AP Psychology - Development Psychology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Developmental Psychology
a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span.

Zygote
the fertilized egg; it enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo.
Embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month.
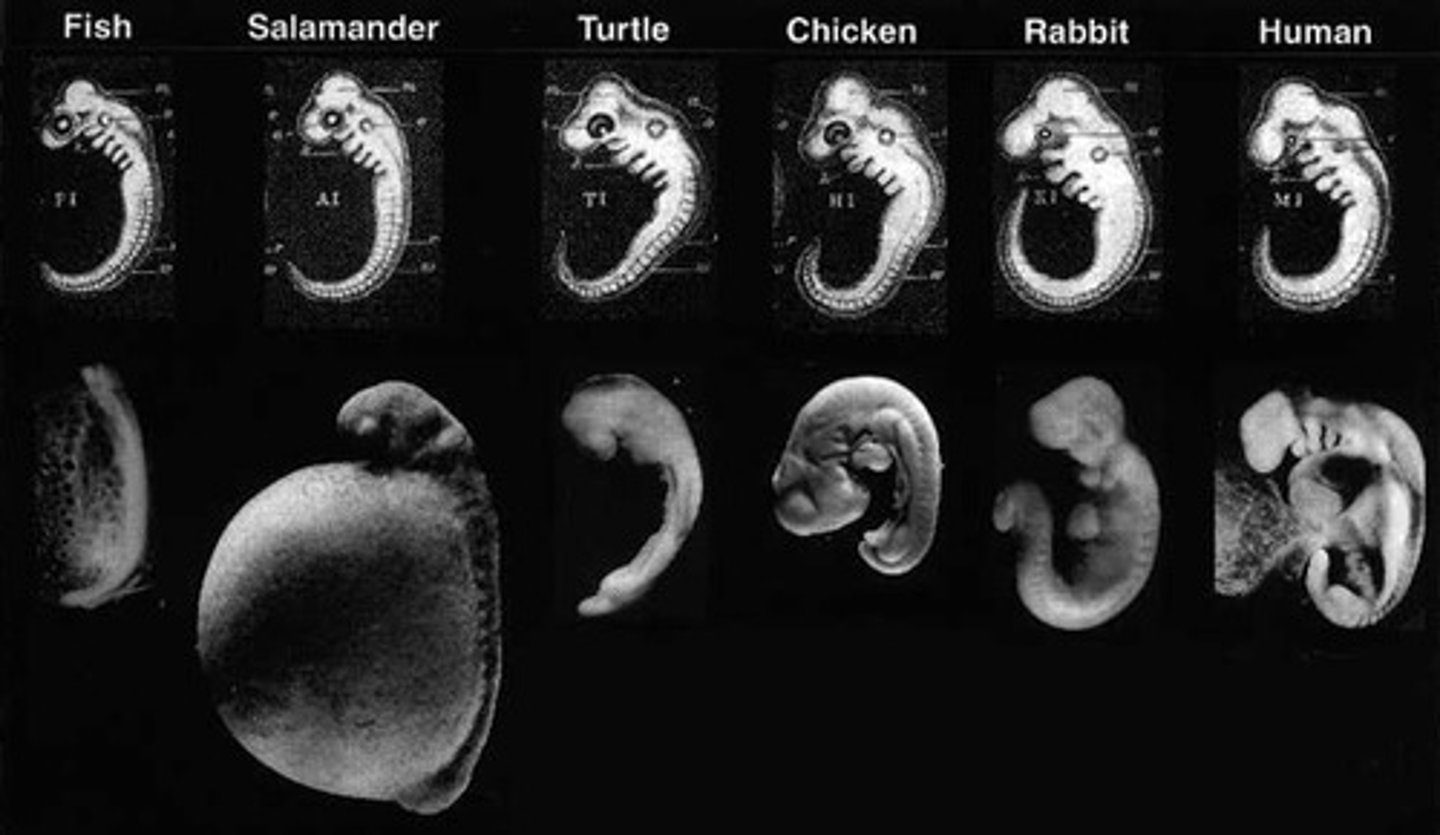
Fetus
the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth.
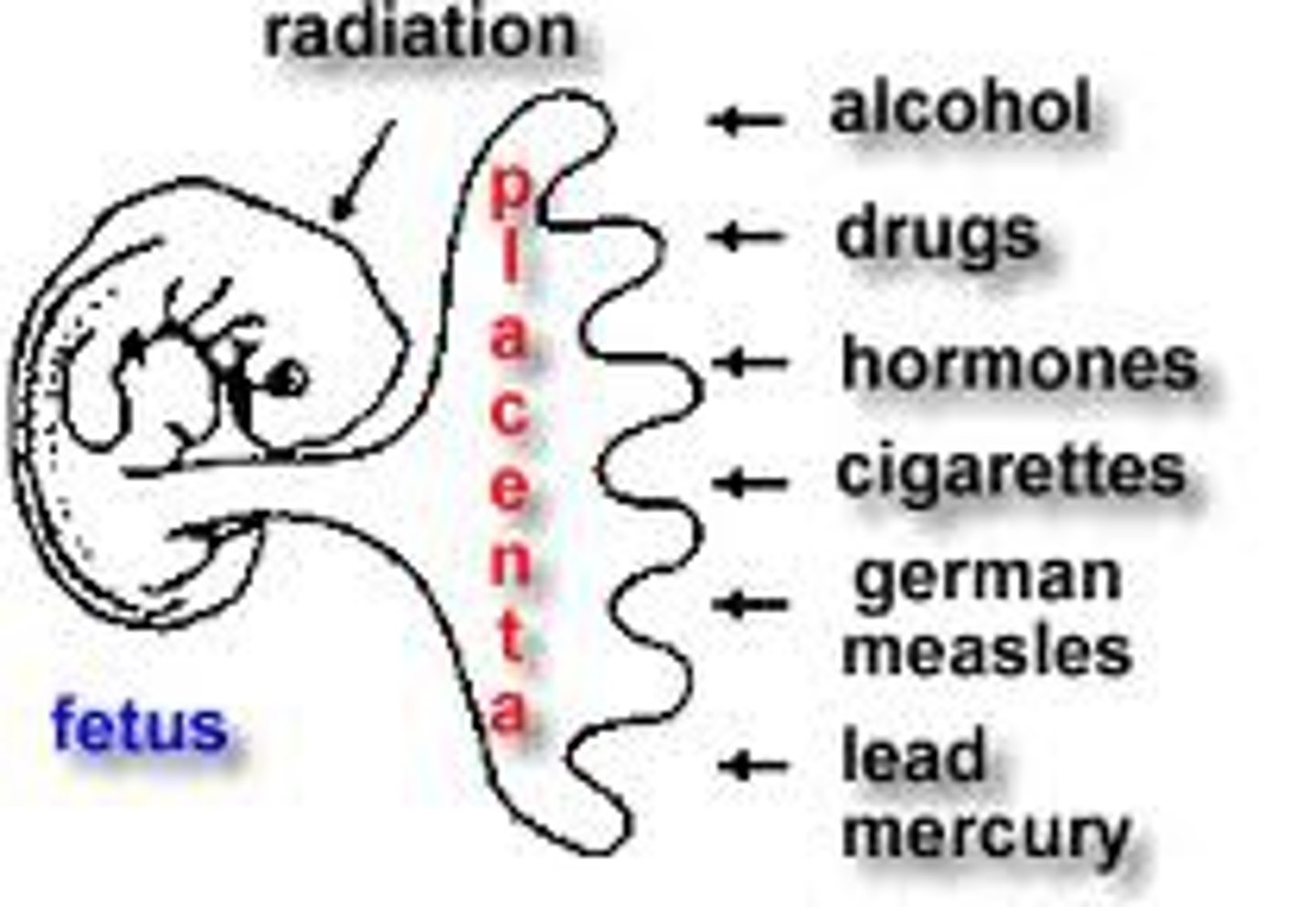
Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm.
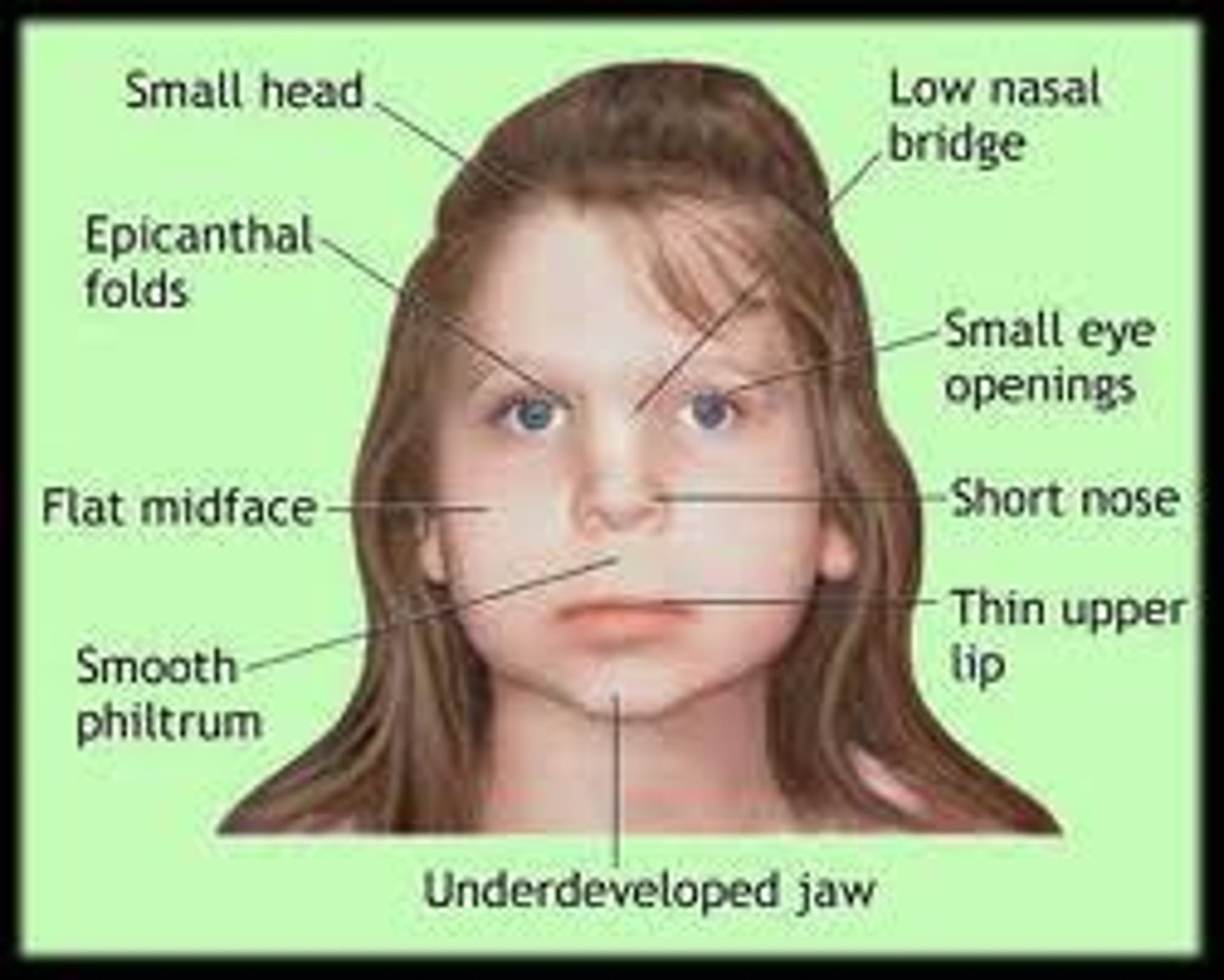
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking. In severe cases, symptoms include noticeable facial misproportions.
Maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience.
Cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating.

Schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information.

Assimilation
interpreting our new experience in terms of our existing schemas.

Accommodation
Development - adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information.

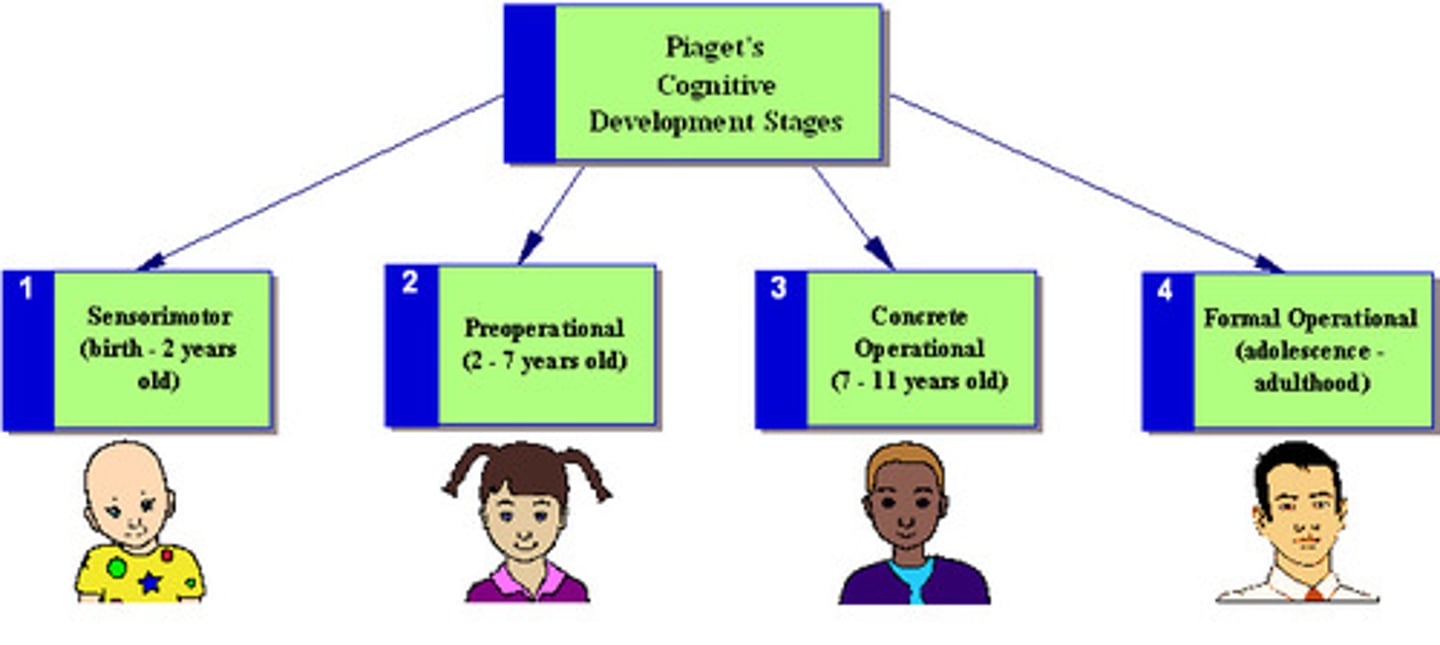
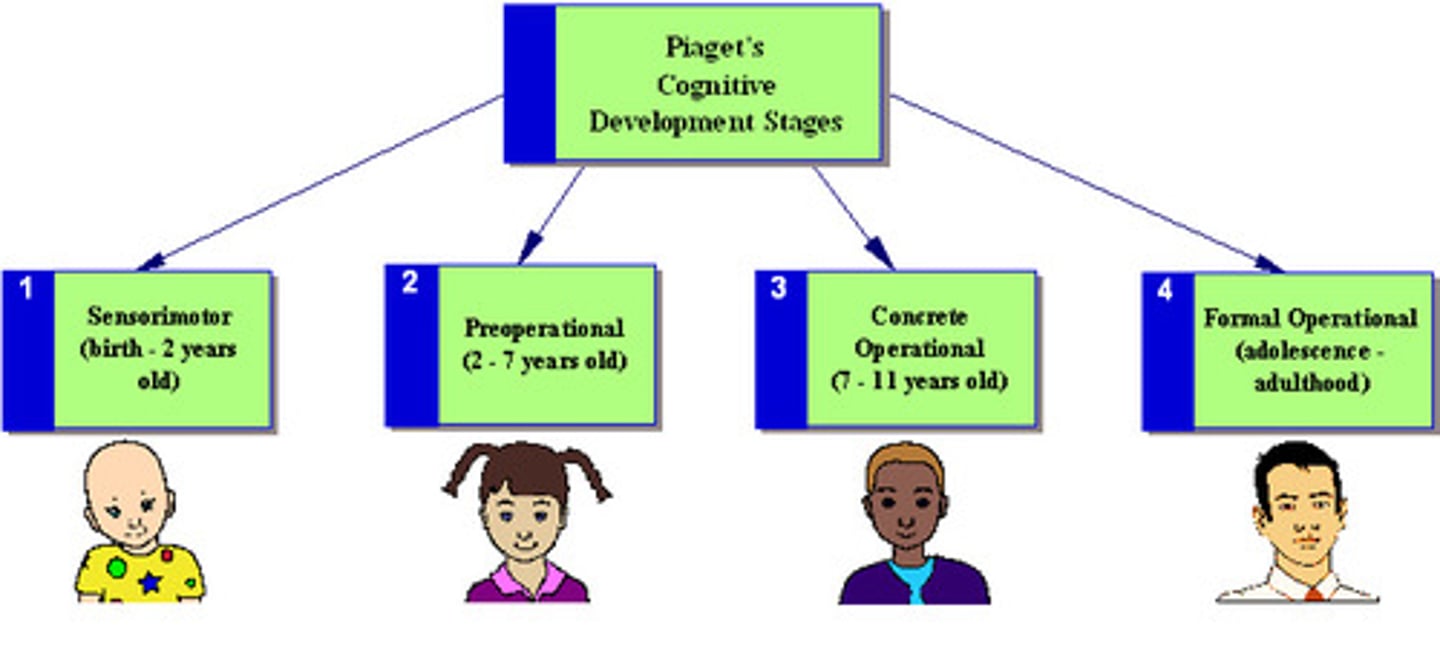
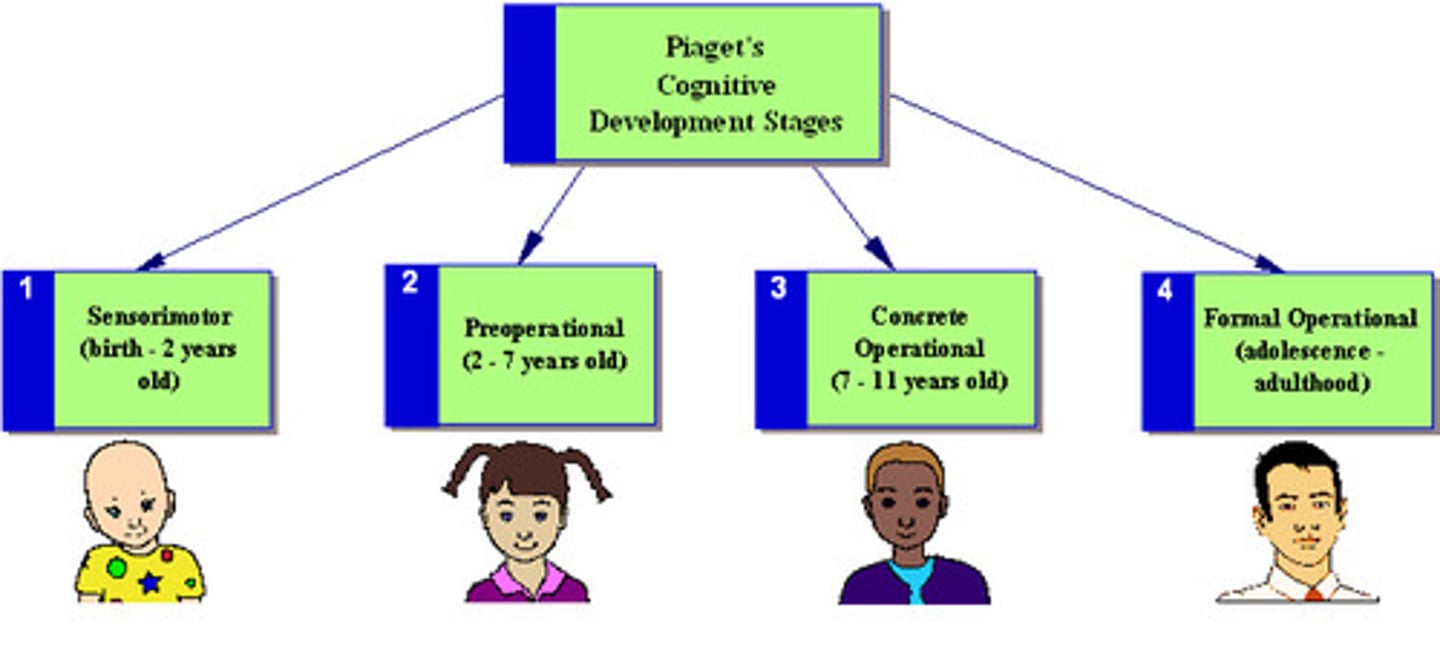
Sensorimotor Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities.
Object Permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived.

Preoperational Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from 2 to about 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic.
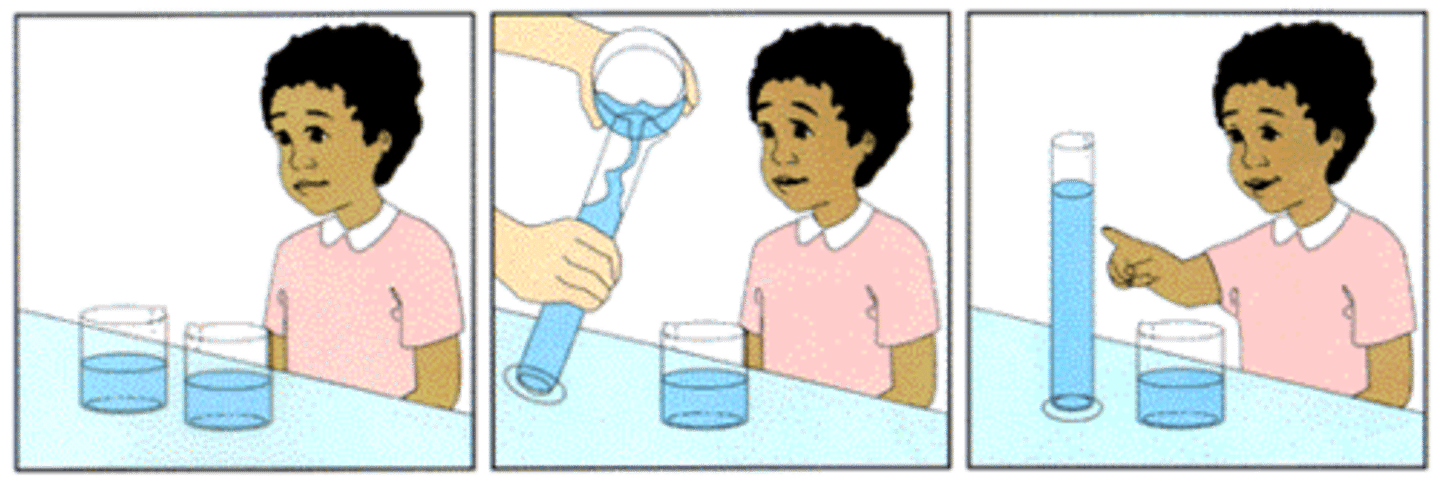
Conservation
the principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects.

Egocentrism
in Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view.
Concrete Operational Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events.
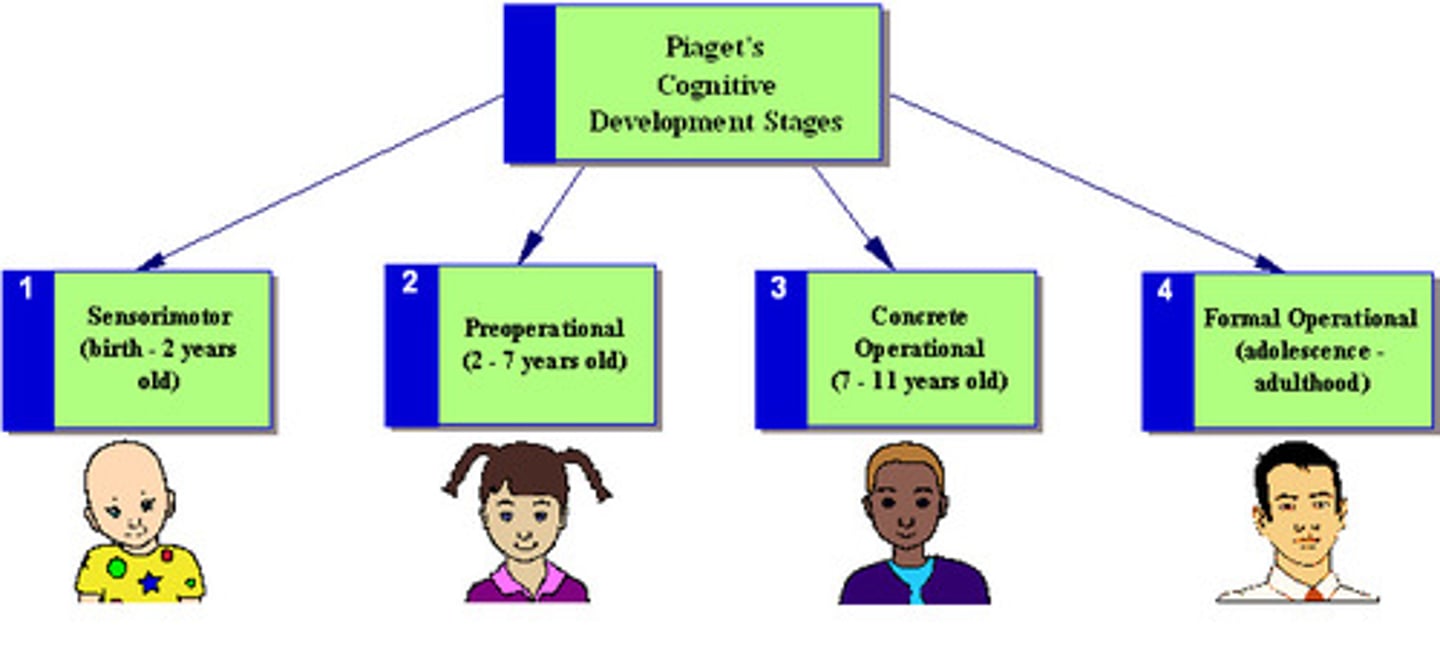
Formal Operational Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts.
Stranger Anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age.
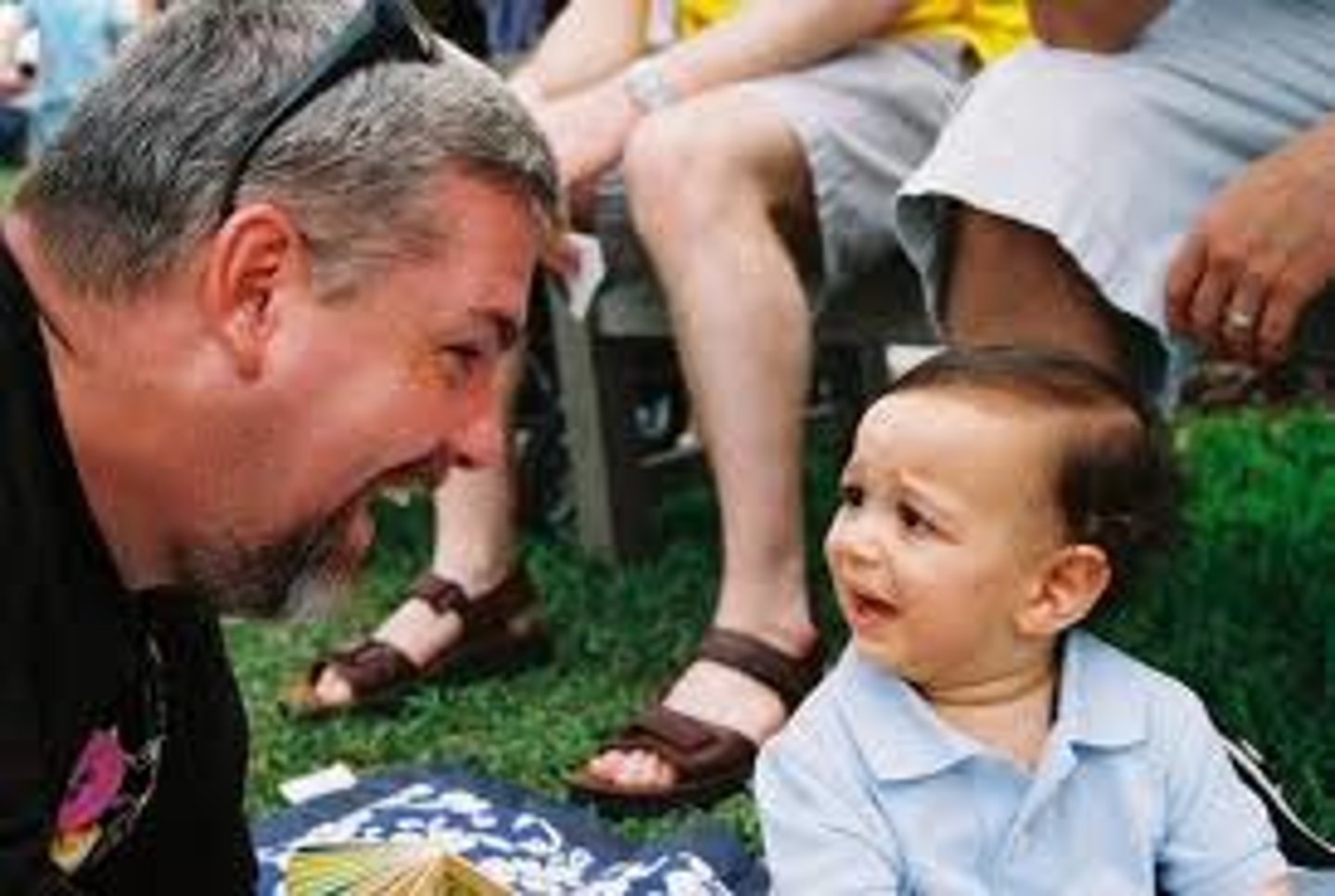

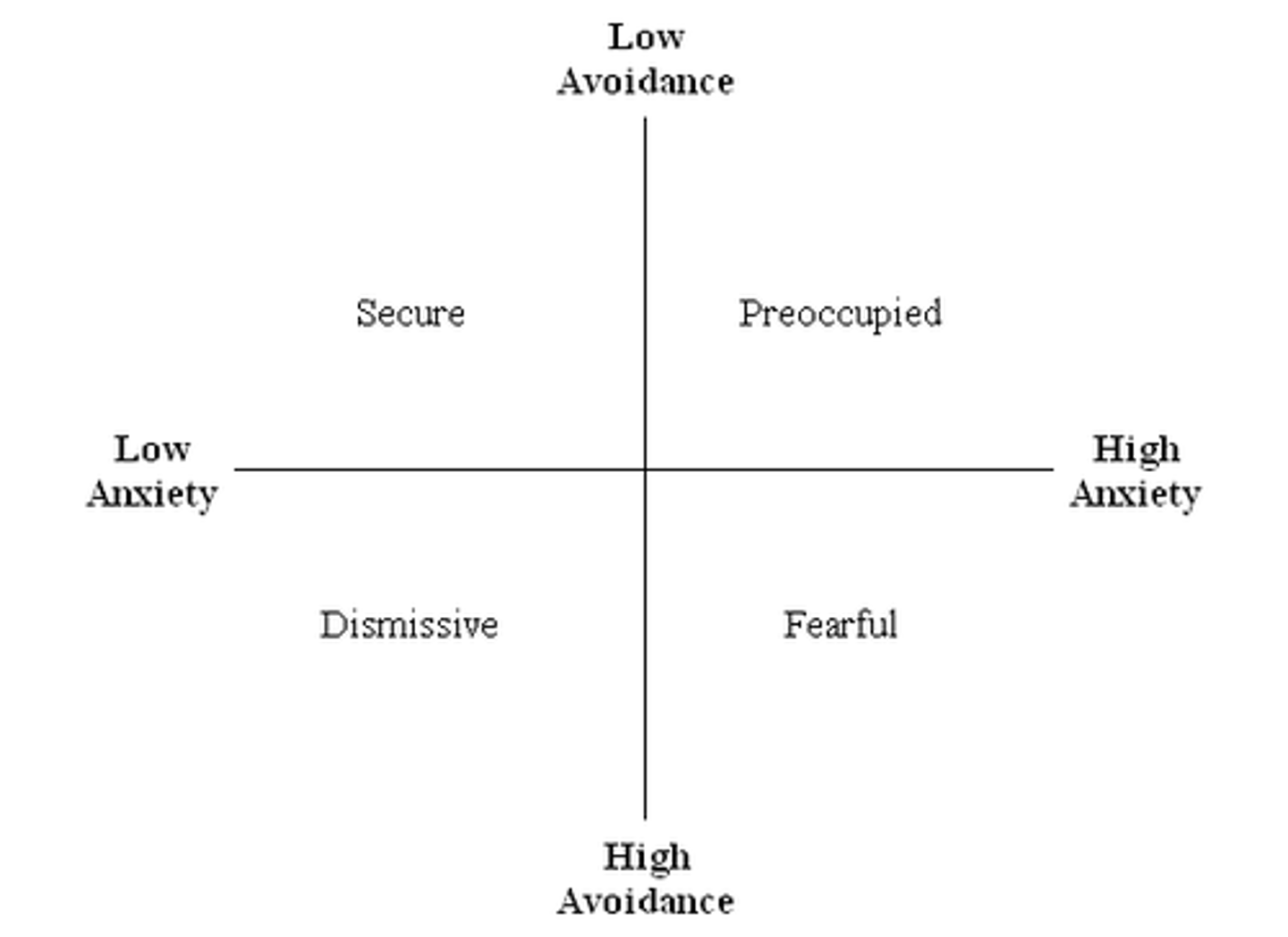
Attachment
an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation.
Critical Period
an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces proper development.
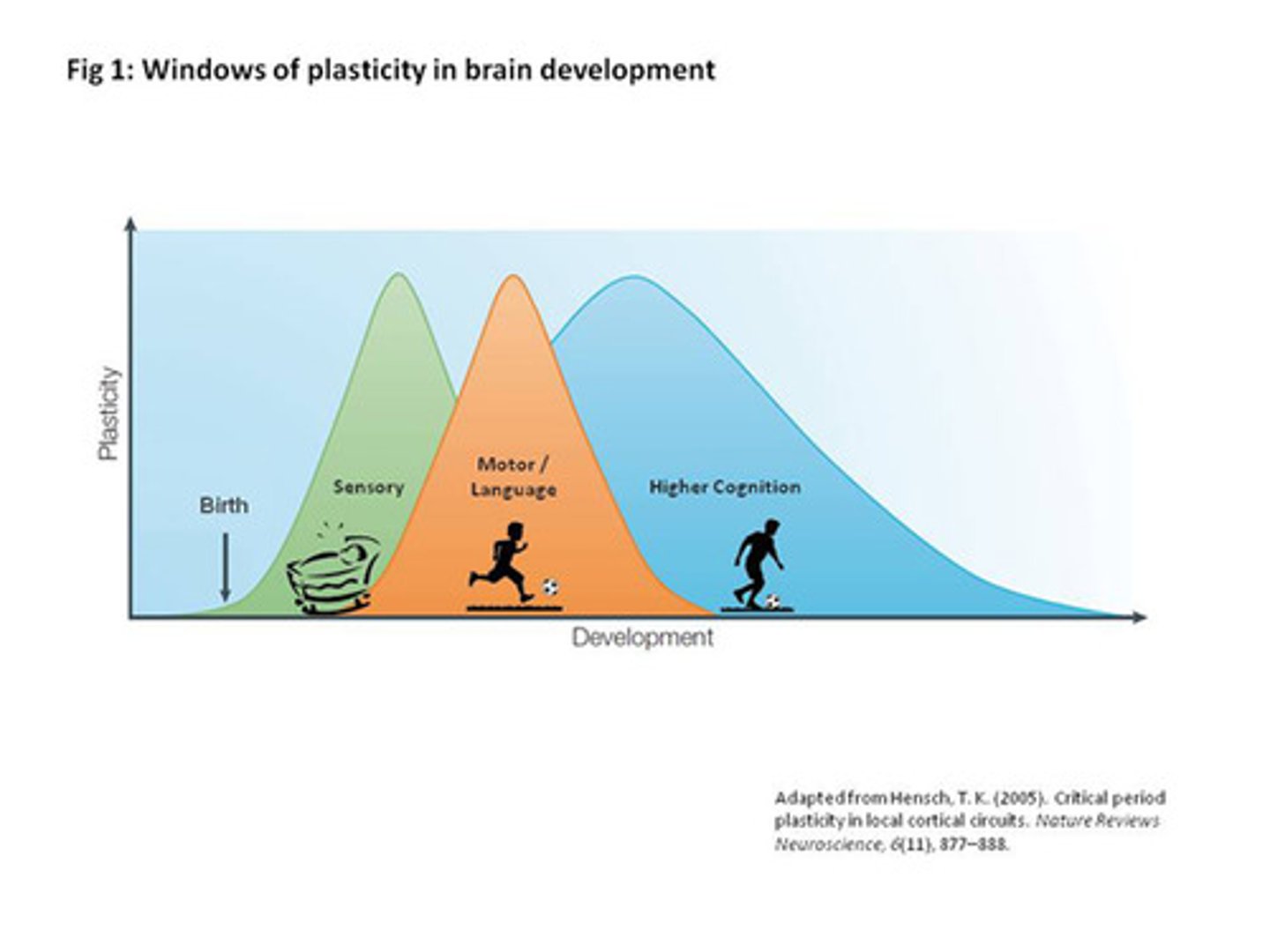
Imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life.

Temperament
a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity.

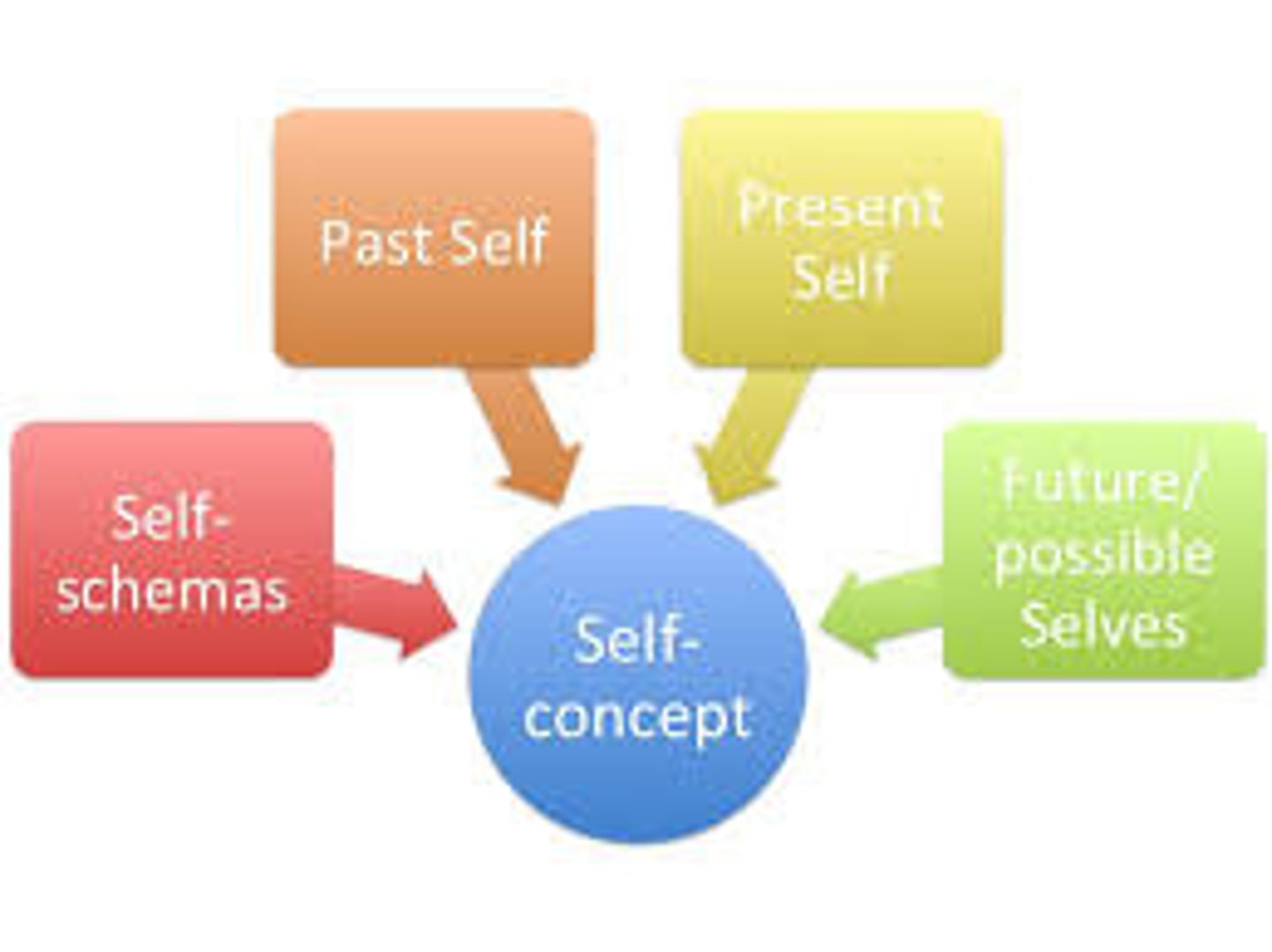
Self-Concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, "Who am I?"
Adolescence
the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence.
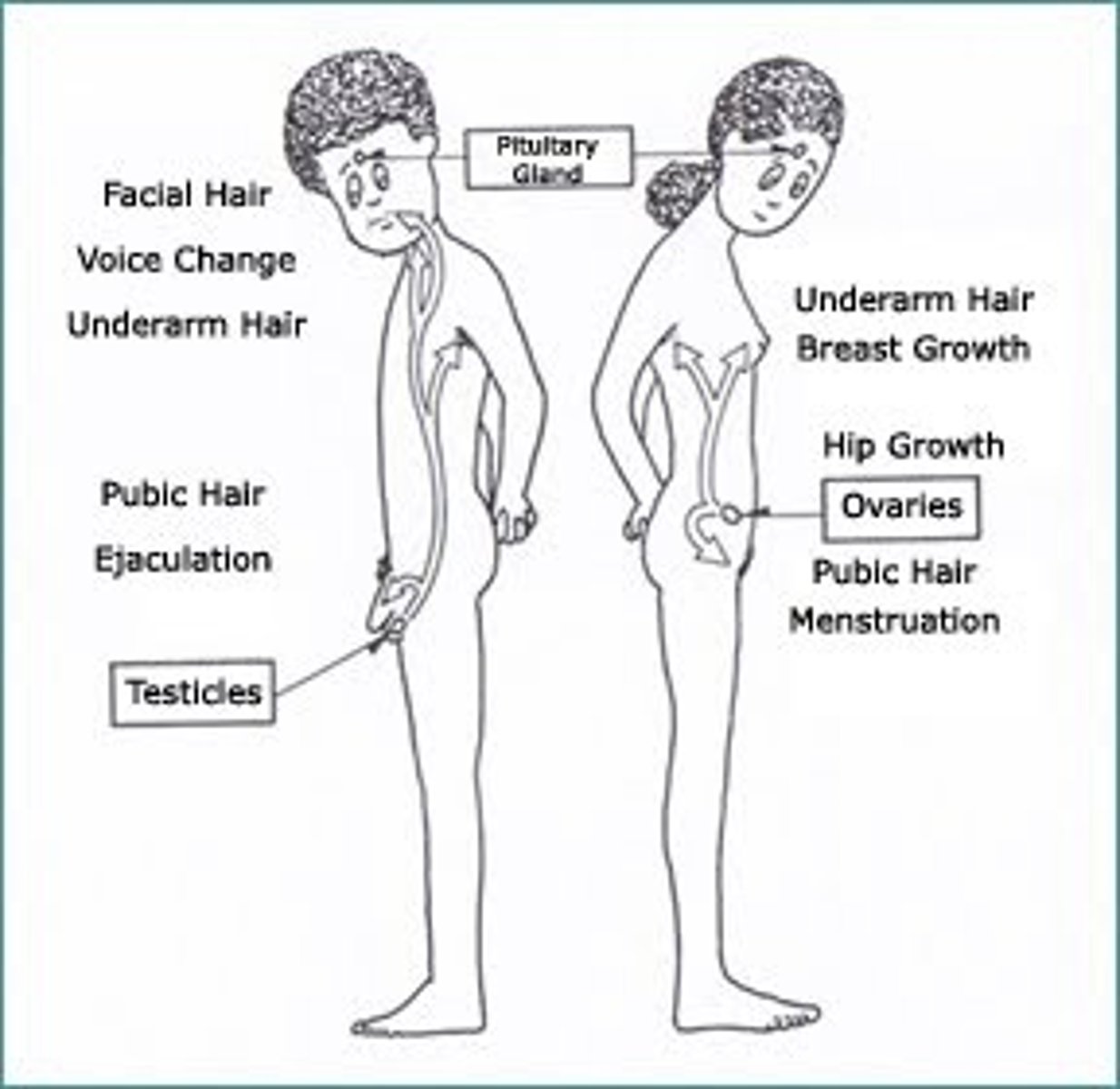
Puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing.
Identity
our sense of self; according to Erikson, the adolescent's task is to solidify a sense of self by testing and integrating various roles.
Intimacy
in Erikson's theory, the ability to form close, loving relationships; a primary developmental task in late adolescence and early adulthood.

Emerging Adulthood
for some people in modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood.

Cross-Sectional Study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another.
Longitudinal Study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period.
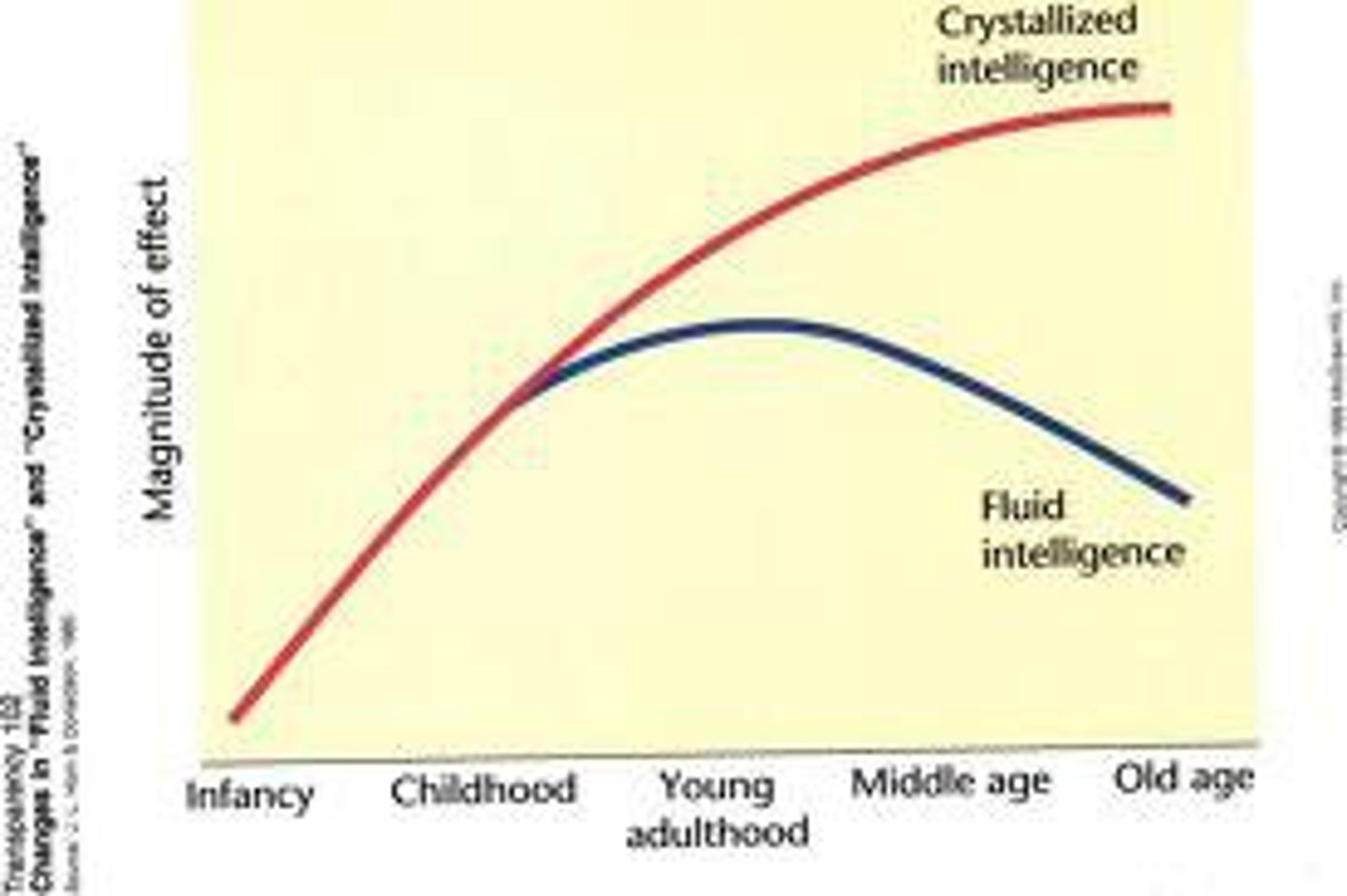
Crystallized Intelligence
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age.
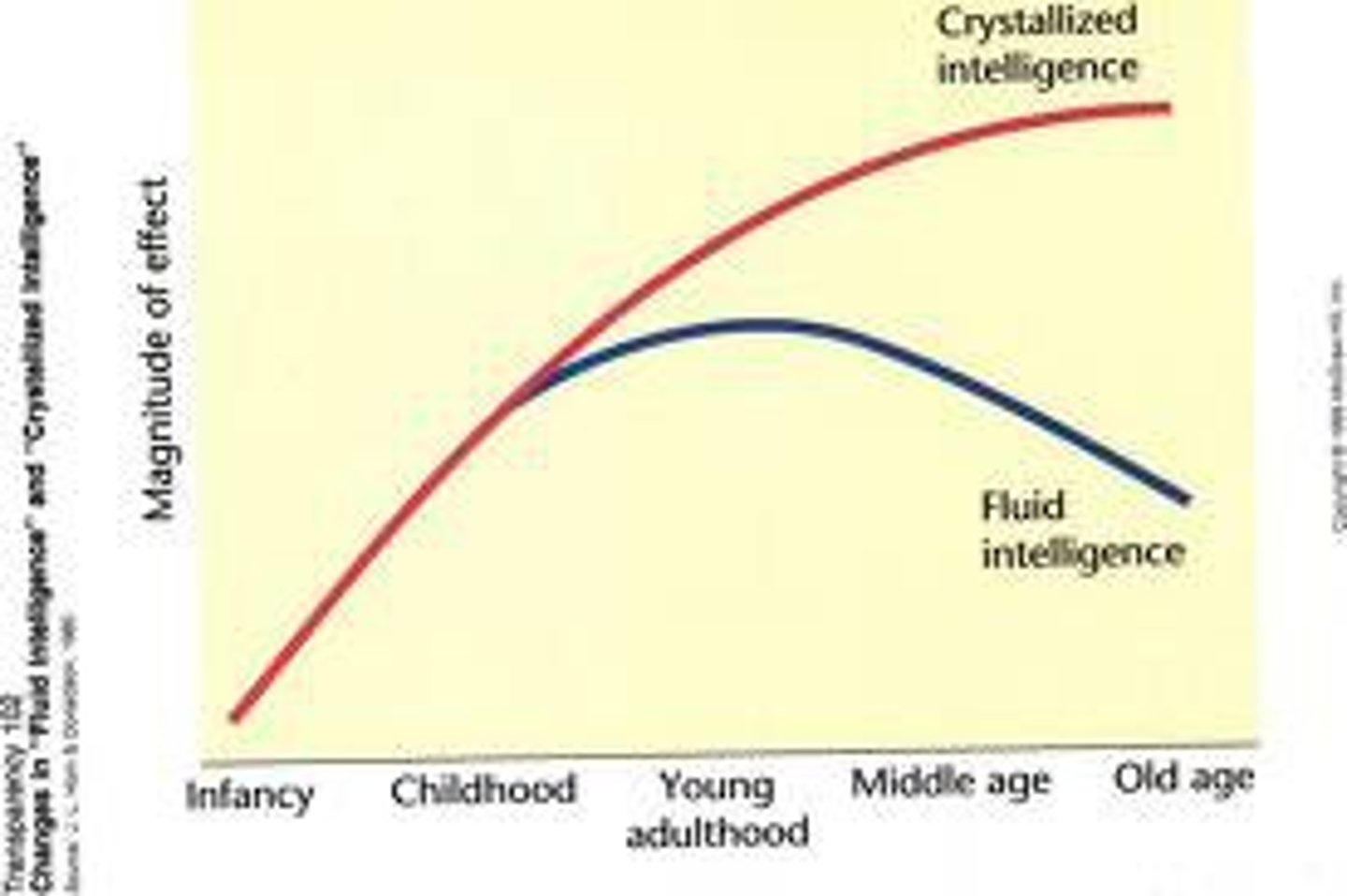
Fluid Intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood.
Mary Ainsworth
studied how different attachment styles affected kids
Konrad Lorenz
researcher who focused on critical attachment periods in baby birds, a concept he called imprinting
Diana Baumrind
her theory of parenting styles had three main types (permissive, authoritative, & and authoritarian)
Harry Harlow
Studied attachment in monkeys with artificial mothers
Jean Piaget
Known for his theory of cognitive development in children
Erik Erikson
neo-Freudian, humanistic; 8 psychosocial stages of development: theory shows how people evolve through the life span. Each stage is marked by a psychological crisis that involves confronting "Who am I?"