Pharmacology
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What is pharmacology
The study of drug action on animals, organs, tissues or cells
How do drugs work
By mimicking or blocking endogenous signalling molecules
What are examples of signals used in pharmacology
Hormones
Cytokines
Growth factors
Neurotransmitters
Pheromones
What causes specific effects of drugs
The drugs chemical structure as a result of binding to specific targets
What causes non-specific effects of drugs
The drugs physiochemical characteristics
What are the typical targets of drugs
Enzymes
Ion channels
mRNA, DNA or epigenetics
Receptors
What chemical bonds are involved in drug action
Covalent bond
Ion - ion
Ion - dipole
Dipole - dipole
Hydrogen bond
Van der Waals
What is affinity
How tightly a ligand binds to receptor
What is specificity
The geometry of a drug
What is LD50
The dose of a drug which kills 50% of recipients when given to them
What is EC50
The concentration of a drug which is 50% effective on its recipients
How is the therapeutic index calculated
LD50 / EC50
What are the principles of mADME
The mechanism of action of
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Elimination
How do receptors work as drug targets
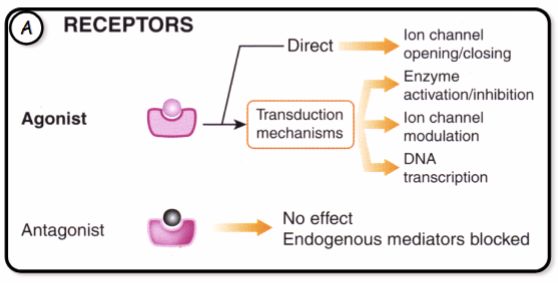
What are most drug receptors actually receptors of
Endogenous hormones or neurotransmitters
How are receptors specific
Each receptor only recognised a small number of molecules which all have some structural similarity
Is cannabinoids an agonist or antagonist
Agonist
Central and peripheral effects depending on orientation
Is histamine an agonist or antagonist
Antagonist in the gut
H1 causes smooth muscle cell contraction
H2 causes parietal cell acid secretion
What are the types of opiod receptors
δ receptors - hallucinations, agitation
μ receptors - pain relief, euphoria, respiratory depression, physical dependance
κ receptors - spinal analgesia, sedation
What is a ligand
A molecule that binds to a specific receptor
What is an agonsit
A molecule that binds to a receptor causing a conformational change that activates a response in the target cell
What is an antagonist
A molecule that binds to a receptors but initiates no response so is inhibitory to agonists
What is efficacy
The ability of a bound drug to activate the receptor and produce a response
How much concentration of a high affinity drug is required
Low concentration of ligand is required before all the receptor binding sites are occupied
What type of processes do agonists typically evoke
Reception
Transduction
Response
What is the reception of an agonsist
The binding between a signal molecule and receptor is highly
specificA shape change in a receptor is often the initial transduction of the
signalMost signal receptors are plasma membrane proteins
What is signal transduction
Usually involved multiple steps
Relay molecules amplify a signal and proves more opportunities for coordination and multiple cellular responses
What are some examples of the end point target of drugs
Calcium
An enzyme
A structural protein
A transcription factor
What are metabotropic receptors
G-Protein Couples Receptors
Single polypeptide
7 transmembrane domains
Ligand binds to either extracellular domain or within transmembrane domain
What are the common G-protein activated enzymes
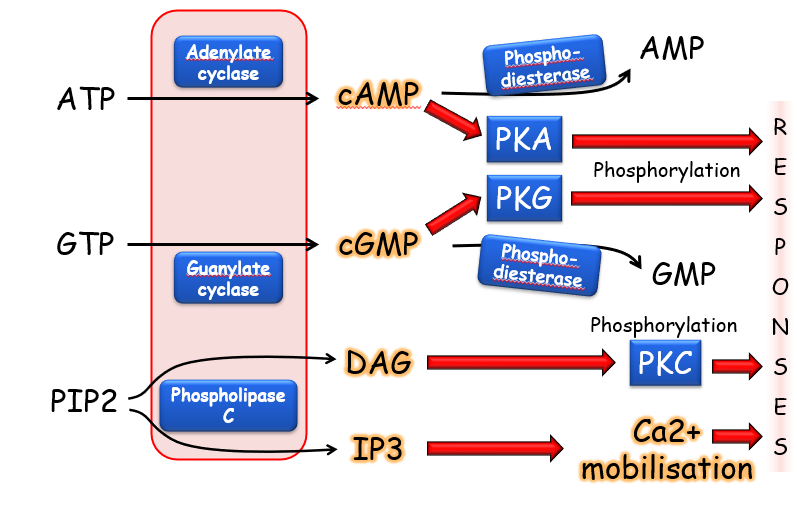
How do G protein couple receptors work
A ligand binds to the GPCR on extracellular side of cell membrane
Causes conformational change in GPCR
Activates G protein on the inside of the membrane
Made of three subunits, alpha, beta and gamma
GPCR causes alpha subunit to exchange GDP for GTP activating G protein
Gamma and Beta can now interact with target protein in the cell
How many genes code for GPCRs
800 genes which is about 4% of entire mammalian protein coding geonome
How does phosphorylation switch proteins on
Signal in on inactive protein
Phosphorylation by a kinase enzyme
Protein is now active and signal exits
Dephosphorylation by a phosphate enzyme
How does noradrenaline cause bronchodilation
Noradrenaline binds to beta 2 receptors
This activated G proteins which activated adenylyl cyclase
Activates cAMP
Activates protein kinase A which inhibits MLCK
Causes bronchodilation
What are the types of adrenoreceptors and what do they do
Alpha increase blood pressure and cause bronchoconstriction in the lungs
Beta 1 increase heart rate
Beta 2 causes bronchodilation in the lungs
What is the effect of adding an -OH group to noradrenaline
Greater activity of alpha and beta adrenoreceptors
What is a kinase-linked receptor
An enzyme linked receptor
Alpha subunit at the binding domain
Beta subunit at the kinase domain
Includes insulin-receptor
How do receptor tyrosine kinases work
Lignads bind to extracellular ligand binding domains of RTKs
Causes receptor monomers to pair up
Activated intracellular tyrosine kinase domains
Kinase domains phosphorylate each other on specific tyrosine residues
Intracellular signalling proteins bind to phosphorylated tyrosines
Activate signalling cascade
What are ionotropic receptors
Receptors linked to ion channels which are nicotinic
What are examples of nicotinic receptors
Cigarettes
Toxins
Poisons
What are examples of GABA
Alcahol
Sedatives
Are agonists and antagonists reversible
Agonists are always reversible
Antagonists can be irreversible or reversible
a-bungarotoxin is irreveriable
d-tubocurarine is reversible
What are the action of toxins on nicotinic ACh receptors
Block the receptors stopping muscle contractions
How does snake toxin poisoning cause death
Blocks nAChR of the mammalian end plate
Causes diaphragm paralysis
Leads to death
What is the structure of nAChR
5 subunits joined together
How are nAChRs involved in the central nervous system
Nicotine rich blood passes from the lungs to the brain within seven seconds
Stimulates immediate release of neurotransmitters
Responsible for nicotine’s effects
WHat is a GABAa receptor
GABA is an agonist
An inverse agonist binds to the agonist site and has the opposite effect to the agonist
Instead of enhancing GABAs inhibitory effect it reduces the activity of the GABA receptor
What is an allosteric modulator
Binds to a receptor on an allosteric site and changes the activity of the agonist
What are intracellular receptors
Typically steroid hormones
Hormones cross plasma membrane to bind to cycoplasmic receptors
This alters receptor conformation so it no longer binds inhibitor
Translocates to nucleus
Binds to DNA turning on transcription
Causes change in gene expression
What do transporters move across membranes and how
They move ions and chemicals against their electrochemical gradient using energy from ATP or ion gradients
Give an example of a drug that blocks a transporter
Digoxin blocks the Na+/K+ ATPase
How do tricyclic antidepressants and SSRIs affect monoamine transporters
Tricyclics block reuptake of noradrenaline and serotonin
SSRIs selectively block serotonin reuptake
Which neurotransmitter system is most linked with aggression according to transporter pharmacology
The serotonin system and low serotonin turnover is associated with increased aggression
What role to MAO inhibitors play in neurotransmitter regulation
They prevent the breakdown of monoamines like serotonin and dopamine, increasing their availability
What is an example of a calcium channel blocker and its clinical use
Verapamil used for hypertension, angina and arrhythmias
What ion channels do local anaesthetics like lidocaine block
Voltage gated sodium channels
What is the use of sulphonylureas and what channels do they block
Used as an anti-diabetic drug which block potassium channels in pancreatic beta cells
Why are local anaesthetics sometimes combined with vasoconstrictors
To prolong their effect by reducing systemic absorption
What are the characteristics of some local anaesthetics
Procaine - sort duration, poor tissue penetration
Lidocaine - moderate toxicity, fast onset
Mepivacaine - longer duration
Bupivacaine - high toxicity, very long duration
What type of inhibition does aspirin perform and on which enzyme
Irreversible, non-competitive inhibition of cyclooxygenase
Name two modern COX-2 selective NSAIDs used in veterinary practice
Firocoxib and Robenacoxib
What enzyme is targeted in the treatment of myasthenia gravis
Acetylcholinesterase, inhibited by neostigmine and edrophonium
What is the mechanism of neostigmine in myasthenia gravis
It inhibits acetylcholinesterase, increasing ACh levels at neuromuscular junctions
What is Michaelis-Menten
The binding of a drug to a receptor follows the same kinetics as an enzyme reaction
What does the Michaelis-Menten curve look like
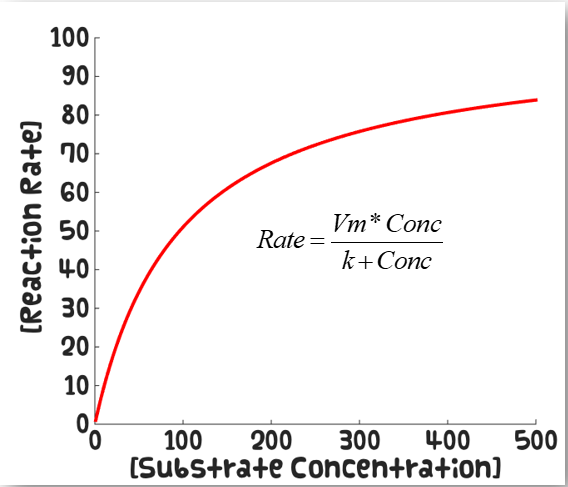
How do high and low affinity drugs differ on the Michaelis-Menten curve
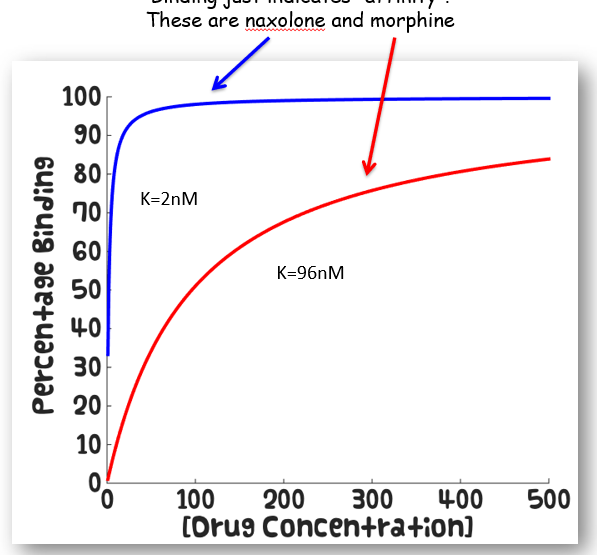
How do drugs with high and low efficacy appear on the Michaelis-Menten curve
Calculate EC50 by taking the log and reading at 50% response
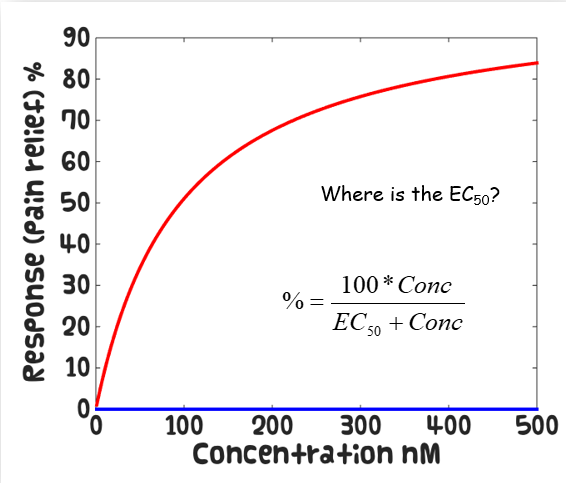
How do competitive antagonists effect the Michaelis-Menten curve
Causes parallel shifts
How do non-competitive antagonists effect the Michaelis-Menten curve
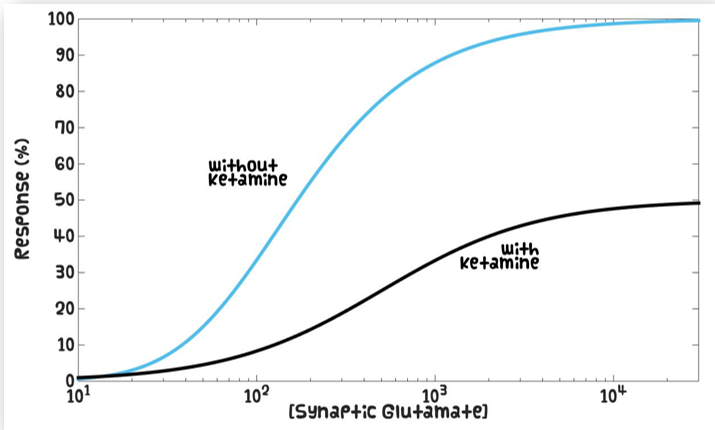
What factors effect drug absorption from the site of administration
Physical and chemical properties
Dosage form
Route of administration
What are the main routes of drug administration
Oral
Intravenous
Intramuscular
Subcutaneous
Inhalation
Topical
Which route of drug administration bypasses the absorption phase
Intravenous administration
What is bioavailability
The fraction of an administered dose of a drug that reaches systemic circulation in an active form
What is the first-pass effect
The metabolism of a drug in the liver after oral administration and before it reaches systemic circulation
What is the main barrier to drug absorption in the GI tract
The lipid bilayer of epithelial cells
What properties of a drug favour passive diffusion across cell membranes
Lipid solubility
Non-ionized state
Small molecular size
What determines the ionization state of a drug
The drugs pKa and the pH of the surrounding environment
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation used for in pharmacology
To determine the degree of ionization of a drug at a given pH
What is drug distribution
The reversible transfer of a drug from the bloodstream to tissues and organs
What factors influence drug distribution
Blood flow to tissues
Drug binding to plasma proteins
Capillary permeability
Lipophilicity of the drug
What is the volume of distribution
A theoretical volume that relates the amount of drug in the body to the concentration of drug in the plasma
What does a high volume of distribution indicate
Extensive distribution of the drug into tissues
What does a low volume of distribution indicate
The blood in mainly confined to the plasma
How does plasma protein binding affect distribution
Only free unbound drug is active and can cross membranes, binding slows distribution and elimination
Which proteins commonly bind drugs in plasma
Albumin (acidic drugs) and α1-acid glycoprotein (basic drugs)
What is redistribution of a drug
The movement of a drug from one tissue to another affecting drug action duration
Why is the blood-brain barrier significant for drug distribution
It restricts drug entry to the CNS due to tight junctions and efflux transporters
What is meant by perfusion limited distribution
When a drug distribution is determined by blood flow
What is permeability limited distribution
When a membrane permeability limits drug entry into tissue
What is a prodrug
An inactive drug that requires metabolism to become active
What are the two phases of drug metabolism
Functionalisation reactions
Conjugation reactions
What is the main purpose of functionalisation reactions in drug metabolism
To introduce or expose a functional group to make the molecule more polar
Name some examples of functionalisation metabolic reactions
Oxidation
Reduction
Hydrolysis
Which enzyme family is most involved in functionalisation oxidation reactions
Cytochrome P450 enzymes
What is the main purpose of conjugation reactions in drug metabolism
To conjugate the drug with a polar molecule, increasing water solubility for excretion
Give examples of conjugation reactions in phase II metabolism
Glucuronidation
Sulphation
Acetylation
Methylation
Conjugation with amino acids
Conjugation with glutathione
Where do most drug metabolism reactions occur
In the liver
What is an example of a drug that undergoes significant first-pass metabolism
Morphine
What is enzyme induction drug metabolism
When a drug increases the activity or amount of metabolising enzymes, accelerating metabolism
What is enzyme inhibition in drug metabolism
When a drug reduces the activity of metabolising enzymes, slowing down metabolism