AP Environmental Science: Unit 2 Biodiversity
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Biodiversity
the number, variety, and variability of Earth's organisms that consists of three level of diversity
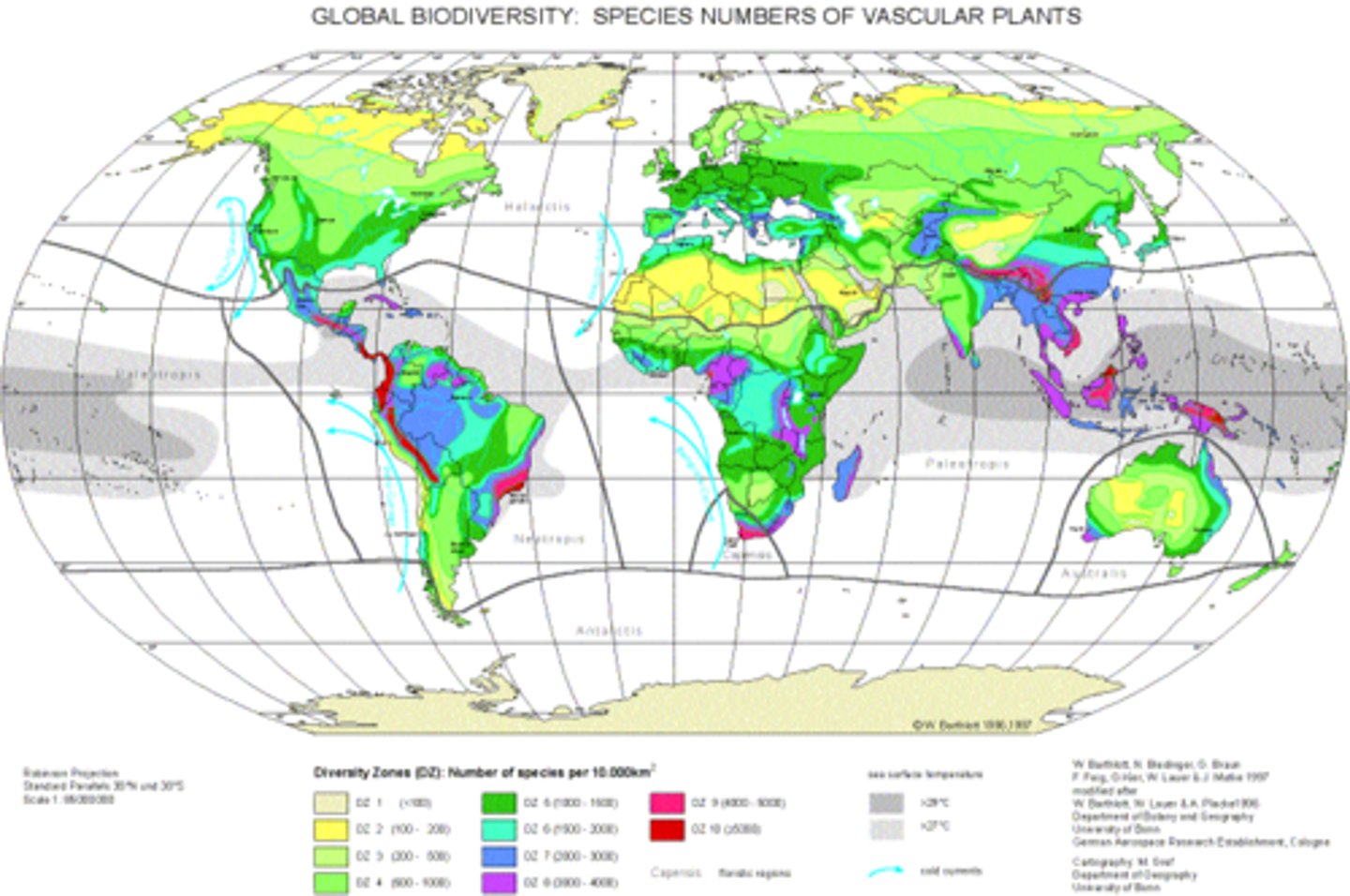
Species Diversity
number of different species (species richness) combined with the relative abundance of individuals within each of those species (species evenness)
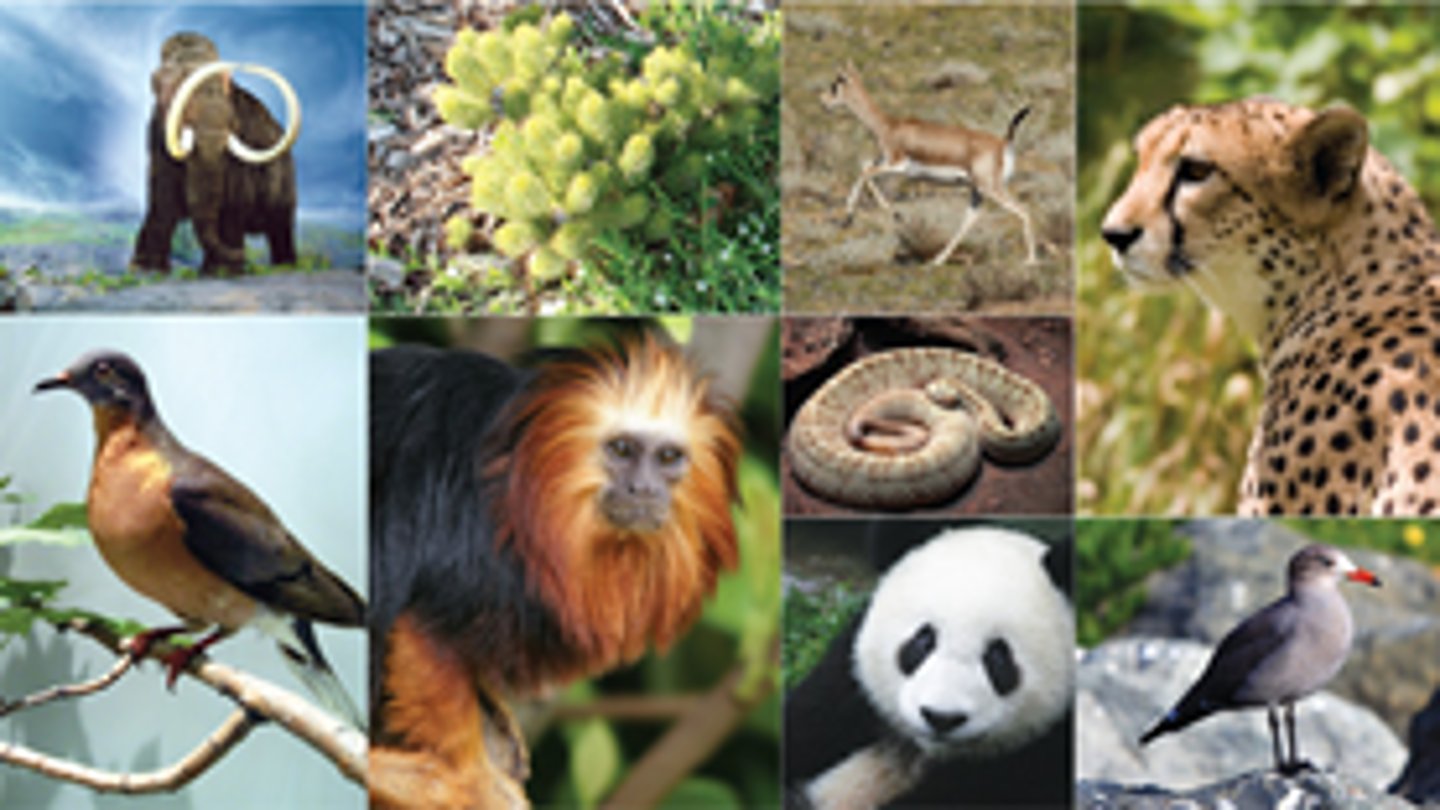

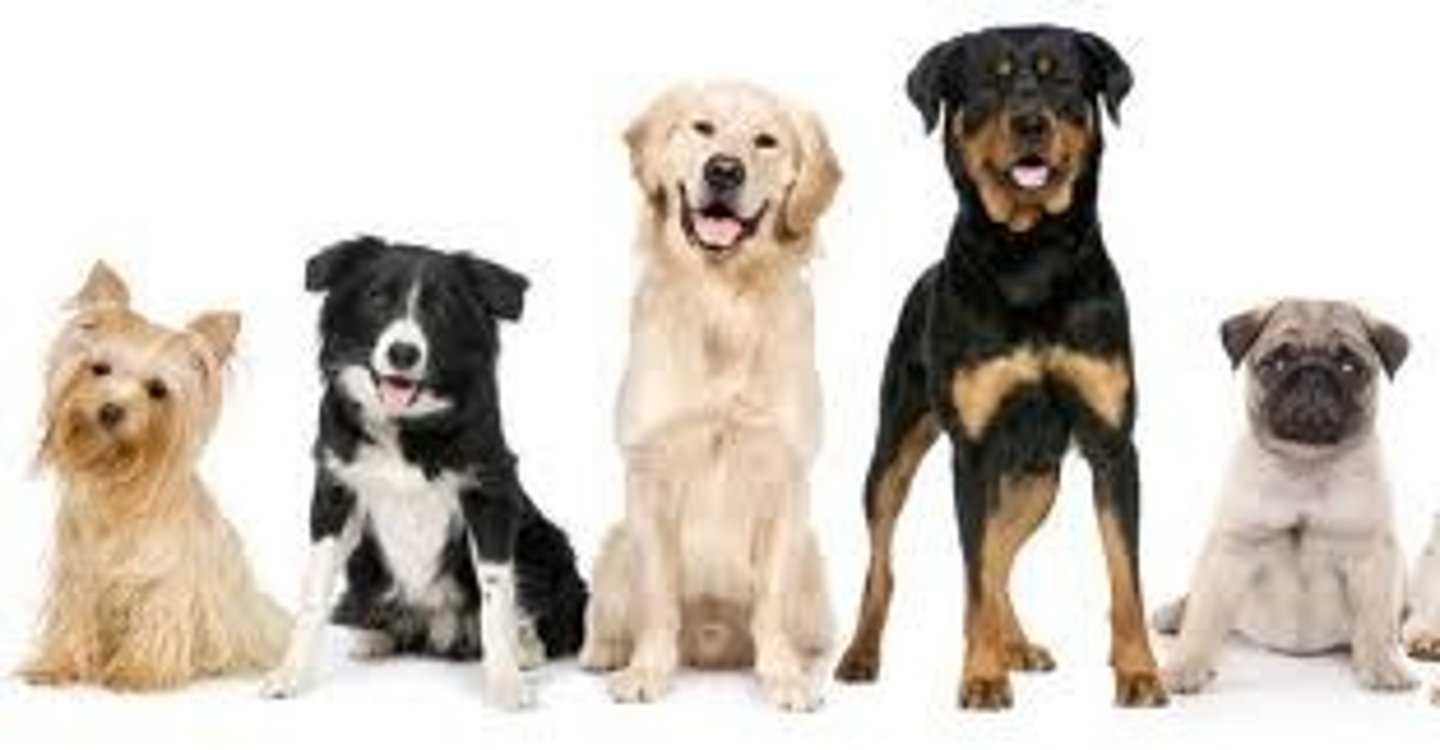
Genetic Diversity
variability in the genetic makeup among individuals within a single species and is vital to the sustainability of life on Earth

Ecosystem Diversity
Earth's variety of deserts, lakes, oceans, forests, wetlands, coral reefs, etc.
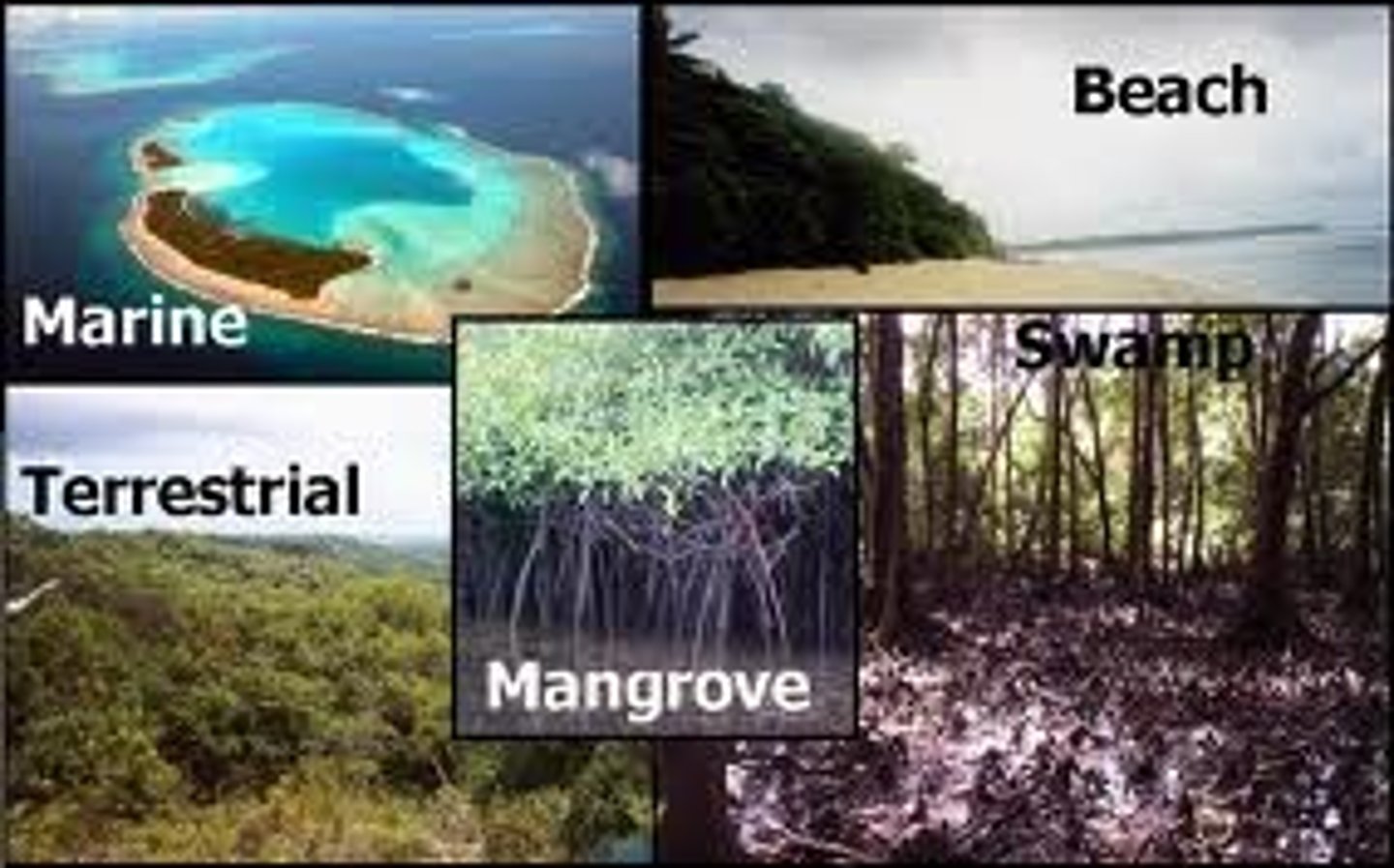
Ecosystem Services
important environmental benefits provided to people such as clean air and water and fertile soil

Extinction
the elimination of a species from Earth
Endangered Species
a species that faces threats that may cause it to become extinct within a short period of time

Threatened Species
a species whose population has declined to the point that it may be at risk of extinction

Endemic
species not found anywhere else

Genetic Resistance
the ability of one or more organisms in a population to tolerate a chemical designed to kill it
(Ex: antibiotics and bacteria)
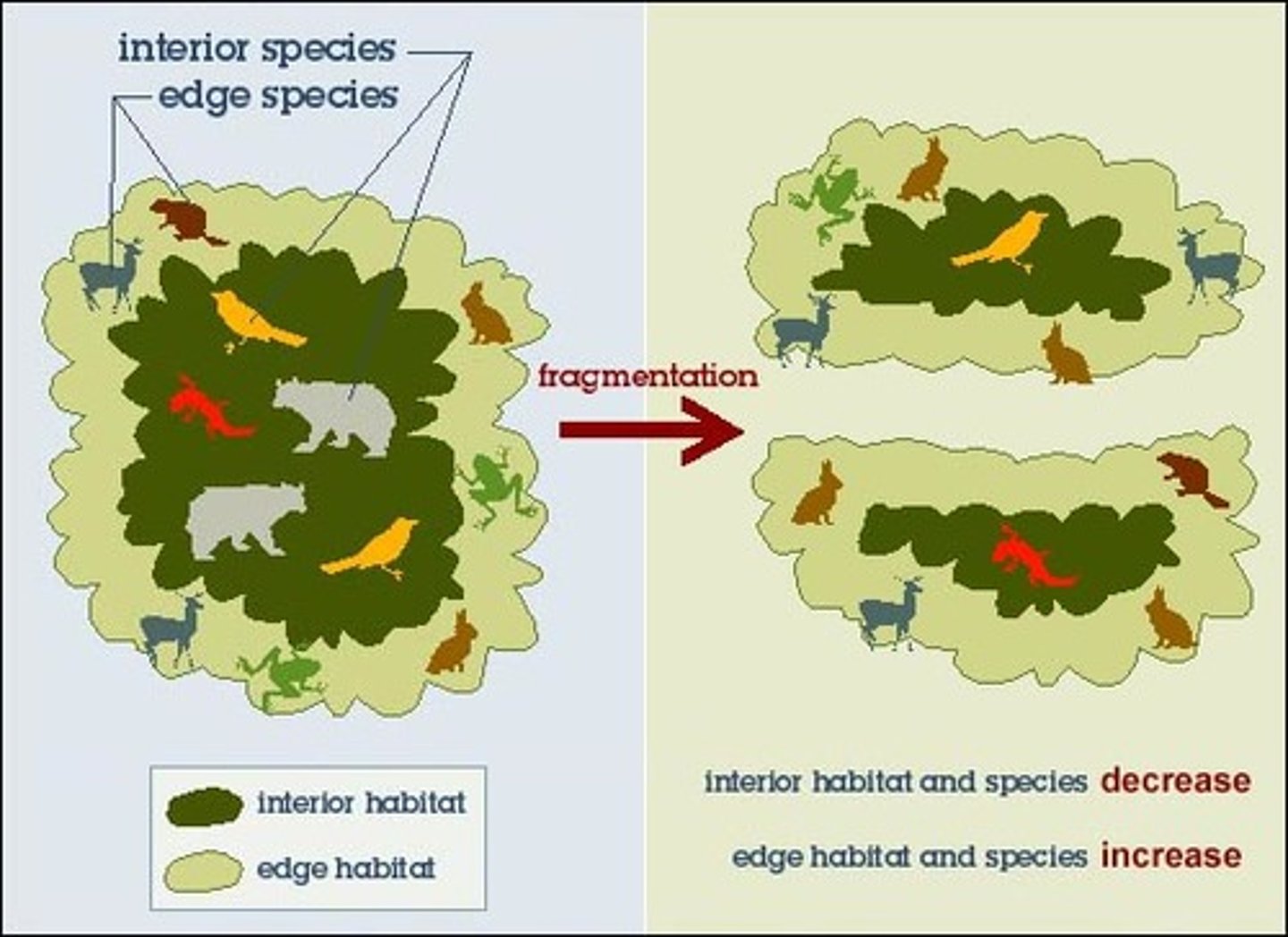
Habitat Fragmentation
the breakup of large areas of habitat into small isolated patches and is a major threat to long-term survival of many species
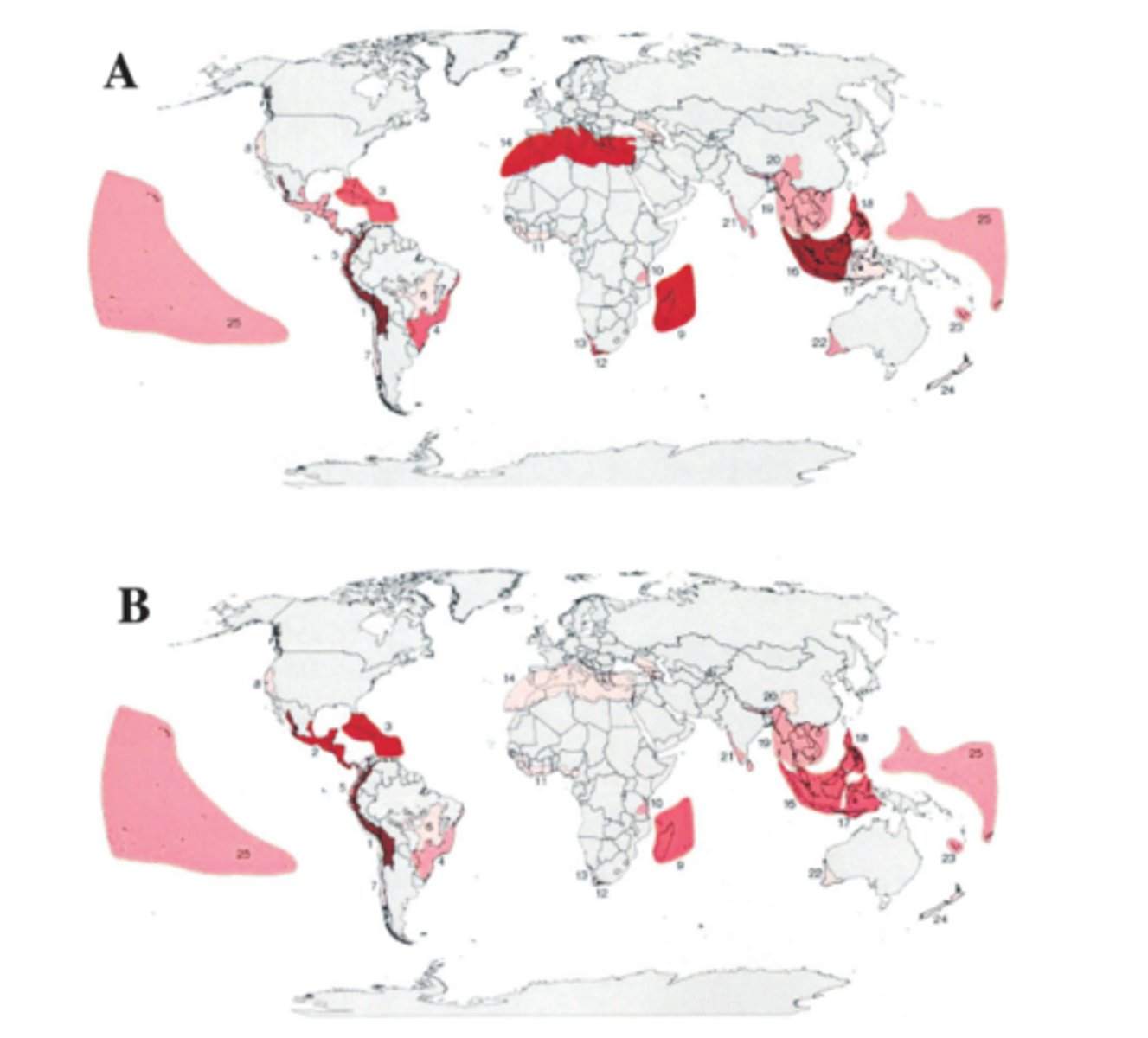
Biodiversity Hotspot
relatively small areas of land that contain an exceptional number of endemic species that are at high risk from human activities
Invasive Species
foreign species that spread rapidly in a new area where they are free of predators, parasites, or resource limitation that may have controlled their populations in their native habitat

Biotic Pollution
the introduction of a foreign species into an ecosystem in which it did not evolve; often upsets the balance and interferes with functioning in the ecosystem

Indicator Species
provides an early warning of environmental damage; amphibians are an example because they lay gelatinous, unprotected eggs and breathe through their permeable skin

Conservation Biology
the study of how humans impact organisms and of the development of ways to protect biological diversity
In Situ Conservation
done through the establishment of parks and reserves to preserve biological diversity in nature

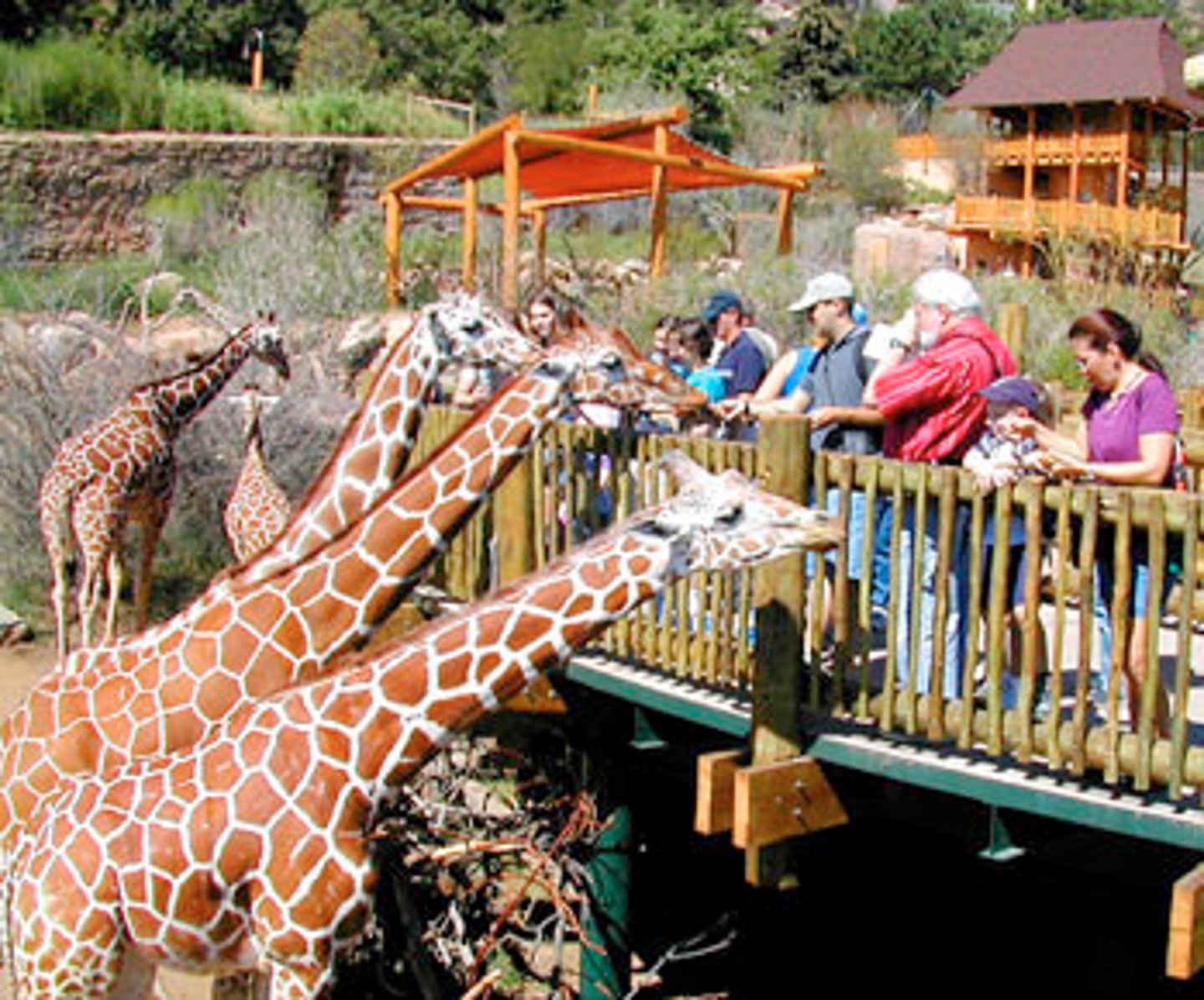
Ex Situ Conservation
involves conserving biological diversity in human-controlled settings such as zoos, aquaria, and seed banks

Restoration Ecology
the study of the historical condition of a human-damaged ecosystem with the goal of returning it as close as possible to its former state

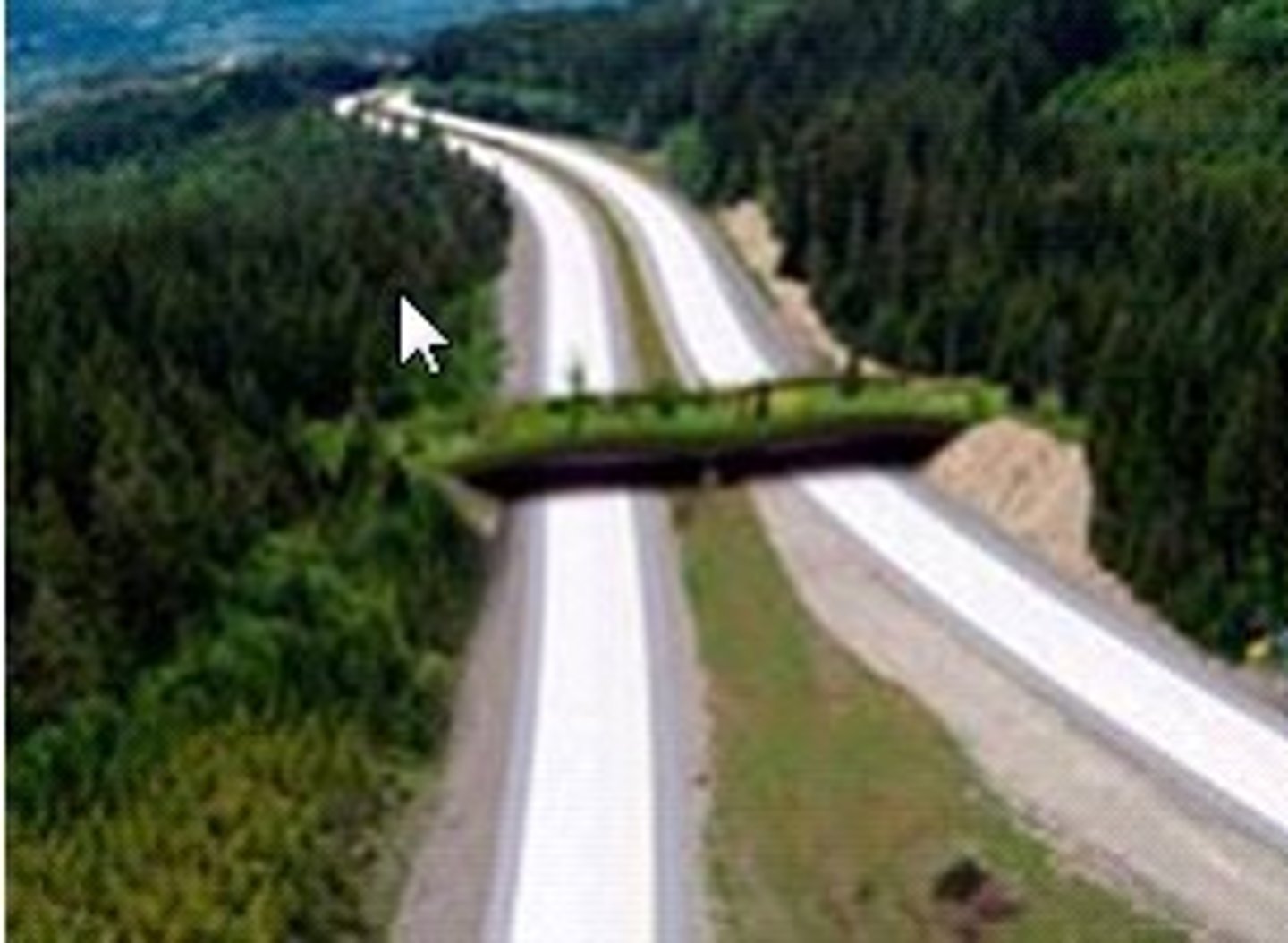
Habitat Corridors
strips of habitat that connect isolated habitat fragments

ESA -- Endangered Species Act
authorizes U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to protect endangered and threatened species

CITES -- Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species
bans hunting, capturing, and selling of endangered and threatened species and regulates the international trade of these species

Wildlife Mangement
the application of conservation principles to manage wild species and their habitats for human benefit or the welfare of other species
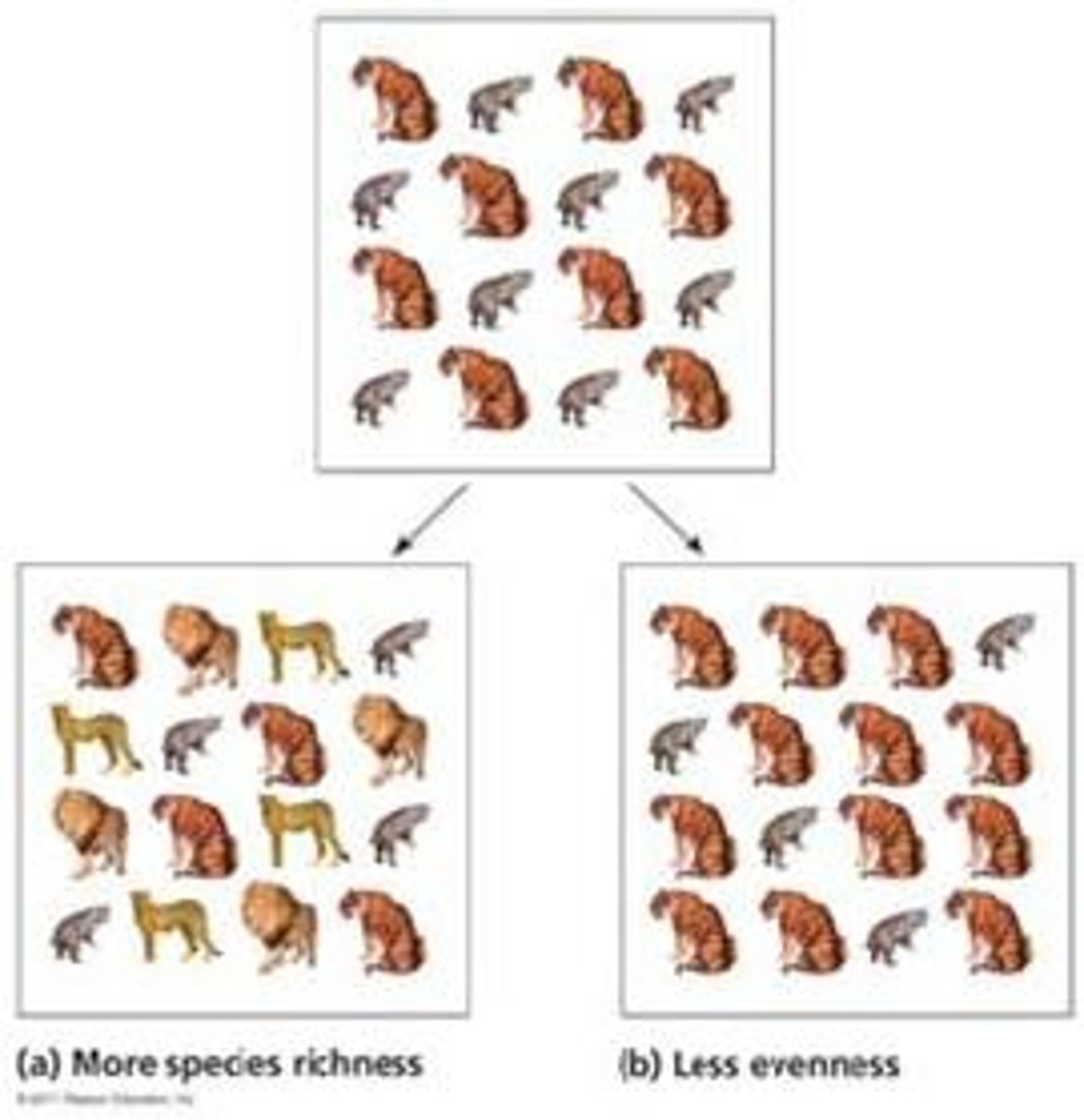
species richness
The number of different type of species
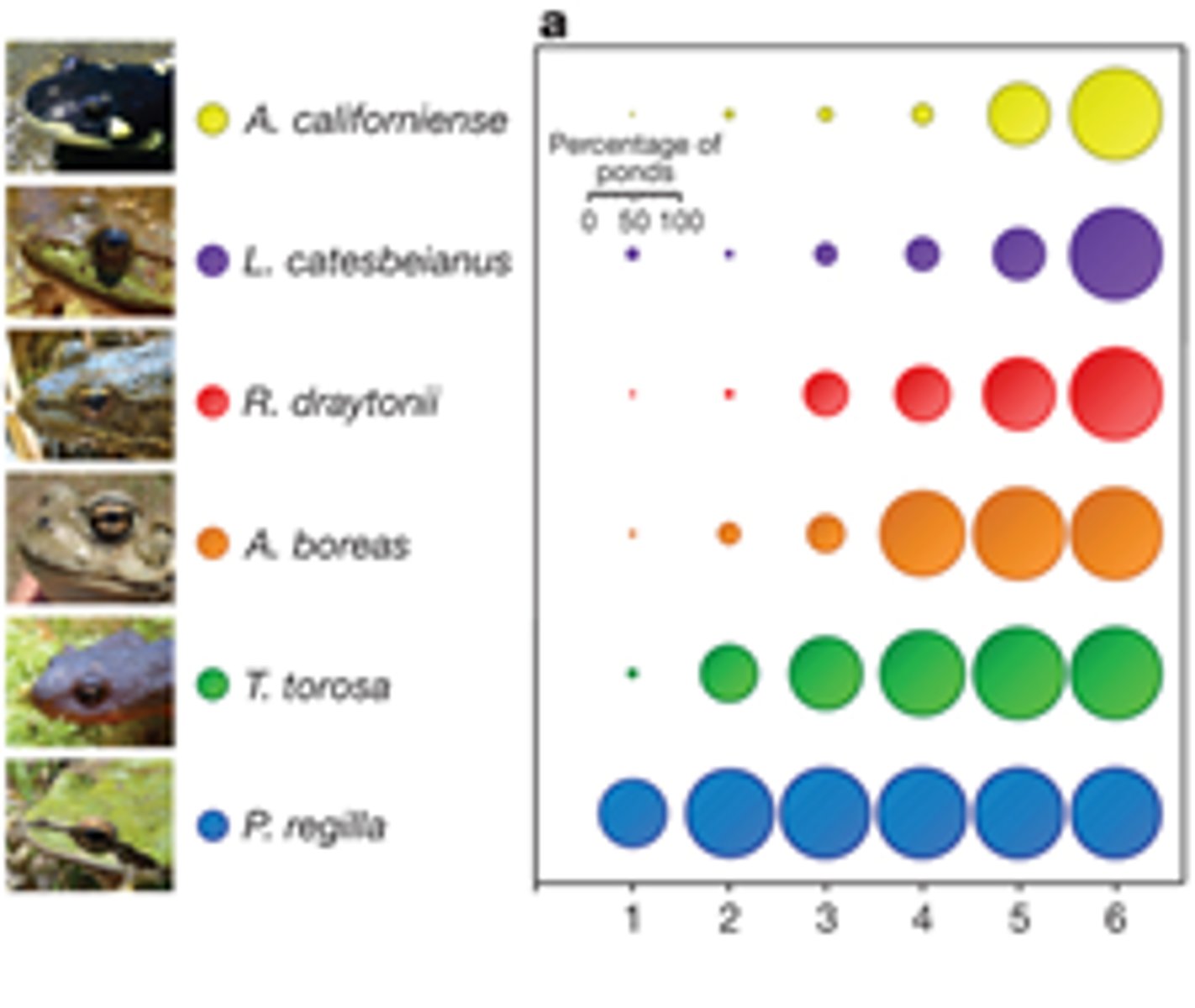
species abundance
The total number of species represented
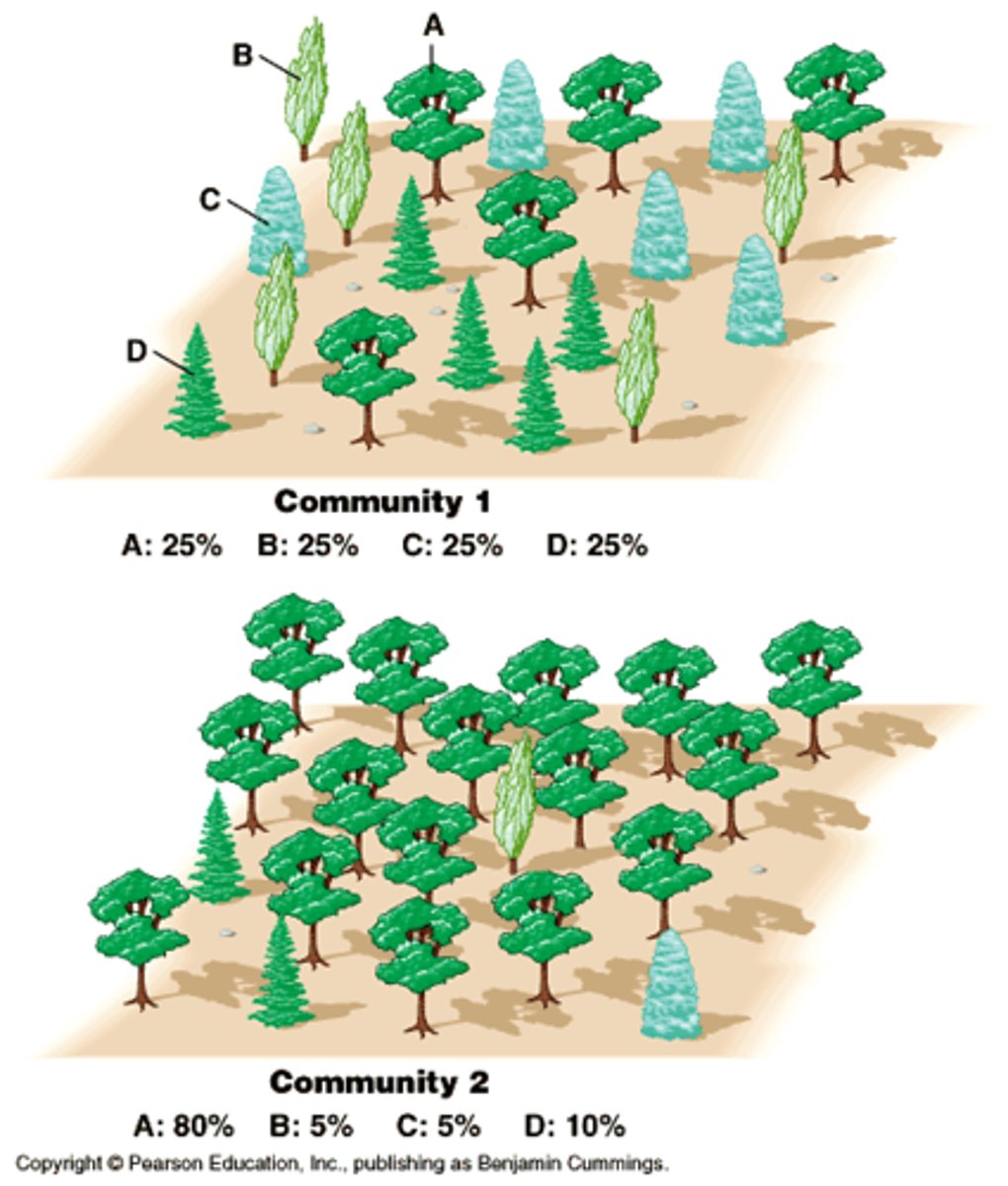
species evenness
The distribution of species in a community
Predators
The most likely threatened organism after habitat fragmentation
Generalist species
Organisms with a very broad niche

Specialist species
Organisms likely to become extinct due to their limited niche

keystone species
a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem

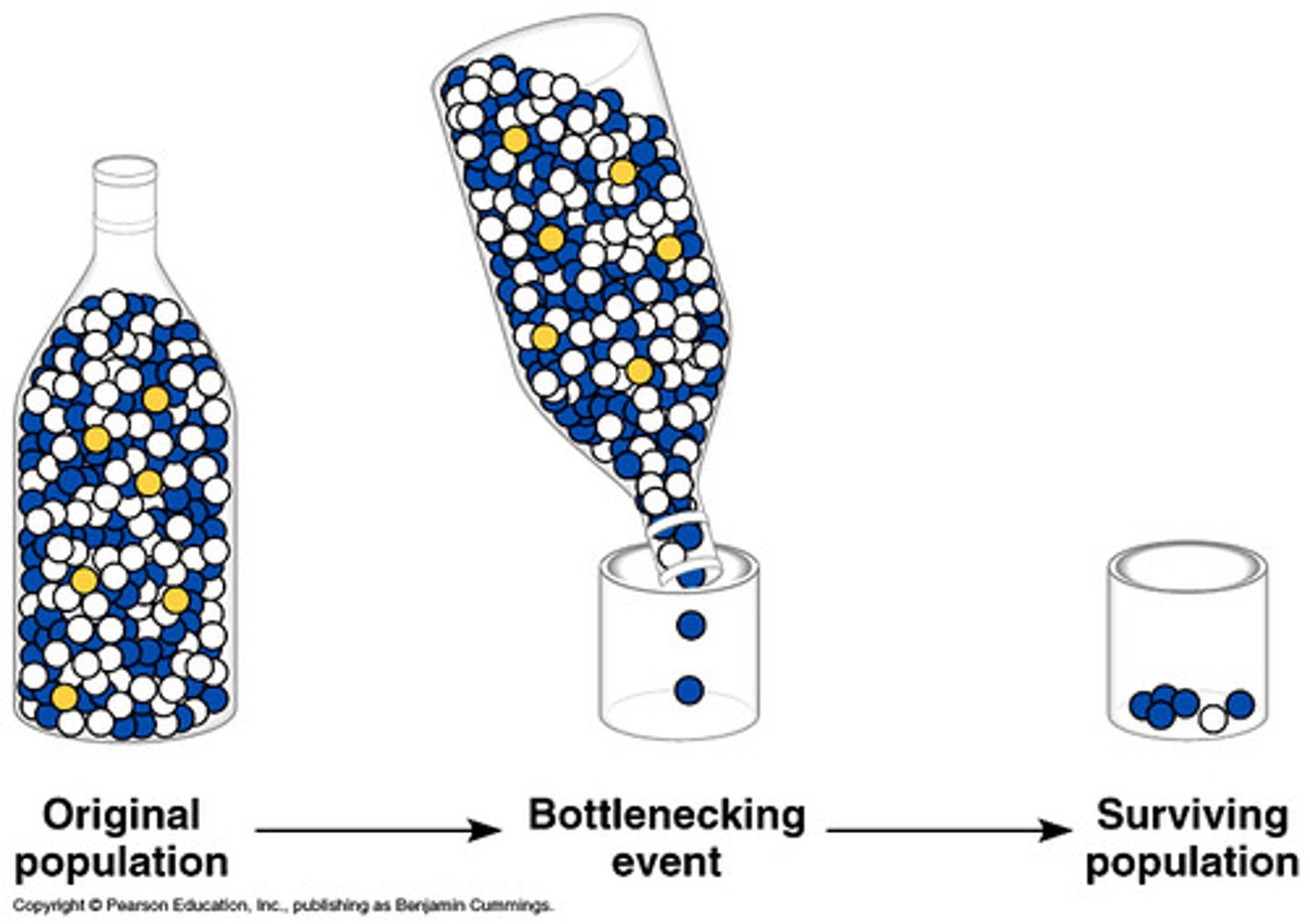
bottleneck effect
A change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population
ecological tolerance
the range of conditions in which a species can survive
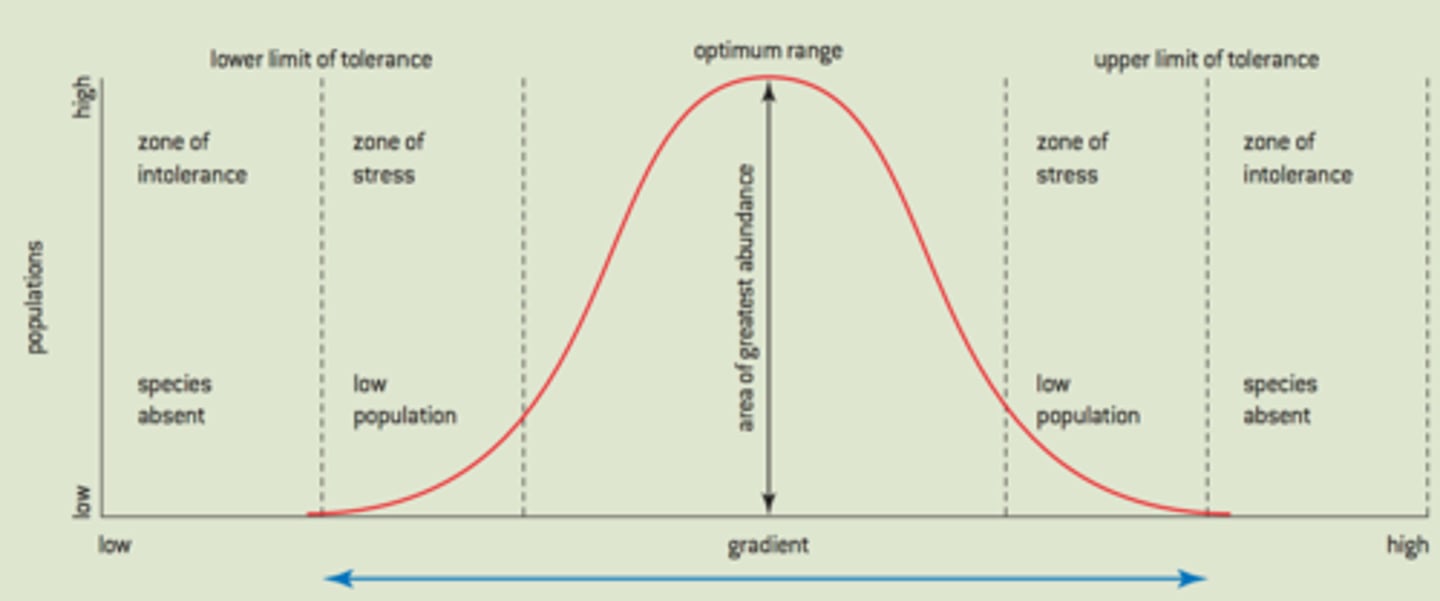
Succession
A series of predictable and orderly changes within an ecosystem over time.
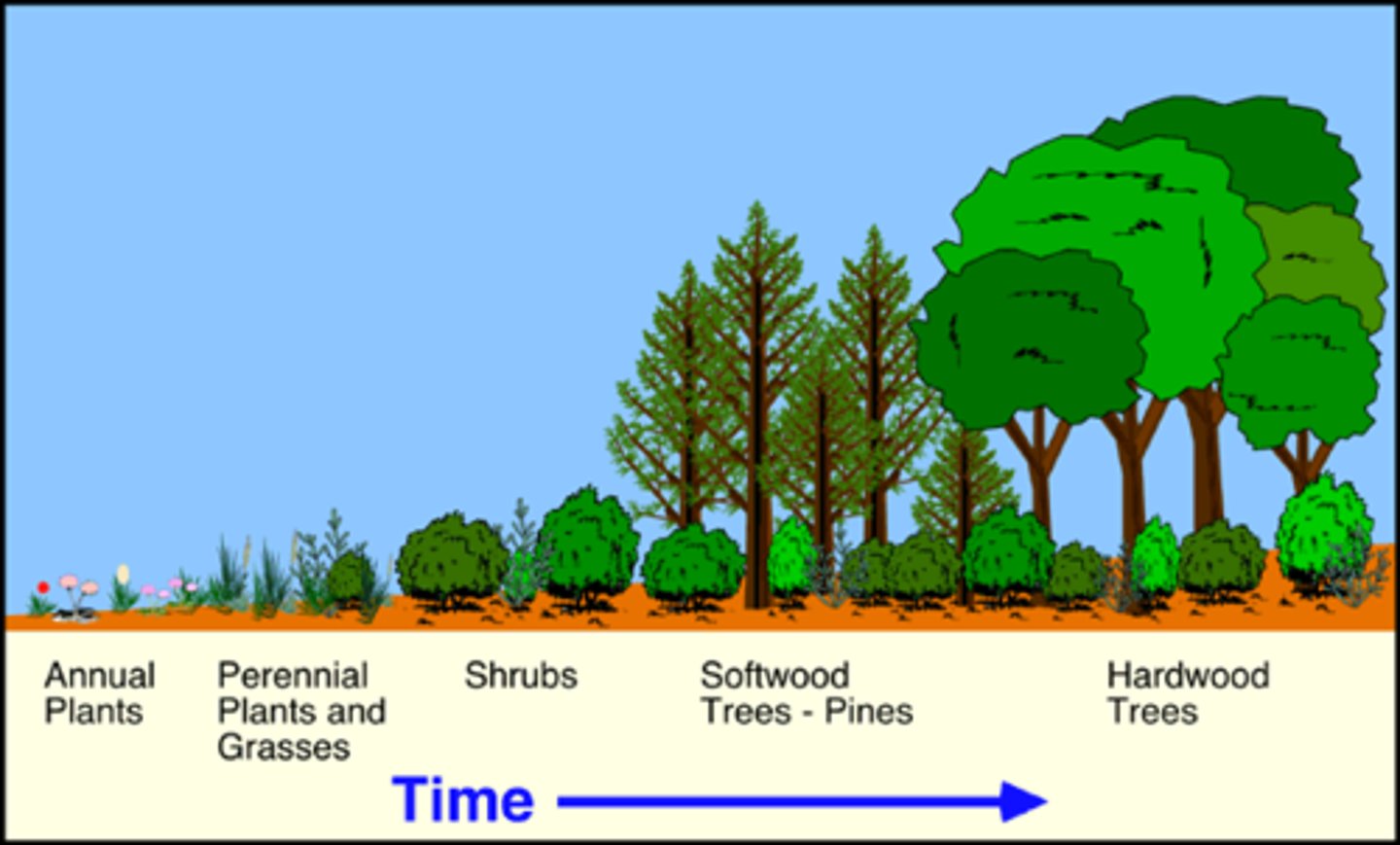
primary succession
succession that occurs on surfaces where no soil exists

secondary succession
Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
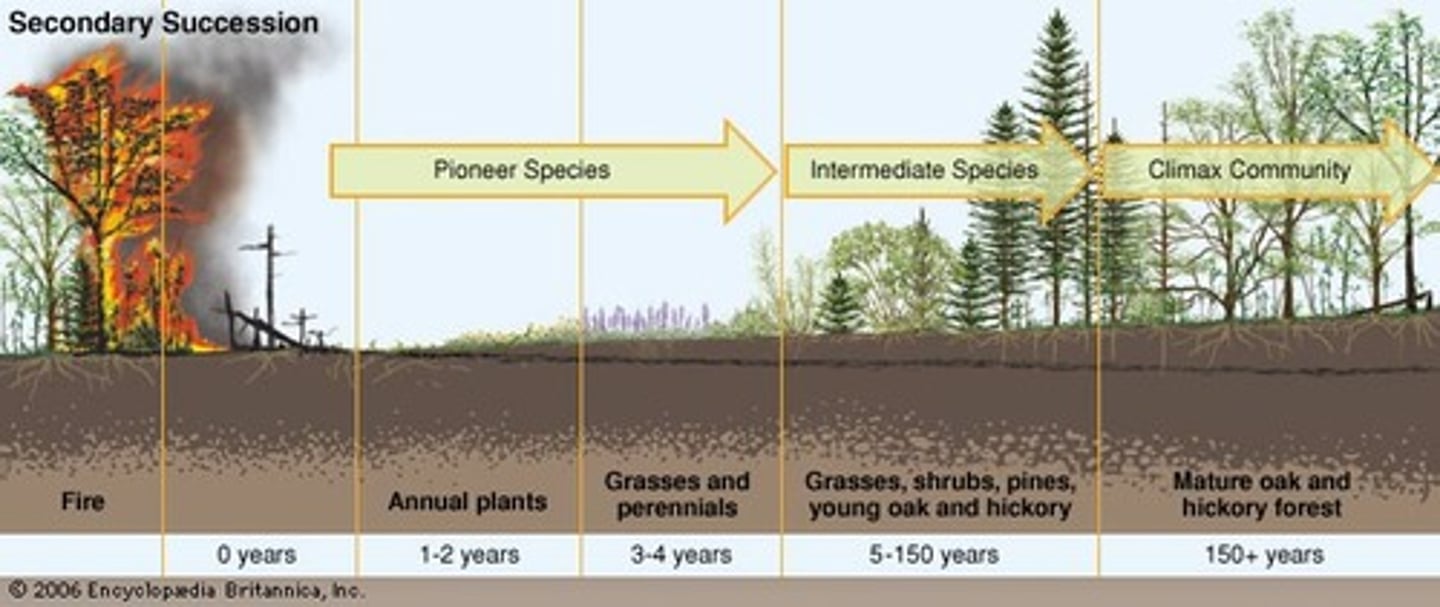
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession

Externality
unintentional side effects of an activity affecting people other than those directly involved in the activity. A negative ____ is one that creates side effects that could be harmful to either the general public directly or through the environment