Week 2 - Lacrimal gland and tears
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
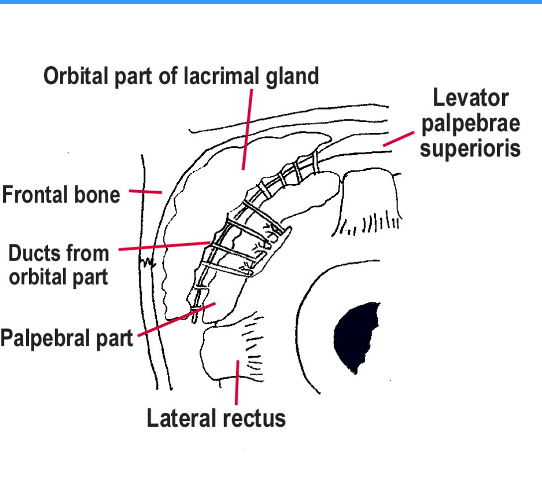
What are the 2 types of lacrimal gland lobes?
Orbital lobe
Palpebral lobe
What is the difference between the orbital and the palpebral lobe?
Orbital lobe is larger and above the levator aponeurosis
Palpebral lobe is smaller and below the levator aponeurosis
What are the 2 lacrimal gland lobes divided by?
Levator aponeurosis tendon
What are the sizes of the orbital and the palpebral lobe?
Orbital lobe is large
Palpebral lobe is small
Where is the orbital lobe located?
In front lacrimal fossa
Where is the palpebral lobe located?
Near conjunctival surface inside eyelid
Diagram of lacrimal gland
What does serous mean?
Producing / resembling serum
What does tubuloracinar mean?
Gland having branching tubules which end in secretory alveoli
Secretion and transport of exocrine gland via serous gland
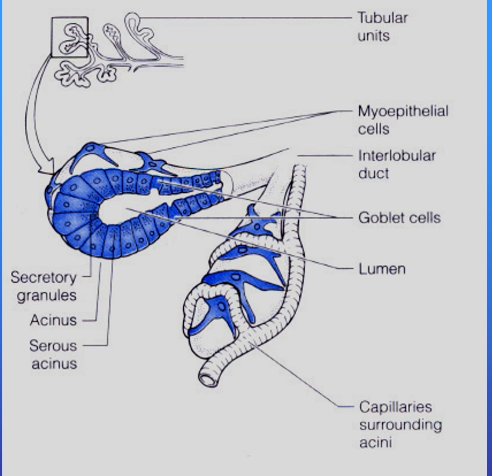
What happens in the secretion and transport of exocrine cells such as lacrimal gland?
Serous acini produce protein rich aqueous
Myoepithelial cell contract so move secretion to interlobular duct
Duct further modify composition
Transport fluid to ocular surface
Goblet cell contribute mucin for tear stability
What are goblet cells?
Specialised cells tha tproduce mucins
Located with ducts to stabilism tear film
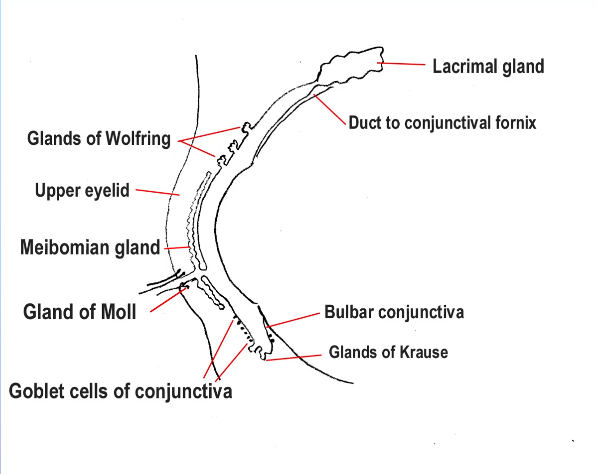
Diagram of accessory glands
What are the function of tear film?
Maintain smooth refracting surface
Transport metabolic products to epithelium cells
Prevent desiccation of epithelium
Lubricate eyelids
Bactericidal
Pathway for white blood cells
Nutrients
What percentage of tear fluid is lacrimal or accessory gland?
90% lacrimal
10% accessory
What is the resting tear fluid level?
1.5 ml/day
What are the 3 layers of the tear film?
Lipid layer
Aqueous and mucus layer
Mucous layer
What does the lipid layer do?
Inhibit tear evaporation
Protect aqueous layer from polar contamination
What is the function of the mucous layer?
Enable tears to wet epithelium
Maintain stability of tear film during blinking
What are the 2 main cell types in the tear gland?
Secretory and myoepithelium cells
What is the role of myoepithelial cells in the tear gland?
Surrounding acini and produce contractile force to push tears into ducts
What is the role of secretory cells int he tear gland?
Produce tears
How are tears carried out of the tear gland?
Small lumens in lacunae combine form larger ducts, merge into main drainage duct
What do tears mainly contain?
Proteins
Name 4 important components of tears beside proteins?
Lysozomes, lactoferrin, B-lysin, lgA
What is the function of lysozymes in tears?
Fight bacteria
What do lactoferrin do in tears?
Binds iron, reduce bacterial growth
What is the function of lgA in tears?
Provide immune protection against infections
What is the function of B-lysin in tears?
Helps kill bacteria