Gas exchange in humans
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
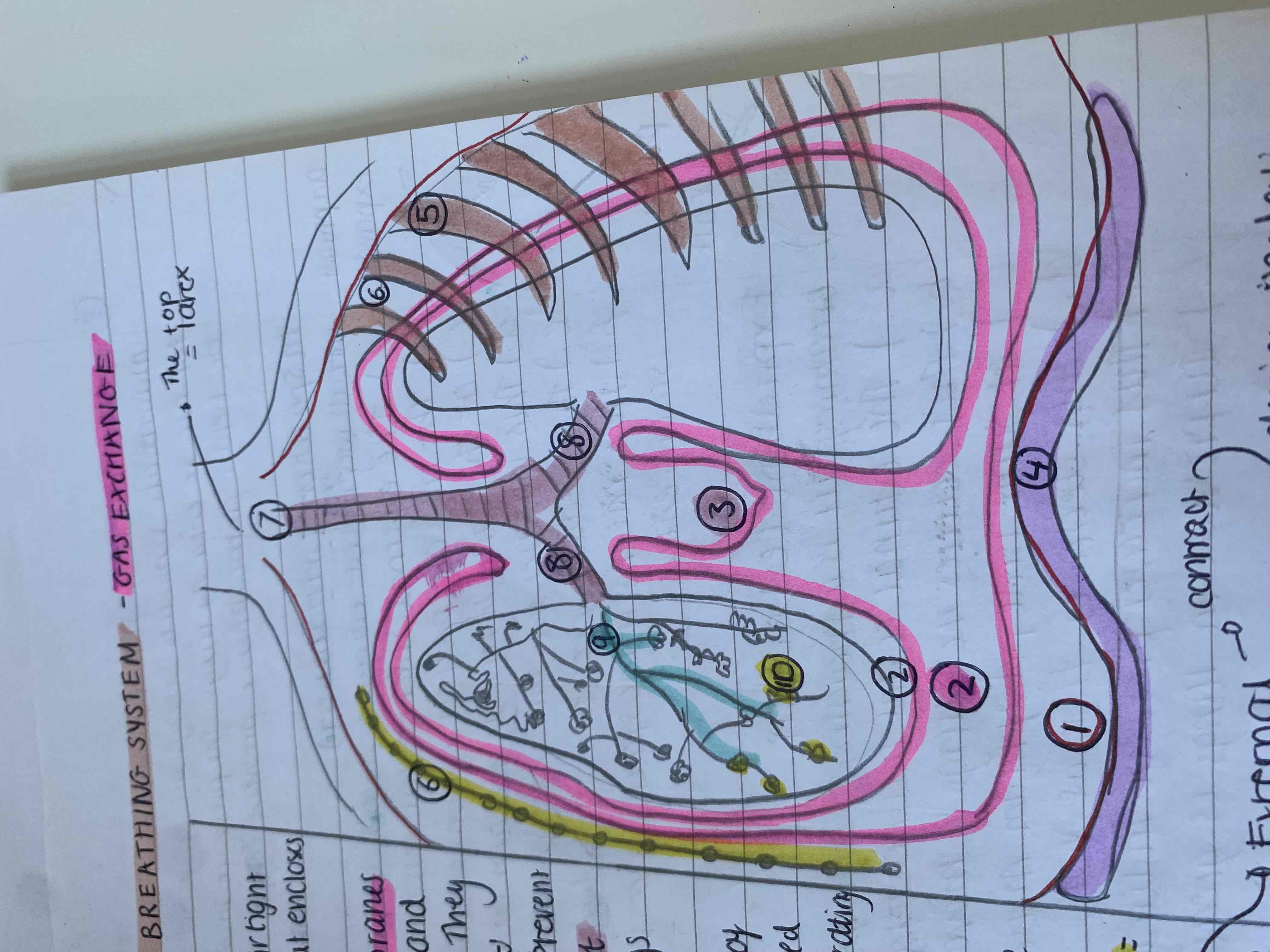
What is the structure of the human breathing system
Thorax - an airtight compartment that encloses the lungs and respiratory system
Pleural membranes - line the thorax and cover each lung. They have a fluid called the pleural fluid which is a lubricant between them to stop the lung friction and chest cavity as the lungs move
Diaphragm- the base of the thorax and it is a done shaped sheet of muscle seperating the thorax from the abdomen
Ribs - surround thorax - protect lungs and help inspiration
Lungs - the tissue is elastic and so they recoil and return to their original shape. This recoil helps push the air out of the lungs
Intercostal muscles - between ribs and there is external and internal parts. During inspiration the external contracts and internal relaxes
The larynx - top of trachea
Trachea - a flexible airway to bring air into the lungs they have semi circles of cartilage to ensure the lungs don’t collapse under negative pressure
The two bronchi - branch of trachea
Alveoli- air sacs where gas exhange occurs
explain the key terms: breathing, ventilation
Breathing is a physical action performed by the diaphragm and inter coastal muscles for ventilation
Ventilation is the refreshing of the air in the lungs so there is a higher oxygen conc in the lungs than the blood for a faster diffusion and faster respiration
Explain ventilation of the lungs and inspiration steps and expiration steps
Ventilation in mammals like humans is by negative pressure breathing as the air in the lungs needs to be below atmospheric pressure for air to enter
Inspiration - breathing in
External intercostal muscles contract
Ribs move upwards and outwards pulling on the outer pleural membrane and the pressure in the pleural cavity decreases
The inner pleural membrane pulls on the lungs outwards
The diaphragm contracts and flattered
Volume inside the thorax increases
Pressure Decreased in the thorax below atmospheric pressure
Air rushes into lungs to maintain conc gradient for efficient gas exchange
For expiration - breathing out - opposite
Explain the layers of the trachea
Cilia on the columnar epithelium move unwanted particles back up the airway
Ciliated Columnar epithelium
Goblet cells - secrete mucus to trap bacteria to prevent lung infections
Elastic tissue
Blood vessels with blood cells
Smooth muscle fibres in bundles
Cartilage- chondrocytes - they are c-shaped so the open part can accommodate for tbe movement of the oesophagus to aid digestion - as well as support for lungs in negative pressure breathing
outside trachea
Explain how the alveoli are adapted for efficient gas exchange
they have a large surface are to volume ratio due to there numbers and sphere shape
Surfactant lining enables gases to dissolve easily and diffuse across the alveoli - they are permeable - the surfactant is a soapy substance containing phospholipids and proteins in water to stop the alveoli sticking together during exhaling as it reduces surface tension because the hydrogen bonds don’t fully form in the water and stick the lungs together when pressure is low.
They have thin walls made of one layer of squamous epithelium cells so diffusion pathway is short
An extensive capillary network surrounds the alveoli for the maintenance of the conc gradient and to be a short diffusion pathway. Each blood vessel is made of endothelial one cell thick
Concentration gradient is maintained by haemaglobin carrying away oxygen on red blood cells so low concentration in blood and ventilation by breathing meaning a high conc in lungs so quick rate of diffusion
Explain how o2 enters and co2 exits
Deoxygenated blood enters the capillaries around the alveoli and oxygen diffuses across alveoli from lungs into blood and co2 diffuses out of plasma in blood to alveoli for expiration