Clin Med II Exam 2 - HEME (LEUKEMIAS)
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gbalsam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
leukemia
malignant hematologic disorder characterized by a proliferation of abnormal white cells that infiltrate the bone marrow and organs
pancytopenia
deficiency of all types of blood cells (neutropenia, anemia, and bleeding from thrombocytopenia)
progression of acute leukemia
quick
acute leukemia
characterized by the proliferation of undifferentiated cells in the bone marrow (blasts) causing increased infection as immature WBCs are incapable of fighting & reduced bone marrow ability to produce normal cells
progression of chronic leukemia
slow
chronic leukemia
uncontrolled expression of mature cells
myelogenous leukemia
those that are from hemopoietic stem cells (usually causing an overgrowth of myeloblasts)
lymphocytic leukemia
arise from the lymphocytic line in the bone marrow
general symptoms of leukemia
- leukemic cells accumulating in bone marrow hampering the production of normal blood cells
- anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia all causing fatigue, pallor, bleeding, increased infections
general signs of leukemia
- non-tender lymphadenopathy in the neck, supraclavicular are, and axilla (cervical adenopathy in 80-90% of cases)
- mediastinal adenopathy (more than 50% at diagnosis)
- prone to infections (i.e., herpes zoster in 1/4th of patients and fungal or mycobacterial infections)
French-American-British leukemia classification (AML)
AML M0-M7
French-American-British leukemia classification (ALL)
ALL L1-L3
acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
the most common pediatric cancer
etiology of ALL
unknown with some hereditary and environmental factors
patho of ALL
characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of lymphoblasts limiting the production of other cells by overcrowding and inhibiting cell growth/differentiation
subtypes of ALL
- B-cell
- T-cell
- null type
clinical presentation of ALL
present with symptoms related to anemia, leukopenia (neutropenia), and thrombocytopenia
~ fatigue, pallor, bruising, bleeding, infections
other common symptoms of ALL
- liver, splenic, and testicular enlargement in males
- anorexia, weight loss, abdominal distention or pain, or an abdominal mass
- may mimic RA with swollen joints, bone pain, and tenderness causing a child to limp or not walk
- vomiting, headaches, papilledema (vision changes), neck stiffness, and cranial nerve palsy
when do symptoms typically occur in ALL?
rarely more than 6 weeks before diagnosis
cervical adenopathy in ALL
one of the indications of extramedullary leukemic spread
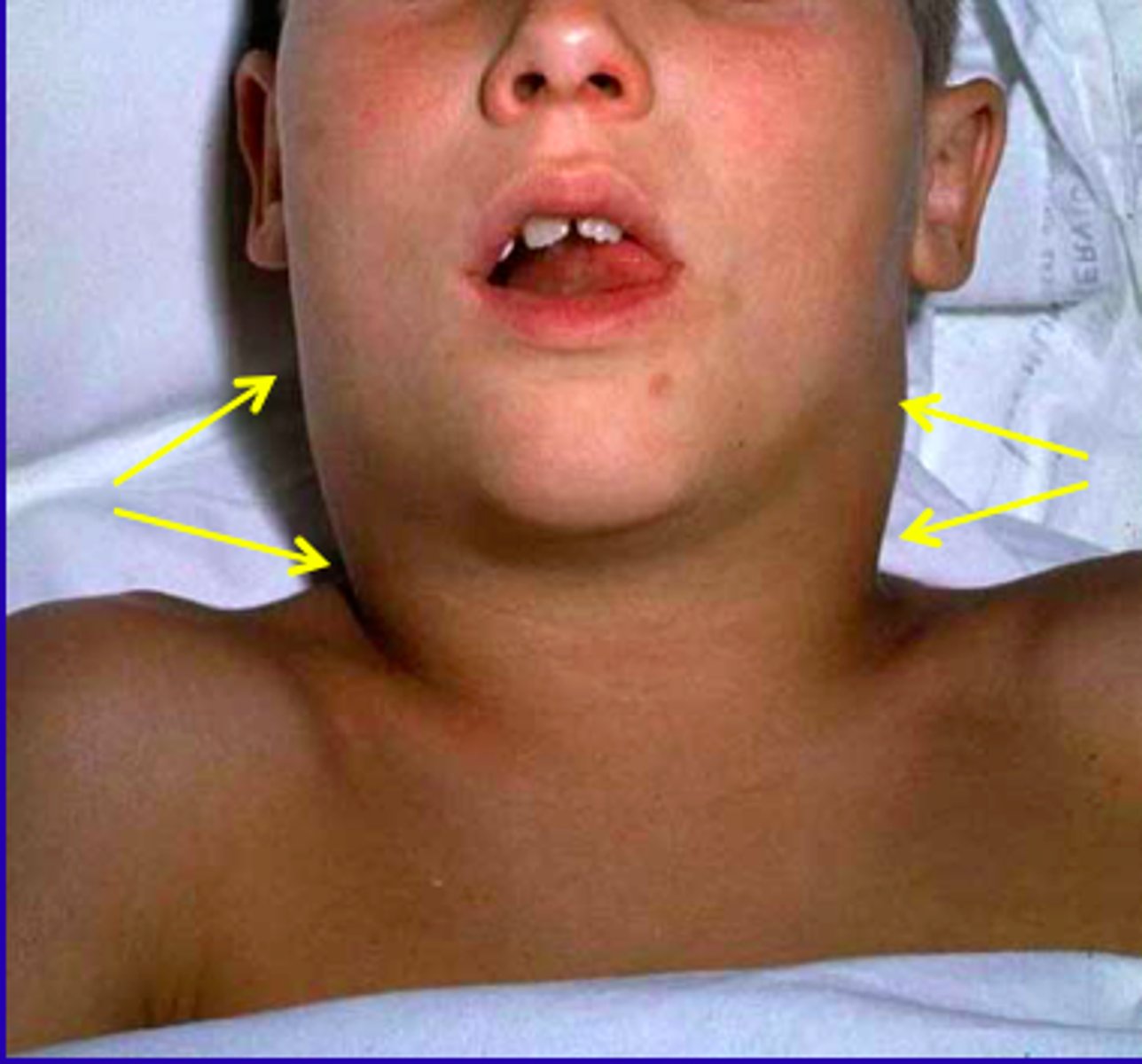
what is an enlarged lymph node?
>10 mm in its greatest diameter
what is an enlarged epitrochlear lymph node?
>5 mm
what is an enlarged inguinal lymph node?
>15 mm
what is an enlarged cervical lymph node?
>20 mm
characteristics of malignant lymphadenopathy
non-tender, firm, rubbery, and matted
WBC counts in ALL
varies from 5-100 thousand
what would indicate a poorer prognosis in ALL?
an abnormal increase in WBC
immunophenotyping
morphological evaluation, special stains, electron microscopy, and surface markers establish diagnosis of ALL in about 90% of cases
gold standard for diagnosing ALL
bone marrow biopsy
bone marrow biopsy of ALL
hypercellular, >20% lymphoblasts
indications for bone marrow biopsy
- atypical cells in the peripheral blood
- unexplained depression of more than one peripheral blood element (cytopenias)
- unexplained lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly associated with cytopenias
what are the two most common sites for extramedullary leukemia?
CNS and testes
staging of ALL
FAB: classified according to cell size, nuclear shape, number of nuclei, prominence of nuclei, and amount of cytoplasm (L1, L2, and L3)
WHO: cytogenic, molecular, and immunophenotype information (precursor B or precursor T)
acute treatment of ALL
- emergency treatment (ABCs)
- radiation therapy
- 3 stages of chemo based on protocol (induction, consolidation, and maintenance)
- bone marrow transplant
what is the treatment of choice for ALL, AML, and CML?
bone marrow transplant
induction stage of chemotherapy
trying to get the abnormal cells to be as active and as abnormal as possible to easily differentiate before treatment
transient complications of total body irradiation (TBI) in ALL
- GI (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, and malaise)
- mucosa of the mouth, pharynx, bladder, and rectum may be affected
- skin reactions, alopecia, interstitial pneumonitis
- decreased blood counts
chronic complications of total body irradiation (TBI) in ALL
- permanent sterility
- cataracts
- hepatic fibrosis and radionecrosis of genital tissue, muscle, and kidney
- secondary malignancy (esp. lymphoma)
- lung and heart problems
- retarded growth
poorer prognosis of ALL based on age
- children <2 and >10 years old
- children <1 year old
- any adult (specifically >50 years old)
poorer prognosis of ALL based on WBC
- initial count of <10,000
- count of >50,000
classic presentation of ALL
lymphadenopathy + bone pain + bleeding + fever in a child
acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
occurs 5x greater than ALL as it can occur at any age
etiology of AML
idiopathic
patho of AML
proliferation of precursor cells that have lost the ability to differentiate resulting in the gradual accumulation of undifferentiated cells in marrow or other organs
signs/symptoms of AML
- increasing fatigue or decreased exercise tolerance
- excessive bleeding
- fevers or recurrent infections
- headache, vision changes, confusion, TIA
- early satiety
- history of cancer
- abrupt onset
- similar symptoms to ALL
- increased susceptibility due to neutropenia
- respiratory distress or dyspnea
diagnosis of AML
>20% myeloblasts from bone marrow biopsy
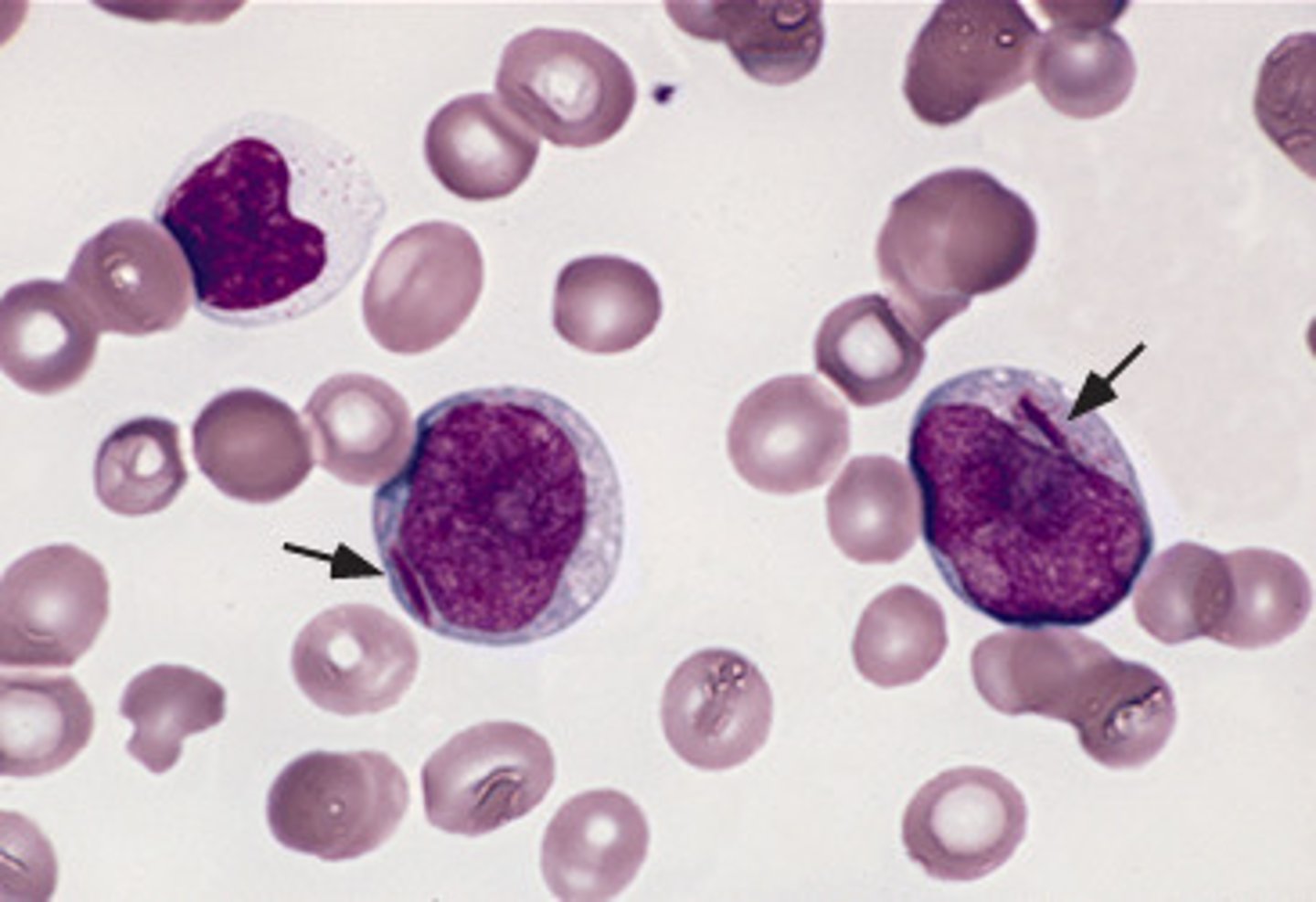
what might you see on a peripheral blood smear in diagnosing AML?
Auer rods
Auer rods
structures in the cytoplasm of myeloblasts, myelocytes, and monoblasts
staging of AML
FAB is used for morphological evaluation; maturation states are categorized from M0 (undifferentiated) to M7 (megakaryocyte)
AML M0
minimally differentiated acute myeloblastic leukemia
AML M1
acute myeloblastic leukemia without maturation
AML M2
acute myeloblastic leukemia with granulocytic maturation
AML M3
promyelocytic or acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
AML M4
acute myelomonocytic leukemia
AML M4eo
acute myelomonocytic leukemia with bone marrow eosinophilia
AML M5
acute monoblastic leukemia (M5a) or acute monocytic leukemia (M5b)
AML M6
acute erythroid leukemias, including erythroleukemia (M6a) and pure erythroid leukemia (M6b)
AML M7
acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
acute treatment of AML
combination of chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant
leukostasis management in AML
leukapheresis or chemotherapy
tumor lysis syndrome
potentially lethal side effect to chemotherapy initiation due to the large number of cells being destroyed leading to hyperuricemia, increased potassium, decreased calcium, increased phosphate, and acute renal failure
prognosis of AML based on WBC count
- <20,000 most favorable
- 20,000-49,000 in the middle
- >50,000 worst prognosis
unfavorable prognosis of AML
- >50 years old
- poor performance status
- low serum albumin
classic presentation of AML
blasts + Auer rods + adult patient
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
most common leukemia in Western countries
etiology of CLL
hereditary factors with possible links to immunodeficiency syndromes and viruses
patho of CLL
increased number of leukemic cells in bone marrow, blood, lymph nodes, spleen, resulting in an enlarged spleen and decreased bone marrow function
what is the most common chromosomal abnormality seen in CLL?
deletion at 13q14
signs/symptoms of CLL
- new lymphadenopathy
- fatigue
- dyspnea on exertion
- frequent infections
- bone pain
- excessive sweating
- generalized itching
- easy bruising
- lymphadenopathy
- spleno/hepatomegaly
- lymphocytosis
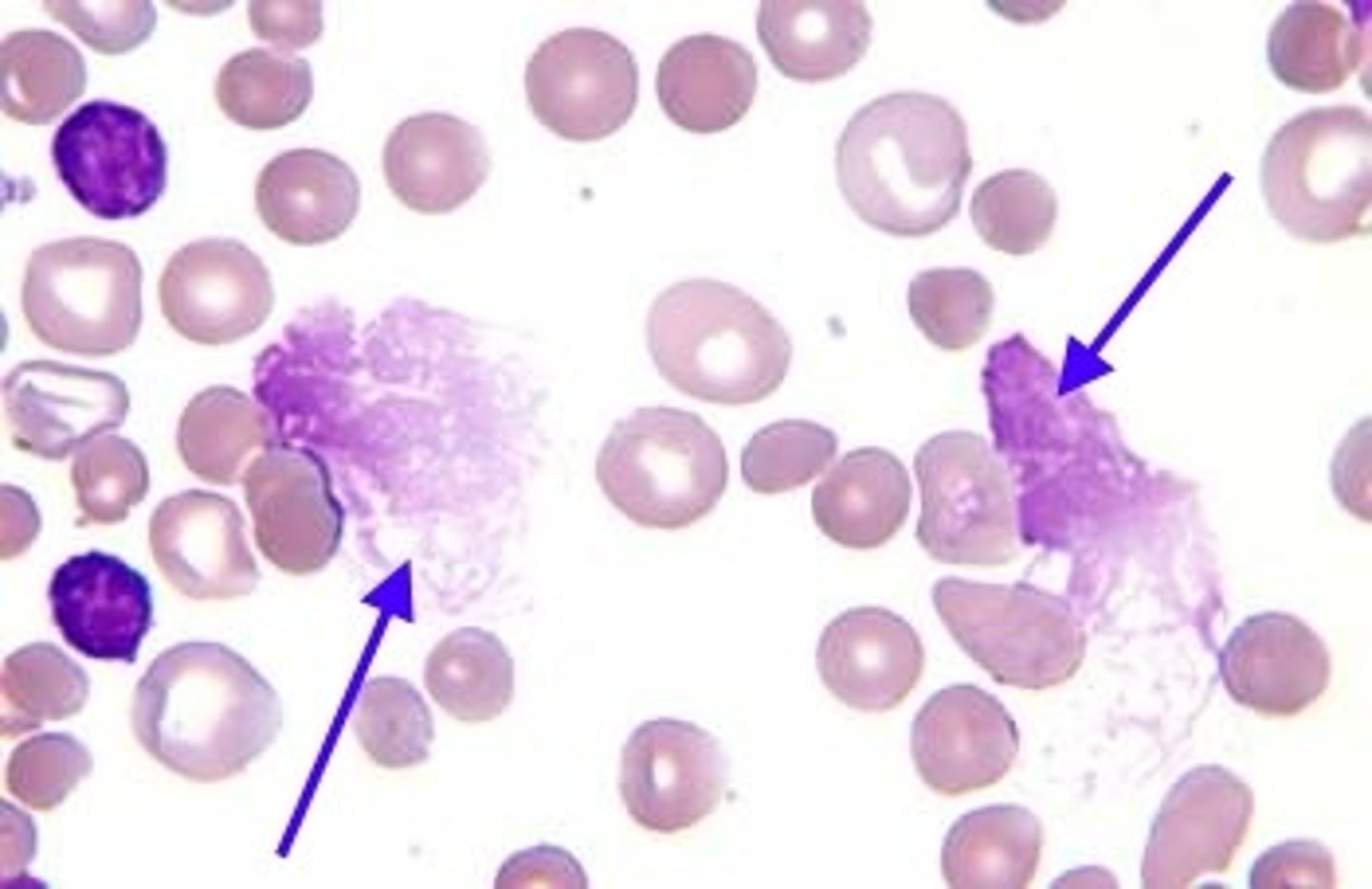
CLL peripheral blood smear
well-differentiated lymphocytes with scattered "Smudge cells"
Smudge cells
fragile B-cells that often smudge during slide preparation
immunophenotyping in CLL
- CD5 and CD23 markers
- >30% CD38 marker (worse prognosis)
Rai's staging system (stage 0)
low risk
Rai's staging system (stages I and II)
intermediate risk
Rai's staging system (stages III and IV)
high risk
staging of CLL
based on presence of adenopathy, splenomegaly, anemia, and thrombocytopenia
Binet staging of CLL
based on the involvement of cervical nodes, axillary nodes, inguinal nodes, spleen, and liver
CLL subtypes
B-cell or T-cell
CLL Rai stage 0
over 10,000 lymphocytes of blood (some doctors will diagnose if the count is over 5,000 and the cells have the same chemical pattern)
CLL Rai stage I
lymphocytosis plus enlarged lymph nodes
CLL Rai stage II
lymphocytosis plus an enlarged spleen (and possibly liver), with or without enlarged lymph nodes
CLL Rai stage III
lymphocytosis plus anemia, with or without enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, or liver; platelet counts near normal
CLL Rai stage IV
lymphocytosis plus thrombocytopenia, with or without anemia, enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, or liver
treatment of CLL
- observation in an early stage patient
- PO chemotherapy used to treat anemia, thrombocytopenia
- treat acute blastic crisis like AML
- radiation used palliatively for localized tumors of lymph tissue
- possible splenectomy
what do patients with CLL most often die from?
infection or bone marrow failure
classic presentation of CLL
middle age patient + blasts + Smudge cells on peripheral smear
chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
abnormal hematopoietic stem cells that contain the Philadelphia chromosome (present in >95% of cases)
patho of CML
linked to radiation and benzene exposure
three stages of CML
- chronic phase
- accelerated phase
- blast crisis
early clinical presentation of CML
- malaise, fatigue, sweating, intolerance to heat, easy bruising, and weight loss
- splenomegaly
- early satiety, weight loss, peripheral leg edema
blast crisis of CML
occurs about 3-4 years after diagnosis
clinical presentation of CML blast crisis
all organs invaded by the leukemic blast cells resulting in fever, bone pain, and weight loss
clinical presentation of active CML
- weight loss (>10% in <6 months)
- fever
- extreme fatigue
- anemia, thrombocytopenia
- organ involvement (other than lymph nodes, spleen, liver, and bone marrow)
- progressive or painful enlargement of spleen
most important diagnostic indicator of CML
presence of Philadelphia chromosome
diagnosis of CML chronic phase
<5% blasts
diagnosis of CML accelerated phase
>5-30% blasts
diagnosis of CML blast crisis
>20% blasts when accompanied by fever, malaise, and progressive splenomegaly
CML disease acceleration
- increasing anemia
- blood or marrow blasts between 10 and 20%
- blood or marrow basophils >20%
- platelet count <100,000
treatment of Philadelphia-positive CML
- PO chemotherapy (Imatinib, hydroxyurea)
- radiation
- chemotherapy
- stem cell transplant
classic presentation of CML
adult patient + strikingly increased WBC count (>100,000) + hyperuricemia + Philadelphia chromosome