BYU Marketing 201 [Swenson] ALL TERMS-FINAL
1/382
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
383 Terms
Marketing
the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large
Marketing Strategy
A cohesive marketing mix of product, place, price, and promotion, designed for a specific target market. Marketing strategy answers the question, "How do we orchestrate the marketing mix to deliver value to a particular market segment?"
Three important components of marketing
1) Marketing is the exchange that takes place between sellers and buyers.
2) Marketing creates, communicates, and delivers value to facilitate exchanges.
3) By delivering value, marketing satisfies customer needs and wants at a profit (marketing concept)
Marketing Concept
By delivering value, marketing satisfies customer needs and wants at a profit.
Markets
the aggregate of individuals and organizations that have (1) needs and wants and (2) the ability, willingness, and authority to purchase products and services that satisfy their needs and wants.
Business Market (business-to-business market)
individuals within organizations and companies purchasing products and services for use or consumption within their organization or for resale.
Consumer Market (business-to-consumer market)
Individuals buying products and services for personal consumption or use
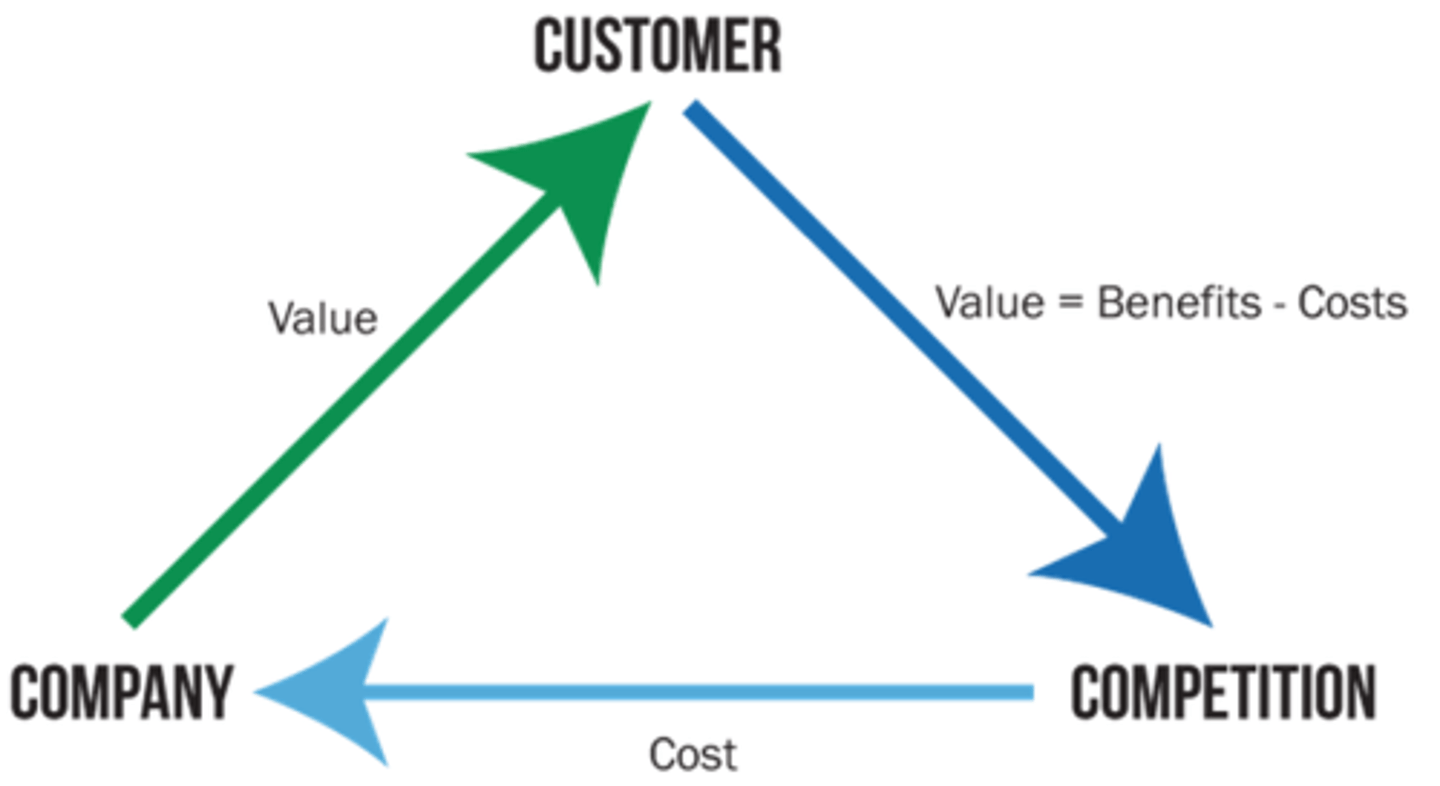
Strategic Triangle
Customer, Company, Competition (customer is the central point)
Corporate Strategy
What businesses should we be in? (Marketing firm considers types of business to include in its portfolio)
Strategic Business Unit (SBU)
How do we compete effectively in a given business?
BCG Growth Model
stars, cash cows, question marks, dogs
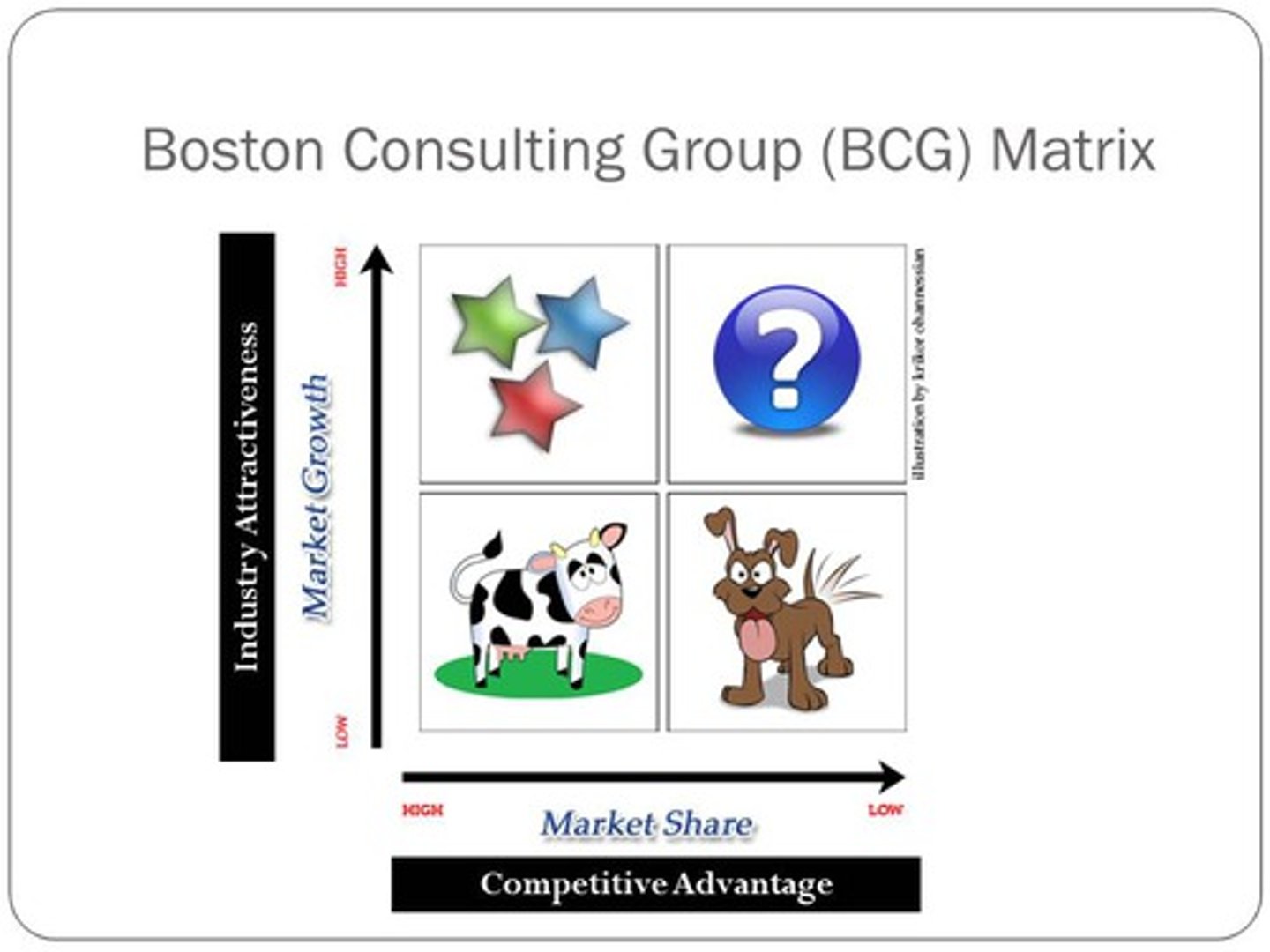
Stars
high growth, high market share
Cash Cows
low growth markets that generate more cash than they need (high market share)
Question Marks
high growth, low market share
Dogs
low growth, low market share
Marketing Mix
Product, Price, Place, Promotion
Product
A bundle of attributes in which each attribute and combination of attributes creates value for customers
Place
Where products are purchased
Price
the amount of money made for a product
Promotion
refers to many different marketing activities, such as advertising, public relations, sales promotions, trade promotions, personal selling, and digital marketing.
Brand Champions
Customers who love the firm's products and then advocate or champion the products to others.
Market Penetration
selling more of the existing products in existing markets
Product Development
introducing new products to existing markets
Market Development
introducing existing products to new markets
Diversification
Introducing new products into new markets
Marketing Plan
a marketing strategy with a budget and a timeline
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
determines the economic value a customer brings over the lifetime with the business.
3 Ways marketers can boost sales per customer
(1) persuading customers to buy more of their products
(2) generating add-on sales (complementary products and services),
and (3) partnering with other firms to create add-on sales opportunities.
Customer Aquisition
how can we acquire (and keep) customers
Customer Retention
the practice of keeping customers by building long-term relationships
Margin
difference between sell price and cost to make
Marketers can increase margin by...
(1) increasing price
(2) shifting the mix of purchases toward higher-margin products
(3) changing customer behavior so customers are less expensive to serve
(4) discouraging unprofitable customer behavior.
How to Achieve Success
1) focus on solving customer problems
2) chase customers, not competitors
Product Orientation
based on the belief that supply generates its own demand
Sales Orientation
based on the belief that marketing's only role is to sell products once they are already made
Marketing Orientation
Based on the belief that every product or service should focus on satisfying customer needs and wants a profit
Societal Orientation
Based on the belief that every product or service should provide value to the customer as well as to society as a whole.
Culture
Shared values, attitudes and practices that shape human behavior
Demographics
statistical data that describe a population
Generational Cohorts
People born during the same period and who share common life experiences.
Which generational group has the highest buying power?
Baby Boomers
Gross Income
the total amount of income received by a person, family or household
Disposable Income
money available to spend or save after taxes have been paid
Discretionary Income
money left after taxes and necessities have been bought and paid for
Technology
the application of science and research to solve a problem more effectively
Five Forces Model
A model developed by Michael Porter that helps us understand the five competitive forces that determine the level of competition and profitability in an industry.
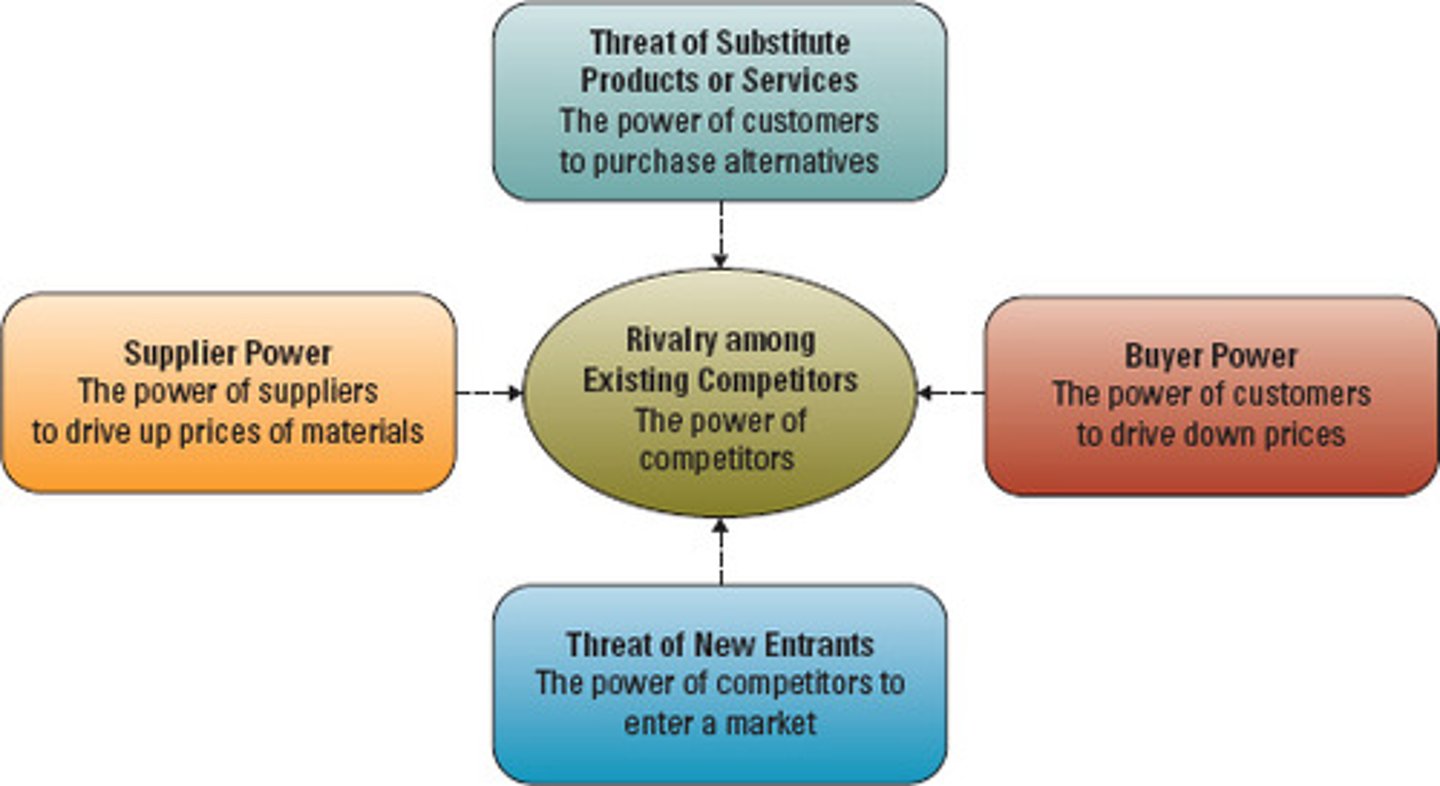
What are the five forces?
1) competitive rivalry
2) power of suppliers
3) power of buyers
4) threat of entrants
5) threat of substitutes
Regulations
Protect consumers and businesses by promoting competition and fair business practices.
SWOT Analysis
a planning tool used to analyze an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
Strengths
the firm's core competencies, abilities, and capacities that provide an advantage when meeting the needs of target customers. (play to)
Weaknesses
Limitations a firm faces when seeking to deliver value to customers. (moderate)
Opportunities
Favorable conditions and trends in the external environment (exploit)
Threats
conditions, trends, and barriers in the external environment that hinder firm performance (minimize)
Manufacturing products requires three things:
People, Knowledge, and Resources
What are the three types of geographic marketing?
Domestic, International, Global
Domestic Marketing
Focuses on customers in the home country
International Marketing
Exporting products to one or more countries outside the domestic market while remaining invested solely in the domestic country
Global Marketing
Selling or licensing products for sale in countries throughout the world
What are the four risks of global market expansion?
Competitive, economic, legal and political
Competitive Risk
competitors' responses to the new product's entry into the local market.
Economic Risk
Considers the potential mismanagement of a country's economy as exhibited in inflation and government debt
Legal Risk
inadequate protection of contracts and intellectual property.
Political Risk
demonstrations, strikes, civil strife, abrupt government changes, violence, or terrorism that influences business performance.
Market Entry Strategies
exporting, licensing, joint venture, foreign direct investment
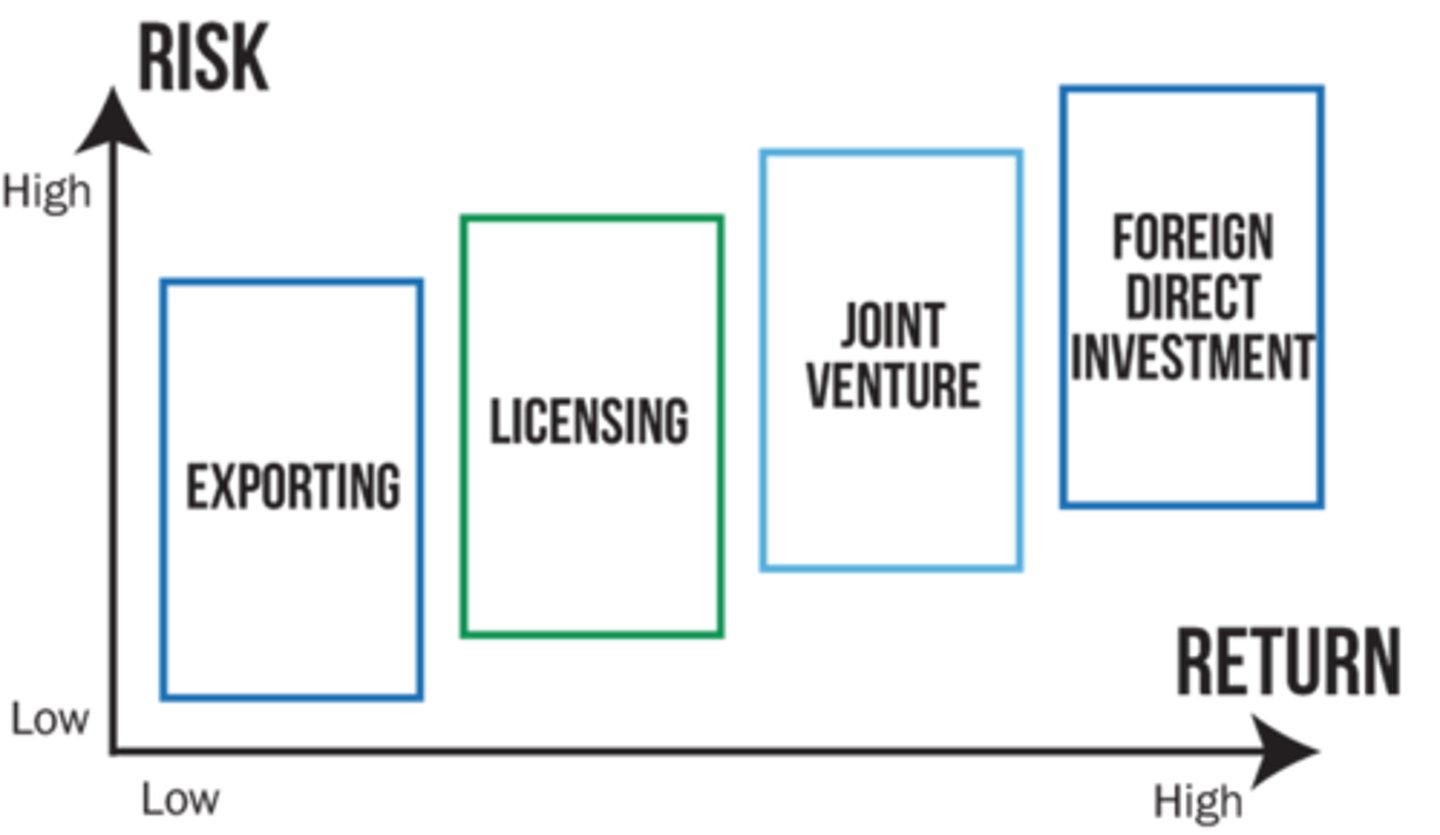
Exporting
Shipping goods produced in the home country to a distributor or retailer in the foreign market
Licensing
A firm in one country (the licensor) agrees to allow a firm in another country (the licensee) to use its manufacturing, processing, trademark, know how, patent or some other skill or value.
Joint Ventures
Two or more businesses agree to create a new business, jointly owned by the participating companies.
Foreign Direct Investment
Companies decide to make direct investments in building up wholly owned operations in other countries.
Standardization
the firm uses the same marketing mix in the foreign market as it does in its domestic market
What are some advantages of standardization?
cost reductions, savings in product and promotion (lower production and advertising costs)
What are some disadvantages of standardization?
Standardized products might not fit the needs of the local market
Customization
adapting or modifying the marketing mix to suit the local market
Glocal
Go global, act local
Ethics
the principles of right and wrong that guide an individual in making decisions
What are AMA's three ethical norms?
1) do no harm
2) foster trust in the marketing system
3) embrace ethical values
What are the four myths of unethical marketing?
1) marketers push products customers don't want to buy
2) customers are no match for the power of marketing
3) marketing is deceptive and not truthful or honest
4) marketers believe in planned obsolesce (purposefully making sure a product becomes obsolete over time)
The Fraud Triange
Opportunity, Motivation (Pressure),
Rationalization
Opportunity
condition or situation that allows fraud to occur
Motivation (Pressure)
pressure or need felt by person who commits fraud
Rationalization
the process of reconciling or justifying fraudulent behavior
What is the framework for ethics?
Personal ethical understanding, applications of ethics to business situations,
ethical courage, and ethical leadership.

Social Responsibility
businesses and organizations are part of a larger society and that they are accountable to that society for their actions.
Sustainability
the creation of alternatives to the depletion of natural resources
Green Marketing
When companies engage in the production and promotion of environmentally safe products.
What are the five steps of the marketing research process?
1) define problem
2) design research project
3) collect data
4) analyze data
5) take action
Exploratory Research
general; identify problems and opportunities, small groups (ex: personal interviews or focus groups)
Conclusive Research
specific; confirm impressions and insights, large and objective sample (ex: surveys)
Syndicated Data
data collected for specific industries
Secondary Data
Data previously collected for any purpose other than the one at hand
Primary Data
information collected for the specific purpose at hand
Data Wrangling
the process of unifying, cleaning, and preparing unorganized or scattered data for analysis
Data Exploration
Discovery through numerical summaries and visualizations
Data Modeling
- Transform the data to extract insights
- Build a model to represent the phenomenon of interest
Deployment and Socialization
communicate the results to the users, tell your story with data
Null Hypothesis
states that "the differences we observe are due only to random error."
Random Error
error that comes about from taking a sample from the population rather than getting data from every member of the population. Chance of random error decreases when sample size increases.
Nominal Scale
classifies data into distinct categories
Ordinal Scale
uses numbers ordered into an increasing size like finishers in a foot race (1 is better than 2, 2 is better than 3)
Interval Scale
Assumes an equal distance between numbers.
Ratio Scale
have equal intervals and equal ratios.