Section 2 - Thermodynamics, Fluid Principles, and Waves
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Archimedes Principal
An Object that is wholly or partially immersed in a fluid experiences a Buoyant force equal to the force of gravity on displaced fluid.
The Effect of gravity on a fluid
The deeper you go in a fluid, the greater the pressure. This added or guage pressure is equal to the density of the fluid. P=PfluidGH
Pascal’s Principal
for a fully enclosed fluid at rest, any added pressure is transmitted equally and undiminidhed to all points of that fluid.
Continuity Equation
Due to the conservation of mass, the mass flow rate for a non leaking fluid is constant. PVA=CONSTANT
Bernoulli’s Principal
Due to the conservation of Energy, at a constant elevation, a fluids speed and pressure are inversely proportional to each other.
fast water=low pressure
slow water=high pressure
Ideal gas law
For gasses that only interact via collisions, the gas absolute temerpature total pressure and volume are all connected. PV=NRT
Temperature
Scalar – The macroscopic quantity related to the kinetic energies of the particles in a system – Units of Kelvin, K, where T(K) = T(°C) + 273.15
Heat
Q – Scalar – The macroscopic form of energy that is spontaneously transferred between objects or systems at different temperatures – Units of Joules, J
Imagine a gas sealed within a beaker that has a movable piston on the top. The gas pushes up on the piston, doing 30 J of work. In this same amount of time 10 J of heat flows from the gas to the room. What was the change of internal energy of the gas? Has the gas’s temperature increased, decreased, or remained constant? Has the entropy of the gas and room system increased, decreased, or remained constant?
Since the internal energy has decreased, the temperature has decreased as well. Any time there is heat flow, energy gets distributed, and the combined entropy of the two systems increases.
Seeing this all take place, you go over and compress the gas quickly,
doing 60 J of work. 30 J of heat flows into the gas during this process.
What was the change of internal energy of the gas? Has the gas’s
temperature increased, decreased, or remained constant? Has the
entropy of the gas and room system increased, decreased, or remained
constant?
Since the internal energy has increased, the temperature has increased as well. Any time there is heat flow, energy gets distributed, and the combined entropy of the two systems increases.
True or False: The Temperature and Pressure can be used to determine what phase a substance is in.
True
True or False: At any given temperature or pressure, a substance can only exist in one phase of matter
False. A substance can potentially exist in two or three phases at specific temperatures and pressures.
True or False: Absolute Zero is the theoretical limit where the system’s particles have zero kinetic energy and are motionless
True
True or False: An object needs to have a very high temperature in order for it to radiate any kind of light
False. All objects radiate light. They just need to be at very high temperatures in order for them to emit in the visible range. At everyday temperatures, it’s all in the infrared.
True or False: It does not take much energy to change a metal’s temperature due to its low specific heat capacity.
True
As a fluid flows through a thin pipe and then fully through a wider pipe,
what happens to its speed and pressure?
From the Continuity Equation, the Mass Flow Rate for a non-leaking fluid must
be constant: 𝜌𝐴𝑣 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
As the water flows from a thin pipe to a filled wider pipe, the cross-sectional area
increases. In order for the mass flow rate to be constant, the fluid’s speed must then
Decrease!
To find out what happens to the fluid’s Pressure, we use Bernoulli’s Principle,
where at a constant elevation, the fluid’s speed and pressure are inversely proportional.
1
2 𝜌𝑣2 + 𝑃 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
Since the fluid’s speed Decreases, the Pressure must Increase to compensate.
A loss in kinetic energy must correspond with a gain in potential energy
True or False: Due to Pascal’s Principle, for a fully enclosed fluid at rest, a small force applied over a small area in the fluid gets translated into a smaller pressure further away in the fluid.
FALSE: Pascal’s Principle is that for a fully enclosed fluid at rest, any added pressure is transmitted equally and undiminished throughout the fluid
For an Ideal Gas, if the number of gas particles and the temperature of the
gas are held constant, what happens to the pressure of the gas as the
volume increases?
The ideal gas law is PV=NRT
If the Temperature (P) and number of Particles (N) are held constant, then the Volume
and Pressure are inversely proportional to each other. So, as the volume increases, the
pressure must decrease.
True or False: For a sinking object in the ocean, the buoyant force is equal to zero.
FALSE: Due to Archimedes’ Principle, an object wholly or partially immersed in a fluid is subject to a buoyant force equal to the force of gravity on the displaced fluid
Why does the water pressure of the ocean increase the deeper you go in it?
In Pascal’s principal, which says pressure spreads equally in all directions in a fluid.
So as depth increases—-→ weight on water increases——> pressure increases
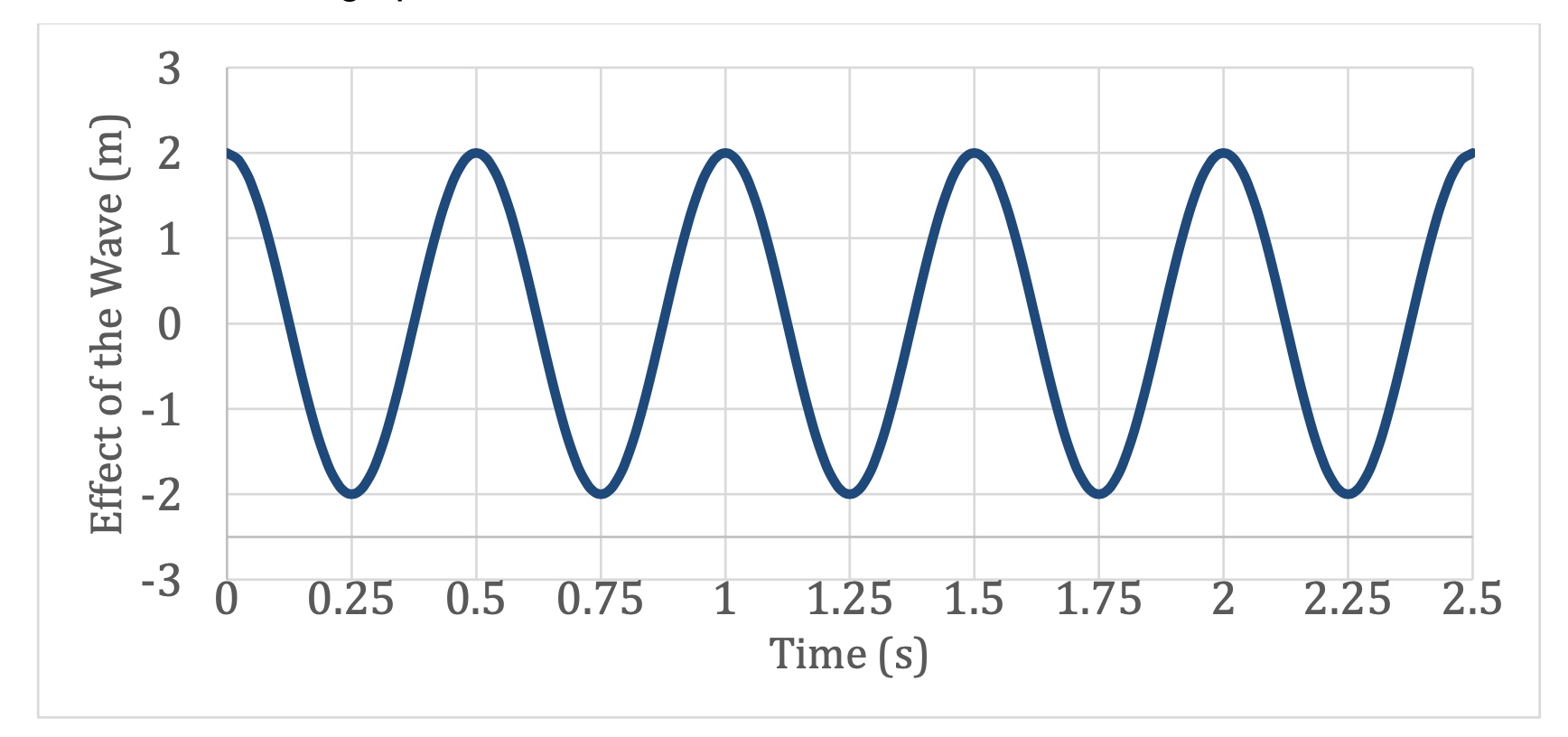
What is the Amplitude of this Wave?
tHE DISTURBANCE is 2
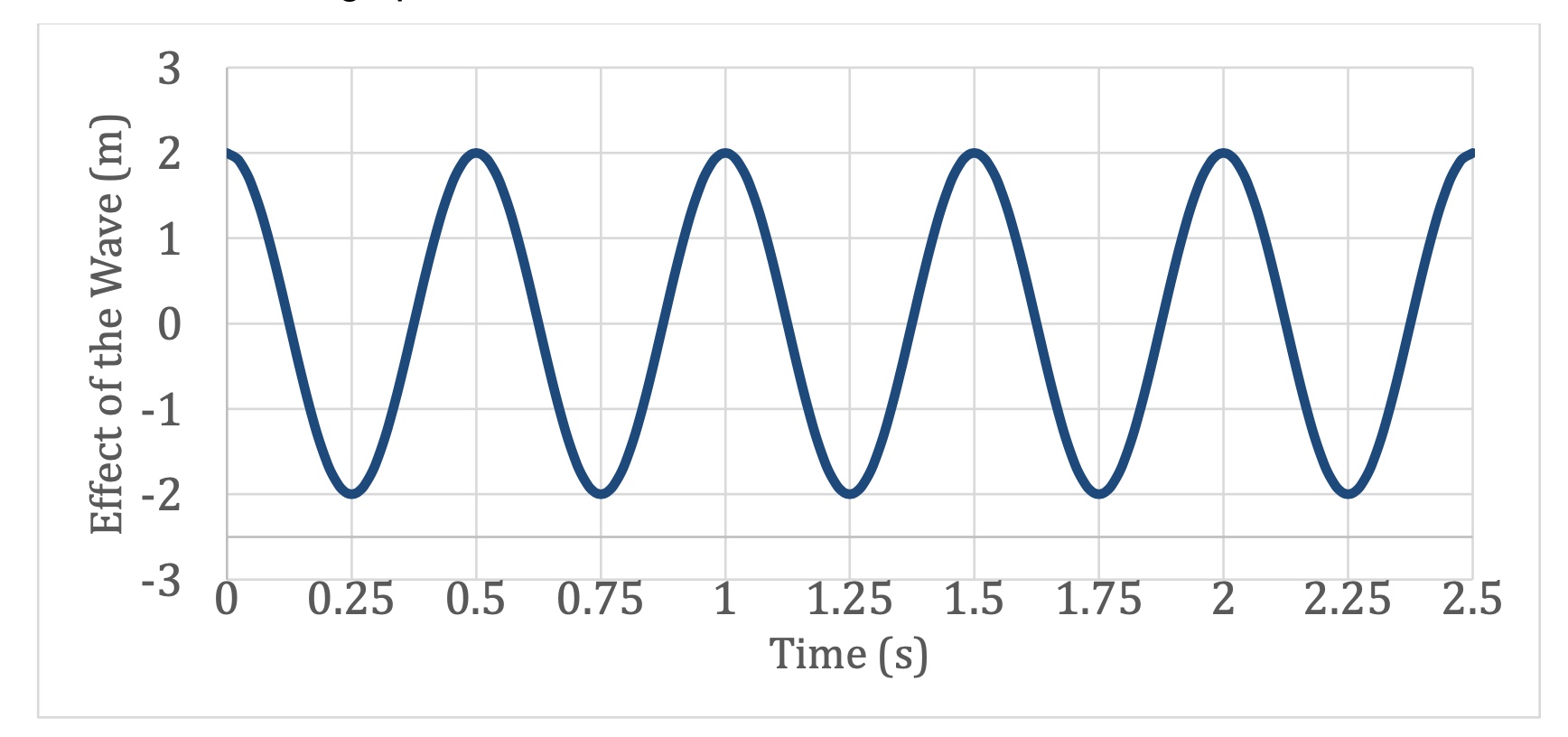
What is the Period of this Wave?
0.5 s.
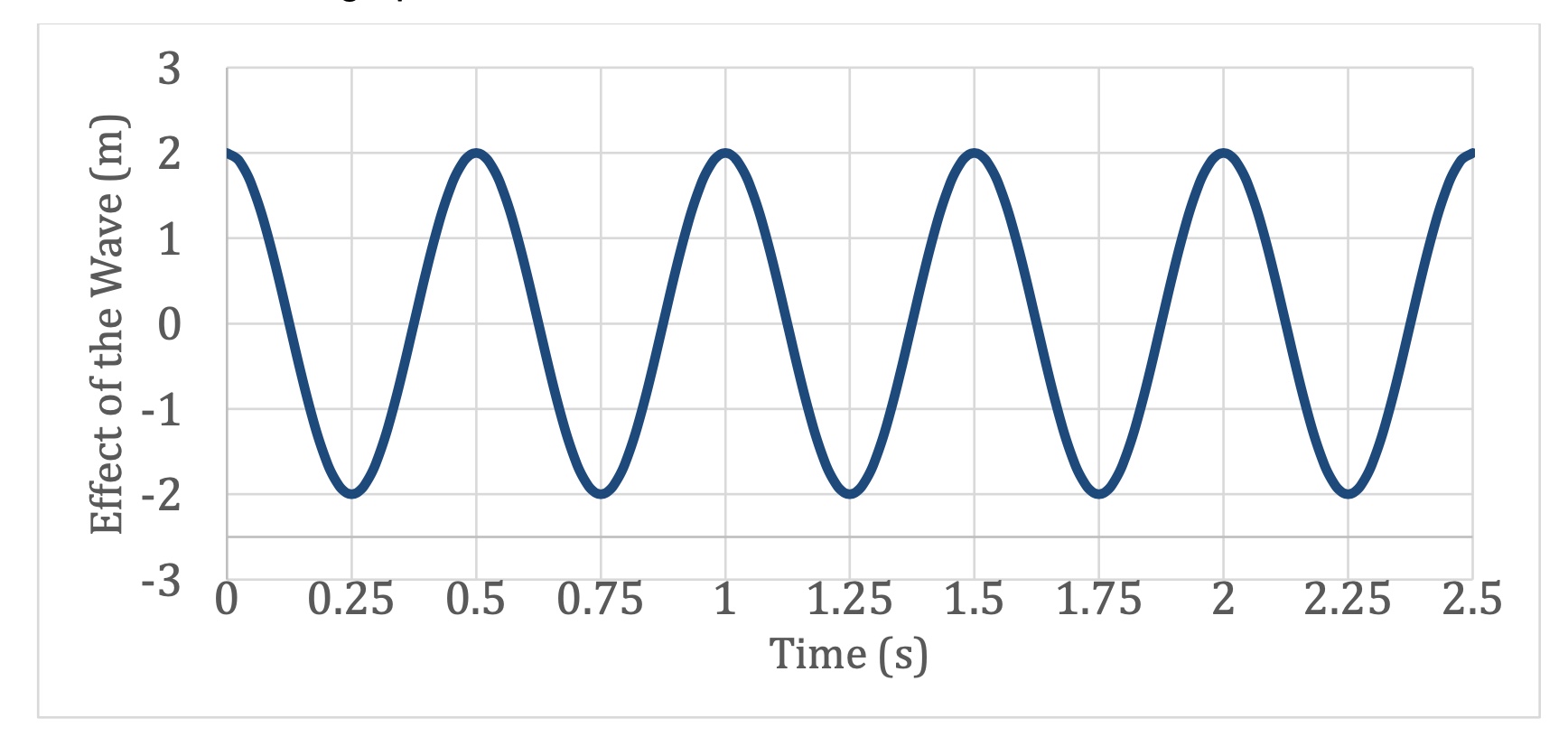
What is the Frequency of this Wave?
𝑓 =1/T=1/0.5s=2HZ
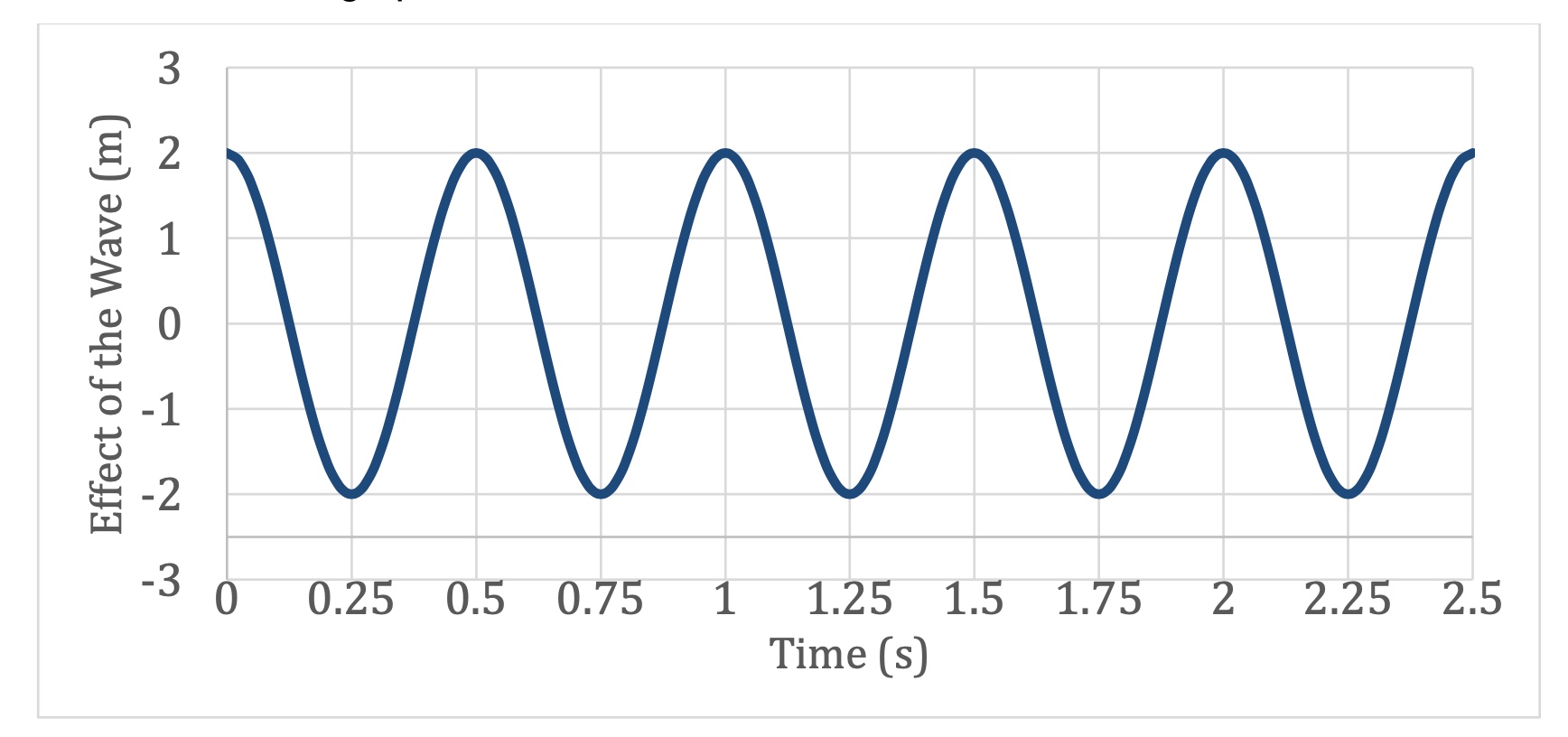
If the speed of the wave is 10 m/s, what would be its wavelength?
5m
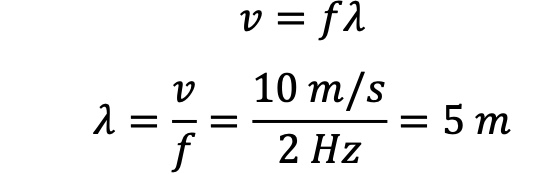
True or False: If a car with a siren is moving faster than you, its frequency will always be higher.
FALSE: The Direction is what is key for the Doppler Effect. The objects need to be moving towards each other for the frequency to be higher
True or False: A longitudinal wave oscillates in the same direction it travels.
true
True or False: The only thing that determines how loud we perceive a sound wave is its amplitude or intensity.
FALSE: Frequency is also a factor in how loudly we perceive sounds
True or False: A sound wave that has 2 times the intensity is perceived to be 2 times louder.
FALSE: The decibel scale for the loudness of sound based on its intensity is logarithmic or exponential in nature, not linear – it is based on powers of ten.
True or False: Harmonics are integer multiples of a base frequency
True
True or False: When two waves with similar frequencies combine, their combined amplitude oscillates slowly, called an envelope or beat, with a frequency that is greater than the frequencies of the two original waves.
FALSE: The beat frequency is the difference of the frequencies for the two original waves
Linear Expansion
ΔL= 𝛼𝐿0Δ𝑇
Lantent heat of fushion-energy or heat needed to melt something
Q=mLf
heat capacity- energy to raise temperature
Q=mcΔT
Energy needed to Vaporize
Q=mLvap
The change in internal energy
ΔU=Q+W
Archimedes Principal
Fbuyoyant=pfluidGVdisplaced
The effect of gravity on a fluid
Added or guage P=pfluidGH
Pascals principal
AddedP1=Addedp2
Continuity Equation
pvA=constant
Bernoulli’s principal
1/2pv²+p=constant
Ideal gas law
PV=NRT
Wavelength λ
Distance/#of cycles
Frequency (f)
F=1/T
Wave speed
v=fλ
Imagine you have a pot of water at 99 °C (so 1°C below its boiling point).Which process requires more heat to flow into the system?
(1) Increasing the water’s temperature by 1 °C
(2) Converting all of that water to steam
2. Phase changes require a ton of energy since they involve the changing of interatomic bonds.
Is the atmospheric pressure on Mount Everest greater than, less than, or equal to the atmospheric pressure here in Jacksonville? Why?
Due to the effect of gravity pressing down on the fluid, the deeper you go in a fluid, the greater the pressure. Conversely, the higher up you go, the lower the pressure, which means that the atmospheric pressure in Mount Everest is much lower than it is in Jacksonville
For an Ideal Gas, if the number of gas particles and the pressure of the gas are held constant, what happens to the volume of the gas as the temperature increases?
so as temp increases volume increases too PV=NRT
what physical constant of a substance corresponds to its temperature changes due to heat flow?
Specific Heat Capacity