Chapters 2 and 3 AP Econ Test
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
economic system
a set of institutional arrangements that deal with the economising problem.
what is produced?
how is it produced?
who gets the output?
how to deal with change and promote technology?
who owns factors of production
how to motivate or direct economic activity?
command system
aka social communism
gov own property
decision making is centralized
gov owns firms and directs desicions
capital goods are allocated based on gov plan
market system
aka capitalism
private ownership
markets and prices determine activity
self interest - individuals make choices
competition
decision making is widely dispersed
gov protects private property and operation of market system
laissez faire - “let it be”
ex: mostly everyone else
free enterprise and choice
free to obtain/use resources to produce and sell goods that they choose
consumers are able to buy whatever they want w money
choice
owners can do what they want with property and money
workers can choose their work
consumers buy what they want
self interest
each group tries to achieve its own goal
owners want to maximize profits
workers want to maximize utility
21st century paradox
we are powerful consumers but powerless workers
specializaton
uses resources to produce one specific good and sell/trade it instead of making everything
human specialization = division of labor
ex: chipotle
how do we decide what a dollar is worth?
money is agreed upon social agreement
active but limited government: “the tragedy of the commons”
when there are common resources available, how do you stop people from abusing them?
things that belong to all are cared for by none
Example: ocean and fishing → too much of it to stop the population from doing it
what will be produced?
production will occur when Total Revenue (TR) exceeds Total Costs (TC).
tells you what to make not how many to make
if TR > TC → its profitable → make it
if TR < TC → its not profitable → don’t make it
how will goods/services (g/s) be produced?
cheapest and most efficient way possible
ideal mix of land labor capital
labor is often the most expensive
demand
curve that shows the quantity of a product that consumers are willing and buy at a specific point of time
always willing - not always able
depends on time → must be specific
immediate short run
short run
long run
immediate short run
all factors of production are fixed → no changes can be made
short run
one or more are fixed → can make some changes but not a lot
long run
depends on variable inputs
theoretical construct
period of time long enough to change resources
change in demand
indicates shift on the curve (left or right)
change in price
indicates movement on the curve
law of demand
negative/ inverse relationship
as price rises, demand drops
as price drops, demand rises
law of demand cont.
1) consistent with common sense
2) buyers derive less benefit for each unit consumed (diminished marginal utility -? additional utility only if price is lower)
3) income effect
price of good falls → purchasing power increases → buyers can afford more → Qd rises
4) substitution effect
lower prices makes other products relatively more expensive, so buyers substitute towards the cheaper good
determinants of demand
T - tastes/preferences
I - income
M - market size
E - expectations of consumers
R - prices of RELATED goods
T- tastes/ preferences
favorable change in consumer tastes
shifts curve left or right depending on reaction
I - income
usually as income increases → demand increases
normal goods: when income increases, you buy more of it (new clothes, restaurant meals etc.)
inferior goods: when income increases, you buy less of it (ramen noodles, bus rides, used cars)
depending on the good and my situation, demand will either increase or decrease
M - market size/number of buyers
more buyers = more demand
less buyers = less demand
E - expectations of consumers
what people expect to happen influences their behavior today
when prices are expected to rise soon → they’ll buy now (current demand increases)
when prices are expected to fall soon → they’ll buy later (or after prices have dropped) → the current demand decreases
R - prices of Related goods
substitute goods: goods that can be in place of each other
good 1 (coke): price increases
good 2 (pepsi): demand increases
complementary goods: goods that are used together
good 1 (ice cream): price increases
good 2 ( ice cream cones): demand decreases
supply (upward/ positive relationship)
a curve showing various amounts of a product that producers are willing and able to make available for sale during a period
law of supply (movements)
producers are motivated by profit
price of good rises → selling it would be more profitable → producers supply more of it
price of good falls → selling it would be less profitable → producers supply less of it
determinants of supply
T - technology
O - other goods
N - number of sellers in the market
E - expectactions of producers
R - resource prices
S - subsidies and taxes
T - technology
allows production at a lower cost of inputs
production price drops (bc of tech) → supply rises
O - prices of Other goods ( not on test ?)
substitutes in production
higher price of one → lower supply of other
N- number of sellers
like the demand determinant
if market increases → supply increases
P - producer expectations
much trickier than consumer expectations
what producers think will happen to the price of their product in the future
future price increases → current supply decreases (wait to sell after prices increase)
future price decreases → current supply increases (sell now before prices decrease)
R- resource prices
higher resource prices raise production costs → supply decreases
lower resource prices lower production costs → supply increases
S - Subsidies and taxes
taxes → increase production cost → supply decreases (shifts left)
subsidies → decrease production cost → supply increases (shifts right)
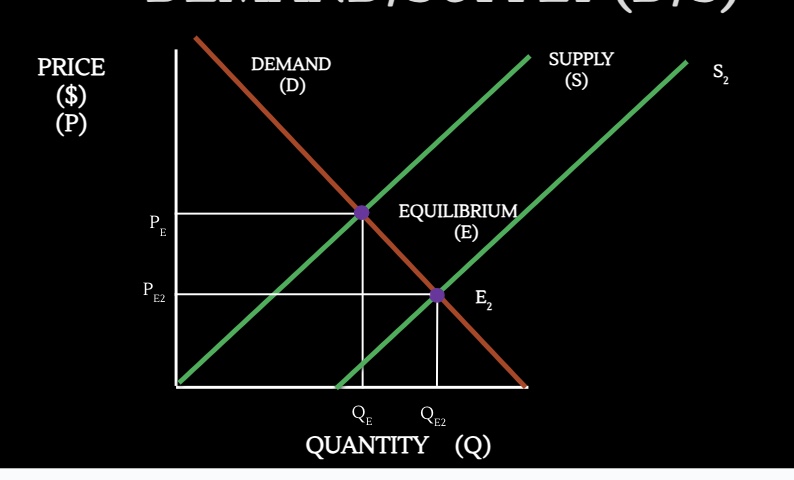
equilibrium price Qd = Qs
price where intention of buyers and sellers match
equilibrium quantity Qd = Qs
quantity demand and quantity supply at equilibrium price
draw a demand/supply graph