B5 - communicable diseases
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
communicable diseases definition
communicable diseases are caused by pathogens such as bacteria n viruses
can be passed on from one person to another
non-communicable diseases definition
non-communicable diseases cannot be transmitted from one person to another
factors affecting health
diet:
if you don’t eat enough nutrients you may suffer from starvation, anaemia or rickets.
if you eat too much, of the wrong food you may suffer from obesity, some cancers or type 2 diabetes.
stress:
high levels of stress can lead to multiple health problems.
include heart diseases, certain cancers n mental health problems.
life situations - include:
where you live
gender
financial status
ethnic group
levels of free healthcare
number of children
local sewage n rubbish disposal
how do pathogens cause diseases?
bacteria rapidly divide (binary fission), produce toxins which cause the feeling of illness.
sometimes they directly damage the cells.
viruses take over the cells of your body, live n reproduce inside the cell, destroying them.
ignaz semmelewis discovery
he insisted that his medical students wash their hands before delivering babies
this decreased the amount of deaths caused by infection in child delivery.
other discoveries
louis pasture developed vaccines against diseases.
joseph lister started to use antiseptic chemicals to destroy pathogens.
microscopes improved, it became possible to see pathogens.
preventing the spread
hygiene
hand washing
using disinfectants
keep raw meat away from cooked food
maintaining hygiene of people working in agriculture
coughing n sneezing into a tissue
vectors
destroying vectors
controlling vectors
vaccinations + isolating individuals
giving individuals vaccinations
isolating individuals
measles
measles is a virus spread by droplet infection.
causes rashes and fever.
prevent spread by isolation or vaccinations.
HIV
flu type illness
early stage can be controlled by antiretroviral drugs
virus attacks the immune system
spread by sexual contact or exchange of fluids
tobacco mosaic
tobacco mosaic virus is spread by contacts n vectors
damages leaves n reduces photosynthesis
prevented by field hygiene n pest control.
salmonella
salmonella is spread through undercooked food n poor hygiene
can cause fever, abdominal cramps, diarrhoea, n vomiting by toxins (produced by bacteria)
poultry are vaccinated to prevent spread
gonorrhoea
gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted disease
can cause discharge from genitals, pain in urination
can be treated with antibiotics.
use condoms n limit sexual partners to prevent spread
rose black spot
rose black spot is a fungal disease of plants where purple or black spots develop on leaves, which often turn yellow and drop early
it affects the growth of the plant as photosynthesis is reduced
it is spread in the environment by water or wind
rose black spot can be treated by using fungicides n/or removing n destroying the affected leaves
malaria
malaria is caused by parasitic protists
it is spread by the bite of a female mosquito
which damages the red blood cells, n causes fevers n shaking.
the spread of malaria is controlled by preventing mosquitos, from breeding n by using mosquito nets to avoid bites
protists
protists group of eukaryotic n usually unicellular organisms
only a small number of protists are pathogenic, but the diseases they cause are often serious
need a vector to transfer from one host to the next
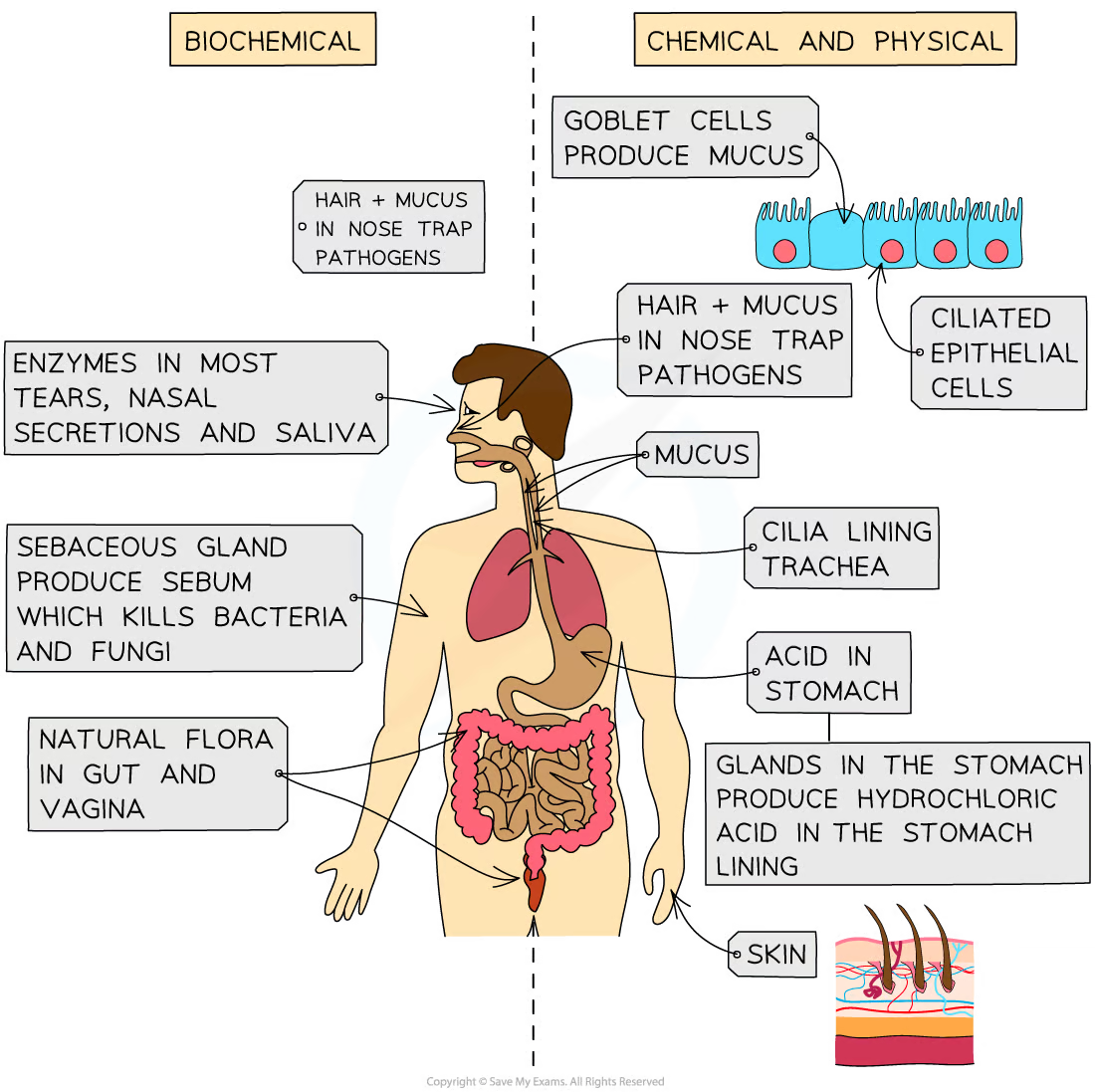
non-specific defences
the non-specific defence systems of the human body against pathogens include:
skin
nose
trachea n bronchi
stomach
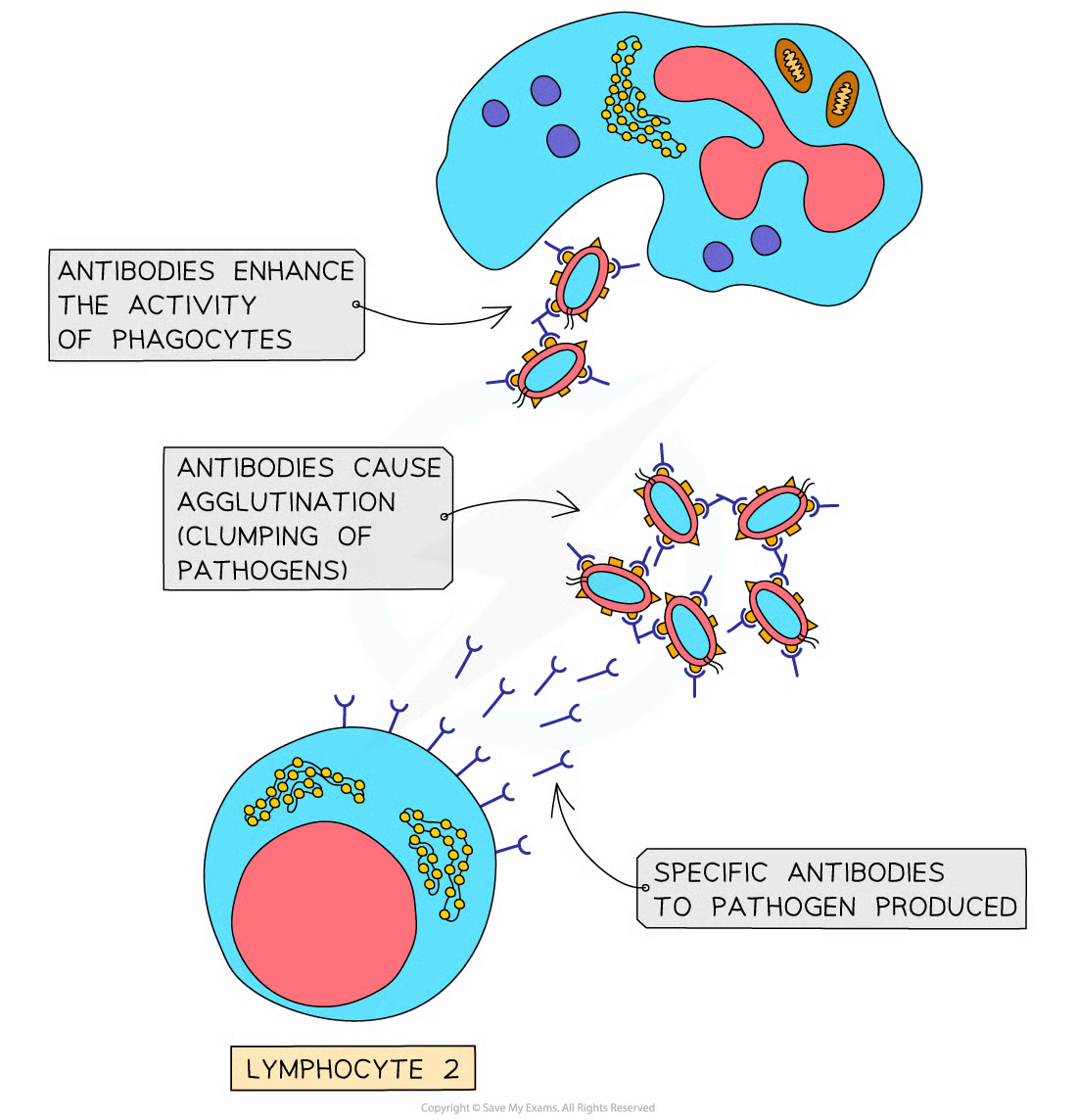
phagocytes
phagocytes engulf n digest pathogens, this can be non-specific or helped by antibodies which cause clumping of pathogens
phagocyte surrounds the pathogen n releases enzymes to digest n break it down to destroy it
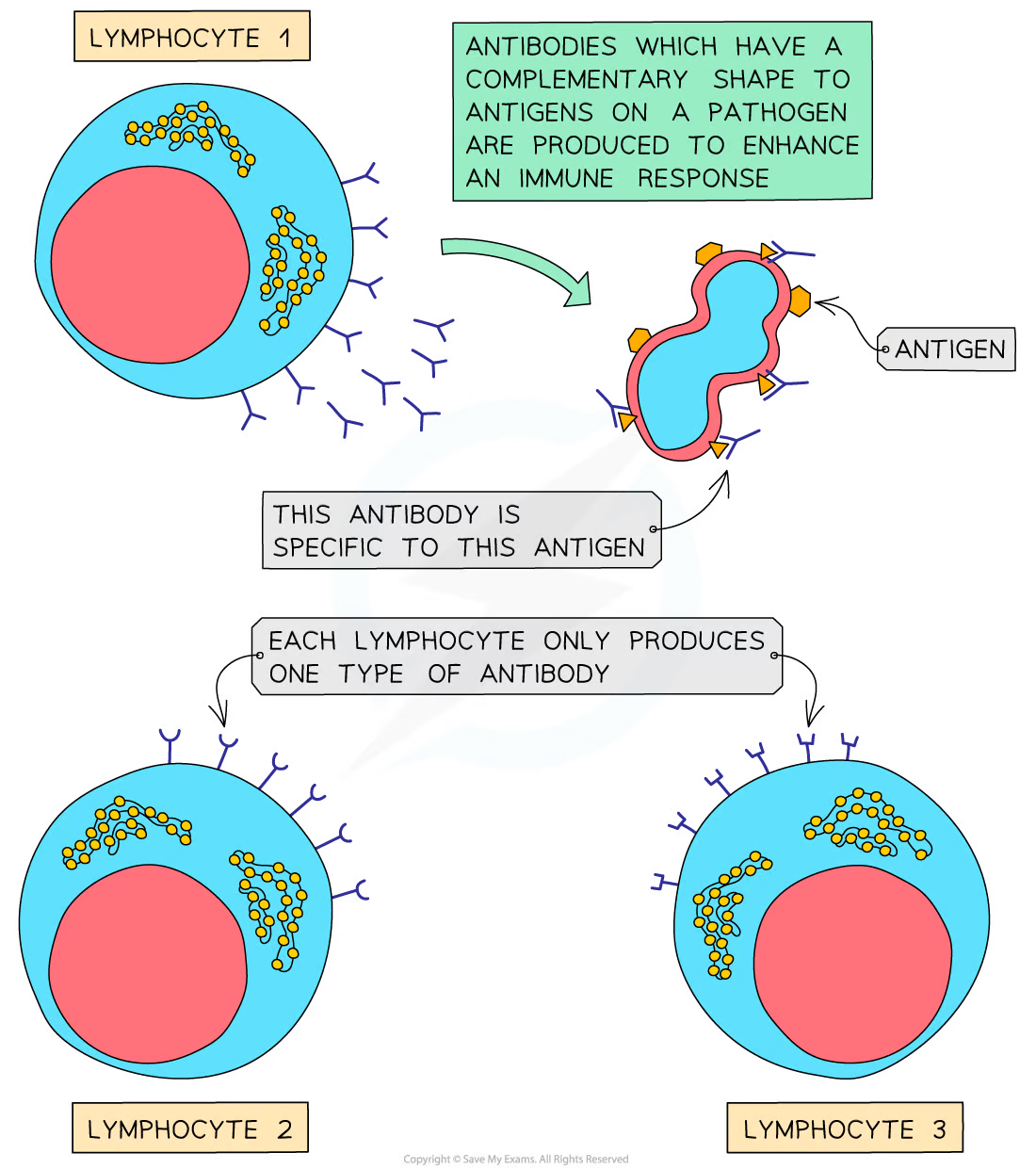
lymphocytes
lymphocytes produce antibodies.
antibodies are Y-shaped proteins – each individual has the potential to make millions of different types of antibodies, each with a slightly different shape
antibody production aims to produce the antibody that is complementary to the antigens on the surface
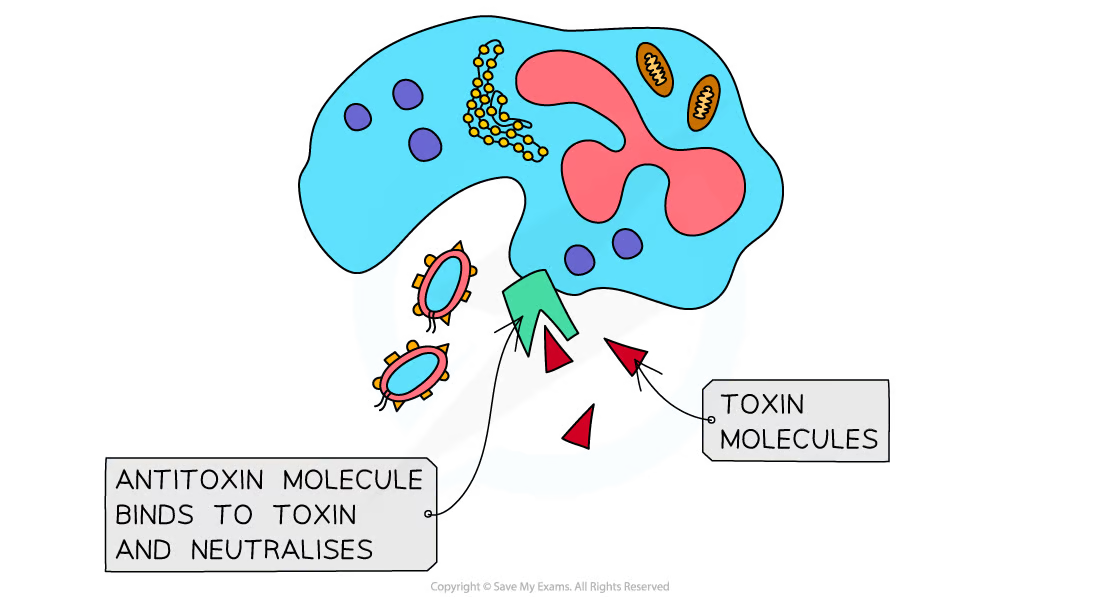
lymphocytes
lymphocytes can produce antitoxins
these counteract the toxins released by pathogens
pathogens spread through air
bacteria, fungal spores n viruses spread through air
spread through droplet infection
droplet infection is caused by coughing/ sneezing - others breathe in the pathogens
pathogens spread through contact
direct contact
animals can act as vectors
sexually transmitted diseases r spread through contact
cuts
scratches
needles
pathogens spread through water
fungal spores in water can spread
eating raw food n sewage
diarrhoea, cholera n salmonella spread