Lung Cancer Tumor suppressors and oncogenes (Fouty)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Additional material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Cancer is caused by the accumulation of genetic and ________ mutations in genes that normally play a role in cell proliferation, thus leading to uncontrolled cell growth
epigenetic
_____ cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in men and women in the united states.
Lung
Dysregulated cell cycle leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation can lead to malignant and non-malignant processes
Like atherosclerosis
Cyclin D binds
cdk4
Cyclin E binds
cdk2
Rb binds
E2F
cdk4/Cyclin D and cdk2/Cyclin E complex phosphorylates __ moving it out of it’s active form where it is not as tightly bound to E2F
Rb
_________ of Rb causes it to let go of E2F which is then free to bind trans activators/ promotors of genes
Hyperphosphorylation
Active and free E2F leads to expression of
genes important in proliferation
c-myc, c-myb, cdc2, and PCNA
Withdrawal of stimulation returns cell to G0 after completion of _____
mitosis
Small proteins called CDK inhibitors block cell proliferation
P21
p53, DNA damage, and oxygen radicals upregulates ___
p21
P21 blocks the hyperphosphorylation of
Rb
CDK inhibitors block cell cycle progression
P16
p21 blocks cdk4/cyclin __ and ckd2/cyclin ___
D; E
p16 binds and blocks cdk_/cyclin _
4; D
p16 is missing in a lot of instances of lung cancers particularly _______ lung cancer
non-small cell and melenoma
CDK inhibitors
p16
p21
p27
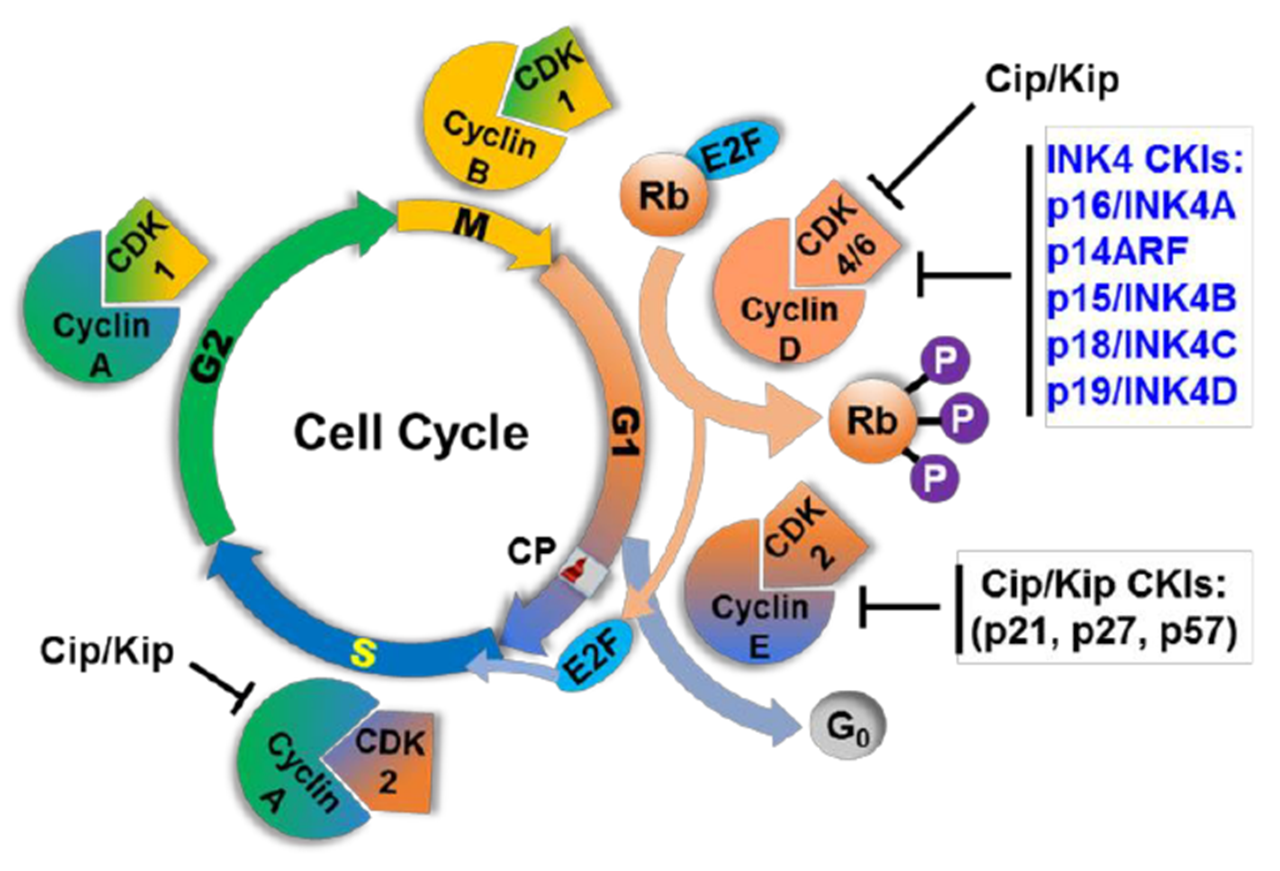
Cell proliferation represents a balance between cyclin-cdk complexes and CDK inhibitors
normal cellular genes whose proteins/products participate in cell growth/proliferation
Proto-oncogenes
any gene that encodes a protein that can induce cell transformation in culture or cancer in animals/humans
Oncogenes
most oncogenes are derived from mutated normal cellular genes
proto-oncogenes
ras gene is proto-oncogene; rasD gene is ______
oncogene
____ Mutations Convert Proto-oncogenes Into Oncogenes
GOF
____ mutations activate cell cycle cyclins
Ras
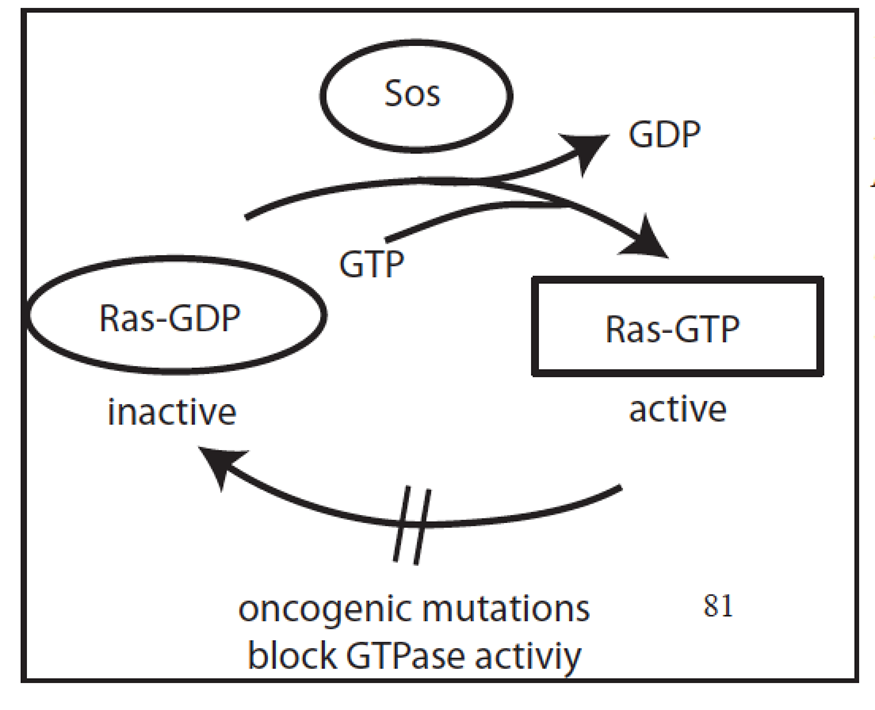
Ras as an oncogene
20-30% of NSCLC have a ___ mutation
Ras
Activation of cyclin __ by chromosome rearrangement
D
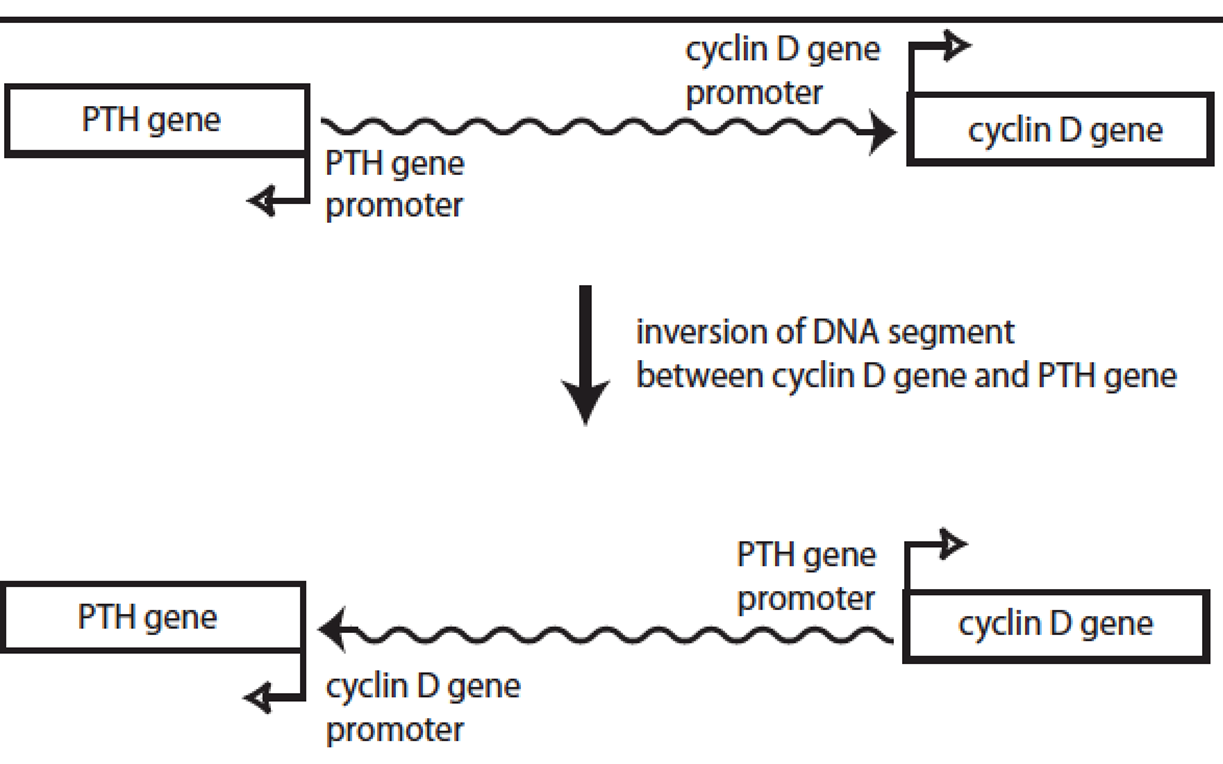
Chromosomal rearrangement
PTH promotor tends to be more active, so you get upregulation of cyclin D
Oncogenes stimulate _______
proliferation
Proto-oncogenes to oncogenes: ___ copy/ies of gene needs to be mutated
1
_____ mutations in tumor suppressor genes are also oncogenic
LOF
______ copy/ies of tumor suppressor genes must be inactivated in cancer
2/Both
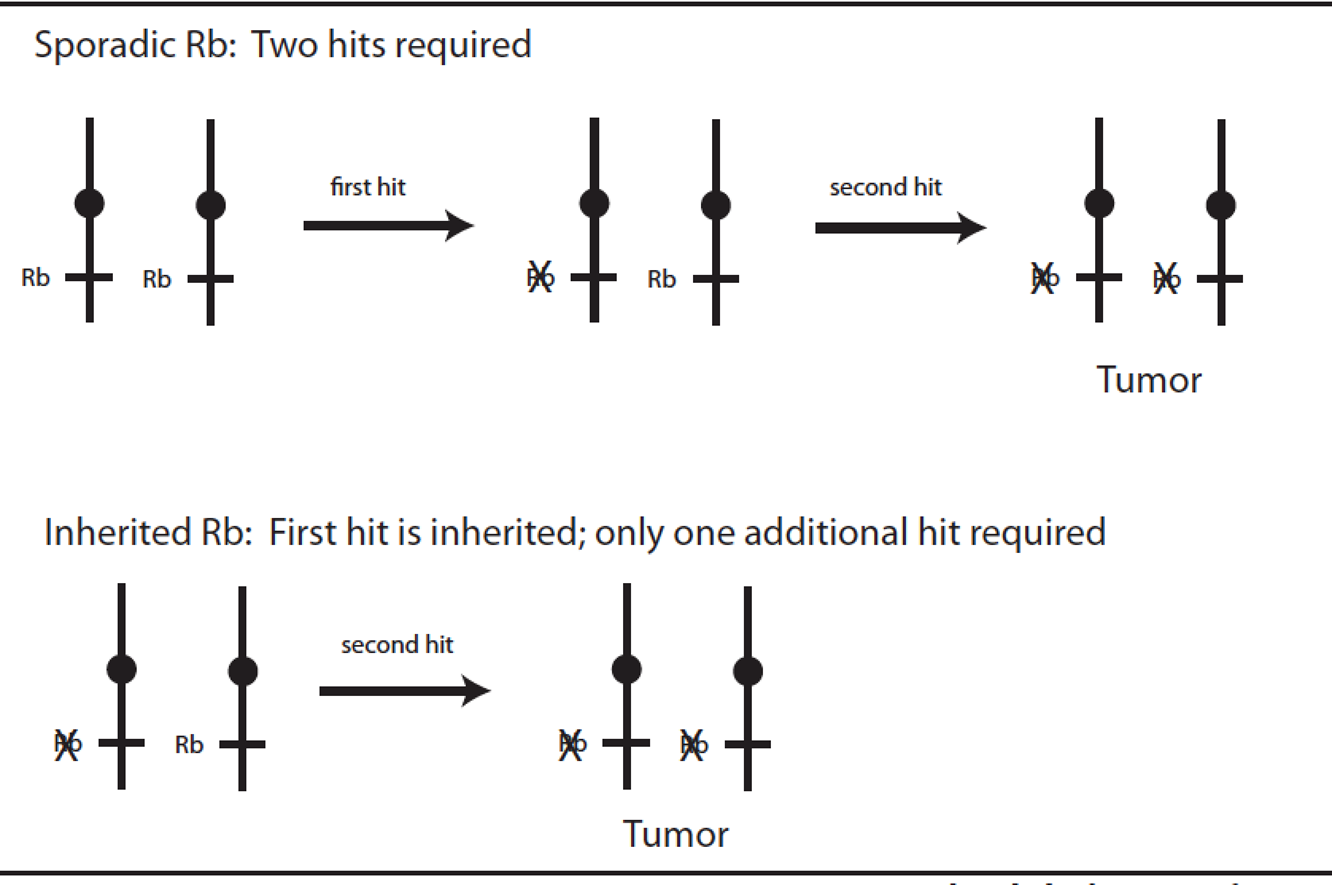
Inactivation of Tumor Suppressors: Retinoblastoma
2 hit theory
This second hit is called ______ and leads to loss of tumor suppressor function
LOH loss of heterozygosity
point mutation or other inactivation of one tumor suppressor allele
First hit
Deletion/mutation of remaining functioning tumor suppressor gene
Second hit
GOF
oncogene
LOF
tumor suppressor
Cyclin D
Cyclin E
Cyclin A
Cyclin dependent kinases 4 and 6
Proto-oncogenes (GOF)
p16
p21
p53
retinoblastoma
Tumor suppressors (Loss of Heterozygosity)
Disease of the cell cycle
Cancer
Introduce simian virus 40 to system its antigens Large T antigen and Small T antigen
Large T antigen blocks p53 and Rb
Small T antigen blocks pp2a (normal state inactivates AKT signaling pathway in proliferation)
(remove the brakes, knocking out 3 tumor suppressors)
It also turns on oncogenic Ras
(start the engine)
hTERT reactivation (Prevents shortening of telomeres hTERT so they can keep proliferating)
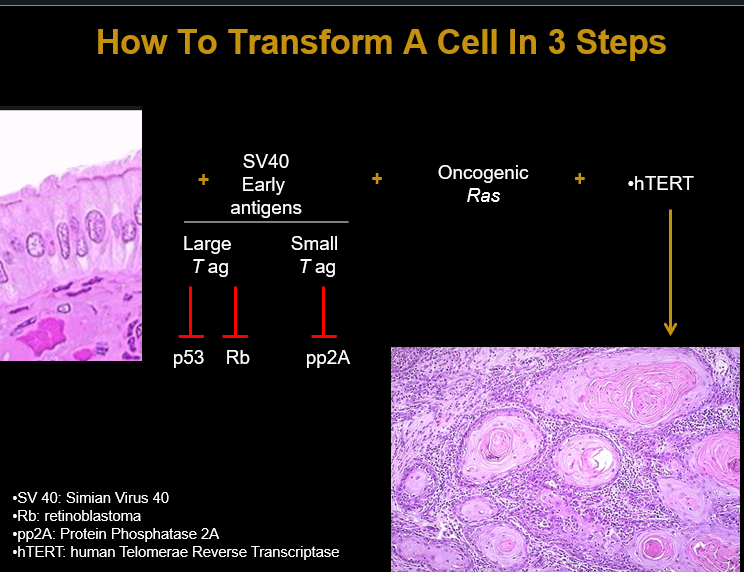
How simian virus introduction can lead to cancer
Cells only divide ____-____ times in a lifetime hayflick
40-60
HPV inactivated ____ and ____ pathways
p53 and Rb
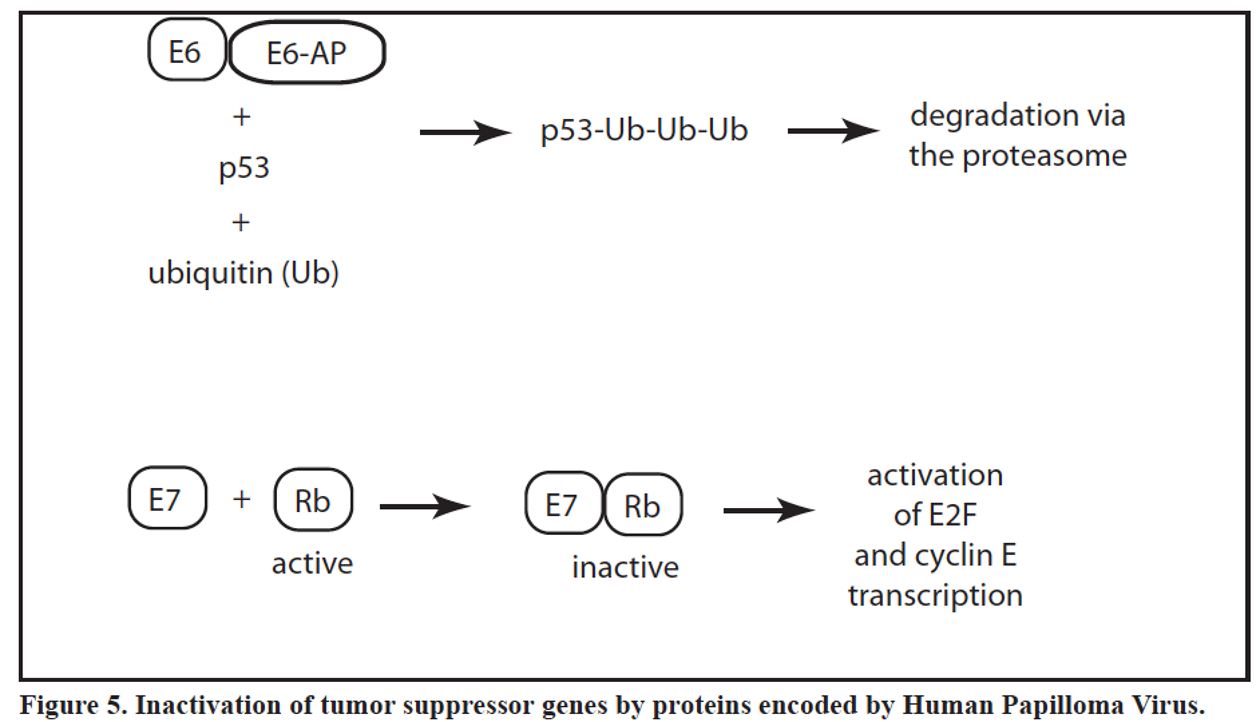
HPV upregulates E6 binds p53 leading to degradation of p53
E7 binds to Rb inactivating it
E6
p53
E7
Rb
Genes that positively regulate cell proliferation
Ras, EGFR, AKT, Cyclin D
Genes that negatively regulate cell proliferation
p16Ink4, Retinoblastoma, PTEN, p53
•Genes that control apoptosis
P53, BAX, MDM2
Genes involved in repair of damaged DNA
Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene (BRCA)
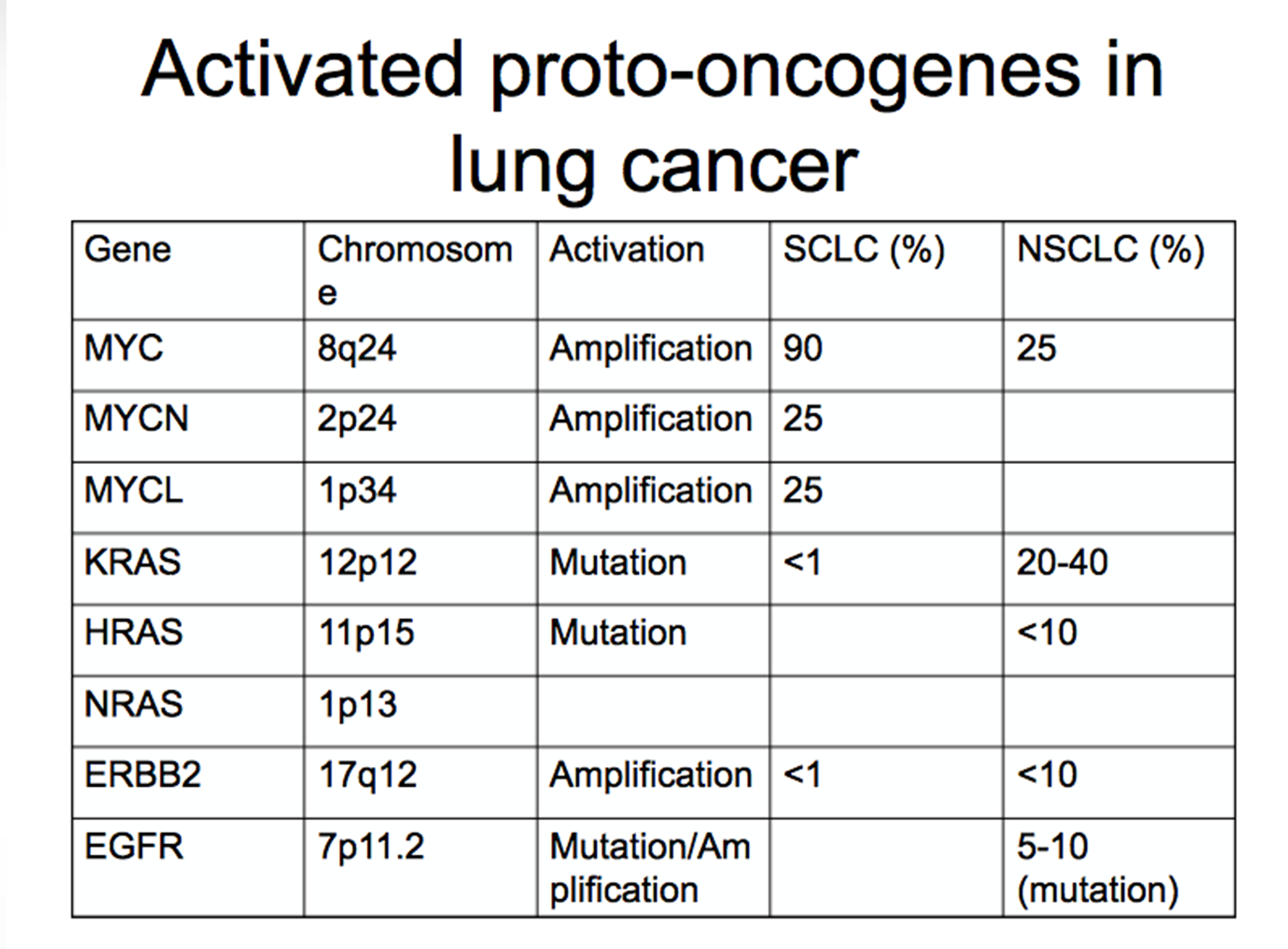
Proto-oncogene chart
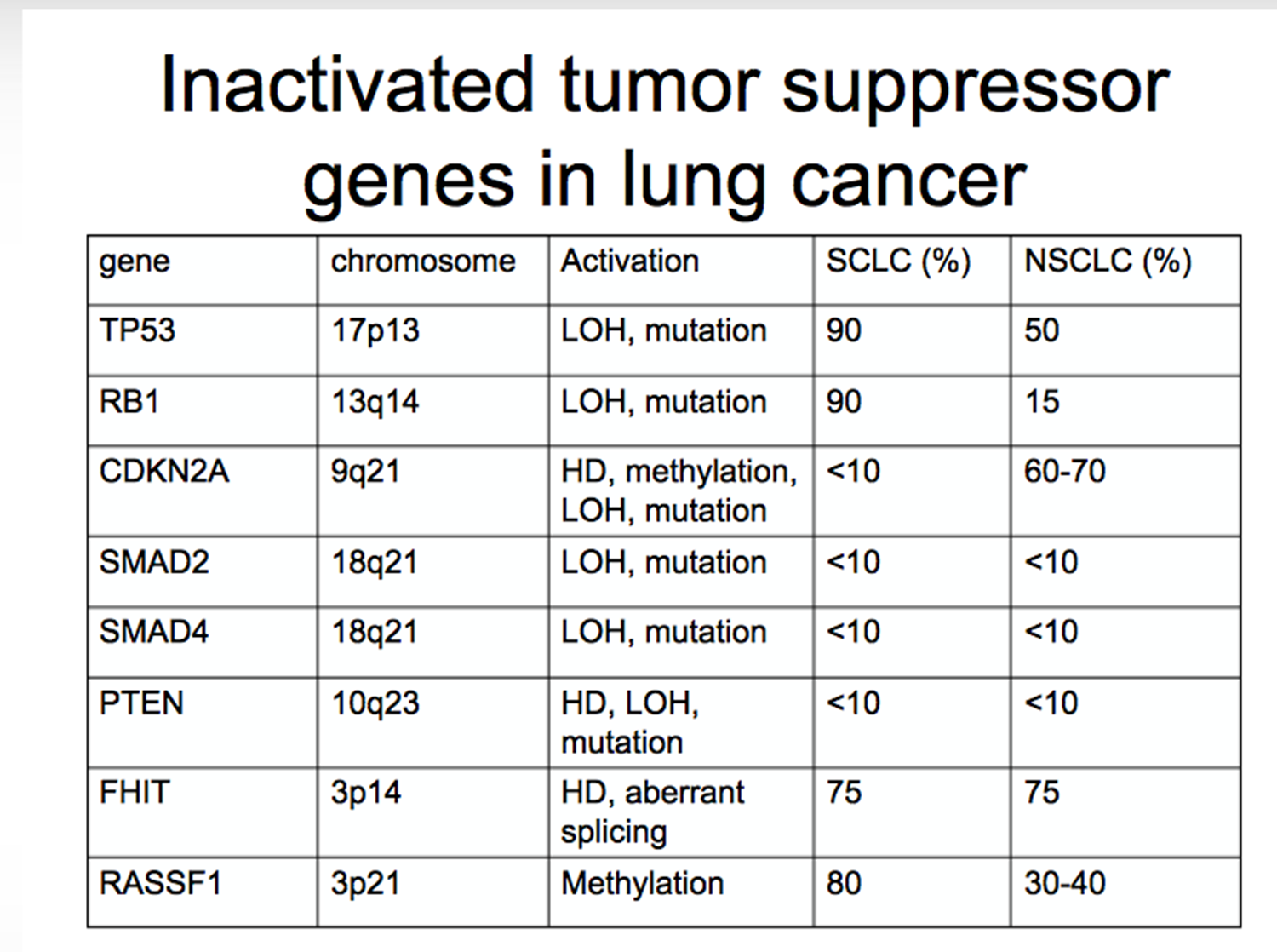
Tumor suppressor gene chart
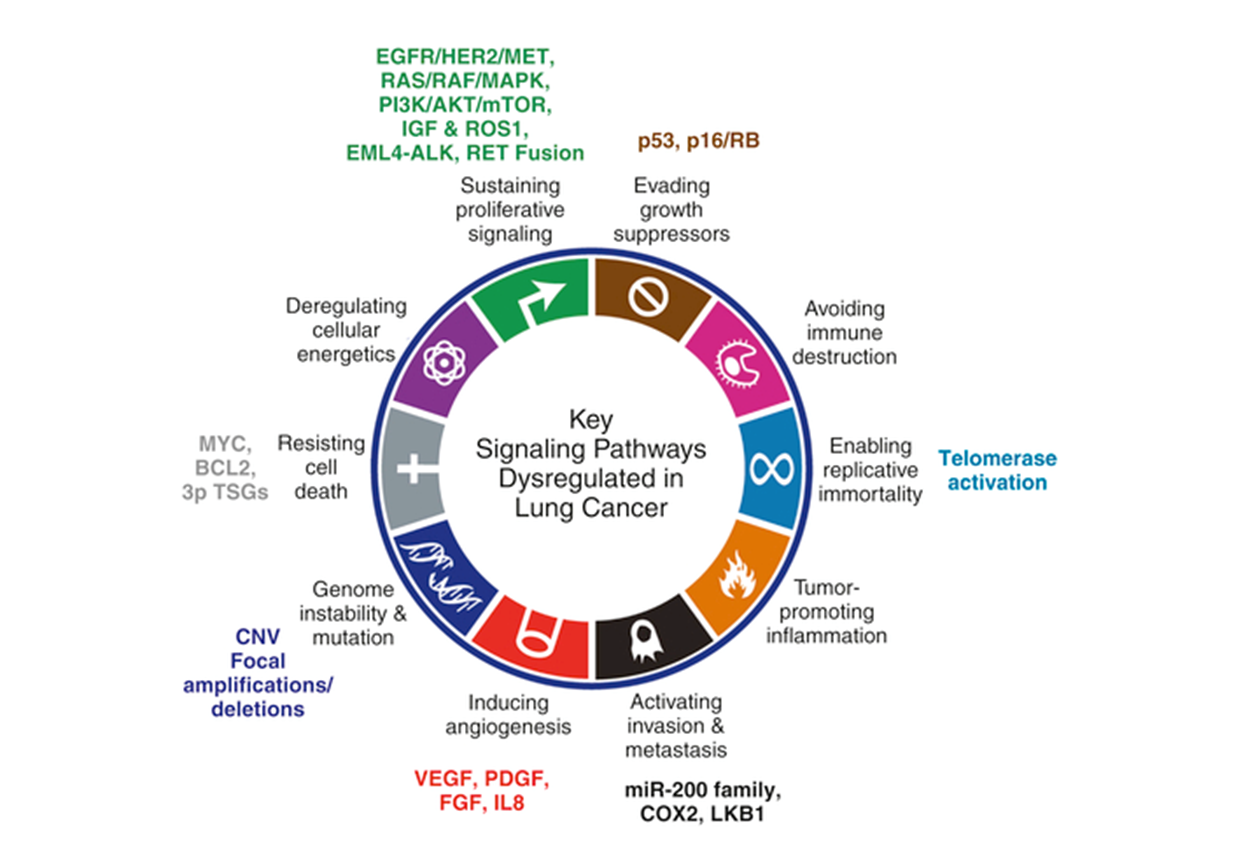
Key Signaling Pathways Dysregulated in Lung Cancer
Things increasing risk of lung cancer:
Smoking
Secondhand smoke
Asbestos (mesothelioma and increases risk of lung cancer especially in smokers)
Radon
Bad luck
____ dominant proto-oncogene in SCLC
MYC
____ dominant proto-oncogene in NSCLC
KRAS
CDKN2A gene encodes ____ really important in NSCLC
p16