Reproduction and Fetal Development Overview
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the four stages of the sexual response cycle?
1. Excitement 2. Plateau 3. Orgasm 4. Resolution
What physiological changes occur during male sexual arousal?
Urethra widens, scrotum skin thickens, cremaster muscle elevates testes, increased heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, erect nipples, and sex flush.
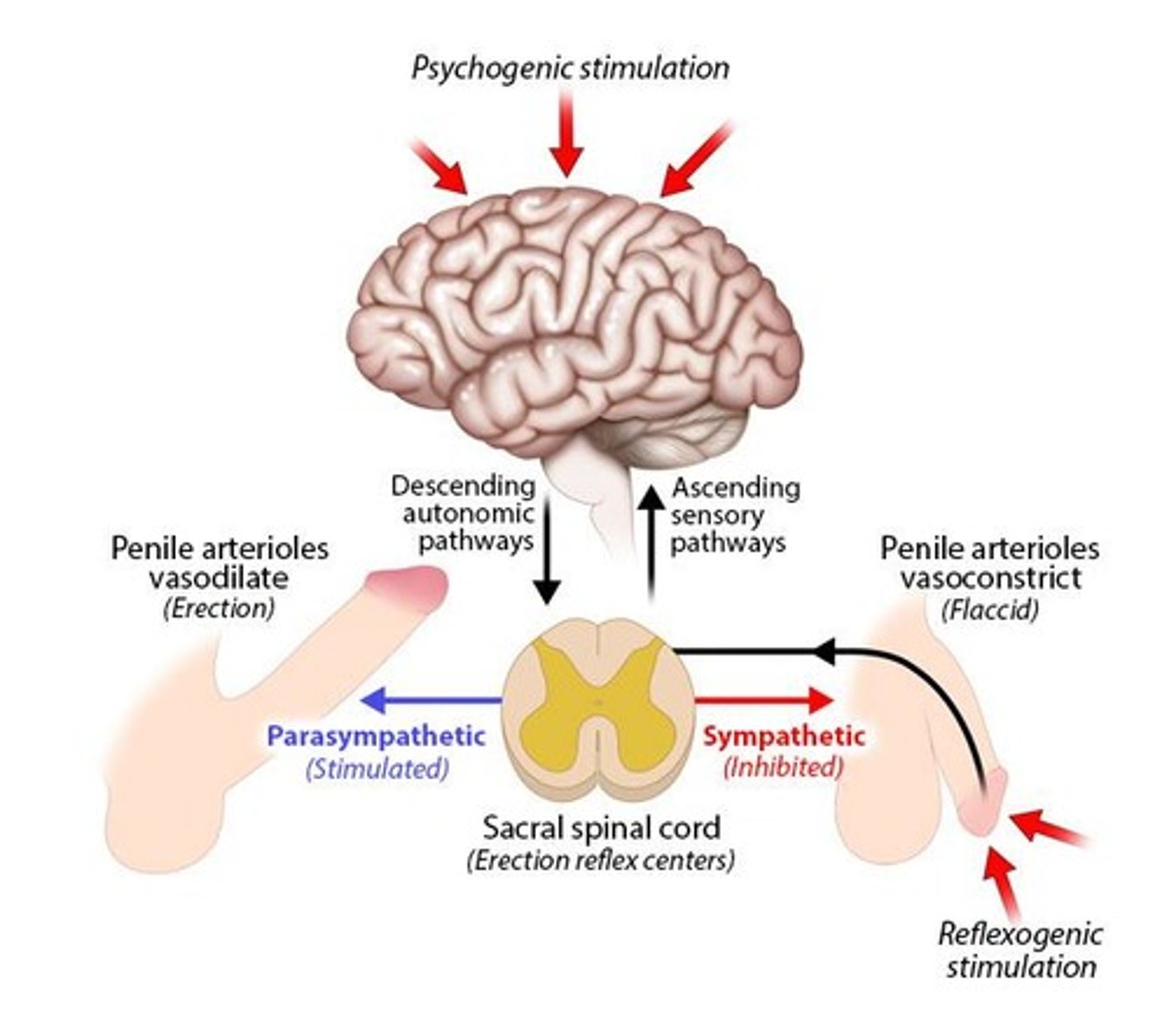
What is the origin of the male erection reflex?
It originates in the erection reflex center of the sacral spinal cord.
What is the difference between reflexogenic and psychogenic erection?
Reflexogenic erection occurs due to direct physical stimulation, while psychogenic erection is triggered by erotic thoughts or stimuli.
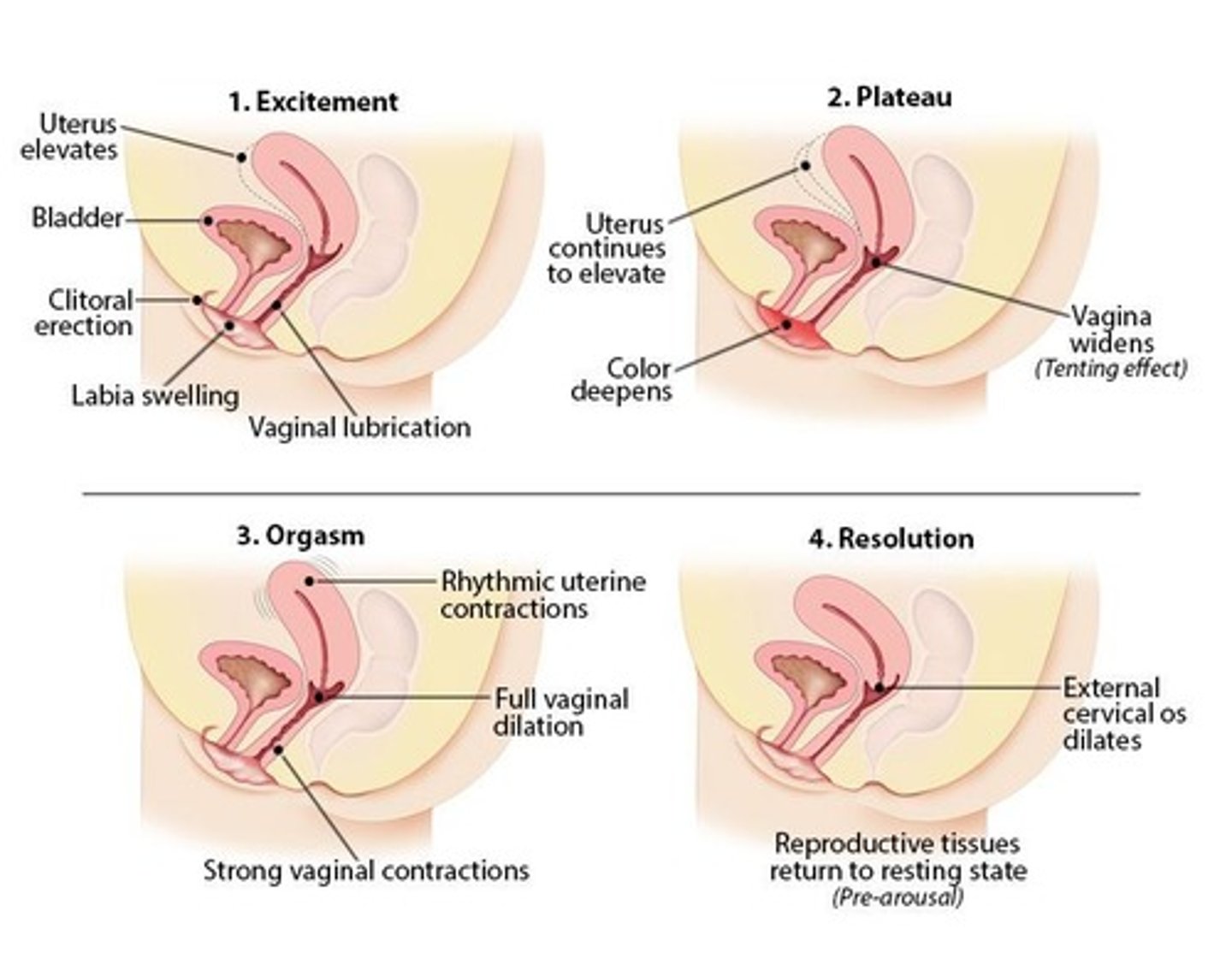
What happens during the female sexual response cycle?
External indicators of sexual arousal increase, including vaginal lubrication, uterine fibrillations, muscle contractions, and vaginal dilation.
What is unique about the female sexual response cycle compared to the male cycle?
The female cycle does not have a refractory period.
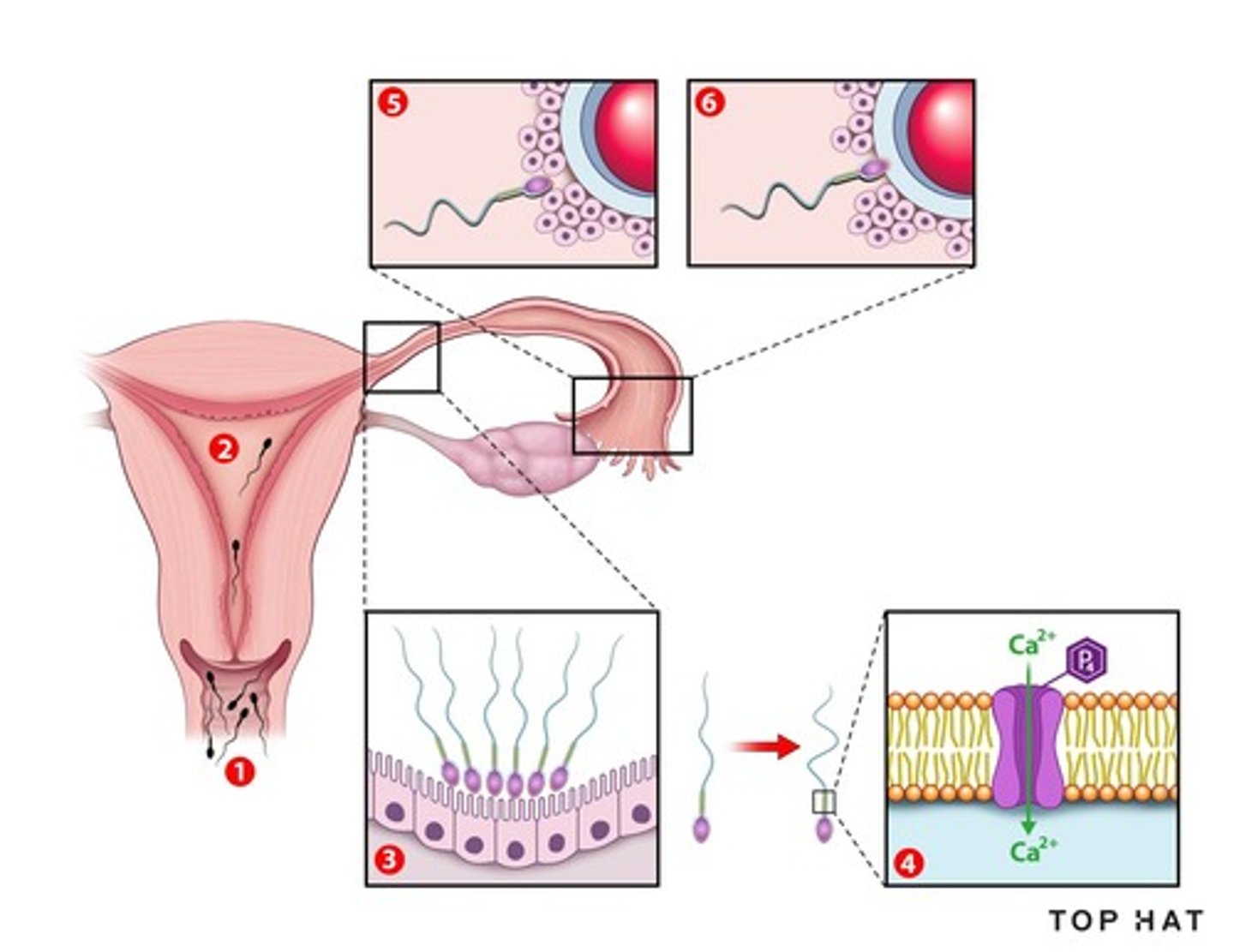
What is capacitation in the context of fertilization?
Capacitation is the last step in the maturation process of sperm, necessary for fertilization.
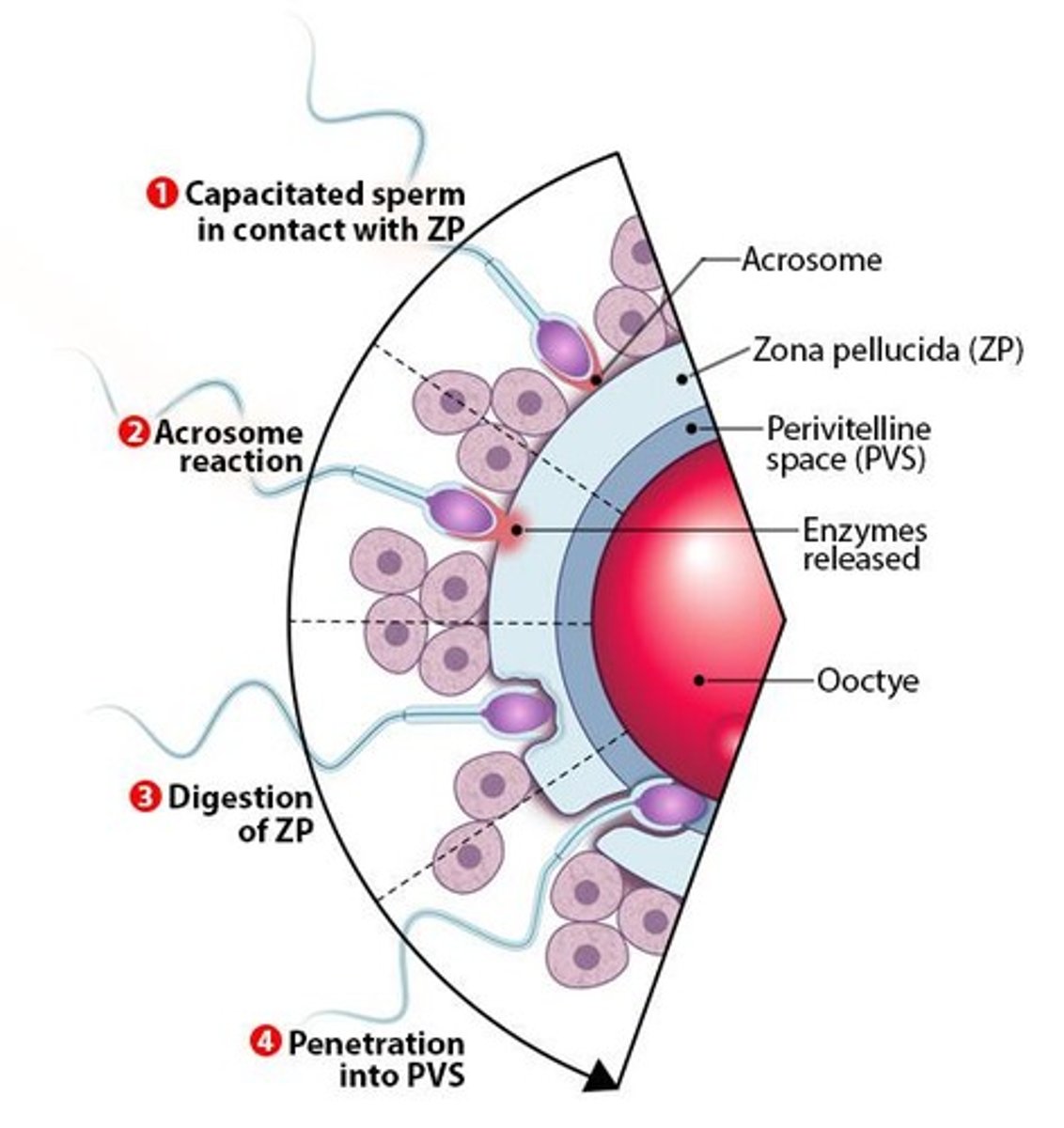
What is the zona pellucida and its role in fertilization?
The zona pellucida is a species-specific barrier that sperm must penetrate during fertilization.
What triggers the acrosome reaction in sperm?
The acrosome reaction is triggered by the sperm's contact with the zona pellucida, leading to the release of proteases.
What occurs during the cortical reaction after oocyte activation?
Cortical granules release contents into the perivitelline space, forming a barrier against further sperm fusion.
What are the three stages of preparation for uterine implantation?
1. Apposition 2. Attachment 3. Penetration.
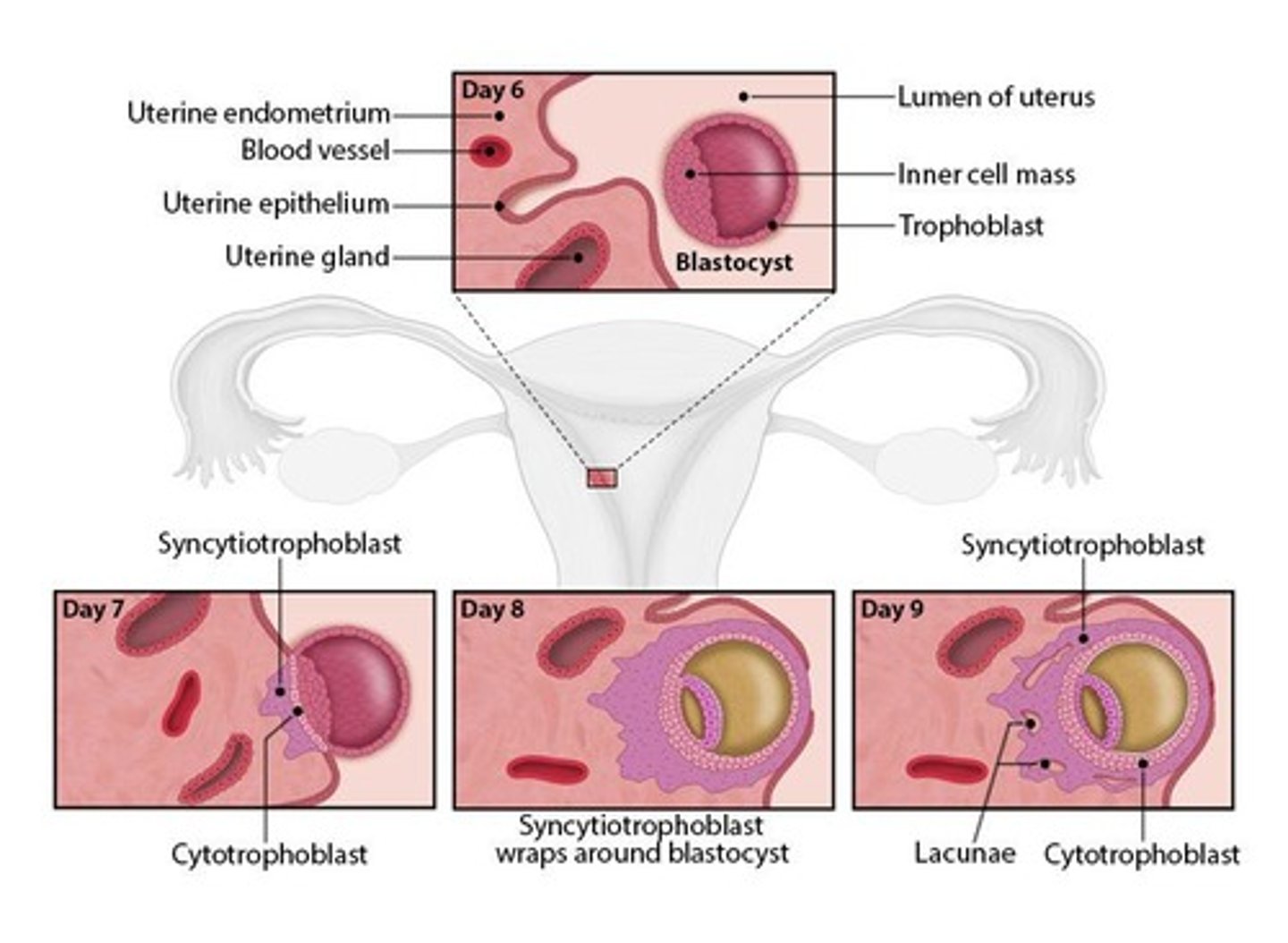
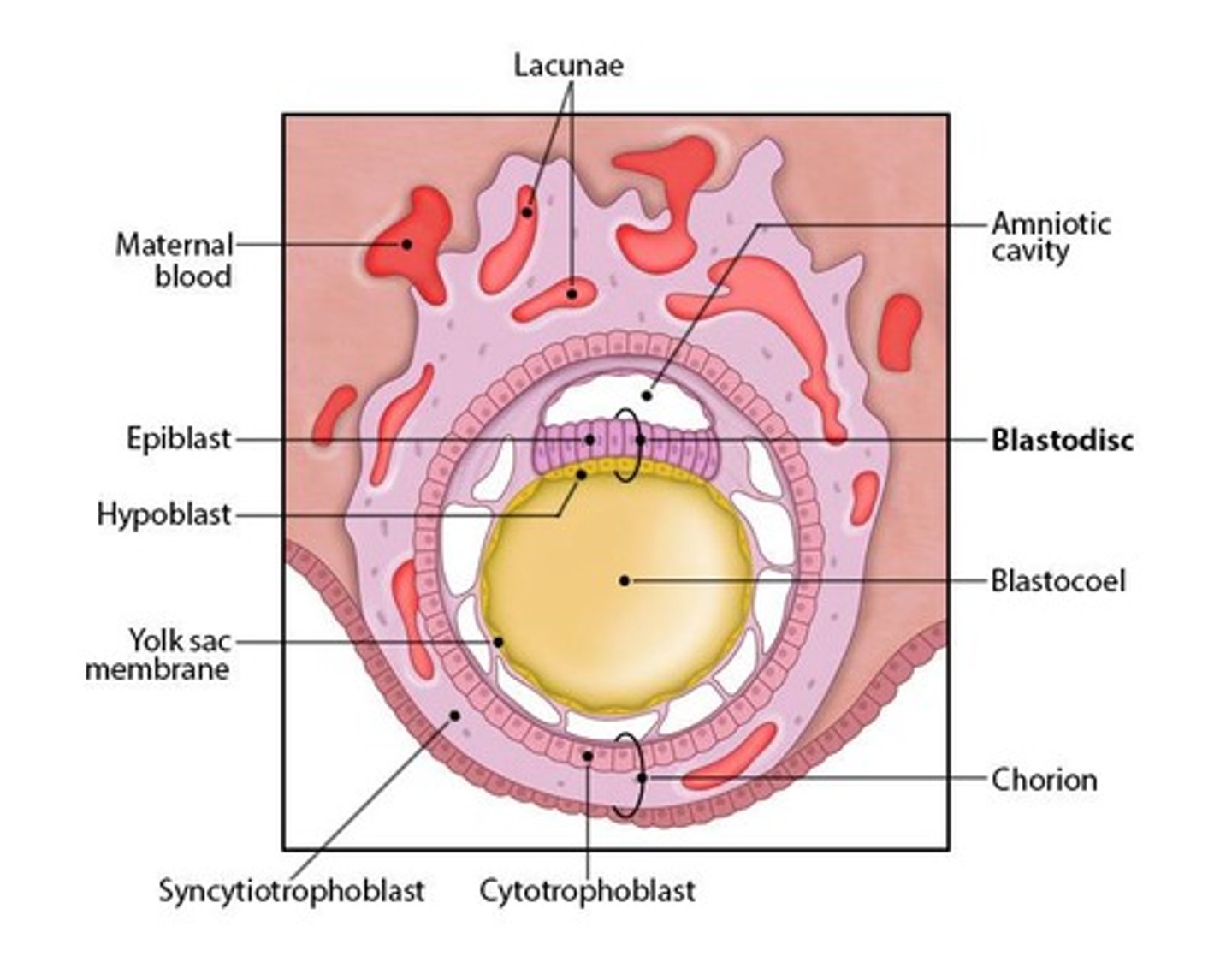
What is the role of the hypoblast in embryonic development?
The hypoblast forms the extraembryonic endoderm.
What does the epiblast give rise to during embryogenesis?
The epiblast gives rise to the embryo proper.
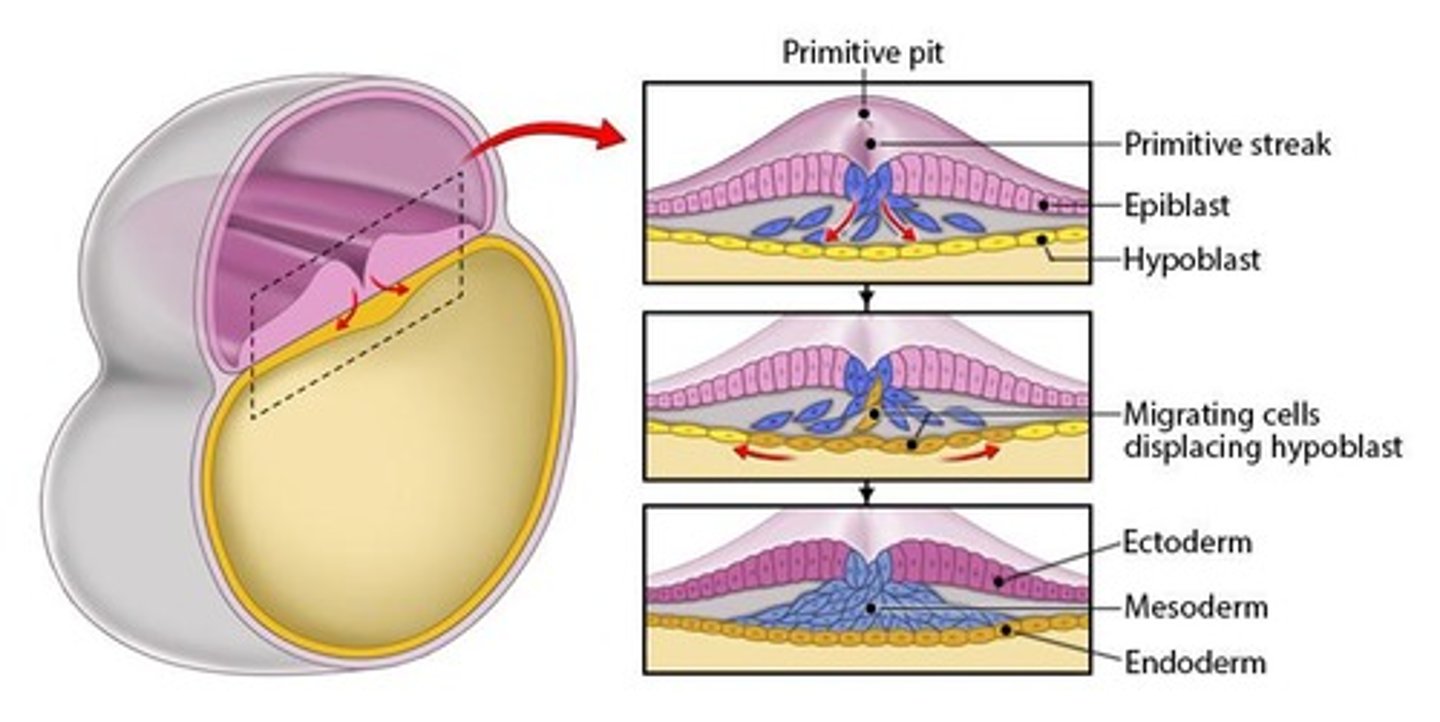
What are the three primary germ layers formed during gastrulation?
Ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
What is the structure of the placenta?
The placenta is a chimeric organ consisting of uterine and embryonic tissue, with several lobes called cotyledons.
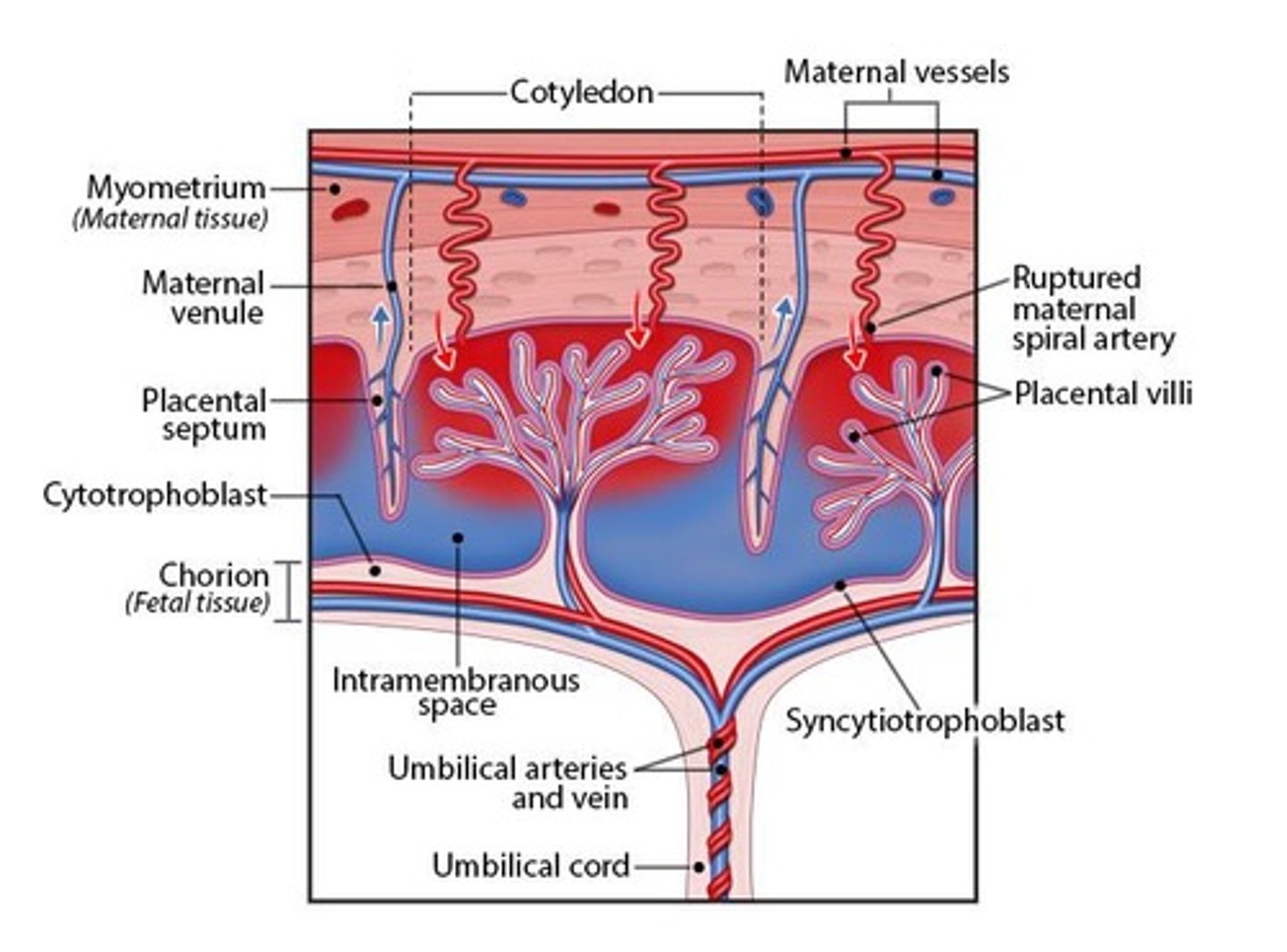
What are the functions of the placenta?
It serves as an organ of material exchange between the mother and developing embryo/fetus and as an endocrine organ producing hormones required for pregnancy.
What is ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy is the development of the embryo or fetus outside of the uterus.
What is placenta previa?
Placenta previa occurs when the placenta implants near or covering the internal os of the cervix, leading to complications.
What is preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is a condition characterized by sudden pregnancy-induced hypertension.
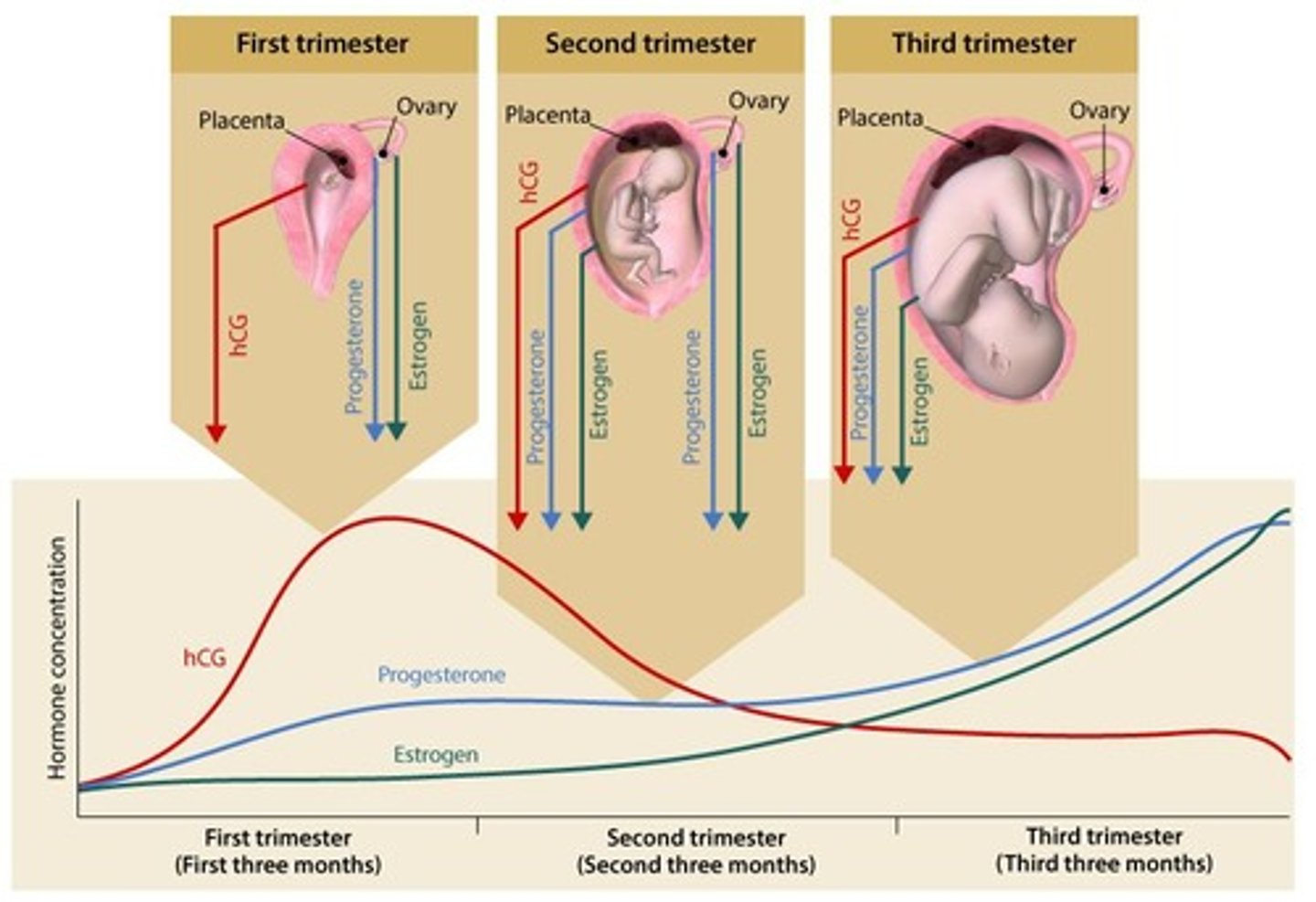
What hormonal changes occur during pregnancy?
Estrogen and progesterone are produced by the corpus luteum and placenta, regulating uterine contractions and maintaining pregnancy.
What is the role of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) during pregnancy?
hCG is produced by the chorion and is detectable about 10 days after ovulation, indicating pregnancy.
What is the significance of relaxin during pregnancy?
Relaxin is produced by syncytiotrophoblast cells and plays important roles in osmoregulation and cardiovascular adaptation.
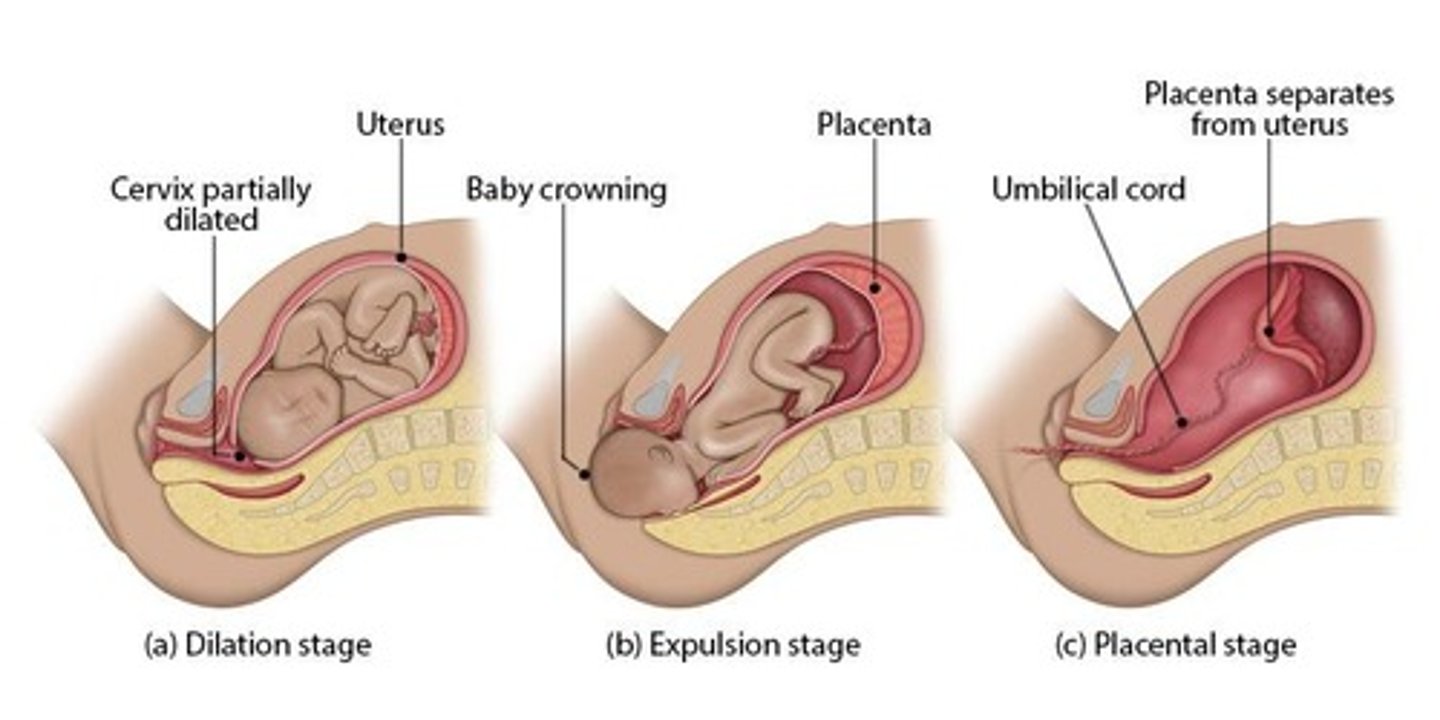
What are the stages of parturition?
1. Cervical effacement and dilation 2. Fetal expulsion 3. Placental expulsion.
What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)?
STDs are infections that spread through sexual contact.
What is the importance of contraceptive methods?
Contraceptive methods help prevent unintended pregnancies, with varying effectiveness rates.