Unit 6 - Brain Anatomy
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Abducens n. CNVI
Location:
Middle cranial fossa
Orbit
Composition:
Motor
Motor:
Lateral rectus muscle
CNS connection:
Pons (abducens nucleus)
Cranial foramina:
Superior orbital fissure
Comment:
Abducens nerve also known as abducent nerve or CN VI
Accessory n. CN XI
Location:
Vertebral canal (spinal root only)
Posterior cranial fossa
Neck
Composition:
Motor
Motor:
Cranial part: joins vagus nerve (CN X) to distribute to muscles of palate (except tensor veli palatini), pharynx (except stylopharyngeus), and larynx (intrinsic muscles)
Spinal part: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
CNS connection:
Cranial root: medulla oblongata (nucleus ambiguous)
Spinal root: ventral horn of C1-4 spinal cord
Cranial foramina:
Foramen magnum (spinal root only)
Jugular foramen
Comment:
Cranial and spinal roots unite in jugular foramen to form accessory nerve
Cranial part of accessory nerve joins vagus nerve (CN X) and is distributed along its branches to muscles of palate, pharynx, and larynx
Accessory nerve also known as CN XI

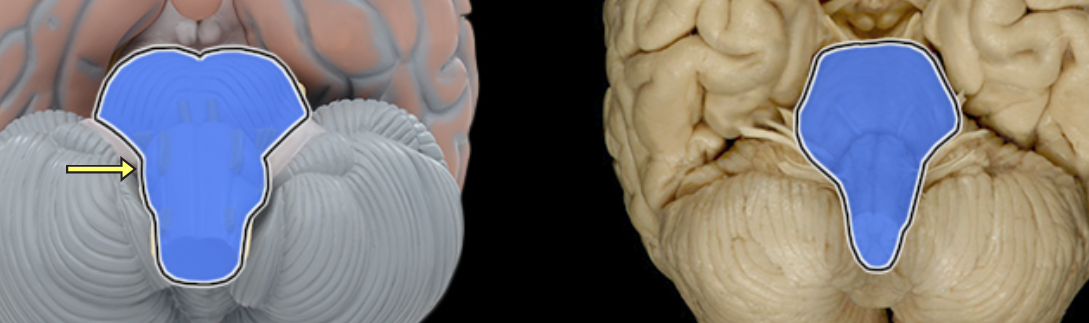
Brainstem
Location:
Caudal portion of brain
Description:
Vertical, stalk-like portion of brain
Includes midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
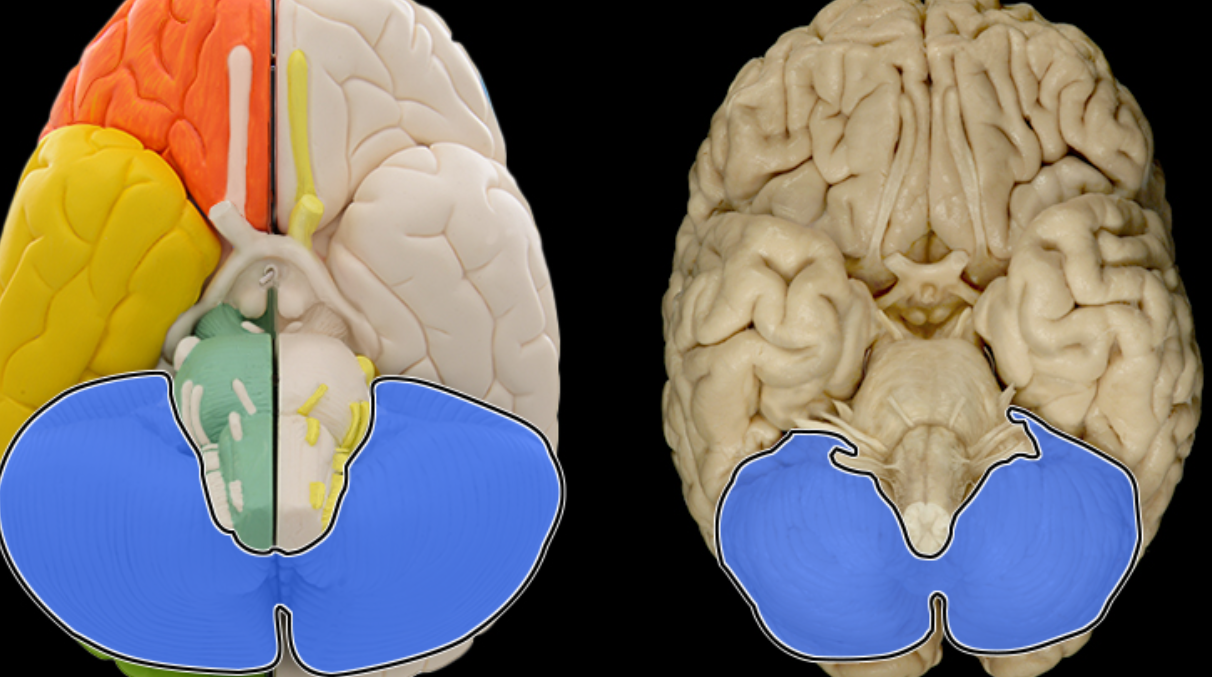
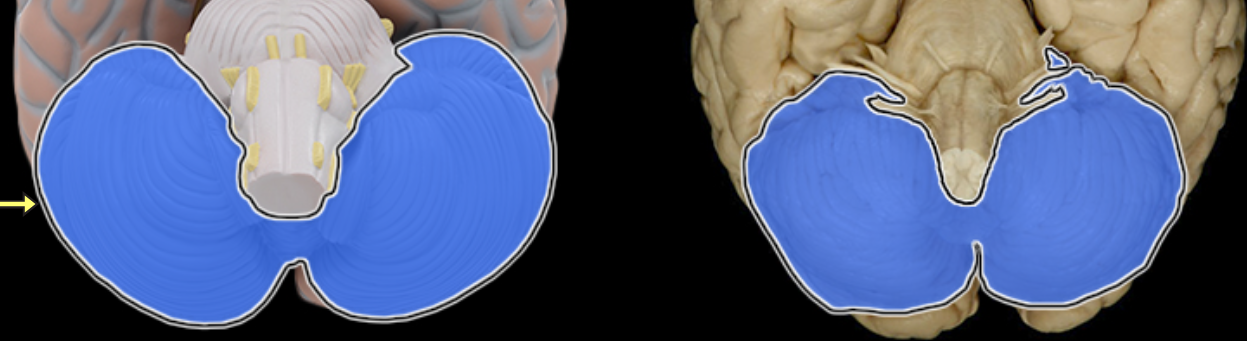
Cerebellum
Location:
Dorsal to brainstem
Description:
Composed of many lobes with highly folded cortex
Attached to pons via cerebellar peduncles
Function:
Coordinates complex movements
Monitors muscles to ensure fluid movements
Comment:
Receives extensive sensory input from body and CNS
Cerebellar cortex has folds known as folia
White matter of cerebellar lobes resembles branching tree and is called arbor vitae
Influences motor function through connections with thalamus and motor cortex
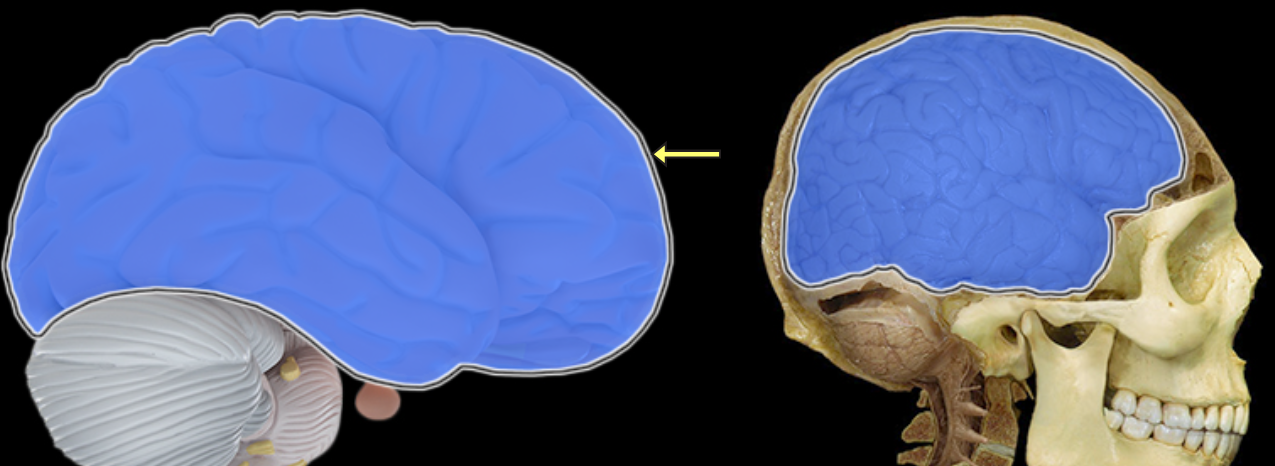
Cerebrum
Location:
Rostral portion of brain
Description:
Includes two large cerebral hemispheres separated by longitudinal fissure
Hemispheres connected by corpus callosum
Surface gray matter of each hemisphere is known as cerebral cortex
Within each hemisphere there is a core of white matter
Additional masses of gray matter located within cerebrum include basal nuclei
Comment:
Rostral = toward the nose (Latin: rostrum = beak)
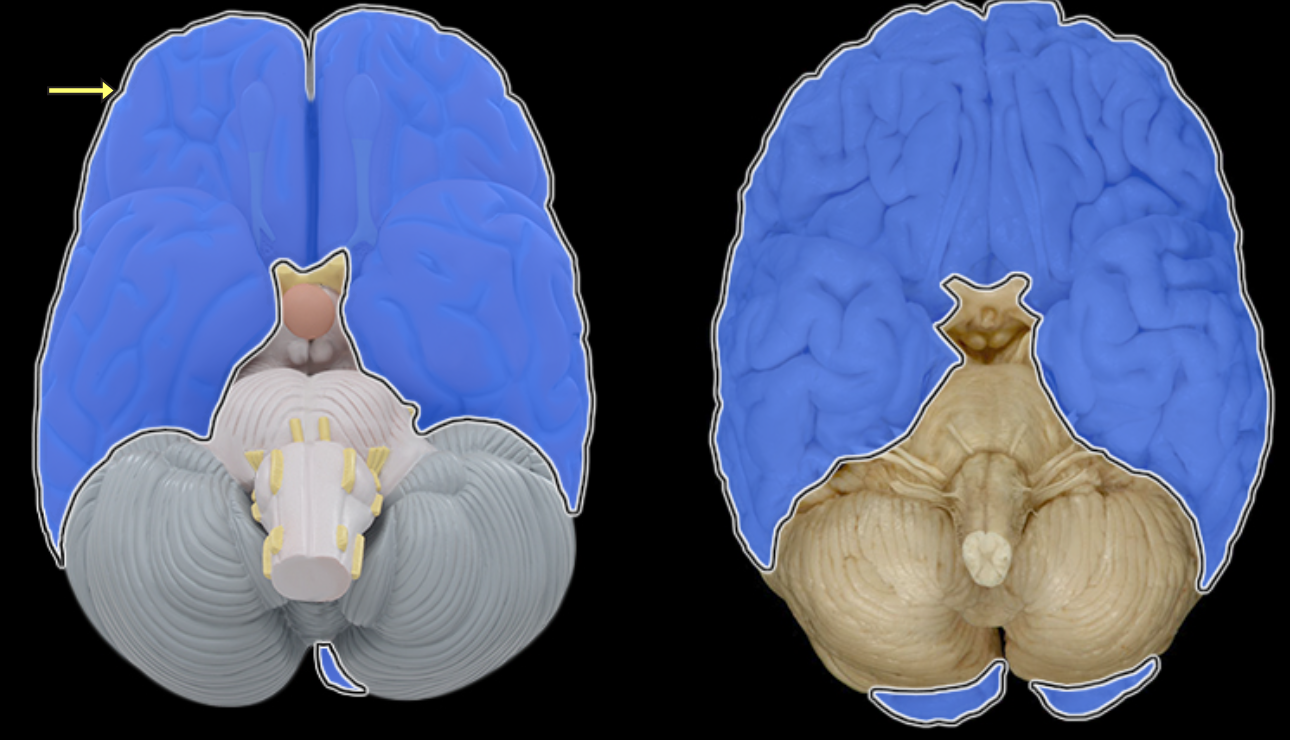
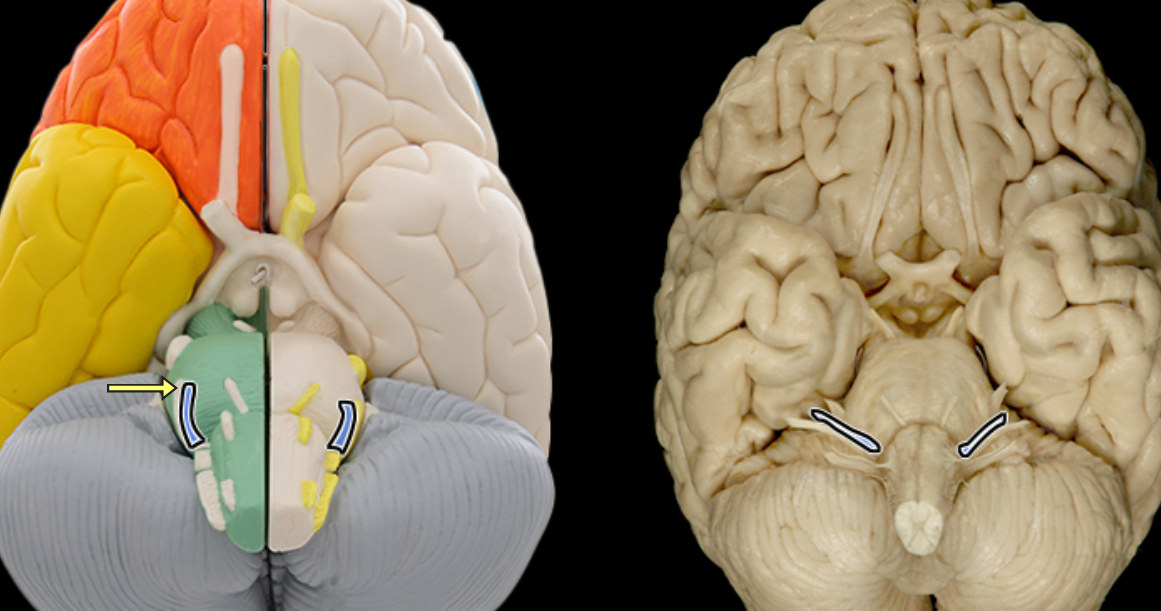
Facial n. CN VII
Location:
Posterior cranial fossa
Facial canal
Middle ear
Face
Infratemporal fossa
Oral cavity
Composition:
Motor
General sensation
Special sensation
Parasympathetic
Motor:
Muscles of facial expression
Posterior belly of digastric muscle
Stylohyoid muscle
Stapedius muscle
General sensation:
Small area of skin of auricle of ear
Special sensation:
Taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue
Taste from palate
Parasympathetic:
Lacrimal gland
Submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
Mucous glands of nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and palate
CNS connection:
Motor: pons (motor nucleus of facial nerve)
General sensation: medulla oblongata (spinal trigeminal nucleus)
Special sensation: medulla oblongata (nucleus of solitary tract)
Parasympathetic: medulla oblongata (superior salivatory nucleus
Sensory ganglion:
Geniculate
Cranial foramina:
Internal acoustic meatus
Pterygomaxillary fissure
Stylomastoid foramen
Also known as:
CN VII
Comment:
Special sensory and parasympathetic axons, together, form the chorda tympani nerve
Postganglionic parasympathetic nerve cell bodies located in pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia
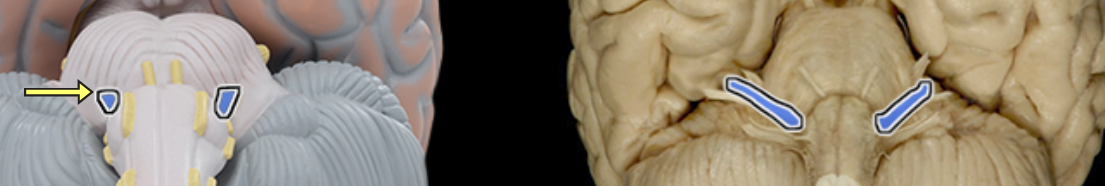
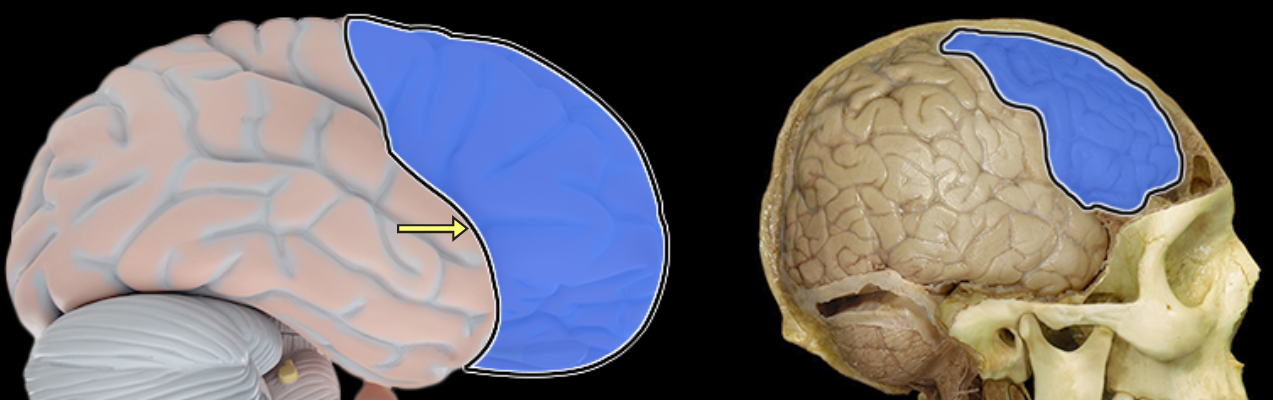
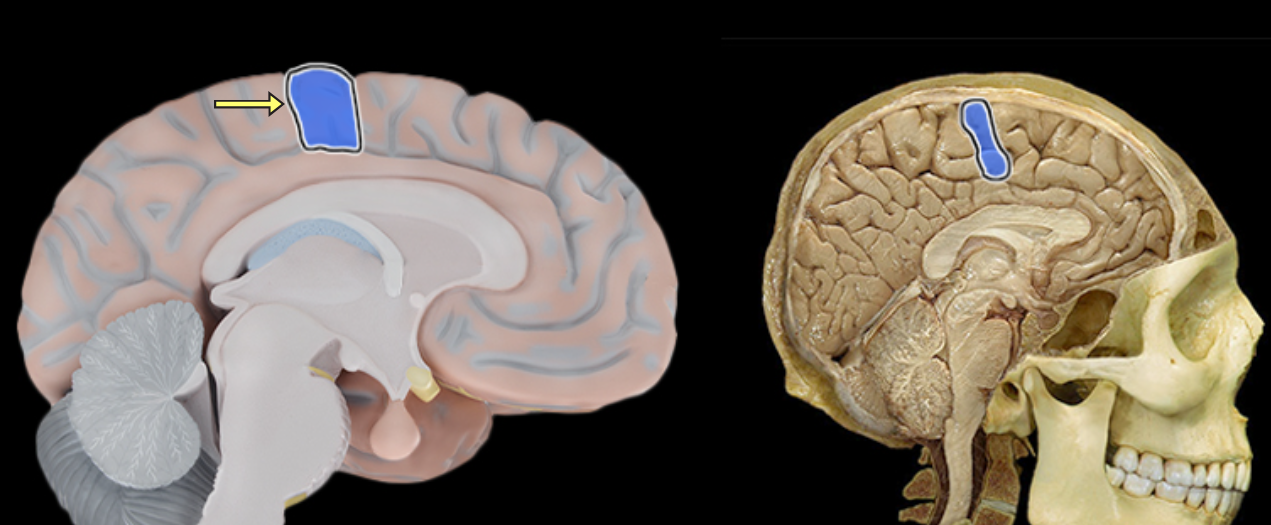
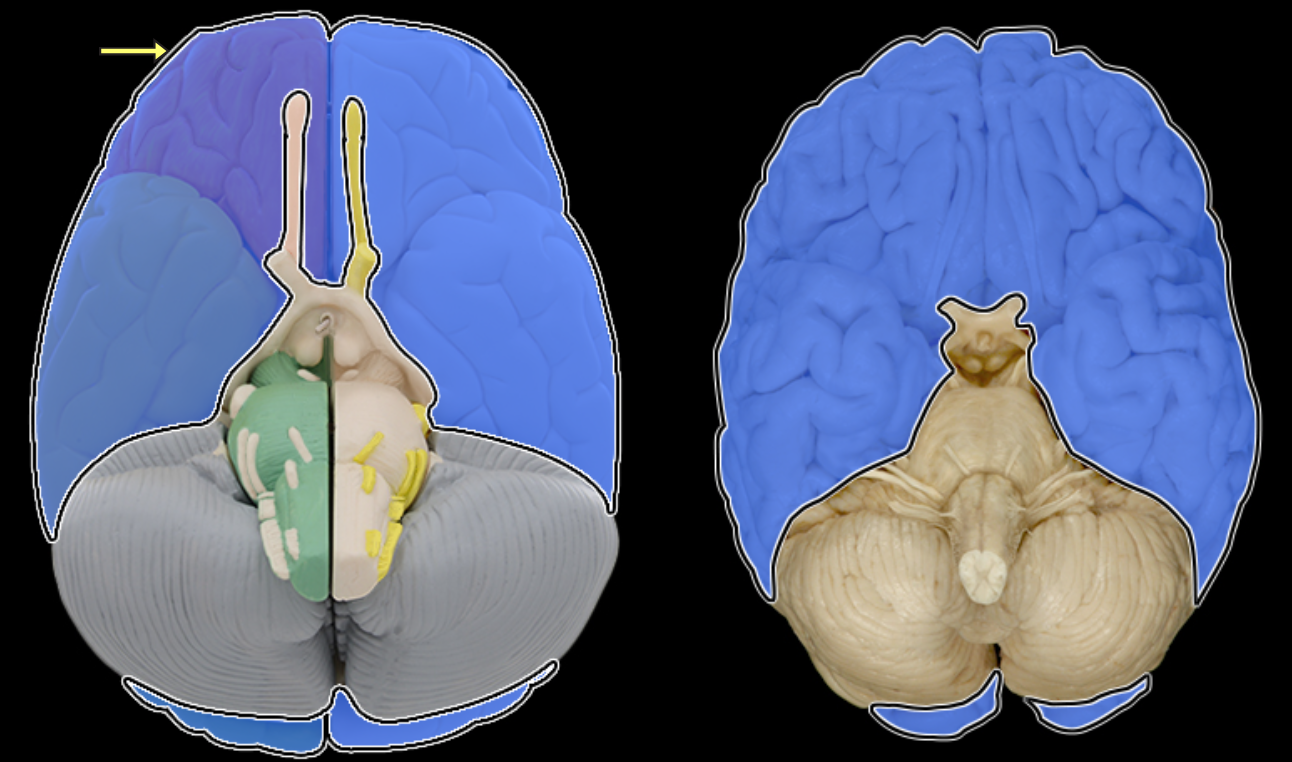
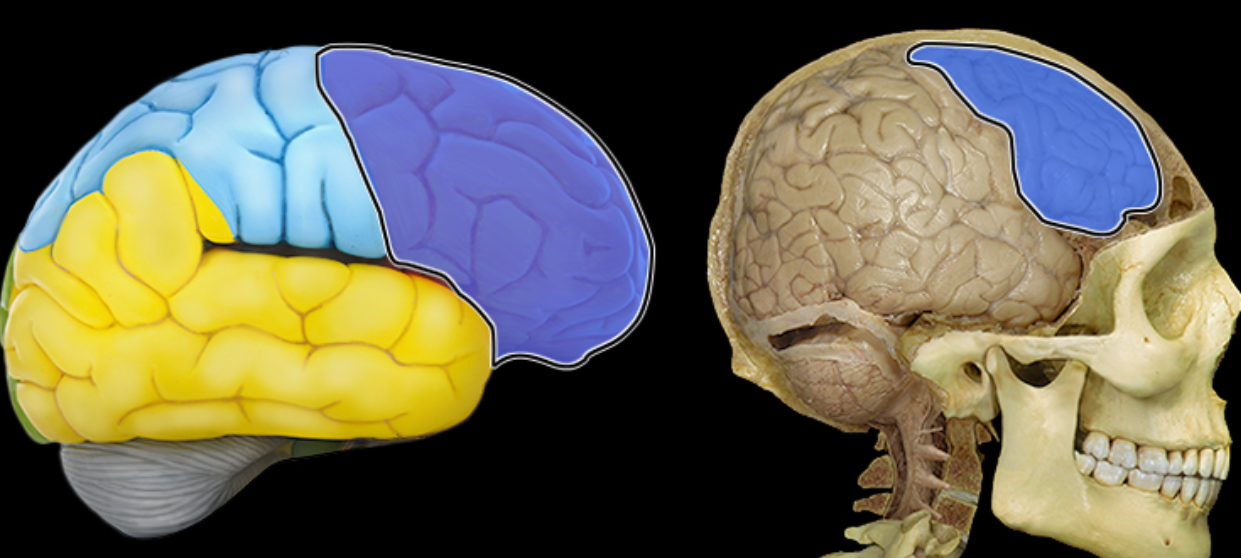
Frontal lobe
Location:
Anterior portion of cerebral hemisphere
Description:
Extends from anterior pole of brain to central sulcus
Contains precentral gyrus
Function:
Controls voluntary motor activity
Higher mental processing
Emotional behavior
Speech output (i.e., Broca's area - usually in left hemisphere)
Comment:
Named for overlying bone
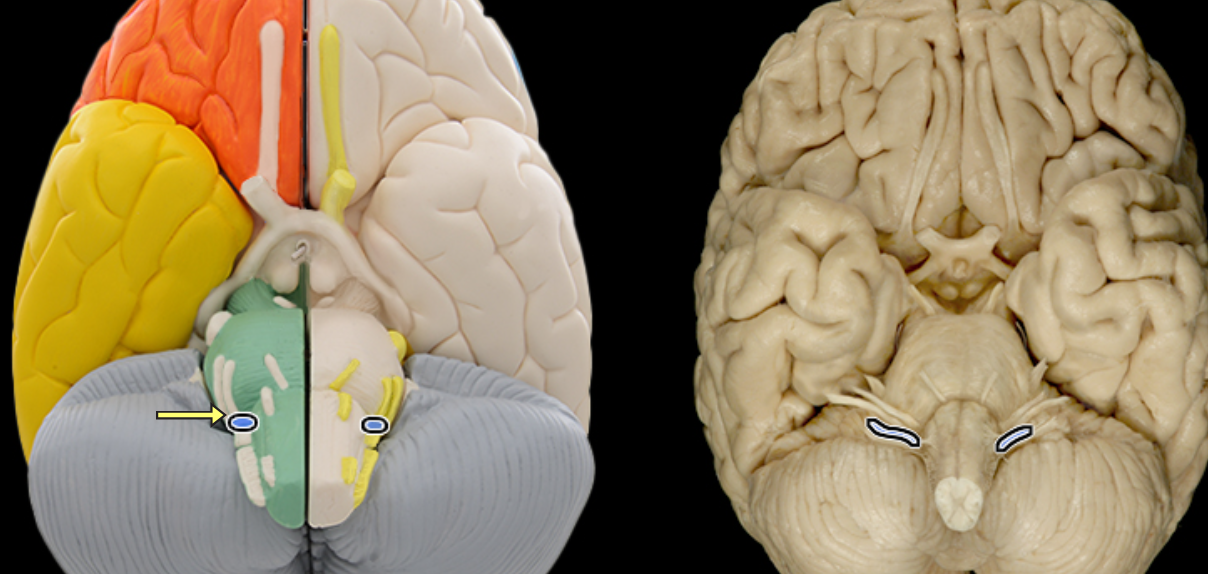
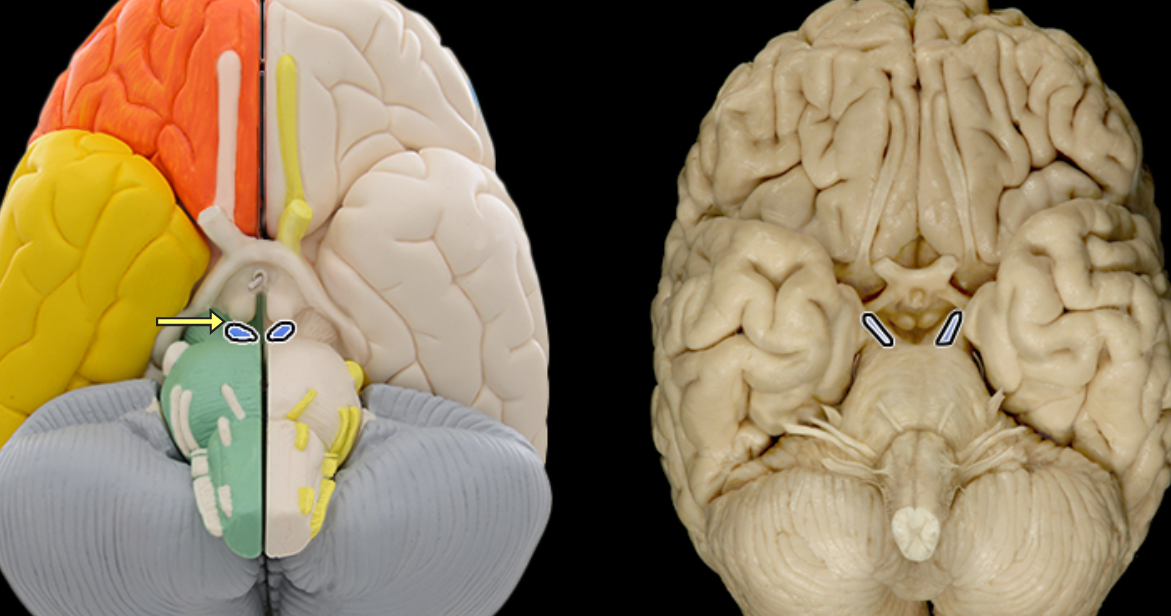
Glossopharyngeal n. CN IX

Location:
Posterior cranial fossa
Neck
Composition:
Motor
General sensation
Special sensation
Parasympathetic
Motor:
Stylopharyngeus muscle
General sensation:
From middle ear, posterior 1/3 of tongue, and pharynx
Special sensation:
Taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue
Sensory ganglion:
Superior and inferior ganglia of glossopharyngeal nerve
Parasympathetic:
Parotid gland
CNS connection:
Motor: medulla oblongata (nucleus ambiguus)
General sensation: medulla oblongata (spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve)
Special sensation: medulla oblongata (nucleus of solitary tract)
Parasympathetic: medulla oblongata (inferior salivatory nucleus)
Cranial foramina:
Jugular foramen
Comment:
Has two sensory ganglia (superior and inferior) on nerve in jugular foramen
Glossopharyngeal nerve also conducts visceral afferent (sensory) impulses from carotid sinus (monitors blood pressure) and carotid body (monitors blood oxygen and carbon dioxide)
Postganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies located in otic ganglion in infratemporal fossa
Glossopharyngeal nerve also known as CN IX

Hypoglossal n. CN XII

Location:
Posterior cranial fossa
Neck
Oral cavity
Composition:
Motor
Motor:
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Intrinsic muscles of tongue
CNS connection:
Medulla oblongata (nucleus of hypoglossal nerve)
Cranial foramina:
Hypoglossal canal
Comment:
Hypoglossal nerve innervates all tongue muscles except palatoglossus (vagus nerve)
Intrinsic tongue muscles originate and insert within tongue
Hypoglossal nerve also known as CN XII

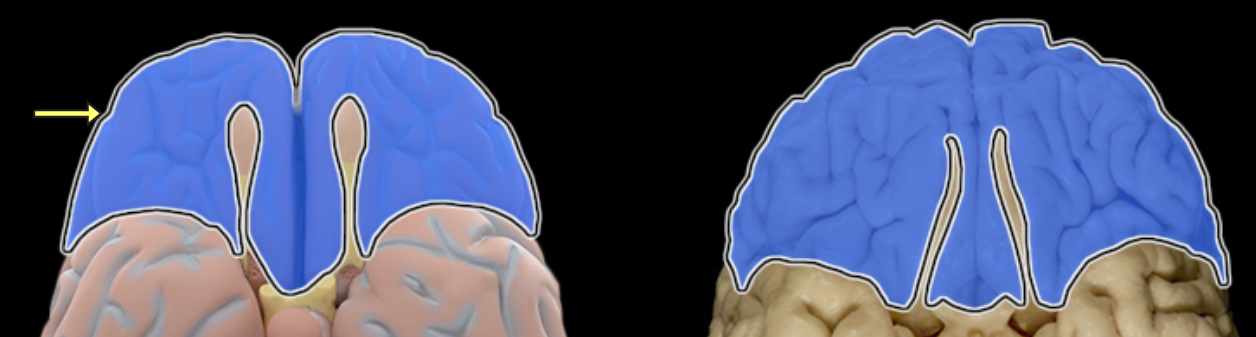
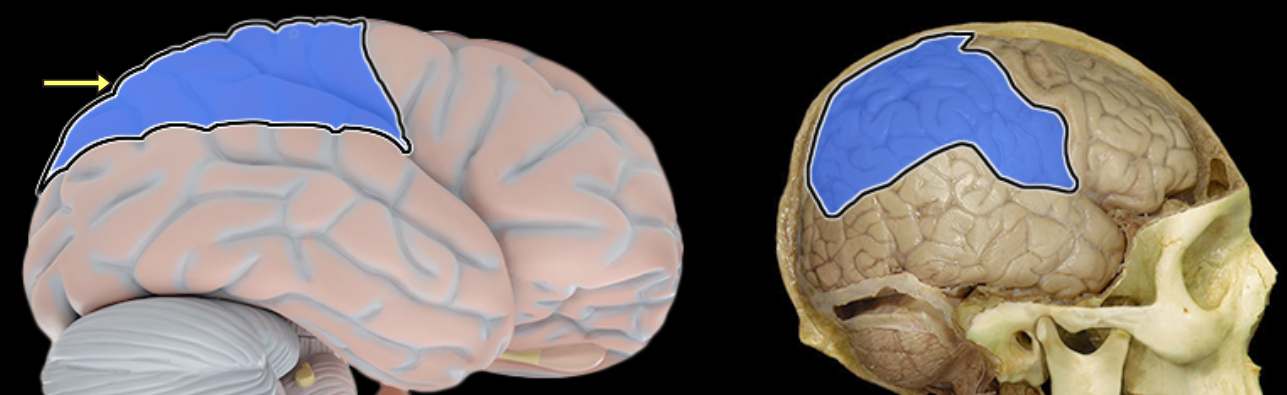
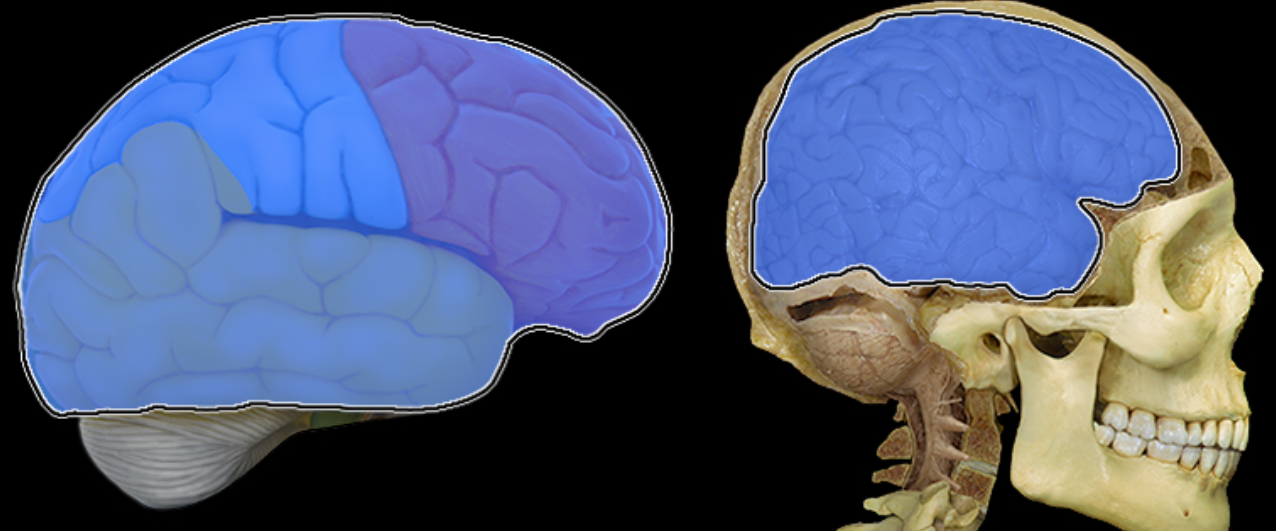
Occipital lobe
Location:
Posterior portion of each cerebral hemisphere
Description:
Extends from parieto-occipital sulcus to posterior pole of brain
Contains lingual gyrus
Function:
Primary visual area
Comment:
Named for overlying bone
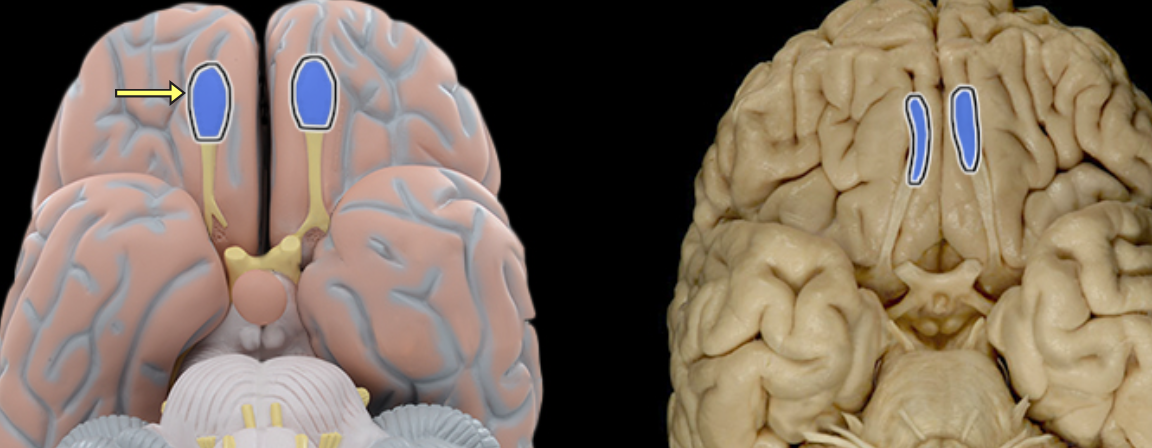
Olfactory bulb
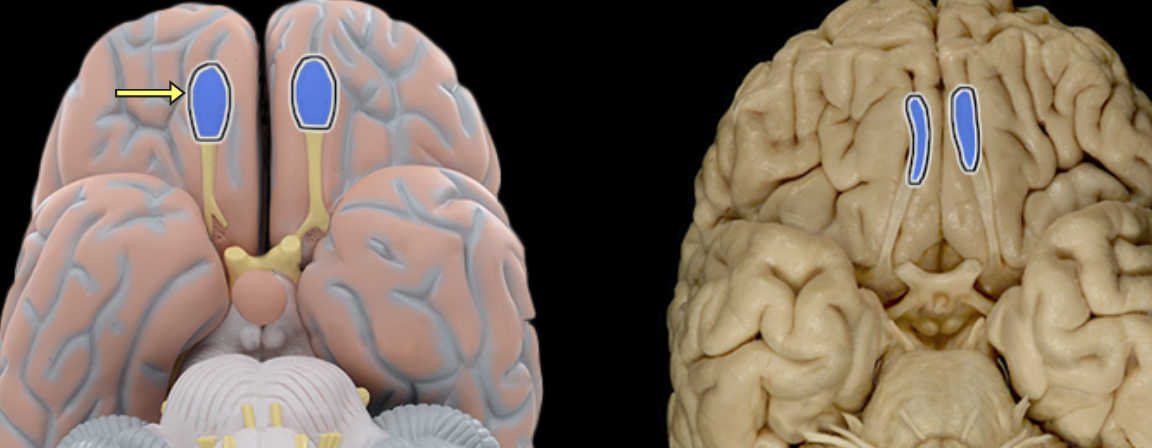
Location:
Lies on cribriform plate of ethmoid bone in anterior cranial fossa
Ventral aspect of frontal lobe of brain
Description:
Expanded anterior end of olfactory tract
Site of synapse for olfactory neurons (CN I) after their axons pass through cribriform plate
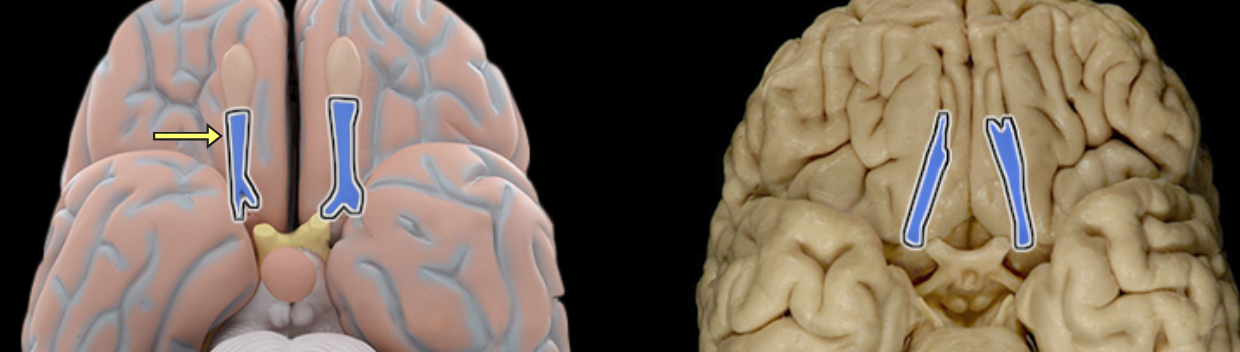
Olfactory tract
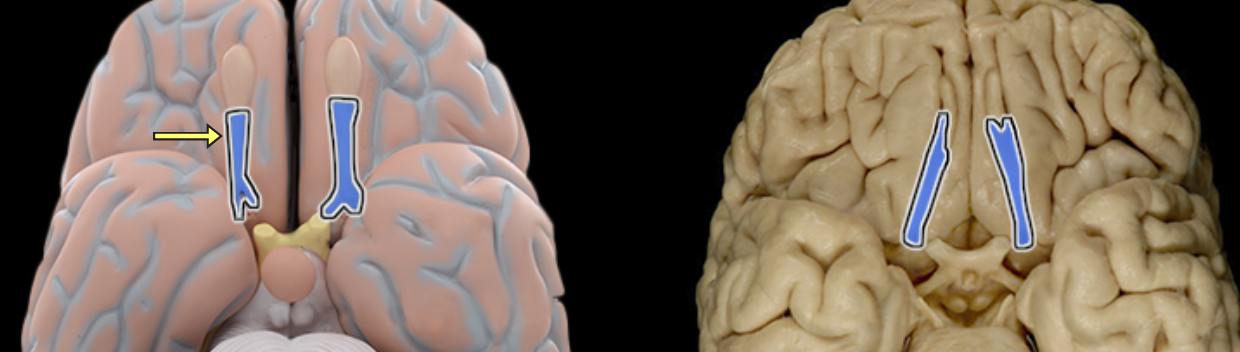
Location:
Ventral aspect of frontal lobe
Between olfactory bulb and medial aspect of temporal lobe
Description:
Bundles of afferent and efferent axons
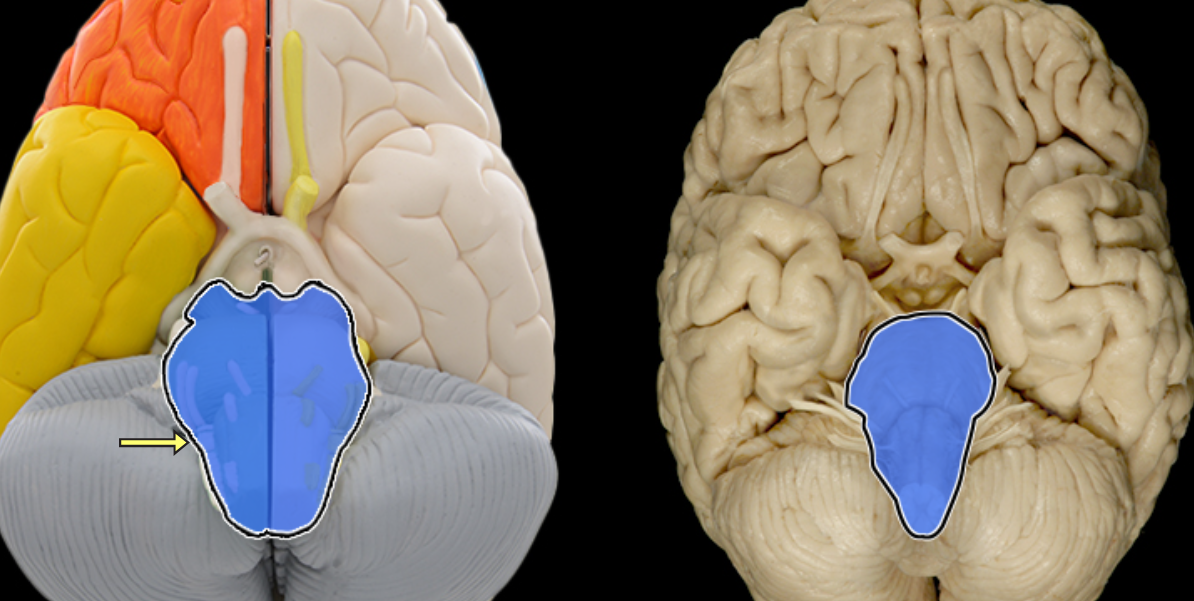
Optic chiasm
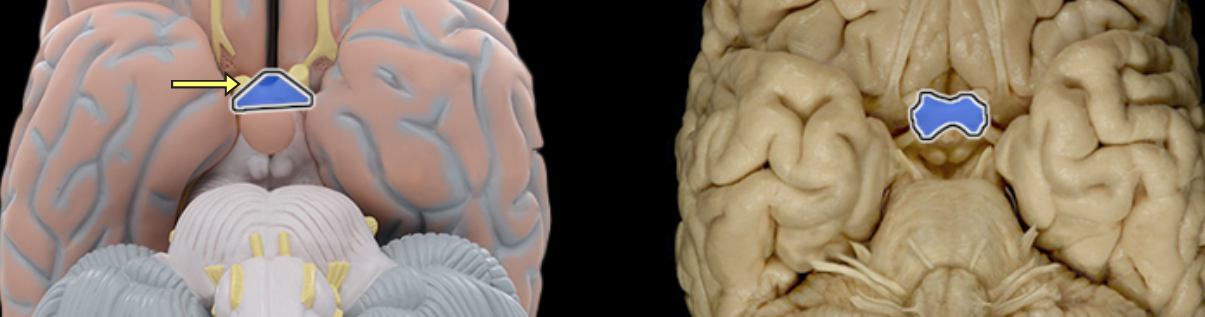
Location:
Ventral aspect of diencephalon
Between optic nerves and optic tracts
Description:
White matter tract composed of axons of retinal ganglion cells from both eyes traveling to thalamus and other brainstem nuclei
Some axons from each retina decussate (cross) in chiasm to enter opposite optic tract
Comment:
Retinal ganglion cell axon pathway: optic nerve > optic chiasm > optic tract > brainstem nuclei (including lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus)
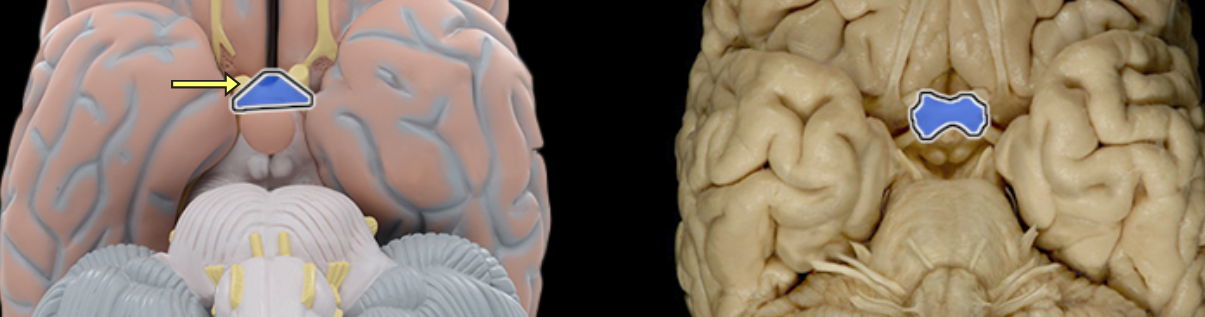
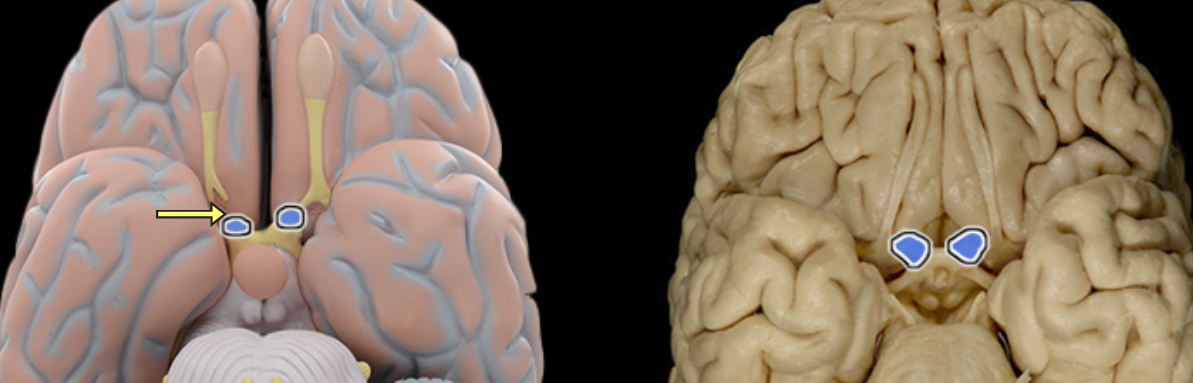
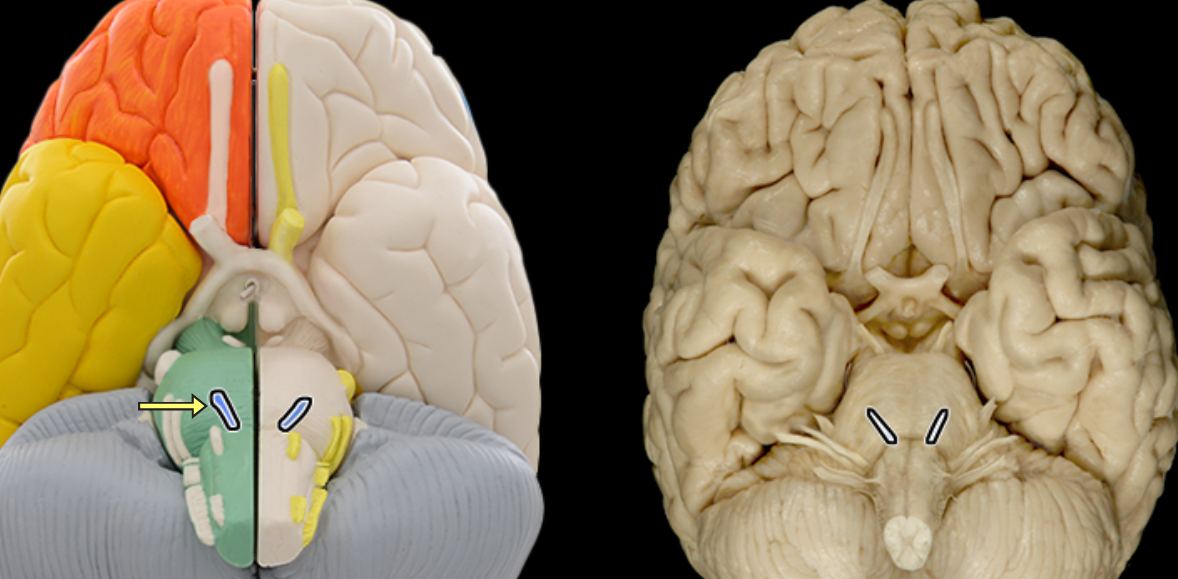
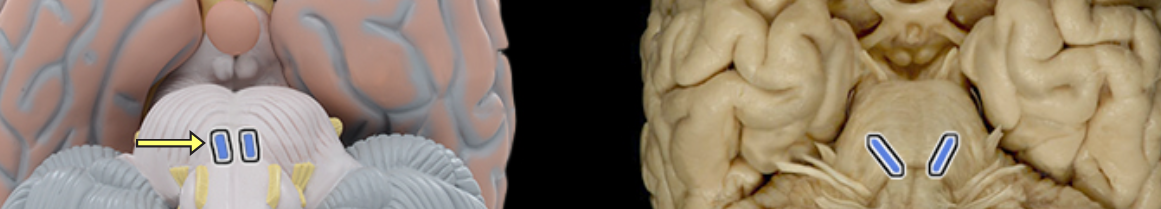
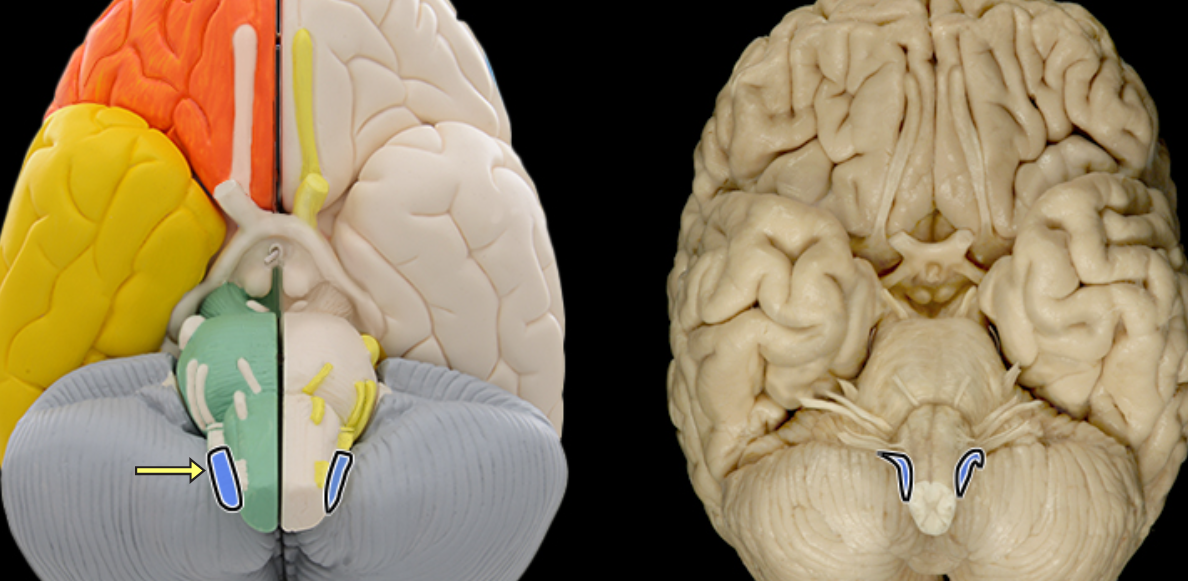
Optic n. CN II
Location:
Orbit
Middle cranial fossa
Composition:
Special sensation
Special sensation:
Vision
CNS connection:
Lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus
Cranial foramina:
Optic canal
Comment:
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
Optic nerve formed by axons of retinal ganglion cells
Retinal ganglion cell axon pathway: optic nerve > optic chiasm > optic tract > brainstem nuclei (including lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus)
Optic nerve also known as CN II
Temporal bone
Location:
Lateral and inferior portion of each cerebral hemisphere
Inferior to lateral sulcus
Description:
Lateral surface has three parallel gyri
Function:
Primary hearing and smell areas
Memory
Speech perception and recognition (i.e., Wernicke's area - usually in left hemisphere)
Comment:
Named for overlying bone
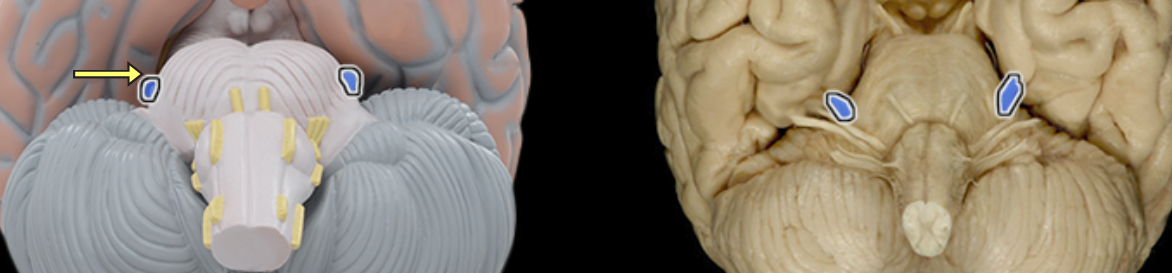
Trigeminal n. (CN V)
Location:
Middle cranial fossa
Ophthalmic nerve (CN V1): face and orbit
Maxillary nerve (CN V2): face, orbit, nasal and oral cavities
Mandibular nerve (CN V3): face, infratemporal fossa, and oral cavity
Composition:
Ophthalmic nerve: general sensation
Maxillary nerve: general sensation
Mandibular nerve: motor and general sensation
Motor:
Muscles of mastication (mandibular nerve)
Mylohyoid (mandibular nerve)
Anterior belly of digastric (mandibular nerve)
Tensor tympani (mandibular nerve)
Tensor veli palatini (mandibular nerve)
General sensation:
Ophthalmic nerve: skin of superior face (forehead, scalp, and upper eyelid), eye, mucosa of anterior nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses (frontal, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal)
Maxillary nerve: skin of middle face (cheek, upper lip, and lower eyelid), maxillary teeth and gingiva (gums), mucosa of palate, posterior nasal cavity, and maxillary sinus
Mandibular nerve: skin of inferior face (mandible, cheek, and lower lip), temple, mucosa lining cheek, mandibular teeth and gingiva (gums), and anterior 2/3 of tongue
Sensory ganglion:
Trigeminal
CNS connection:
Pons (principal sensory and motor nuclei of trigeminal nerve)
Medulla oblongata (spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve)
Cranial foramina:
Ophthalmic nerve: superior orbital fissure
Maxillary nerve: foramen rotundum
Mandibular nerve: foramen ovale
Comment:
Trigeminal nerve (CN V) has three divisions (nerves): ophthalmic (CN V1), maxillary (CN V2), and mandibular (CN V3)
General sensation includes pain, touch, and temperature
Trigeminal ganglion also known as semilunar ganglion
Trigeminal nerve also known as CN V
Vagus n. CN X
Location:
Posterior cranial fossa
Head
Neck
Thorax
Abdomen
Composition:
Motor
General sensation
Special sensation
Parasympathetic
Motor:
Muscles of palate
Muscles of pharynx
Intrinsic muscles of larynx
General sensation:
Thoracic and abdominal viscera
Epiglottis and laryngopharynx
External acoustic meatus
Special sensation:
Taste from epiglottis and surrounding region
Parasympathetic:
Mucous glands of respiratory and digestive systems in neck (pharynx and larynx), thorax, and abdomen
Smooth muscle of respiratory and digestive systems in neck (pharynx and larynx), thorax, and abdomen
Cardiac muscle
CNS connection:
Motor: medulla oblongata (nucleus ambiguus)
General sensation: medulla oblongata (spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve)
Special sensation: medulla oblongata (nucleus of solitary tract)
Parasympathetic: medulla oblongata (dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve)
Cranial foramina:
Jugular foramen
Comment:
General sensation from thoracic and abdominal viscera only involves stretch (e.g., distention of stomach)
General sensation from epiglottis and laryngopharynx includes pain, touch, and temperature
Vagus nerve also innervates carotid and aortic bodies
Parasympathetic impulses from CNS to effector organ involve two neurons in series (preganglionic and postganglionic)
Only cranial nerve that extends beyond head and neck
Vagus nerve also known as CN X
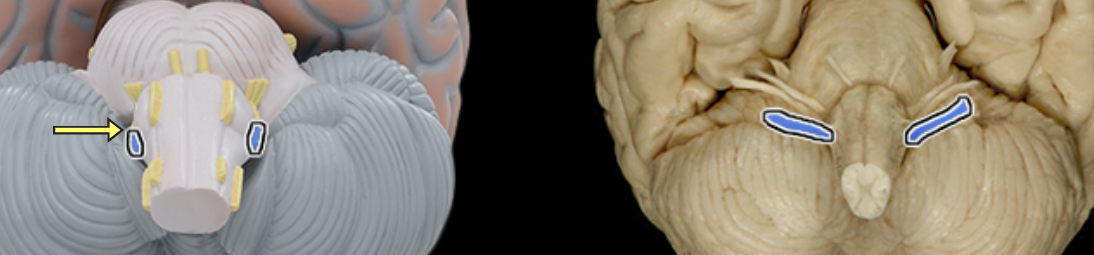
Vestibulocochlear n. CN VIII
Location:
Posterior cranial fossa
Petrous portion of temporal bone
Composition:
Special sensation
Special sensation:
Hearing (cochlea)
Balance (semicircular canals and vestibule)
Sensory ganglion:
Cochlear (spiral) ganglion (cochlear part of CN VIII)
Vestibular ganglion (vestibular part of CN VIII)
CNS connection:
Pons (vestibular nuclei)
Medulla oblongata (cochlear and vestibular nuclei)
Cranial foramina:
Internal acoustic meatus
Comment:
Special sensation includes smell, vision, taste, hearing, and balance
Vestibulocochlear nerve has two distinct functional components: vestibular (balance) and cochlear (hearing)
Vestibulocochlear nerve also known as CN VIII
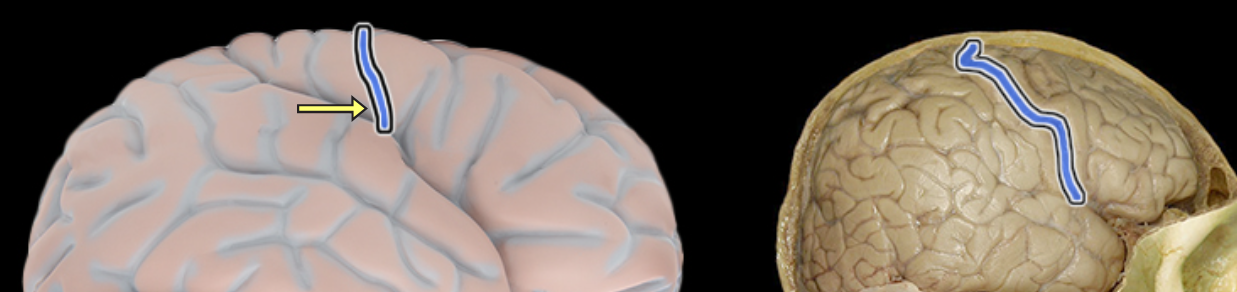
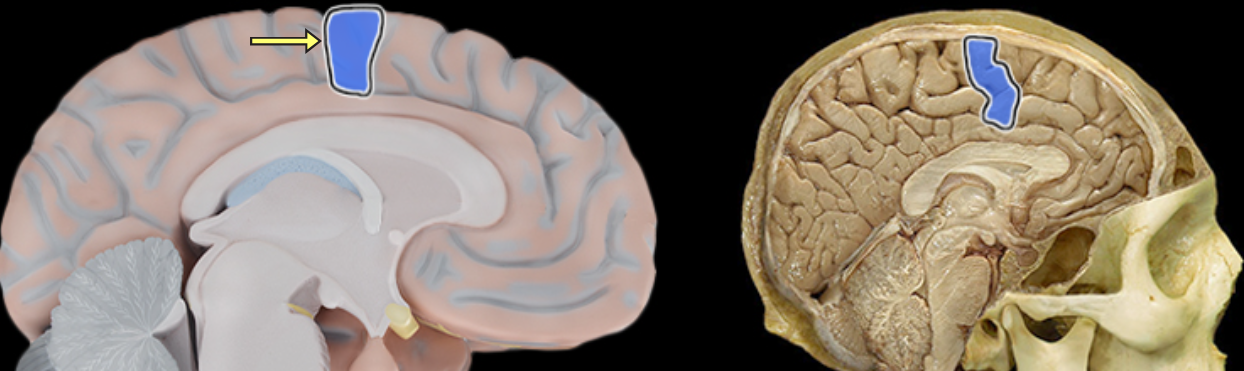
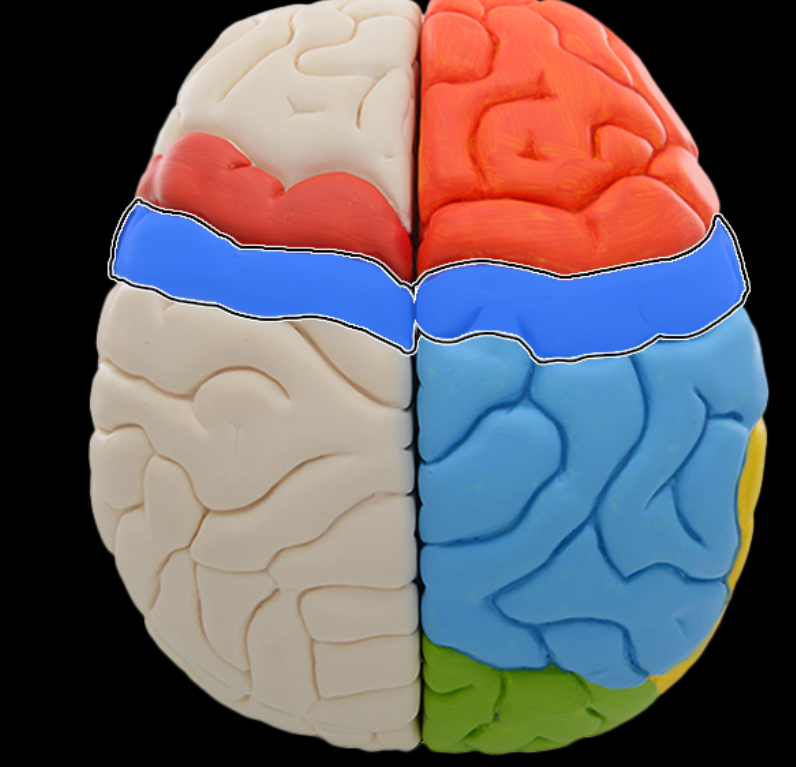
Central sulcus
Location:
Lateral aspect of cerebral hemisphere
Description:
Groove on lateral surface of each cerebral hemisphere
Forms boundary between frontal and parietal lobes
Located between precentral and postcentral gyri
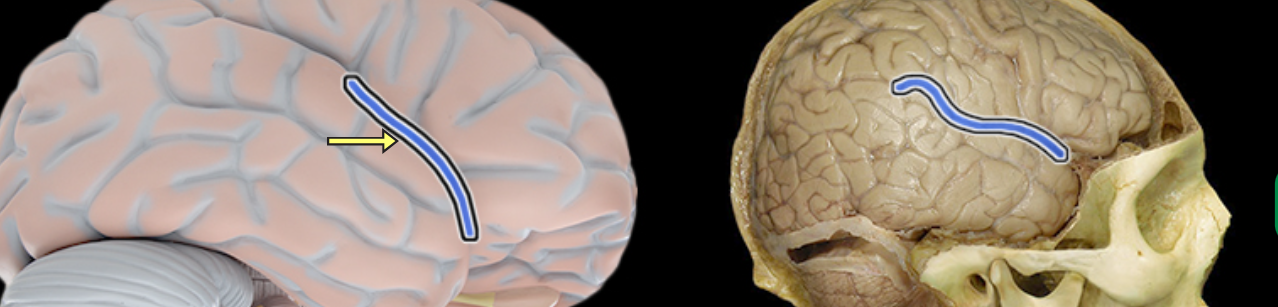
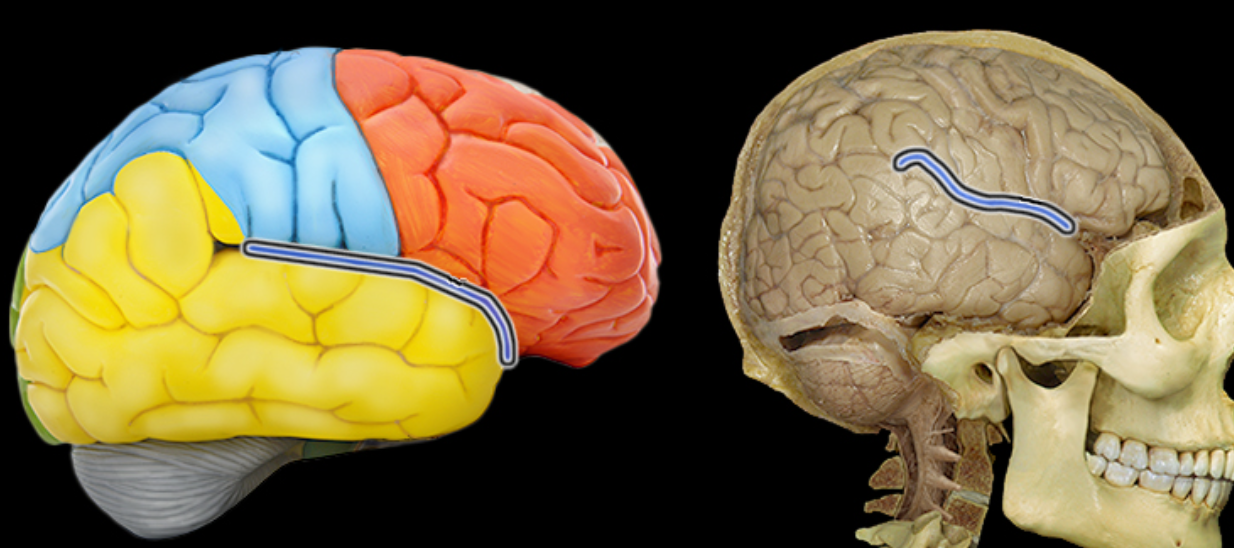
Lateral sulcus
Location:
Lateral aspect of each cerebral hemisphere
Description:
Deep groove separating temporal from frontal and parietal lobes
Occipital lobe
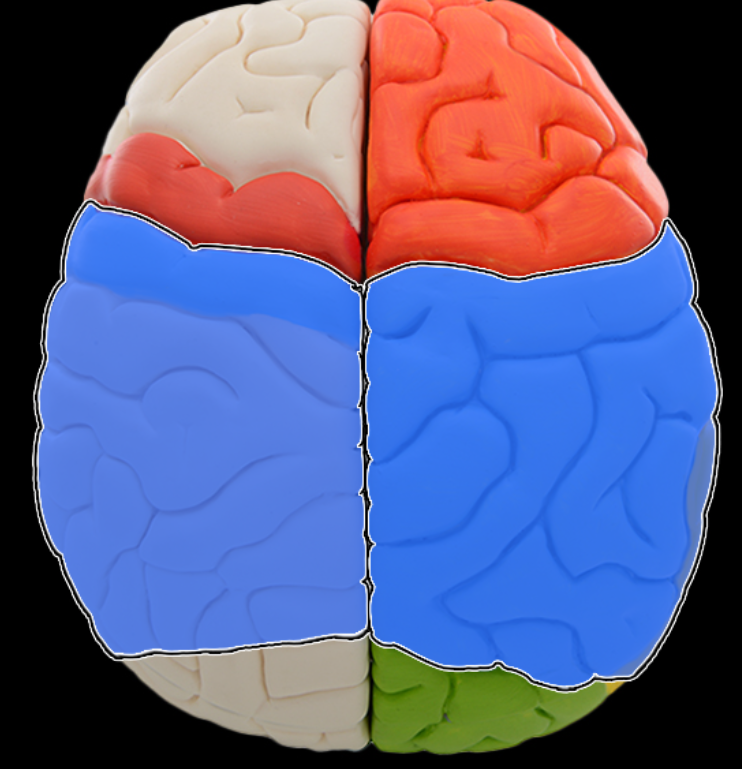
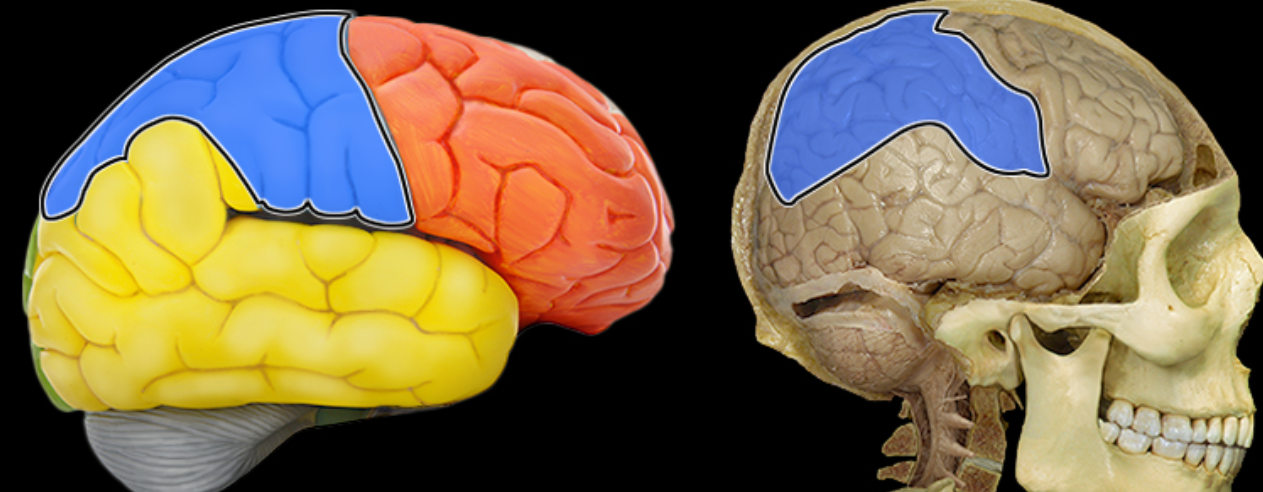
Parietal lobe
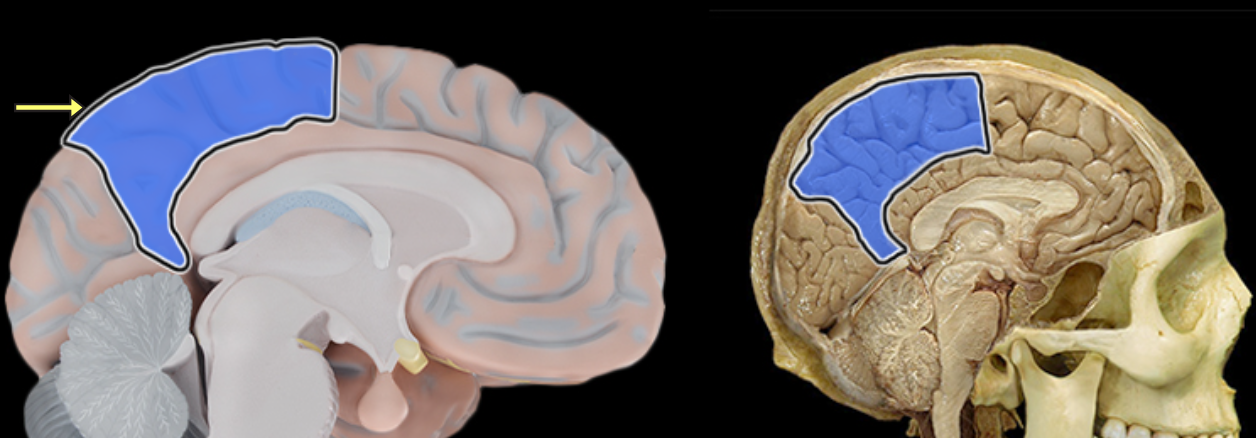
Location:
Lateral surface of each cerebral hemisphere of brain
Description:
Extends from central sulcus (rostral) to parieto-occipital sulcus (caudal)
Includes postcentral gyrus
Function:
Reception of general sensory information from body
Tactile object recognition
Language, verbatim repetition of terms (i.e., Wernicke's area - usually in left hemisphere)
Comment:
Named for overlying bone
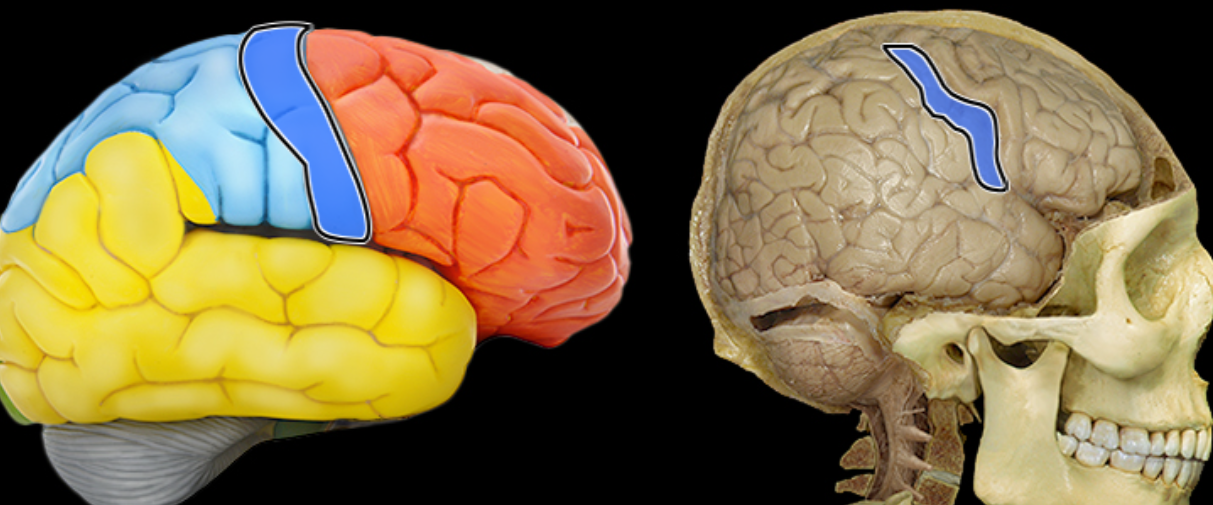
Postcentral gyrus
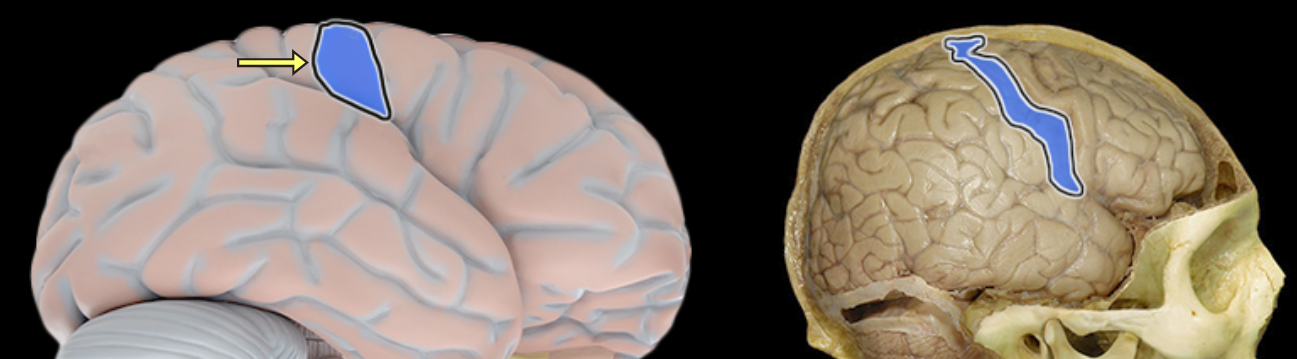
Location:
Lateral aspect of each cerebral hemisphere
Description:
Distinct "fold" at anterior border of parietal lobe
Located along posterior edge of central sulcus
Function:
Receives somatosensory information from body
Comment:
Also called primary somatosensory cortex
Precentral gyrus
Location:
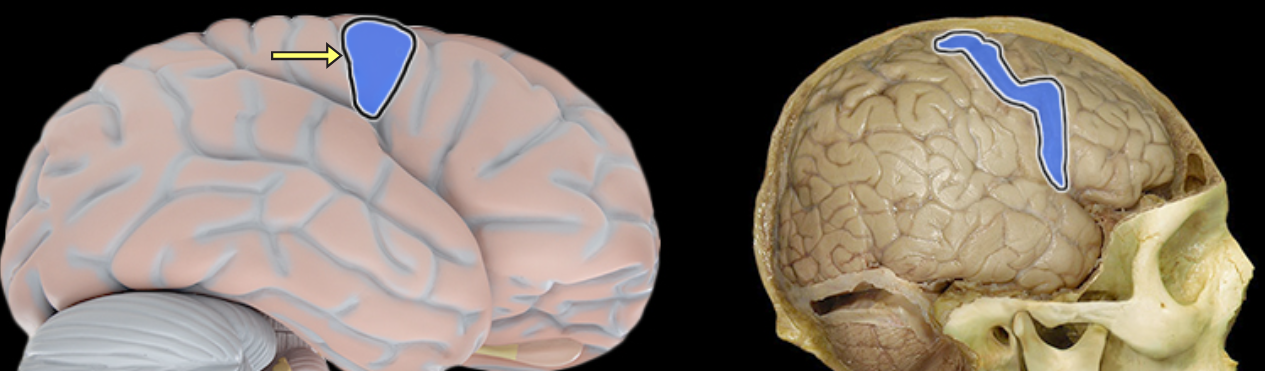
Lateral aspect of each cerebral hemisphere
Description:
Distinct "fold" at posterior border of frontal lobe
Located along anterior edge of central sulcus
Function:
Controls voluntary movement
Comment:
Also called primary motor cortex
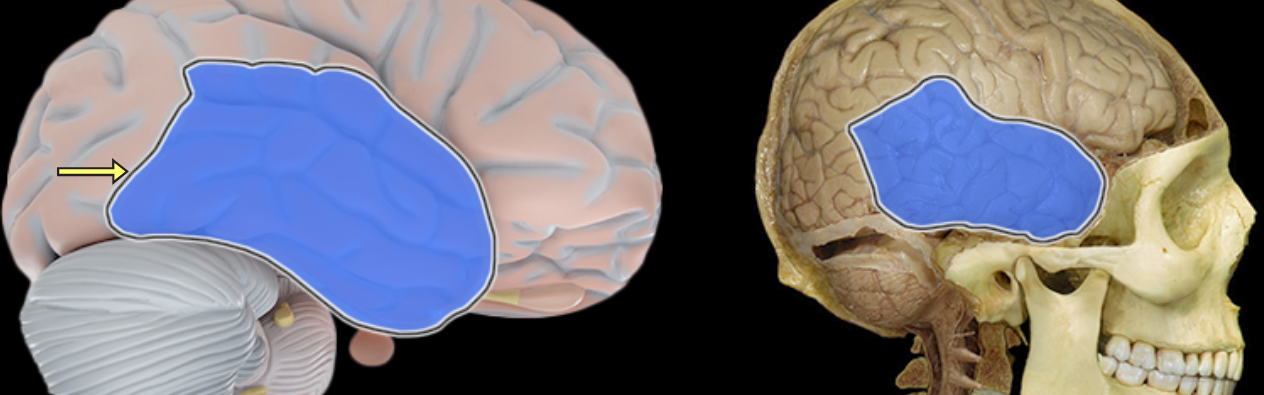
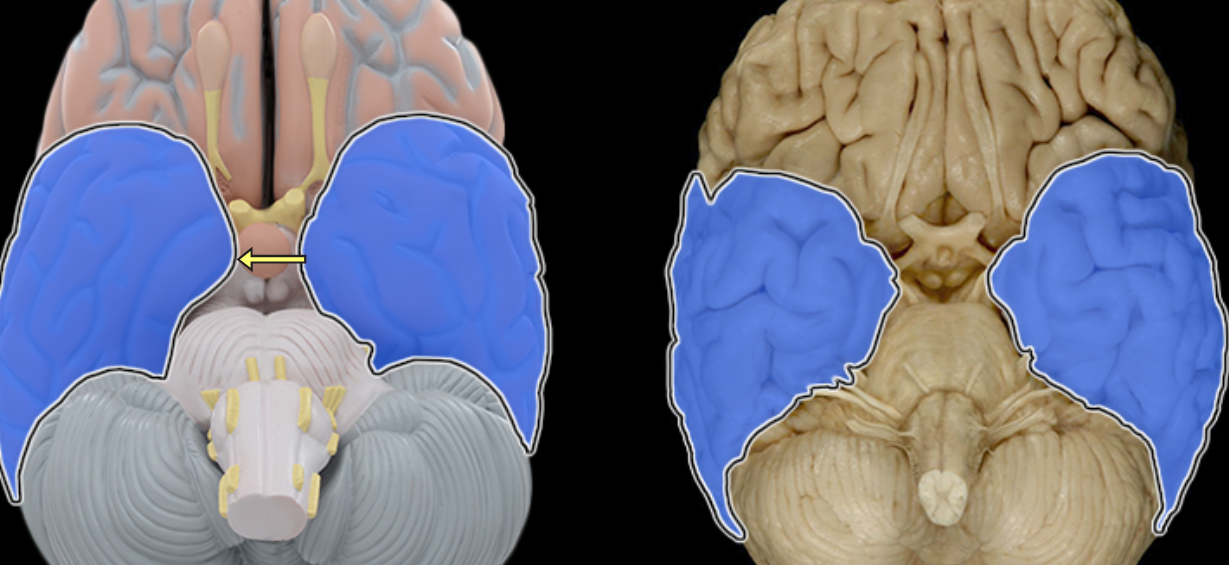
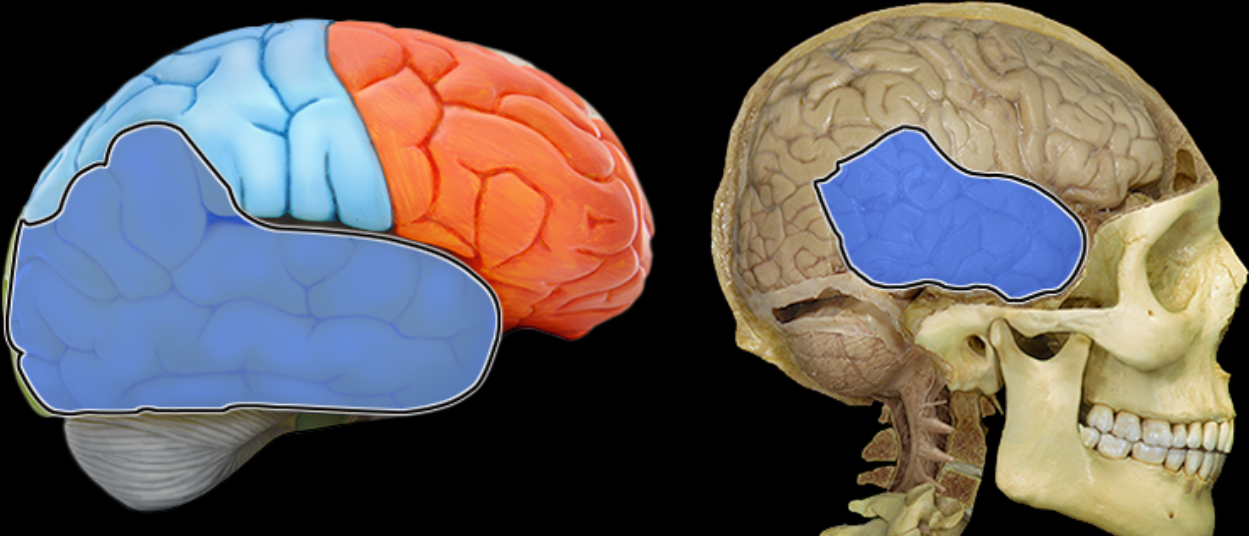
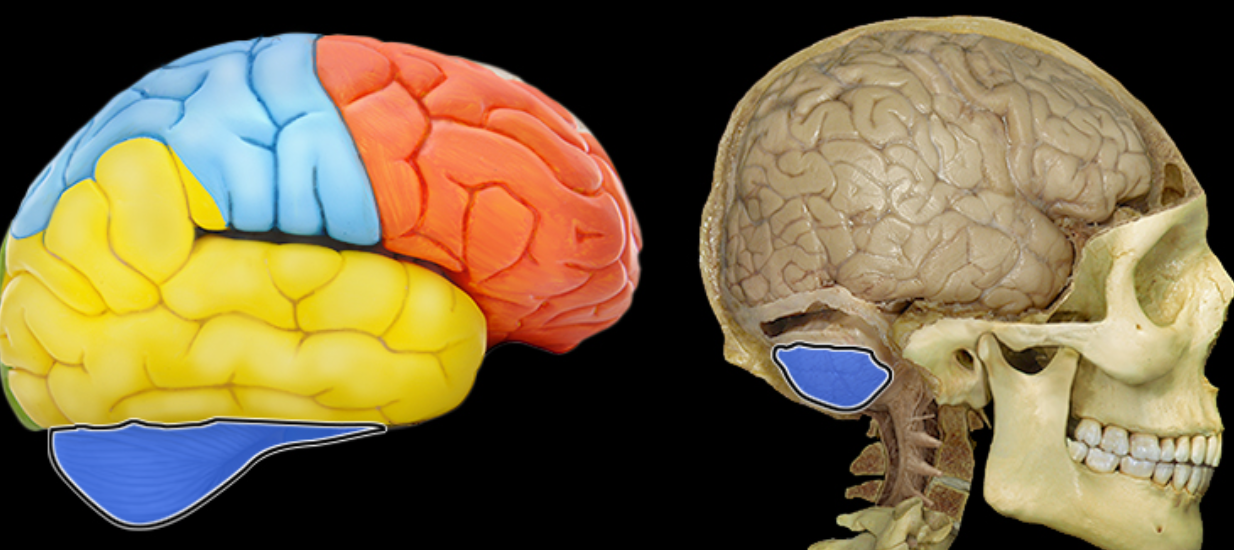
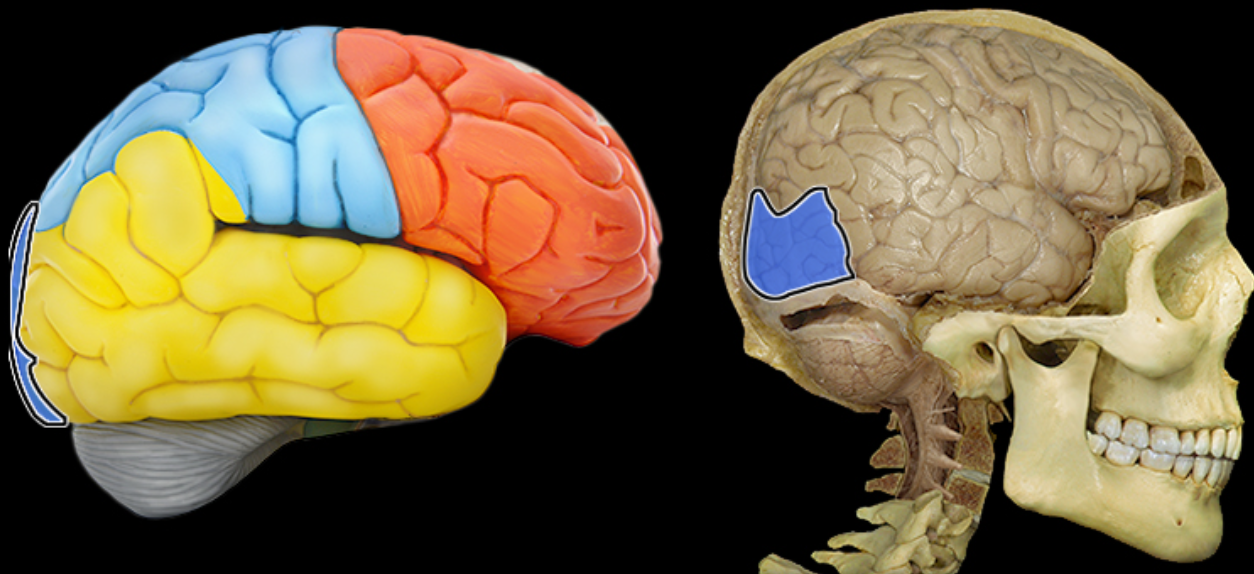
Temporal lobe
Location:
Lateral and inferior portion of each cerebral hemisphere
Inferior to lateral sulcus
Description:
Lateral surface has three parallel gyri
Function:
Primary hearing and smell areas
Memory
Speech perception and recognition (i.e., Wernicke's area - usually in left hemisphere)
Comment:
Named for overlying bone

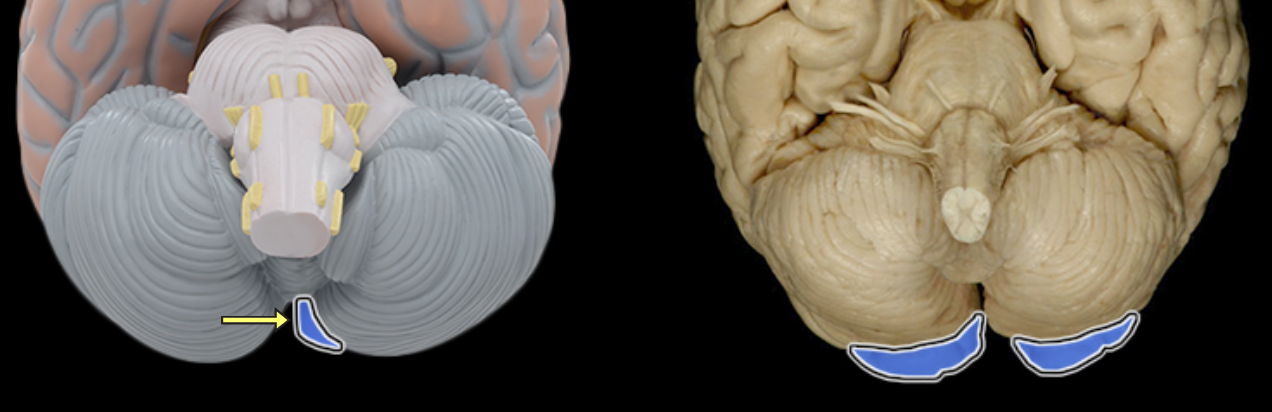
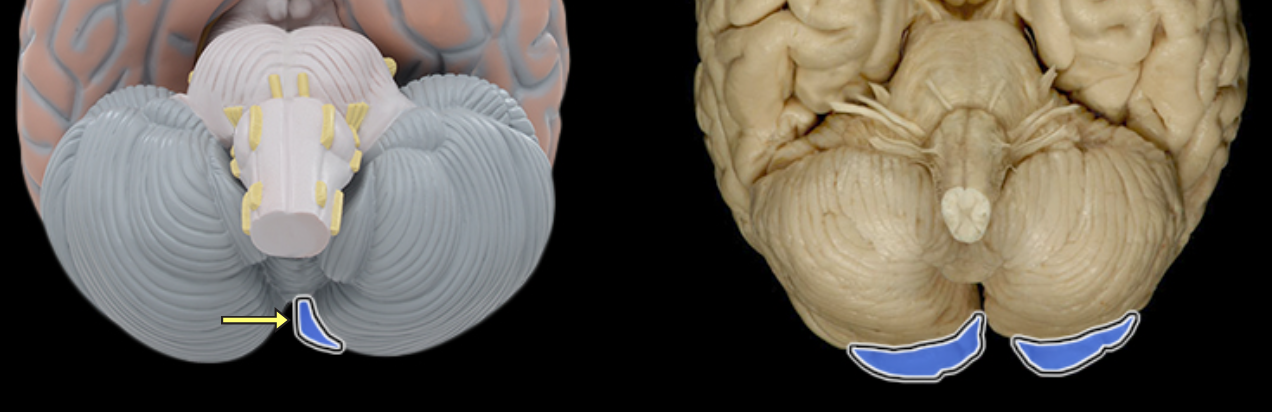
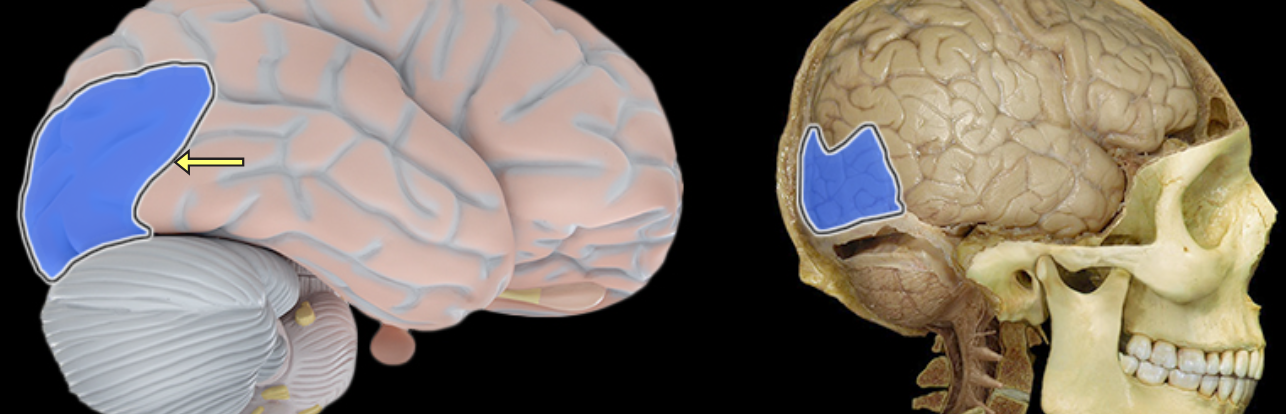
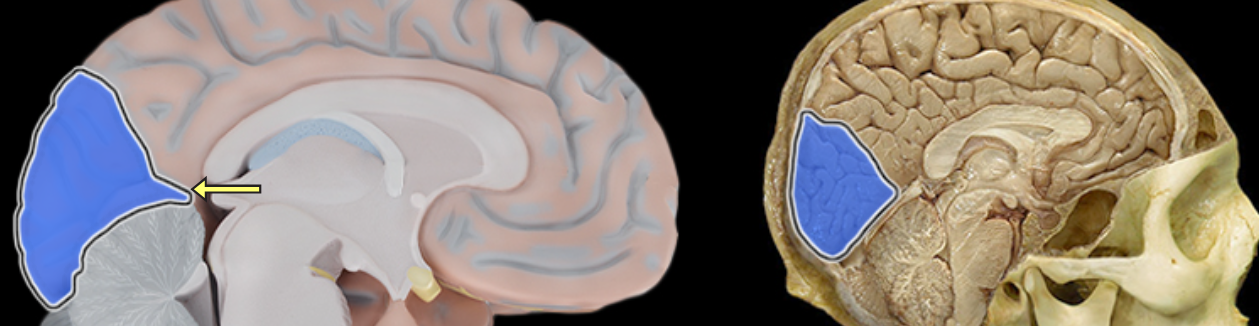
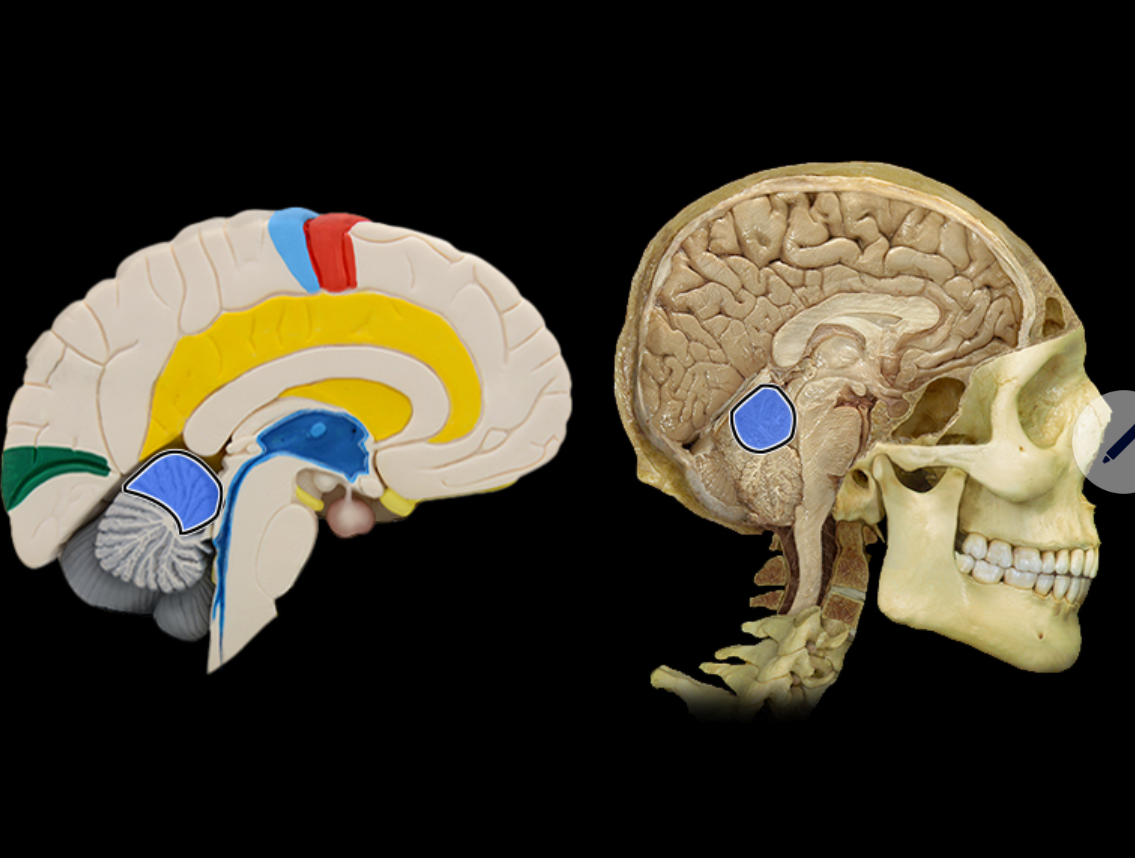
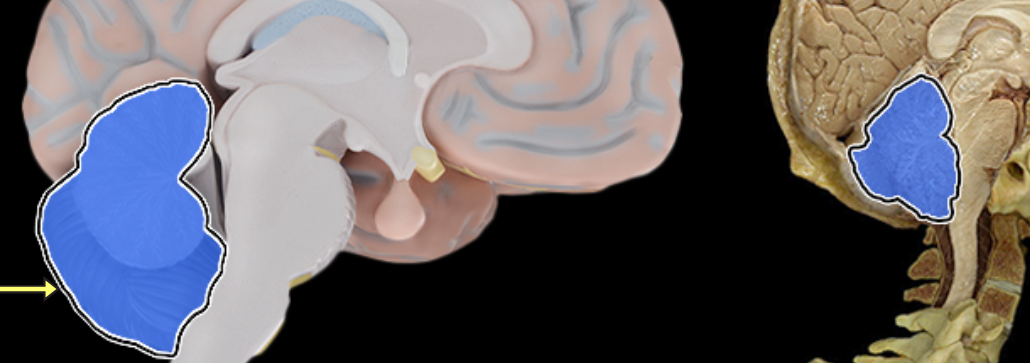
Anterior lobe of cerebellum
Location:
Cerebellum
Description:
The most anterior lobe of the cerebellar hemisphere
There is a right and left hemisphere of the cerebellum

Arbor vitae
Location:
Cerebellum
Description:
Composed of the white matter of cerebellar lobes
It's pattern resembles a branching tree
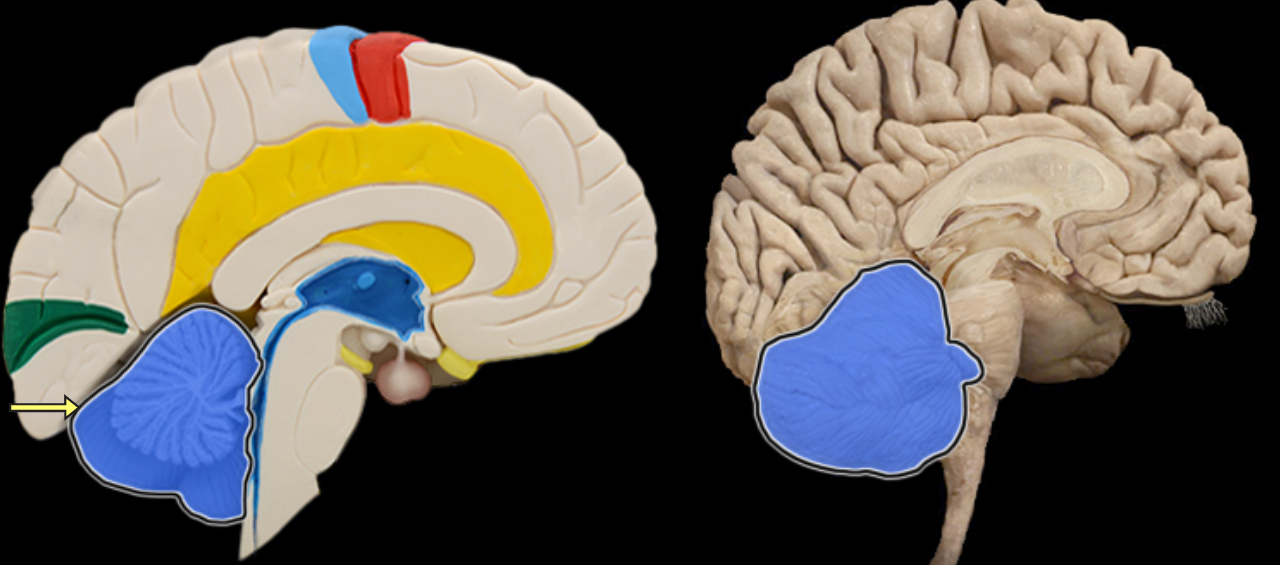
Cerebellum
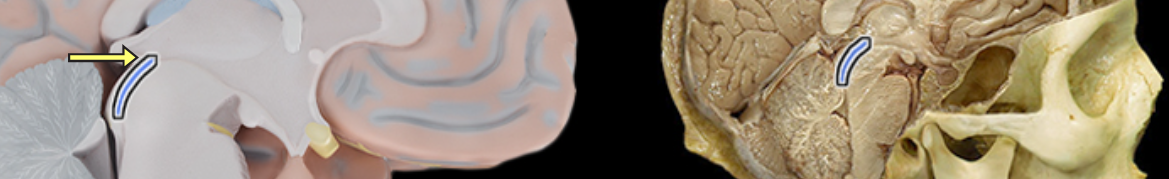
Cerebral aqueduct
Location:
Midbrain
Description:
Narrow midline channel between third and fourth ventricles
Filled with cerebrospinal fluid
Comment:
Cerebral ventricular system includes: (1) paired lateral ventricles; (2) interventricular foramena (Monro); (3) unpaired third ventricle; (4) cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius); and (5) unpaired fourth ventricle
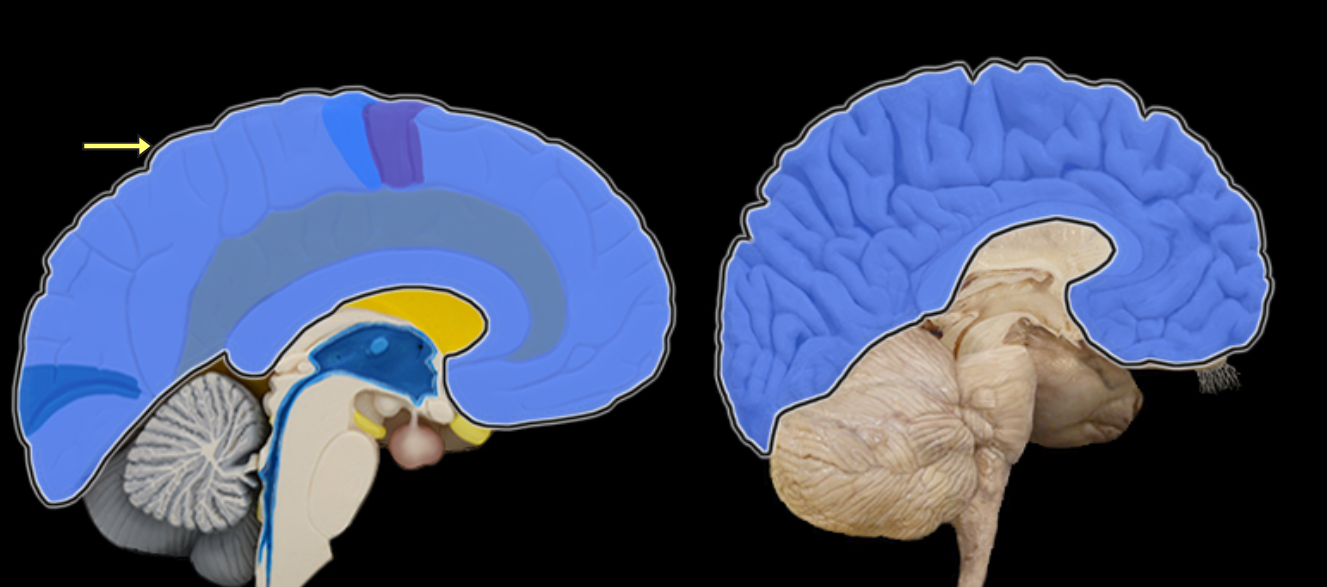
Cerebrum
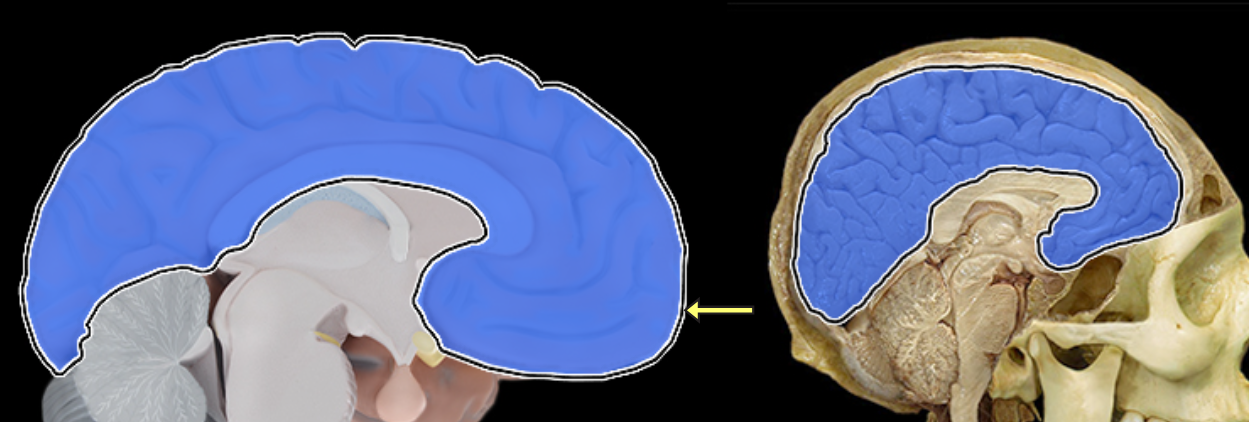
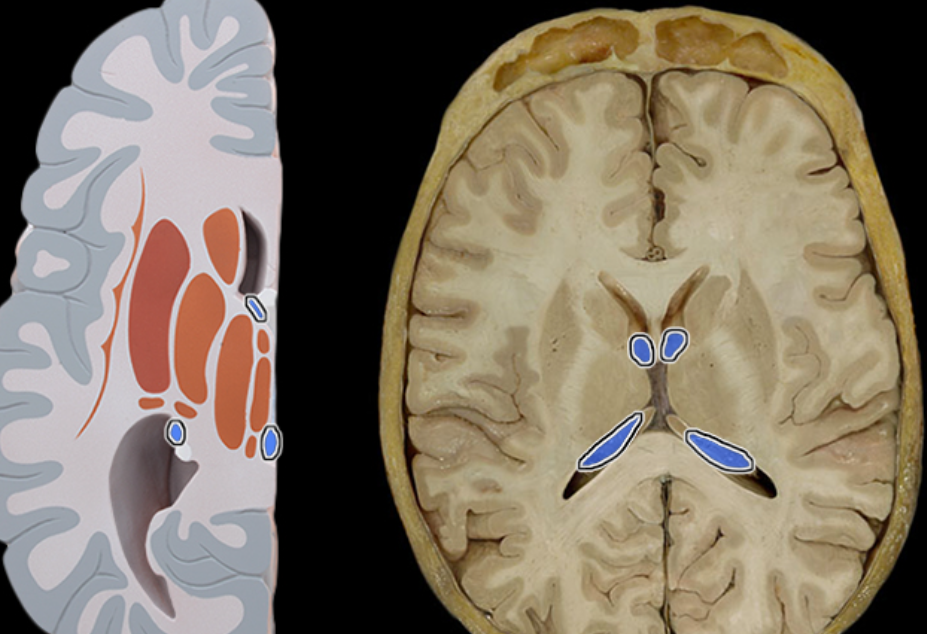
Choroid plexus
Location:
Lateral, third, and fourth ventricles of brain
Description:
Tufts of capillaries covered by specialized ependymal cells that line ventricles
Function:
Specialized ependymal cells produce cerebrospinal fluid
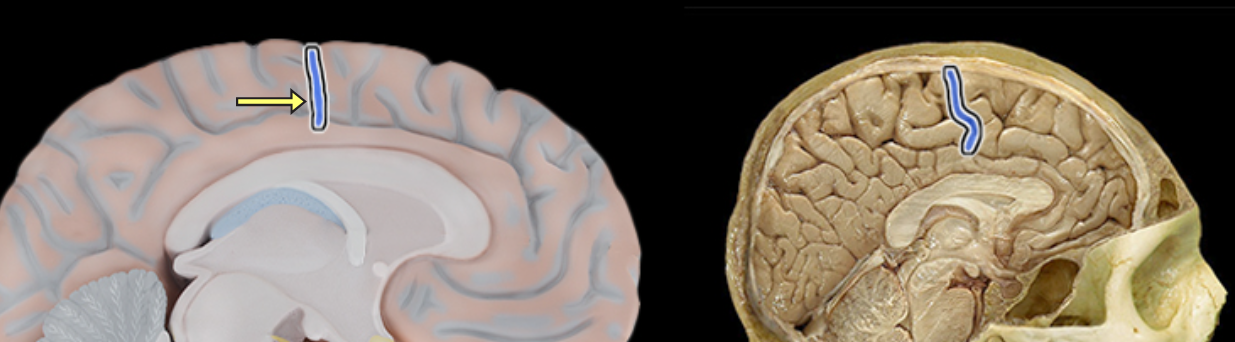
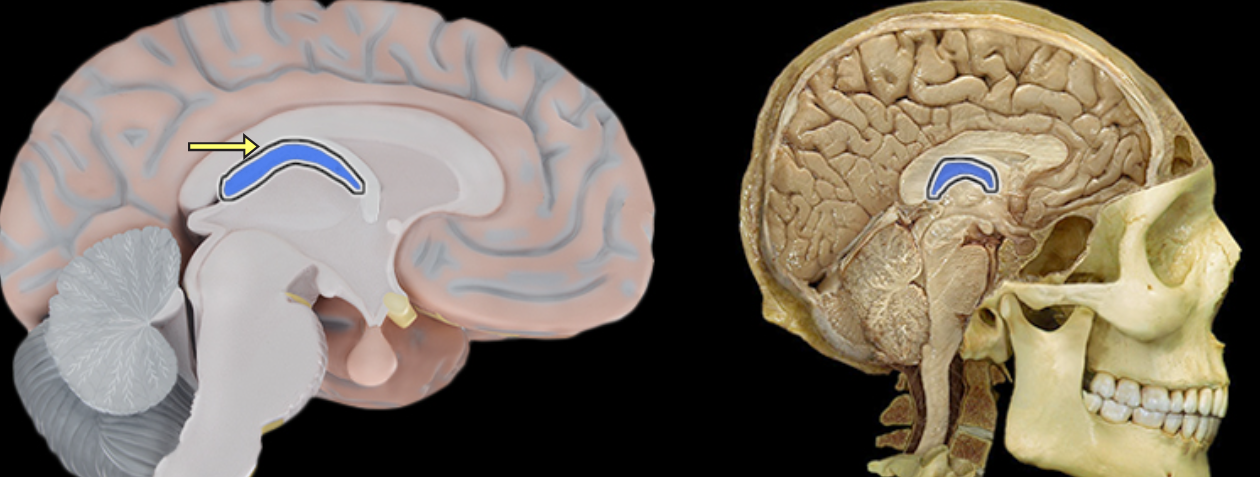
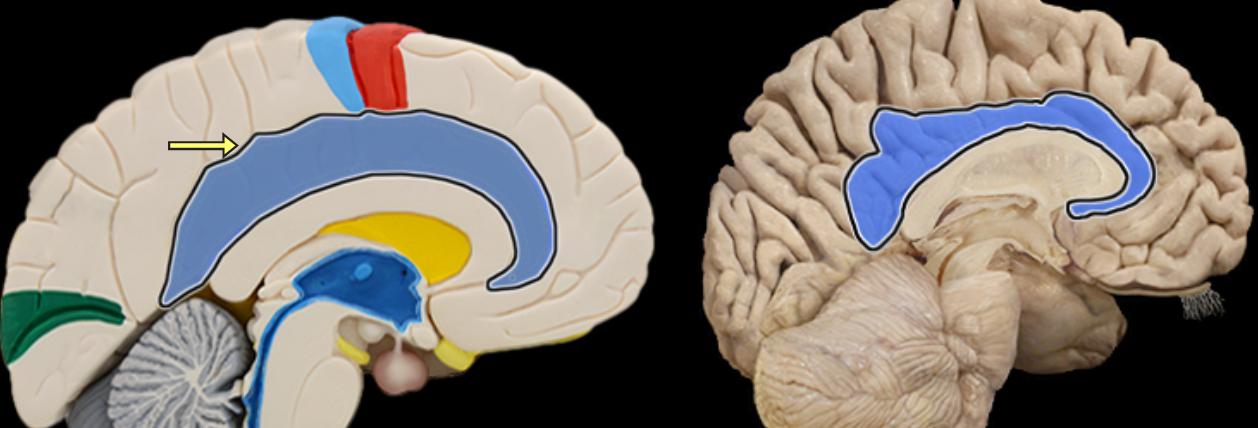
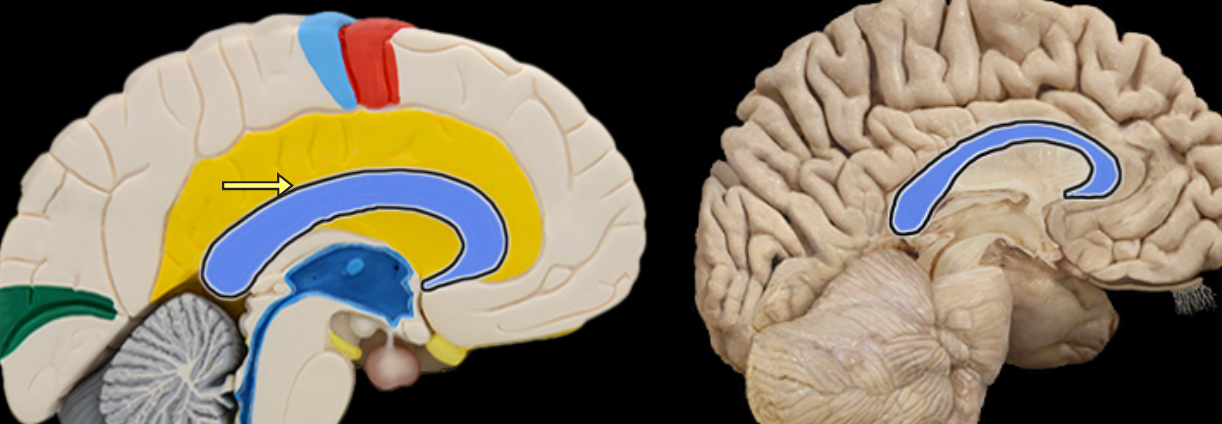
Cingulate gyrus
Location:
Cerebrum
Description:
Located superior to the corpus callosum in frontal and parietal lobes
Part of cerebellar cortex
One component of limbic system, which is important for emotion and learning
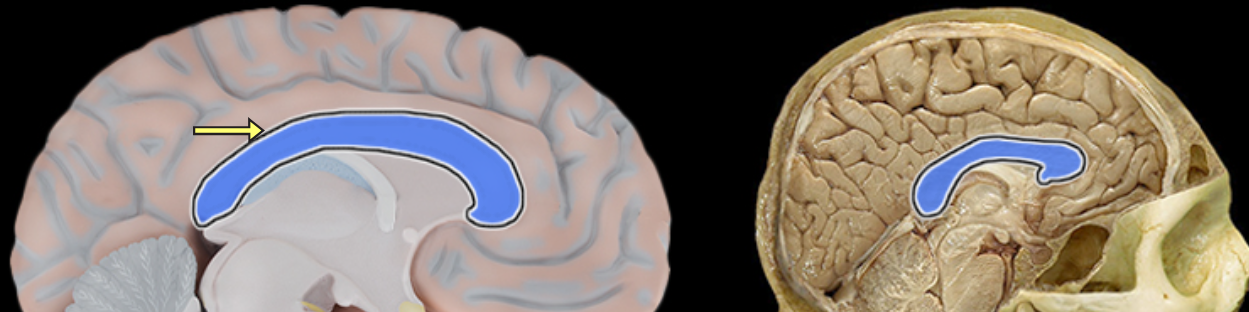
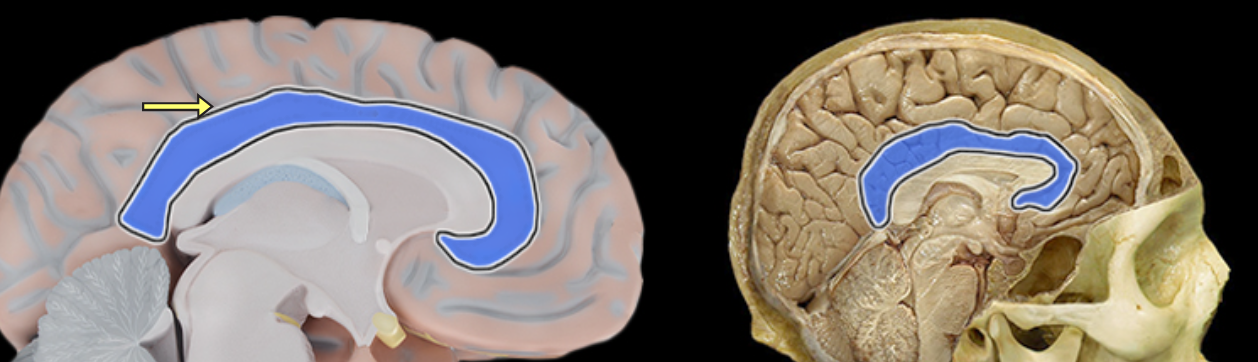
Corpus callosum
Location:
Brain, between cerebral hemispheres
Description:
Large myelinated fiber tract connecting right and left cerebral hemispheres
Forms floor of longitudinal fissure
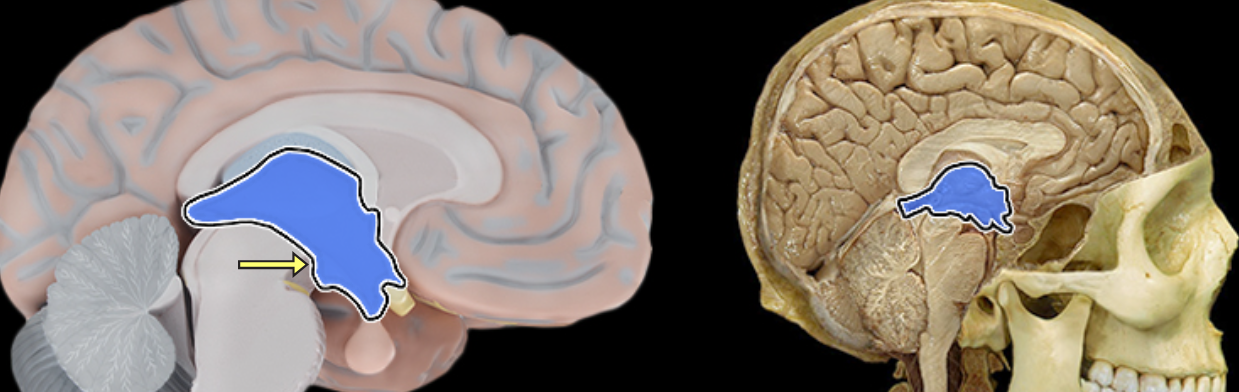
Diencephalon
Location:
Cerebrum
Description:
Composed of thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
Function:
Thalamic nuclei relay sensory information to cerebral cortex
Hypothalamic nuclei maintain homeostasis
Epithalamus includes pineal gland (produces melatonin)

Folia
Location:
Cerebellum
Description:
Folds of the cerebellum cortex
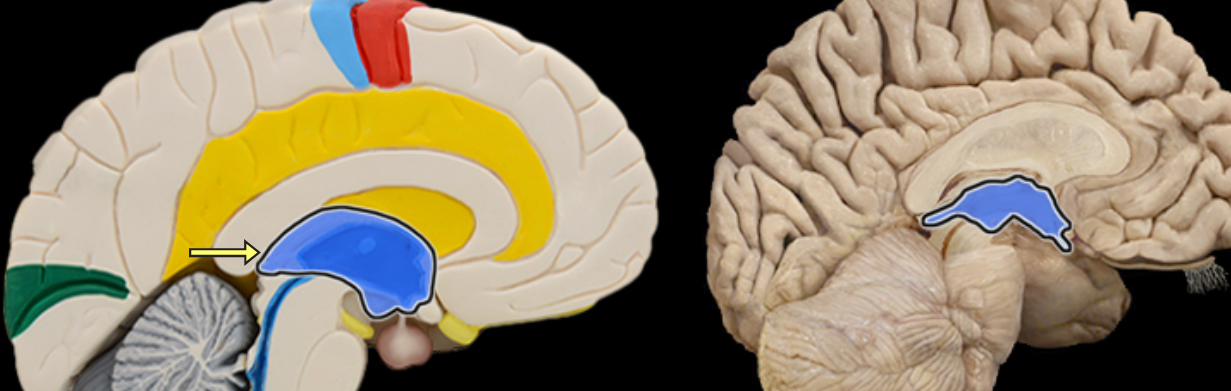
Fornix of brain
Location:
Brain
Suspended from corpus callosum and septum pellucidum
Description:
Arched fiber tract connecting hippocampus to mammillary bodies

Fourth ventricle
Location:
Between cerebellum and brainstem
Description:
Single, midline, pyramidal cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Has choroid plexus that produces CSF
Connected to third ventricle via cerebral aqueduct
Has three foramina that open into subarachnoid space
Continuous with central canal of spinal cord
Comment:
Cerebral ventricular system includes: (1) paired lateral ventricles; (2) interventricular foramena (Monro); (3) unpaired third ventricle; (4) cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius); and (5) unpaired fourth ventricle
Frontal lobe
Hypothalamus
Location:
Ventral diencephalon
Description:
Collection of nuclei located inferior to thalamus
Includes infundibulum and mammillary bodies
Function:
Considered master control center for endocrine system
Secretes releasing and inhibiting hormones that control anterior pituitary gland
Produces hormones that are transported to and stored in posterior pituitary gland
Controls autonomic nervous system
Regulates body temperature, food, and water intake
Regulates emotional behavior
Maintains sleep/wake cycle
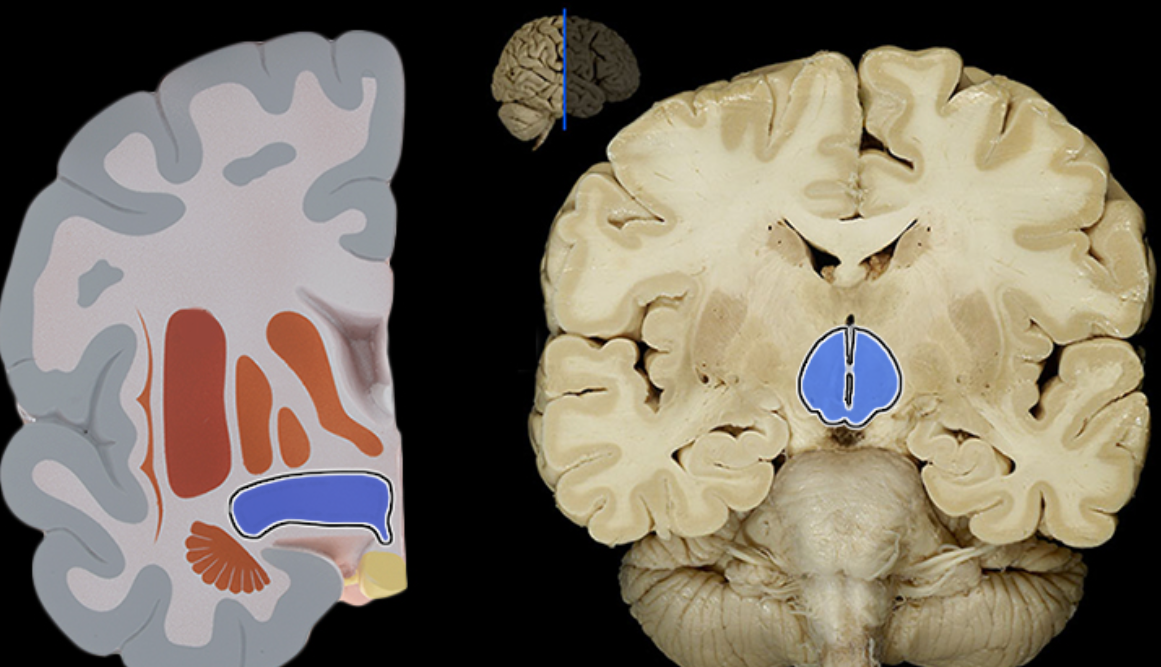
Inferior colliculus
Location:
Midbrain
Description:
Pair of rounded elevations on dorsal aspect of midbrain
Located caudal (posterior) to superior colliculus
Function:
Primary midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway
Important in hearing the origin of sound, understanding human speech, and the auditory reflex
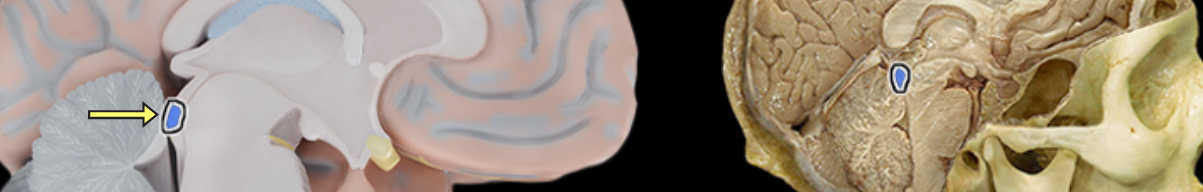
Infundibulum of pituitary gland
Location:
Ventral surface of diencephalon (hypothalamus) at midline
Description:
Contains hypothalamo-hypophysial tract
Contains hypothalamo-hypophysial portal vein that carries hypophysiotropic hormones to the anterior pituitary
Function:
Transmits antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin through hypothalamo-hypophysial tract to posterior pituitary
Comment:
Latin: infundibulum = a funnel
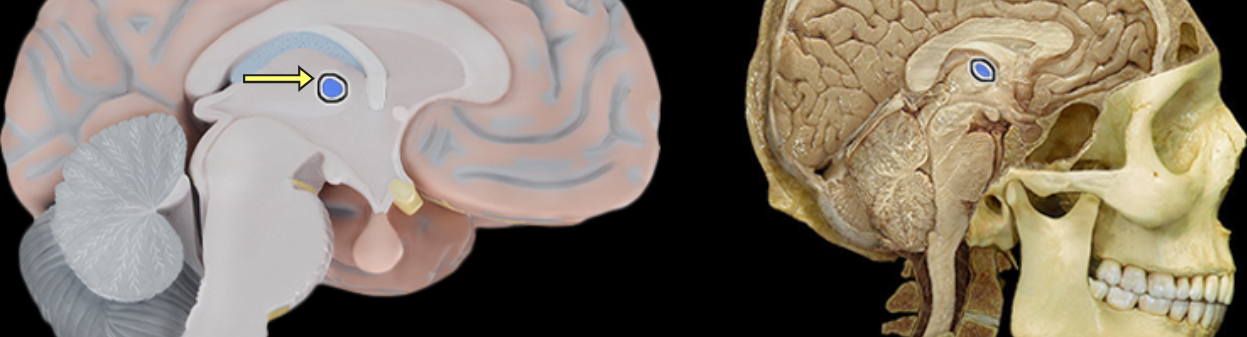
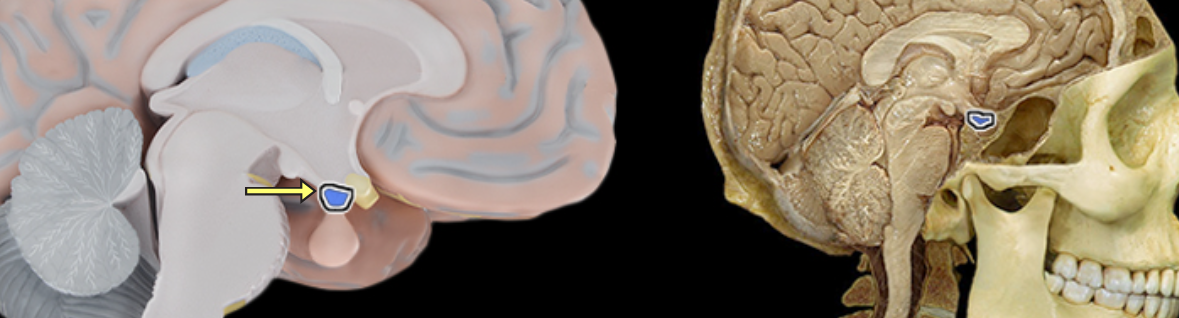
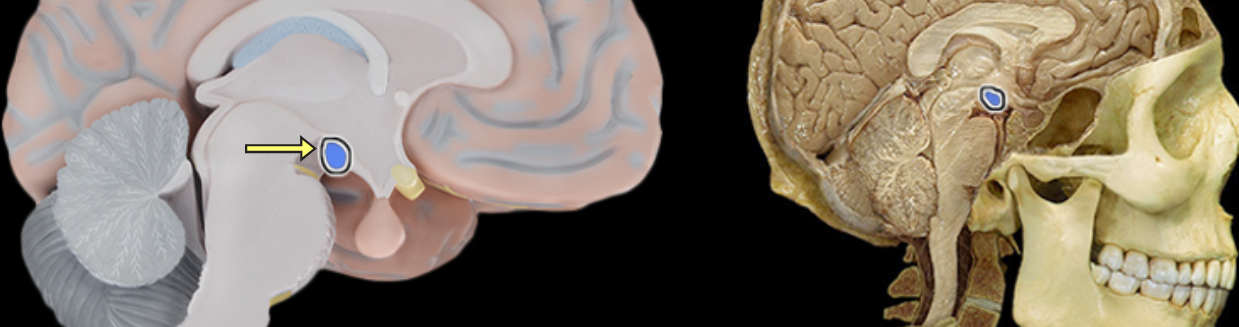
Interthalamic adhesion
Location:
Thalamus
Description
Small structure composed of flattened tissue that contents the two parts of thalamus at medial surface
Also known as middle commissure or intermediate mass
Mamillary body
Location:
Ventral surface of diencephalon (hypothalamus)
Description:
Paired, small, rounded projections
Site of hypothalamic-mammillary nuclear complex
Function:
Involved in regulation of autonomic functions, emotional behavior, and memory
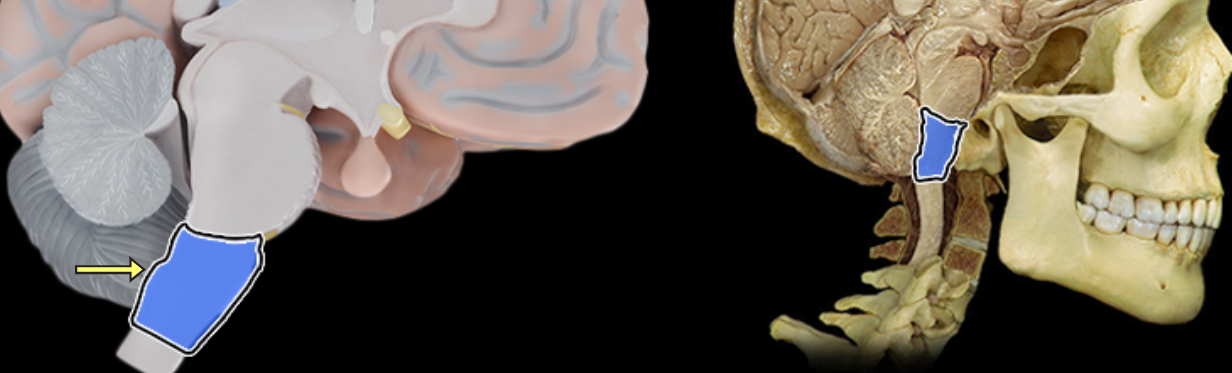
Medulla oblongata
Location:
Most caudal portion of brain
Description:
Extends from pons to spinal cord
Associated with cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII
Function:
Contains respiratory, cardiac, and vasomotor centers
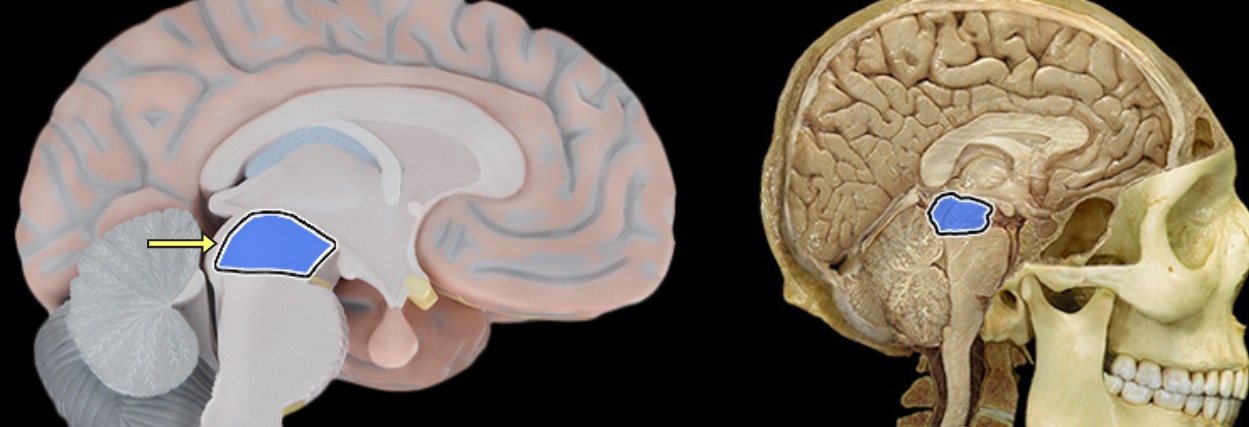
Mesencephalon
Location:
Brainstem
Between diencephalon and pons
Description:
Composed of white matter tracts and gray matter nuclei
Associated with cranial nerves III and IV
Prominent features include superior and inferior colliculi, cerebral peduncles, substantia nigra, and cerebral aqueduct
Function:
Coordinates movements in response to visual and auditory stimuli
Conveys motor information from cerebral cortex to pons
Conveys sensory information from spinal cord to thalamus
Also known as:
Also known as mesencephalon
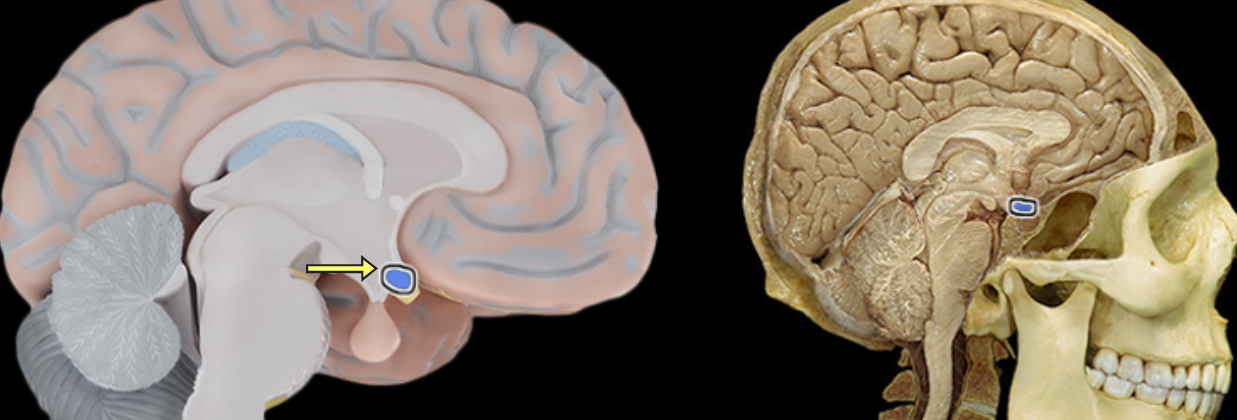
Optic chiasm
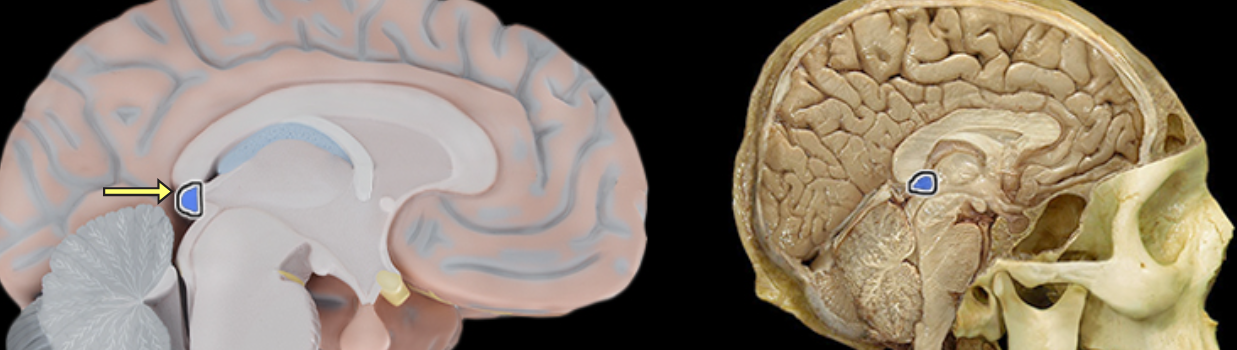
Pineal gland
Location:
Diencephalon (epithalamus)
Description:
Pea-sized endocrine gland
Attached to roof of third ventricle
Function:
Secretes melatonin (involved in sleep/wake cycles)
Modified activity in endocrine organs (pituitary, pancreas, parathyroid, suprarenal, and gonads)
Also known as:
Pineal body
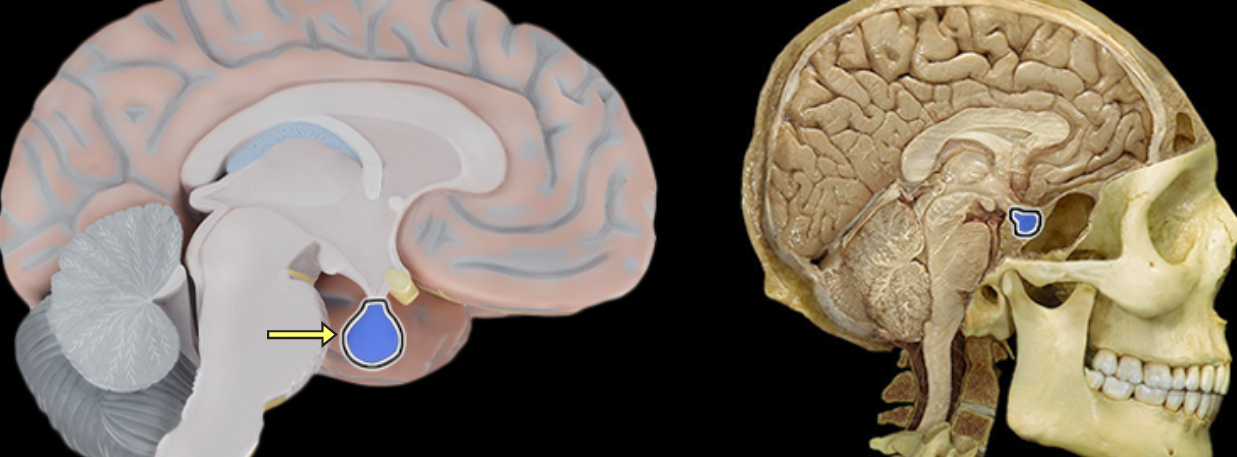
Pituitary gland
Location:
Midline of middle cranial fossa
Rests in hypophysial fossa of sphenoid bone
Description:
Small, oval bilobed endocrine gland
Two functional lobes: anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis)
Connected by infundibulum to hypothalamus
Function:
Anterior pituitary produces the following hormones: thyroid-stimulating (TSH), prolactin (PRL), adrenocorticotropic (ACTH), growth (GH), luteinizing (LH), melanocyte-stimulating (MSH), and follicle-stimulating (FSH)
Posterior pituitary stores and releases: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT)
Also known as:
Hypophysial gland or hypophysis
Comment:
Posterior pituitary does not produce any hormones; ADH and OT produced in hypothalamus
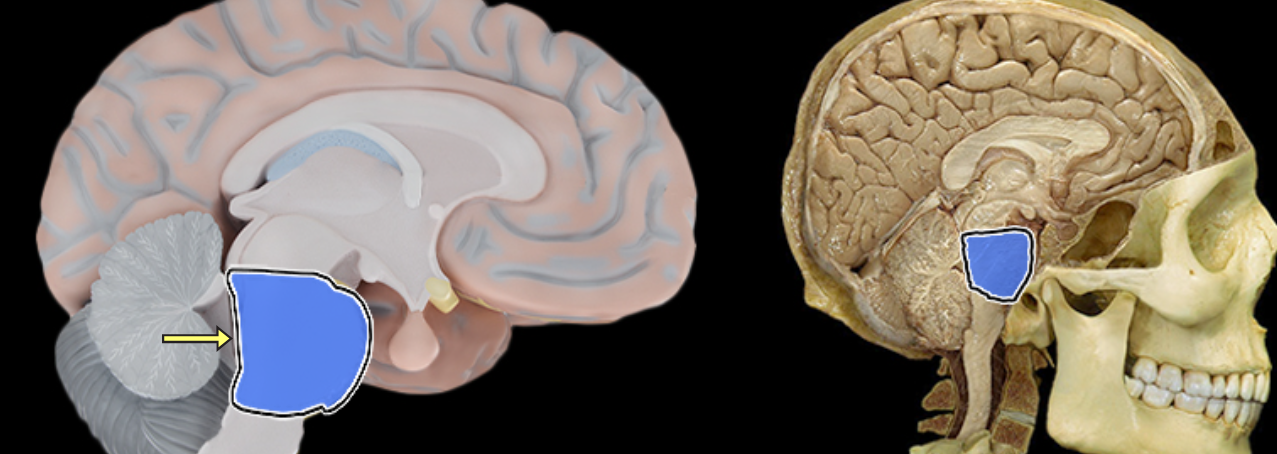
Pons
Location:
Ventral aspect of brainstem
Between midbrain (rostral) and medulla oblongata (caudal)
Description:
Characterized by distinct ventral "bulge"
Attached to cerebellum by middle cerebral peduncle
Associated with cranial nerves V, VI, VII, and VIII
Function:
Involved in control of sleep and respiration
Transfer of information to and between cerebellar hemispheres
Comment:
Latin: pons = bridge
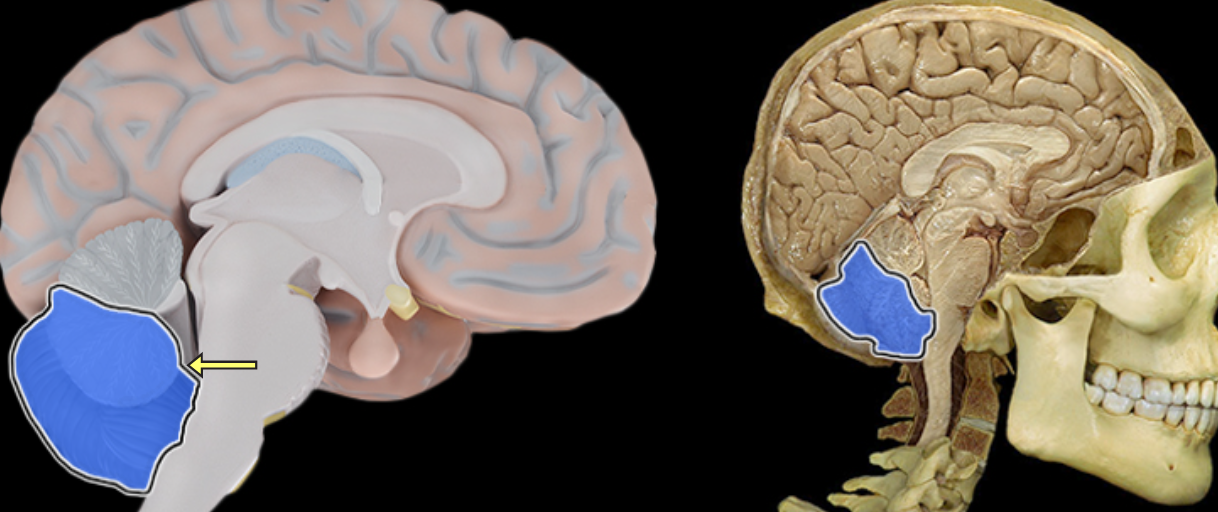
Posterior lobe of cerebellum
Location:
Cerebellum
Description:
The most posterior lobe of the cerebellar hemisphere
There is a right and left hemisphere of the cerebellum
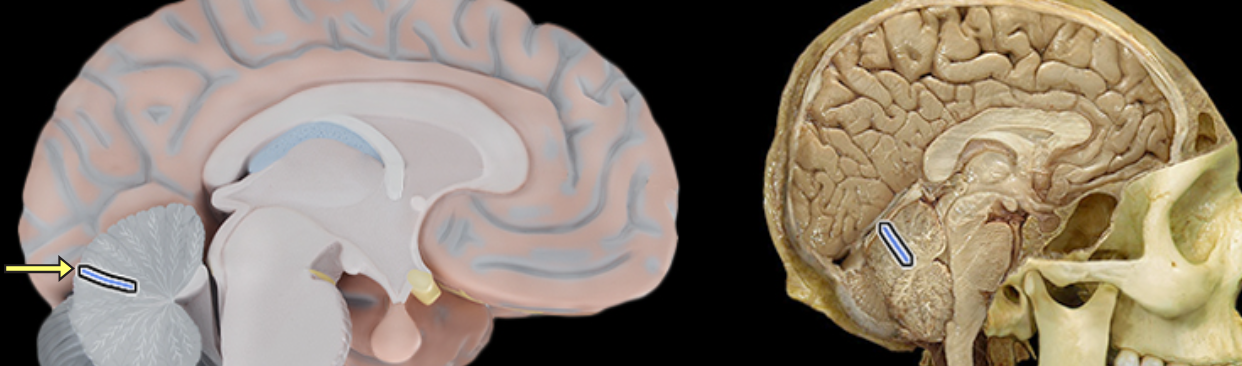
Primary fissure of cerebellum
Location:
Cerebellum
Description:
The fissure that separates the anterior lobe of the cerebellum from posterior lobe of cerebellum in each hemisphere
There is a right and left hemisphere of the cerebellum
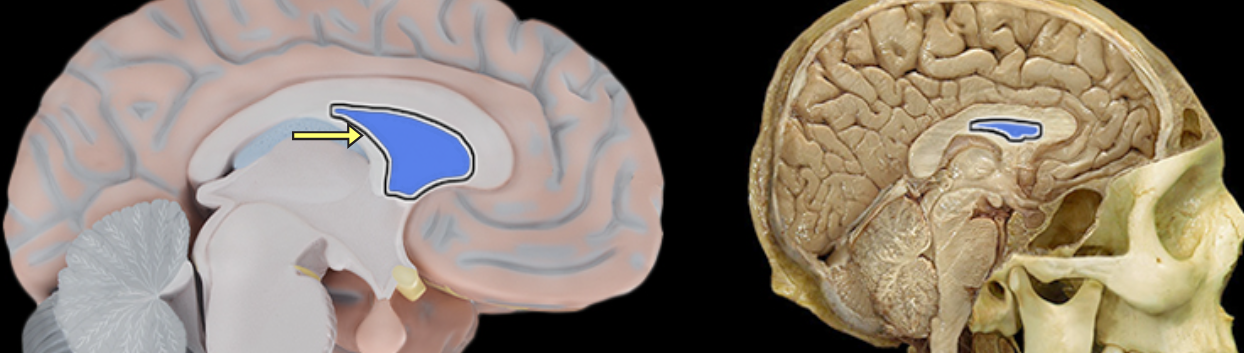
Septum pellucidum
Location:
Suspended between lateral ventricles
Perpendicular to corpus callosum
Description:
Thin sheet of non-neuronal tissue separating right and left lateral ventricles
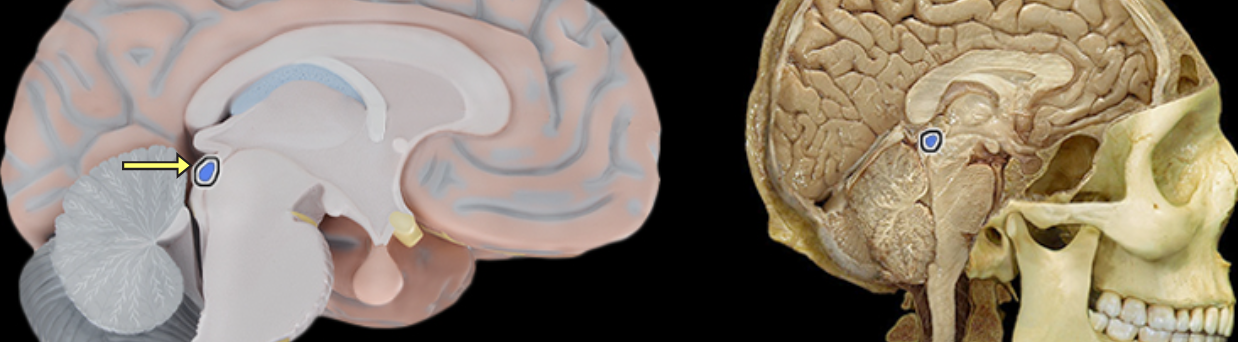
Superior colliculus
Location:
Midbrain
Description:
Pair of rounded elevations on dorsal aspect of midbrain
Function:
Coordinates orienting movements of eyes and head
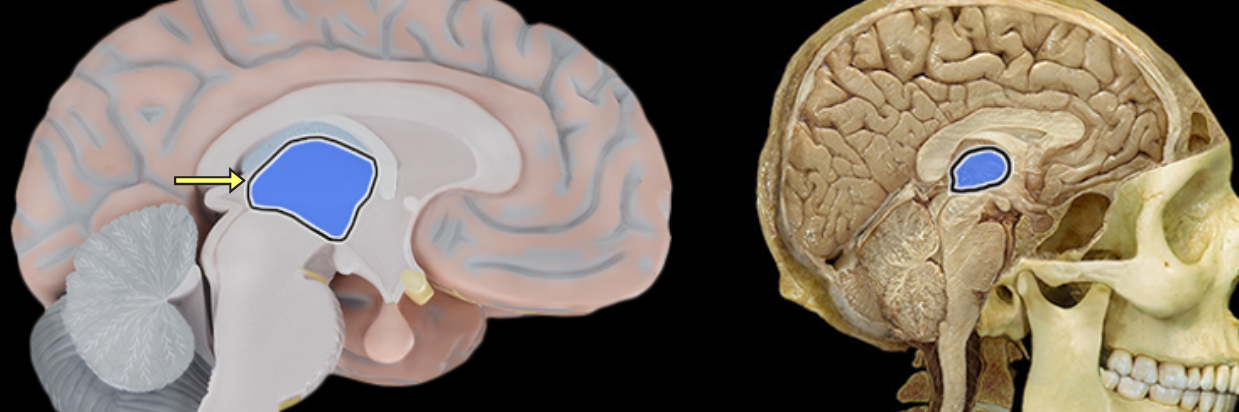
Thalamus
Location:
Diencephalon
Description:
Paired groups of nuclei separated by third ventricle
Largest portion of the diencephalon
Composed primarily of gray matter
Function:
Primarily for relay of sensory information to cortex
Relay of motor information for movement planning
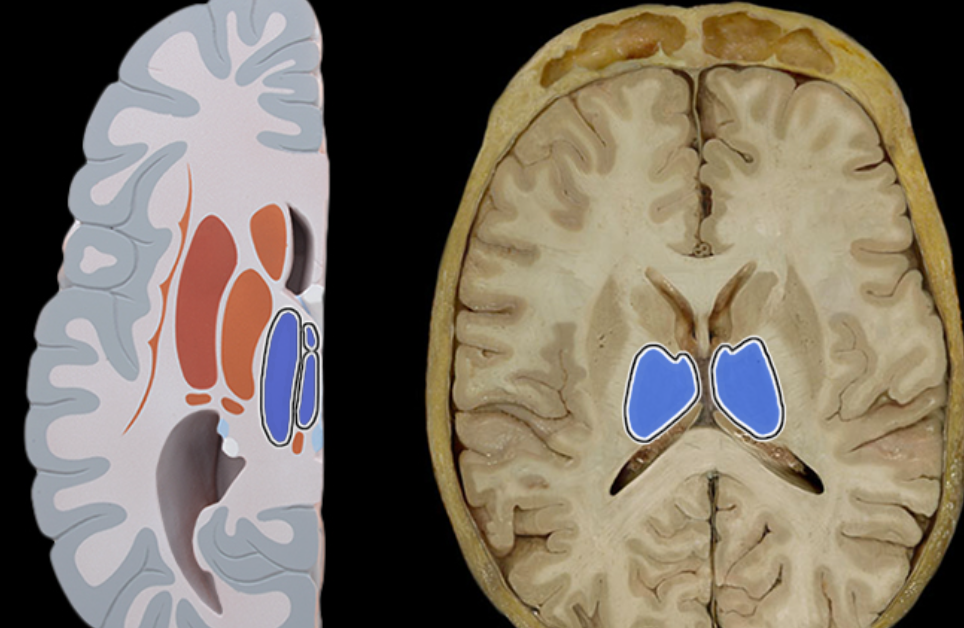
Third ventricle
Location:
Diencephalon
Description:
Single, midline cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Has choroid plexus that produces CSF
Connected to lateral ventricles via interventricular foramena
Connected to fourth ventricle via cerebral aqueduct
Comment:
Cerebral ventricular system includes: (1) paired lateral ventricles; (2) interventricular foramena (Monro); (3) unpaired third ventricle; (4) cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius); and (5) unpaired fourth ventricle
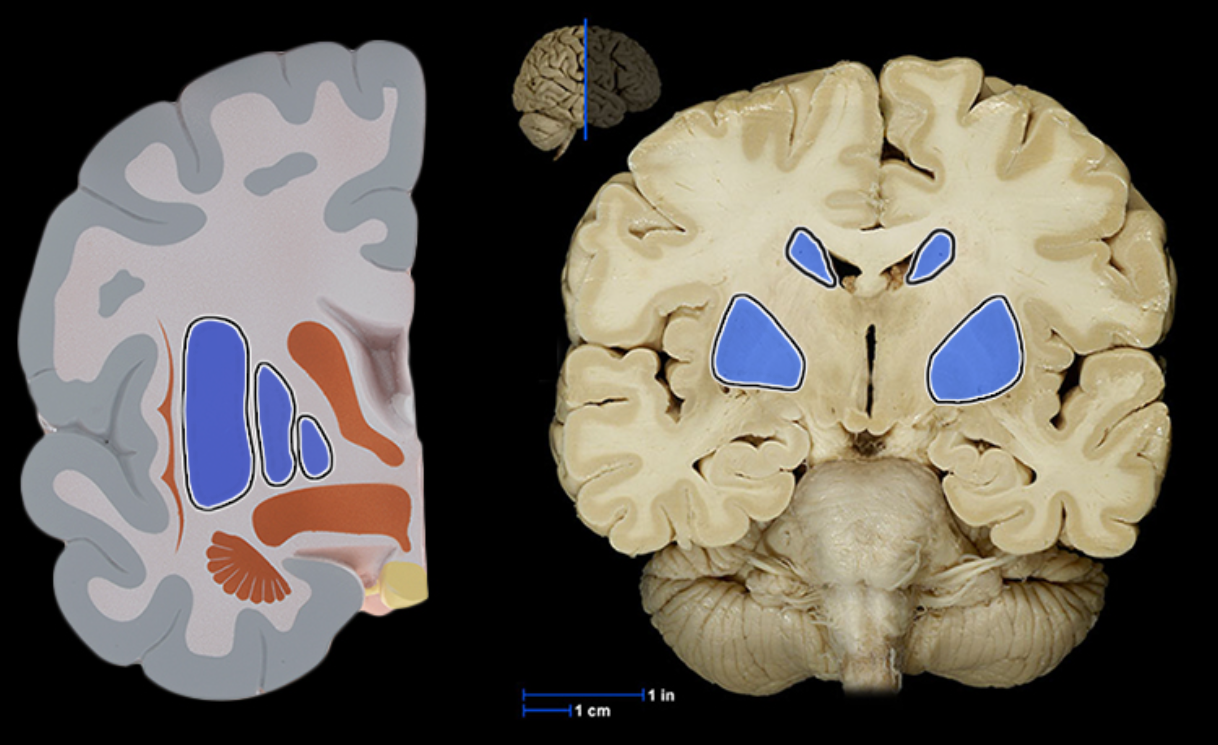
Basal ganglia
Location:
Cerebrum
Description:
Paired masses of gray matter located deep in each cerebral hemisphere
Composed of corpus striatum (caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus), amygdaloid body, and claustrum
Function:
Planning and execution of movement
Controls highly practiced and subconscious movements
Muscle tone and posture
Also known as:
Basal ganglia
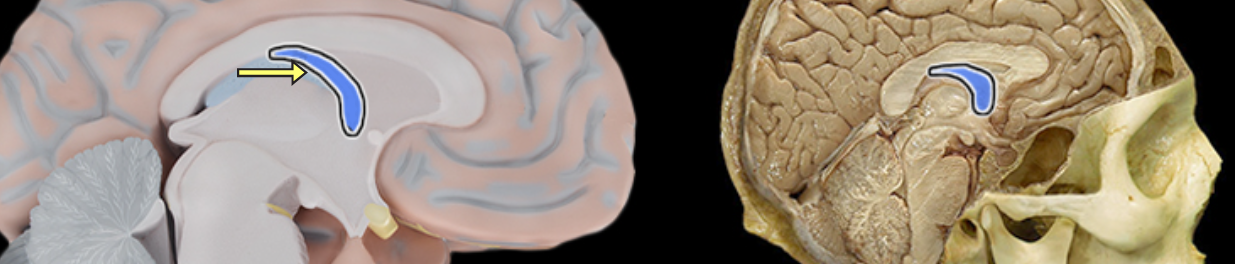
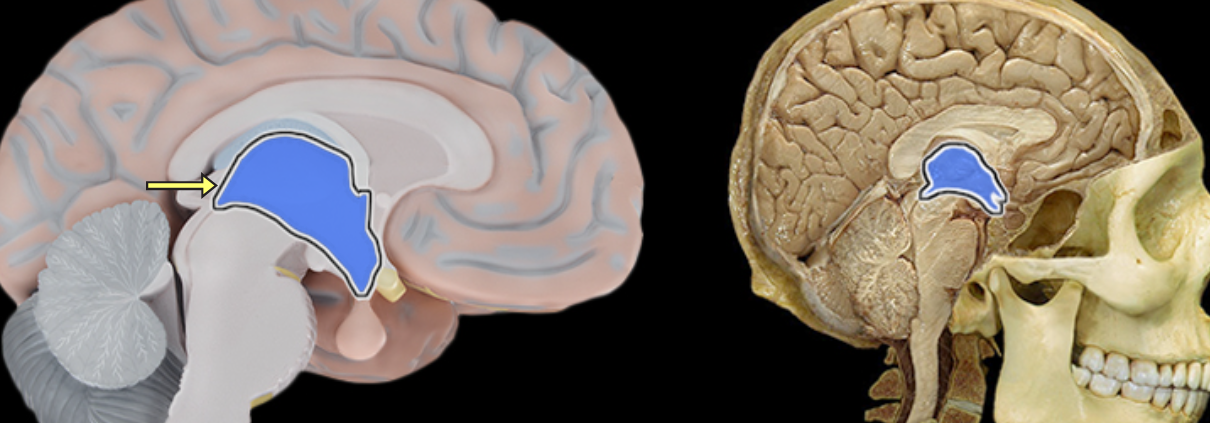
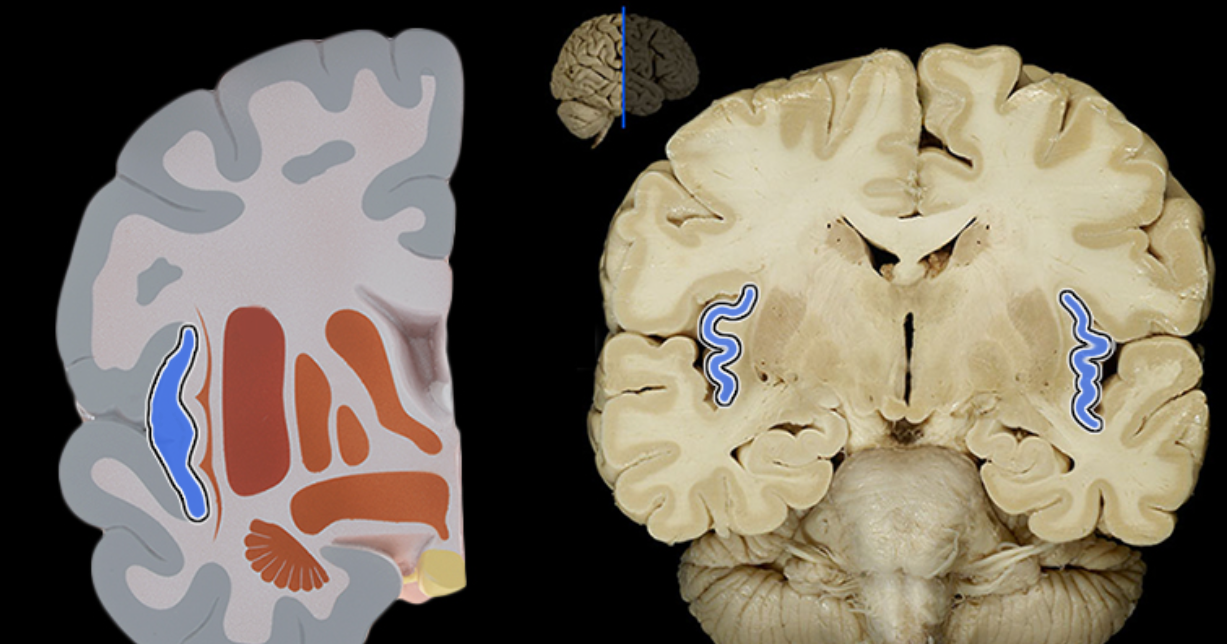
Fornix of brain
Location:
Brain
Suspended from corpus callosum and septum pellucidum
Description:
Arched fiber tract connecting hippocampus to mammillary bodies
Insular lobe
Location:
Deep in each lateral sulcus
Description:
Cerebral lobe
Not visible from surface
Function:
Understanding spoken language
Perception of taste and smell
Integrates information from visceral receptors
Also known as:
Insula or isle of Reil
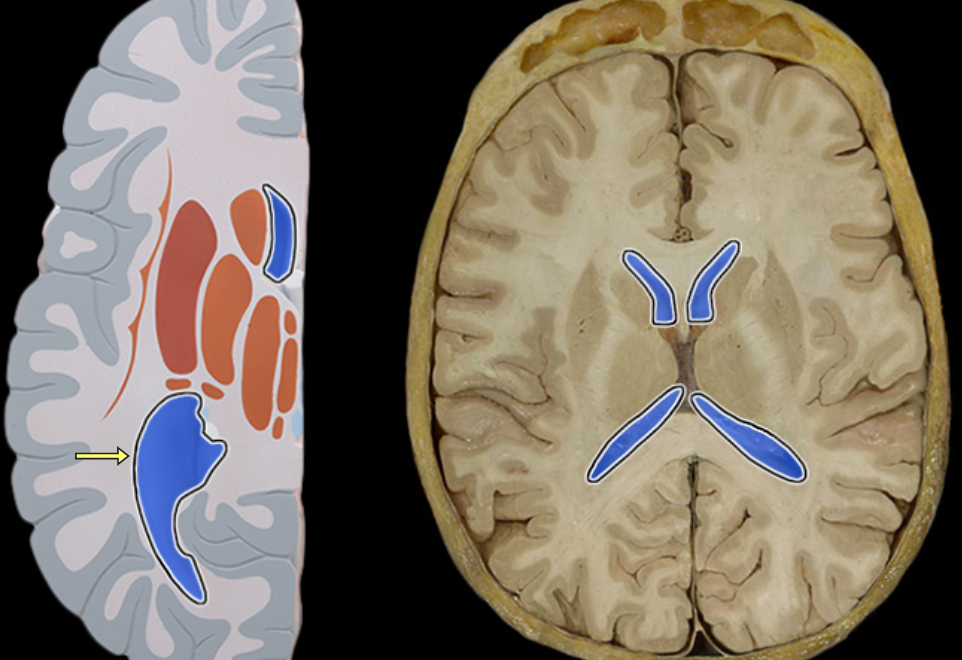
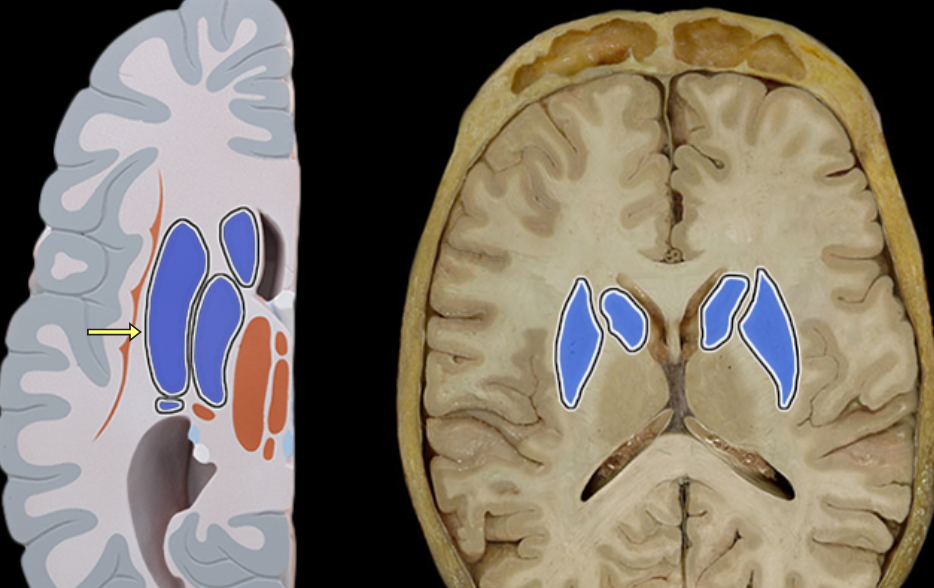
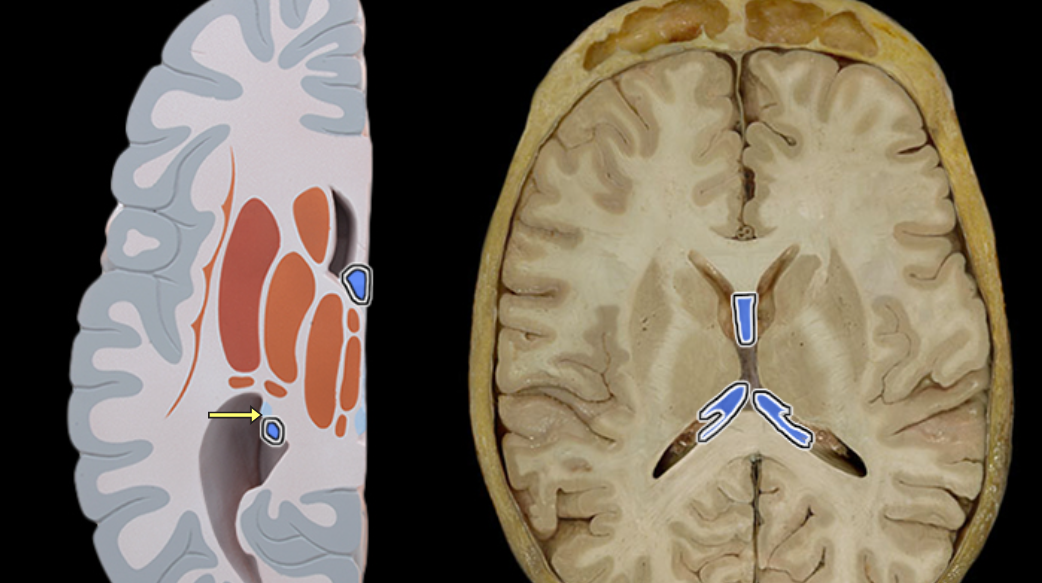
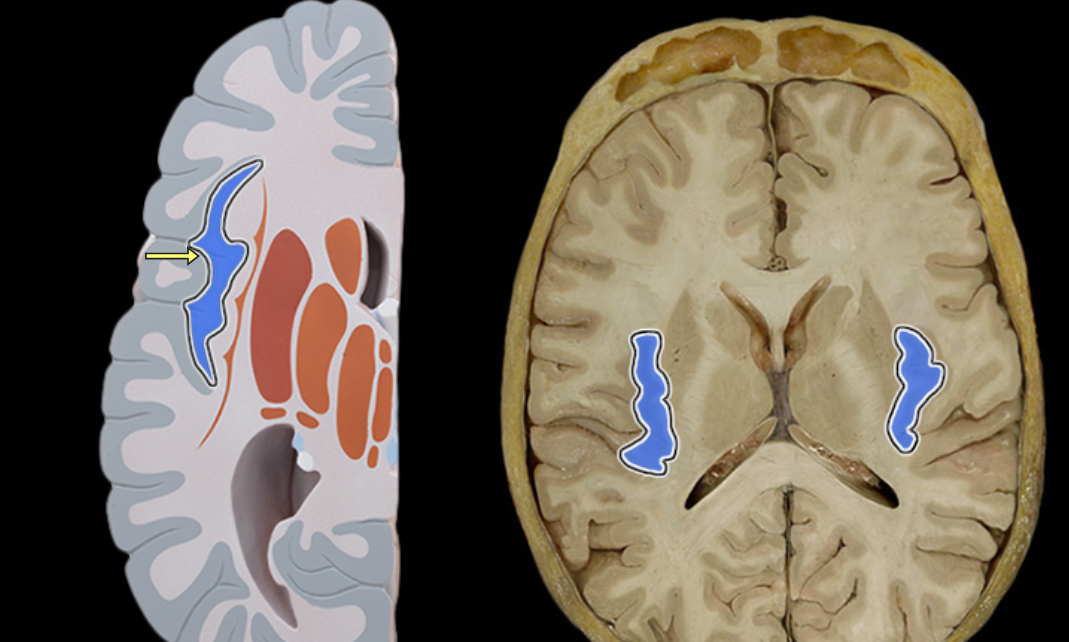
Lateral ventricle
Location:
Deep within cerebral hemisphere
Description:
Paired cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Has anterior, posterior, and inferior extensions (horns)
Has choroid plexus that produces CSF
Connected to third ventricle via interventricular foramen
Comment:
Cerebral ventricular system includes: (1) paired lateral ventricles; (2) interventricular foramina (Monro); (3) unpaired third ventricle; (4) cerebral aqueduct (Sylvius); and (5) unpaired fourth ventricle
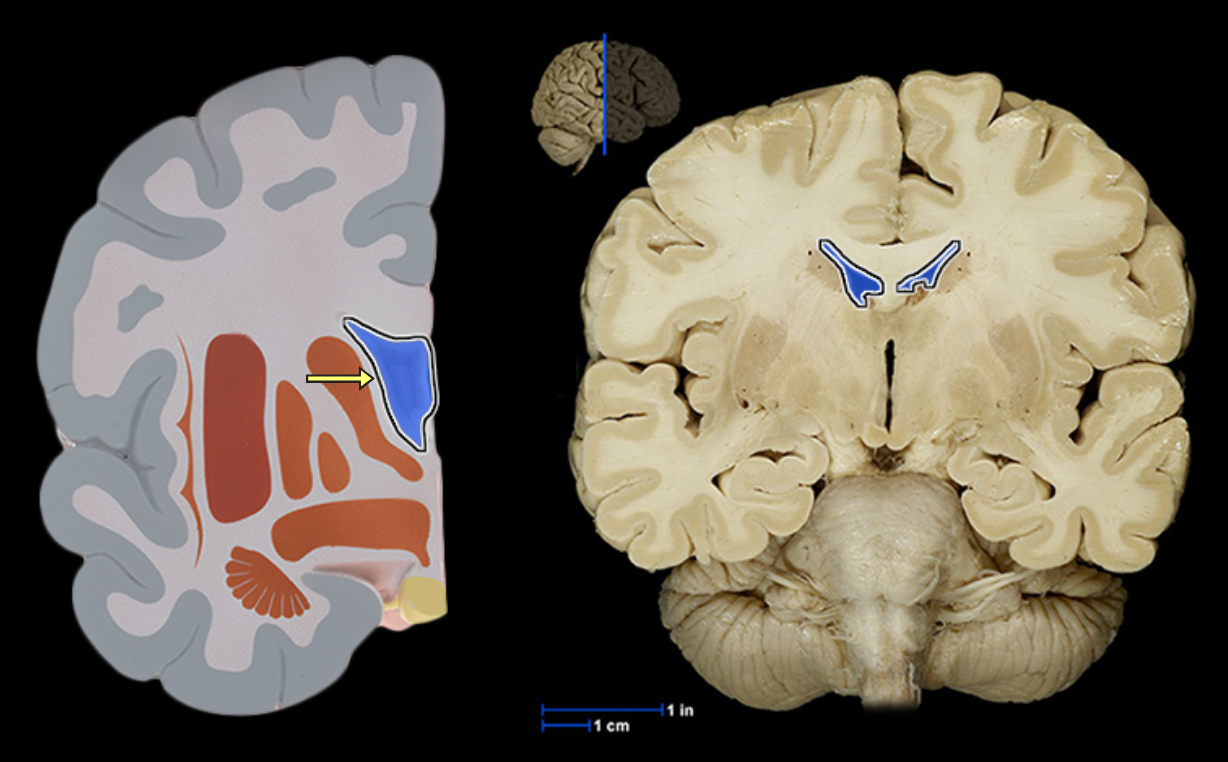
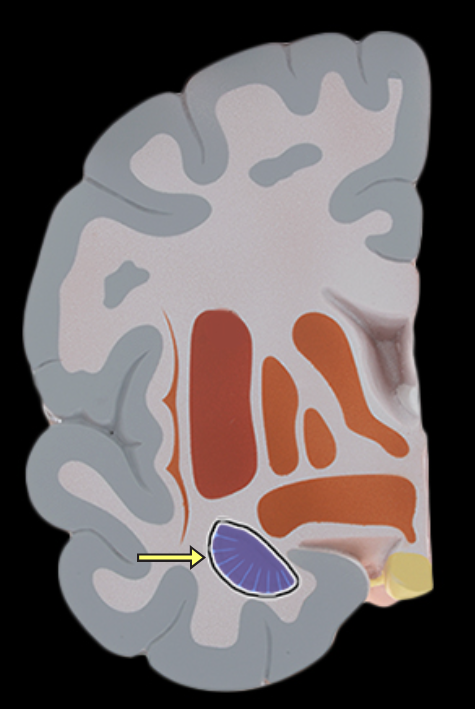
Amygdala
Location:
Cerebral hemisphere
Expanded region at tail of caudate nucleus
Description:
Collection of gray matter deep inside each cerebral hemisphere
Part of basal nuclei
Function:
Involved in expression of emotions, especially fear
Involved in formation of memories related to emotional events
Part of the limbic system
Comment:
Also called amygdaloid body
Basal nuclei also called basal ganglia
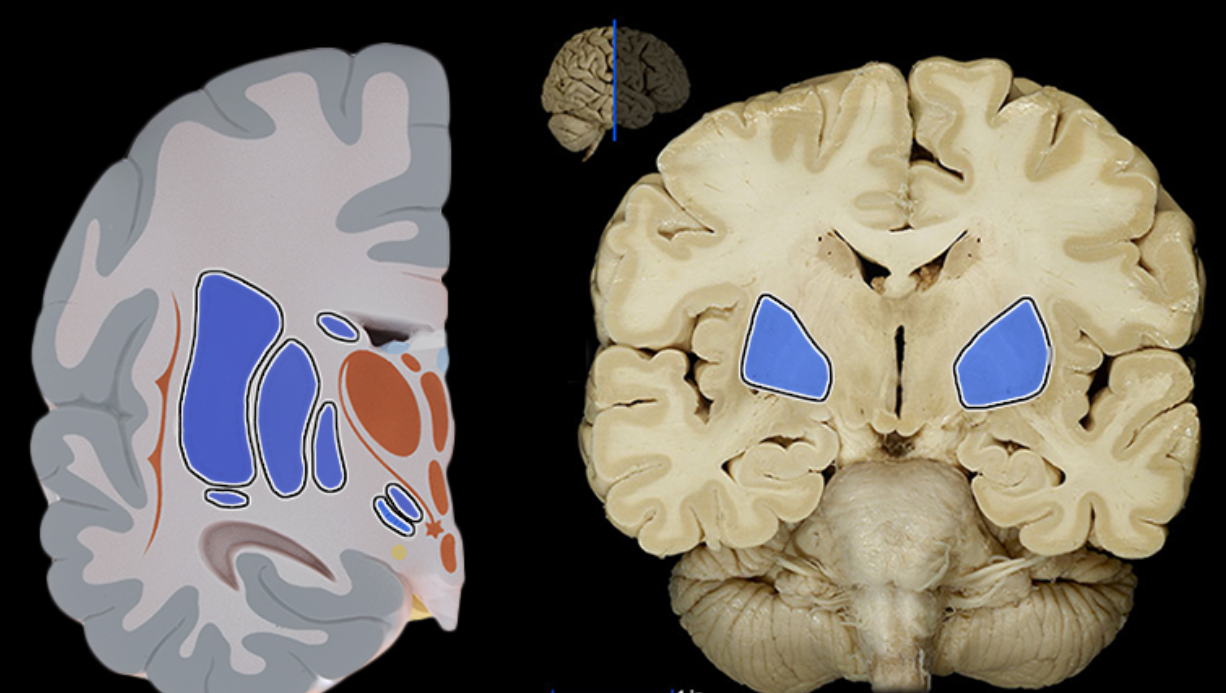
Basal ganglia
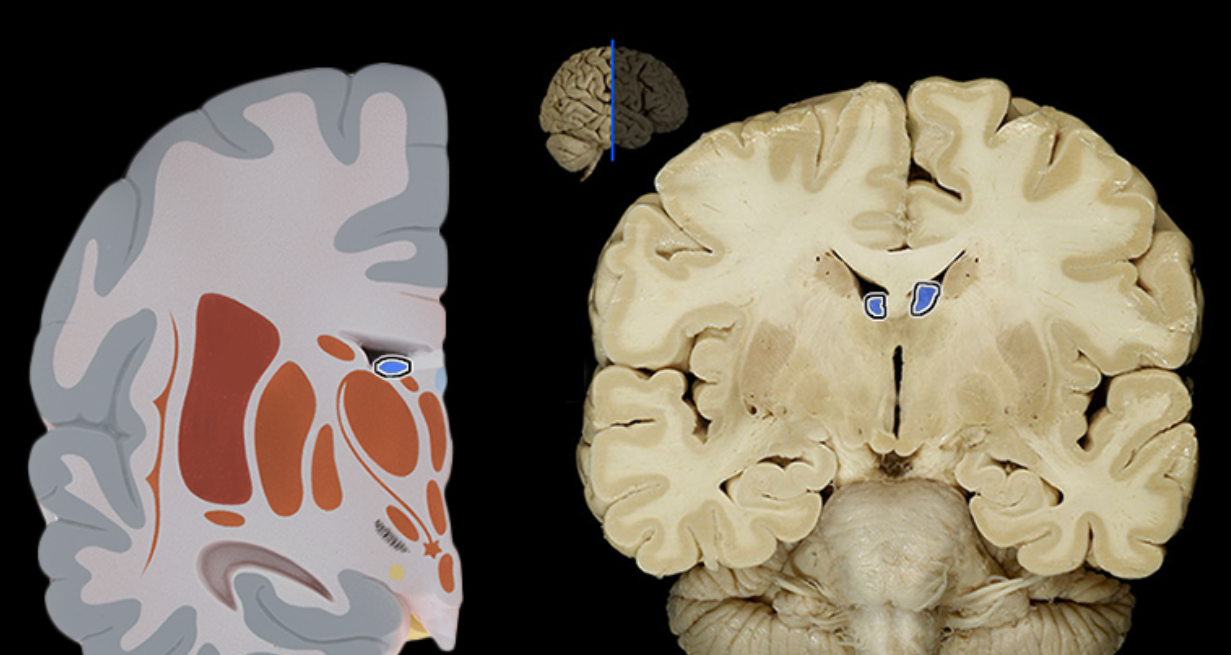
Choroid plexus
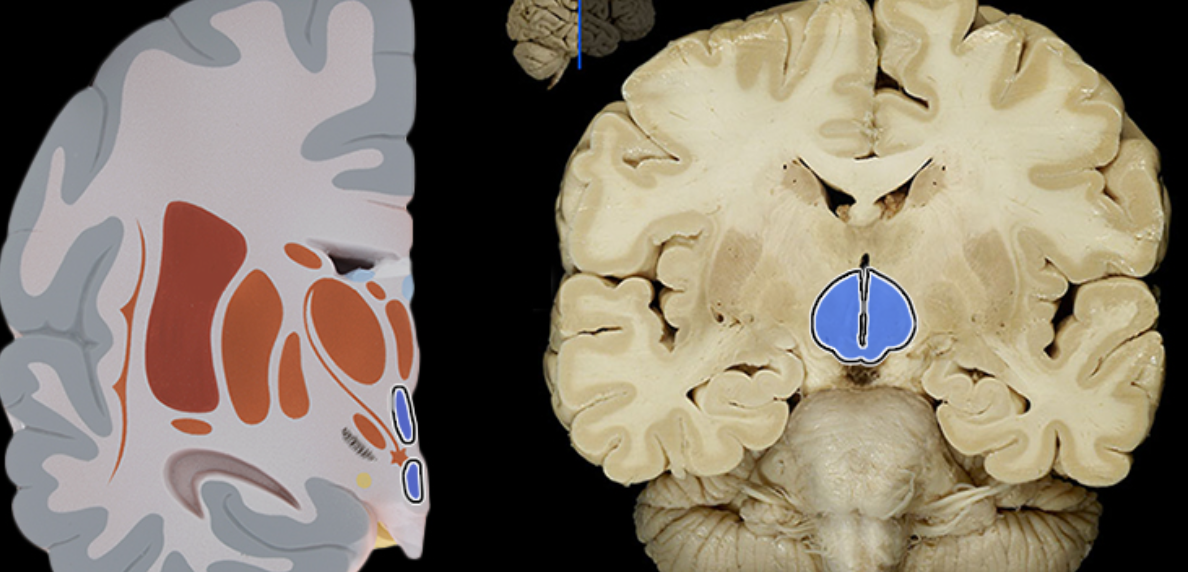
Hypothalamus
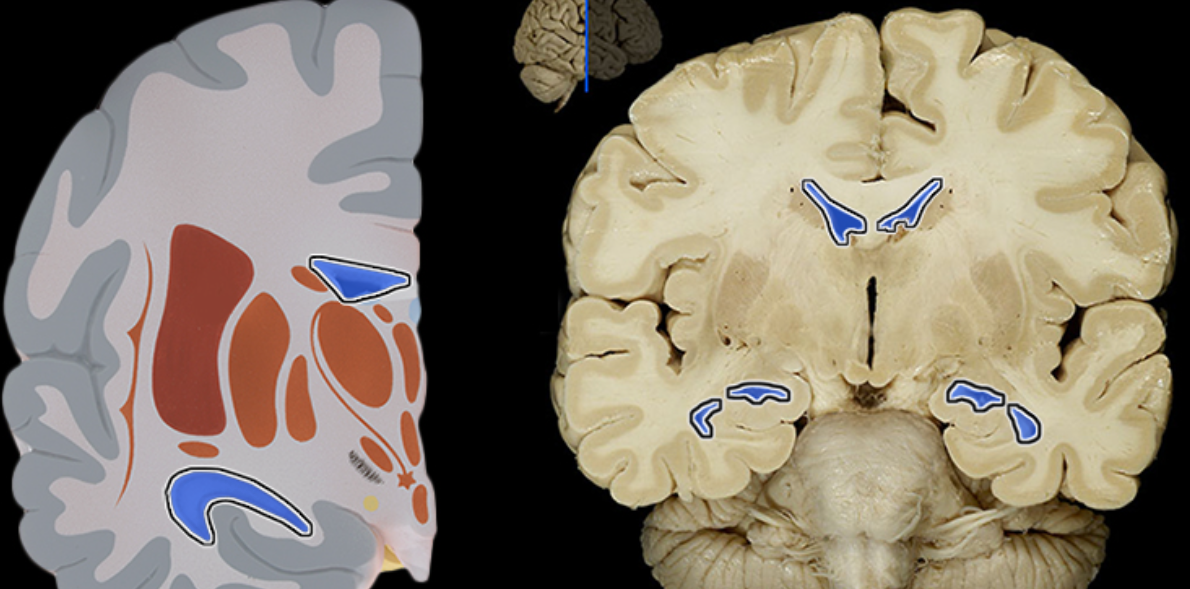
Lateral ventricle
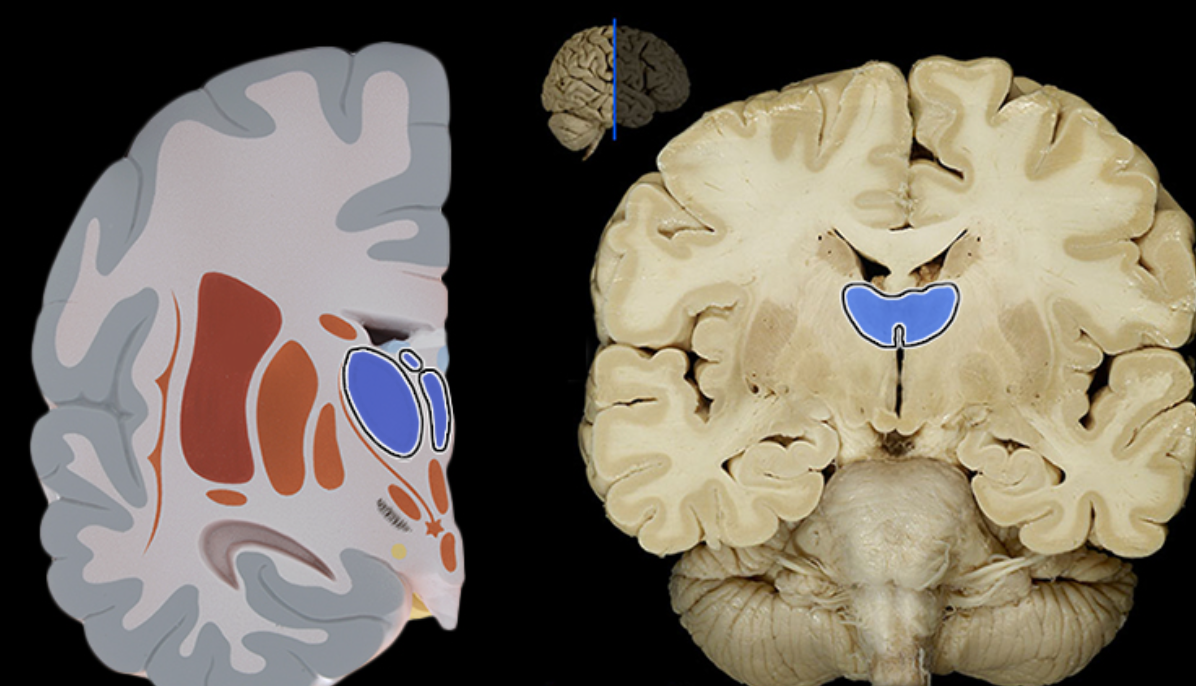
Thalamus
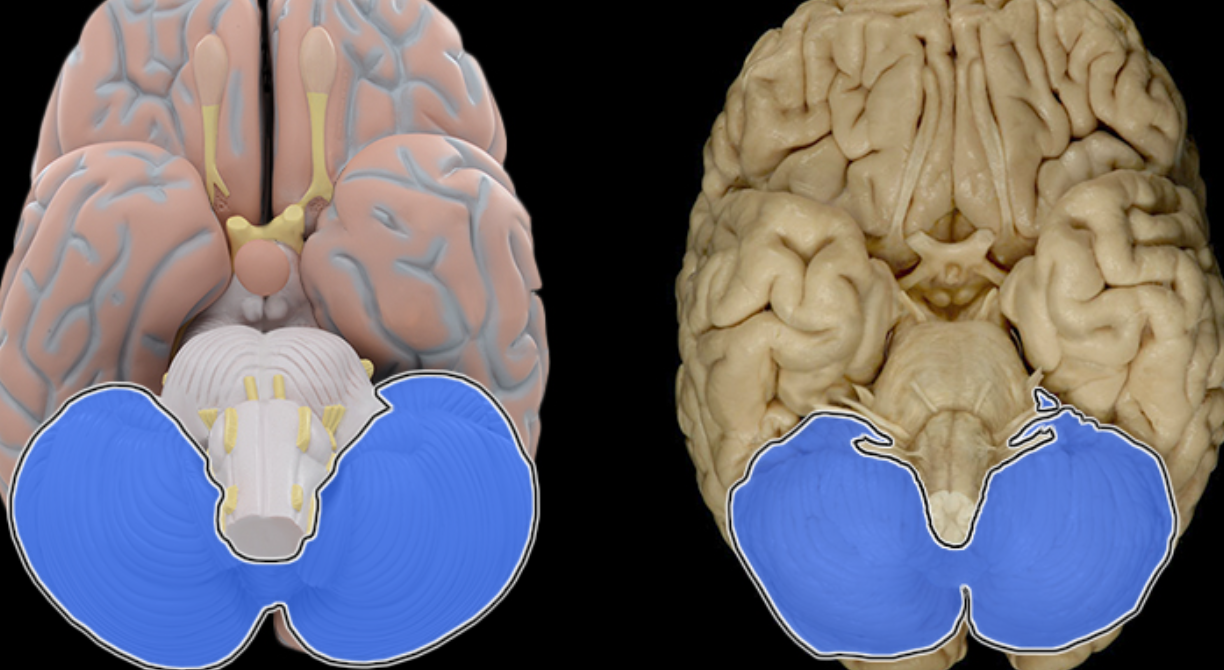
Cerebellum
Cerebrum
Glossopharyngeal
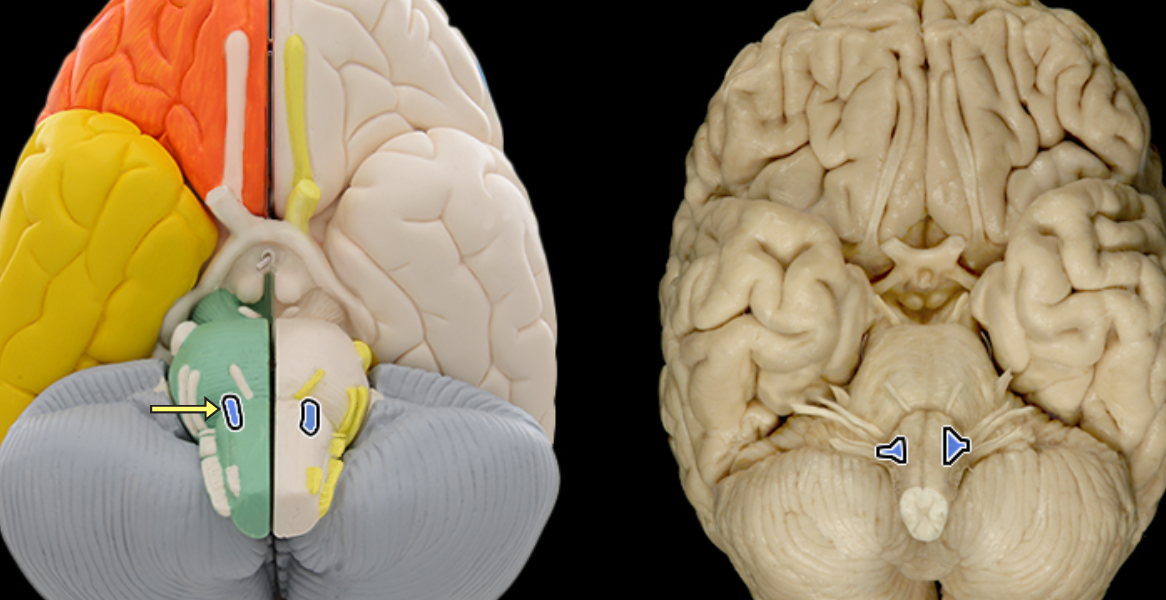
Hypoglossal
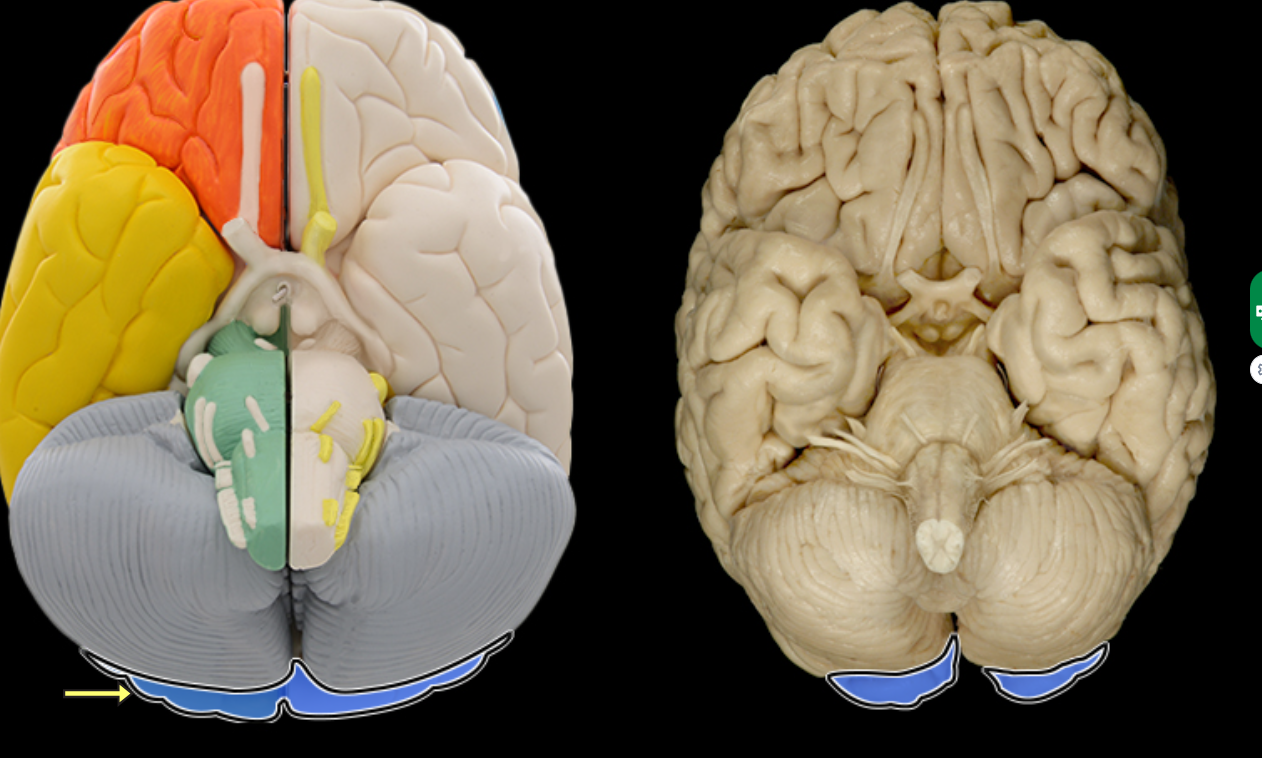
Occipital lobe
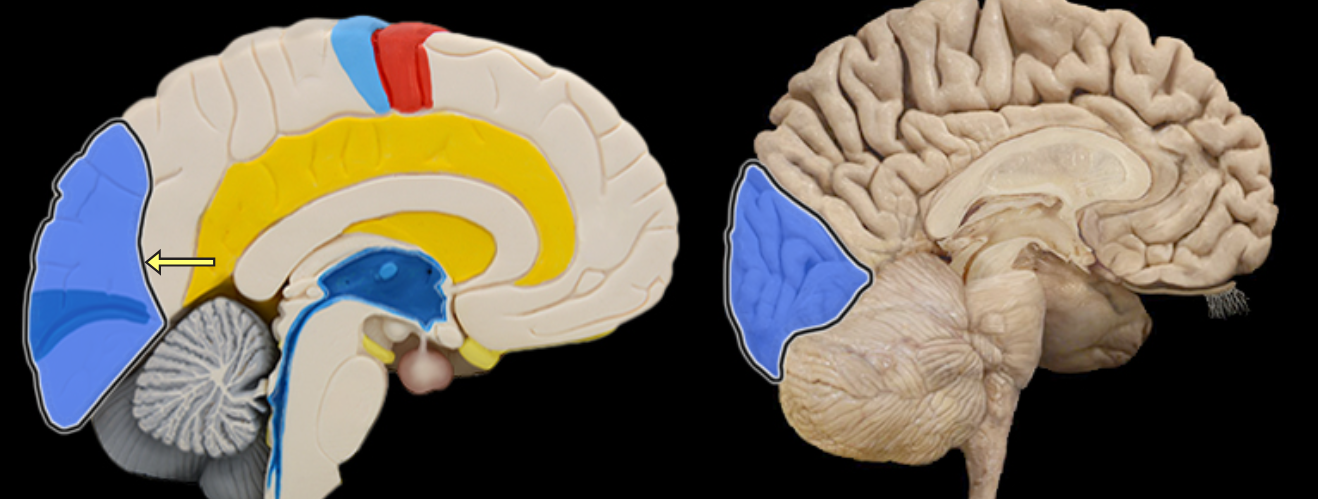
Oculomotor
Location:
Middle cranial fossa
Orbit
Composition:
Motor
Parasympathetic
Motor:
Medial rectus muscle
Superior rectus muscle
Inferior rectus muscle
Inferior oblique muscle
Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
Parasympathetic:
Pupillary sphincter muscle (constriction of pupil)
Ciliary muscle (permits lens to thicken for accommodation)
CNS connection:
Midbrain (oculomotor and accessory oculomotor nuclei)
Cranial foramina:
Superior orbital fissure
Comment:
Rectus and oblique muscles are extrinsic eye (extra-ocular) muscles
Postganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies located in ciliary ganglion in the orbit
Oculomotor nerve also known as CN III
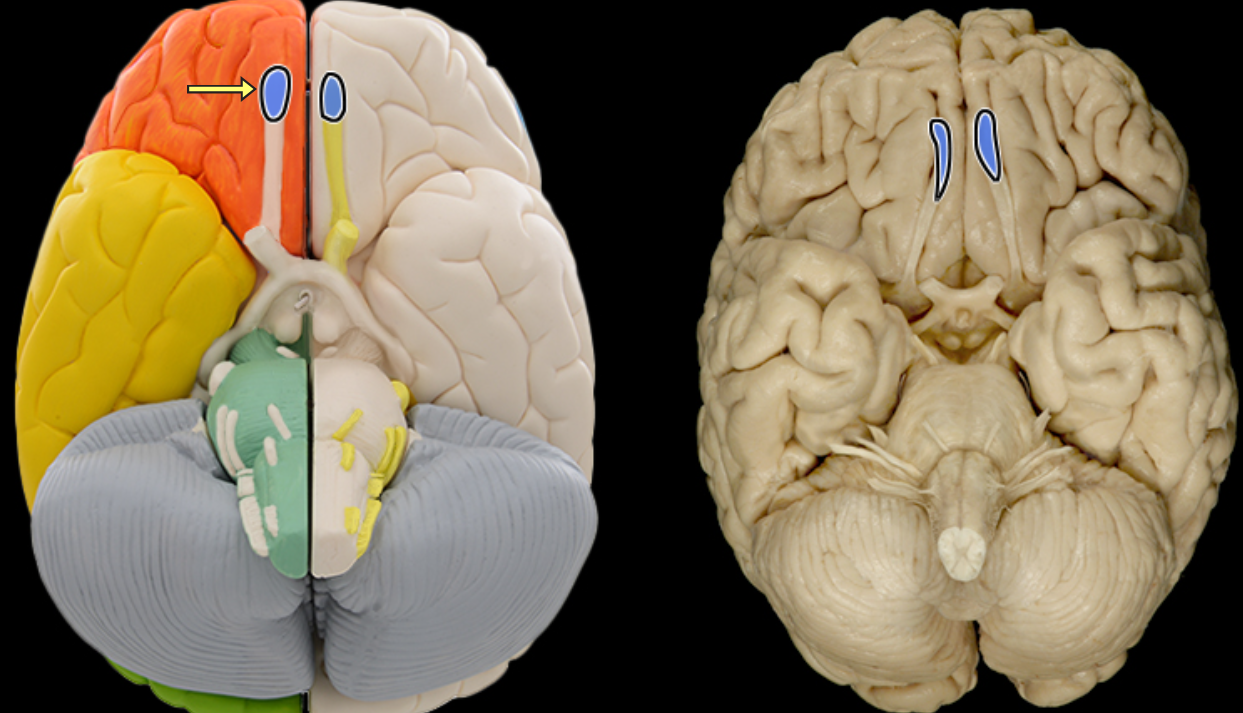
Olfactory bulb
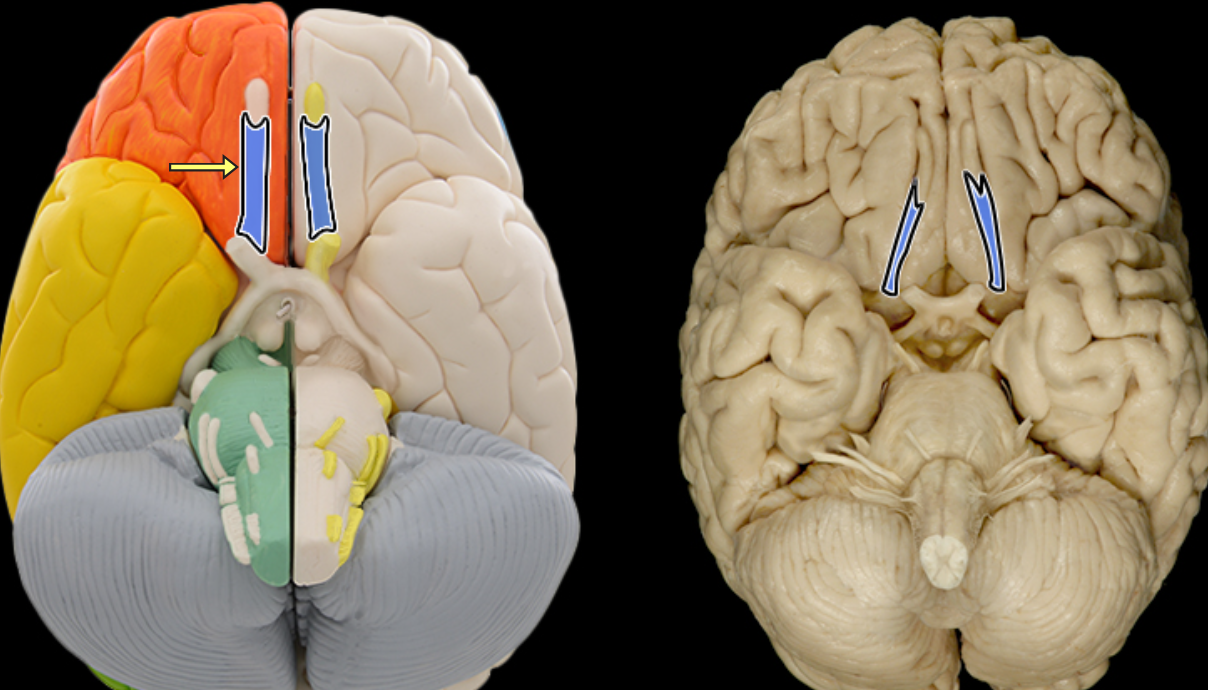
Olfactory tract
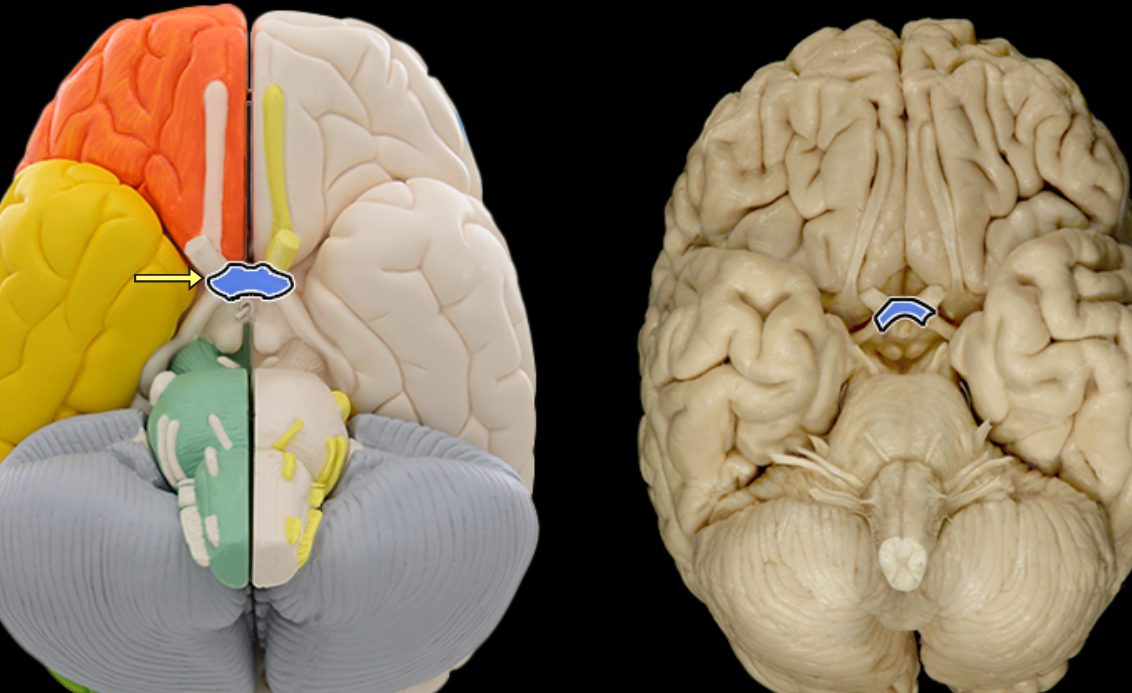
Optic chiasm
Optic n. CN II
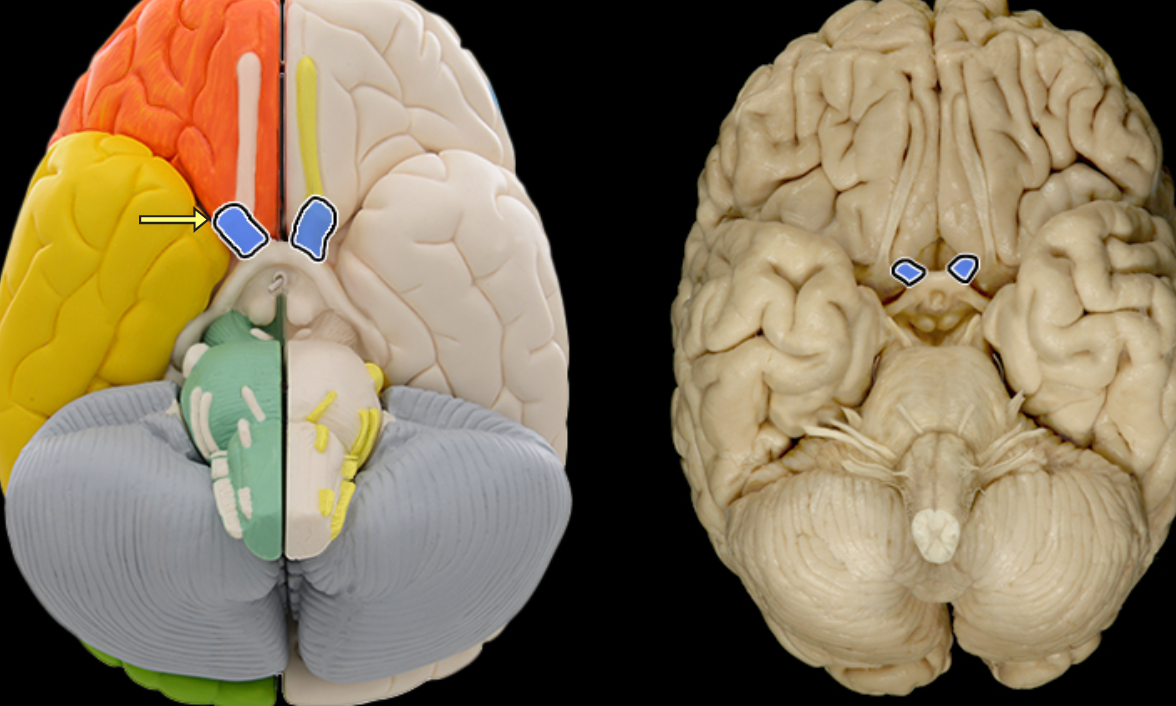
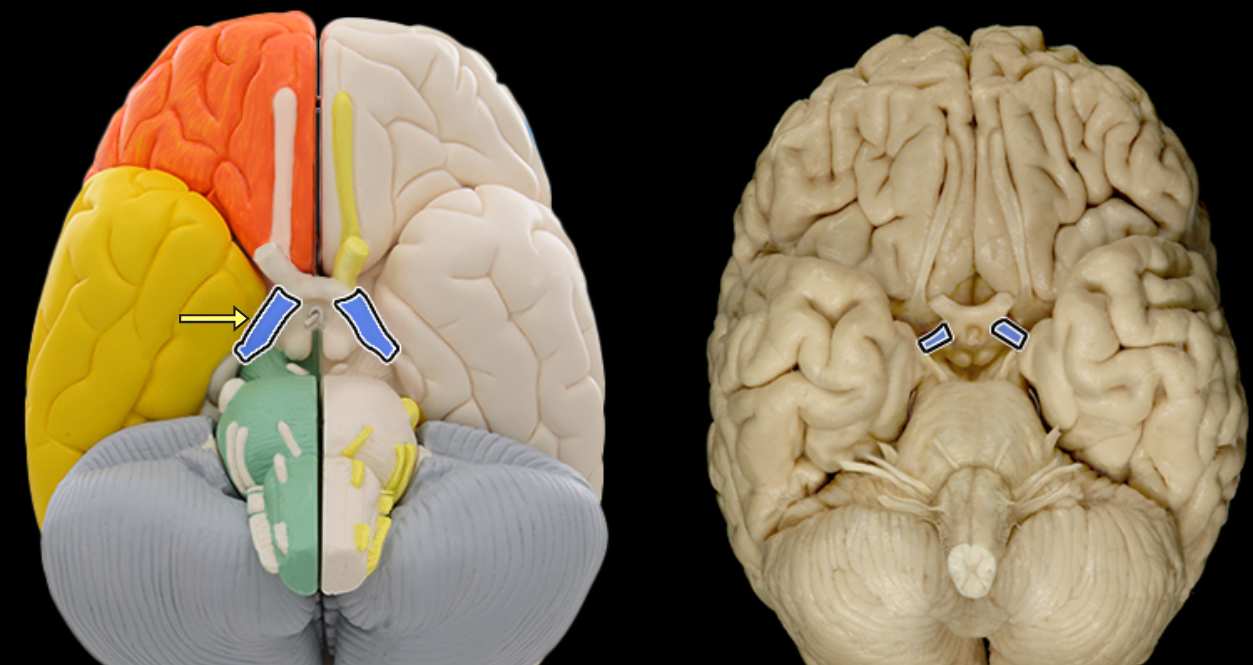
Optic tract
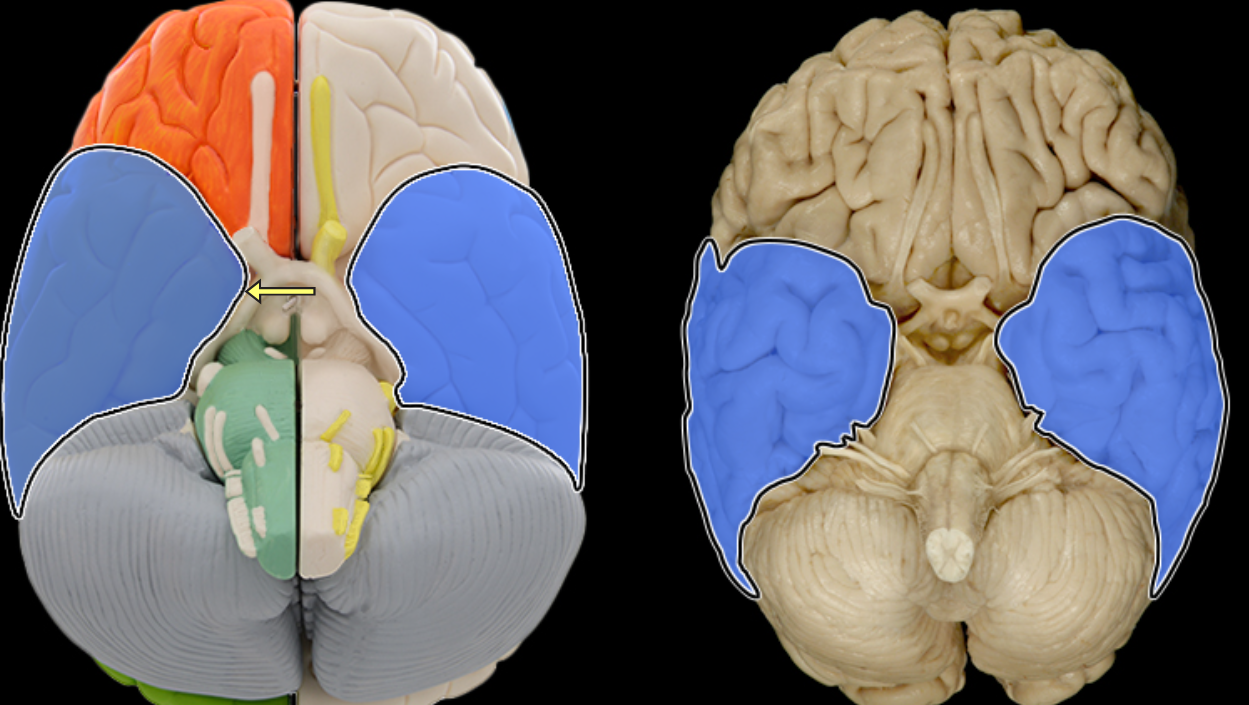
Temporal lobe
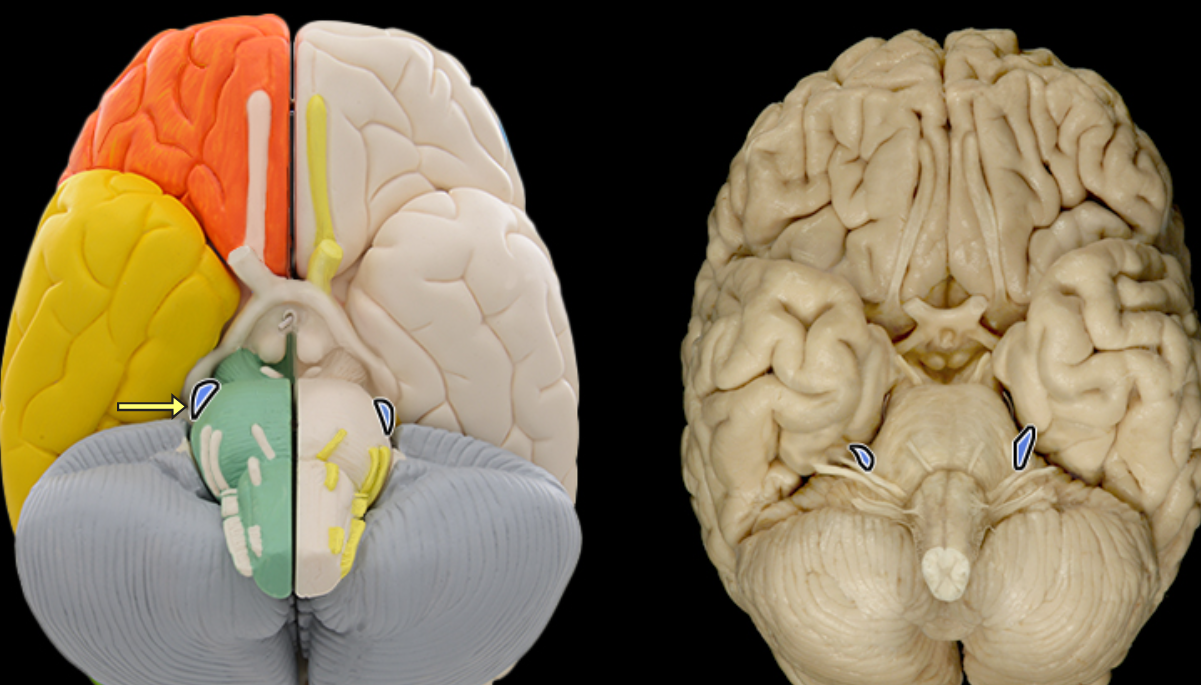
Trigeminal CN V
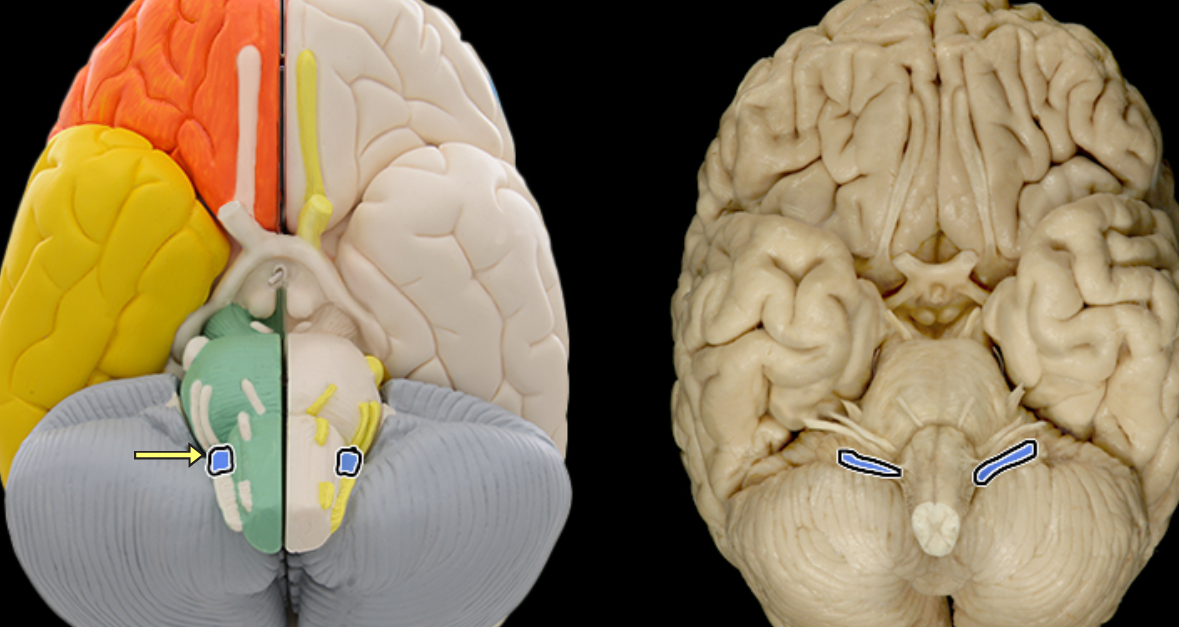
Vagus
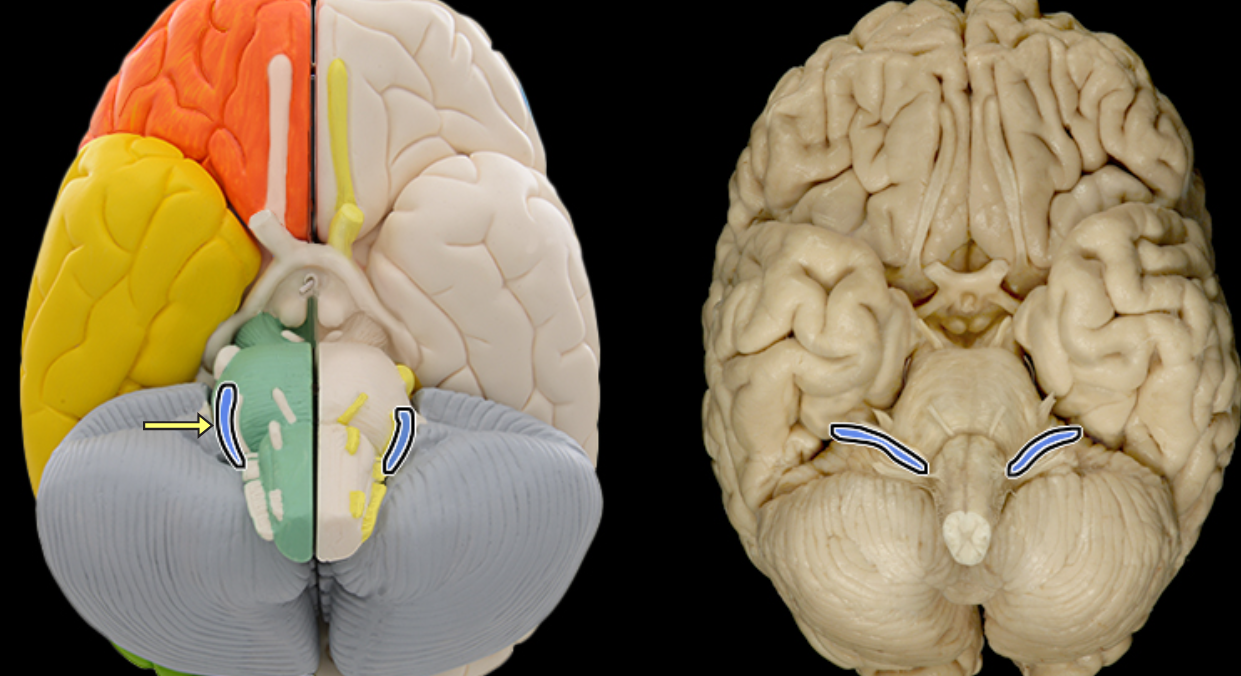
Vestibulocochlear n. CN VIII
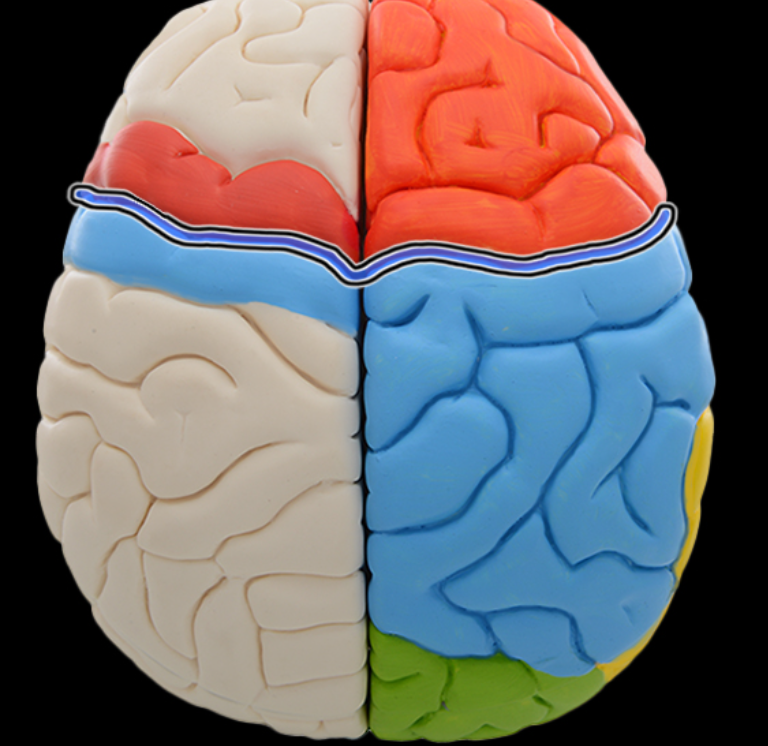
Central sulcus
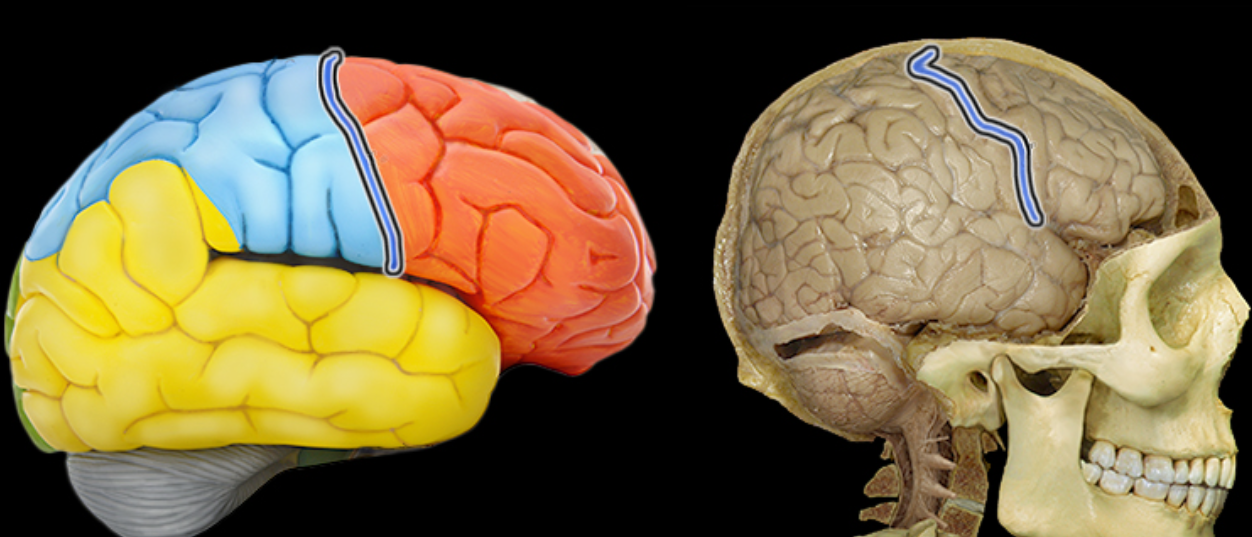
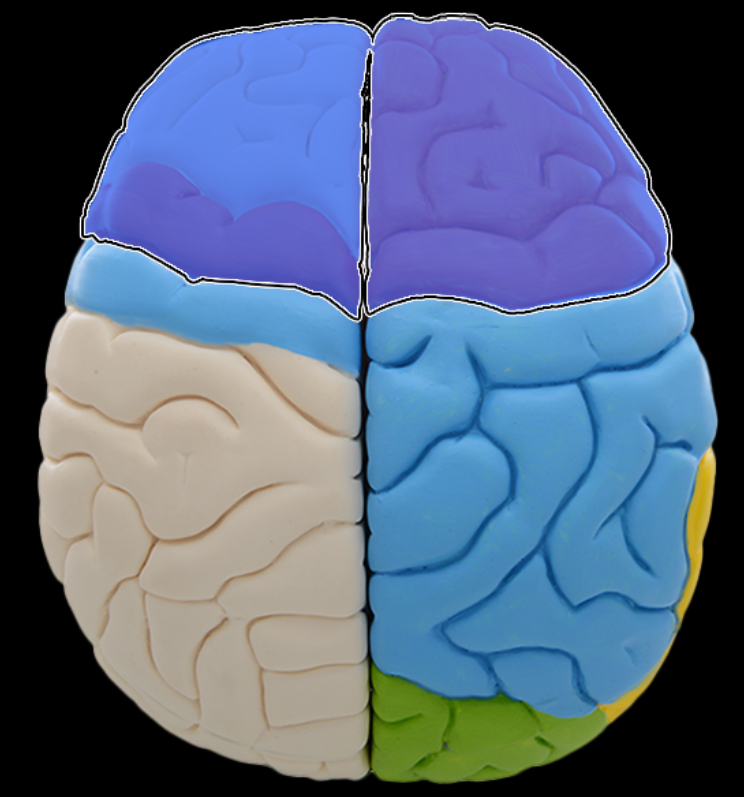
Frontal lobe
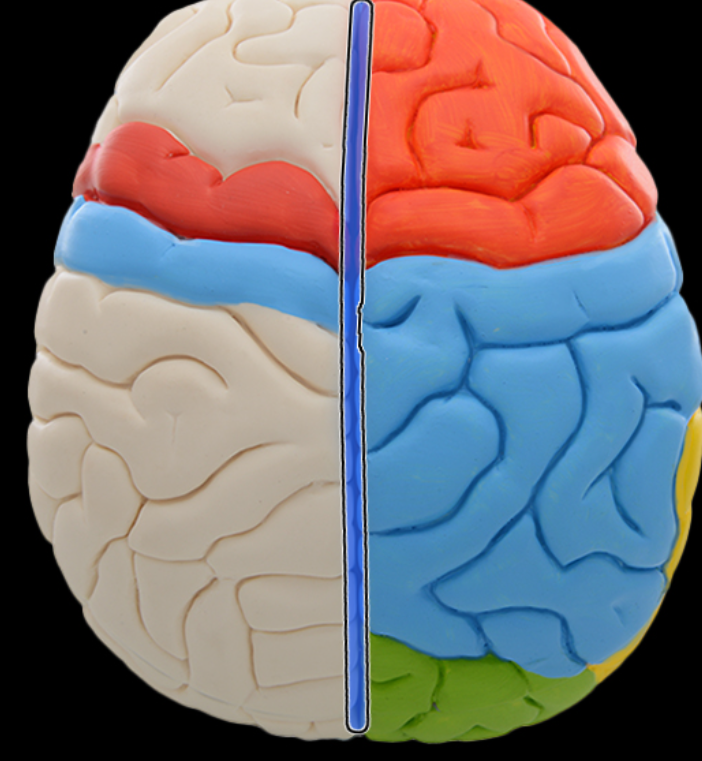
Longitudinal fissure
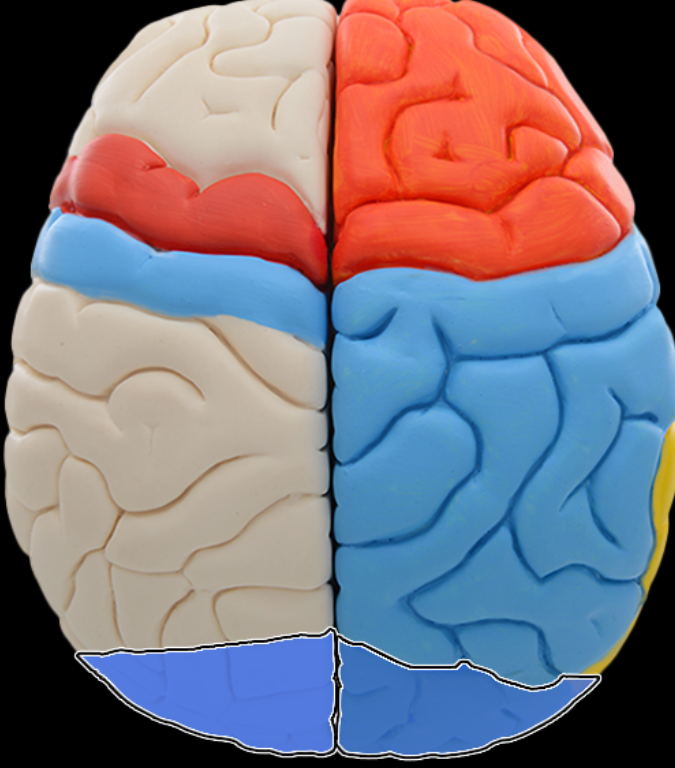
Occipital lobe
Parietal lobe
Postcentral gyrus
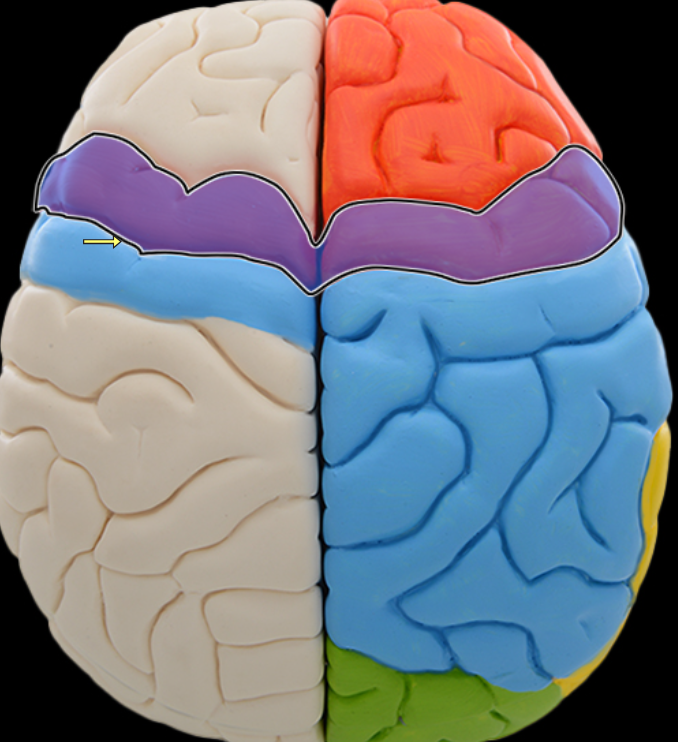
Precentral gyrus
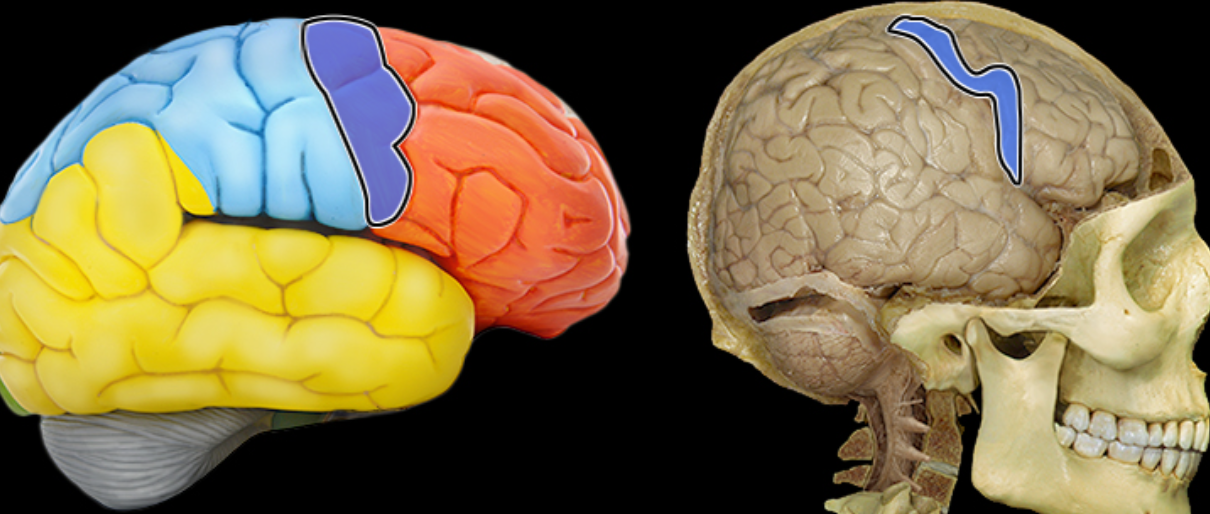
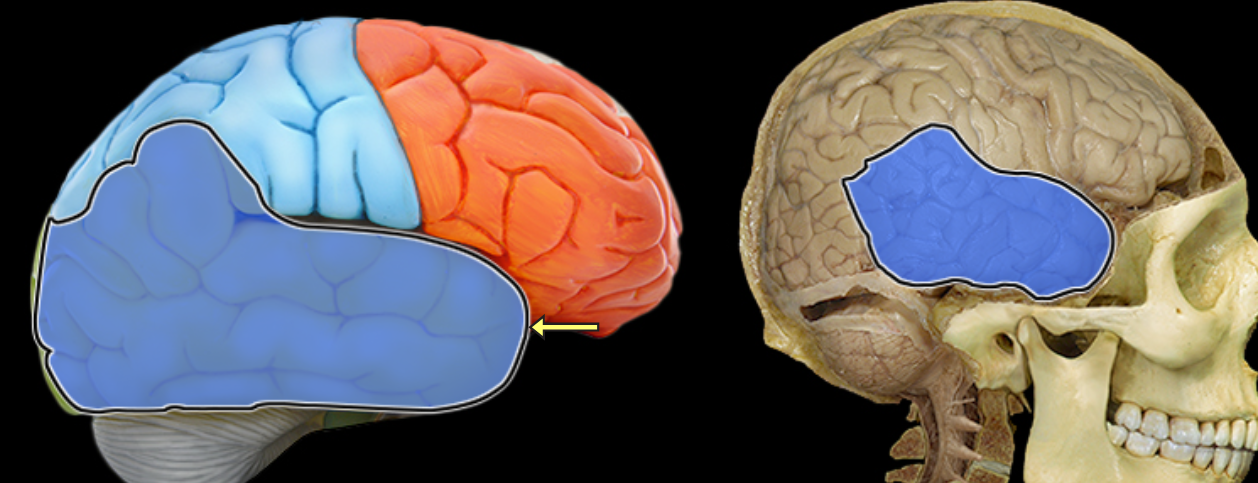
Temporal lobe
Location:
Lateral and inferior portion of each cerebral hemisphere
Inferior to lateral sulcus
Description:
Lateral surface has three parallel gyri
Function:
Primary hearing and smell areas
Memory
Speech perception and recognition (i.e., Wernicke's area - usually in left hemisphere)
Comment:
Named for overlying bone
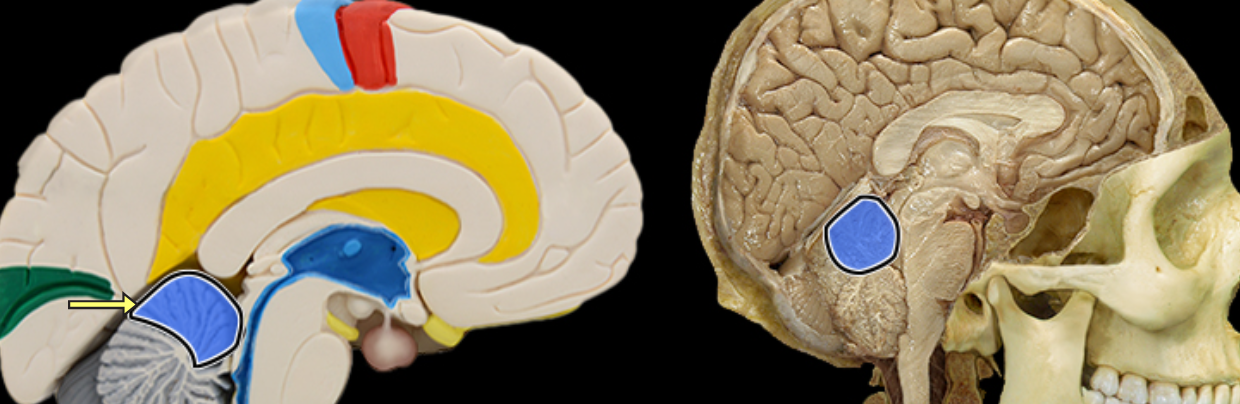
Anterior lobe of cerebellum
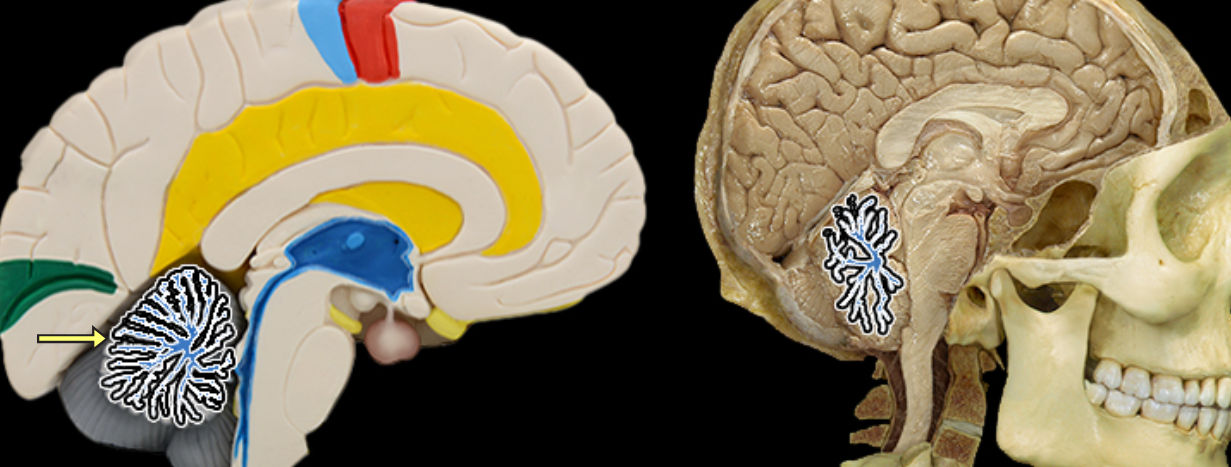
Arbor vitae
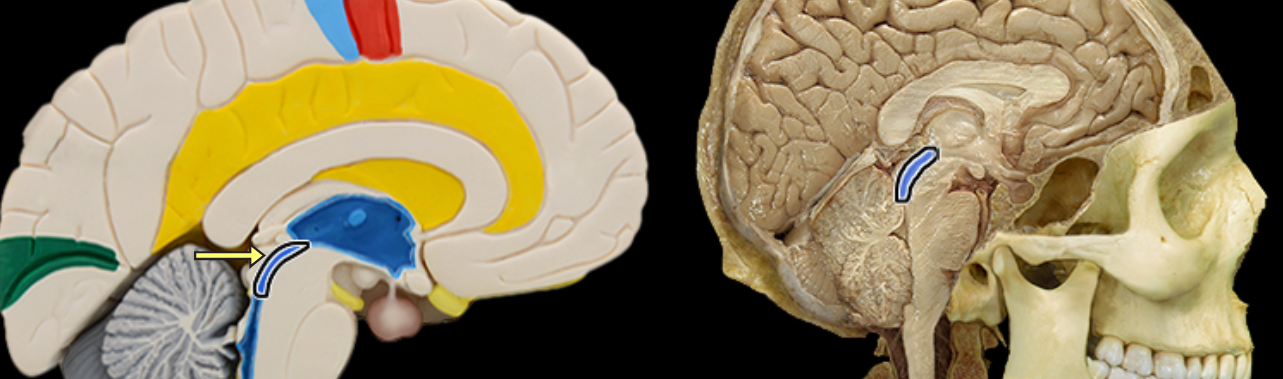
Cerebral aqueduct
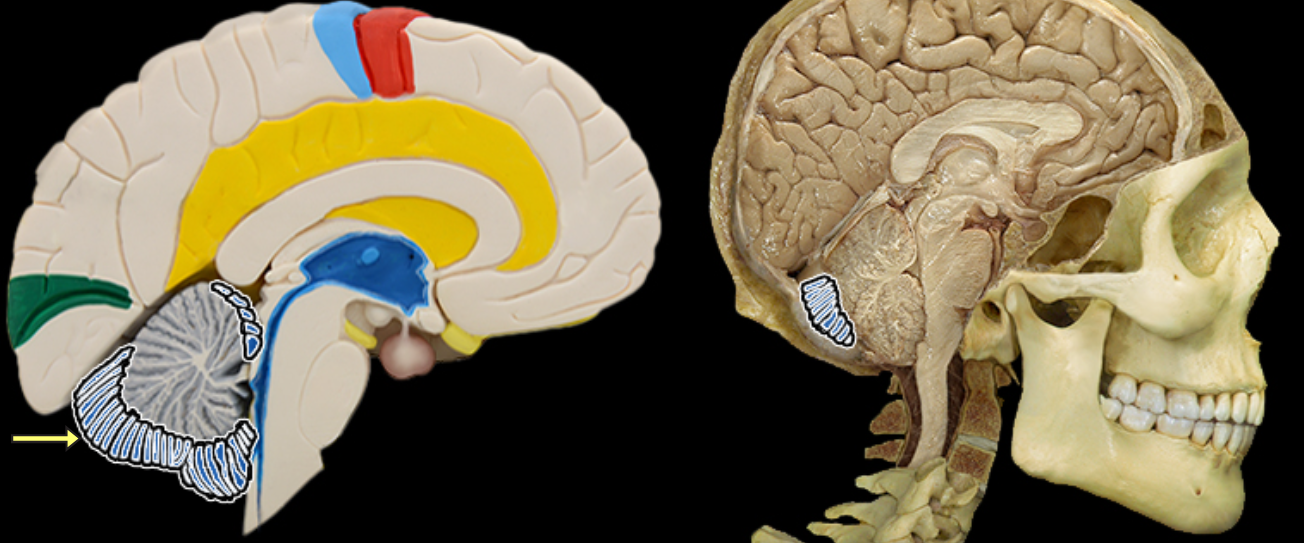
Folia
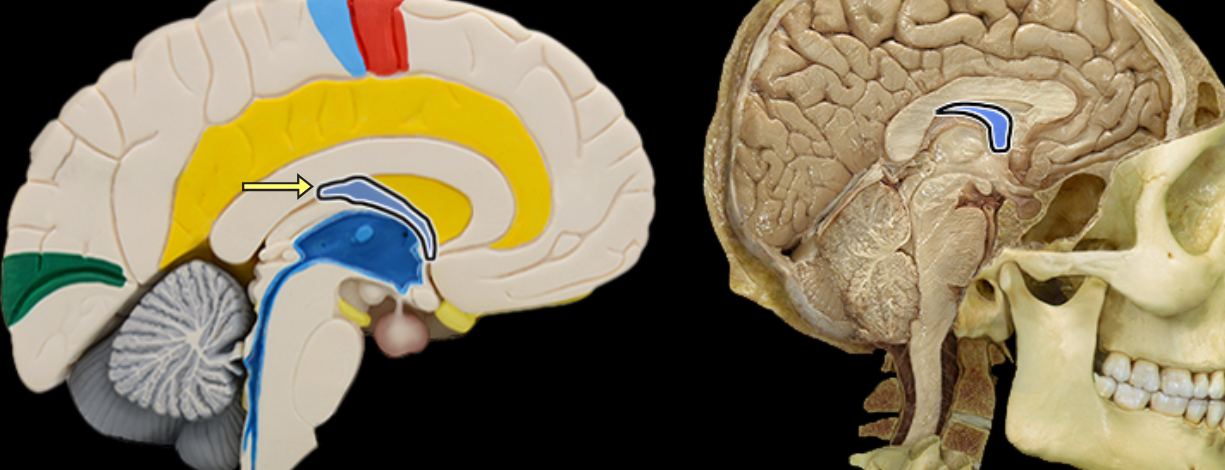
Fornix of brain
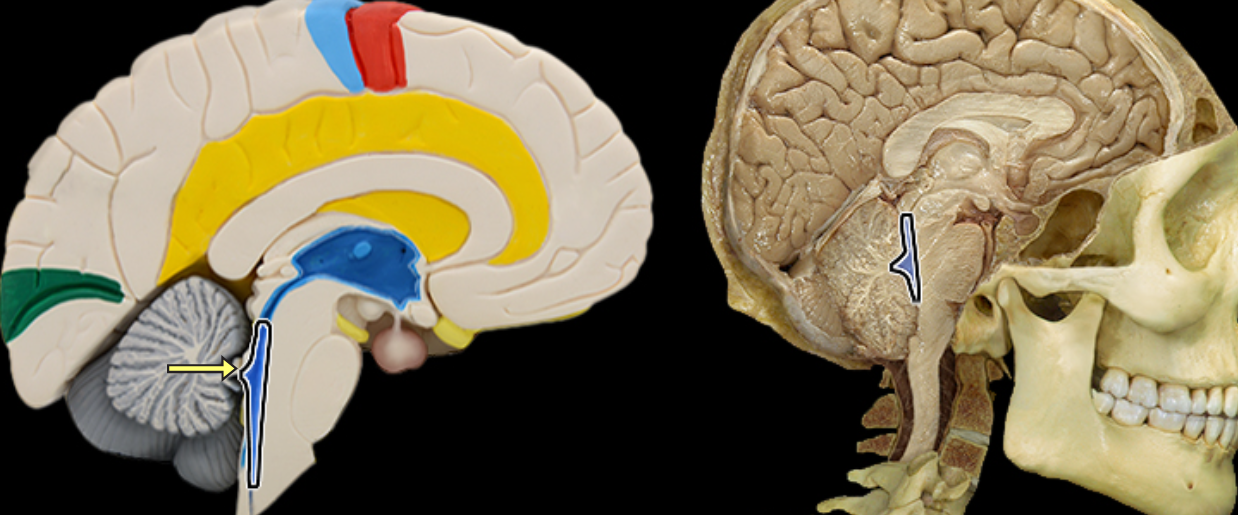
Fourth ventricle
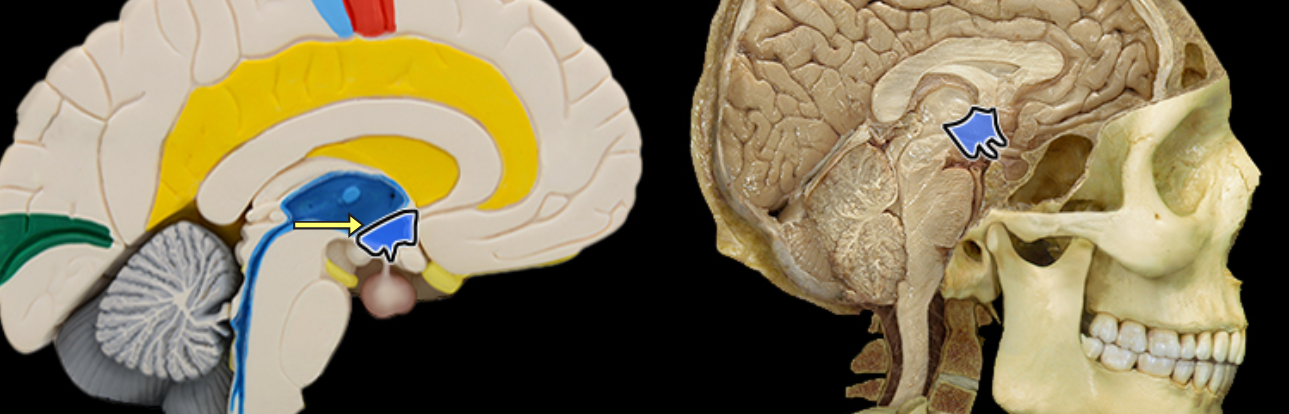
Hypothalamus
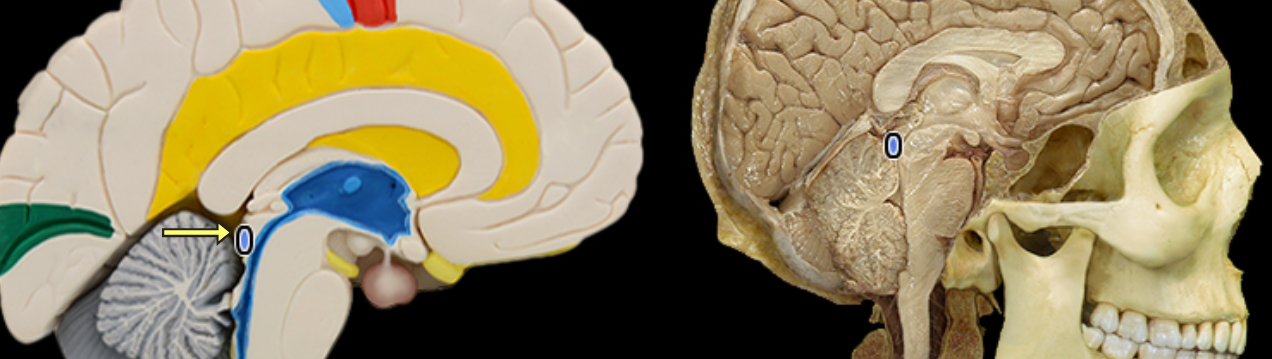
Inferior colliculus
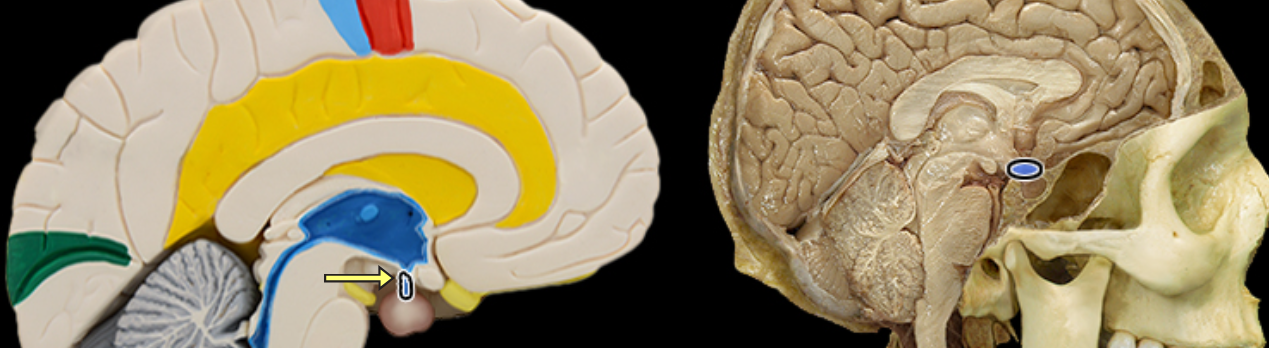
Infundibulum of pituitary gland
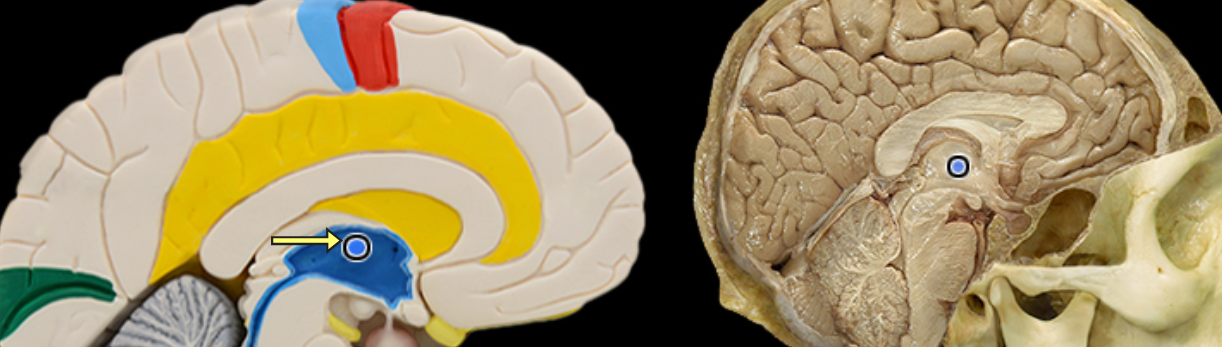
Interthalamic adhesion