BIO 351 Lecture 3 Microbial Cell Structure and Function
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are structures that both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in common?
Cytoplasmic Membrane, Cytoplasm, and a DNA-Based Genome
Core Cellular Processes
Metabolism, Growth, and Evolution
How do all cells exhibit metabolism?
Cells take in nutrients, convert them into energy, and expel waste
What is Catabolism and Anabolism? How do they relate to one another?
Catabolism is the breaking down of molecules for energy
Anabolism builds up molecules using that energy
How do all cells exhibit growth?
Cell use genetic information in order to convert nutrients from the environment into new cells.
How do all cells exhibit Evolution?
Genetic mutations introduce new traits which in turn lead to evolution
How can cellular evolution be tracked?
Phylogentic trees derived from DNA
What are Cytoplasmic Membranes composed of?
Phospholipids
What is the general structure of a phospholipid? What does this imply about the net charge of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids are composed of a fatty acid tail and a phosphate group head attached to a glycerol,
this implies that the membrane is negatively charged
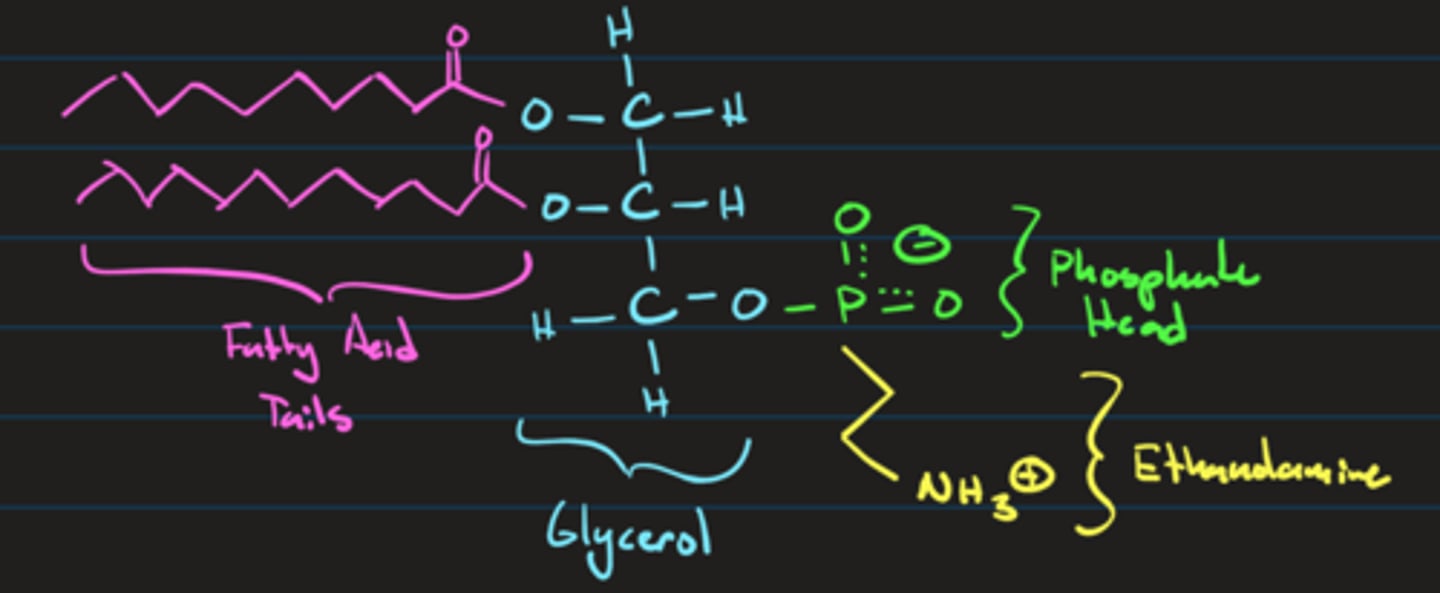
What is the Biomolecular Composition of cells?
55% Protein, 20% RNA, and 10% Lipids
What are the key differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane bound organelles such a nucleus.
What are the functions of the Cytoplasmic Membrane?
Provides a semi-permeable barrier,
Anchor for proteins involved in transport
Generates and utilizes a proton motive force.
What is Passive Diffusion?
The movement of small, non-charged molecules/or hydrophobic down a concentration gradient.
No energy Required
What is Active Transport?
The movement of ions or molecules with the use of an energy source
What is Simple Transport?
The movement of molecules or ions through the membrane with the use of a concentration gradient.
What is an ABC Transporter?
A type of protein found in the cell membranes that utilize the hydrolysis of ATP in order to drive the movement of ions and molecules.
What is group translocation?
The molecule is chemically changed as it is transported in or out of the cell, it usually requires the use of energy released from a chemical reaction
How are Archaeal Membranes different from Bacterial membranes and how does this affect them?
Archeal membranes have Ether linkages, and have isoprene hydrophobic chains, this allows for Archaeal Cells to inhabit harsh environments
How are Archaeal Membranes structured?
They are able to exists as lipid bilayers or, in some cases, monolayers
Archaeal Monolayers structure
They are built up from 2 phytanyl side chains that are covalently bonded together
How do Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria differ from one another?
Gram-Positive have a thick layer of peptidoglycan and lack an outer membrane while Gram-negative have a thin layer of peptidoglycan found in between the cytoplasmic membrane and outer membrane.
What is outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria composed of?
They are composed of LPS (Lipopolysaccharide) which is a large amphipathic molecule
How does the peptidoglycan protect the cell from osmotic stress?
The criss-cross network of glycans and peptides provide a strong surface for the cell
What is Pseudomurein and what does it do?
A structure that is similar to Peptidoglycan found within Archaeal cells, they contain a different repeating unit which is N-Acetyltalosaminuronic acid
What is an S-Layer
A paracrystaline monolayer of interlocking protein or glycoprotein that serves as the outer layer of Archaeal cells.