Bio Hon Unit 2 Chemistry of Life (UPDATED 10-17; Still under construction)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
atom
Basic unit of matter.
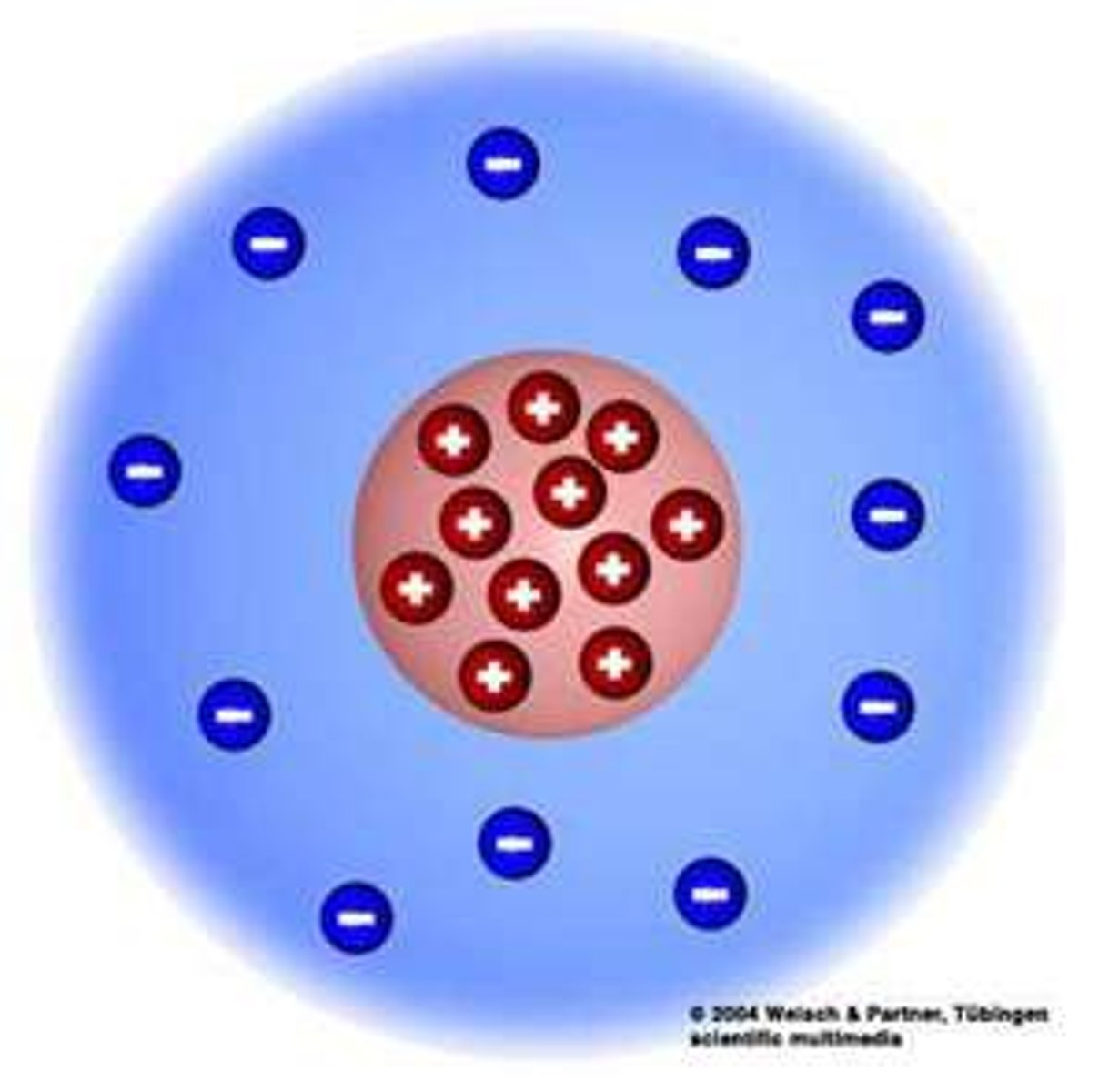
Nucleus
The center of an atom which contains protons and neutrons.
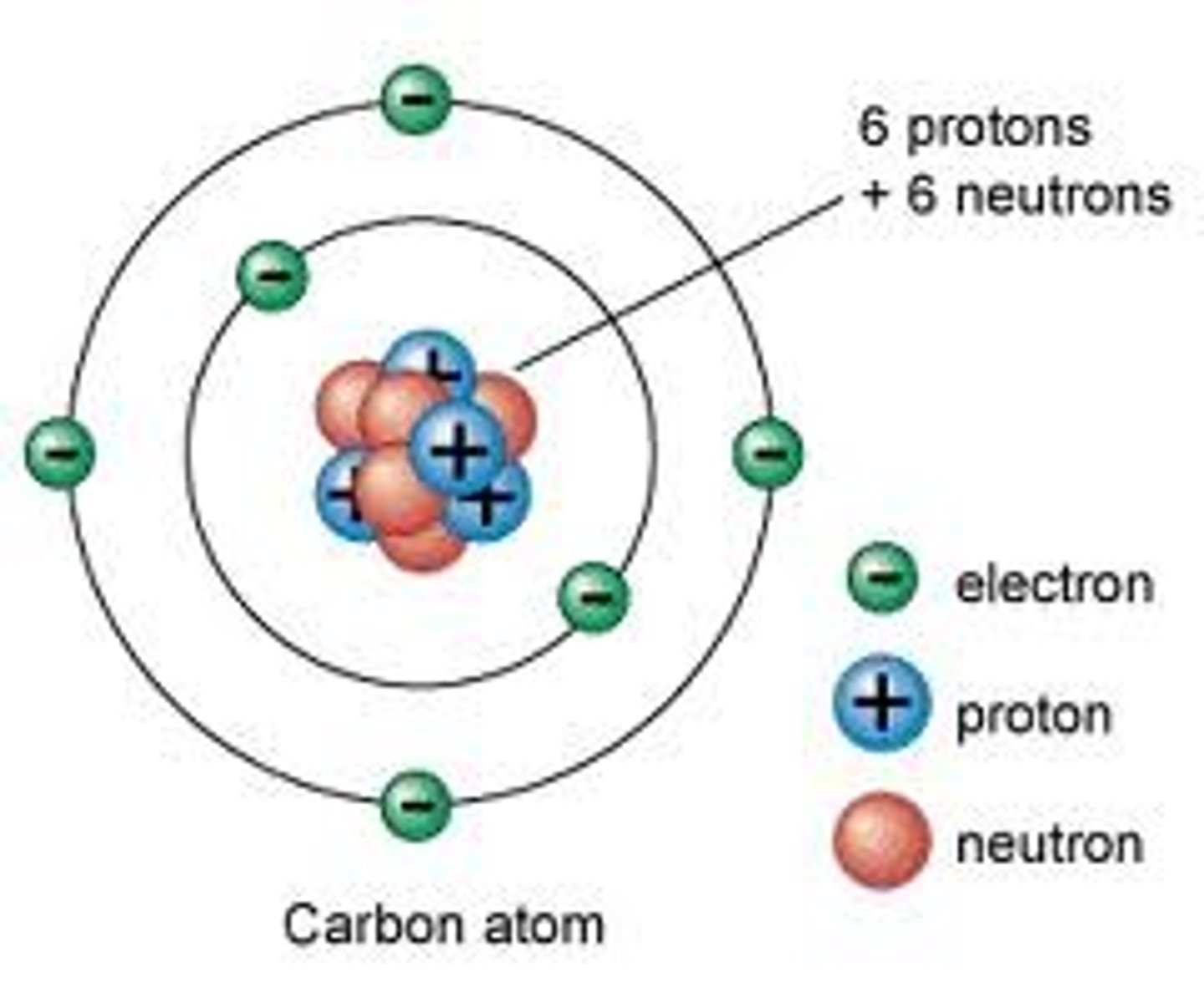
Electron
Negatively charged particle, located outside the atomic nucleus.
Ionic bond
Bond formed by attraction between oppositely charged ions. Occurs when one or more electronss are transferred from one atom to another.
Ion
Atom that has a positive or negative charge.

Covalent bond
Bond formed by sharing electrons.
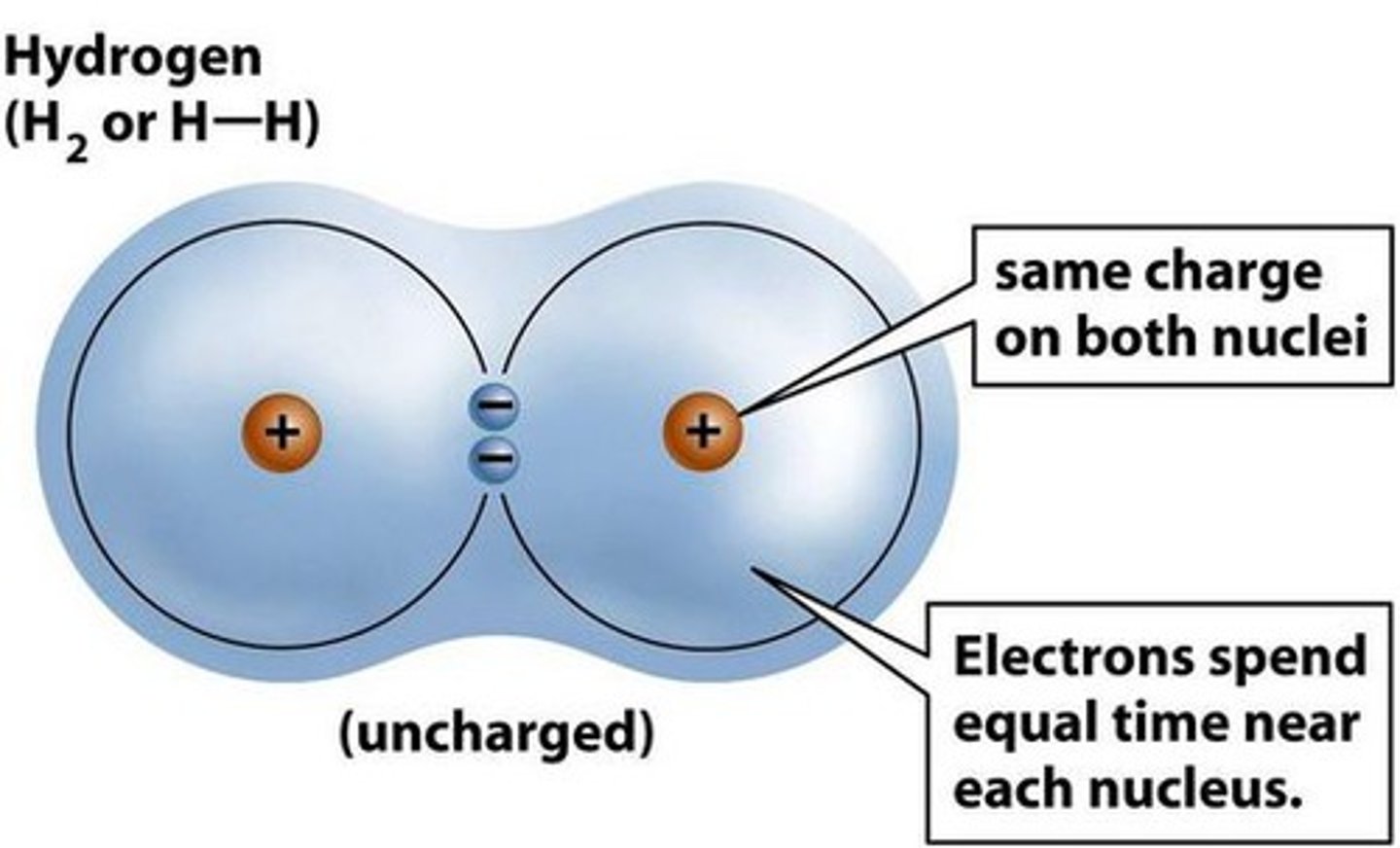
Molecule
Smallest unit of a compound.
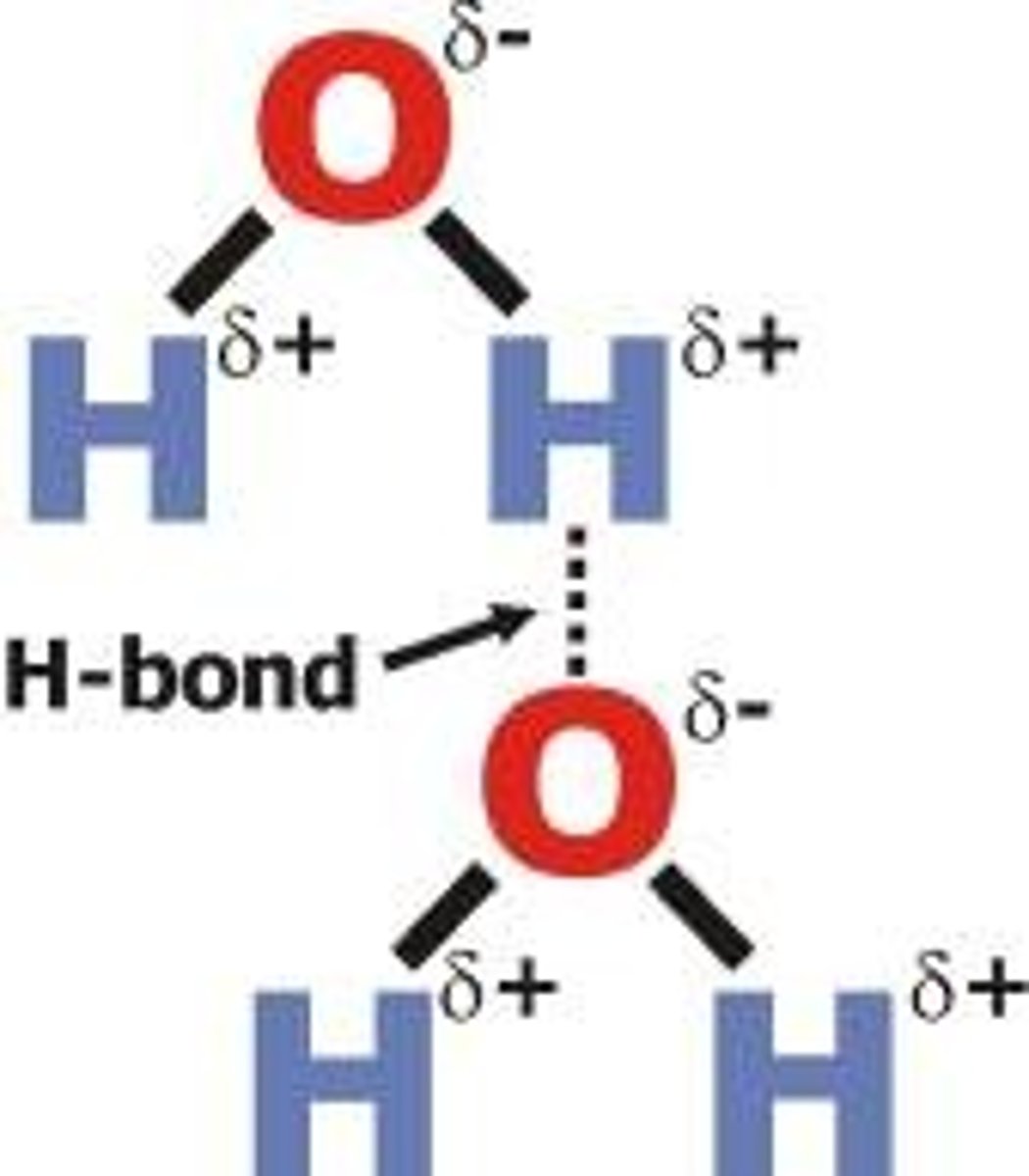
Hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
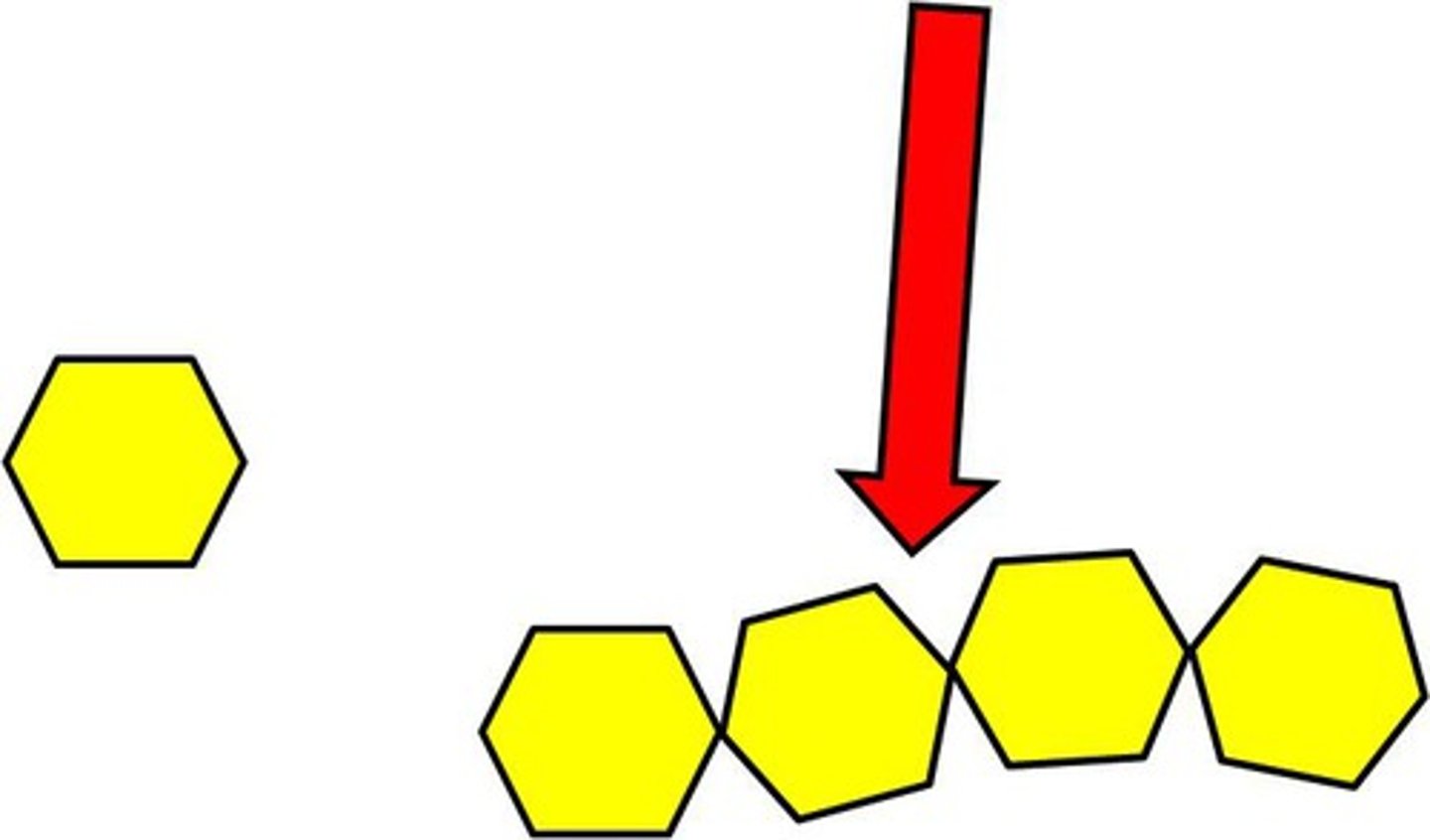
Monomer
Small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers.
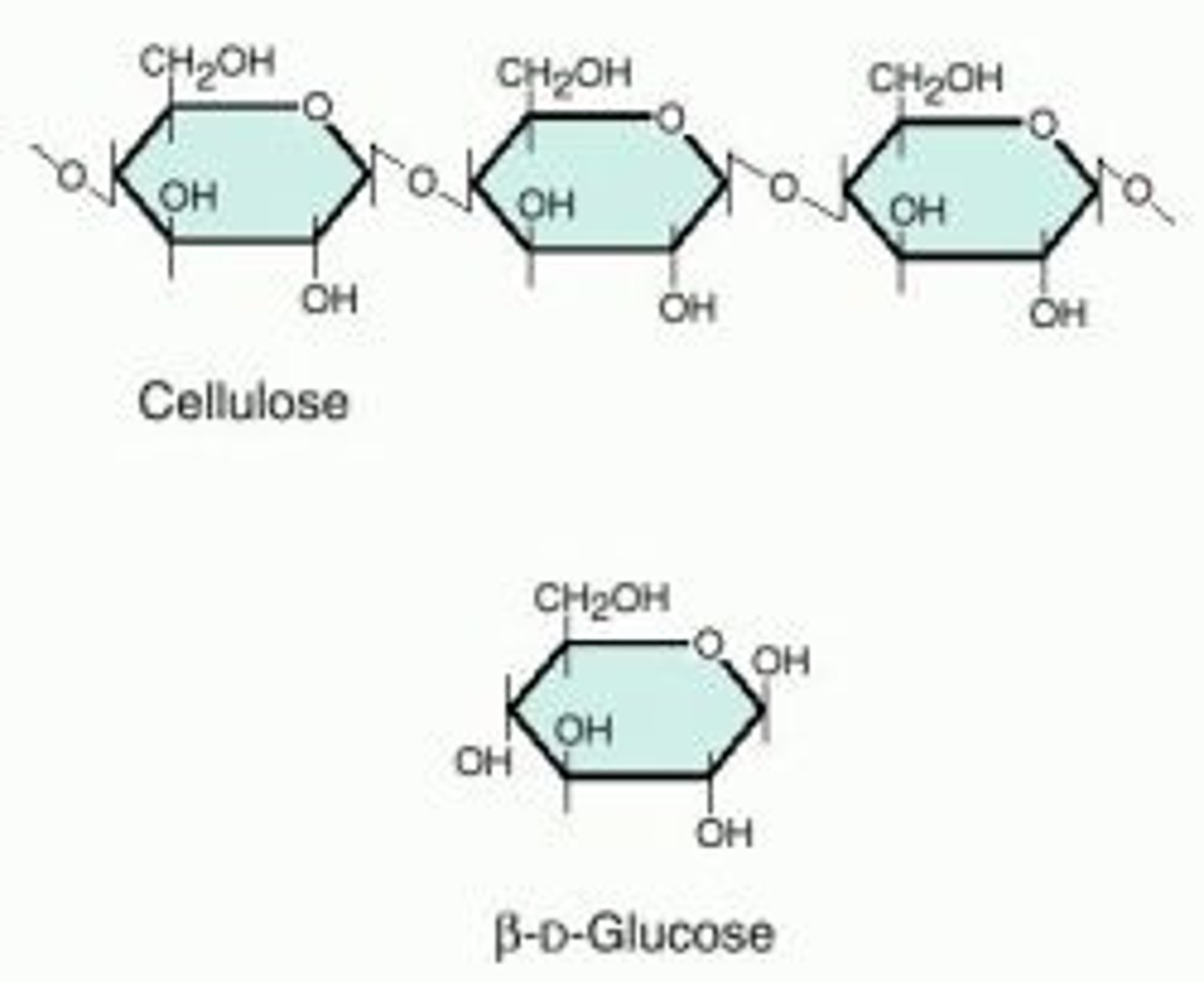
Polymer
Large compound formed from combinations of many monomers.
Carbohydrate
Compound made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Major source of energy for the human body.

Monosaccharide
Single sugar molecule (C6H12O6)
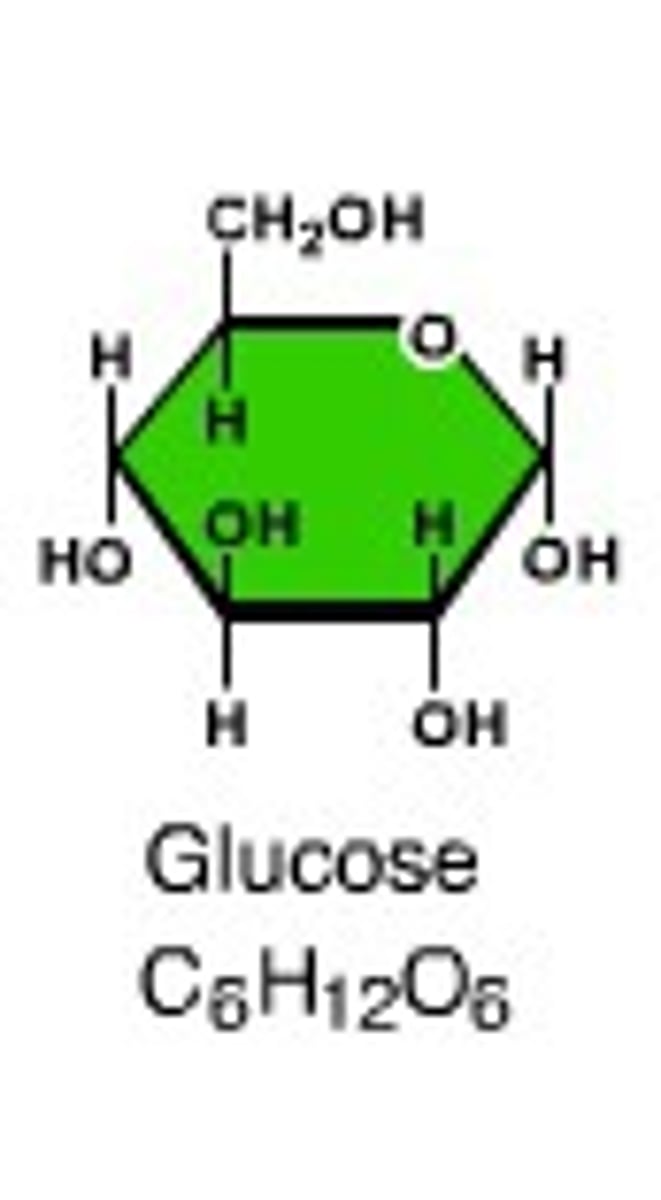
Polysaccharide
Large macromolecule formed from several monosaccharides linked together.
Lipid
Macromolecule made mainly form carbon and hydrogen atoms. Includes fats, oils, and waxes.
hydrogen bond
A type of weak chemical bond formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom in another molecule.
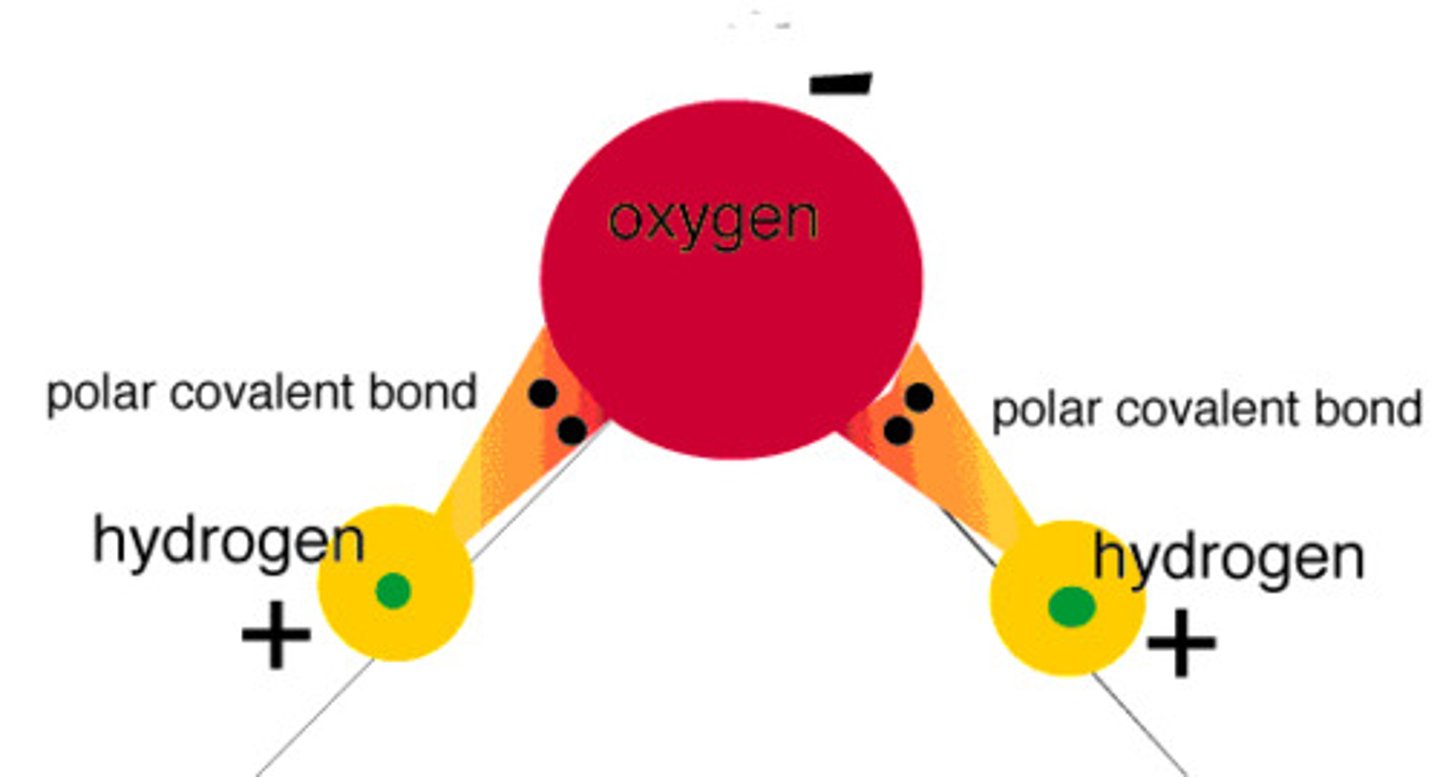
Why is water polar?
has polar covalent bonds; H is partially positive, O is partially negative
polarity of water results in
hydrogen bonding & good solvent of polar molecules
What causes surface tension in water?
strong cohesive forces between water molecules, specifically due to hydrogen bonds

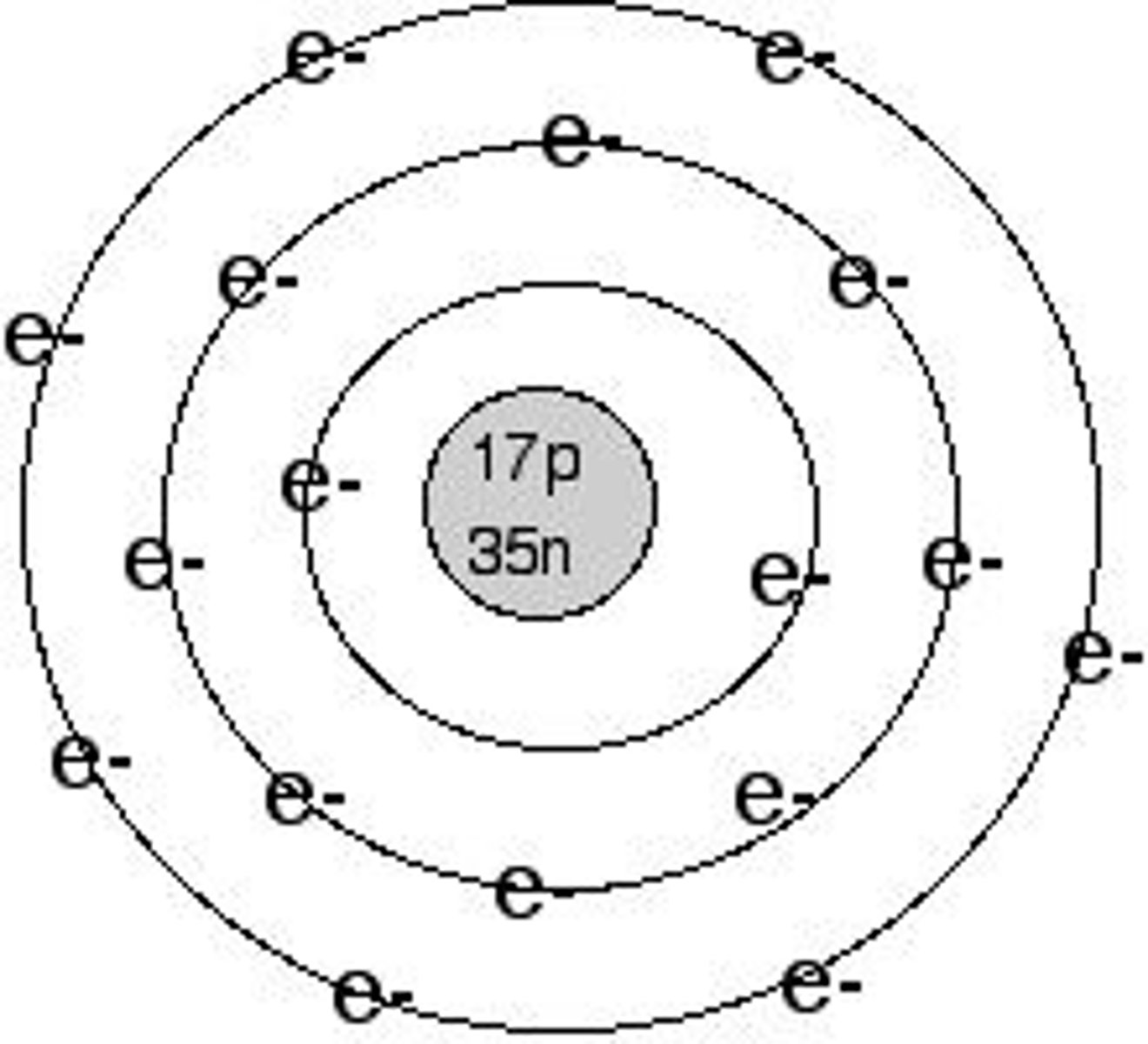
Atoms
The smallest unit of an element that retains all the properties of that element.
Stability of Atoms
An atom is more stable when its outermost energy level is filled.
Electrical Charge
An atom becomes an ion when its number of electrons does not equal its number of protons, resulting in an electrical charge.
Ionic Bond
Some atoms become stable by transferring electrons.
Covalent Bond
Formed when atoms share pairs of electrons in covalent bonds.
Shared Electrons
Shared pairs of electrons fill the outermost energy levels of the bonded atoms.
Water Molecule Properties
The oxygen atom attracts more than its share of electrons.
Hydrogen Bonds
An attraction between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, often oxygen or nitrogen.
Homeostasis
Ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite changing conditions.
High Specific Heat
Water must absorb a relatively large amount of heat energy to increase temperature.
Cohesion
Attraction among molecules of the same substance.
Adhesion
Attraction among molecules of different substances.
Capillary Action
Allowing water to travel upward against gravity.
Macromolecule
These are large molecules, often formed by joining smaller molecules together.
Monomers
Smallest unit of a large molecule (building blocks of things).
Polymers
The large molecule formed by joining monomers.
2 Functions of Carbohydrates
1. Energy source 2. structural.
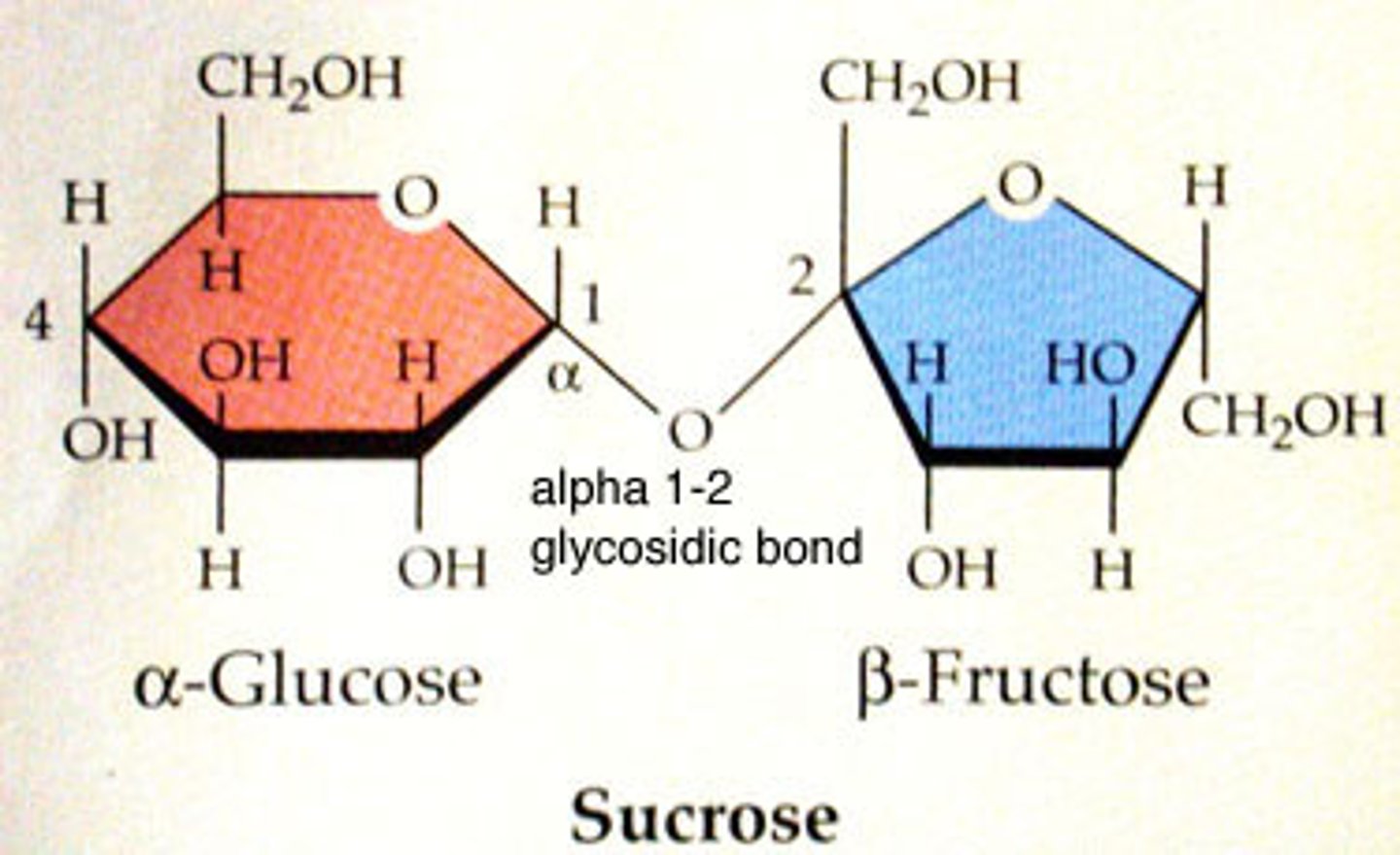
Disaccharide
2 sugars. Ex. sucrose
Elements of Carbohydrates
C, H and O
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars like glucose, galactose, and fructose.
Glucose
Made during photosynthesis; Main source of energy for plants and animals.
Fructose
Found naturally in fruits; Is the sweetest of monosaccharides.
Galactose
Found in milk; Is usually in association with glucose or fructose.
Disaccharide Definition
Two monosaccharides bonded together.
Sucrose
Made up of glucose + fructose bonded together.
Lactose
Made up of glucose + galactose bonded together.
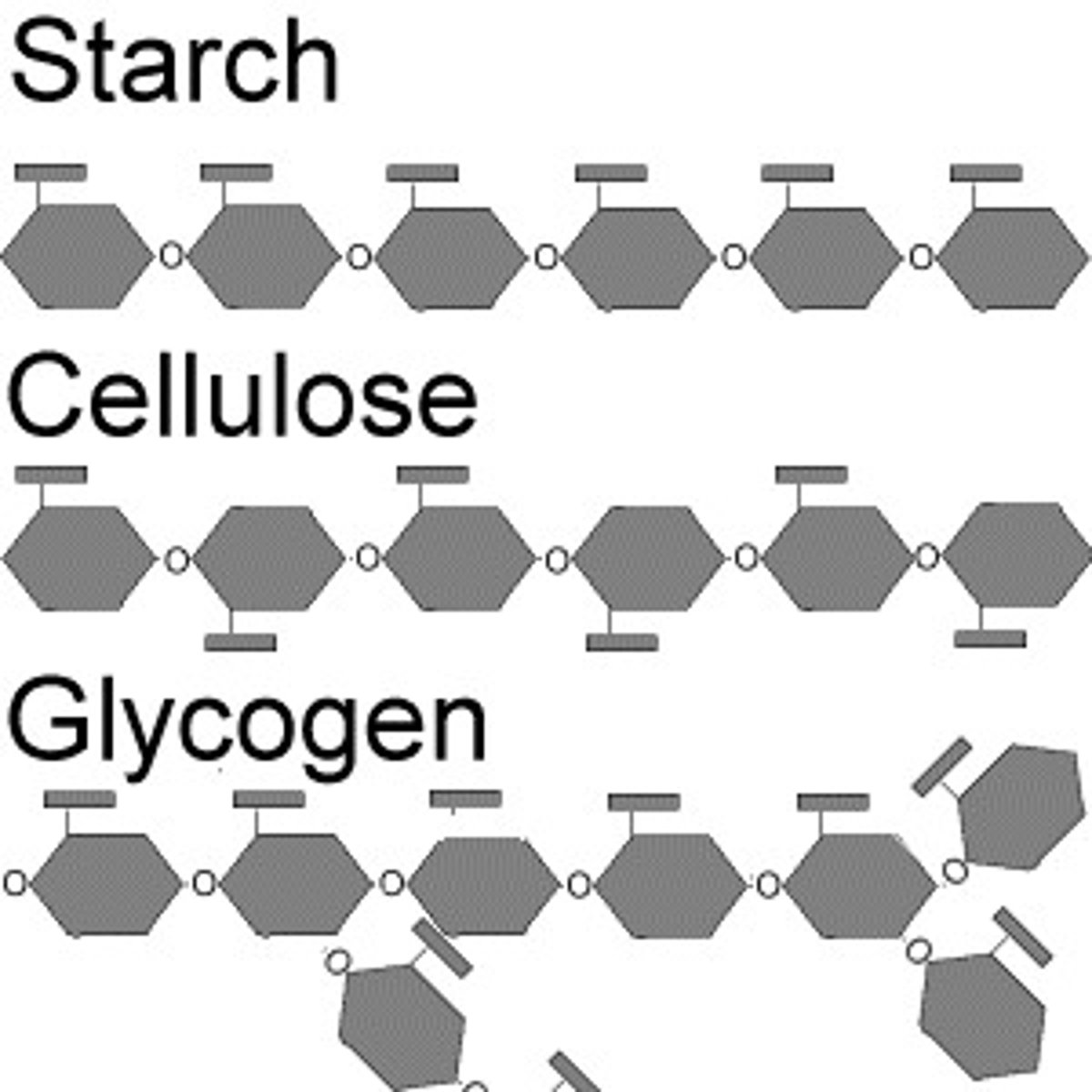
Storage Polysaccharides
Examples include starch and glycogen.
Examples of Structural Polysaccharides
Examples include cellulose and chitin.
Complex Carbohydrate
A polysaccharide with many monosaccharide units.
Lipid polarity
non-polar (hydrophobic)
Elements of Lipids
C, H, O
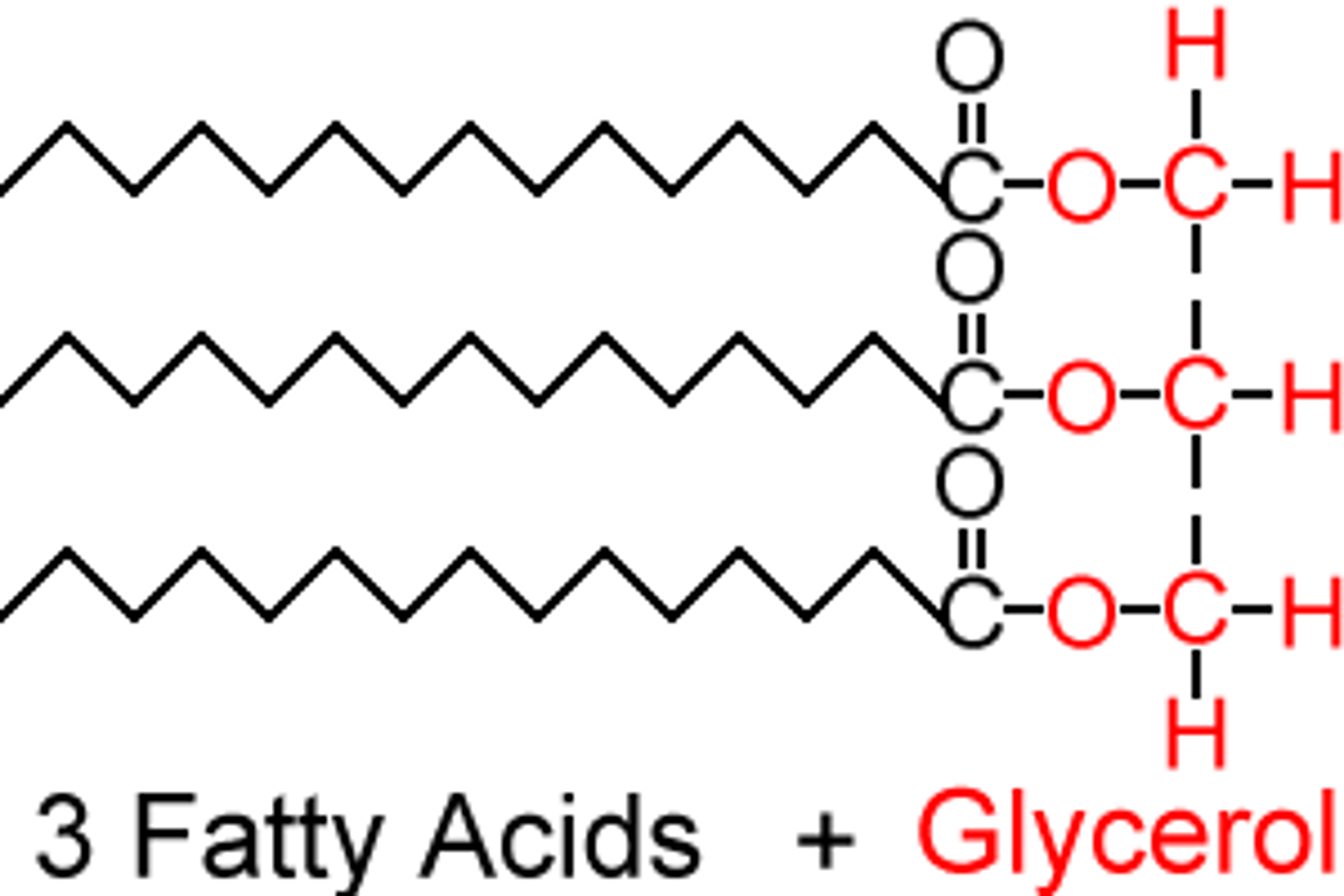
Building Block of Lipids
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
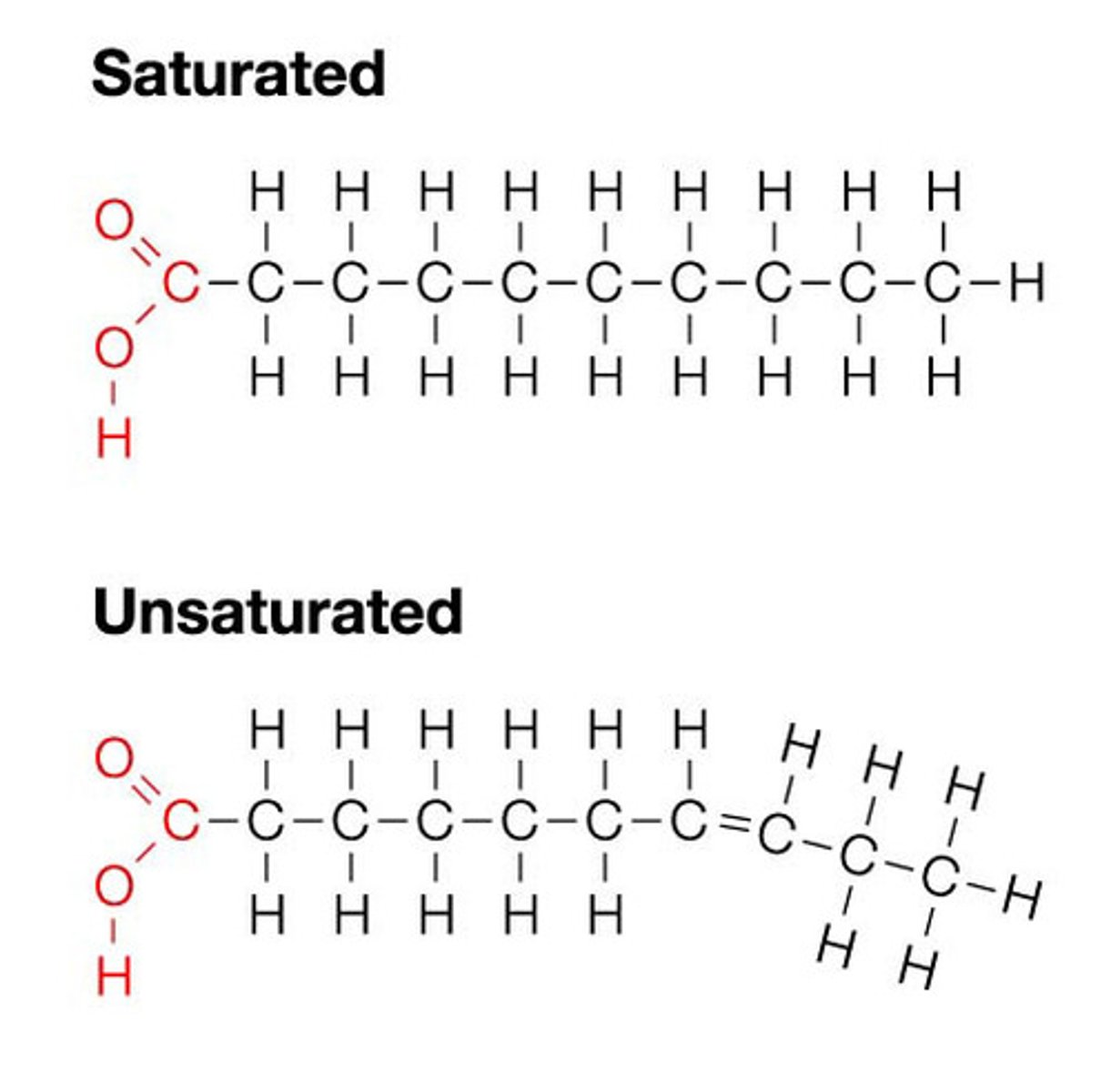
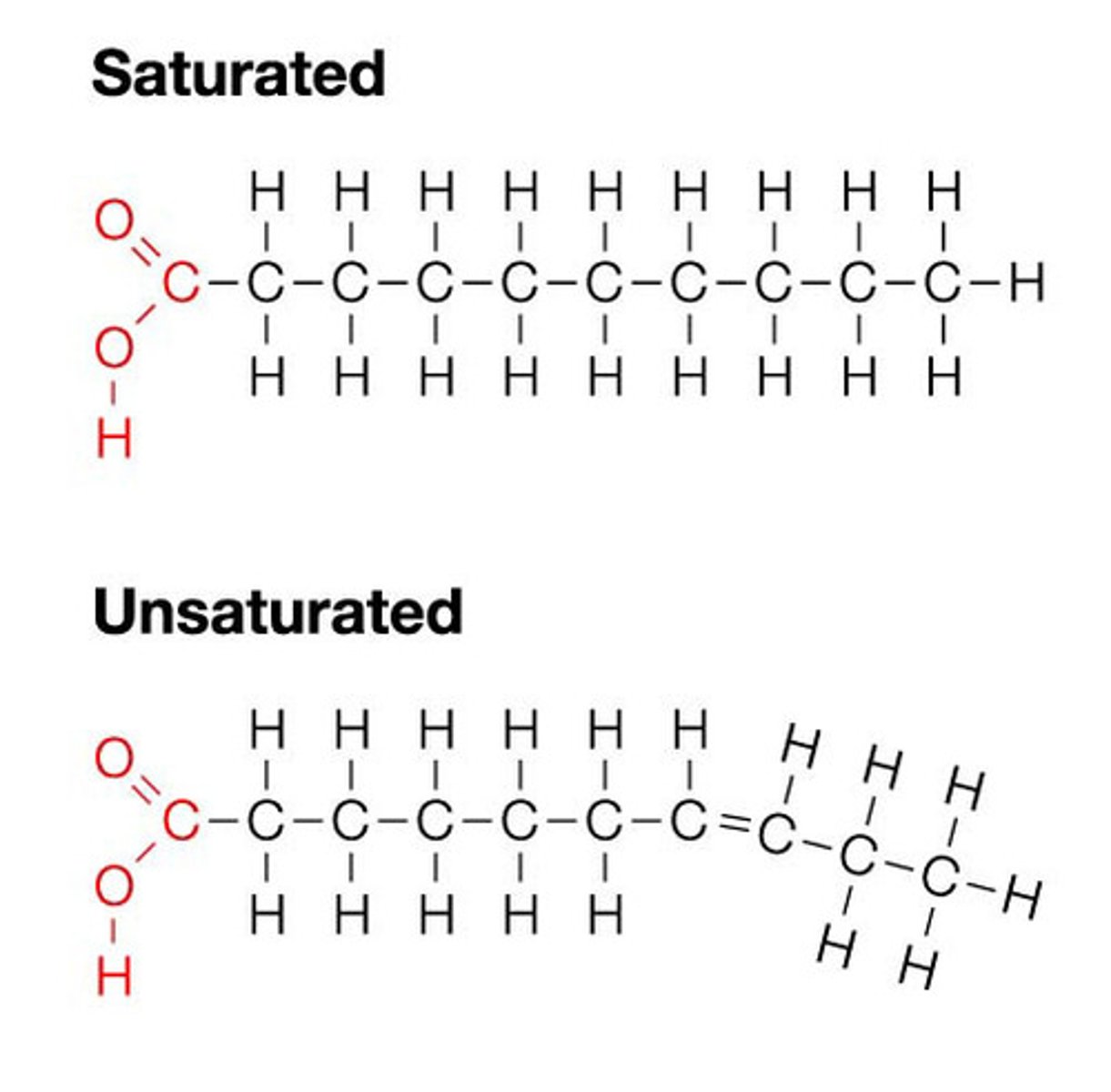
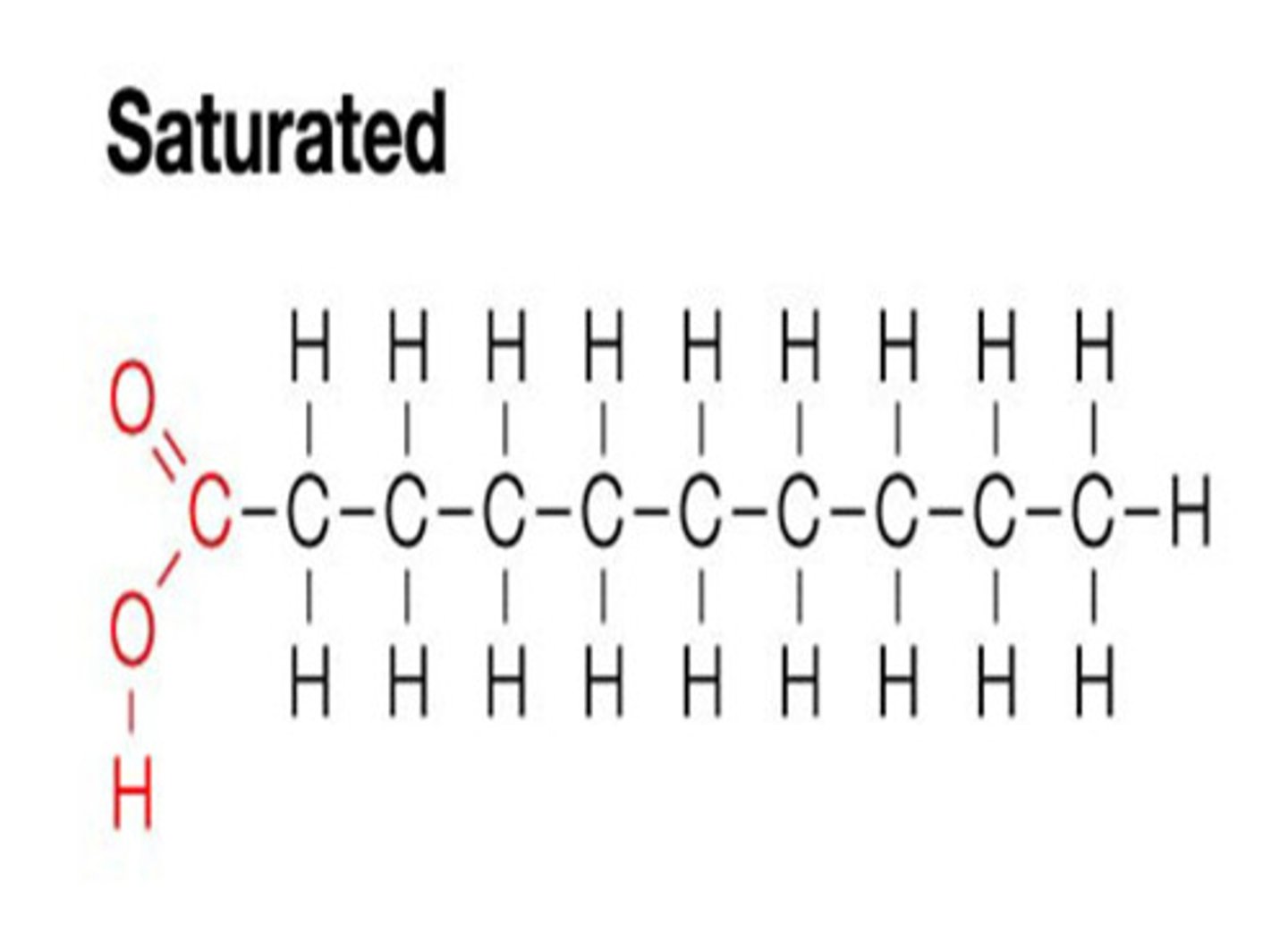
Saturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are 'full' of Hydrogens; all carbon bonds are single. Solid at room temp.
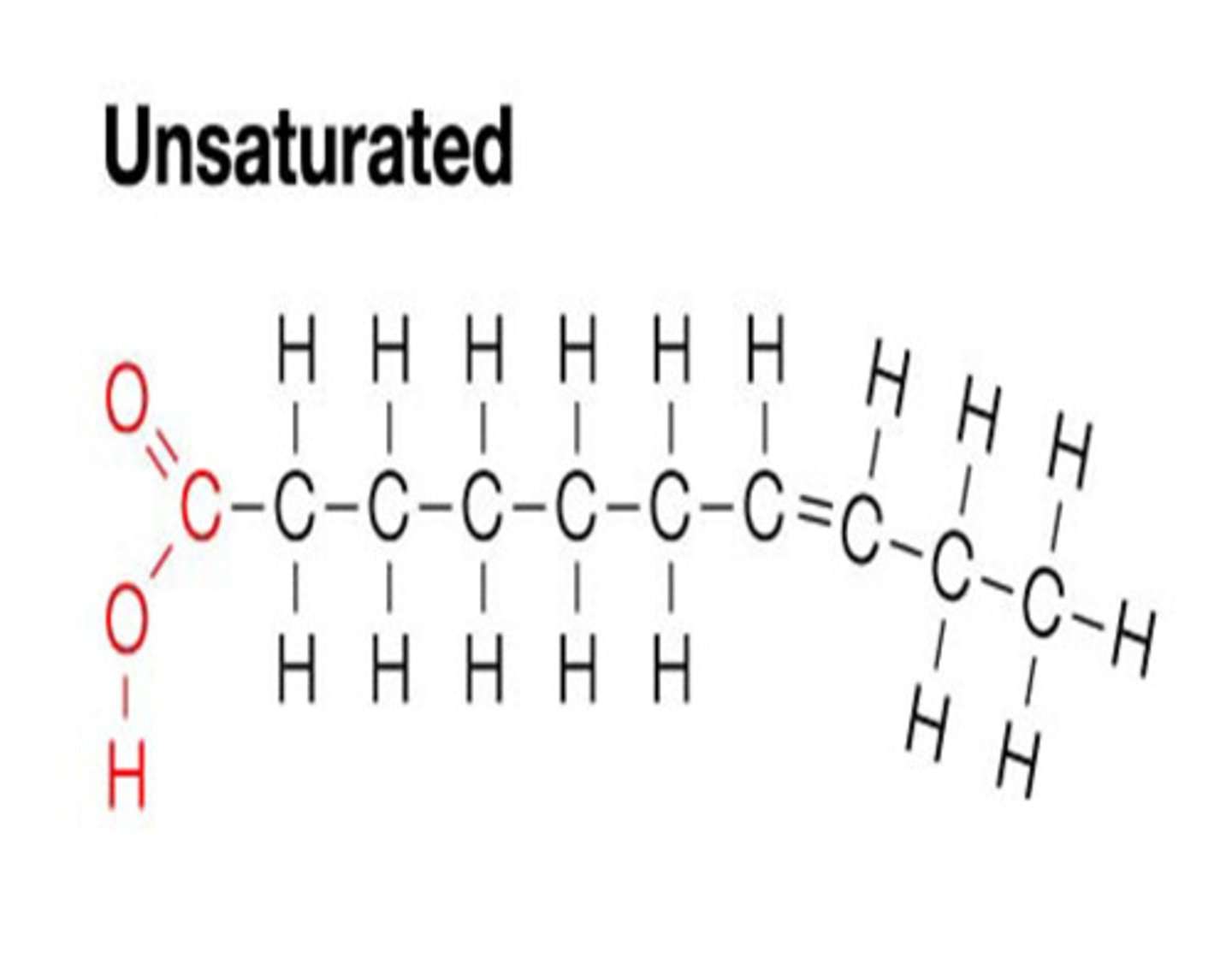
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
At least 1 double bond between carbons. Liquid at room temp.
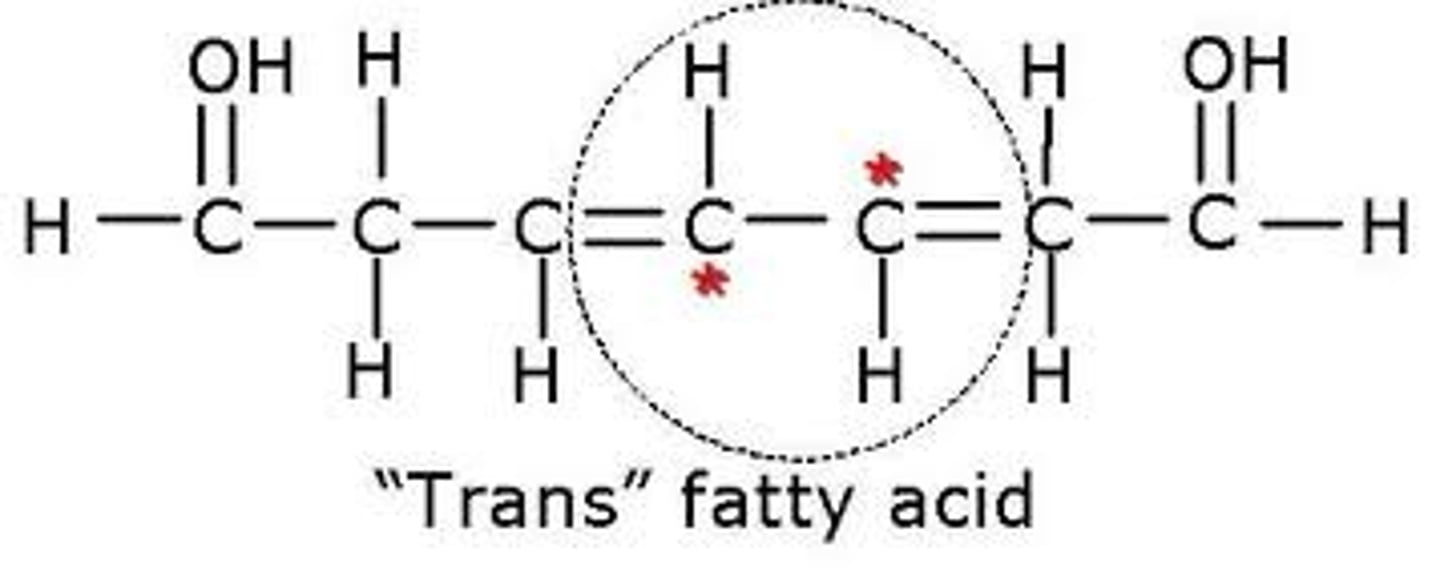
Trans Fats
Made by humans; takes an unsaturated and makes it act saturated.
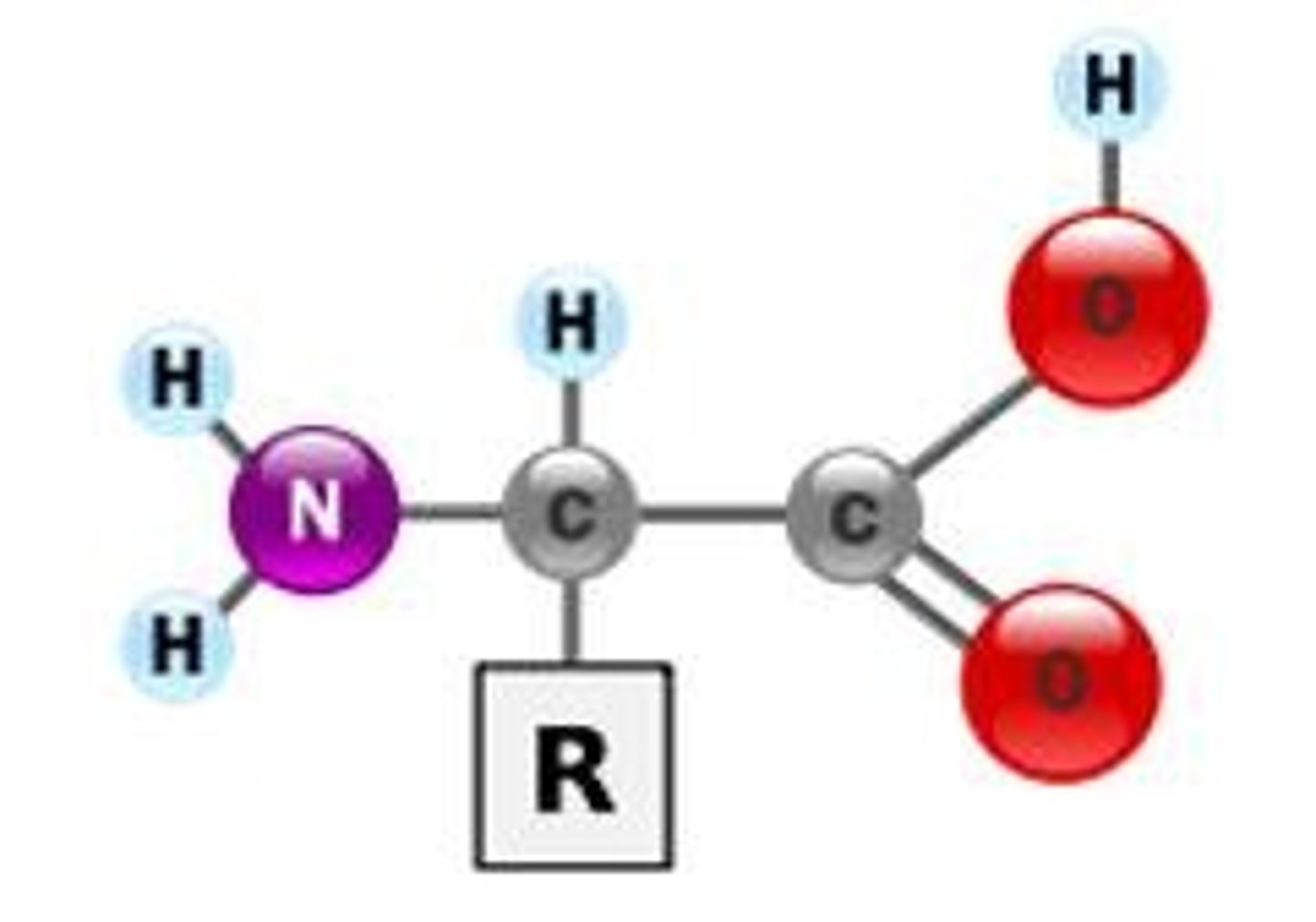
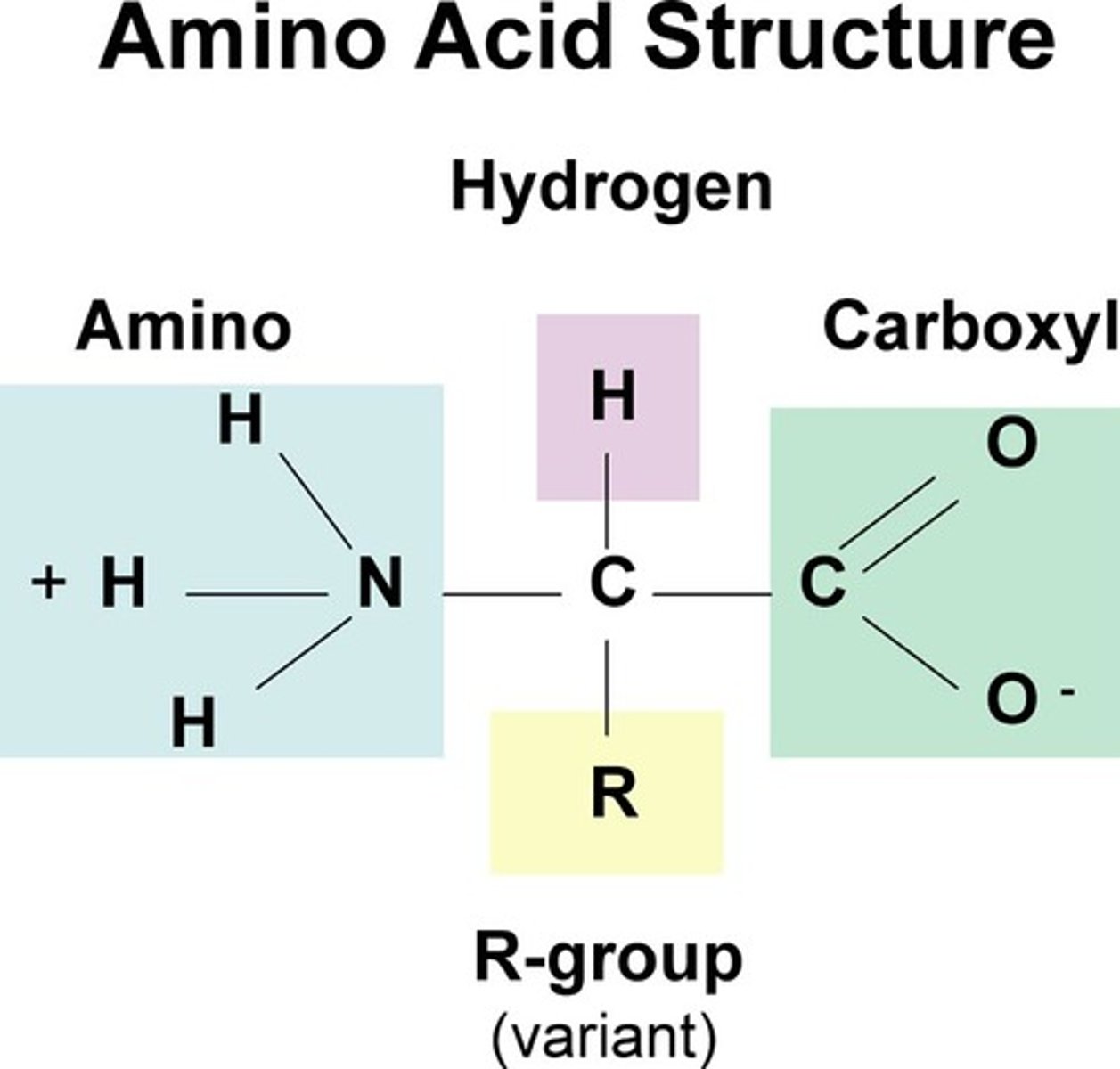
Amino Acid
Monomer of protein with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end.
# of Amino Acids
20
Essential Amino Acids
Amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own and must be obtained through diet.
Non-Essential Amino Acids
Can be synthesized by the body and do not need to be consumed through food.
Functional Groups of Amino Acids (NOT ON TEST)
An amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a side chain (R group).
Functions of Proteins
-controls rate of reactions
-transport
-structural
-protective
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose.
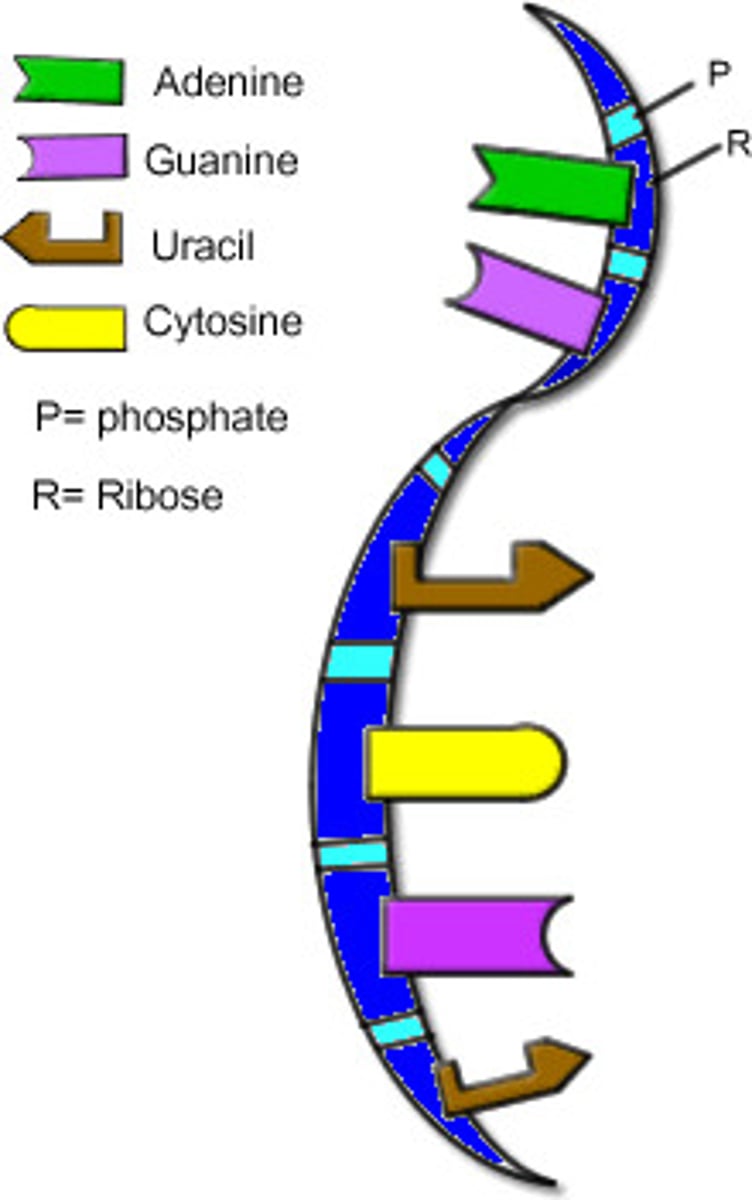
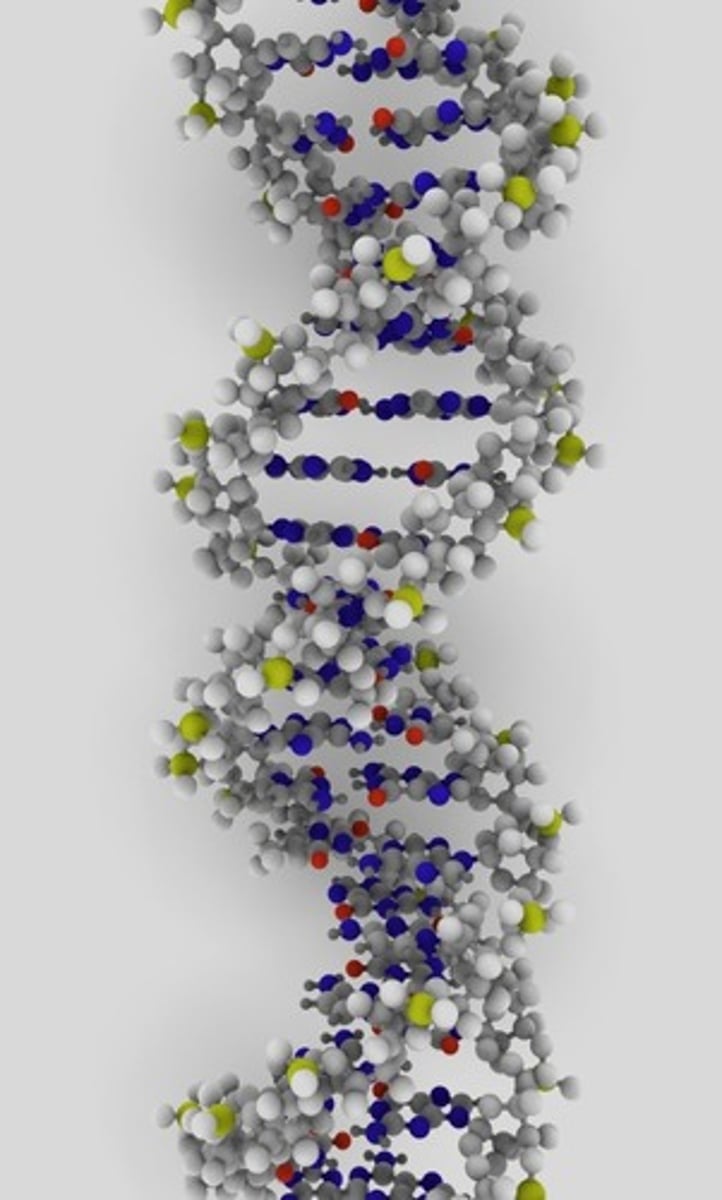
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Double-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar deoxyribose.
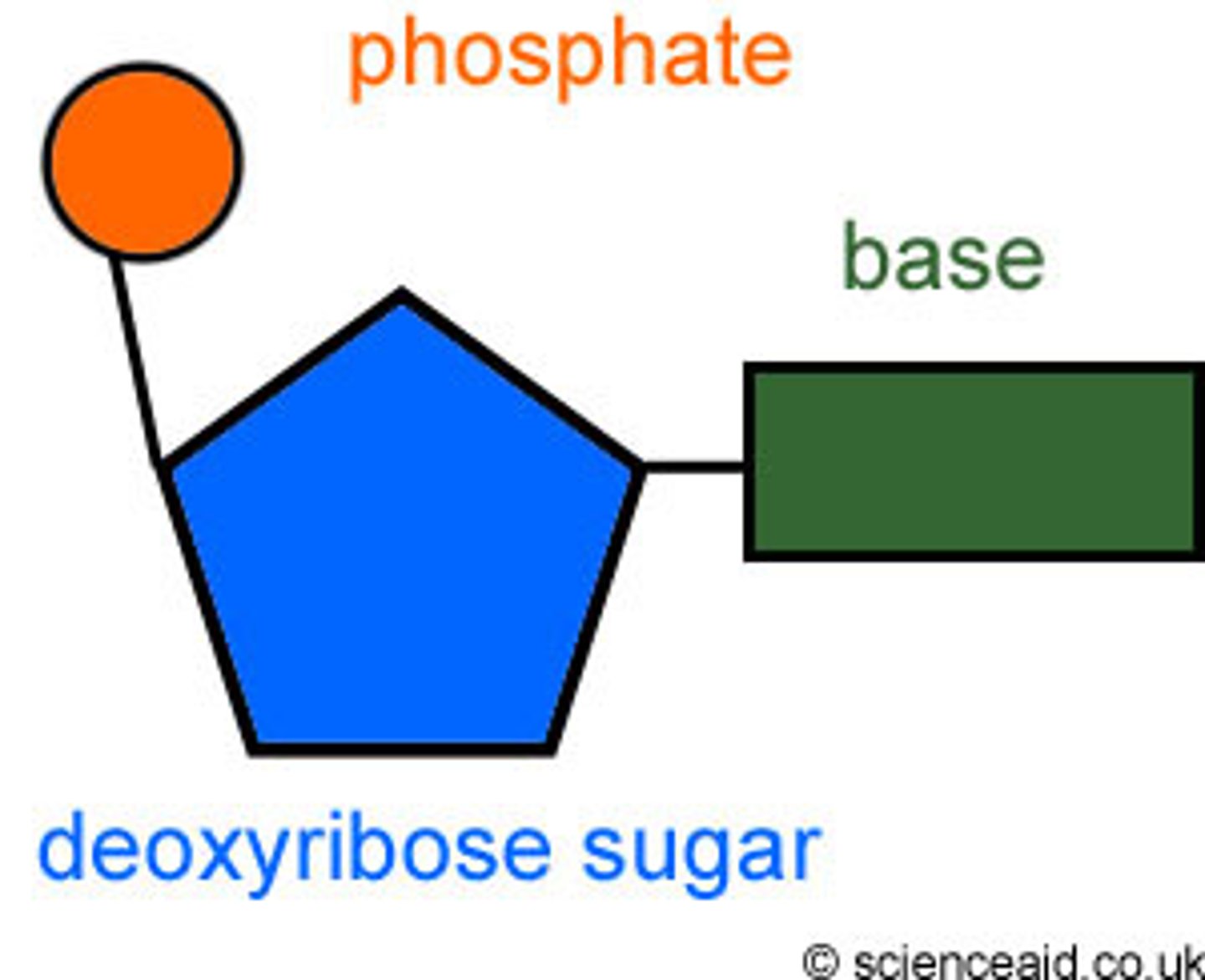
Nucleotide
Monomer of nucleic acids
2 forms of nucleic acids
DNA or RNA (can be single or double-stranded; linear or circular)
functions of lipids
- E storage
-waterproofing
-insulation
-cell membranes
functions of nucleic acids
store and transmit information
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule.
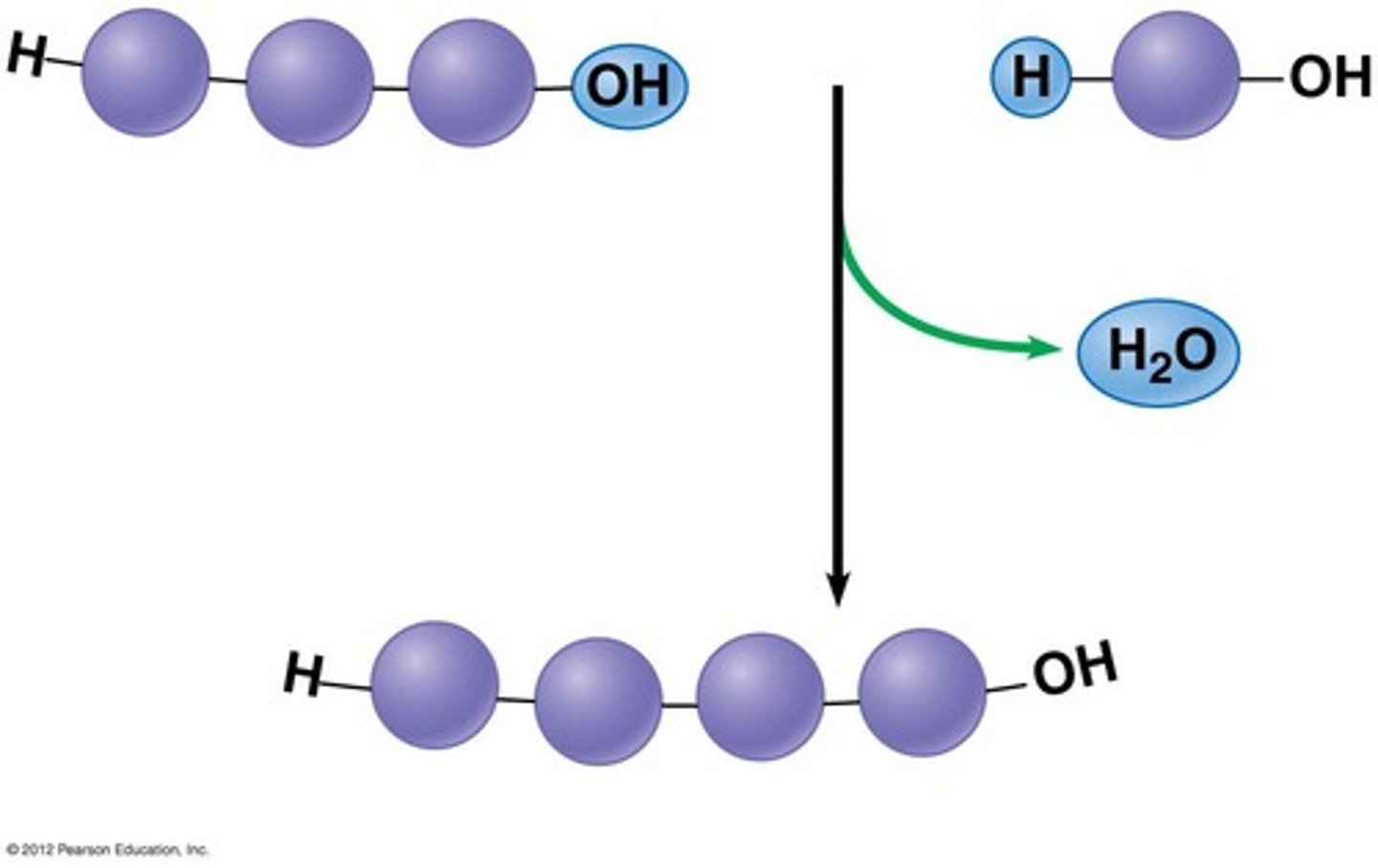
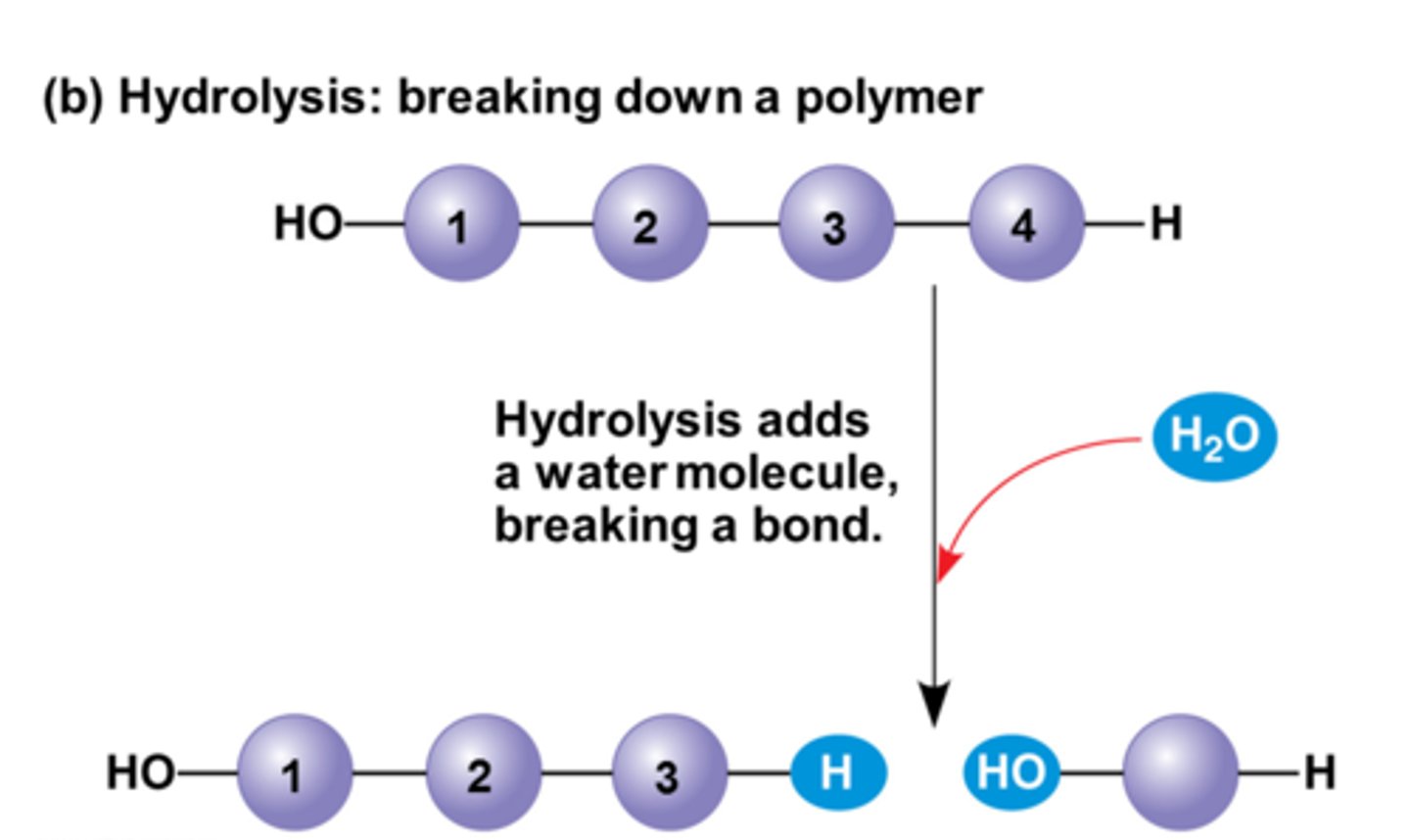
hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water.