Higher Admin & IT
1/60
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
How do you answer an Outline question?
Make a brief description for an answer.
How do you answer a Describe question?
Answer with a thorough answer with possible examples to your questions. (Usually over 2 points help).
How do you answer a Discuss questions?
Examine the question closely in your answer and provide the benefits or negatives of the topic.
How do you answer a Compare question?
Identify similarities or differences of the topic comparing the subjects. (Words such as however, whereas are good words to use).
How do you answer a Justify question?
Give a response which justifies (agrees/accepts with) the topic.
Tasks and duties of administration?
Using IT Software to Create Documents
Managing Information and Documents
Reception and Communication
Organising meetings
Using Office Equipment
Office Admin Procedures
An Administrative Assistant should have personality traits such as?
Hardworking and reliable
Enthusiastic and willing to learn and improve
Approachable and friendly
Tactful and discreet
Trustworthy and reliable
Able to show initiative and work unsupervised
Cooperative and a good team player
Role of Senior Administrative Assistant?
A Senior Administrative Assistant is responsible for ensuring that office systems and procedures are implemented and maintained efficiently.
Typical duties of a Senior Administrative Assistant include?
Overseeing general administrative tasks (copying, filing, meetings, travel)
Organising and allocating resources (people, time, equipment)
Supervising the work of junior staff
Preparing and responding to correspondence
Liaising with management and with different departments
Planning and organising workflow
Solving problems and making decisions
Monitoring and evaluating systems and procedures
Training and appraisal of junior staff
Organising and recording meetings
Researching and presenting information
Arranging events (eg seminars and conferences)
A Senior Administrative Assistant should demonstrate the following skills?
Planning and organisational skills – being able to and plan and organise range of different work tasks and projects, and manage resources effectively
Time and task management skills – being able to multitask, prioritise work, and manage time effectively
Delegation skills - knowing which tasks should be given to co-workers and being able to allocate tasks fairly, taking account of skills, experience and current workload of co-workers
Interpersonal skills – being able to lead, motivate and encourage others
Management skills – being able to solve problems and make decisions
Communication skills – being able to communicate well, both verbally and in writing
Information technology skills - being able to use a range of software to support the administrative function and to aid decision making
Team working skills - being able to work effectively as part of a team
Coaching and mentoring skills – to support and develop staff
What is a personal development plan?
This is a document that allows employees to formally record areas of strengths and areas of training and development.
Employees should discuss the plan with their line manager on a regular basis and it is often discussed annually.
This allows the employee to focus on aspects of their job, identify skills they have that could be shared with others, identify their training needs and prepare them for promotion.
(A way to set a target)
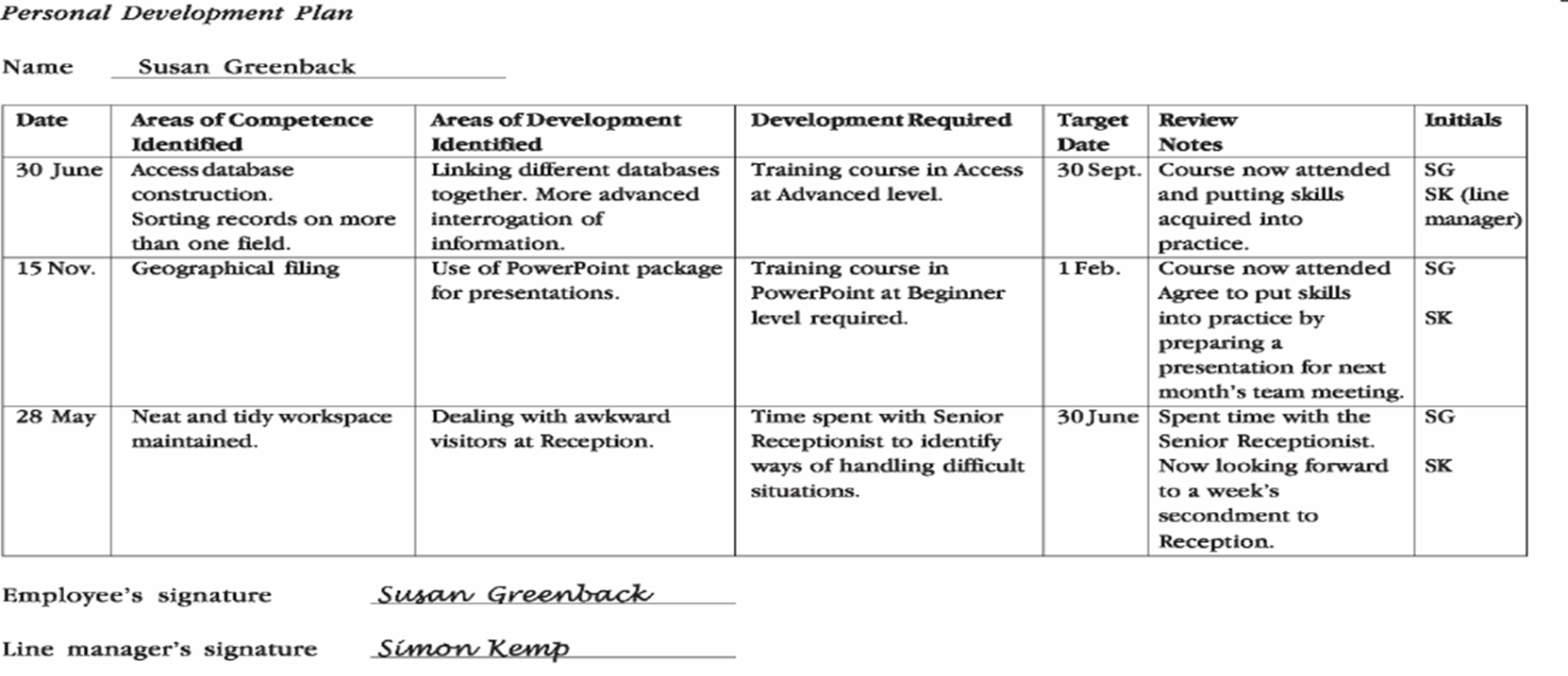
What is an action plan?
This is a document that could be prepared to help a long-term project and show the tasks that need to be completed.
An estimate of how long the tasks should take and any notes to explain actions.
(A way to set a target)
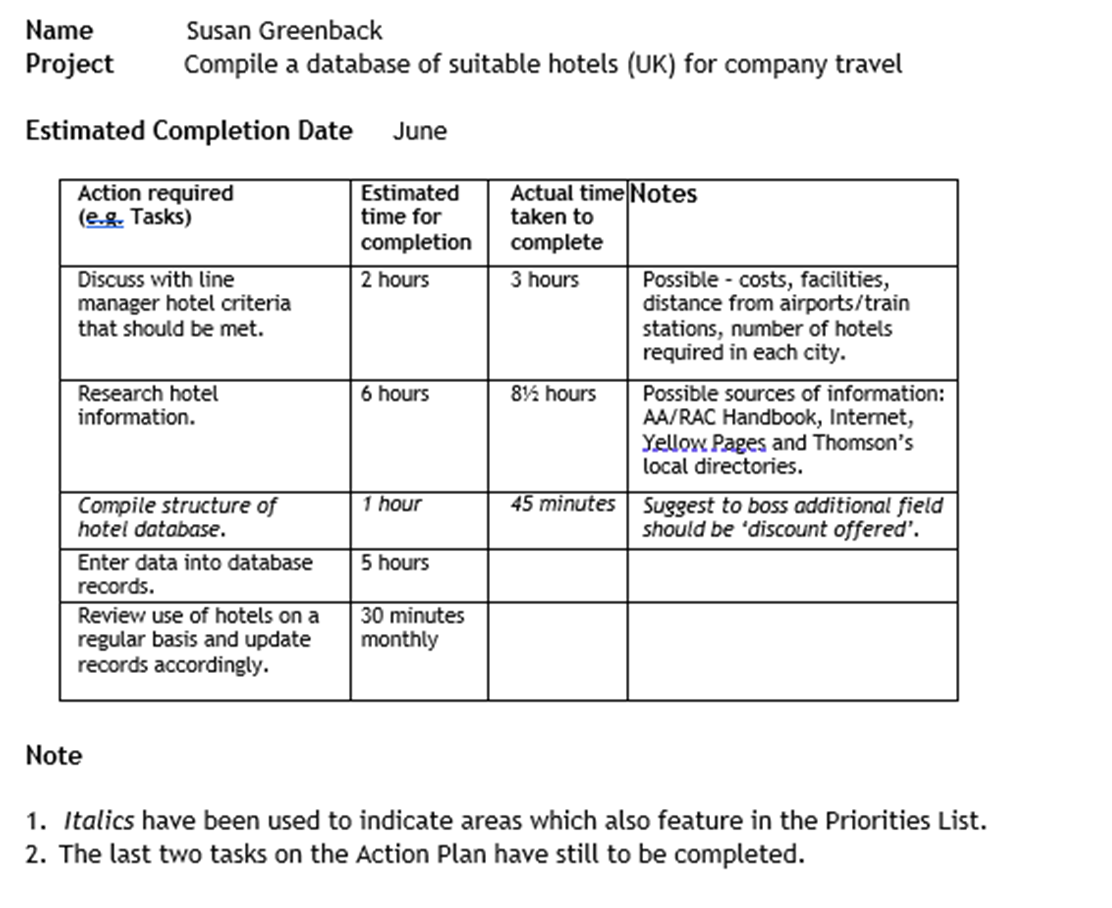
What is a to do list?
This is a document that an individual could use on a day-to-day basis to remind them of the tasks that need to be complete.
(A way to set a target)
What is an E-diary?
Employees can insert tasks onto their E-diary (a digital dairy) which shows them the tasks that must be completed for.
Also gives them a reminder to complete said tasks.
(A way to set a target)
What is a Gantt Chart?
This is a chart that a manger could put up to allow individuals to see at a glance key dates and the tasks that have to be completed.
It can also be used to monitor when tasks have to be complete.
(A way to set a target)
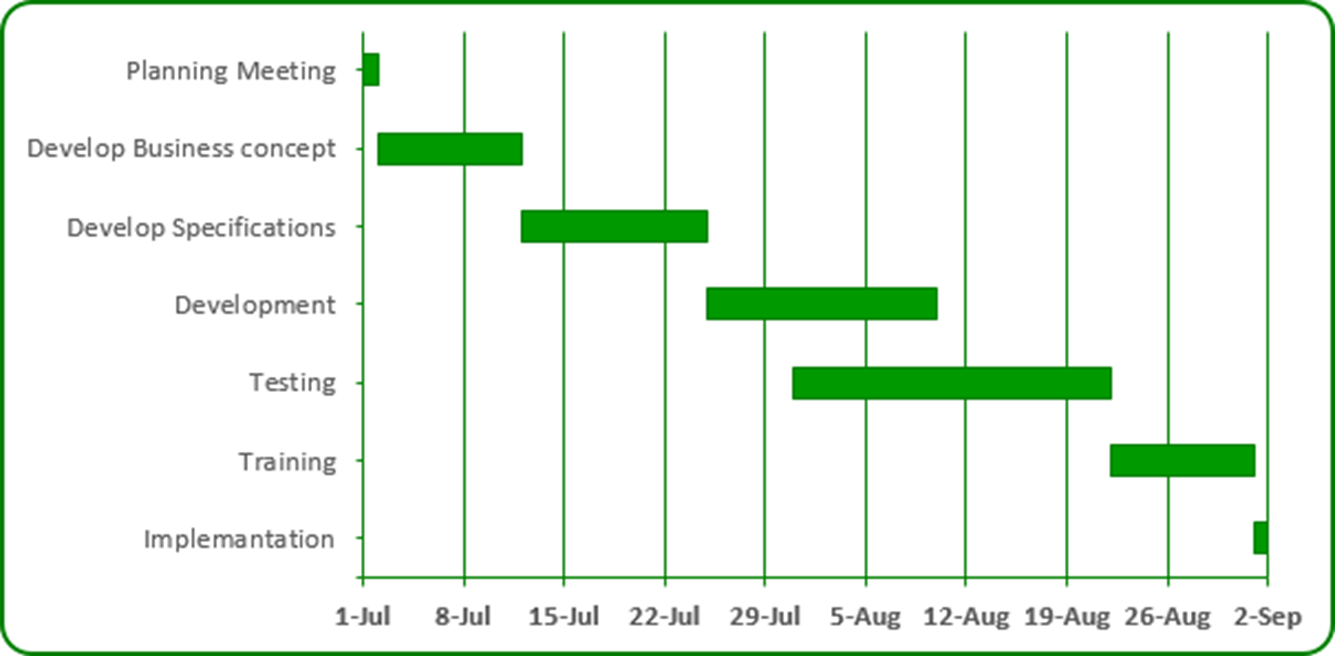
List three (3) examples of circumstances that could affect day-to-day work?
A member of staff failing to show up for work
The network crashing
A manager changing a deadline for a piece of work.
(More examples can be included other than these)
(3) What can an employee do if they haven’t managed to reach their targets?
They should remain calm and possibly ask for help from other peers to complete the tasks.
They could also ask for an extension to the task
The person should be able to refuse any extra unnecessary or additional tasks so that they have time to complete the over due task.
What is Sample Check/Accessing Files?
This is an example of monitoring and evaluating progress of targets
Where some but not all of the tasks are looked over by the immediate supervisor at random times.
What is a Buddy System?
This is an example of monitoring and evaluating progress of targets
Where an employee is paired with a more experienced member of staff who can be called on fro help and advice.
What is a Mentoring System?
This is an example of monitoring and evaluating progress of targets
A senior employee is assigned to a junior employee to assist and support them in reaching their targets.
What is an Appraisal?
This is an example of monitoring and evaluating progress of targets
Reviews current performance and helps identify and evaluate progress an employee had made in reaching their targets
What are Regular Meetings for?
This is an example of monitoring and evaluating progress of targets
Gatherings between employees and line managers to check how the work is progressing.
What is Planning?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
The use of tools that we discussed in target making such as to do lists or action plans depending on the length of the task.
What is Prioritisation?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Deciding what tasks are more important and being able to decide which tasks should be carried out first and which tasks are less important.
What is Organisation?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Being able to look ahead and plan tasks that need to be carried out.
What is Delegation?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Deciding when it is appropriate to ask someone else to do some of your tasks.
(Similar meaning words: assignment, commission, giving)
What is Assertiveness?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Being able to say “no” when necessary when you have taken on too much work.
What is Negotiation?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Being able to negotiate (work out, agree on) deadlines and resources.
What is Control?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Tackling tasks calmly and in order of priority.
What is Evaluation?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Being able to look at tasks, seek improvement and identify the causes of any problems.
What is Resource Management?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Making effective use of time, staff and equipment.
What is Directing?
A skill required for effective time and task management.
Directing (instructing) the employees to get work done. This will involve a manager leading, communicating, and motivating.
List Time Stealers?
Time stealers are things which effect the difficulty or the efficiency of being able to complete a task to the fullest or best quality.
Lack of forward planning
Interruption from the telephone
Interruption from visitors
Taking on too much work
Desk stress (messy work environment)
Procrastination (Jumping from one task to another but not actually completing them)
Meeting overrunning
Making unnecessary journeys
Communication problems
List benefits of effective time and task management?
Increased productivity
Better quality of work
Increased morale (self esteem or confidence) and motivation
Increased job satisfaction and lower staff turnover as employees feel more in control of their workload
Lower stress levels among staff, which will reduce absenteeism (absence)
Better relationships with management
Good customer relations as targets and deadlines will be met.
(These are benefits which effect both the employees and the organisation)
List the consequences of poor time and task management?
Staff being stressed, which leads to absenteeism (absence)
Lower productivity and poor quality of work
Lower staff morale (self-esteem or confidence) and motivation
Poor job satisfaction and high staff turnover (quitting job or being fried)
Poor customer relations and increase in customer complaints
Poor relationships with management
Increased costs to the organisation.
(These factors both impact the employees and the organisation.)
What is Team Composition?
This is a characteristic/Feature of creating an making team.
Consideration should be placed on factors such as personality, interests, age and backgrounds when forming a team.
Why is Team Size important?
This is a characteristic/Feature of creating an making team.
Too few members will lead to heavy workloads or lack of skills/experience
Too many members could lead to underutilised staff, poor communication and management issues.
What is Team Development?
This is a characteristic/Feature of creating an making team.
A group of people who have worked together before who will know each other and will develop more quickly than those who have just started to work together.
What should the Nature of the Task look like?
This is a characteristic/Feature of creating an making team.
Everyone in the team needs to believe in the task to be undertaken
The clearer the task, and the more involved the members feel, the more effectively the team will work together.
If the task isn’t clear the members will disagree and may become disinterested.
What is Team Maintenance?
This is a characteristic/Feature of creating an making team.
It is important that the people who belong to a team identify themselves as a part of the team and are given opportunities to develop as a part of the team.
Opportunities should be given both inside and outside the workplace for the team to take part in activities that allow their relationship as a team to develop.
There should be regular meetings help to discuss issues and sort out problems.
What is Leadership?
This is a characteristic/Feature of creating an making team.
It is important that a team has an effective leader who can motivate the team towards their goal and minimise any conflict in the team.
Poor leadership can lead to demotivated team members, conflict, lack of support and lack of challenge.
What is the Team Formation theory called?
The Tuckman’s Theory
List four (4) stages of the Tuckman’s Theory?
Forming
Storming
Norming
Performance
(There are more however this is the ones we are expected to be familiar with at the higher level)
Define the Forming stage of Tuckman’s theory?
When people get to know each other and their roles.
Define the Storming stage of Tuckman’s theory?
When conflict and friction can arise as people's true characters start to emerge and they start to push against boundaries.
Define the Norming stage of Tuckman’s theory?
Where people start to resolve their differences, appreciate one another's strengths, and respect your authority as a leader.
Define the Performing stage of Tuckman’s theory?
When your team is in flow and performing to its full potential.
What do we call the personalities/roles in a team theory?
Belbin’s Group Roles
What does the Ideas Person do in Belbin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who is creative, imaginative and has the ability to solve problems.
What does the Motivator Person do in Belbin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who can get things moving and drive the team forward.
What does the Organiser Person do in Belbins Group Role theory?
This is someone who can plan and co-ordinate activities and pulls things together.
What does the Implementer Person do in Belbin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who can get tasks started and turn ideas into actions.
What does the Checker Person do in Belbin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who can monitor and ensure that tasks have been carried out correctly.
What does the Finisher Person do in Belbin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who ensures that tasks are complete on time.
What does the Go Getter Person do in Belbin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who develops contacts and seeks out resources.
What does the Team Player Person do in Belbin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who thinks about the people in the group and listens to others to minimise conflict.
What does the the Specialist Person do in Blebin’s Group Role theory?
This is someone who can provide vital knowledge and skills.
What skills are expected of team members?
Leadership skills
Communication skills
Listening skills
Team working skills
Conflict resolution
Benefits of teams to individuals?
Increased morale (self-esteem and confidence) and motivation
Shared knowledge and skills
More chance of risk-taking as the risk is shared between the group (good for challenges and learning)
Sense of being valued.
Benefits of teams to Organisations?
Multi-skilling - Teams allow the workforce to be more flexible and to adapt the needs as required.
Responsibility - Effective teams need less supervision as they are more likely to take on more responsibility. This could result in layers of management being reduced, which would reduce costs for an organisation.
Higher productivity - Because of the increased morale and motivation of the employees, the organisation could benefit from increased productivity and lower staff turnover.
Risk-taking - Teams are more likely to take risks and this can give an organisation a competitive edge.