Rotation in Sport and Motor Control
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Motor Control
Study of how movement is controlled
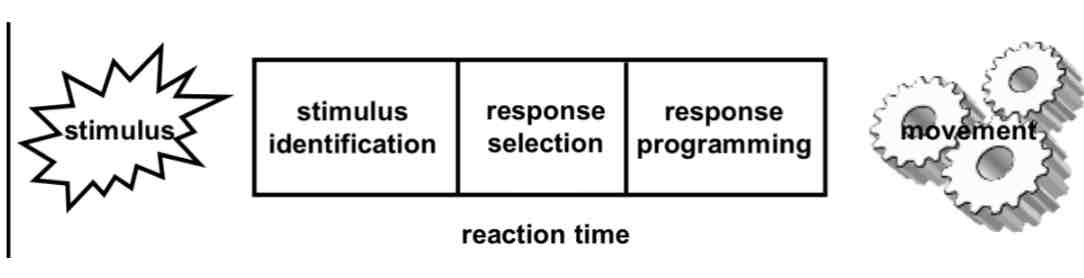
Expanded Info Processing Model
Angular Momentum
defintion
Equation
quantity of rotational motion
Angular Momentum (L) = Moment of inertia x Angular Velocity
L = I x ω
Moment of inertia
defintion
3 axis
Which has bigger I and why
resistance of a body to angular motion
Measure of distribution of mass about an axis (tucking reduces)
3 axis…
Lateral (pole through hips)
Frontal (pole through belly button)
Longitudinal (pole through head to toe)
I = largest in frontal axis
Conservation of Angular Momentum
equation
Definition
Is ωs = It ωt
If moment of inertia changes, angular velocity changes to compensate
Can Angular Momentum be generated in flight?
Generating angular momentum around an axis of a joint whilst decreasing inertia = small angular velocity
CANT generate angular momentum though
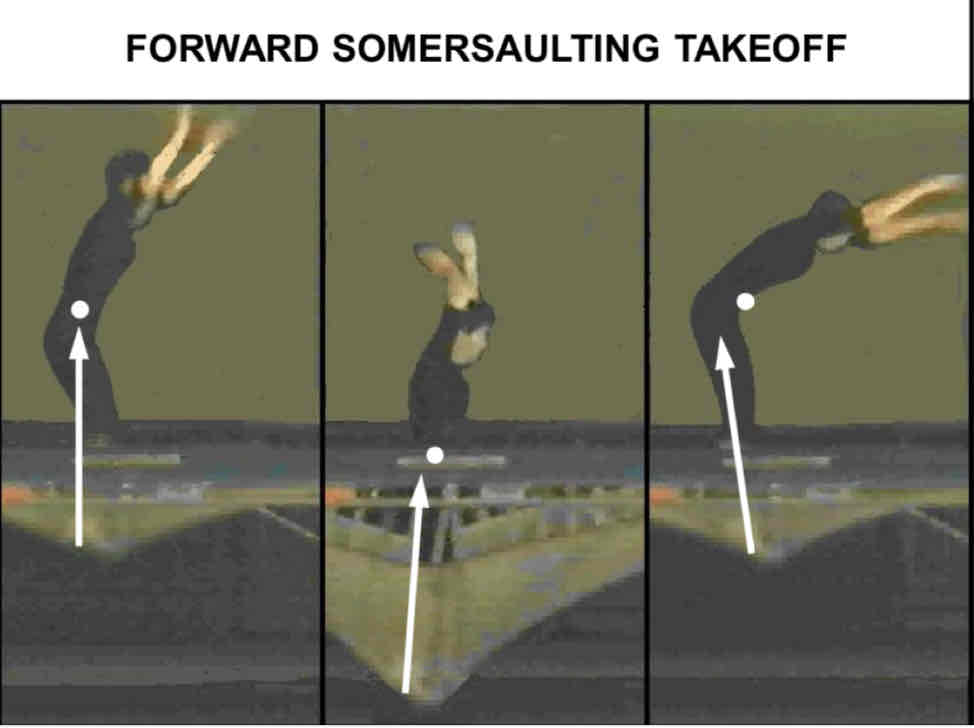
How is a somersault generated at takeoff?
how?
Equation
Create torque by shifting COM foward within the base of support
Generates GRF pointing backwards, then pike at hips and shift COM forward
Torque = Force x Distance
Force from trampoline
Distance from landing point to COM
How do long jumpers cope against forwards somersault momentum during flight?
Circle arms and legs forward = go backwards
High Jumpers
explain their approach
The Curved Approach
curve tightens as they near jump to produce somersault rotation
Gymnasts
how do they maintain rotation
Have to input energy into the bar to keep rotating round
energy lost through friction and elasticity
Energy input through muscle and hip flexion, then straighten
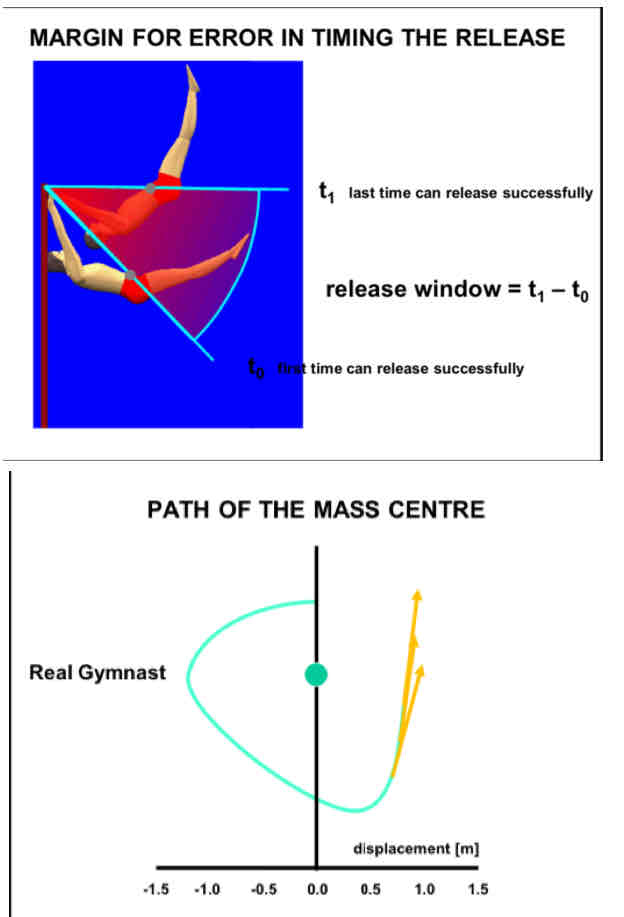
Motor Control of Gymnast bar dismount
Timing
Margin for error in timing of releases is larger due to modified technique
Change the radius to the COM
Tangential release = 90° from path
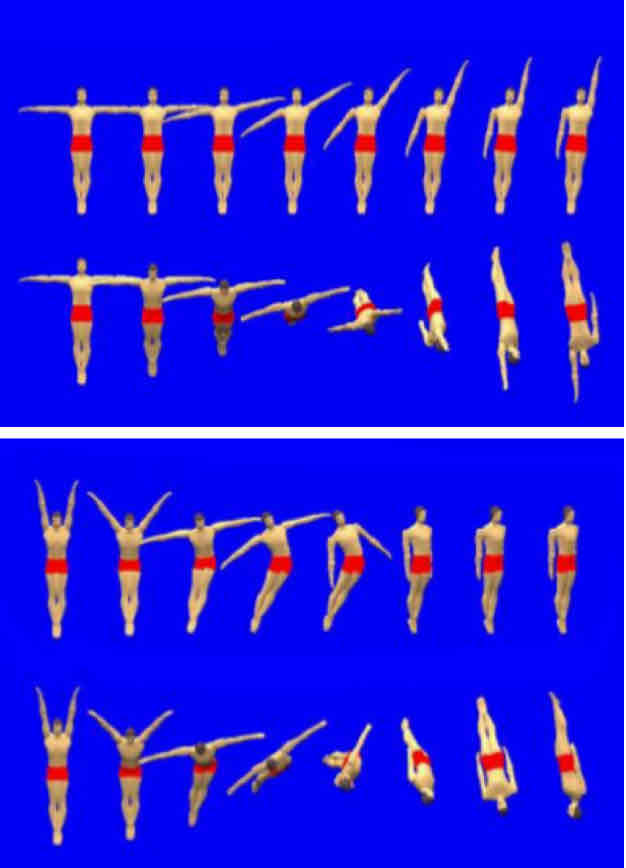
Production of Twist - during takeoff
name
How?
Disadvantage
Contact Twist…
Makes use of Newtons 3rd Law - every action has equal and opposite reaction force
Push back of floor, then move arms in to reduce I and Increase ω
HOWEVER…
taking energy from floor (GRF), so energy in system during the whole movement = less controlled landing
Production of Twist - After takeoff
name
How
Ariel Twist…
Hips rotate in one direction, causing system to maintain angular momentum by rotating in the opposite direction
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Advantages of Hula - 3
Don’t have to worry about twist on take off
Good view of landing spot the entire way
Twist is stopped when hula is stopped
Disadvantages of Hula - 1
Limited amount of twist can be produced
2 ways to produce Tilt
why useful
Asymmetrical Arms
Asymmetrical Hips
Can produce tilt during somersault
Gymnasts use to correct movements in flight
3 Equations for Production of Angular Momentum
Angular Momentum = Moment of Inertia x Angular Velocity
h = Iω
Torque = Force x Distance
T = Fd
Torque = rate of change in angular momentum