Cell Cycle and Mitosis
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L.S
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Cell Cycle
The period during which a cell grows, replicates genetic material and divides is known as the cell cycle.
2 Main Phases of a Cell Cycle
1. Interphase during which the cell grows and replicates its DNA.
2. Mitotic phase (M-Phase) during which the cell divides and forms two identical daughter cells.
Interphase
Longest part of the cell cycle. During this phase the cell grows to its maximum size, performs its normal cellular functions, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division.
Different phases within Interphase
G1 phase: Cell grows and synthesizes proteins.
S phase: DNA replication occurs.
G2 phase: Cell continues to grow, replicates organelles, and prepares for mitosis.
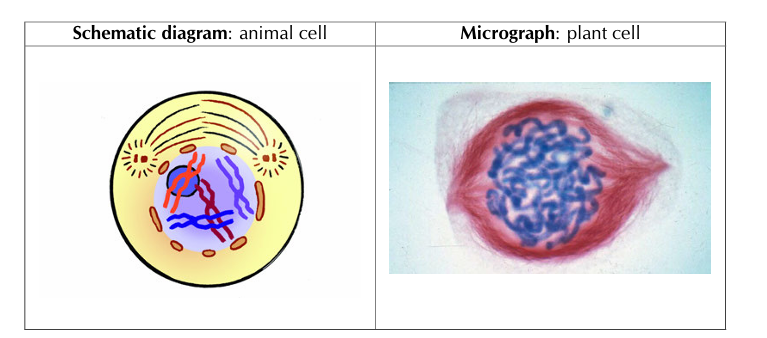
1) Prophase
• Chromatin network shortens and thickens to form individual chromosomes
• Each chromosome consists of two chromatids joined by a centromere
• Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear
• Centrioles separate and move to opposite poles of the cell
• Spindle fibre forms between the centrioles
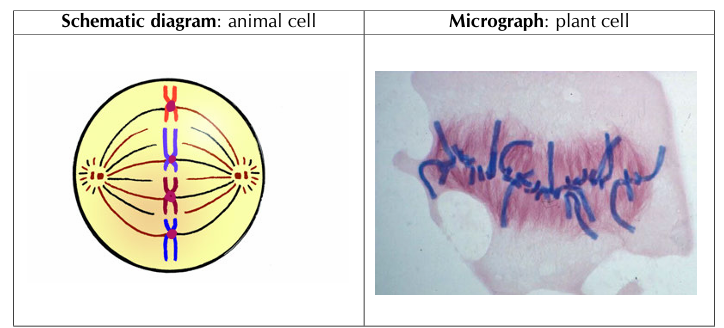
2) Metaphase
• Chromosomes move to the equator and arrange themselves in a single row on the equator
• Each chromosome is attached to the spindle fibres by its centromere
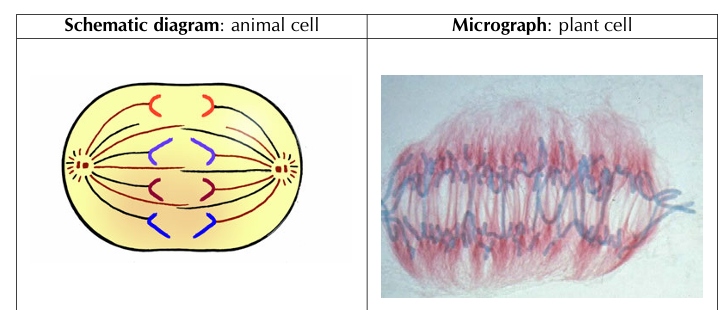
3) Anaphase
• The centromere of each chromosome divides into two. (Called daughter chromosomes)
• The two chromatids separate.
• The spindle fibre contracts and pulls the chromatids to opposite poles.
• The two chromatids move to opposite poles.
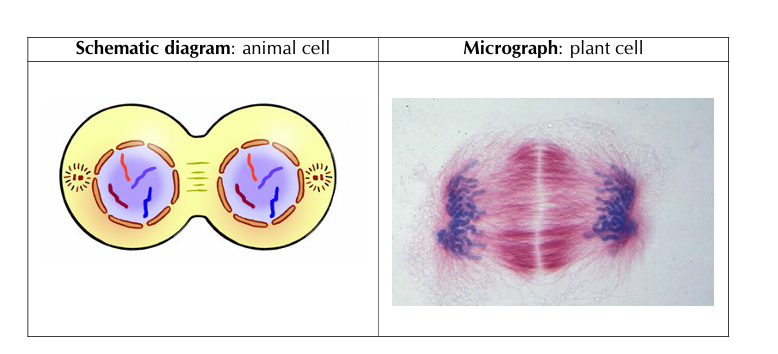
4) Telophase
During telophase, a nuclear membrane forms around the daughter chromosomes that have gathered at each of the poles. The daughter chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin once again. The nuclear membrane reforms.
Cytokinesis
- is the division of the cytoplasm. it is not a stage of mitosis but the process of the cytoplasm splitting into two.
- In an animal cell the cell membrane constricts. In a plant cell wall is formed by the cell plate dividing the cytoplasm in two.
- There are now two genetically identical daughter cells which are identical to the parent cell and to each other.
Differences of mitosis in plant and animal cells
In animal cells the spindle forms between the pairs of centrioles. In plant cells, centrioles are absent, but spindle fibre are formed in the cytoplasm.
In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms and in plant cells, a cell plate develops into a cell wall.
Role of Mitosis
• Development and growth - The number of cells increase by mitosis enabling organisms to grow from a single cell to a complex multicellular organism.
• Reproduction - Some organisms use mitosis to produce genetically identical offspring.
• Cell replacement - Cells are constantly replaced by new ones in the body, for example in the skin.
• Replacement of damaged tissues - some organisms use mitosis to replace body parts.