Glial Cells: Nervous System Support
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Neuroscience
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Types of Glial Cells
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cell, microglia
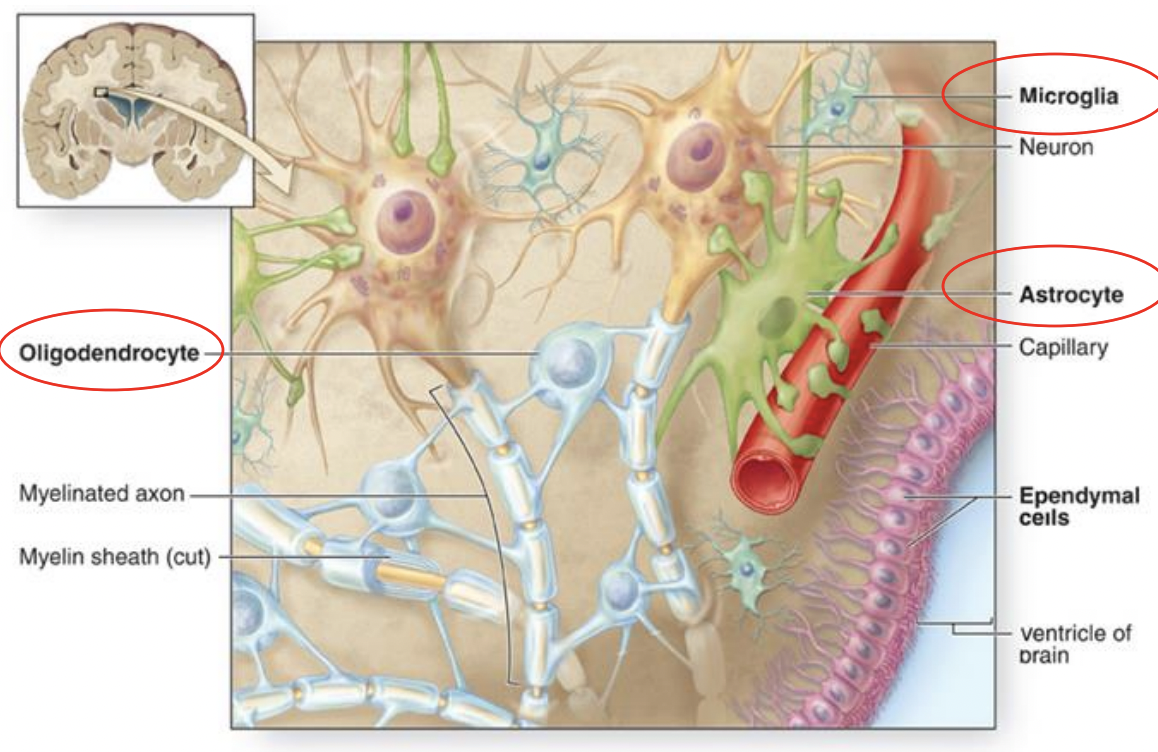
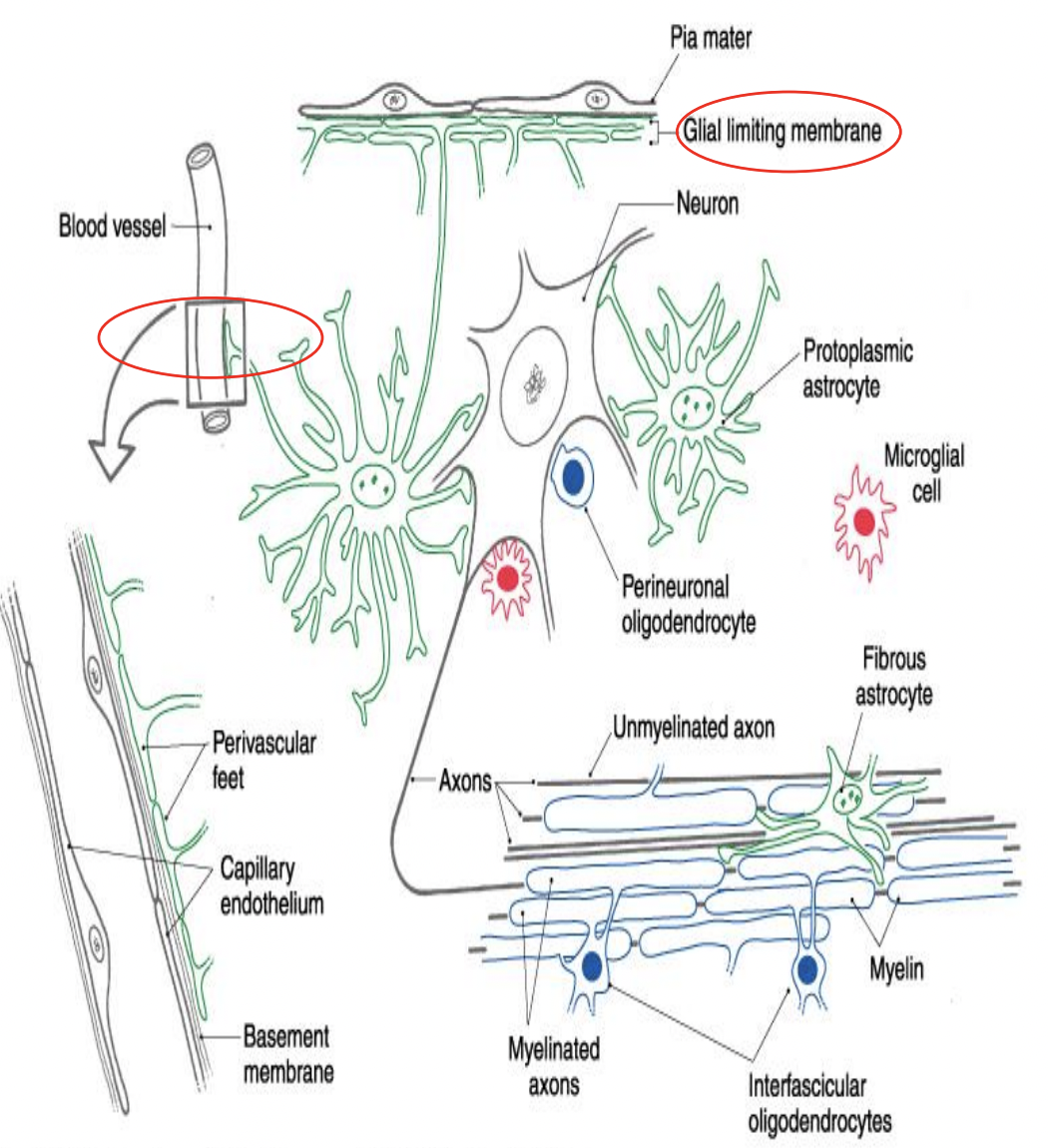
Astrocytes
star shaped, cover surface of most CNS neurons
expansive branches and end-feet
line blood vessels
blood brain barrier (BBB)
participate in neural transmission
structural support and metabolic support of neurons
control of ionic environment and pH
secrete neurotransmitters, cytokines, and growth factors
disease/neurological disorder: MS, Alzheimer’s disease
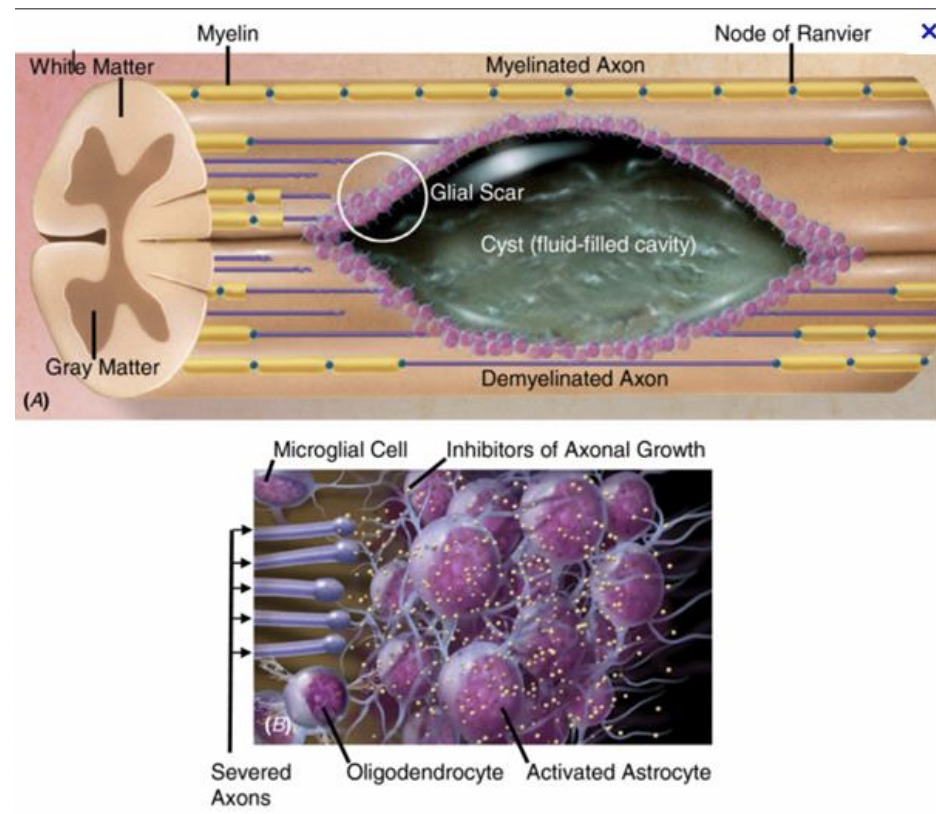
astrocytes: cleaning
response to injury
astrocytes infiltration and proliferation may result in formation of astrocytic scar
CNS injury such as stroke, SCI, and neurodegenerative disease such as multiple sclerosis
may restrict regenerative capacity of CNS
Oligodendrocytes
myelin forming cell in CNS
one cell myelinates multiple axons (sends out multiple processes)
nonmyelinated axons still associated with Oligo
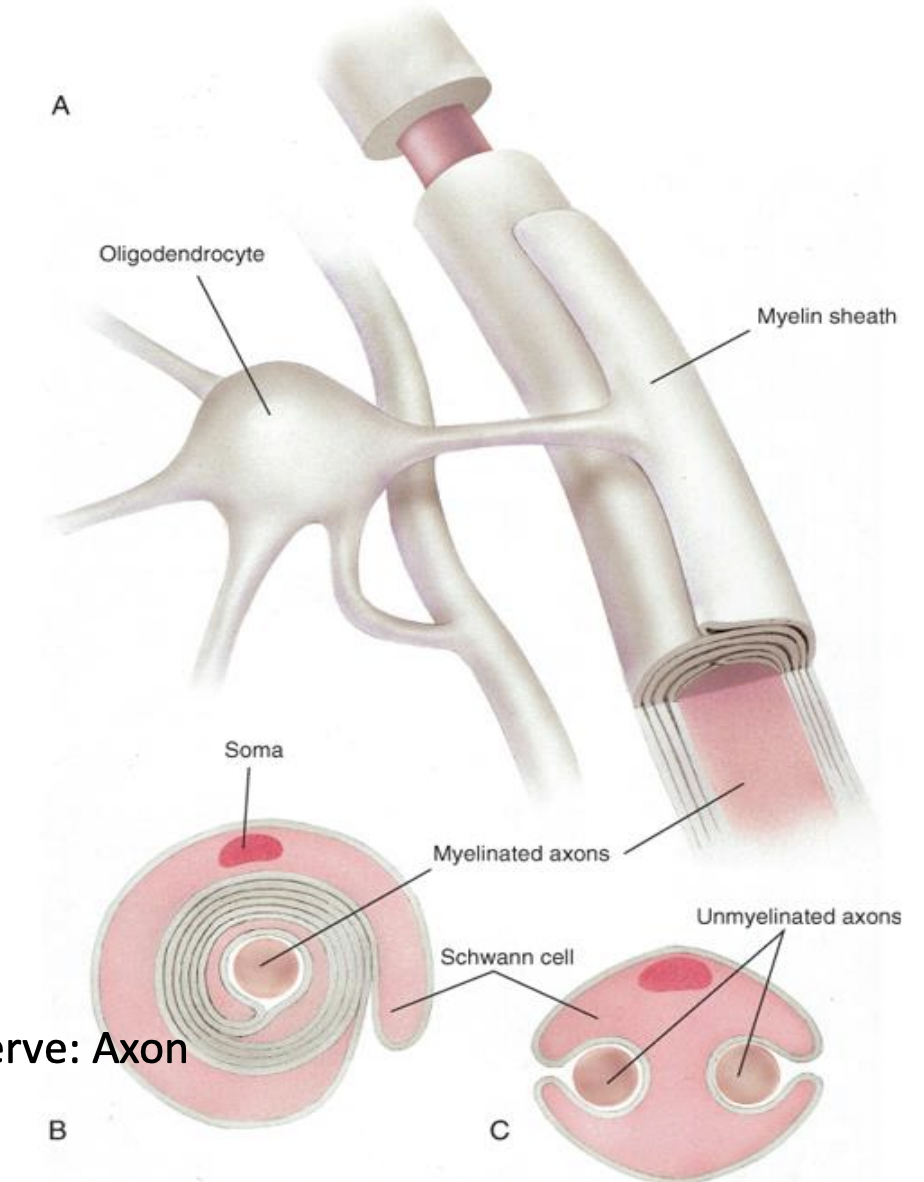
Schwann
myelin forming cell in PNS
may become phagocytic during degeneration and repair
one cell myelinates one axon
nonmyelinated axons still associated with Schwann cells
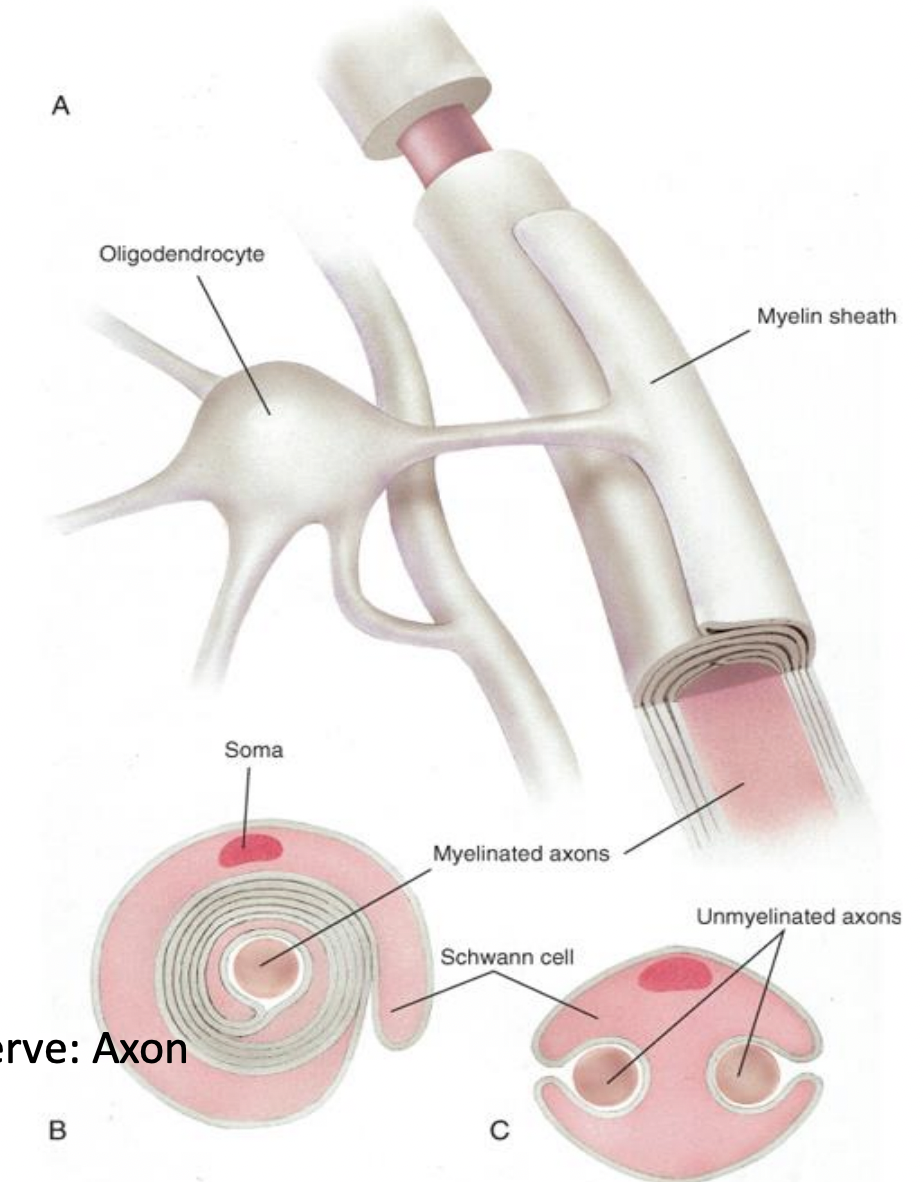
Myelination in the CNS and PNS
Microglia
clean up and removal
comprise 10-20% of all glial cells
immune cells of CNS
become phagocytic in response in injury and damage
involved in CNS inflammation
synaptic pruning
dysregulation implicated in diseases such as
alzheimer’s disease
HIV/AIDS
Chronic/persistent pain
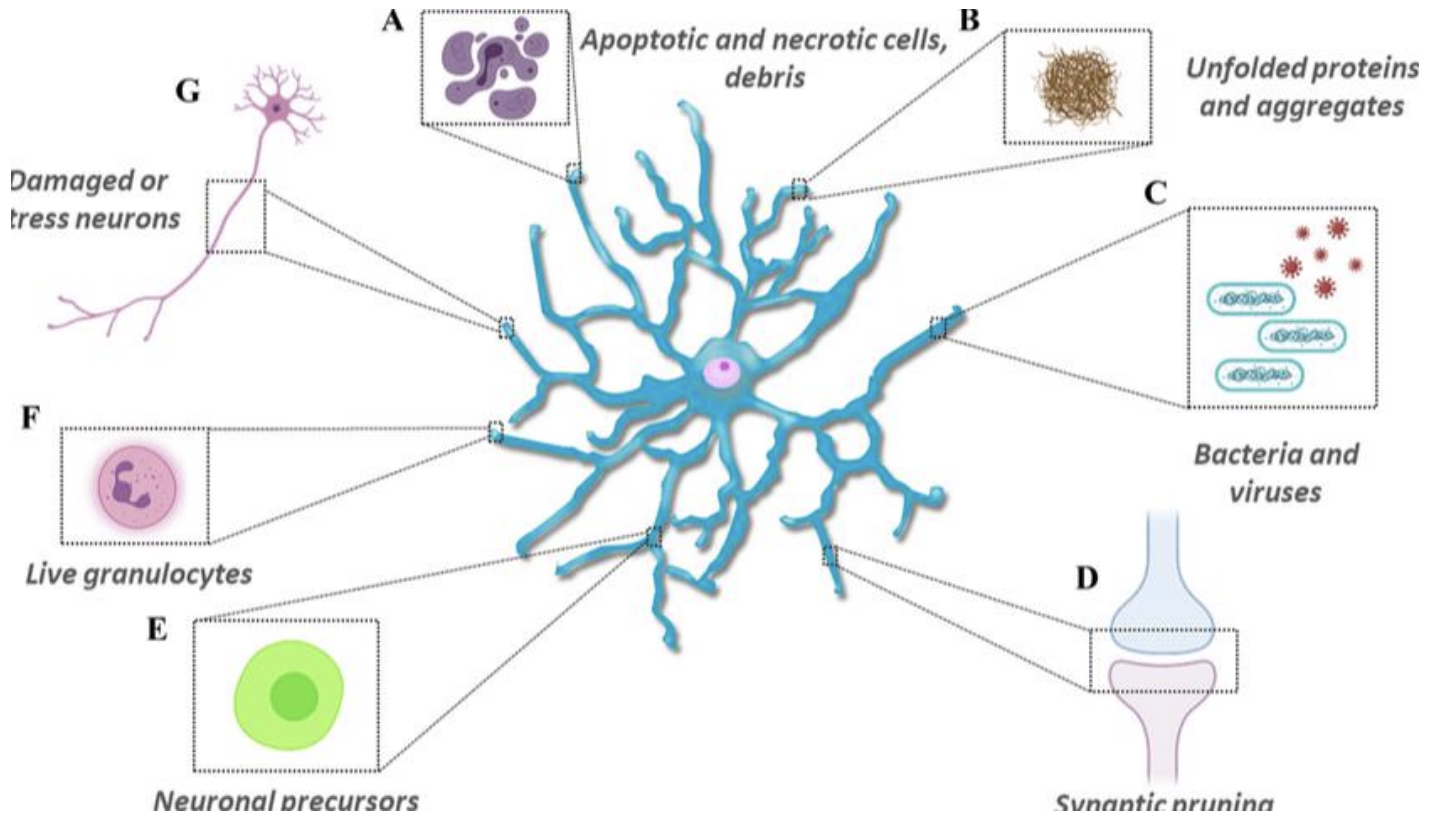
Neuroinflammation
CNS’s response to infections, diseases and injuries
beneficial effect
initiates intervention by astrocytes and microglia and (clean up and removal of debris)
harmful effects
death of neurons and oligodendrocytes, inhibition of neural regeneration
correlation between abnormal glial activity and neural damage in stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and chronic pain
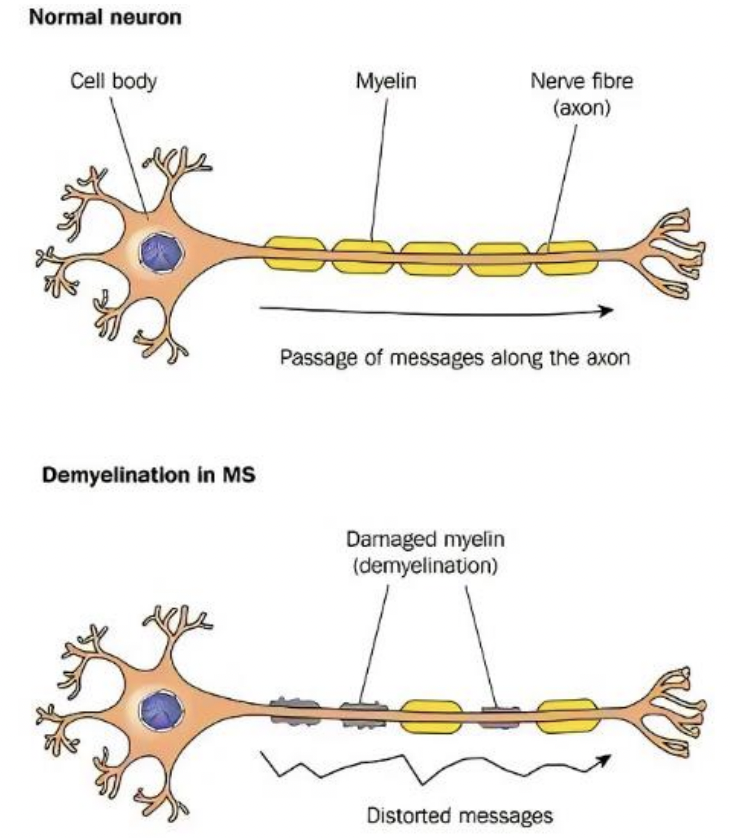
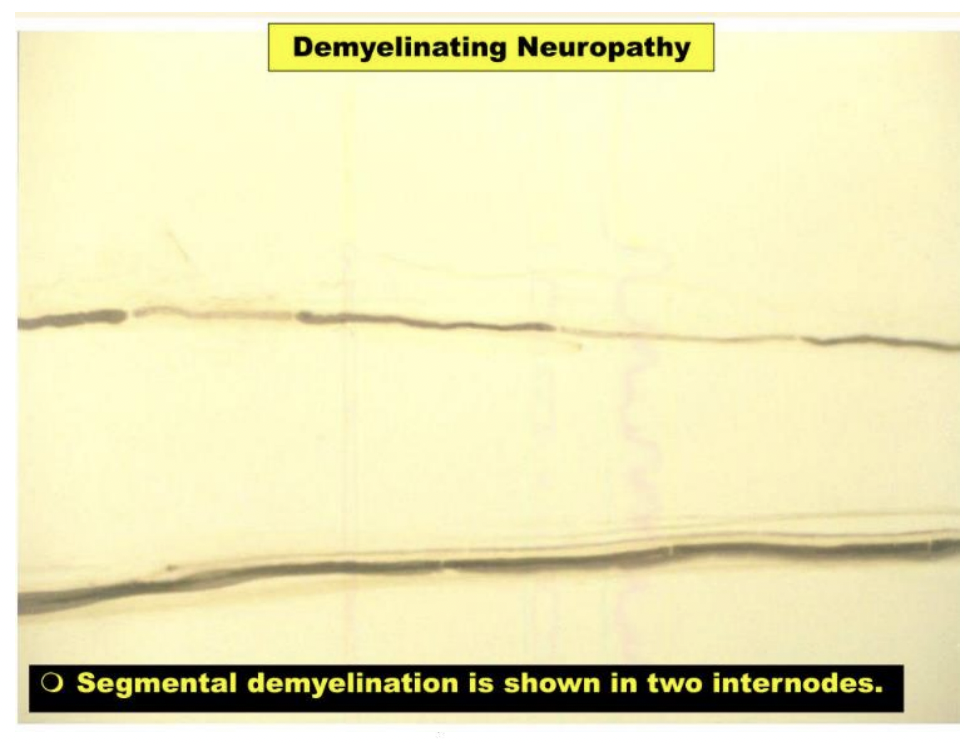
segmental demyelination
regional loss of myelin in CNS or PNS resulting in slowing or blockage of action potential
PNS
guillian barre (acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy)
CNS
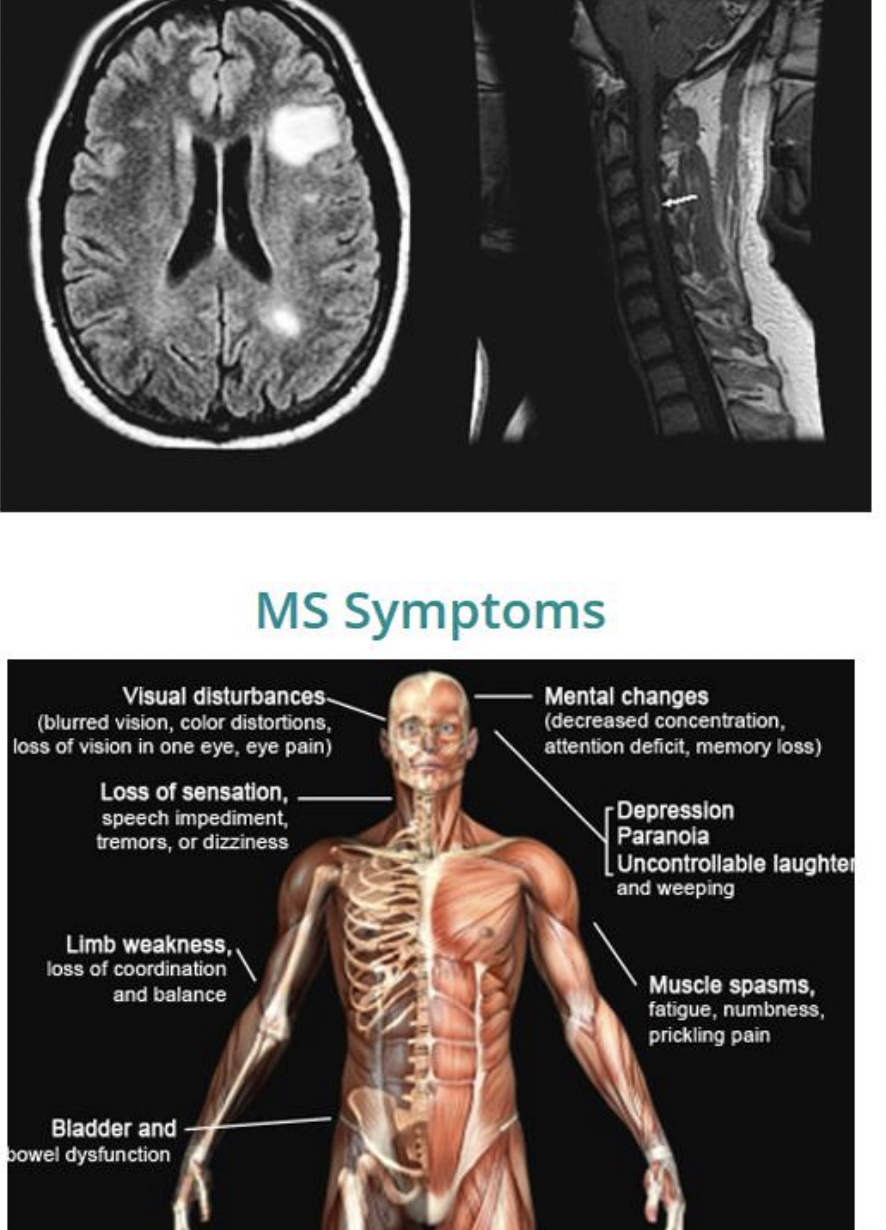
multiple sclerosis: demyelination plus formation of astrocytic scars (sclerotic plaques)
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
involves acute inflammation and demyelination of peripheral sensory and motor fibers
occurs within 2 to 3 weeks after a mild infection
activates the immune system causing production of an antibody that mistakenly cross-reacts with the myelin sheath (Schwann cells)
onset is rapid but followed by plateau then gradual recovery; recovery is usually complete
Tx: plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy, PT/OT
Multiple Sclerosis
antibodies attack oligodendrocytes
produce sclerotic plaques in the white matter of the CNS
signs and symptoms
weakness lack of coordination, impaired vision, double vision, impaired sensation, and slurred speech; may also disrupt of memory and emotions
diagnosis is difficult:
usually manifests with one sign that may completely resolve