Java
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is a stack?
Data structure that removes items in reverse of the order in which they were inserted (Last in, First out → last item inserted will be the next to be removed)
Can stacks be implemented as linked lists?
Yes
How do you create a Stack object?
Stack s = new Stack();What are the two methods of stacks?
· push – adds item to the collection s.push(“A“)
· pop – remove the most recently added item String item1 = s.pop()
How do you implement a Stack as a Linked list?
You have to create a node
What happens to the method when implementing a Stack as a Linked list
· Push replaces add to start of list
· Pop becomes remove from start of list
What is a queue?
A data structure that removes items in the same order in which they were inserted (First in, First out)
What are the methods for queues?
· Enqueue – adds an item to a collection q.enqueue(“A”);
· Dequeue – removes the item that has been in the queue the longest String item1 = q.dequeue;
How do you create a queue?
Queue q = new Queue();What are the requirements of implementing a queue as a linked list?
· Requires some changes to keep track of the end of the list
· Must store a front and back node instead of just head
Can you implement queues as ArrayList?
Yes
Can you implement Stack as an ArrayList?
Yes
What is the benefit for having a doubly linked list?
A doubly linked list allows movement in both directions – has reference to next and previous node
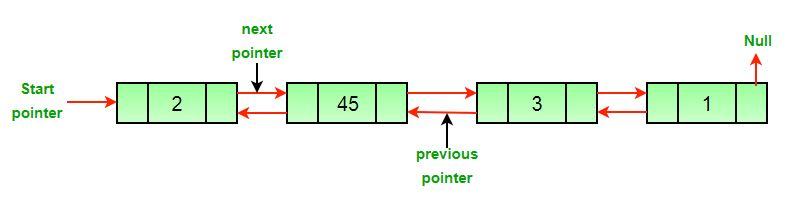
What does the .equals() compare two linked list?
Checks if they have the same node [may be dependent or independent of order]
How to create a deep copy for linked list?
To create a deep copy, you must traverse a linked list and create a (deep) copy of each node
What is an Iterator?
It is an object that enables object to iterator over their elements
How is iterators usually implemented?
Usually implemented as a public inner class
How to create an Iterator?
LinkedList.ListIterator i = list.iterator();
What does the .iterator() method return?
Iterator method returns an iterator
What are the two variables the Iterator uses?
Previous and position (Node type)
Example of how Iterator is implemented

What does the reset method of an Iterator do?
Restart: Resets the iterator to the beginning of the list
What does the hasNext method of an Iterator do?
hasNext: Determines if there is another data item on the list
What does the next method of an Iterator do?
next: Produces next data item, moves iterator one position forward
What does the peek method of an Iterator do?
peek: Produces next data item, without moving iterator forward
What does the addHere method of an Iterator do?
addHere: Add a node at the current position in the linked list
What does the delete method of an Iterator do?
delete: Remove the current node
What does the changeHere method of an Iterator do?
changeHere: Modify the current node
With an iterator - how do you read each element?
i.restart();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
How do you create a generic linked list?

How do you add node in linked list

How do you delete a node (linked list)

How to peek at a node (linked list)

How do you increment in a linked list

What are pros with linked list compared to array?

What are cons with linked list compared to array?
