AP US Gov - Introductory Unit
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Political Spectrum
Far left - radicalism
want immediate and complete change
Far right - reactionary
Want to keep things same or go back to the ideals of the past
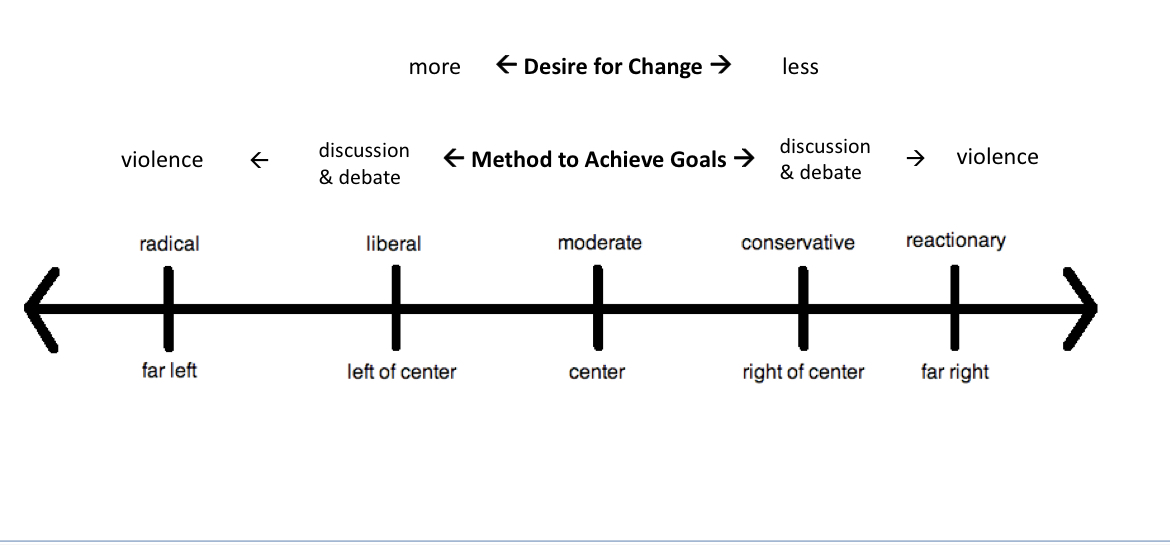
Leftwing perspective
hierarchies can become corrupt
People at the bottom get left behind
Change is important for society
Often an accelerator of change
Rightwing perspective
hierarchies and inequality are natural
Social order is important
Too much change is destabilizing
Often acting as the “brakes” for change
Ideologies
frameworks for understanding the world and directing action within it
Roots of Totalitarianism
in the 1800s, Europe underwent rapid changes during the French & Industrial Revolutions
turned towards Rationalism, logica and reason over faith, leading to the secularization of society
Presented challenges as Christian religion has been the foundation of Western society or “social glue”
Issues identified in the late 1800s
Russian novelist Fyodor Dostoevsky
“If there is not God, everyone is permitted” - no “fear” of God
Removed moral foundation of society, moved away from one’s conscience
German philosopher Frederick Nietzsche
Believed that God had lost meaning
Predicted that the 20th century would undergo pendulum swings between nihilism (life has no meaning) and totalitarianism (contains ideas that create meaning)
Carl Jung
Swiss psychoanalytic psychologist
Believed in the collective unconscious, the fact that the country, as a whole, has an unconscious mind
Believed in the shadow, the inherent human dark side within all of us
Hitler
embodiment of Germany’s shadow
Voiced the dark side of its unconscious
Nothing without the German people who see their darkest beliefs in his beliefs
Purpose of studying Europe Totalitarianism
demonstrates worst case scenario of runaway government power used to enact evil ideologies
1917-1922
Bolshevik Revolution & Russian Civil War
Russia became the Soviet Union, the 1st Communist State, turning towards a Totalitarian system
Vladimir Lenin
adopted Marxism to Russia
Created dictatorship “of the proletariat,” using force and violence to remake society.
Established central planning of economy, requiring the creation of a large bureaucratic government
Caused economic confusion & chaos, leading to a large scale famine
Lenin’s dictatorship “of the proleteriat”
abolished private proverty
Attached “class enemies,” where were kulaks (middle class Russians)
Tried to create new “socialist man,” intending to remold human nature
Force people unto reeducation camps or gulags
Otherwise people would not believe in his ideologies
Targeted the Church
Since Communism is militant atheism
Lenin’s death
1924
Joseph Stalin took control, winning power struggled with Leon Trotsky
Despite Lenin not wanting Stalin to take over
Established “Socialism in One Country”
Theories of Communism (no definition)
Classical Marxism
Marxist - Leninism
Classical Marxism
theory that in a society the proletariat would need to rise up and bring down the upper classes of the bourgeoisie and rules in a violent struggle among social classes in order to create a classless society
Marxist - Leninism
theory that in a society a small group of proletariat (“Vanguard of the Revolution”) would need to take over the government and destroy the class system
Then the group would use government to enforce a classless society in a top-down revolution
Stalinist goal
make Russia an industrial power quickly (fear of being left behind)
government central planning forced collectivization of Russian people
Totalitarian control
Used propaganda and terror in the form of informants, secret police, and labor camps against criticism, etc.
Stalinist collectivization
loss of property led to loss of selfownerrship
Workers sent to factories
State-run farms full of forced labor
Led to large scale famines
1932: Ukrainian famine of the Holodomor (6 million dead)
“The Great Terror”
1930s
Stalin felt paranoid, pursing political enemies
Showed trials and mass executions, killing 1 million
Gulags
forced labor/prison camps in the middle of nowhere
Gulag systems empowered violent criminals to control political prisoners
Often harsher on prisoners than regular guards
History of Italy
long history of regional, social, and political division
Government was unable to deal with problems
Wanted to re-establish the Roman Empire (the ideal)
1920s Italy
faced threat of communism
Right wing reacted with creation of fascism
Benito Mussolini
leader of Fascist Party
Mussolini’s followers referred to as Black Shirts
Fought to gain power, attacking communists
Lead with intense nationalism, hoping to restore the glory of the ROman EMpire
1922 Mussolini
used the March on Rome movement, utlilizing mass mobilization, intimidation, and elite support to legally seize power as prime minister
Called “Il Duce” (The Leader)
Post WWI Germany
Treaty of Versailles left German bitter and desperate
Led by the Weimar Republic that created economic and social problems
Full of hyper-inflation and the threat of communism
1920s Adolf Hitler
leader of National Socialist (nazi) Party
History of Hitler
soldier in WWI and failed artist, but a powerful speaker
Belief in Nazi ideology of intense nationalism and racial homogeneity
Anti-communist and anti-Jewish
1933: appointed chancellor
Right after the Reichstag Fire, a crisis that led to the Enabling Acts (granted dictatorial power)
Nazi Rule
Hitler had unlimited power
Arrested communists and restricted freedom and liberties
Secret policed silence opposition
Controlled press and education system
Use of propaganda to boost popularity and create cult of personality
Stocked and unleashed German anti-semitisM, blaming Jews for German problems
1938: 1st mass arrest then Holocaust
German Nazis
rejected laissez faire, wanting Government to control private business
Ultimate goal was autarky, or national self-sufficiency
No dependence on foreign trade
British hunger blockade in WWI which was scarring to country
Made war and expansion inevitable
Policies & Actions of 1930 German Nazis
was initial success
Expanded the military → decreased unemployment
Industrial policy (similar to fascism)
Tariffs on foreign competition
Bullies business on prices and production decisions
Intended to limit private ownership
Controlled money supply
Suspended the gold standard
Expanded credit (debt) by printed money
Huge public works programs
Instituted jobs programs (Decr. unemployment)
Created autobahns or highways
Healthcare
National healthcare and unemployment insurance
Ran huge deficits → increased national debts
Nazi Germany (1930s–1945):
Extreme nationalist and reactionary ideology suppressed minorities and political opponents to enforce a “traditional” social hierarchy.
1840s-1940s China
western imperialism weakened China politically and socially, creating the “Century of Humiliations”
Long period of foreign domination and internal crisis made radical solutions, including communism, appealing as a path to national revival and independence
1949 China
Communist forces defeated Western supported Nationalist Chinese government
Mao Zedong declared the People’s Republic of China
Maoism
adaptation of Marxist-Leninism to China
Anti-imperialism and class based social revolution
Targeted “class enemies” (property owners and counterrevolutionaries)
“Bitterness meetings” used to identify and mobilize against class enemies
1949 - 1976 China
Communists purged, planned, and scapegoat killing as high as 100 mil.
1957 China
Hundred Flowers Campaign (“Let a hundred flowers bloom”
Allowed dissent and expression to identify class enemies, purging them
1958 - 1962 China
“the Great Leap Forward”
Forced industrialization so used agricultural collectivization
Caused famine of 55 million dead
1966 - 1976 China
“The Cultural Revolution”
Mao’s comeback where he purged enemies in society and government and increased his cult of personality
Utilization Red Guards, gangs of youth/teens ideologically possessed by Maoism
Harassed, arrested, tortured, and executed
Destroyed ancient artifacts
Implemented “out of Countryside Movement” in which urban people moved to rural land for forced labor
2 - 20 mill died
Ancient Roots Of Democracy
Western Civilization governed by Greek rationalism, Roman Law, and Judeo-Christian ethic
Ancient Greece
birthplace of Western Civilization
Politically divided into city-states, but culturally united
Usage of political terminology we know today: Oligarchy, aristocracy, monarchy, etc.
Governing philosophy of rationalism
Thinkers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle
Ancient ROme
built on Greek achievement
Republic of 3 parts
Pioneered checks and balances
Senate influenced decisions
Executive figures: 2 consuls
Popular assemblies passed laws
Embraced imperialism, becoming an empire
Influential figures: Cincinnatus (aligned with GW), Cicero (aligned with J Adams), Marcus Aurelius
Post-Fall of Rome
Europe was politically shattered
Developed decentralized feudalism
Germanic tribes formed small kingdoms
Culturally unified by Catholicism
late Middle Ages
France governed by decentralized feudalism, then a centralized absolute monarchy
England governed by an absolute monarchy, and then a limited monarchy
Re-emergence of trade
created a money economy
As Europe politically decentralized, there was relatively more freedom esp in travel, leading to economic growth
15 & 1600s
Reformation in Europe, breaking Church’s monopoly
Unleashed chaos on Europe, including wars of religion killing millions
30 Years War, which started as religious war then turned into a national war
Reinforced importance of separation of Church and State
English History
overall a struggle to enlarge freedom
Magna Carta, Parliament, Civil War, the Glorious Revolution
The American Revolutionaries’ aligned with this struggled, seeing themselves as Englishmen trying to regain rights
1700s Europe
The Enlightenment, built on the Scientific Revolution
Applied logic and reason to the social world
Theories of human nature: Hobbes, Locke, Rousseau, etc.
Informed and inspired American revolutionaries
1700s Britain
mercantilist empire
Government had an active role in economy
Granted monopolies, like the British East India Company
Colonies exist for benefit of Britain
Set prices on goods
Limited colonial economies
1777 Continental Congress
made 1st national constituency (Articles of Confederation)
Ratified in 1781
U.S. established as loose confederation or league of independent states
Cont. Congress’s Power
purposely limited
Could declare war & conduct foreign policy and administer relations with Native Americans
Could not tax or regulate interstate commerce or foreign trade
Problems of Continental Congress
economic & political
Couldn’t tax, increasing the nation debt + the gov’t could default on debt
Post-war depression deepened
Debts, bankruptcies, and foreclosures created an uneasy economic situation
Foreign nations didn’t respect US
Britain denied access to to British West Indues and right to export goods to Britain on American ships
Spain forbade American trade with New Orleans
British soldiers in frontiers forts, occupying the Northwest territory
Who wanted revision to A of C?
nationalists/Federalists
Hamilton
Madison
Franklin
Shays’ Rebellion
catalyst for change
MA govt printed money during war
Inflation led to & losing value
Desperate veterans sold at small % of value to “speculators” or wealthy investors (many in gov’t or connected)
State gov’t voted to refund bills at face value
Tax people to pay, leading people to foreclose on their farms when couldn’t pay
Daniel Shays
1787, Rev. War officer
1000 farmers protested taxes and farm enclosures, so the courts had to close
State send militia, who ended up joining the rebellion
Shays and men tried to raid federal arsenal
Revolt failed
Chaos scare people, especially GW
Nationalists pushed for stronger central gov’t
1786 Const. Convention
Annapolis Convention where only 4 states sent delegates
Issued report calling for wider convention
Not much happened
1787 Const Convention
convention in Philadelphia in response to Shays Rebellion
Stated purpose of revising Articles of Confederation
Instead created a new cont. (“runaway convention”)
Opponents were either absent or unprepared
Madison had created a thorough plan, researching how to create Const.
Views of 1787 Cont. Convention
top-down counter revolution
Pushed against ideas of 1776, hoping to create a more centralized document/government
Counter argument: opponents were included in new government
Constitutional Convention
53 delegates from 11 states came
Most helped write state consistitions
21 fought in resolution
8 signers of Decl of Independence
Most were rich, lawyers, merchants, and planter elites
North was underrepresented (RI and NH absent, NY left midway)
Gave southern states and reps advantage
James Madison
leading Nationalists (Federalists)
“After of the onstitution”
Served in Cont Congress
Came prepared to convention, creating plan of gov’t
Alexander Hamilton
leading nationalist (federalist)
Strong nationalist prescience
Served under GW in war
Supported powerful central government (shifting convo to centralized systems)
Argued for British model
Will see in his economic system as treasurer
GW
leading nationalist/federalist
President of convention
Gave legitimacy to convention
Celebrity, attracting crowds
Ben Franklin
leading nationalist/federalist
Elder statesman
Added experience, wisdom, and prestige
Also international celebrity
James Madison Ideas
legislative republicanism (central gov’t to counteract state gov’ts)
Emphasized legisl. Branch
Understood “paradox of gov’t”(checks and balances)
Originated theory of a large republic
Federalist #51 and Madison
understood the “paradox of government” (system of checks and balances)
Distrusted state governments, viewing them as ridden with corruption and threat to liberty
Wanted stronger national government to check and balance and nation gov’t to have them too
Federalist #10 and Madison
originated theory a large republic
Historically republics had been small
Believed large could work
Many diverse interests so they need to check each other to preserve te common good
Appreciated dynamism of PA vs. stagnation of VA
Protect minority rights against tyranny of majority
Individuals most vulnerable of minority
Alexander Hamilton views
executive republicanism
Emphasized the executive branch
Believed in a strong executive to effectuate laws
Conservative, distrusted democracy
Wanted balance of aristocracy/oligarcy, monarchy, and republicanism
Federalist #70 and HHamilton
believed in a a strong executive to effectuate laws
Wanted to be a prime minister figure
Very influential on government function post-ratification
Proposed Plan
James Madison’s VA PlaN
VA Plan
strong national government
Can tax, regulate commerce, and veto state laws
Senate and a house of reps based on popul
Bad for small states
Individual executive
Command military/manage foreign relations
Designed with GW in mind
Opposition Plan
William Patterson’s NJ Plan
NJ Plan
Unicameral legislature
1 vote per state
Good for small states
Executive by committee, not 1 leader
States retain sovereignty
National gov’t w few powerS
“Great Compromise” Or CT Compromise
2 House in Congress
Lower house w rep by state popul
Upper house w each state having 2 senators
Secured support of small states
Federal vs. Nationalist System
Federal system - power divided between national and state gov’ts
States still retained sovereignty
Nationalist system → central gov’t is dominant
Certain powers forbidden to states
3/5 Compromise
3/5 of enslaved population counted towards representation
Congress and electoral votes for pres elections
Illogical position of southerners viewing enslaved people as property
Slave trade protected for 20 yrs
Fugitive Slave Law created
Slave Rep in Congress
big issues in convention
Southern states more represented at Convention so more control
Demanded special privileges in Const
Ratification
convention created new process
Special state conventions not state legislatures (elected by ppl)
9 out of 13 needed to ratify (no longer 13/13)
Federalists view on Constitution
united in support
Key voices of the Federalists
James Madison, John Jay, and Alexander Hamilton
Wrote the Federalist Papers
Series of essays to persuade/defend the Const
Federalist 10 summary
Madison warns factions are unavoidable because of human differences, but dangerous since they threaten minority rights.
Instead of eliminating them, the Constitution controls their effects through a large republic.
In a big, representative republic, diverse interests make it harder for one faction to dominate, protecting liberty and stability.
Federalist 51 summary
Madison argues that government must control itself to prevent abuse of power
He proposes separation of powers, giving each branch indep authority and the ability to check the others
But letting each branch’s ambition counteract the others, and combining this with federalism, liberty and individual rights are better protected
Federalist 70 summary
Hamilton argues that a strong, energetic executive is essential for good government.
A single president, rather than a group, ensures accountability and clear decision-making.
Unity in the executive allows for swift action, protects the public, and defends against legislative encroachment.
Federalist 78 summary
Hamilton argues that an independent judiciary is essential to uphold the Constitution.
Judges should have lifetime appointments to remain impartial and resist political pressure.
Judicial review allows courts to strike down laws that violate the Constitution, protecting liberty and preventing legislative overreach.
Those in favor of Const. Besides Federalists
Ben Franklin & GW
Frontiersmen/land speculators
actively want to go west, would be protected by military against natives
Artisans/manufacturers
Central gov’t regulate interstate and national trade
Standardization of currency
Big businesses could petition for tariffs against foreign businesses
Opposition to const
Anti-Federalists who oppose ratification
Anti-Federalists
seen as losers in American history but made many important contributions to US gov’t
Many key figures in gov’t anti-Fed
Against concentration of power in distant elite
Local gov’t easy to monitor for corruption
Didn’t believe in Madison’s large repub theory
Feared a loss of individual liberties
Concerned by lack of a bill of rights
Problem: not united or prepared
Anti-Federalist constituents
Samuel Adams, George Clinton (govt of NY), and Patrick Henry (big figure in VA)
Henry didn’t attend Cont Convention
Farmers (avg citizens)
General distrust in lawyers and wealthy ppl
Const threatened debtor relief laws in states
Ratification Process for Constitution
Mid - Jan 1788 - 5 states ratified
PA ratified as part of Fed rush job
Inc A.F. suspicions
Promise of Bill of Rights led to 4 states ratified
NY & VA were most important states left
VA down to Henry vs. Madison
Ratify in end
NY down to Clinton vs. Hamilton
Bill of Rights
product of Anti-Fed opposition
Unofficial 8th section of Const
Compiled and edited by Madison
Led 4 states to ratify in Jan 1788 after initial 5
Political and historical significance of Bill of Rights
republicanized and liberalized the Const at points of contact w citizens
Police, military, courts
Enshrined certain individual rights as a defense against gov’t oppression
Until 14th amendment, only applied to nat gov’t not states