Multi Store Model
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Multi Store Model
Who made it and what does it describe?
Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968, 1971):
How information flows through the memory system
suggests memory is made up of three stores linked by processing
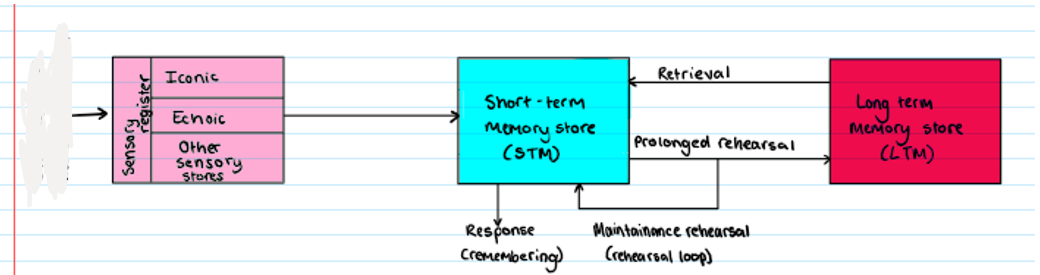
Multi Store Model
What is missing?
Stimulus from the environment
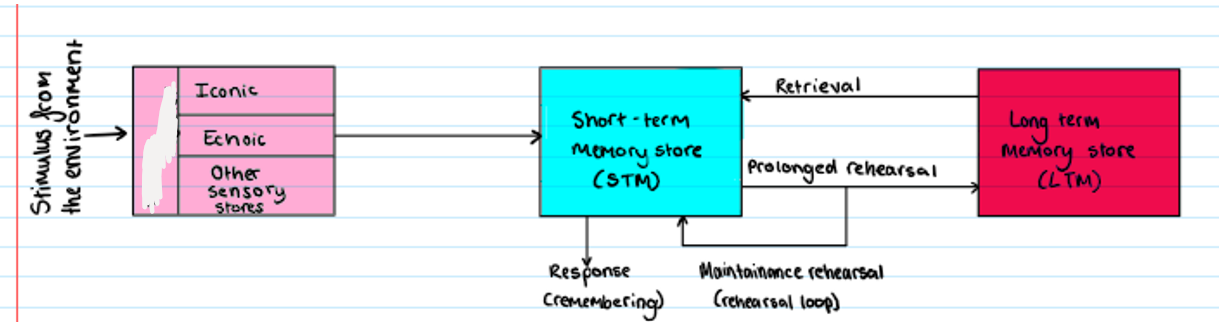
Multi Store Model
What is missing? (+capacity, duration, coding)
sensory register
Capacity:
Theoretically unlimited - environmental stimuli enters memory via SR
If pay attention → moves to STM
If not, filtered out by the bottleneck filter
Duration:
<1 sec
Coding:
Iconic - visual sensory memory
Echoic - auditory sensory memory
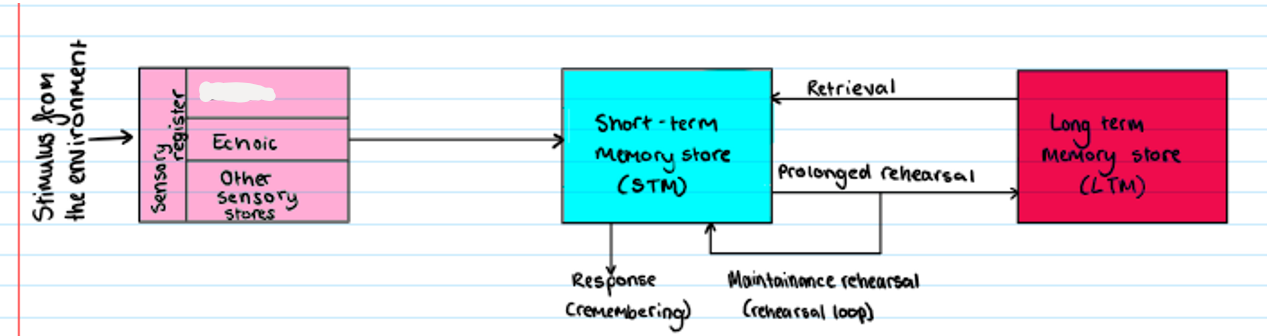
Multi Store Model
what is missing?
iconic
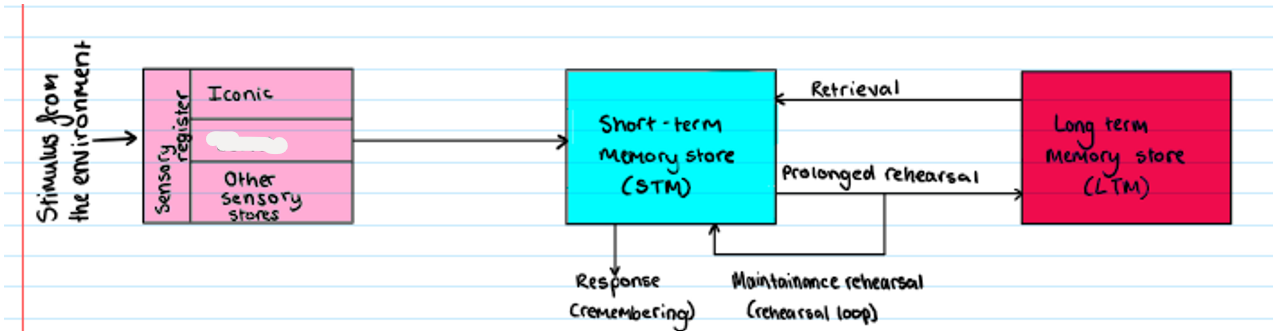
Multi Store Model
What is missing?
Echoic
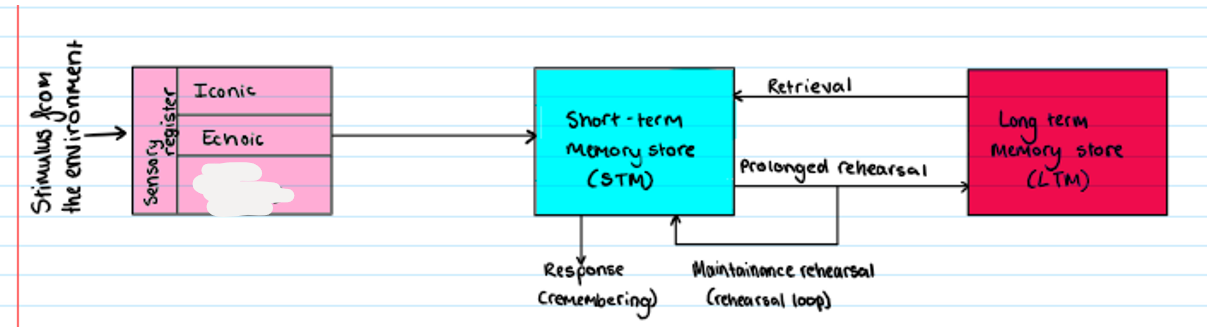
Multi Store Model
What is missing?
other sensory stores
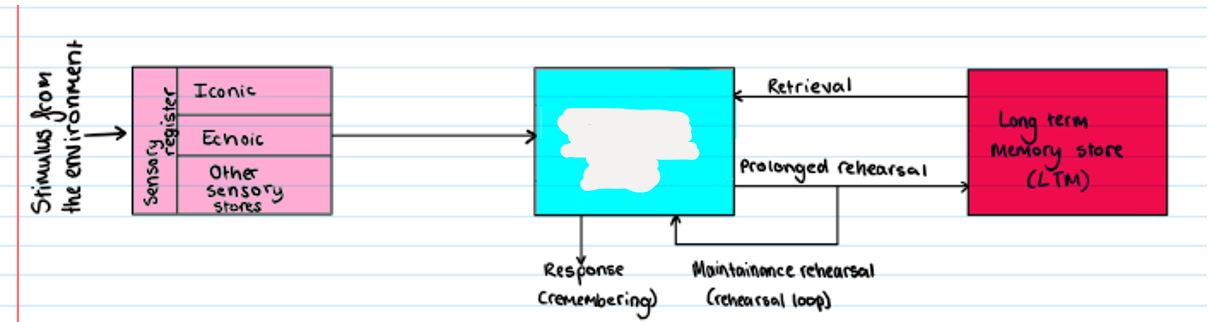
Multi Store Model
What is missing (+capacity, duration, coding)?
STM
Coding: acoustically (Baddeley (1966))
Capacity: limited (Miller (1956): 7+/- 2)
Duration: 18-30 secs unless rehearsed (Petersen et al (1959) - increasing retention intervals decreased accuracy of recall of consonant syllables in 24 Ps when counting down from a 3 digit number (preventing mental rehearsal))
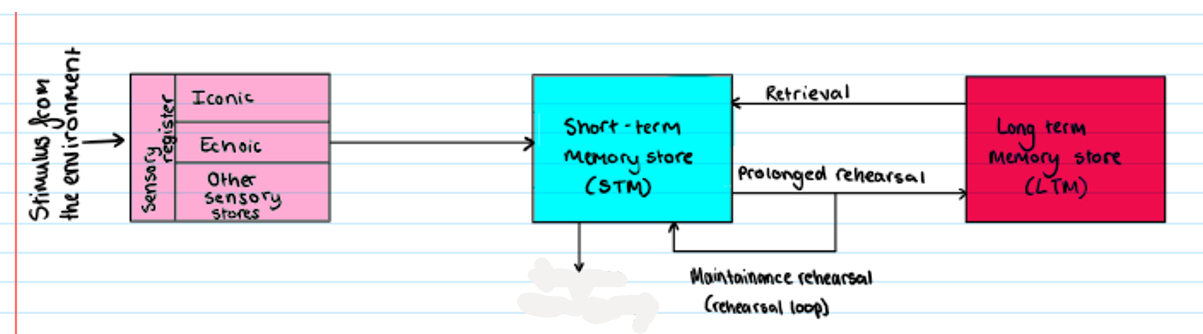
Multi Store Model
What is missing?
response (remembering)
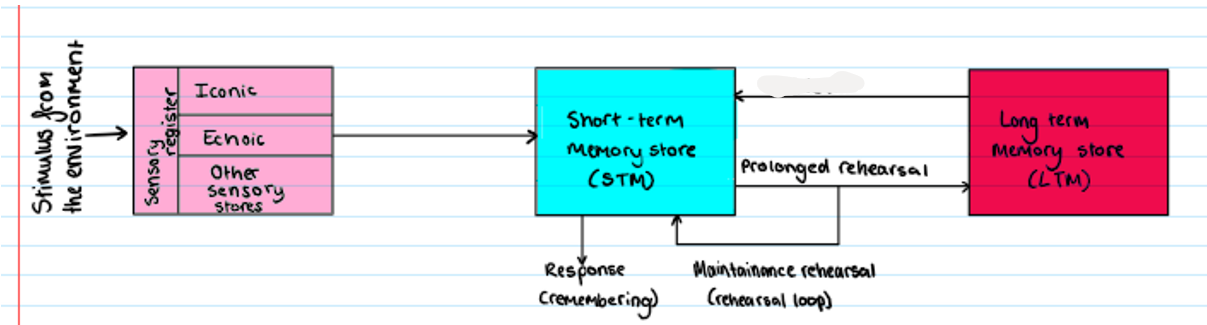
Multi Store Model
what is missing, and what is it?
retrieval
needed for remembering, when info is transferred back into the STM + will continue to pass through the maintenance loop after
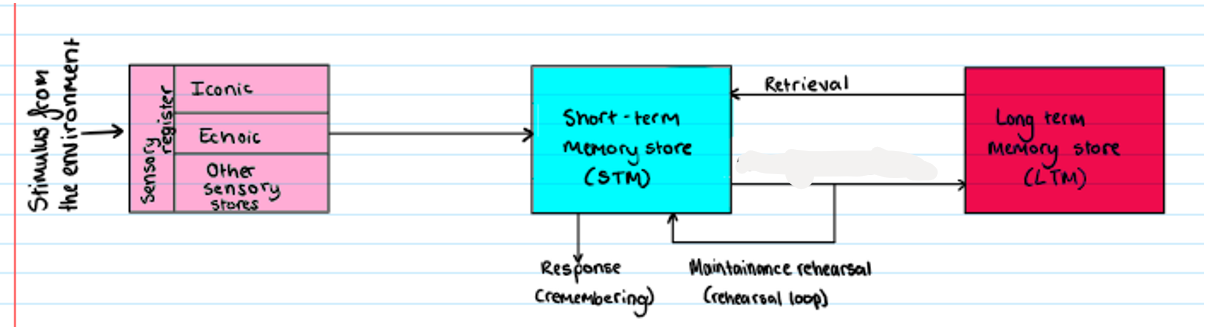
Multi Store Model
What is missing?
prolonged rehearsal
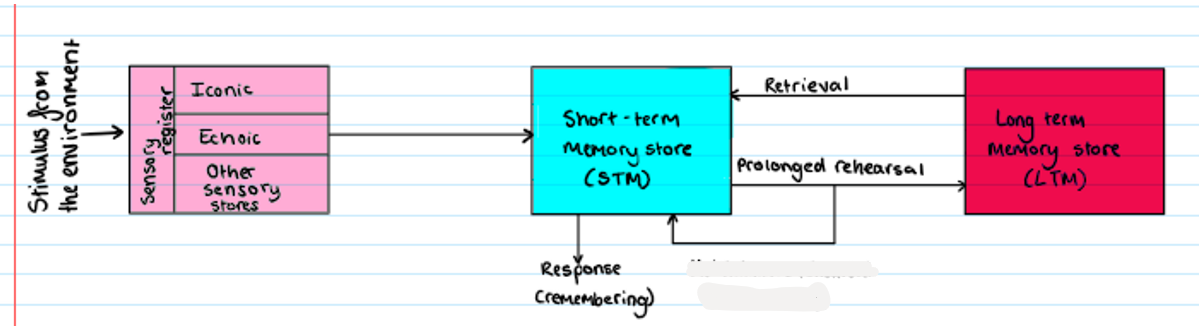
Multi Store Model
What is missing, and what is it?
maintenance rehearsal (rehearsal loop)
when we repeat new info to ourselves, allowing it to be kept in STM: prolonged maintenance rehearsal → LTM, lack of maintenance rehearsal → forgetting
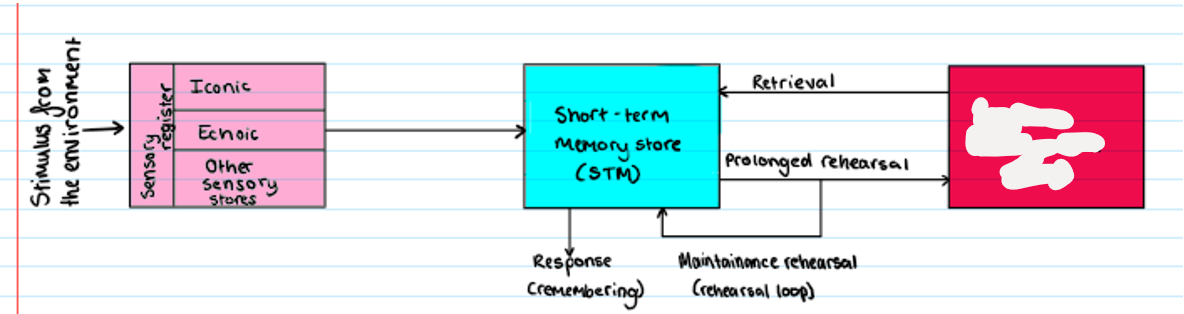
Multi Store Model
what is missing? (+capacity, duration, coding)
long term memory store (LTM)
Coded: semantically (Baddeley (1966)
Capacity: potentially infinite
Duration: at least 46 yrs (Bahrick et al (1975) photo recognition of graduating classmates of Ps → 90% to 70% b/w 15 to 46 years of graduating)
Multi Store Model
Evaluation: supporting evidence for STM + LTM = distinct stores + ISSUE w/ STM’s presentation
case study = KF’s STM = impaired following a motorcycle accident, but his LTM remained intact → suggests that they are stored differently + separately BUT MSM incorrectly represents STM as a single, unitary store → KF had poor STM recall for auditory stimuli, but increasingly accurate recall for visual stimuli suggests there may be multiple types of STM
Multi Store Model
Evaluation: oversimplifies LTM
MSM sees LTM as a single unitary store BUT Tuvling et al: types of LTM = procedural, semantic + episodic. ALSO doesn’t represent how types of LTM are retrieved - some unconsciously (eg: procedural) whilst others must be consciously (eg: semantic) → not reflected in the universal process of info being consciously transferred to STM during retrieval
Multi Store Model
Evaluation: contradicting evidence
MSM suggests amount of maintenance rehearsal determines the likelihood info = pass into the LTM BUT Craik and Watkins (1973) TYPE of rehearsal = more important (elaborative, instead of prolonged rehearsal, is needed to transfer info from the STM into the LTM, by making links with existing knowledge)
Multi Store Model
Evaluation: alternative
WMM → theorises STM is not a unitary store, but made up of different stores (phonological loop, visuospatial sketchpad, episodic buffer) → suggests that MSM = too simplistic a model of memory as STM is unlikely to be a unitary store
Multi Store Model
Evaluation: support for LTM and STM being distinct (coding)
Baddeley (1966) → list of ten words - one at a time → had to write down as many as they could remember in 30s: 1) acoustically similar, 2) semantically similar: 2 = higher recall, difficulty remembering acoustically similar words STM, not in LTM, + vice versa for semantically similar words → supports coding + the idea that LTM + STM are coded differently