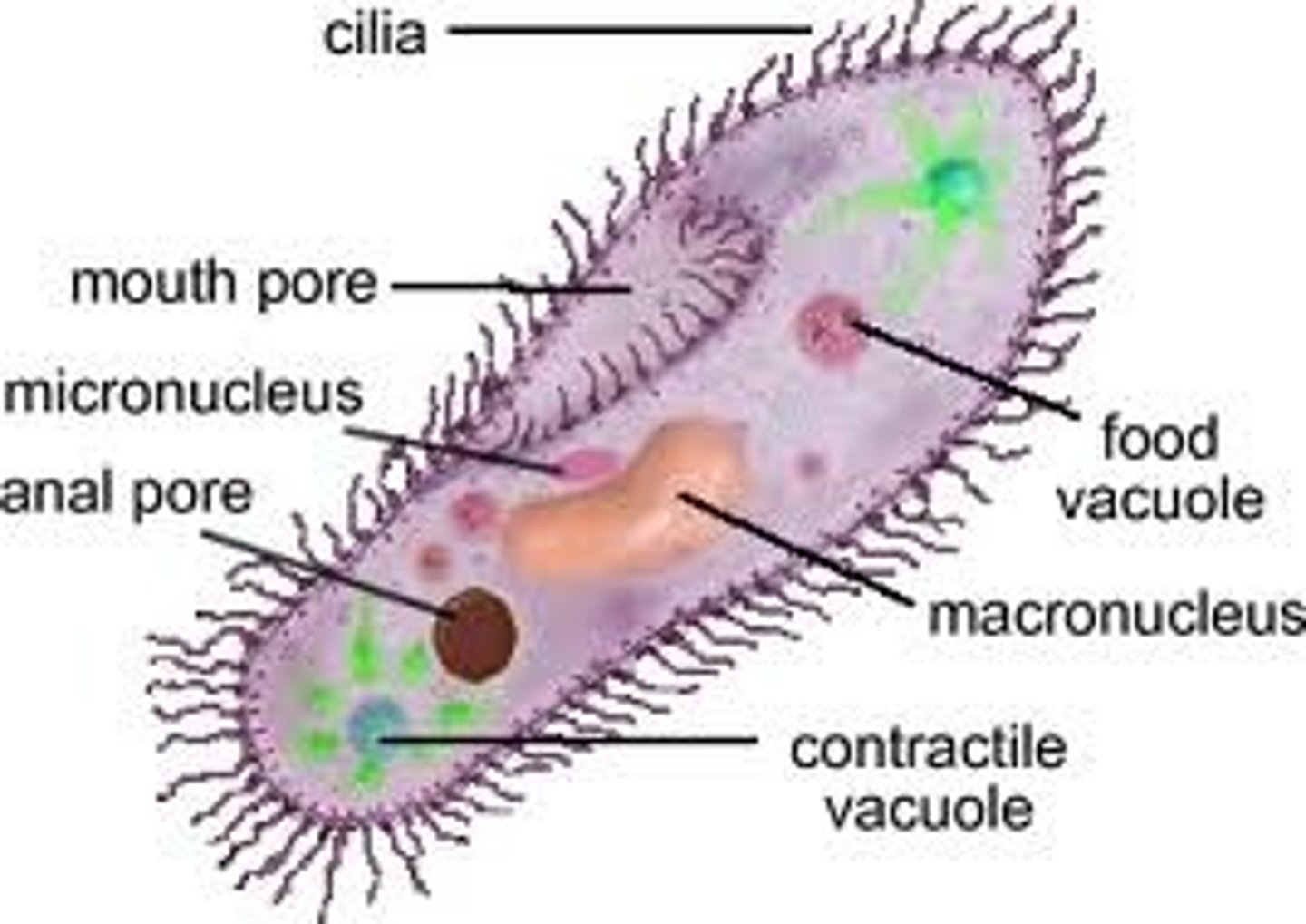
cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion