Comprehensive Skin, Eye, Urogenital, Respiratory, Gastrointestinal, and Systemic Bacterial Diseases
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What does pyoderma mean?
Pus filled.
What is folliculitis?
Invasion of Staphylococcus aureus through a hair follicle, commonly referred to as pimples.
What is a sty?
An infected follicle of an eyelash.
What is a boil?
A deeper pus-filled infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus, also known as a furuncle.
What is a carbuncle?
A further spread of a Staphylococcus aureus infection beyond a boil.
How can Staphylococcus aureus evade the immune response?
It can prevent movement of phagocytic cells to the infection site and kill macrophages with leukocidin.
What is the significance of coagulase in Staphylococcus aureus?
It is coagulase positive, which helps in its identification and pathogenicity.
What is impetigo?
Pyoderma lesions caused by Staphylococci or Streptococcus pyogenes, sometimes as a mixed infection.
What causes Scalded Skin Syndrome?
Two different exotoxins (exfoliative toxin A and B) produced by Staphylococcus aureus.
What is Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)?
A life-threatening condition caused by the release of Toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST-1) into circulation.
What is the role of erythrogenic toxin in Streptococcus pyogenes infections?
It can cause a scarlet fever rash as a complication of strep throat.
What are some virulence factors produced by Streptococcus pyogenes?
Hemolysins, streptolysin, M protein, a capsule, streptokinase, hyaluronidase, and deoxyribonucleases.
What is acne, and which organism is associated with it?
Acne is associated with the anaerobic organism Propionibacterium acnes, which thrives on excess oil from sebaceous glands.
What is Pseudomonas dermatitis?
An infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, known for its resistance to antibiotics and disinfectants.
What is ophthalmia neonatorum?
Conjunctivitis of the newborn caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis.
What is 'Pink Eye'?
Bacterial conjunctivitis caused by organisms such as Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and others.
What is trachoma?
A condition caused by certain strains of Chlamydia trachomatis that can lead to blindness if untreated.
What are the two types of urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
Ascending and descending, depending on where the infection starts in the urinary system.
What organism causes 80% of urinary tract infections?
E. coli.
What is bacterial vaginitis?
An infection caused by Gardnerella vaginalis interacting with anaerobic bacteria when vaginal pH increases.
What are the stages of syphilis?
1. Incubation, 2. Primary (chancre), 3. Secondary (skin eruptions), 4. Latent, 5. Tertiary (gummas).
What is the causative organism of gonorrhea?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
What is Chlamydia trachomatis responsible for?
Causing nongonococcal urethritis (NGU) and can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
What is diphtheria, and what causes it?
A disease caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produces an exotoxin that inhibits protein synthesis.
What is the organism that causes Whooping Cough?
Bordetella pertussis
What are the three stages of Whooping Cough?
1. Catarrhal stage (common cold symptoms), 2. Paroxysmal stage (violent coughing), 3. Convalescent stage (chance for secondary infections)
What is the major virulence factor of Streptococcus pneumonia?
The capsule
What type of pneumonia is caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
Primary atypical pneumonia or 'walking pneumonia'
What organism causes Legionnaires Disease?
Legionella pneumophila
How is Legionnaires Disease transmitted?
By aerosol from sources like air conditioners and hospital waterlines
What organism causes Tuberculosis?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
What are tubercles in the context of Tuberculosis?
Lung lesions with tissue death
What is the treatment for Tuberculosis?
Drug cocktails often include isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol
What is the main cause of food poisoning due to preformed toxins?
Intoxications caused by organisms like Staphylococcus, Clostridium, and Bacillus cereus
What toxin does Staphylococcus aureus produce?
Enterotoxin A
What is Clostridium perfringens known for?
Making an enterotoxin and being an endospore former
What are the two enterotoxins produced by Bacillus cereus?
One induces vomiting and the other causes diarrhea
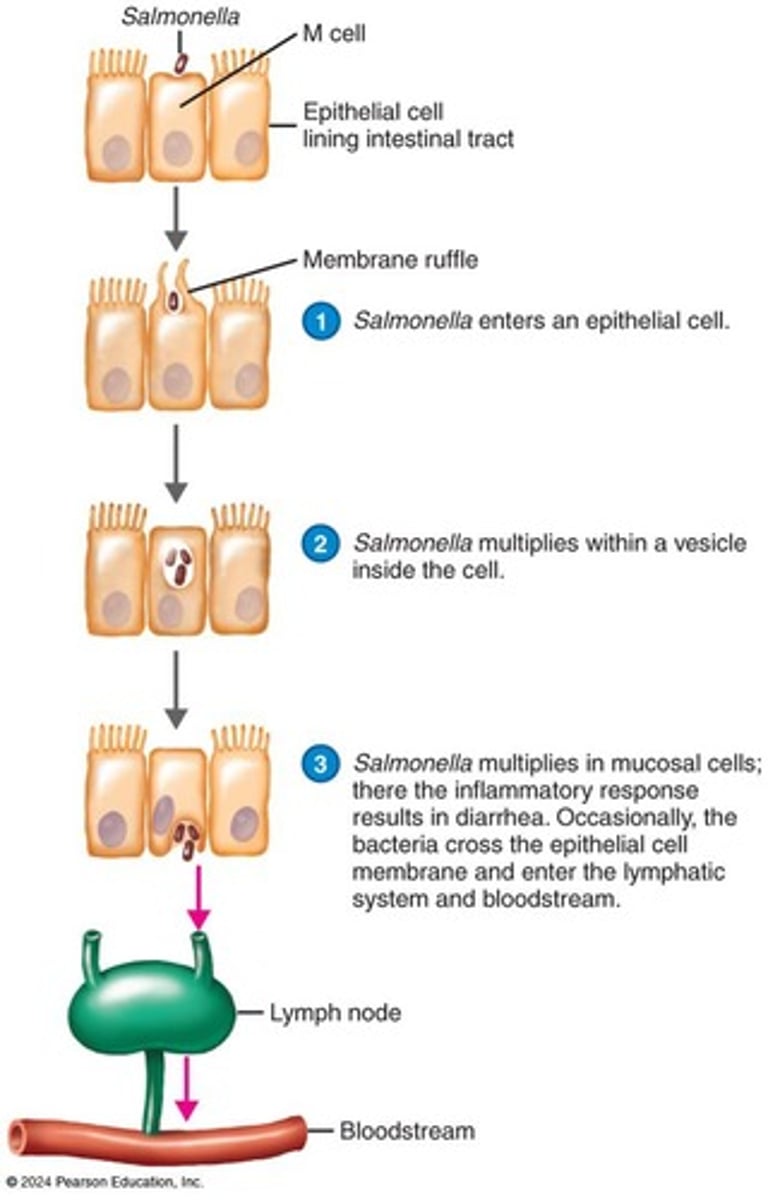
What organism is primarily responsible for Salmonellosis?
Salmonella enterica
What is Typhoid Fever caused by?
Salmonella typhi
What is a significant complication of Typhoid Fever?
Septicemia
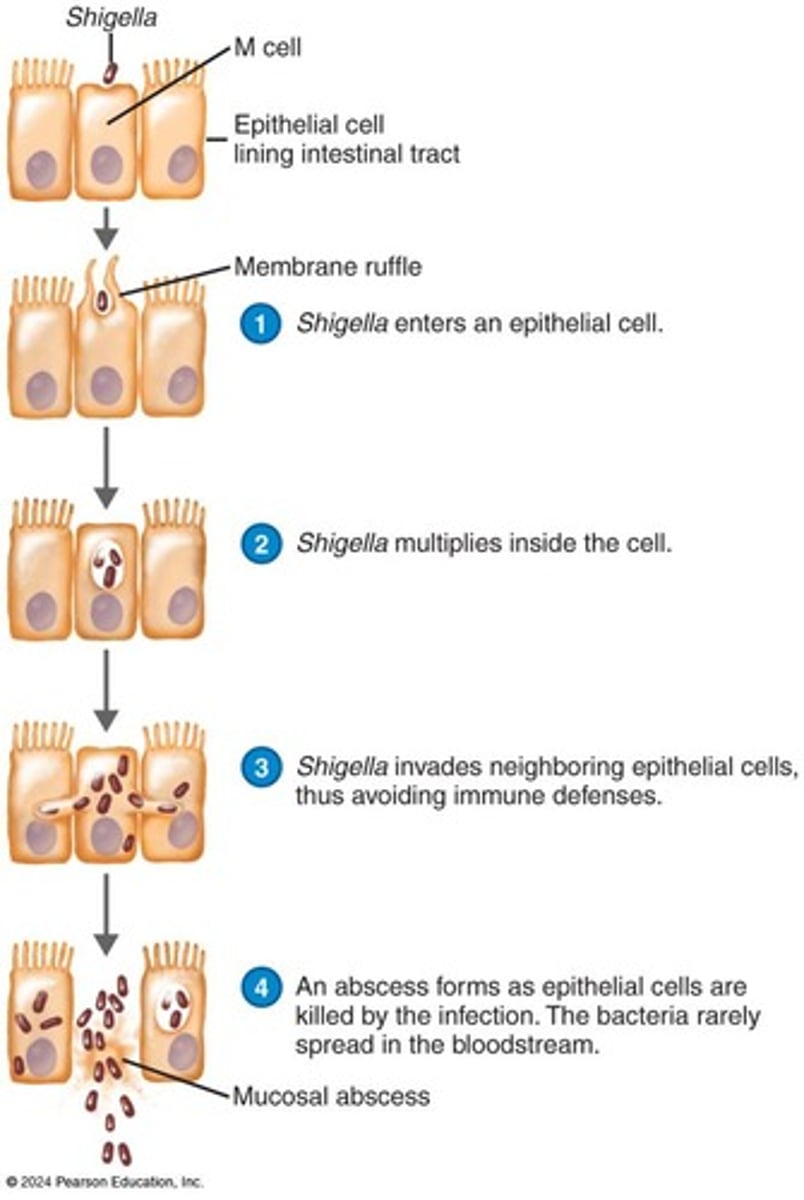
What is Shigellosis commonly referred to as?
Bacillary dysentery
What toxin does Vibrio cholerae produce?
Cholera toxin
What are 'rice water stools' associated with?
Cholera infection
What is the significance of Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)?
It can cause severe dehydration and is often the cause of traveler's diarrhea
What complication can arise from Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)?
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
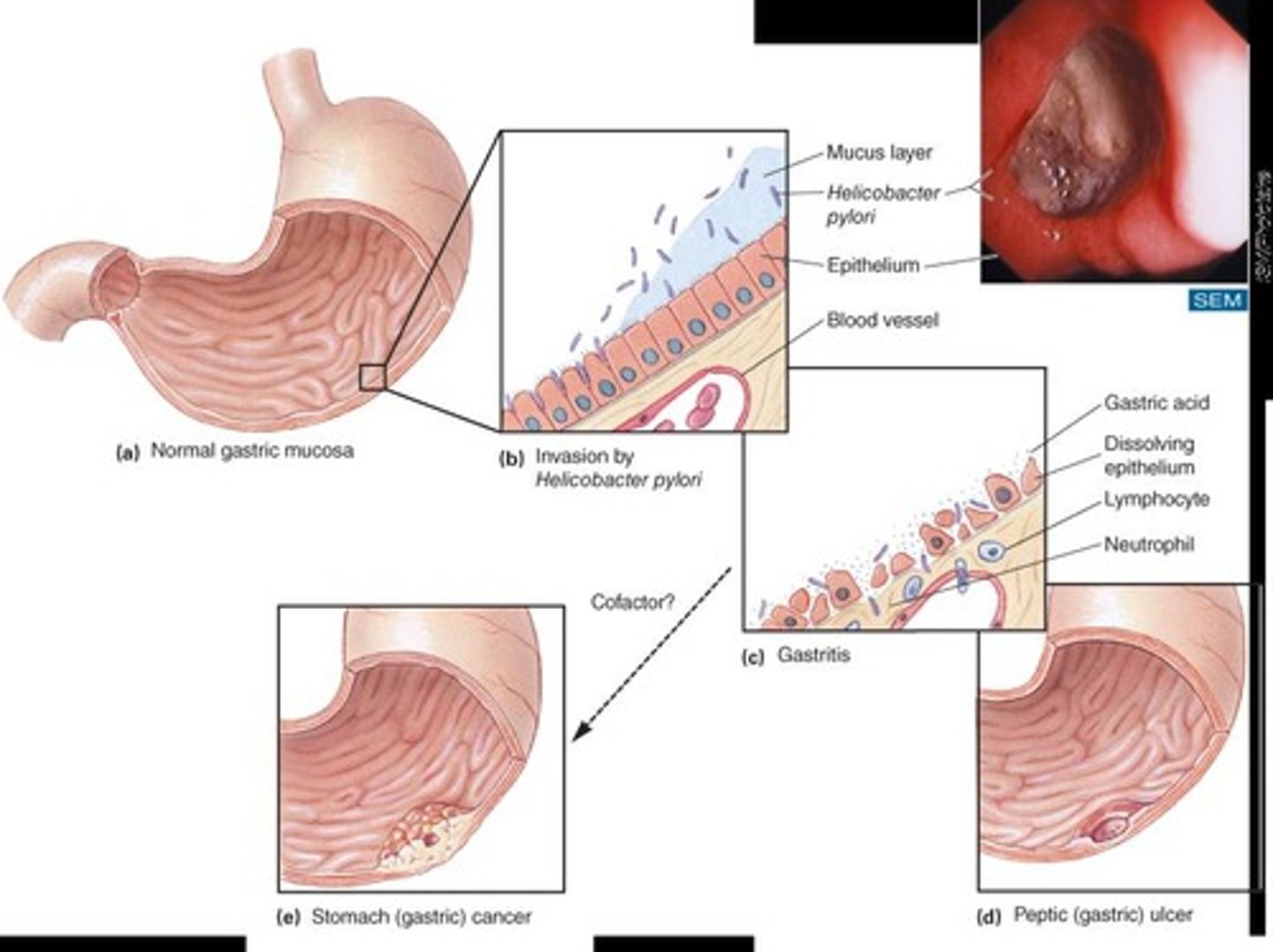
What organism is linked to peptic ulcers?
Helicobacter pylori
What is Clostridioides difficile known for?
Being a major cause of antibiotic-associated colitis and pseudomembranous colitis
What type of bacteria is Clostridioides difficile?
Gram-positive, anaerobic, endospore-forming rod
What is sepsis?
A systemic inflammatory response syndrome caused by mediators of inflammation entering the bloodstream due to an infection.
What is septicemia?
The presence of pathogenic microorganisms or their toxins in the blood.
What causes Puerperal Fever?
It is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, which can enter the bloodstream after vaginal delivery due to uterine wall irritation.
What is Group B Streptococci (GBS) and its significance?
Specifically Streptococcus agalactiae, it can cause neonatal sepsis with meningitis as a potential complication, transmitted through the birth canal.
What is Rheumatic Fever and its association with Strep Throat?
Caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, it can lead to complications like fever, rash, arthritis, and heart damage due to cross-reactive antibodies.
What organism causes Anthrax and how is it transmitted?
Bacillus anthracis causes Anthrax, transmitted through ingestion of contaminated food or inhalation of endospores.
What are the three forms of Anthrax?
Cutaneous, respiratory, and intestinal.
What is the role of exotoxins in Anthrax?
Exotoxins inhibit macrophages and interfere with the immune system, leading to septic shock and potential death.
What causes Gangrene and its mechanism?
Clostridium perfringens, an anaerobic endospore former, grows in oxygen-deprived tissues, leading to blood supply cut-off and potential death.
What is the causative agent of Plague?
Yersinia pestis, which produces exotoxins that inhibit macrophages and can cause pneumonic plague if it enters the bloodstream.
How is Lyme Disease transmitted and what is a key symptom?
Transmitted by ticks from deer and rodents, with the 'Bull's Eye Rash' being a telltale sign.
What are Rickettsial Systemic Diseases and their common symptoms?
Caused by gram-negative obligate intracellular parasites, they can cause fever, headache, weakness, and liver and spleen enlargement.
What causes Typhus Fever and its transmission method?
Caused by Rickettsia prowazekii, transmitted through body lice bites that release the organism into the skin.
What is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and its treatment?
Caused by Rickettsia rickettsia, transmitted by ticks, and treated with antibiotics.
What is Meningitis and its common causative organism?
An infection often caused by Neisseria meningitidis, which can lead to shock due to endotoxin production.
What is Listeriosis and its risk for certain populations?
Caused by Listeria monocytogenes, it can contaminate food and is particularly dangerous for immunocompromised individuals and fetuses.
What is Tetanus and its associated symptoms?
Caused by Clostridium tetani, it leads to muscle contraction and can result in death; commonly known as 'lockjaw'.
What is Botulism and how does it affect the body?
Caused by Clostridium botulinum, it produces a neurotoxin that prevents muscle contraction, leading to flaccid paralysis.
What is the risk associated with improperly canned food?
It can be a source of botulism due to the anaerobic conditions allowing endospores to germinate and produce neurotoxin.