Concepts in Human Physiology
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mid-Term 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What are the levels of structural organization in order
Atoms
Molecules
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Organisms
Homeostasis
-Maintenance of stable internal environment despite constant changes occurring externally
-dynamic state of equilibrium
-internal conditions varying but within narrow margins
-specialized organ systems allow movement of chemicals from the external to the internal or from the internal to the external
-blood is maintained at a relatively constant composition to provide the stable conditions necessary for cell function
-cells of the body are bathed in extracellular fluid and this internal medium is separated from the external environment by an impervious skin
-Specialized organ system are the portals for the movement of chemicals from the environment into the organism, or out of the organism into the environment
What do homeostatic control mechanisms have?
-Receptor
-Control centre
-Effector
Homeostatic control mechanism: receptor
Sensor that monitors and responds to changes in the environment (stimuli), then sends information (input) to the control centre. This input flows from the receptor to the control centre along the afferent pathway
Homeostatic control mechanism: control centre
Determines the level (set point) at which a variable is to be maintained. It also analyses the information it receives and determines the appropriate course of action
Homeostatic control mechanism: Effector
In charge of the control centre’s response (output) to the stimulus. Information from control centre flows along the efferent pathway. The results of the response then feed back to influence the stimulus.
Negative feedback in homeostasis
Intended to shut off or reduce the effect of the stimulus
Positive feedback in homeostasis
Rare in the body as they normally increase the original stimulus and push the variable farther from its original value. In the body mainly for blood clotting.
Homeostatic imbalance
Results in stress or disease
Homeostatic control relies on
-constant monitoring of blood composition
-responding to changes in blood composition
How the body communicates
The body communicates through neural (fast) and hormonal (fast and slow, with “memory”) control systems
96% of the body is made up of what elements?
-Carbon
-Oxygen
-Hydrogen
-Nitrogen
Inorganic compounds
-Lack carbon
-Tend to be simpler
-Include water, salts, and some acids and bases
Organic compounds
-Contain carbon
-Most are covalently bonded
-Include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, ATP
Important inorganic compounds: Water
-most abundant inorganic compound in the body
-all physiological processes take place in an aqueous medium
-high heat capacity, solvent properties, cushioning (CSF around brain), chemical reactivity (hydrolysis/breakdown of foods)
Important inorganic compounds: Salts
-easily dissociate into ions charged ions in water
-electrolytes conduct electrical currents
-vital in many bodily processes
Important inorganic compounds: Acids and bases
Acids:
-release hydrogen ions (H+)
-are proton donors
Bases:
-release hydroxyl ions (OH-)
-are proton acceptors
when neutralized with one another they make water and a salt
Important Inorganic compounds: Carbohydrates
-made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
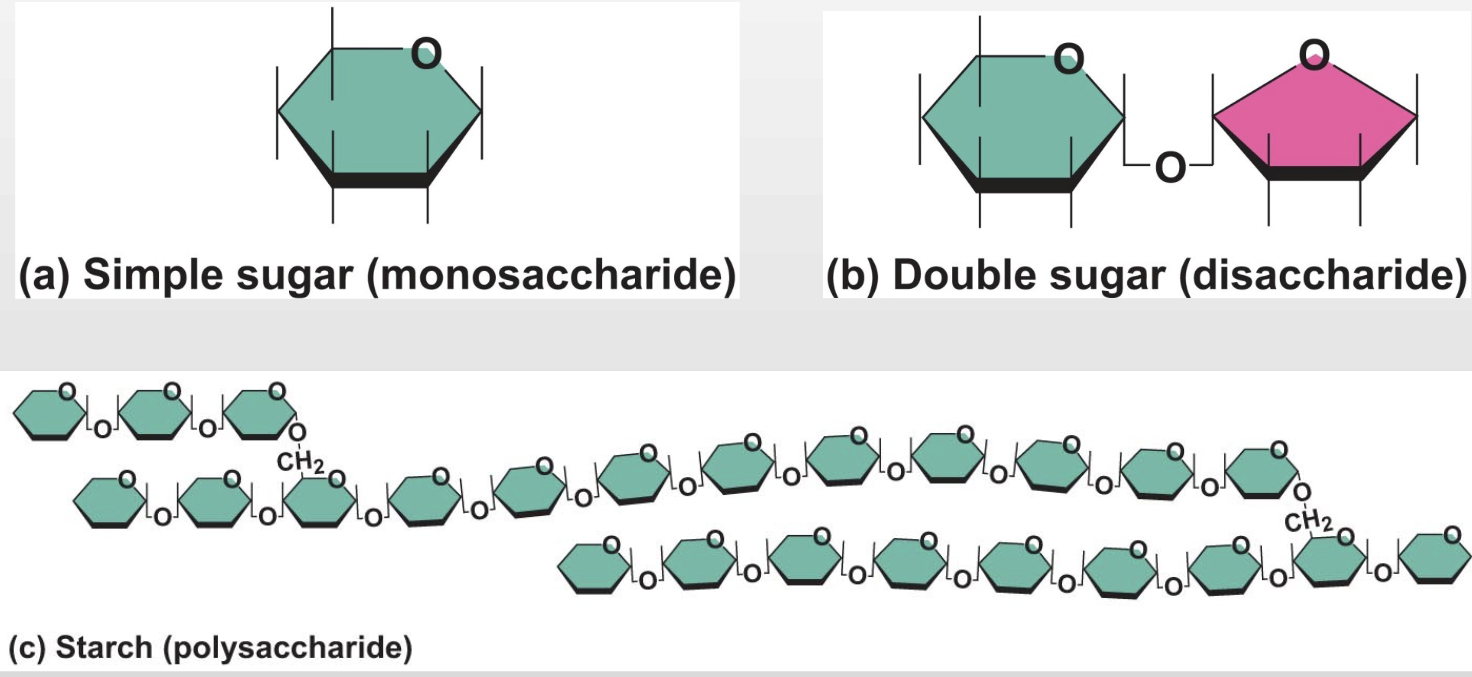
Important Inorganic compounds: Lipids
-made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
-insoluble in water
3 main categories:
-fats and oils
-cholesterol
-phospholipids
Organelles in the cell
-nucleus
-mitochondria
-ribosomal endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
-smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
-golgi
-lysosome
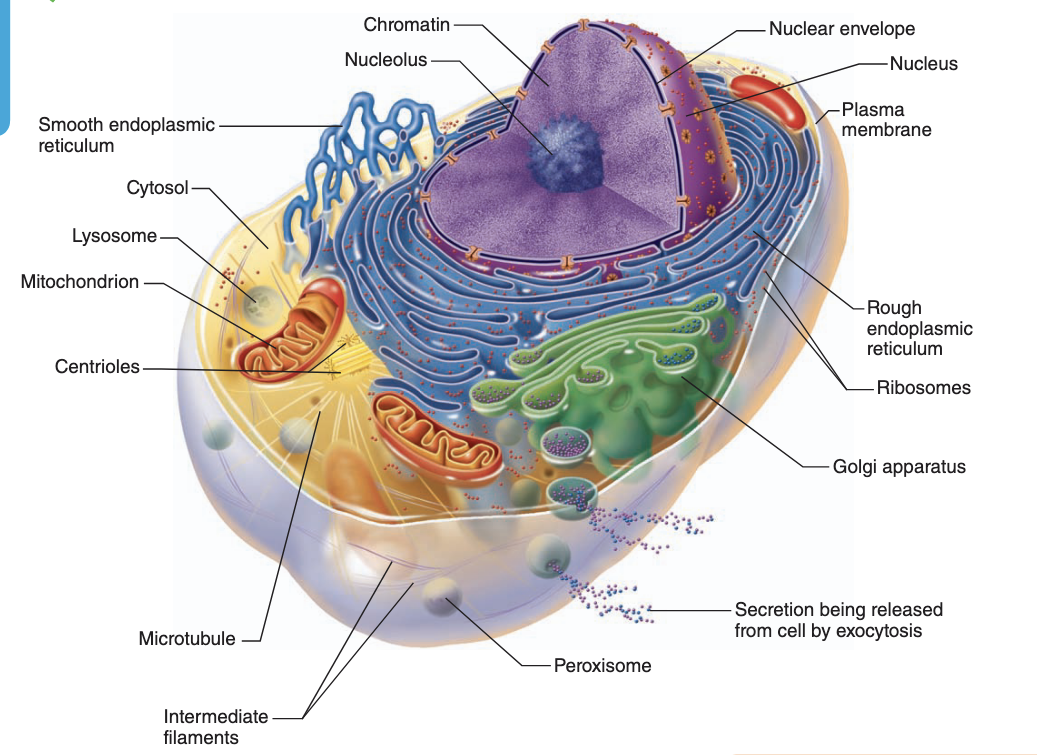
Not all cells are the same but they…
-share general structure
-have three main regions: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
Plasma membrane
-barrier for cell contents
-double phospholipid layer
- proteins, cholesterol, glycoproteins
Double phospholipid layer
-hyrophillic heads (likes water)
-hydrophobic heads (doesnt like water)
-semi permeable
Mincrovilli
finger-like projections that increase surface area for absorption on the plasma membrane
Cell junctions
-tight junctions
-desmosomes
-gap junctions
Occluding (tight) junctions
-seals cells together in an epithelium
-prevents small molecules from leaking from one side of the sheet to the other
Anchoring junctions (desmosomes)
attach cells and their cytosomes to their neighbours or the extracellular mix
Communicating (gap) junctions
mediate the passage of electrical/chemical signals from one interacting cell to it’s partner
Nucleus
-control centre of the cell
-contains genetic material
-genetic material is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane which has nuclear pores
Ribosomal endoplasmic reticulum
is the site of protein synthesis
Cytoplasm
-the material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane
-site of most cellular activities
-contains organelles
Buffers
chemicals that can regulate pH change
Fats & oils
-major part is triglycerides
-3 molecules of fatty acids + 1 molecule of glycerol
Cholesterol
-important constituent of cell membranes
-essential for steroid hormone production
-majority of cholesterol in the body is synthesized within body tissues, only %15 from diet
Phospholipids
-common in the human body
-form cell membranes (lipid bilayer)
-contain 2 fatty acids
Proteins
-make up over ½ of body’s organic matter
-construction materials for body tissues
-vital to cell function
-built from amino acids
-contain C,O,H,N
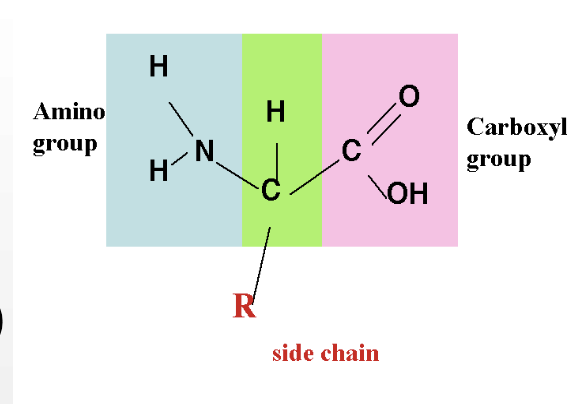
Amino acid structure
-contain an amine group
-contain an acid group
-vary only by R groups (side chains)
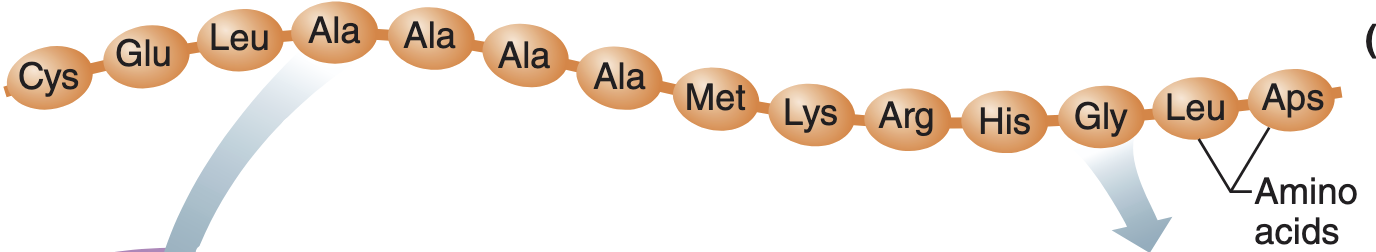
Primary structure protein
sequence of amino acids in a poly peptide chain
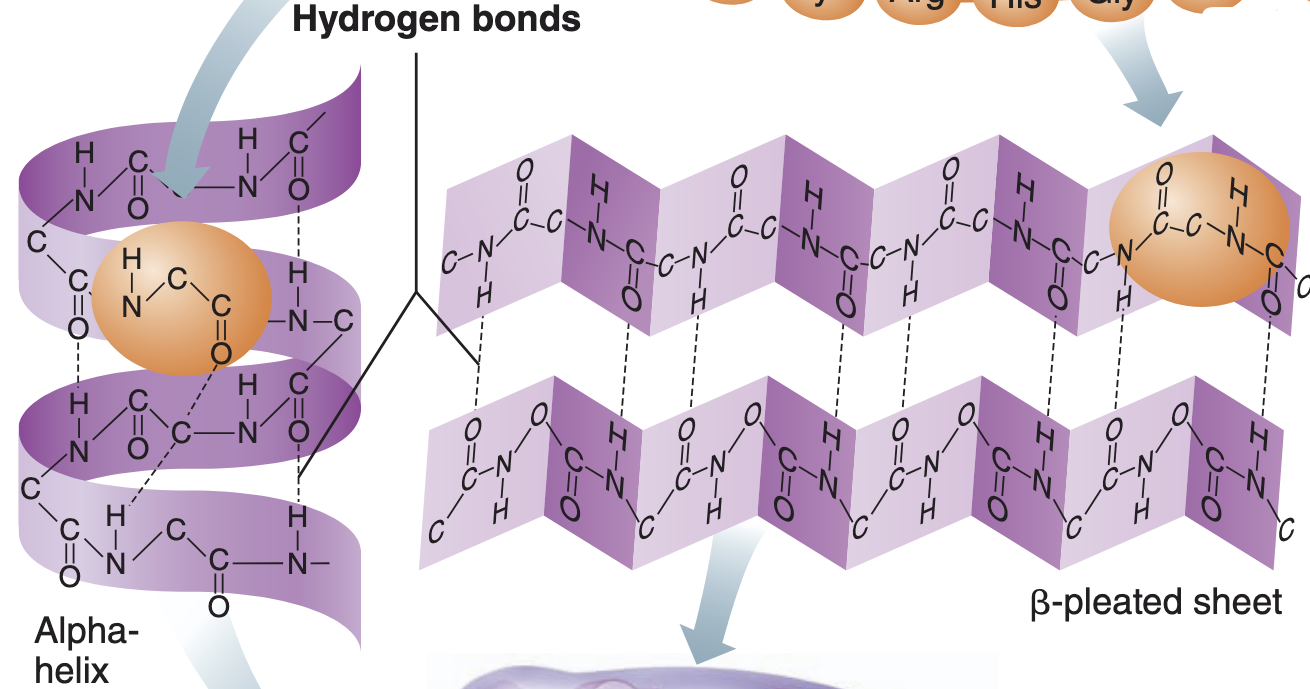
Secondary structure protein
-two types of secondary structure are the alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet
-secondary structure is reinforced by hydrogen bonds
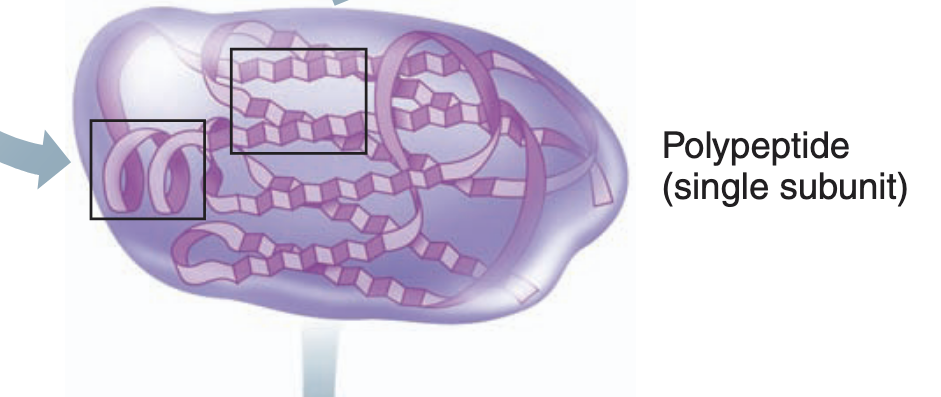
Tertiary structure
-the overall three-dimensional shape
-reinforced by chemical bonds between the R-groups of amino acids in different regions of the polypeptide chain
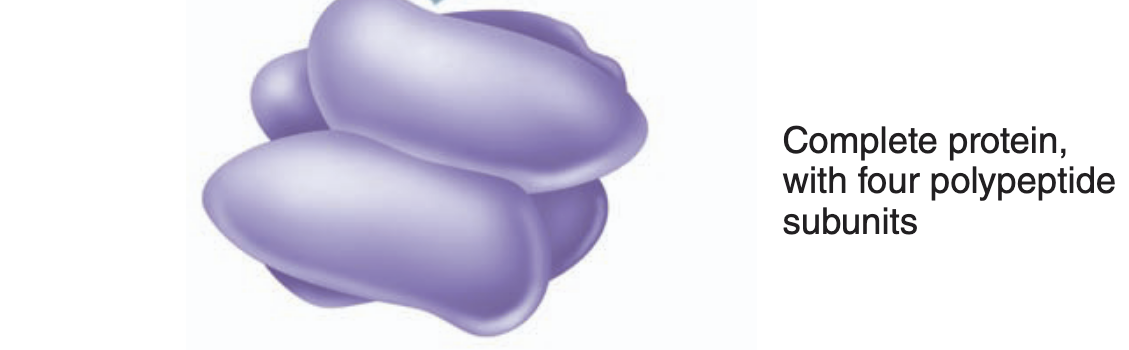
Quaternary structure
proteins consist of two or more polypeptide chains
Peptides
related to proteins but the chains of amino acids are shorter
Structural proteins
-strandlike fibrous proteins
-appear most often in body structures
-some exhibit only secondary structure but most have tertiary or quaternary structure
-important in binding structures together and providing strength in certain body tissue
-ex) collagen, keratin, cartilage
Functional proteins
-mobile
-generally compact, spherical molecules that have at least tertiary structure
-water-soluble proteins
-have crucial roles in virtually all biological processes, because they do things rather than just form structures
-ex) antibodies, hormones, enzymes
Enzymes
-biological catalysts
-bind substrates at an active site
Source of energy
-the food that we eat is the source energy used for almost all cell functions
-we digest the food to get the nutrients in the food
-energy is released by oxidizing the nutrients
-chemical energy released from nutrients is transferred to an intratracellular energy shuttle molecule, ATP
How ATP is made
-nutrients are partially broken down in the
cytoplasm of cells
-then are delivered to the mitochondria, where they are further broken down
-then captured in the form of high energy phosphate bonds in ATP, phosphate molecule is added to make ATP
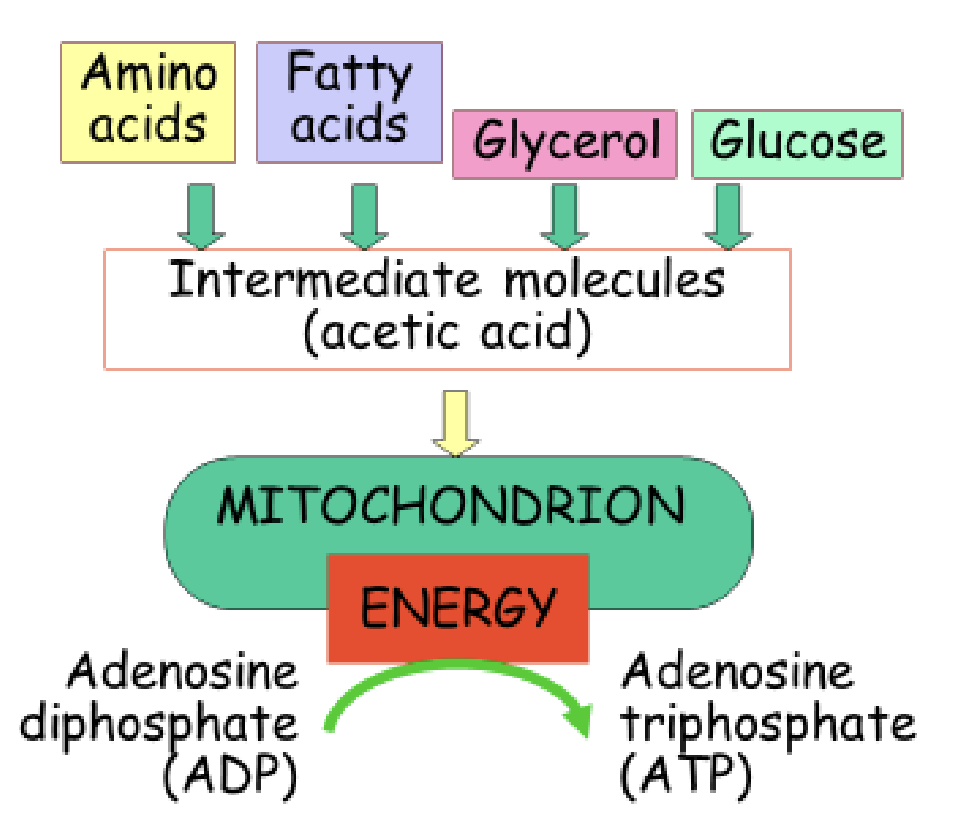
Important organic compound: ATP
-composed of a nucleotide built from a ribose sugar, adenine base, and three phosphate groups
-is the chemical energy used by all cells
-energy released by breaking a high energy phosphate bond
-ATP replenished by oxidation of food fuels
Uses of ATP
-drive energy absorbing chemical reactions
-helps with transport of some solutes across cell membrane
-activate contractile proteins to preform mechanical work
Important organic compounds: nucleic acids
-adenosine, thyamine, cytosine, uracil, guanine
-built from nucleotides
-made up of a phosphate group, pentose (sugar), nitrogenous base
DNA
-double stranded helix
-instructions to build proteins
-contains the nucleic acids A,G,C,T
-found in nucleus
-replicates before cell division
RNA
-puts DNA’s info into action
-created from DNA template
-single-stranded helix
-contains nucleic acids A,G,C,U
-messenger (mRNA), transfer (tRNA), and ribosonal RNA
mRNA
-a single stranded copy of a gene; it moves from the nucleus, where it is produced, into the cytoplasm
-in the ribosomes of the endoplasmic reticulum of the cytoplasm, mRNA interacts with rRNA and tRNA
rRNA
-oversees the assembly of the encoded protein
tRNA
delivers the amino acids used to make the protein
A cell
-the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms
Tissue
a group of cells that are similar in structure and function
Nuclear membrane
separates genetic material from the cytoplasm also has nuclear pores
Protein synthesis in RER
-protein is synthesized on ribosome
-protein folds into functional shape
-protein is packaged into vesicle
-vesicle buds off and moves to Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus
-the site of protein packaging into granules or vesticles
Secretory vesicles
contain proteins that will be secreted by the cell
Lysosomes
secretory vesicles containing enzymes
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
the site where steroids are synthesized
Mitochondria
-where ATP is made
-powerhouse of the cell
Plasma membrane
-forms a barrier to the movement of some types of molecules
-controlled movement of molecules is essential
-some transmembrane processes are passive, and some require use of energy
Membrane transport
-passive, no energy required
-active, needs metabolic energy (ATP)
Diffusion
-particles want to be evenly distributed in a solution
-movement from high concentration to low concentration or down a concentration gradient
Passive (simple diffusion)
solutes are lipid-soluble materials or small enough to pass through membrane pores
Passive (osmosis)
-highly polar water molecules easily cross the plasma membrane through aquaporins
-From dilute to more concentrated solution (still H to L with respect to water volume)
Passive (facilitated)
-substances require a protein carrier for passive transport
-transports lipid-insoluble and large substances
Passive (filtration)
-water and solutes are forced through a membrane by fluid, or hydrostatic pressure
-pressure gradient needed for this
Active processes
-substances that can’t pass through diffusion are transported
-they may be too large, or unable to dissolve in lipid core of membrane, they may need to move against the concentration gradient
-ATP used for transport
Active transport (solute pumping)
-amino acids, some sugars, and ions are transported by protein carriers called solute pumps
-ATP provides energy to protein carriers
-most often moved against concentration gradients L to H
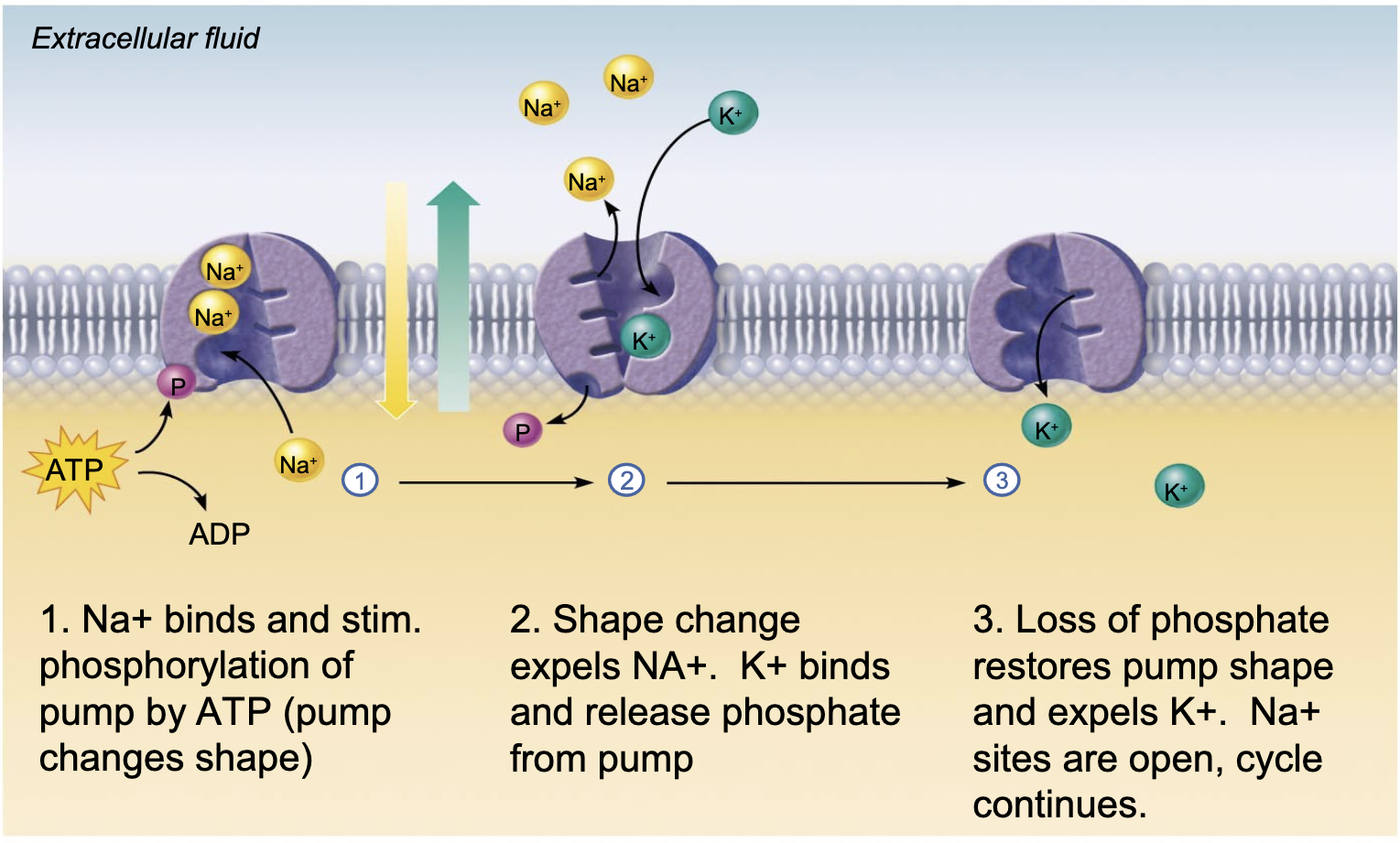
Sodium potassium pump
-soduim in the pump plus phosphate from ATP
-phosphate changes pump’s shape
-sodium realsed on other side
-phosphate unbinds on the same side as where it attached
-pump’s shape changes
-potassium comes in from outside and is let out on inside
Active transport (bulk or vesicular)
-endocytosis
-exocytosis
Endocytosis
-movement of substances into a cell
-ex) white blood cell eating bacteria
-extracellular substance enclosed in a membranous vesicle
-phagocytosis (cell eating)
-pinocytosis (cell drinking)
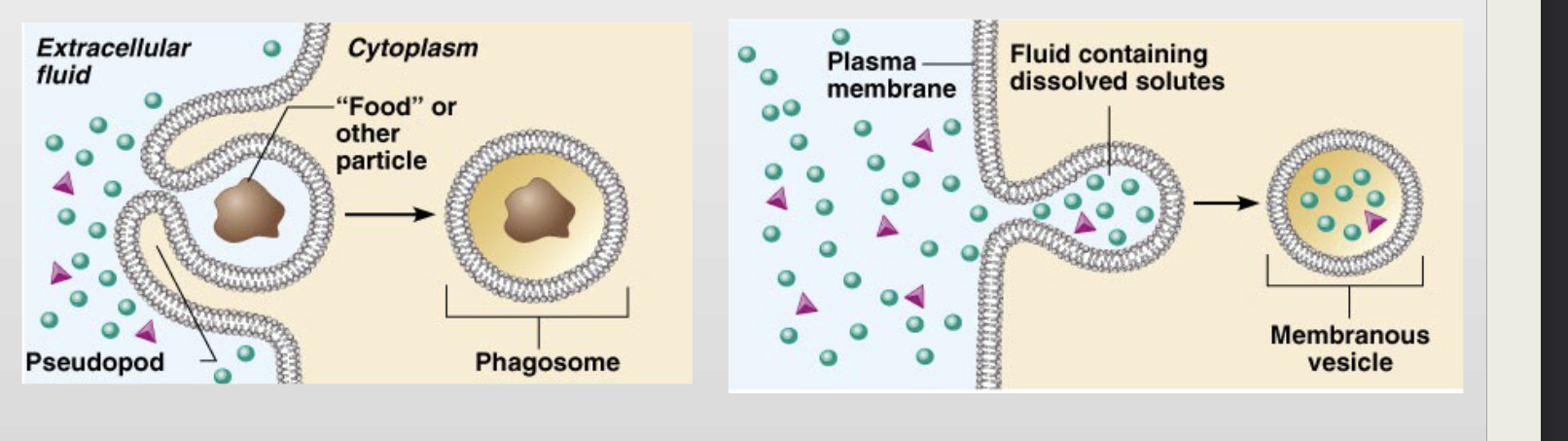
Exocytosis
-movement of substances outside of a cell
-ex) secretion of enzymes
-moves materials out of cell in membranous vesicle
-vesicle move to and combines with plasma membrane
-material emptied outside
Discharges of RPM
-equates to depolarizations or electrical signals (nerve impulses)
-depolarization occurs when a stimulus causes Na+ channels in the membrane to open and Na+ enters the cell quickly down its concentration gradient
Resting membrane potential (RMP)
the charge difference due to unequal dist of NA+ and K+ on outside and inside of a cell opposed to the inside of the plasma membrane where it is negatively charged compared to the outside
Action potential
-propagation of depolarizations of the membrane equates to action potentials
-movement of ions initiates AP
-graded potential exists (localized depol.) inside of membrane more positive then outside
-enough Na+ enters the cell action potential starts and is propagated over the entire axon
Resting neuron
-at rest plasma membrane is polarized
-less positive inside vs more positive outside
Depolarization
-stimulus depolarizes membrane
-membrane permeable as sodium channels open and sodium enters
Mylien sheath
-allows for faster travel of action potentials
-made up of schwan cells around the axon
Repolarization
-Potassium ions rush out of neuron
-restoring negative charge inside the membrane and positive charge on the outer surface
-Sodium potassium pump restores initial ionic conditions
-three sodium ejected out while two potassium go in
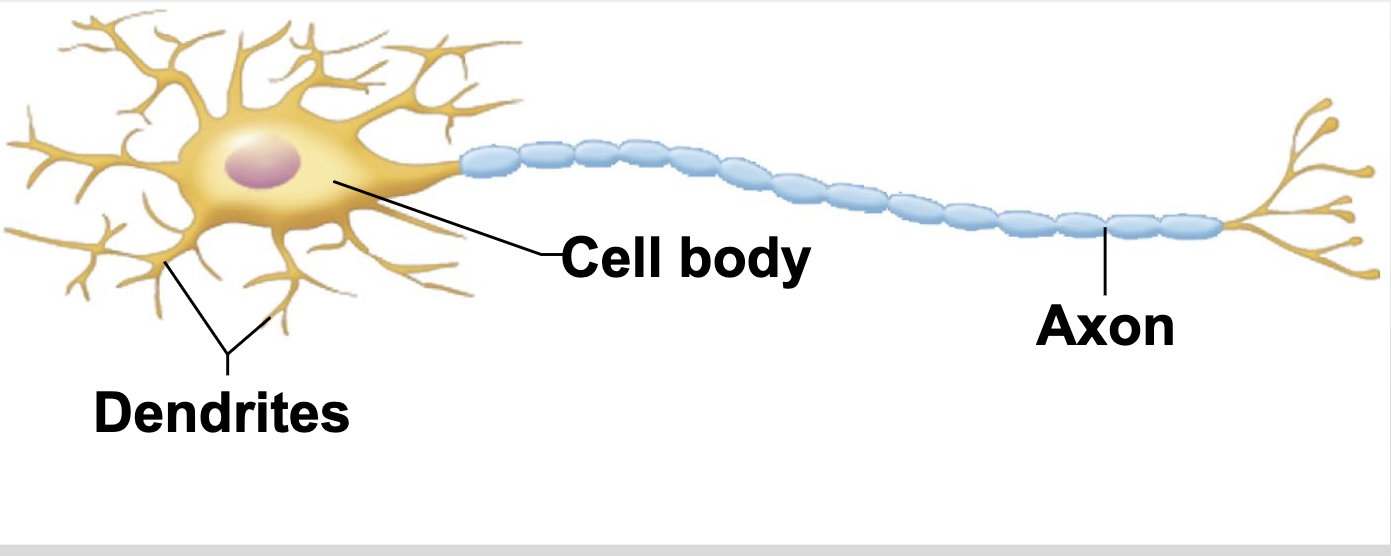
Structure of neuron
-cell body (holds nucleus)
-axon
-dendrites
-synapses
axon
carries the nerve impulse (action potentials)
dendrites
the “docking” cite of other neurons synapses
synapses
-at the end of an axon
-contains vesicles with neurotansmitter susbstance used to activate other cells
-when action potential arrives at synapse initiates controlled release of NTS
Multipolar neurons
-many extensions from the cell body
-most common
-mylenated
Bipolar neurons
-one axon and one dendrite attached to cell body
-in sense organs
-rare in adults
-unmylenated
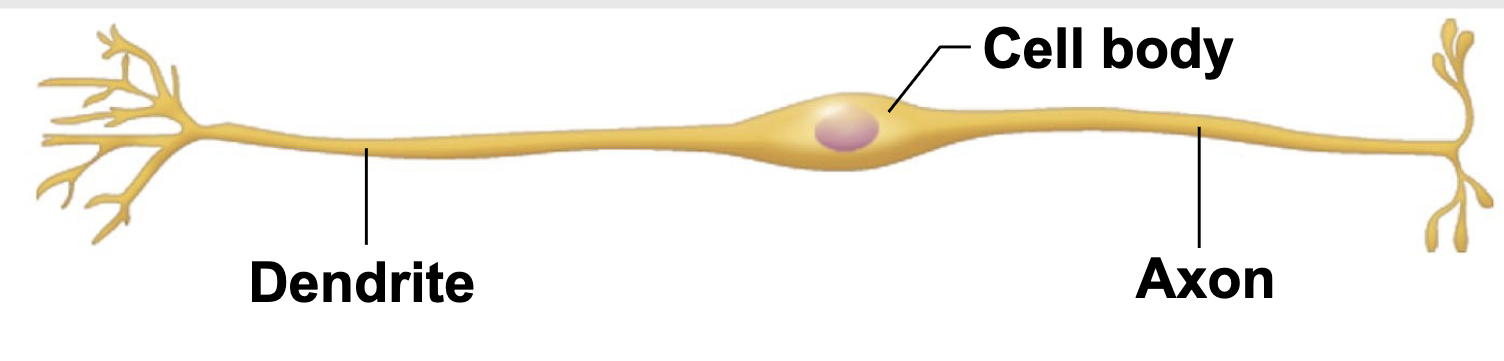
Unipolar neurons
-short single process leaving the cell body
-found in PNS ganglia
-mylenated
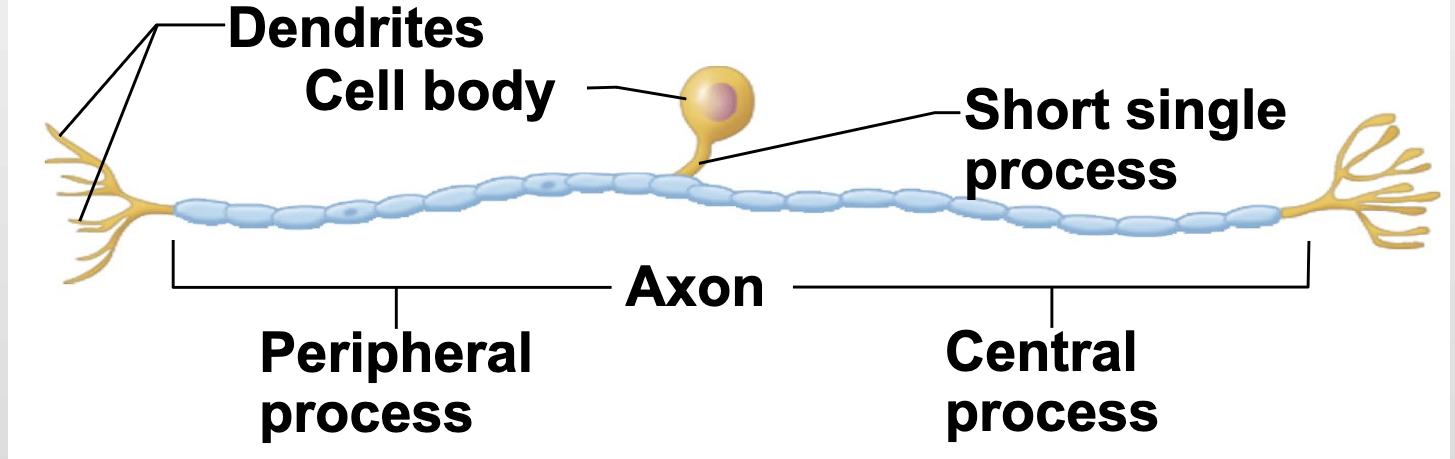
Nerve impulse movement
-action potentials move from dendrites toward the synapses (axon terminals)
-from cell bodies towards axon terminals
Saltatory conduction
-when action potential jumps along the axon
-allows signal to travel faster
-reduced energy needed to re-instate resting potential
Nodes of ranvier
-the gaps between schwan cells in the myelin sheath
-reduces energy needed to re-instate the resting potential
Synapse anatomy
-closely associated with the cell they stimulate
-NTS released into synaptic cleft
-NTS activates rece