class 13 artifacts
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
first assumption (beam pattern assumption)
the beam is narrow/uniform in width/intensity
types of Beam Pattern Artifacts
Axial/lateral Resolution, Partial Vol, Speckle, 2nd Lobes and Focal Banding
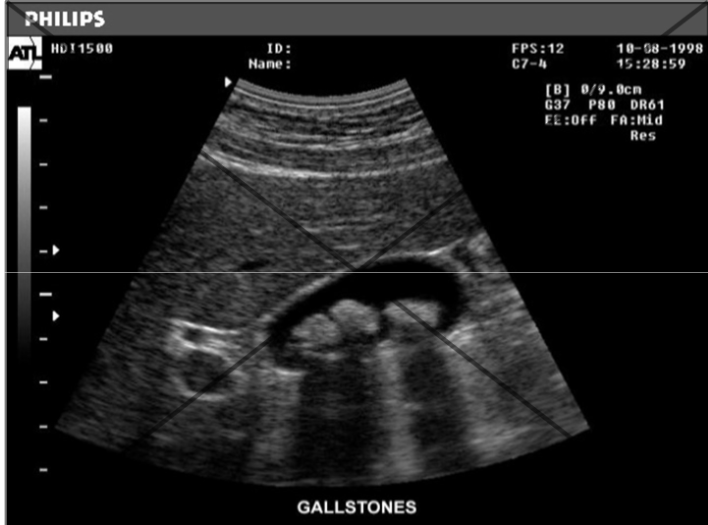
Partial Volume / Slice Thickness (beam pattern artifact) is caused by
multiple tissue types within the beam
most likely affected by partial volume (beam pattern artifact)
cysts and the gall bladder
partial volume (beam pattern artifact)
Fills in hypoechogenic structures
scatter (beam pattern artifact)
interference pattern where the brightness doesnt relate to the tissues properties
Speckle pattern changes with
wavelength and acoustic beam pattern
types of secondary lobes
Side lobes and Grating lobes (linear array)
Focal Banding (beam pattern artifact)
alternating bright and dark bands and inc brightness at the focal zone
Attenuation Artifacts
shadowing and Enhancement
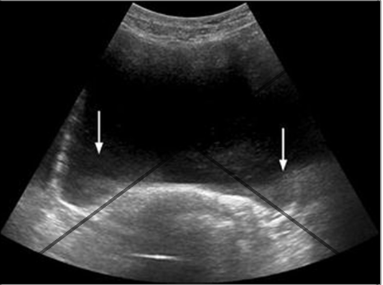
shadowing (Attenuation Artifacts)
dec reflection below a strong reflector/attenuating structure (sound waves are blocked)
Enhancement (Attenuation Artifacts)
inc reflection (brighter) in areas below a weak attenuating structure
in Enhancement artifact
Depth varying gain is overcompensated since attenuation is less than expected
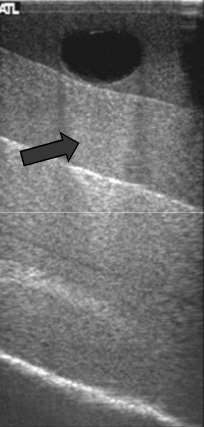
Enhancement
shadowing
Propagation Artifact assumes that the
beam travels in a straight/direct path
Propagation Artifacts
Reverberations (multiple reflections) and Refraction (change in beam direction)
Propagation Artifacts types of Reverberations
Comet Tail, Ring Down and Mirror Image
Propagation Artifacts types of Refractions
duplication and Edge Shadow
reverberations can occur
between the object and xdcr or within objects
in reverberations (Propagation Artifact)
a single interface is displayed more than once
Comet Tail causes
Multiple reverberations between closely spaced surfaces
Ring-Down (reverberations)
Continuous emission of US from resonance (gas bubbles)
Refraction (Propagation Artifact)
a change in the speed of sound from one medium to the next causes the beam to bend causing the reflector to be in the wrong position
Edge Shadow (Refraction)
Shadowing at the edges of curved structures (defocuses the beam inc attenuation)
Edge Shadow usually affects
vessel walls, fetal skull or cysts
If c > 1540 m/s
structures look artificially shallow
If c < 1540 m/s
structures look artificially deep
Range Ambiguity dec
FR/image clarity
Range Ambiguity assumes
echoes come from the most recent pulse
Spectral Doppler Artifacts
Aliasing and Spectral Mirror
Spectral Mirror
pattern is mirrored above and below the baseline
partial volume
in speckle constructive interference creates
brighter spots and destructive creates darker spots creating a random pattern of light/dark spots
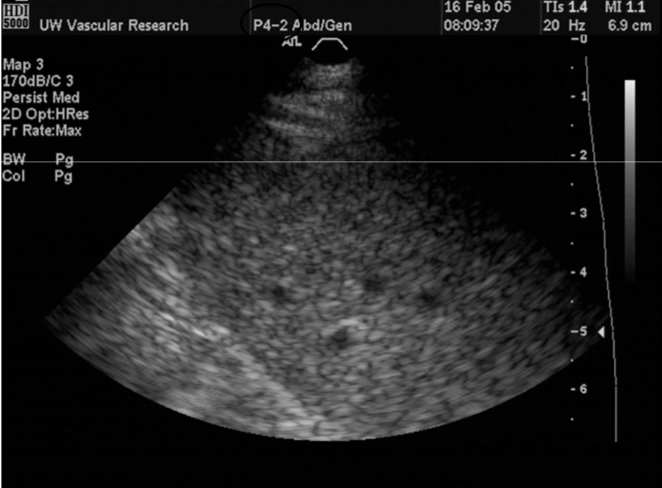
speckle (light/dark pattern)
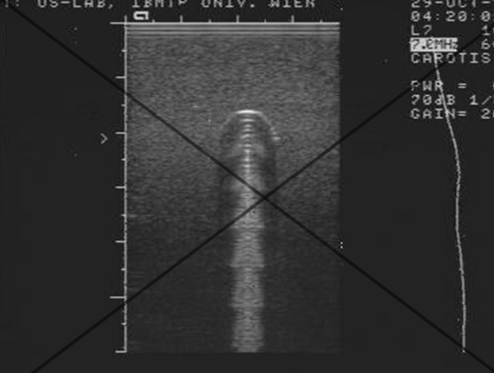
reverberation
refraction is displayed as multiple
equally spaced horizontal lines (Spacing corresponds to the distance between the two reflecting surfaces)
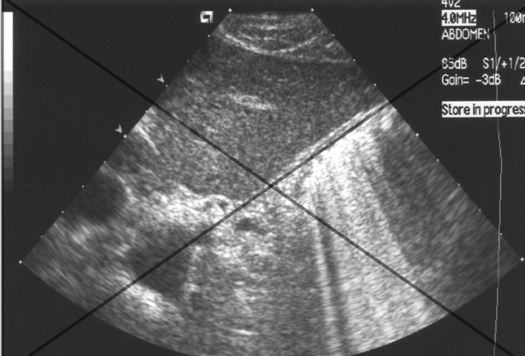
ring down
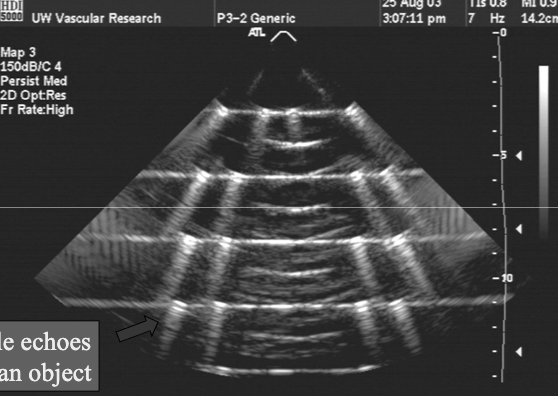
comet tail
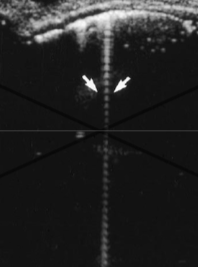
ring down
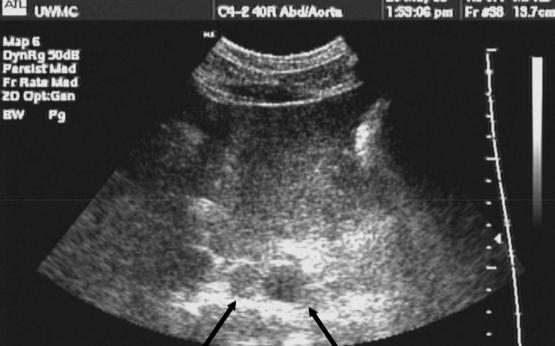
refraction (causes side by side duplication)
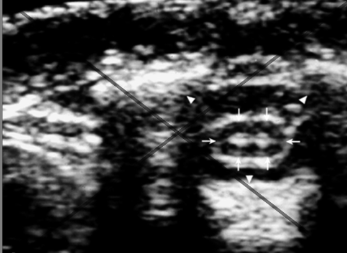
refraction