Thermodynamics Chapters 1-3
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Primary (fundamental) Dimensions
mass
length
time
temperature
Secondary (derived) Dimensions
velocity
energy
volume
System
a region in space chosen for study or a quantity of matter
Boundary
Real or imaginary surface separating the system from the surrounding
Surrounding
the mass or region outside of the system
Closed System
Has a fixed amount of mass
No mass crosses the boundary
Energy CAN cross the boundary
Isolated System
Has a fixed amount of mass AND energy
No mass crosses the boundary
No energy crosses the boundary
Open System (control volume)
Encloses a device that involves mass flow
e.g., compressor, turbine, nozzle
Can include real, imaginary, fixed, or moving boundaries
Control Surface
the boundaries of a control volume
Property
Any characteristic of a system (e.g., P, T, m)
Two types
Intensive
Extensive
Specific
Intensive Properties
properties independent of mass
T
P
ρ
Extensive Properties
properties dependent on mass or related to system size
m
V
specific properties are a subsection of these
Specific Properties
Extensive properties per unit mass
specific volume: v=V/m
specific total energy: e=E/m
Thermal Equilibrium
When the temperature is the same throughout the system
Mechanical Equilibrium
When there is no change in pressure at any point of the system with time
Phase Equilibrium
When the system has 2 phases and when the mass of each phase reaches an equilibrium level and stays there
Chemical Equilibrium
When chemical composition does not change with time
State Postulate
The state of a simple, compressible system is specified by two independent, intensive properties
Process
Any change the system goes from one phase to another
Path
A series of states the system passes through during the process
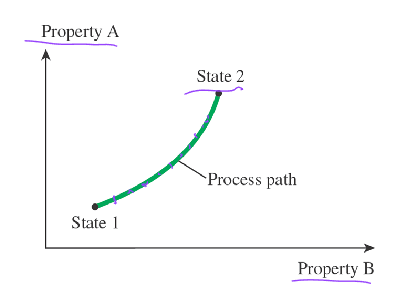
Quasi-Equilibrium (quasi-static) Process
When a process occurs in a way that the system remains infinitesimally close to an equilibrium state at all times
Isothermal Process
A process where temperature remains constant
Isobaric Process
A process where pressure remains constant
Isochoric (isometric) Process
A process where specific volume (v) remains constant
Cycle
A process where the system returns to the initial state it began the process with at the end
Steady
No change in time
Unsteady or Transient
When there is a change in time
Uniform
No change with location over a specific region
Steady-flow Process
A process where a fluid flows through a control volume steadily
these conditions can be considered for turbines, pumps, and boilers
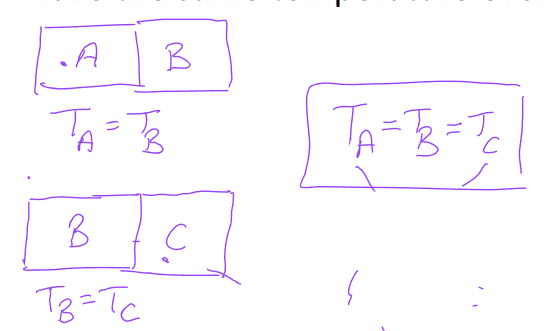
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
If two boundaries are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, they are both in thermal equilibrium as well
two bodies are in thermal equilibrium if both have the same temperature even if they are not in contact
First Law of Thermodynamics
The conservation of energy principle
energy is a thermodynamic property
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy has quality as well as quantity
Absolute Pressure (Pabs)
The actual pressure at a given position
Gage Pressure (Pgage)
The difference between the absolute pressure and the local atmospheric pressure
Pgage = Pabs - Patm
Vacuum Pressure (Pvac)
The pressure below atmospheric pressure
Pvac = Patm - Pabs
Barometer
Device that measures atmospheric pressure
Manometer
Uses a glass/plastic U-tube filled with fluid to measure pressure differences according to fluid column height
Total Energy (E)
The sum of all types of energy (potential, kinetic, and internal)
Total Energy Per Unit Mass (e)
e=E/m
Internal Energy
The sum of all microscopic (related to molecular structure of an atom) forms of energy
Kinetic Energy
Energy related to a system’s motion
Potential Energy
Energy of a system due to the elevation in a gravitational field
Mass Flow Rate
The amount of mass flowing through a cross section per unit time
Internal Energy
There are 3 types:
Sensible energy
Latent energy
Nuclear energy
Sensible Energy
The internal energy of a system related to a molecule’s kinetic energy
Latent Energy
Internal energy associated with a system’s phase
Nuclear Energy
Internal energy associated with strong bonds within the nucleus of atoms
Mechanical Energy
A form of energy that can be converted to mechanical work completely and ideally with an ideal mechanical device
Heat (Q)
A form of energy that is transferred between two systems because of a temperature difference
Adiabatic Process
A process where NO HEAT TRANSFER occurs
This means
the system is well insulated
NO pressure difference between the system & surrounding
Conduction
Energy transfer from more energetic particles of a substance to the adjacent less energetic ones
Convection
Energy transfer between the solid surface & adjacent fluid in motion
Radiation
Energy transfer due to the emission of electromagnetic waves
Work
The energy transfer associated with a force acting through a distance
if the energy crossing the closed system boundary is not heat, it MUST be work
Power
Work done per unit time (kJ/s or kW)
Energy Transfer by Work
Heat and work are both vectors (have magnitude and direction)
Positive Sign: Heat transfer TO a system and work done BY a system
Negative Sign: Heat transfer FROM a system and work done ON a system
Electric Work
Electrons crossing the system boundary to do the electrical work on a system
Mechanical Forms Work
Two Requirements
There must be a force acting on a boundary
the boundary must move
Energy Balance
The net change in the system’s total energy is equal to the difference between total energy entering the system and the total energy leaving the system during the process
Efficiency
Indicates how well the energy conversion/transfer is achieved
When efficiency < 100%, the conversion is less than perfect/there is some losses that have occurred during the conversion
Pure Substance
A substance with a fixed chemical composition
includes the mixture of two or more phases of the same substance
does NOT include the mixture of liquid and gaseous air
Homogenous Substance
A substance with a mixture of various chemical elements
Compressed (subcooled) Liquid
A liquid that is not about to vaporize
Saturated liquid
a liquid that is about to vaporize
Saturated vapor
vapor that is about to condense
Superheated vapor
vapor that is not about to condense
Saturation Temperature (Tsat)
the temperature at which a pure substance changes phases
Saturation Pressure (Psat)
the pressure at which a pure substance changes phases
Latent Heat
the amount of energy absorbed or released during a phase change
Latent Heat of Fusion
The amount of energy released during freezing
Latent Heat of Vaporization
The amount of energy released during condensation
Critical Point
The point at which saturated liquid and saturated vapor states are identical
Critical Temperature (Tcrit)
The temperature at which a substance reaches its critical point
Critical Pressure (Pcrit)
The pressure at which a substance reaches its critical point
Critical Specific Volume (vcrit)
The specific volume at which a substance reaches its critical point
Enthalpy
the parameter used in power generation and refrigeration
Enthalpy of Vaporization (latent heat of vaporization)
the amount of energy needed by a unit of saturated liquid at a given P and T
Quality (x)
The ratio of the vapor mass to the total mixture’s mass
Characteristics of a saturated vapor
higher specific volume (v > vg at a given P or T)
higher internal energies (u > ug at a given P or T)
higher enthalpies (h > hg at a given P or T)
higher temperature (T > Tsat at a given P)
lower pressures (P < Psat at a given T)
Characteristics of a compressed liquid
lower specific volume (v < vg at a given P or T)
lower internal energies (u < ug at a given P or T)
lower enthalpies (h < hg at a given P or T)
lower temperature (T < Tsat at a given P)
higher pressures (P > Psat at a given T)
Equation of State
any equation related to the P, T, and v of a substance
Ideal-Gas Relation
The simplest and best-known equation of state
Compressibility Factor (Z)
Used to account for the deviation in ideal gas behavior at a given T and P
Principle of Corresponding States
Z factor for all gasses in approximately the same at the same PR and TR