Biology Unit 5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/172
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
1
New cards
How long is the DNA in our cells if it was stretched out?
6ft
2
New cards
How long would the DNA from ALL of your cells be?
It would be ale to stretch to the sun and back 61 times
3
New cards
How does all of our DNA fit in a single eukaryotic cell?
DNA packaging
4
New cards
Genome
total genetic material in an organism
5
New cards
as organisms get bigger…
their genome size increases
6
New cards
Chromatin
Loosely wound substances found in eukaryotic cells that consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins (form of DNA in non actively dividing cells)
7
New cards
Histones
family of proteins that are associated with DNA packaging in the form of chromatin
8
New cards
photo of histone
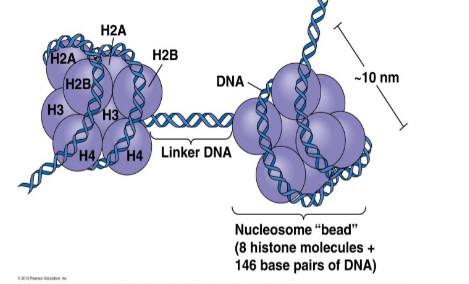
9
New cards
nucleosome
fundamental subunit of chromatin
10
New cards
What is a nucleosome composed of?
a little less than two turns of DNA wrapped around a set of eight proteins called histones
11
New cards
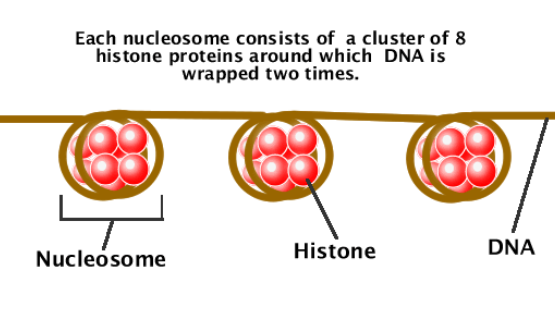
dna composition
12
New cards
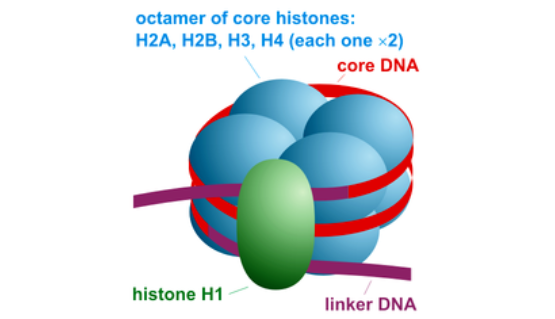
octamer
13
New cards
chromosome
tightly wound (condensed) substance found in dividing eukaryotic cells. Essentially the chromatin gets more tightly packed/wound
14
New cards
chromosome photo
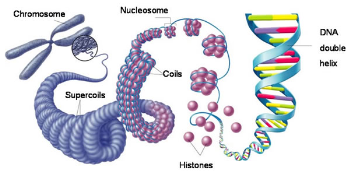
15
New cards
chromatid
one-half of two identical threadlike strands of a replicated chromosome
16
New cards
chromosome & chromatid photo
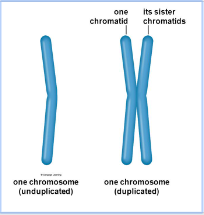
17
New cards
centromere
the region of a chromosome where chromatids are joined
18
New cards
labelling a chromosome
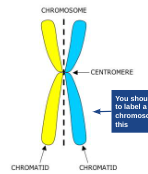
19
New cards
benefits of chromosomal packaging?
easy to move around the cell during cell division
20
New cards
disadvantages of chromosomal packaging?
difficult to access the genes during transcription
21
New cards
chromosome #…
increases as organism becomes more complex
22
New cards
Prokaryotic DNA Characteristics
circular, single chromosome, naked (not bound with histone proteins), compact (few repetitive sequences or introns)
23
New cards
prokaryotic DNA image
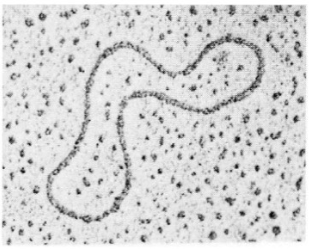
24
New cards
prokaryotic chromosomes image
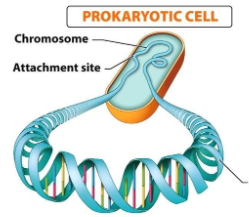
25
New cards
eukaryotic chromosome image
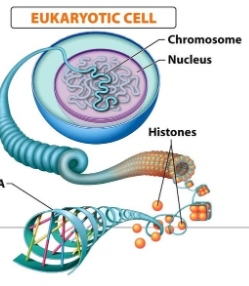
26
New cards
genophore
DNA found in a prokaryotic cell
27
New cards
plasmids are in…
prokaryotes
28
New cards
plasmid
a small dna molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. Mostly associated with prokaryotic cells
29
New cards
organelle dna
mitochondria/chloroplast, some like yeast can have plasmids too
30
New cards
prokaryotic DNA organization
single loop of naked DNA (no histones)
31
New cards
prokaryotic number of chromosomes
1
32
New cards
prokaryotic extra genetic material
plasmids (rings of extra non-essential DNA
33
New cards
eukaryotic dna organization
dna is wrapped around histone proteins (linear)
34
New cards
eukaryotic number of chromosomes
multiple, normally multiples of 2
35
New cards
eukaryotic extra genetic material
mitochondra, chloroplast, occasionaly plasmids like yeast
36
New cards
asexual reproduction
no exchange of genetic material
37
New cards
sexual reproduction
exchange of genetic material
38
New cards
continuity of life is based on…
cell division
39
New cards
unicellular organisms
organisms where division of one cell reproduces the entire organism
40
New cards
multicellular organisms
organisms that depend on cell division for development from a fertilized cell, growth, and repair
41
New cards
cell division is an integral part of what?
the cell cycle
42
New cards
what does cell division result in? (most of the time)
daughter cells with identical genetic information, DNA
43
New cards
what do some specialized types of cell division produce
non-identical daughter cells (gametes, or sperm and egg cekks)
44
New cards
asexual reproduction example
mitosis & binary fission
45
New cards
sexual reproduction example
meiosis
46
New cards
cell cycle
the series of events that take place from when a cell forms until when it divides to produce daughter cells, the life of a cell
47
New cards
cell cycle consists of…
interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
48
New cards
interphase
cell growth and copying of chromosomes in preparation for cell division
49
New cards
mitotic phase
mitosis and cytokineses
50
New cards
cell cycle image
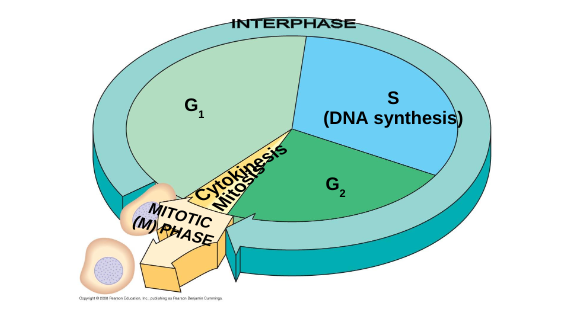
51
New cards
interphase subphases
G1, S, and G2
52
New cards
G1 phase
first growth phase. the cell carries out routine functions, grows larger, and makes new proteins and organelles
53
New cards
S phase
“synthesis”, when dna is replicated
54
New cards
G2 phase
second growth phase. the cell prepares for division by forming microtubules and other organelles or molecules that they cell may need to divide
55
New cards
interphase is not a what
resting phase
56
New cards
% of cell cycle that is interphase
90%
57
New cards
when is dna duplicated in cell cycle?
s phase
58
New cards
cell cycle control system function
direct the sequential events of the cell cycle
59
New cards
what is the cell cycle control system regulated by?
internal and external controls
60
New cards
cell cycle control system is similar too..
a clock
61
New cards
checkpoints
places in the cell cycle control system where the cell cycle stops until a go ahead signal is received
62
New cards
different checkpoints
G1 checkpoint, G2 checkpoint, M checkpoint
63
New cards
G0
a phase where the cell is not preparing to divide, and therefore is not going to progress through the cell cycle. cells will perform normal metabolic processes during G0. some cells can re-enter the cell cycle after being in G0, althought some cells are in terminal G0 and cant re-enter the cell cycle
64
New cards
what are the types of regulatory proteins involved in cell cycle control
cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks)
65
New cards
relationship between cyclin and cdks
cycle activates cdks
66
New cards
what does the activity of cyclins and cdks do?
fluctuate during cell cycle
67
New cards
mpf
maturation-promoting factor, a cyclin-cdk complaex that triggers a cell’s passage past the g2 checkpoint into the m phase
68
New cards
fluctuation of mpf activity and cyclin concentration during the cell cycle
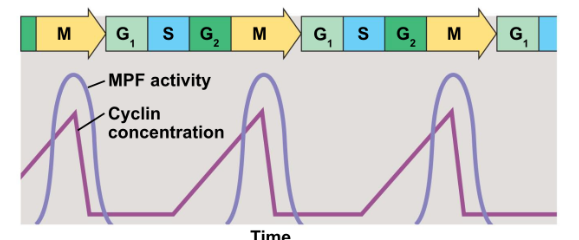
69
New cards
molecular mechanisms that help regulate the cell cycle image
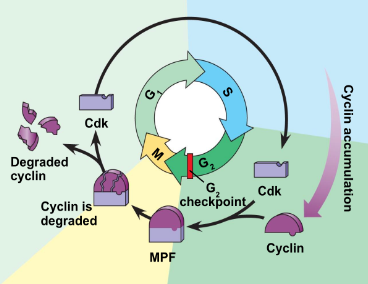
70
New cards
cdks are…
always present but not always active
71
New cards
cdks are activated when…
a cyclin binds to it
72
New cards
mpf function
go signal for the g2 checkpoint, allows cell to enter m phase
73
New cards
eukaryotic cell division consists of…
mitosis and cytokinesis
74
New cards
mitsosis
division of the nucleus
75
New cards
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
76
New cards
why can’t prokaryotes perform mitosis
they do not have a nucleus, and sincce mitosis is the division of the nucleus, they cant do it
77
New cards
phases of mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telopahse
78
New cards
cytokinesis occurs simultaneously with
telophase
79
New cards
g2 of interphase
formation of the centrosomes, structures that will direct formation of mitotic spindle
80
New cards
centrioles
component of the centrosomes in animal cells.
81
New cards
prophase
mitotic spindle grows, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, mitotic spindle attaches to chromosomes (microtubules), nuclear envelope breaks down
82
New cards
mitotic spindle
apparatus of microtubules & centrosomes that controls movement during mitosis
83
New cards
where/when does the assembly of the mitotic spindle begin?
during prophase in the centrosome
84
New cards
as the mitotic spindle grows..
the centrosome replicates, forming 2 centrosomes that migrate to opposite ends of the cell
85
New cards
kinetochores
protein structures that are located in the centromere region where microtubules attach and help to facilitate chromosome movement
86
New cards
where do spindle microtubules attack to move the chromosome?
on the kinetochore
87
New cards
metaphase
the chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate.
88
New cards
what does the m checkpoint do
checks to make sure the chromosomes have lined up at the metaphase plate during metaphase before anaphase begins
89
New cards
nonkinetochore microtubules
microtubules from opposite poles that overlap and push against each other, elongating the cell
90
New cards
anaphase
sister chromatids separate and move along the kinetochore microtubules towards opposite ends of the cell
91
New cards
during anaphase, what direction do chromosomes move?
towards spindle
92
New cards
telophase/cytokinesis
genetically identical daughter nuclei form at opposite ends of the cell. nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes unwind back into chromatin
93
New cards
animal cell cytokineses
occurs by a process known as cleavage, forming a cleavage furrow, pinching inwards until the cells separate
94
New cards
plant cell cytokinesis
cell plate forms during and grows outwards
95
New cards
binary fission (prokaryotes)
the chromosomes replicates and the 2 daughter chromosomes actively move apart as the cell divides
96
New cards
why did mitosis probably evolve from binary fission
prokaryotes evolved before eukaryotes
97
New cards
certain protists (eukaryotes) exhibit what type of cell division?
mix between binary fission and mitosis
98
New cards
regulatory proteins
proteins inside and outside the cell that control cell cycle, stop/go signals
99
New cards
internal regulators
proteins that respond to events inside a cell and allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain events have occured, ex cyclins/cdks
100
New cards
external regulators
proteins that respond to events outside the cell, often directing cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle