Week 2: Learning, peer collaboration, and group work in the classroom
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Behaviourist approach
rewards and sanctions are used to shape student behaviour
Disequilibrium
the uncomfortable state of having to accept new information to your current worldview
Mayer (2004)
suggested that pure discovery fails to promote selecting relevant information
Socio-cultural approach
the relationship between intramental thinking and intermental action
Scaffolding
supporting students with what they are struggling with so they can reach their potential
Vygotsky’s zone of proximal development
out of reach
zone of proximal development
current understanding
Radiziszewska & Rogoff (1991)
Child paired with either trained adult, trained child, or untrained child
Presence of trained adult or child did the task effectively
BUT a week later only adult could support child to do the task
Mercer & Howe (2012)
dialogic talk and collaboration are important in the classroom
Reciprocal teaching
the child takes turns being the teacher or learner
Jigsaw classroom
split groups into expertise and then pool information together
Information processing theories
hardware → processing speed, memory capacity
software → strategies, knowledge
Craik & Lockhart (1972)
deeper levels of processing improved recall
Schneider et al (1993)
study asked child experts and adult novices to memorise chess pieces
meaningful positions (32% variance explained)
random positions (9% variance explained)
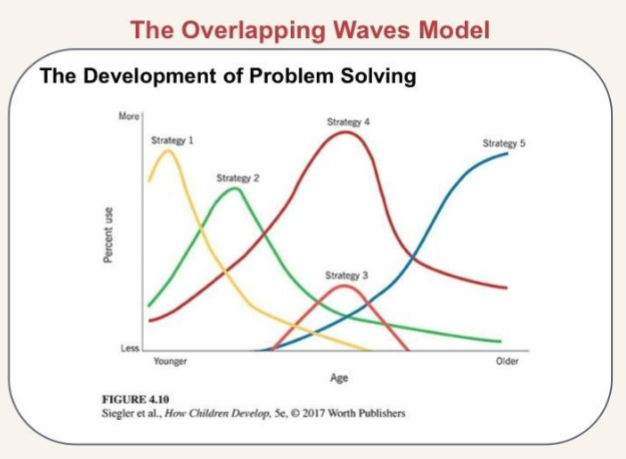
Sieglar (2005)
researched how children choose and change strategies
Smart & Csapo (2003)
groups need to be selected by teachers and ideally 5-7 students for optimal collaboration
Flipped classroom
where students study content before the class so they are more confident with peer discussion
Role of teacher in collaborative dialogue
explaining task expectations
forming groups
designing group task
teacher discourse
Saito et al (2021)
in south east asia cooperative learning is popular but collaborative is not, there is a culture that is reluctant for students to ask others for help
Markham (1977)
as metacognition increases with age, so does comprehension
Lange & Pierce (1992)
young children can use memory strategies and recall better when they do so