Biology - Term 2 2025
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
What is DNA?
A chemical substance present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms.
What does DNA do?
control all the chemical changes which take place in cells and control the kind of organism produced.
What is DNA made up of?
millions of long chains of sub-units called nucleotides
What are nucleotides made of?
sugar (called deoxyribose), a phosphate group (PO4) and an organic base
What is deoxyribose?
A sugar similar to ribose but lacks one oxygen atom
What is ribose?
A sugar with only 5 carbon atoms in its molecule
What are the sugars in DNA represented by?
A hexagon
What are the 4 types of bases in DNA?
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G)
what are the bonds of the nucleotides held together by?
Hydrogen bonds
What does adenine always bond with?
Thymine
What does cytosine always bond with?
Guanine
What is it called when bases pair up together?
complementary base pairing
What is a double helix?
When the paired strands are coiled into a spiral
What are chromosomes?
Long, thin thread-like structures found in the nucleus and made of human DNA and protein
How many chromosomes are in human cells?
46
what are the human cells that contain less than 46 chromosomes?
Sperm and egg cells (23), red blood cells (no nucleus, therefore 0)
What are autosomes and what do they do?
Non-sex chromosomes that regulate all inheritance of an organism's characteristics (excluding sex-linked traits)
How many sets of autosomes do humans have?
22
How are autosomes labelled?
numerically from 1-22 and grouped according to their shape, size, etc
What are autosomes responsible for?
transferring genetic information from parents to their offspring
What are homologous chromosomes?
Two of the same type of chromosomes, each coming from a different parent
What similarities do homologous chromosomes have?
same length, have the centromere (point where two chromosomes join) in same position, have genes for particular characteristics at same location along their length.
What do sex chromosomes do?
Determine a species' sex
What are sex chromosomes labelled as?
x and y
For humans, what pair of chromosomes is the male sex?
xy
For humans, what pair of chromosomes is the female sex?
xx
What are y chromosomes typically involved in?
tesis and male sex organ development
Why are genes on the x chromosome less specific?
both males and females possess it
What is a diploid chromosome number?
the number of chromosomes in cells
What is diploid number also described as?
2n (2 sets)
What is the difference between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid cells have half the number of chromosomes as diploid cells
Why are sex cells (gametes) haploid?
They have 23 chromosomes instead of 46
What forms the genetic code?
sequence of bases in DNA
What does a group of 3 bases do in the genetic code?
control production of amino acid in the cytoplasm of the cell
What determines the protein being produced (genetic code)?
Different amino acids and the order which they are joined
How are part of proteins coded (genetic code)?
Amino acids are joined together in the correct sequence
How are genes formed?
sequence of triplets in the DNA molecule are coded
How does a gene turn into a trait?
The protein product controls/contributes to trait
What is the process from DNA to trait?
DNA - gene - protein - trait
What is the definition of inheritance?
Passing down of traits for generation to generation
How many genes are passed down to offspring?
two copies - one copy inherited from mother and one copy inherited from father
What is a genotype?
The entire genetic makeup of an organism; versions of alleles/genes carried by an organism
What is a phenotype?
Observable characteristics or traits as a result of your genotype
What are alleles?
Different versions of cells
What is an example of an allele?
Different versions of the hair colour gene (red & brown hair)
What does homozygous mean?
Both inherited alleles are the same
What does heterozygous mean?
Both inherited alleles are different
What needs to happen before a cell divides?
DNA needs to be copied from the parent cell to the daughter cell (DNA replication)
When does DNA replication occur?
At the beginning of every cell division (mitosis and meiosis) during interphase
What is the first step in DNA replication?
Unwinding the DNA
What occurs during the first stage of DNA replication?
Enzyme called DNA helicase unwinds the double-stranded DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
What is the purpose of the first stage of DNA replication?
to expose sections of single strand DNA
What is the second step in DNA replication?
Making new DNA strands
What occurs during the second stage of DNA replication?
Enzyme called DNA polymerase “walks” down DNA strands and adds new nucleotides via complementary base pairing
What is the third stage of DNA replication?
Rewinding the DNA molecule
What occurs during the third stage of DNA replication?
DNA ligase glues the fragments into one new continuous strand, sugar and phosphate molecules bond with neighbouring
What is the result of DNA replication?
two new DNA molecules that are identical to one another
What is mitosis?
The process in which one cell (parent cell) divides into two genetically identical daughter cells
What is the mitotic index?
The ratio between the number of cells in mitosis and the total number of cells
What does the mitotic index measure?
The proliferation status of a cell population (ie: proportion of dividing cells)
How can the mitotic index be determined?
By analysing micrographs and counting the relative number of mitotic cells vs non-dividing cells
What is meiosis?
The process in which sex cells (male and female gametes) are produced with only half the genetic material of the original cell (haploid cells)
Where does meiosis occur in females?
ovaries
Where does meiosis occur in males?
testes
What is the purpose of meiosis?
To make daughter cells with exactly half as many chromosomes as starting cells
What is meiosis comprised of?
two nuclear divisions called meiosis I and meiosis II
What does meiosis result in?
Four haploid cells are produced which are genetically different from one another and from the parent cell.
What are the 11 steps in meiosis?
Interphase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Cytokinesis I, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II, Cytokinesis II
What is the mitotic index formula?
Cells in mitosis/total number of cells
What is the acronym for remembering the stages of Meiosis?
“I pay money at the casino” x2
What occurs during prophase I in mieosis?
DNA condenses and coils into visible chromosomes, spindle fibers form and attach to centromere, homologous chromosomes come together, “crossing over” occurs
What is “crossing over” (prophase I, meiosis)?
Mutual exchange of genetic material (pieces of DNA) between homologous chromosomes
What occurs during Metaphase I in meiosis?
Paired homologous chromosomes line up along equator (middle) of cell
What occurs during anaphase I in meiosis?
Spindle fibers shorten, homologous chromosomes start to separate from each other.
What occurs during telophase I in meiosis?
Spindle fibers break down, new nuclear membrane forms, cytoplasm of cell divides, resulting in 2 daughter cells (diploid), meiosis II commences.
What occurs during prophase II during meiosis?
chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form, nuclear envelope or membrane breaks down
What occurs during metaphase II during meiosis?
sister chromatids of each chromosome are lined up along the equator (middle) of cell
What occurs during anaphase II during meiosis?
spindle fibers shorten, sister chromatids separate and move to opposite sides.
what occurs during telophase II during meiosis?
spindle fibers break down, nuclear membrane forms, cytoplasm of each cell divides, four haploid cells are produced
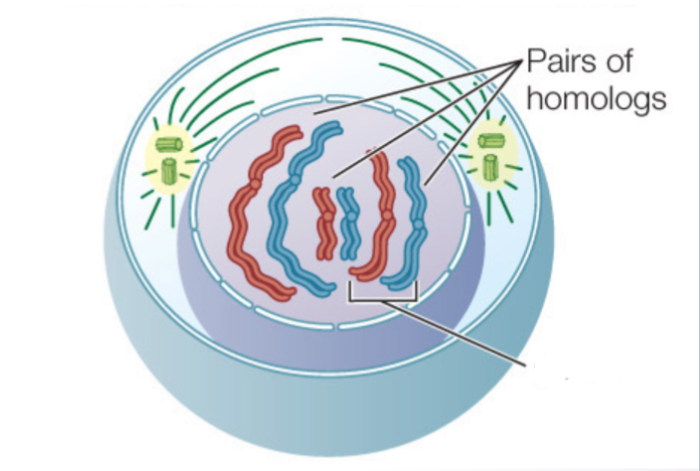
what stage of meiosis is this?
prophase I
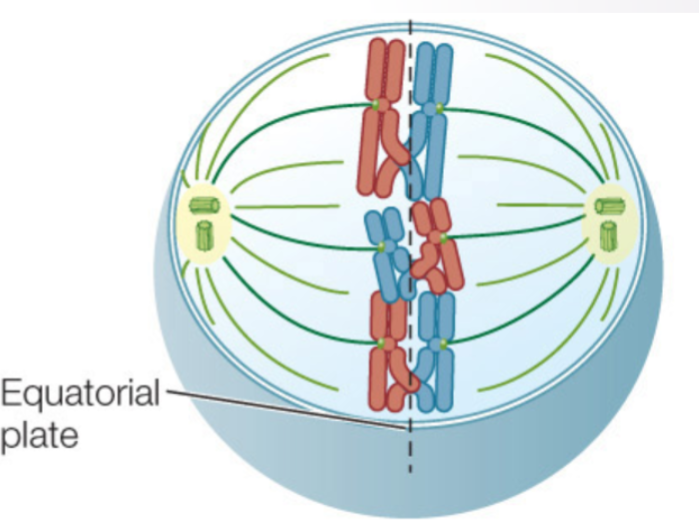
what stage of meiosis is this?
Metaphase I
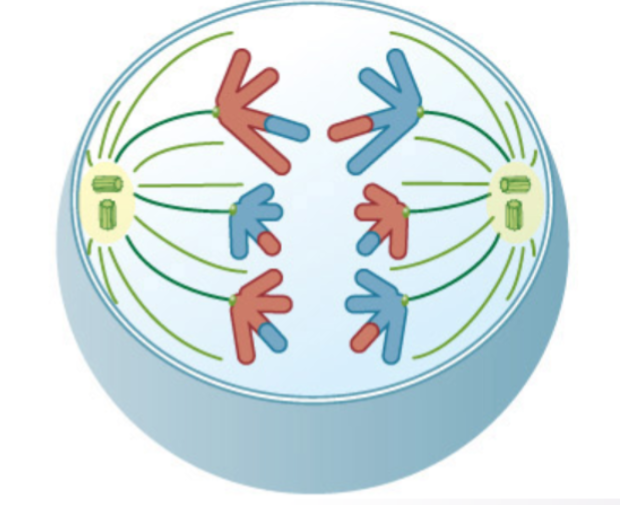
what stage of meiosis is this?
anaphase I
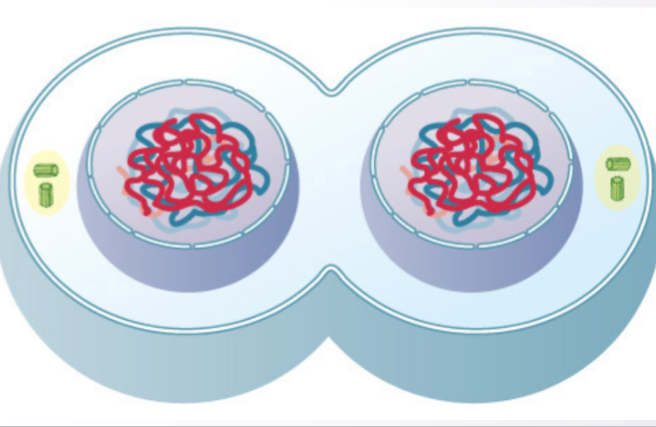
what stage of meiosis is this?
Telophase I
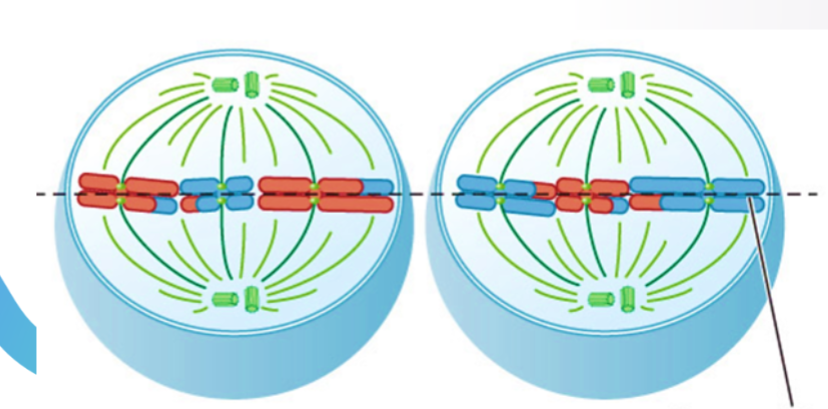
what stage of meiosis is this?
Metaphase II
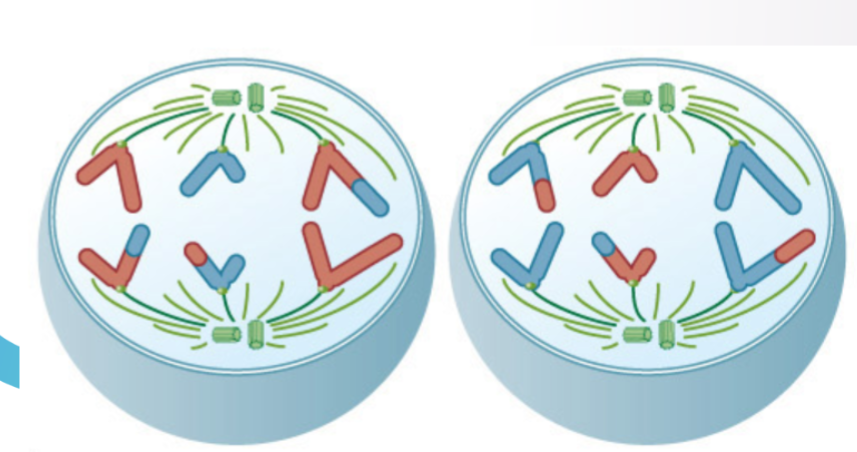
what stage of meiosis is this?
Anaphase II
What do Gregor Mendel find?
traits can be observed in predictable ratios, depending on the phenotypes of the parents.
What 3 laws of inheritance did Gregor Mendel come up with?
Law of segregation, law of independent assortment, principle of dominance
What did Mendel’s 1st experiment conclude?
1: There are different versions of genes called alleles. 2: for every characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles of a given gene - one from each parent. These alleles may be the same or different. 3: when two different alleles are inherited, one allele may be dominant, while the other allele may be recessive.
What are some examples of genotypes, using p or P?
PP, Pp, pp
What does the law of dominance state?
Some alleles are dominant and cover up the recessive alleles.
What does the law of segregation state?
an organism has 2 alleles for each gene but they can only pass on one
What is a monohybrid cross?
A cross between two individuals where only one characteristic (trait) is examined. The two individuals differ in that single characteristic.
what are homozygous genes?
two identical alleles for a specific gene
what are heterozygous genes?
having two different alleles for a specific gene
what is a trait?
a specific characteristic of an individual
what is an allele?
a different version of a gene
what happens when a dominant and recessive allele cross?
recessive allele is hidden or silenced by dominant allele
when are recessive alleles expressed?
in absence of a dominant allele
what do Punnett squares do?
determine possible genotypes (allele combinations) and phenotypes (observable traits) of the offspring