Project Management W3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Project Integration Management
refers to the processes required to ensure that the various elements of the project are properly coordinated. In short, itis the tying together of all of the other aspects involved in a project to make it a success.
Strategic Planning and Project Selection
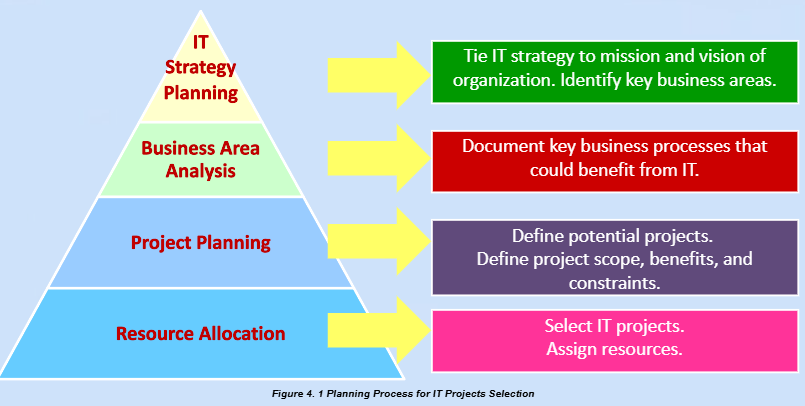
Identifying long-term objectives through the following:
analyzing the organization’s strengths and weaknesses;
studying opportunities and threats in the business environment;
predicting future trends; and
projecting the need for new products and services.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats
used as aid in strategic planning
Business Area Analysis
outlines documents the business processes that are vital to achieving strategic goals, sand aids in discovering which ones could most benefit from IT
Methods for Selecting Projects
Focusing on broad organizational needs
Categorizing IT projects
Performing NPV or other financial analyses
Using weighted scoring model
Implementing balanced scorecard
Focusing on broad organization needs
Top managers need to focus on achieving the various needs of the organization when deciding what projects to undertake, when to undertake them, and to what level.
One method for project selection based on broad organizational needs is determining whether they meet the first three important criteria: need, funding, and will.
Categorizing IT Projects
Problems
Opportunities
Directives
Problems
These are unwanted situations that prevent an organization from achieving its goals.
Opportunities
These are chances to improve the organization.
Directives
These are new requirements imposed by management, government, or some external influence.
Net Present Value
the method of calculating the expected net monetary gain or loss from a project by discounting all expected future cash inflows and outflows to the Net Present Value (NPV) present point in time
A positive NPV means the return from a project exceeds the cost of capital - the return available by investing the capital elsewhere.
Determine the cash inflows and outflows for the project.
Determine the discount rate.
A discount rate is the minimum acceptable rate of return on an investment. It is also referred to as the capitalization rate or opportunity cost of capital.
Calculate the NPV.
The mathematical formula for NPV is: NPV = Σt=0…n At / (1+r)t where t =year of the cash flows, A = amount of cash flow each year, and r =discount rate.
Return of Investment (ROI)
income divided by investment
required rate of returnfor projects
the minimum acceptable rate of return on an investment
based on the return that the organization could expect to receive else where for an investment of comparable risk
formulas for calculating financial ROI for an IT project or any other investment
Payback Period
Is the amount of time it will take to recoup the net amount invested in a project in the form of net cash inflows.
Payback Analysis
Determines how much time will lapse before accrued benefits overtake accrued costs.
When does Payback occurs?
It occurs when the net discounted cumulative benefits and costs reach zero.
Weighted Scoring Model
Is a tool that provides a systematic process for selecting projects based on various criteria:
Meeting broad organizational needs;
Addressing problems, opportunities, or directives;
The amount of time it will take to complete the project;
The overall priority of the project; and
The projected financial performance of the project.
These are needed to identify the criteria required to the project selection process:
Support for key business objectives
Has strong internal sponsor
Has strong customer support
Uses realistic level of technology
Can be implemented in one year or less
Provides a positive net present value
Has low risk in meeting scope, time, and cost objectives
Weights
Indicate how much you value each criterion or how important each criterion is.
Who developed a methodology called balanced scorecard?
Drs. Robert Kaplan and David Norton
Balanced Scorecard
Aids in the selection and management of projects in alignment with the business strategy.
It is used to convert an organization’s value drivers, such as , innovation, operational efficiency, and financial performance, into a series of defined metrics.
Metrics
were analyzed and recorded by the organizations to determine how well the projects have helped them in achieving strategic goals
Project Charter: INPUTS
Project statement of work
Business case
Contract
Enterprise environmental factors
Organizational process
Project Charter: TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
Expert Judgement
Project Charter: OUTPUT
Project Charter
Statement of Work (SOW)
Is a narrative description of products and services to be delivered by the project.
References the business need, product scope description and strategic plan
Business Case
Is a document that provides the required information from a business perspective to determine whether or not the project is worth investing for.
Contract
Specifies if the project is being done for an external customer.
The enterprise environmental factors that can influence the development of project charter include, but are not limited to:
Government or industry standards
Organization infrastructure
Marketplace conditions
The organizational process assets that can influence the development of project charter include, but are not limited to:
Organizational standard processes, policies, and standardized process definitions to be used in the organization
Project charters templates
Historical information and lessons learned knowledge base
Expert Judgement
Is used to evaluate the inputs that are used to develop the project charter.
Project Charter
Formally recognizes the existence of a project and provides direction on the project’s objectives and management
Allows a project manager to use the organizational resources to complete the project
Should be signed by key project stakeholders to acknowledge agreement on the need for and the intent of the project
Inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs
It specifies the following:
business needs;
current understanding of the customer’s needs; and
the new product, service, or result
Project Management Plan
It is a formal document used to coordinate all project planning documents and help guide a project’s execution and control.
It documents project planning assumptions and decisions regarding choices, facilitate communication among stakeholders, define the content, extent, and timing of key management reviews, and provide a baseline for progress measurement and project control
It is dynamic, flexible, and subject to change when the environment or project changes
It assist the project manager in leading the project team and assessing the project status
Its common elements are:
introduction or overview of the project
description of how the project is organized
management and technical processes used on the project
sections describing the work to be done, schedule, and budget information
Stakeholder Analysis
Documents information such as key stakeholder’s names and organizations, their roles on the project, unique facts about each stakeholder, their level of interest in the project, their influence on the project, and suggestions for managing relationships with each stakeholder.
Project Execution
Involves managing and performing the work described in the project management plan
Project manager and the project management team direct of the planned project activities, and manage the various technical and organizational interfaces that exist within the project
The main function of creating project plans is to guide project execution.
Having a good plan would result to good products and it should document the good work results included in it.
o improve the coordination between project plan development and execution, follow the rule: Those who will do the work should plan the work.
Tools and Techniques in Project Execution
Project management methodology
Project management information systems
Project management methodology
It follows a methodology describing not only what to do in managing a project, but how to do it
Project management information systems
Various organizations are using powerful enterprise project management systems that can be accessed via the internet
Monitoring and Controlling Project Work
It involves the following to determine what process improvements can be made:
collecting, measuring, and disseminating
performance information;
assessing measurements; and
analyzing trends
Project Performance
Should be monitored continuously by the project team to assess the overall condition of the project and to identify the areas that require special attention.
Tools and Techniques for Monitoring and Controlling Projects
Project management methodology
Project management information systems
Expert judgment
Earned value management
Inputs necessary to monitor and control project work:
Project management plan
Work performance information
Performance reports
Change requests
Outputs in Monitoring and Controlling Project Work:
Corrective actions
Preventive actions
Integrated Change Control
It identifies, evaluates, and manages changes throughout the project life cycle
Objectives of Integrated Change Control
Influencing the factors that create changes to ensure that changes are beneficial
Determining that a change has occurred
Managing actual changes as they occur
Inputs of Integrated Change Control
Project management plan
Work performance information (in a form of performance reports)
Requested changes
Recommended preventive and corrective actions
Recommended defect repair
Deliverables
Outputs of Integrated Change Control
Approved and rejected change requests
Approved corrective and preventive actions
Approved and validated defect repair
Deliverables
Updates to the project management plan
Change Control System
Refers to a formal, documented process that describes when and how the official project documents may be changed
It describes the people who are authorized to make changes, the for the change, and any automated or manual tracking systems that will be used by the project
Control Board (CCB)
It is a formal group of people who are responsible for approving or rejecting changes on a project.
It provides guidelines for the following:
preparing change requests
evaluating change requests
managing the implementation of approved changes
It consumes time in making decisions on proposed changes because they often meet only once a week or once a month and may not be able to make decisions in one meeting.
Configuration Management
It ensures that the descriptions of the project’s products are correct and complete, and concentrates on the management of technology by identifying and controlling the functional and physical design characteristics of products and their support documentation
Configuration Management specialists identify and document configuration requirements, control changes, record and report changes, and audit the products to verify conformance to the requirements
Communication
It is a written and oral performance reports are used by project managers to aid in identifying and managing project changes
Stand-up meetings are performed by project managers once a week to communicate what is most important on the project
Closing Projects
To close a project, all the activities must be finalized and the completed or cancelled work must be transferred to the appropriate people
Major Outputs:
Administrative closure procedures;
Contract closure procedures;
Final products, services, or results; and
Organizational process asset updates.