Option B
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Define the term personality
those relatively stable and enduring aspects of individuals which distinguish them from other people, making them unique but at the same time permit a comparison between individuals
Discuss social learning theory and personality
States that behaviour changes with the situation and we learn from other people.
Discuss the interactionist approach to personality
a persons behaviours are shaped by constant interaction between the person and their enviorrment. It is expressed as Behavior = f(Person x Environment)
Outline issues associated with the measurement of personality
imitations of data collection method ‹interviews, questionnaires, observations›
valid tests reliably developed can have measurement error
Evaluate the issues in personality research and sports performance
Not a single personality profile that distinguishes athletes from non-athletes. Team sports athletes tend to be more dependent than individual athletes.
no clear personality differences between male and female athletes (at the elite level)
difficulty measuring personality due to varying definitions and validity issues surrounding testing
Define the term motivation
internal mechanisms and external stimuli which arouse and direct our behaviour
How Specific attitudes and behaviours toward sport and exercise are learned:
through modelling / observational learning
reinforcement
Intrinsic motivation theory
comes from within
pride and satisfaction of having a good game
can come from a need, a desire to learn to swim to survive
Extrinsic motivation theory
comes from an outside source
intangible - raise from coaches
tangible - winning a trophy
Intrinsic Issues
Player may lose interest
difficult to maintain levels of interest
Extrinsic issues
only want to play for material rewards
decreases intrinsic motivation
want to win, less focus is put on personal improvement
Describe Atkinson’s model of achievement moti- vation
shows how someone’s motive to achieve and avoid failure will change their behavior when their performance is compared against a standard of excellence. a person is generally high in achievement motivation if the desire to succeed is greater than the fear of failure. a person is low in achievement motivation if the fear of failure is greater than the desire to succeed.
Outline goal orientation theory
how people evaluate/judge their competence and define successful accomplishments. It refers to personal interpretations they have about what achievement means to them within a specific task.
FOUR AREAS OF SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY
Attention, retention, reproduction, motivation
Goal orientation factors , three factors combine to determine motivation:
Achievement goals
Perceived ability
Achievement behavior
Ego-Oriented:
measure their success based on beating others and being the best (Extrinsic motivation)
Task-Oriented
: measure their success against themselves, how well they complete a task (personal bests) (Intrinsic motivation)
Describe attribution theory and its application to sport and exercise
Attribution theory is a concept that explores what people attribute their success and failures to. -
AT: Internal attribution
performance , characteristics
AT: External atribution
coach, environment, team mates
Locus of control
the extent to which an individual can influence the outcome.
Define the term arousal
Arousal is an alertness or state of readiness (ranging from deep sleep to intense alertness) of the body for an action
Discuss the emotions that may influence an athlete’s performance or experience in a physical activity
Negative emotions can help us remember unsuccessful performances including poor decisions in the game
emotions that are linked to decreased levels of performance like anger, or shame
positive emotions linked to successful performances can help athletes recall the skills and strategies needed to achieve their goals
theoretical approaches to arousal: Drive reduction theory: .
Deviations from homeostasis create physiological needs. These needs result in a drive to return the body back to homeostasis
Theoretical Approaches to Arousal: Inverted U Approach:
Peak performance is achieved when people experience a moderate level of pressure. Too little or too much, and performance declines.
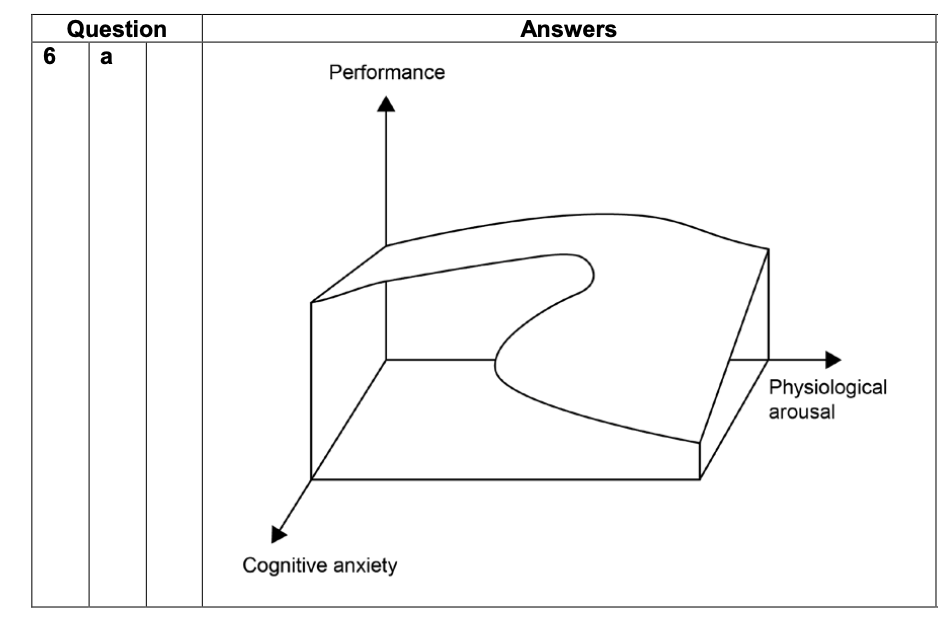
Theoretical Approaches to Arousal: Catastrophe Model:
Suggests that when cognitive anxiety was high, then continued increases in physiological arousal would result in a catastrophic decline in performance.
Define the term anxiety
A negative emotion of apprehension and tension (stress), which includes irrational thoughts, fear of failure, self-doubt and worry.
Distinguish between cognitive and somatic anxiety
-
cognitive anxiety
.....is characterized by thoughts and perceptions of worry/doubt and negative expectations (mind), about performance, self- evaluation and evaluation by others.
somatic anxiety
...relates to our perceptions of our bodily state (physiological arousal), for eg, such as awareness of a pounding heart (increased heart rate), increased blood pressure, clammy hands, trembling legs, butterflies in the stomach, shaking, pacing, sweating,
trait anxiety
a general level of stress that is a characteristic of an individual; a trait related to personality. People with a high trait anxiety experience more intense degrees of state anxiety. Trait anxiety describes a personality trait versus a temporary feeling.
state anxiety
is a temporary negative emotion of apprehensiveness and tension experienced in threatening situations and is situation specific
Evaluate how anxiety is measured from (CSAI-2R) State anxiety test:
CSAI-2R is an instrument that measures competitive state anxiety.
this information can be beneficial for sports coaches and athletes as it identifies an worries. they can then implement strategies or seek professional help to address any anxiety issues.
Participants complete a question consisting of 3 dimensions: cognitive anxiety, self-confidence and somatic anxiety. These scores are then recorded and compared to a scale to predict levels of anxiety.
Trait anxiety test:
Trait anxiety:
measured using Sport Competition Anxiety Test (SCAT) ✔
the test can be performed at any time/before competition ✔
questions refer to how the participant generally feels in competitive sport situations
Describe the stress process in sports
The stress process involves the effect on performance, the way an athlete responds to the stress and the management of the stress
Stage 1: involves the environmental demand (environmental demand)
Stage 2: involves the athlete's perception of the environmental demand (psychological interpretation)
Stage 3: involves the stress response to the environmental demand (person's reactions)
Stage 4: involves the behavioural consequences of the stress response to the behavioural demand (outcome)
Discuss psychological skills training (PST)
developing psychological skills involves three phases: general education phase, acquisition phase, and practice phase✔
education phase: the athlete learns about the importance of psychological skills and how they can affect performance✔
acquisition phase: the athlete learns about the strategies and techniques to improve the specific psychological skills that they require✔
practice phase: the athlete develops their appropriate psychological skills through repeated practice, simulations and actual competition✔
Example of PST
setting effective goals involves using the SMARTER process (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-based, Exciting, Review
Outline goal setting
is specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time, evaluate, review goals
internal mental imagery
emphasizes the feel of the movement.
refers to the execution of a skill from the athlete’s own vantage point
Outline relaxation techniques
progressive muscular relaxation: involves large muscle groups being contracted and relaxed.
breathing techniques: involves breathing in, holding for a short time and breathing out.
external mental imagery
very little emphasis on the kinesethic feel of the movement.
the athelte pictures there whole performance from an outsiders perspective.
Outline self-talk techniques
Use of logs (record thoughts and identify whether they are positive, negative or neutral).
Cognitive reconstructing (negative thoughts are reconstructed to positive ones).