biology unit 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what are monomers for carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
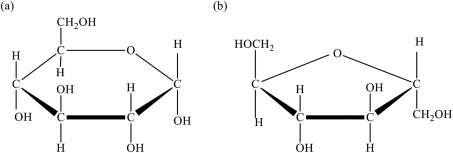
what makes up the structure of a monosaccharide?
a sugar backbone
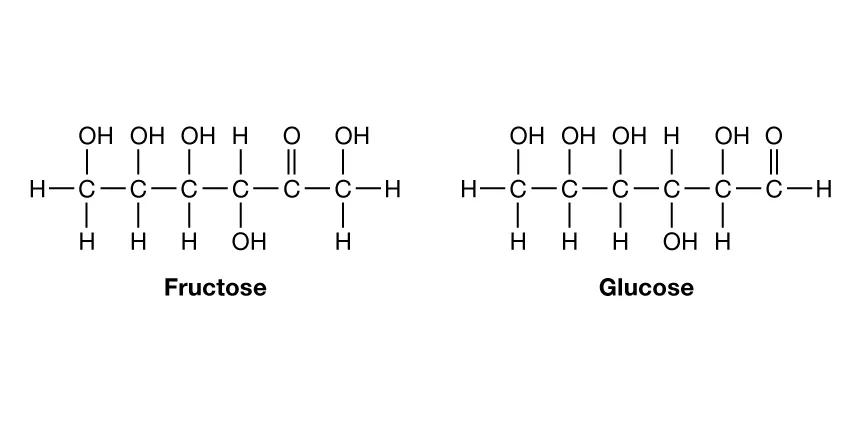
what does the structure of a carbohydrate look like?
carbon backbone w/oxygen attatched
what’s the role/function of carbohydrates in our bodies?
quick energy
what are the 3 types of carbs? examples?
fibers, sugars, and proteins. fibers occur in most vegetables and fruits. sugars (mostly refined sugars) occur in processed foods - like pastries, candy, and etc. carbs and proteins occur in greener vegetables.
what elements are in a carbohydrate macromolecule?
carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, in a 1:2:1 ratio. the other molecules are bonded to carbon
what are some foods that have carbohydrates?
bread products/other processed foods, milk and dairy products, lentils and beans, pasta, etc.
what are monomers for lipids? (2 parts)
glycerol and fatty acids.
the chain on the bottom would be monounsaturated, because it’s bent. if it had multiple bends, it would be polyunsaturated.
also unsaturated fats are better for you, because saturated fats stack up and block your arteries
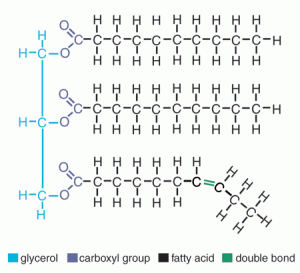
what makes up the structure of lipid monomers?
one backbone of glycerol and 3 chains of fatty acids.
can you recognize the structure of a lipid?
yes u can 👍
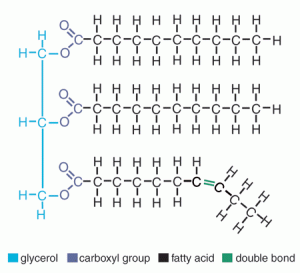
what is the role/function of lipids in our bodies?
they are a part of the cell membrane and help control what comes in/out of cells.
what elements are in lipids?
CHO, in no particular order
what foods have lipids?
cooking oils, and other oily foods
what’s a monomer for proteins
amino acid
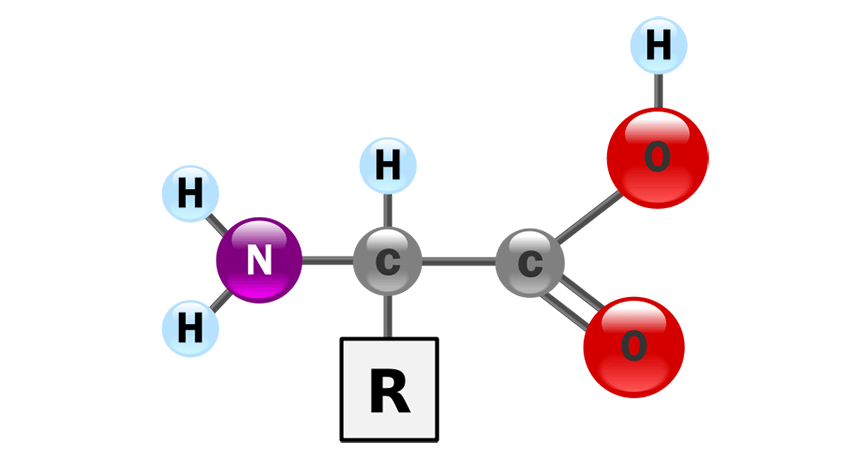
what makes up the structure of an amino acid?
molecules 👍👍
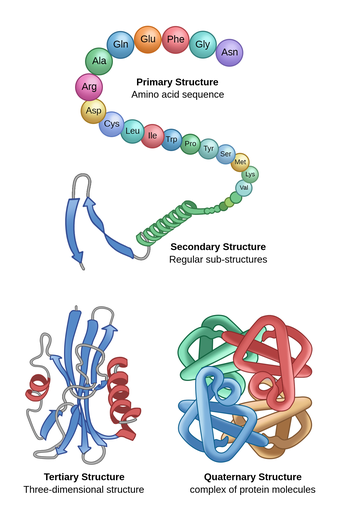
what does the structure of a protein look like?
proteins are polypeptide structures consisting of one or more long chains of amino acids (monomers). it has multiple different levels of structures.
what are the roles/functions of proteins?
providing structure, regulating body processes, transporting materials, balancing fluids, helping with immunity, and providing energy
what elements are in proteins?
CHONPS - proteins have all the major biological elements
what foods have proteins?
meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, etc.
what are the monomers of nucleic acids?
neucleotides
what makes up the structure of a nucleotide?
a sugar phosphate backbone attached to a base (ATGC), put together they create DNA (deoxyribo nucleic acid)
can you recognize the structure of a nucleic acid?
its dna
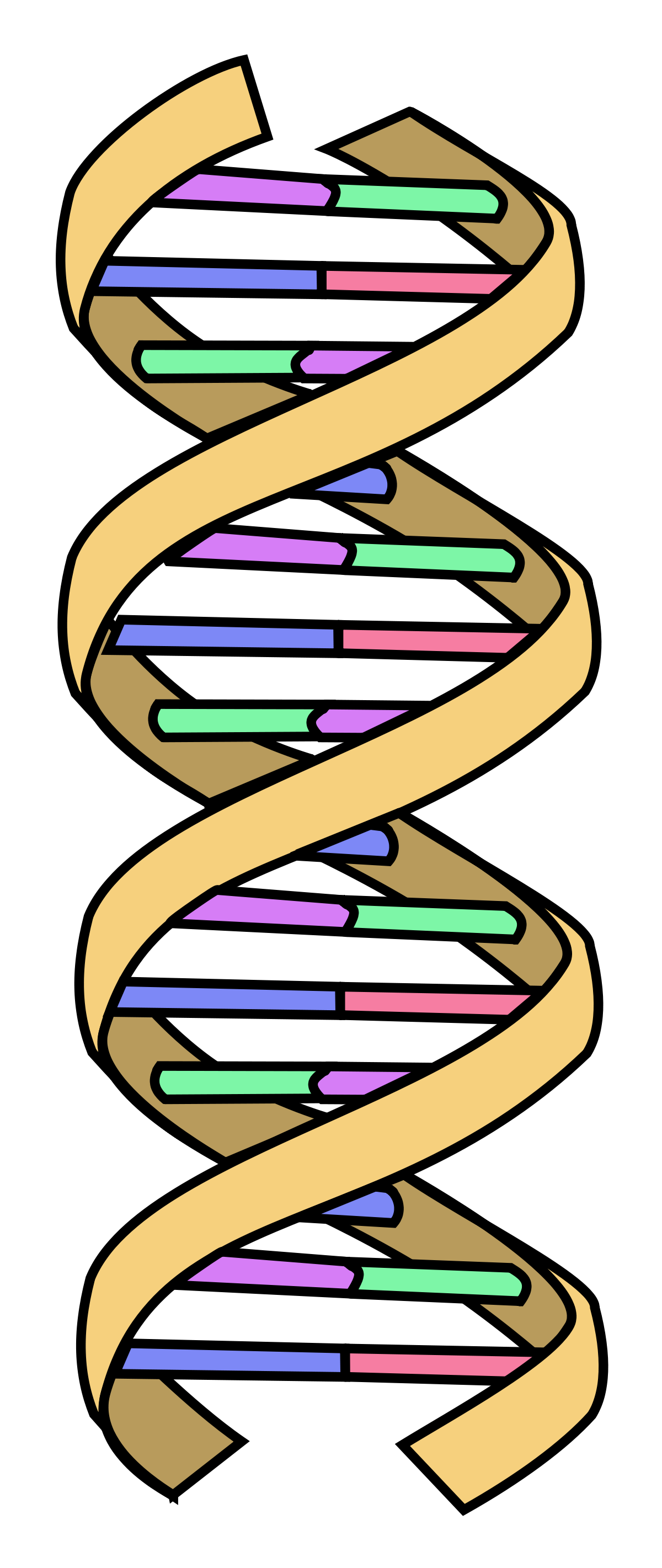
what is the role/function of nucleic acids in our bodies?
dna (and also rna)
what are the two types of nucleic acids?
dna and rna (deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid)
what elements are in nucleic acids?
CHONP
what foods have nucleic acids?
everything bc its dna
where is the chemical energy in our food?
molecular bonds
these molecular bonds represent potential energy, which is either very stable, such as in fat molecules, or very active and transitory, such as in ATP molecules.
what does a carbon atom look like? label the subatomic particles
this 👍
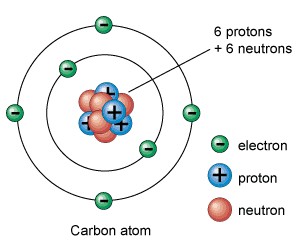
why is carbon important to living things?
regulate the Earth's temperature, make up the food that sustains us, and provide energy that fuels our global economy. its in the atmosphere and in every macromolecule, etc
what is digestion doing in our bodies? example?
enzymes break down food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth, and cell repair.
LDL = low density lipoproteins. HDL = high density lipoproteins. they are both packages that carry cholesterol and other lipids, but LDLs bring their contents to the body’s tissue, whereas HDLs bring their contents to the liver.
what is the purpose of digestion?
to break food down into smaller molecules, like mono/disaccharides, so your body can use them or dispose of them.
what is biosynthesis doing in our bodies? example?
biosynthesis is the creation of macromolecules by living things through chemical reactions and cellular processes.
it’s done by enzymes building back up micromolecules, and photosynthesis is an example of this.
what is the purpose of biosynthesis?
you need it to survive ??? by building up micromolecules you get the macromolecules your body needs